Submitted:
14 September 2023
Posted:
15 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
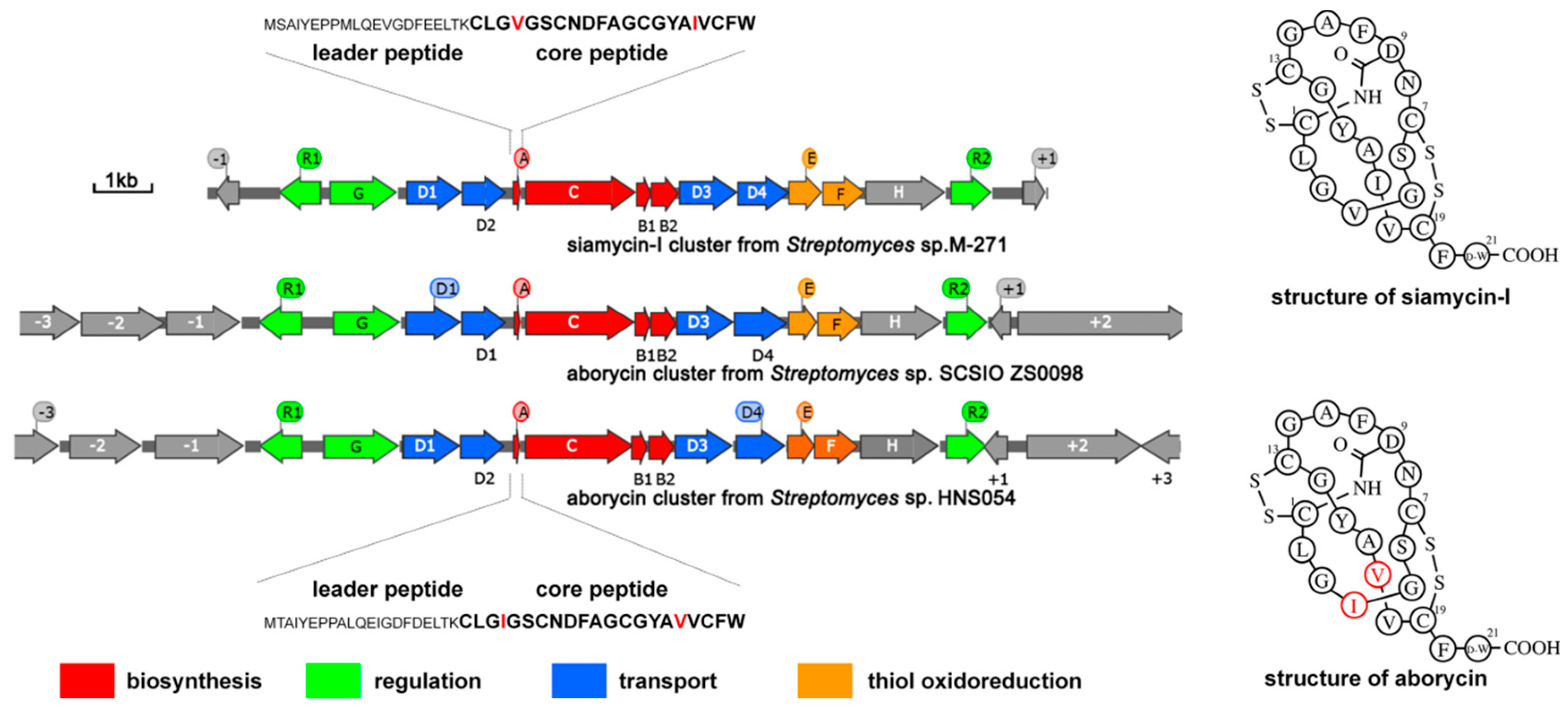
2.1. General information on the aborycin gene cluster from Streptomyces sp. HNS054
2.2. Cloning of the gul BGC and construction of strains for heterologous expression of aborycin
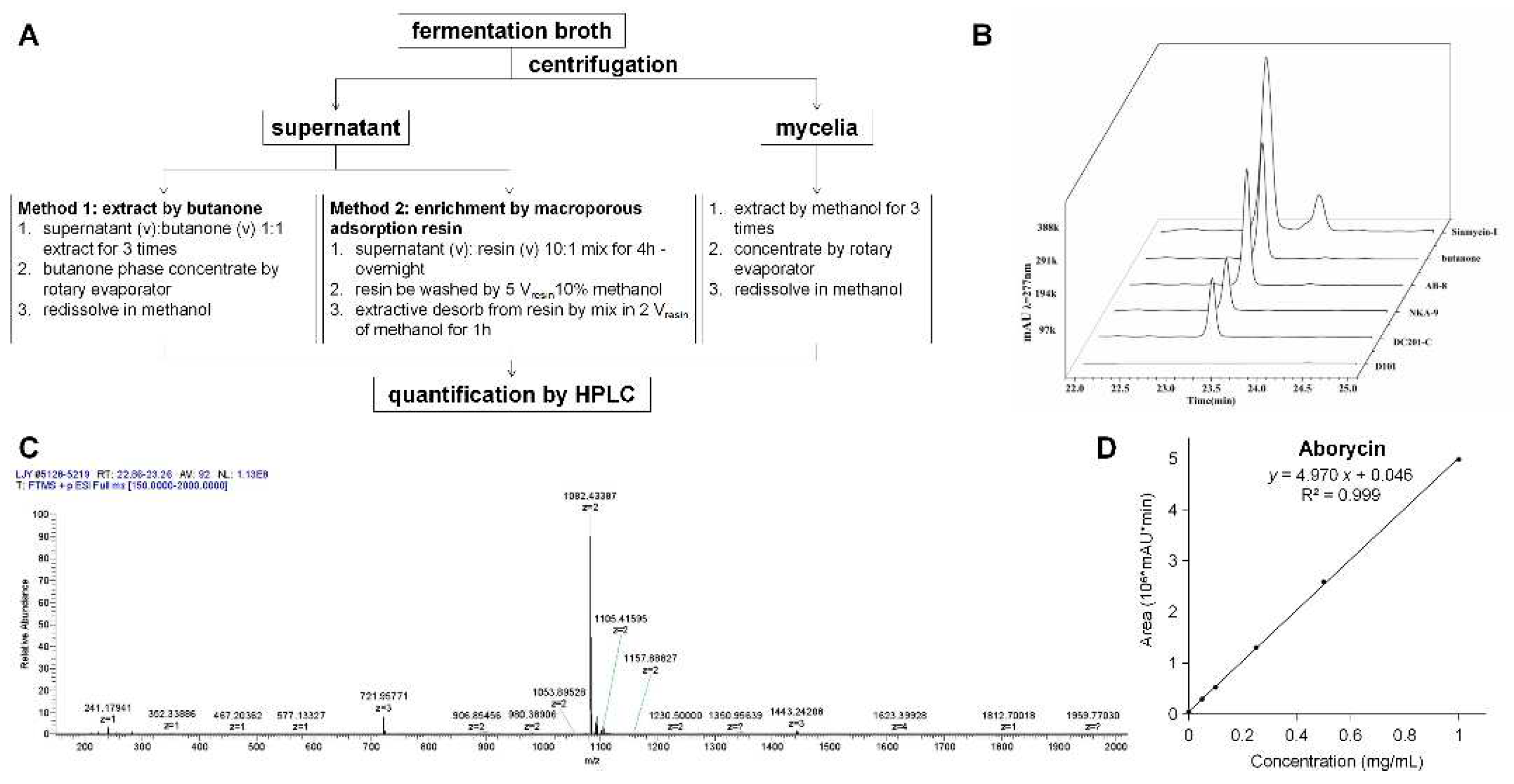
2.3. Extraction and detection of aborycin
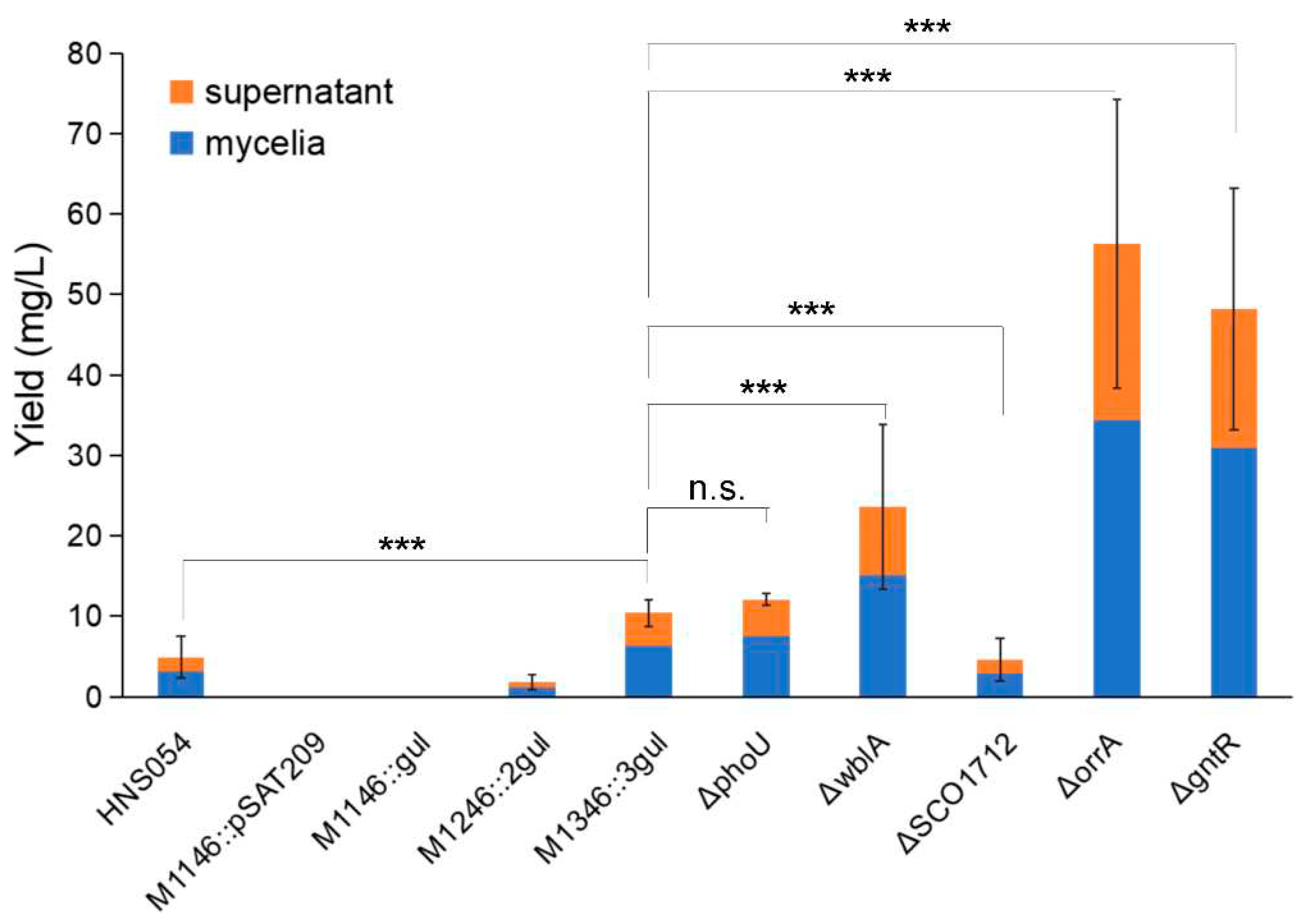
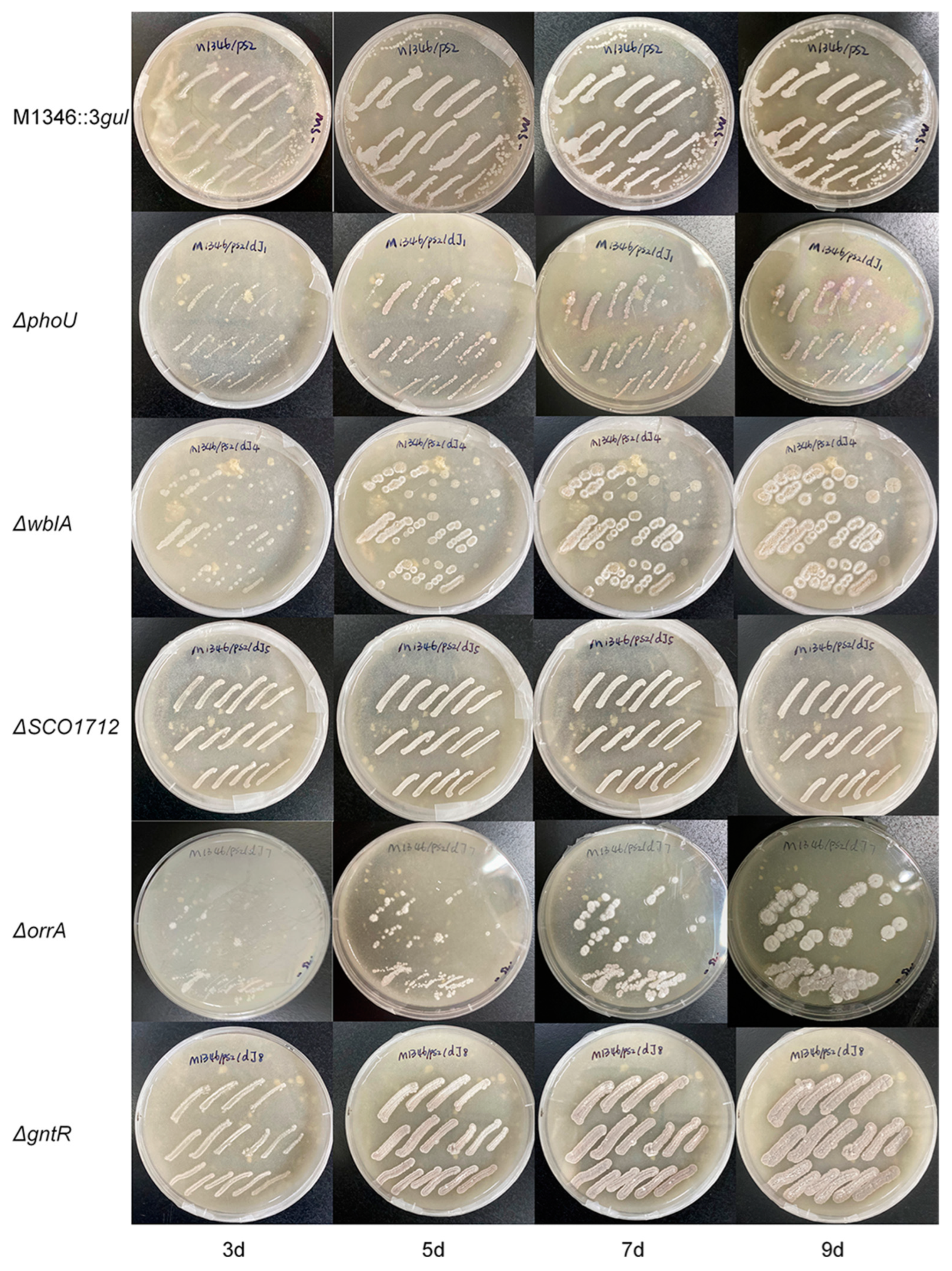
2.4. Yield comparison among different strains
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Strains, plasmids and primers
4.2. Construction of heterologous expression strains to produce aborycin
4.3. Gene knockout in S. coelicolor M1346::3gul by the CRISPR/Cas9 method
4.4. Metabolite analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Helynck, G.; Dubertret, C.; Mayaux, J.F.; Leboul, J. Isolation of RP 71955, a new anti-HIV-1 peptide secondary metabolite. The Journal of antibiotics 1993, 46, 1756–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fréchet, D.; Guitton, J.D.; Herman, F.; Faucher, D.; Helynck, G.; Monegier du Sorbier, B.; Ridoux, J.P.; James-Surcouf, E.; Vuilhorgne, M. Solution structure of RP 71955, a new 21 amino acid tricyclic peptide active against HIV-1 virus. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potterat, O.; Stephan, H.; Metzger, J.W.; Gnau, V.; Zähner, H.; Jung, G. Aborycin – a tricyclic 21-peptide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces griseoflavus. Liebigs Annalen der Chemie 1994, 1994, 741–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ma, J.; Li, Q.; Ju, J. Identification of the anti-infective aborycin biosynthetic gene cluster from deep-sea-derived Streptomyces sp. SCSIO ZS0098 enables production in a heterologous host. Marine Drugs 2019, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Huang, Z.; Gui, X.; Xiang, W.; Jin, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhao, J. Multi-omics comparative analysis of Streptomyces mutants obtained byiterative atmosphere and room-temperature plasma mutagenesis. Frontiers in microbiology 2020, 11, 630309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimov, M.O.; Pan, S.J.; James Link, A. Lasso peptides: structure, function, biosynthesis, and engineering. Natural product reports 2012, 29, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.; Hua, Z.C. Lasso peptides: heterologous production and potential medical application. Frontiers in bioengineering and biotechnology 2020, 8, 571165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnison, P.G.; Bibb, M.J.; Bierbaum, G.; Bowers, A.A.; Bugni, T.S.; Bulaj, G.; Camarero, J.A.; Campopiano, D.J.; Challis, G.L.; Clardy, J.; et al. Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Natural product reports 2013, 30, 108–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegemann, J.D.; Zimmermann, M.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Lasso peptides: an intriguing class of bacterial natural products. Accounts of chemical research 2015, 48, 1909–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knappe, T.A.; Manzenrieder, F.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Linne, U.; Sasse, F.; Kessler, H.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Introducing lasso peptides as molecular scaffolds for drug design: engineering of an integrin antagonist. Angewandte Chemie (International ed. in English) 2011, 50, 8714–8717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscotta, F.J.; Tharp, J.M.; Liu, W.R.; Link, A.J. Expanding the chemical diversity of lasso peptide MccJ25 with genetically encoded noncanonical amino acids. Chemical communications (Cambridge, England) 2015, 51, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, C.; Maksimov, M.O.; Link, A.J. Construction of lasso peptide fusion proteins. ACS chemical biology 2016, 11, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knappe, T.A.; Linne, U.; Zirah, S.; Rebuffat, S.; Xie, X.; Marahiel, M.A. Isolation and structural characterization of capistruin, a lasso peptide predicted from the genome sequence of Burkholderia thailandensis E264. Journal of the American Chemical Society 2008, 130, 11446–11454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tietz, J.I.; Schwalen, C.J.; Patel, P.S.; Maxson, T.; Blair, P.M.; Tai, H.C.; Zakai, U.I.; Mitchell, D.A. A new genome-mining tool redefines the lasso peptide biosynthetic landscape. Nature chemical biology 2017, 13, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stariha, L.M.; McCafferty, D.G. Discovery of the class I antimicrobial lasso peptide arcumycin. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2021, 22, 2632–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ducasse, R.; Zirah, S.; Blond, A.; Goulard, C.; Lescop, E.; Giraud, C.; Hartke, A.; Guittet, E.; Pernodet, J.L.; et al. Characterization of sviceucin from Streptomyces provides insight into enzyme exchangeability and disulfide bond formation in lasso peptides. ACS chemical biology 2015, 10, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevaere, J.; Goulard, C.; Schneider, O.; Sekurova, O.N.; Ma, H.; Zirah, S.; Afonso, C.; Rebuffat, S.; Zotchev, S.B.; Li, Y. An orthogonal system for heterologous expression of actinobacterial lasso peptides in Streptomyces hosts. Scientific reports 2018, 8, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobb, R.E.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, H. High-efficiency multiplex genome editing of Streptomyces species using an engineered CRISPR/Cas system. ACS synthetic biology 2015, 4, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zheng, G.; Jiang, W.; Hu, H.; Lu, Y. One-step high-efficiency CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing in Streptomyces. Acta biochimica et biophysica Sinica 2015, 47, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zheng, G.; Chen, J.; Ge, M.; Jiang, W.; Lu, Y. Multiplexed site-specific genome engineering for overproducing bioactive secondary metabolites in actinomycetes. Metabolic engineering 2017, 40, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Ogasawara, Y.; Nomura, S.; Dairi, T. Biosynthetic gene cluster of a d-tryptophan-containing lasso peptide, MS-271. Chembiochem : a European journal of chemical biology 2018, 19, 2045–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.W.; Lee, B.R.; You, S.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, J.N.; Song, E.; Yang, Y.H.; Hwang, D.; Kim, B.G. Transcriptome analysis of wild-type and afsS deletion mutant strains identifies synergistic transcriptional regulator of afsS for a high antibiotic-producing strain of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2018, 102, 3243–3253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Huang, J.; Lee, H.N.; Hur, Y.A.; Cohen, S.N.; Kim, E.S. Interspecies DNA microarray analysis identifies WblA as a pleiotropic down-regulator of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Journal of bacteriology 2007, 189, 4315–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.N.; Huang, J.; Im, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Noh, J.H.; Cohen, S.N.; Kim, E.S. Putative TetR family transcriptional regulator SCO1712 encodes an antibiotic downregulator in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 2010, 76, 3039–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Liu, P.; He, W.; Tao, H.; Yang, Z.; Sun, C.; Wang, W.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, W. Identification of the cognate response regulator of the orphan histidine kinase OhkA involved in both secondary metabolism and morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor. Applied microbiology and biotechnology 2021, 105, 5905–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsypik, O.; Makitrynskyy, R.; Bera, A.; Song, L.; Wohlleben, W.; Fedorenko, V.; Ostash, B. Role of GntR family regulatory gene SCO1678 in gluconate metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor M145. BioMed research international 2017, 2017, 9529501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalbán-López, M.; Scott, T.A.; Ramesh, S.; Rahman, I.R.; van Heel, A.J.; Viel, J.H.; Bandarian, V.; Dittmann, E.; Genilloud, O.; Goto, Y.; et al. New developments in RiPP discovery, enzymology and engineering. Natural product reports 2021, 38, 130–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manderscheid, N.; Bilyk, B.; Busche, T.; Kalinowski, J.; Paululat, T.; Bechthold, A.; Petzke, L.; Luzhetskyy, A. An influence of the copy number of biosynthetic gene clusters on the production level of antibiotics in a heterologous host. Journal of Biotechnology 2016, 232, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyeon, H.R.; Nah, H.J.; Kang, S.H.; Choi, S.S.; Kim, E.S. Heterologous expression of pikromycin biosynthetic gene cluster using Streptomyces artificial chromosome system. Microbial cell factories 2017, 16, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, G.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y. Challenges and advances in genome editing technologies in Streptomyces. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín, J.F.; Rodríguez-García, A.; Liras, P. The master regulator PhoP coordinates phosphate and nitrogen metabolism, respiration, cell differentiation and antibiotic biosynthesis: comparison in Streptomyces coelicolor and Streptomyces avermitilis. The Journal of antibiotics 2017, 70, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler-Goldsworthy, K.; Gust, B.; Mouz, S.; Chandra, G.; Findlay, K.C.; Chater, K.F. The actinobacteria-specific gene wblA controls major developmental transitions in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microbiology (Reading, England) 2011, 157, 1312–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, H.J.; Park, J.; Choi, S.; Kim, E.S. WblA, a global regulator of antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces. Journal of industrial microbiology & biotechnology 2021, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lee, H.N.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, E.S. Transcriptome analysis of an antibiotic downregulator mutant and synergistic Actinorhodin stimulation via disruption of a precursor flux regulator in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 2011, 77, 1872–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskisson, P.A.; Rigali, S. Chapter 1: Variation in form and function the helix-turn-helix regulators of the GntR superfamily. Advances in applied microbiology 2009, 69, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smanski, M.J.; Peterson, R.M.; Rajski, S.R.; Shen, B. Engineered Streptomyces platensis strains that overproduce antibiotics platensimycin and platencin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2009, 53, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhan, X.; Mao, X.M.; Li, Y.Q. The regulatory cascades of antibiotic production in Streptomyces. World journal of microbiology & biotechnology 2020, 36, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierman, M.; Logan, R.; O'Brien, K.; Seno, E.T.; Rao, R.N.; Schoner, B.E. Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 1992, 116, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluskal, T.; Castillo, S.; Villar-Briones, A.; Oresic, M. MZmine 2: modular framework for processing, visualizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry-based molecular profile data. BMC bioinformatics 2010, 11, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Trial | Gene Code | Symbol | Relevant Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| J01 | SCO4228 | phoU | ΔphoU mutant showed 6-fold increase in ACT production when phosphate starvation | [22] |
| J04 | SCO3579 | wblA | ΔwblA mutant showed 1.5-fold increase in doxorubicin production | [23] |
| J05 | SCO1712 | SCO1712 | ΔSCO1712 mutant showed 1.62-fold or 1.22-fold increase in ACT or RED production, respectively | [24] |
| J07 | SCO3008 | orrA | ΔorrA mutant showed great increase in ACT and RED production | [25] |
| J08 | SCO1678 | gntR | ΔgntR mutant altered the secondary metabolite profile of S. coelicolor | [26] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





