Submitted:
13 September 2023
Posted:
15 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Raw materials
2.2. Preparation of the nanoparticle hydrophobic materials
2.3. Preparation of the hydrophobic coatings
2.3.1. Application method
2.3.2. Preparation of coated Marshall specimens
2.4. Characterization of superhydrophobic materials and coatings
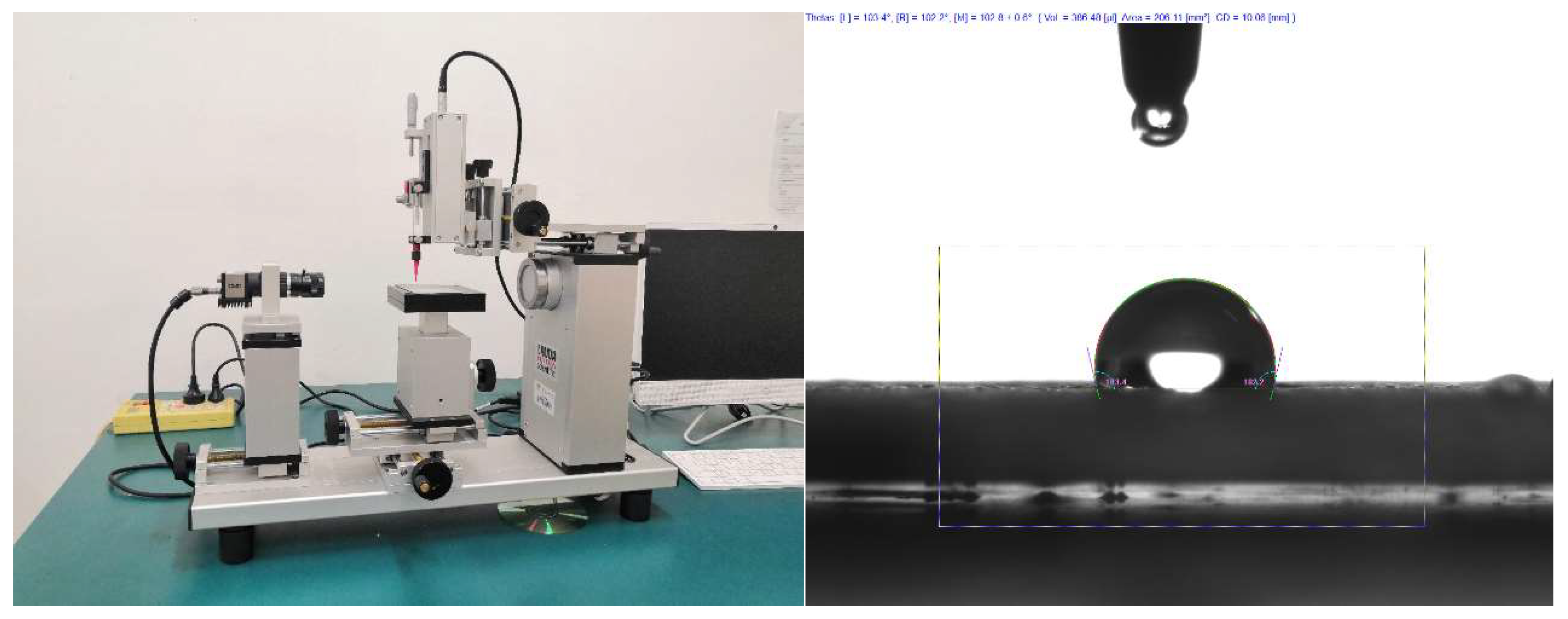
2.5. Adhesion test

2.6. Simulation test of icing
2.7. Durability test of coatings
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Determination of the optimum preparation method
3.1.1. Dispersion method
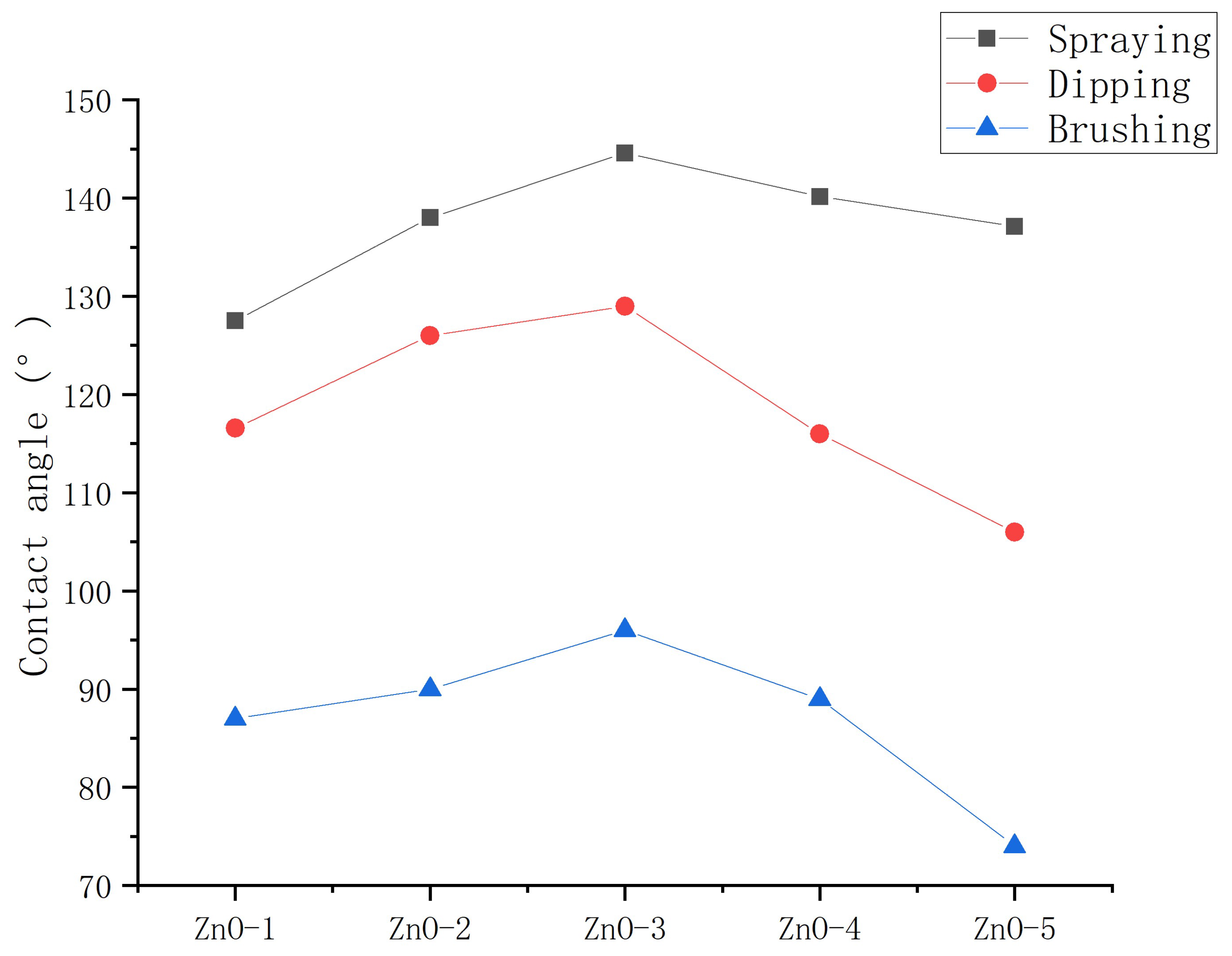
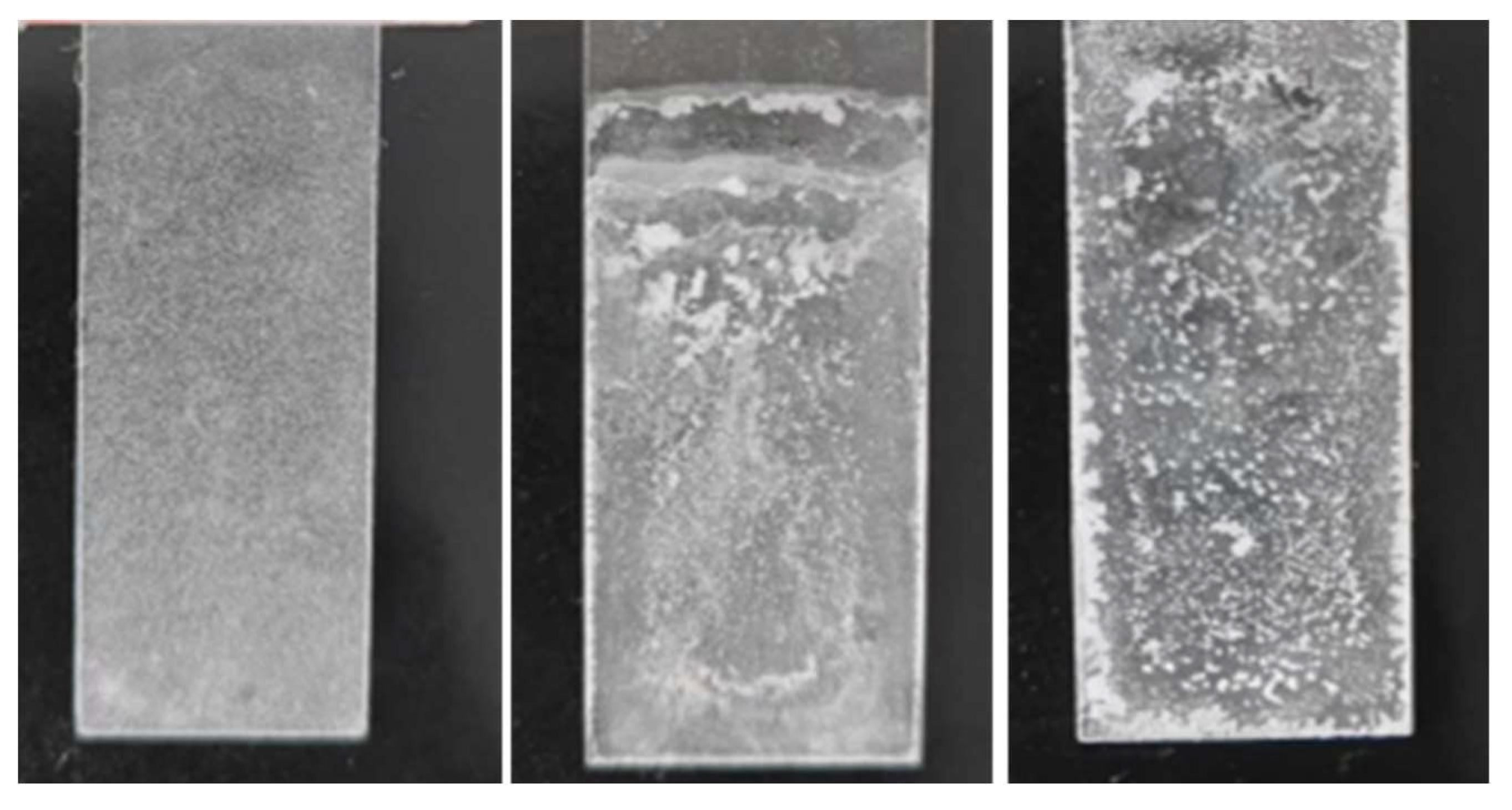
3.1.2. Application method
3.1.3. Introduction method of epoxy resin
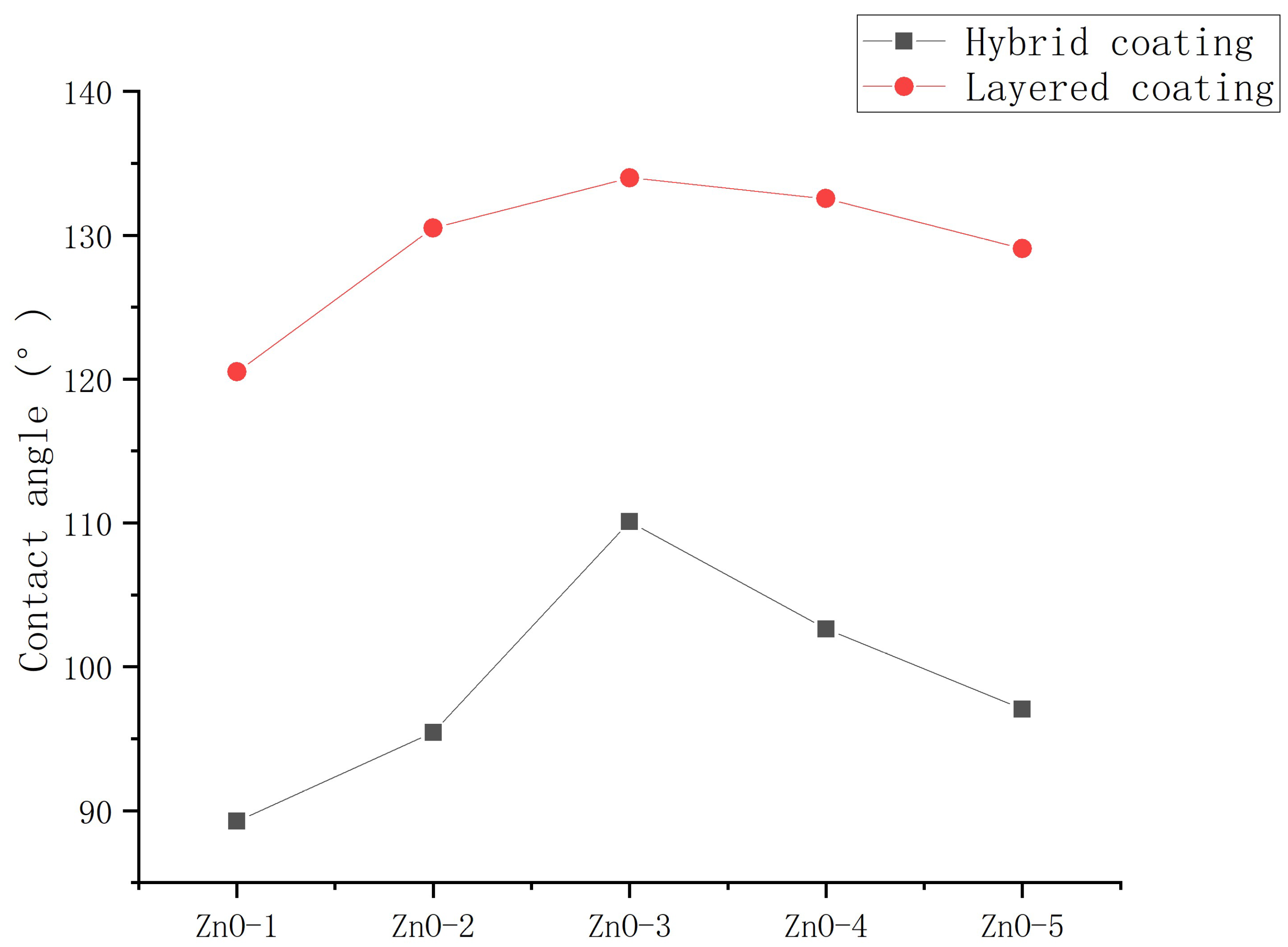
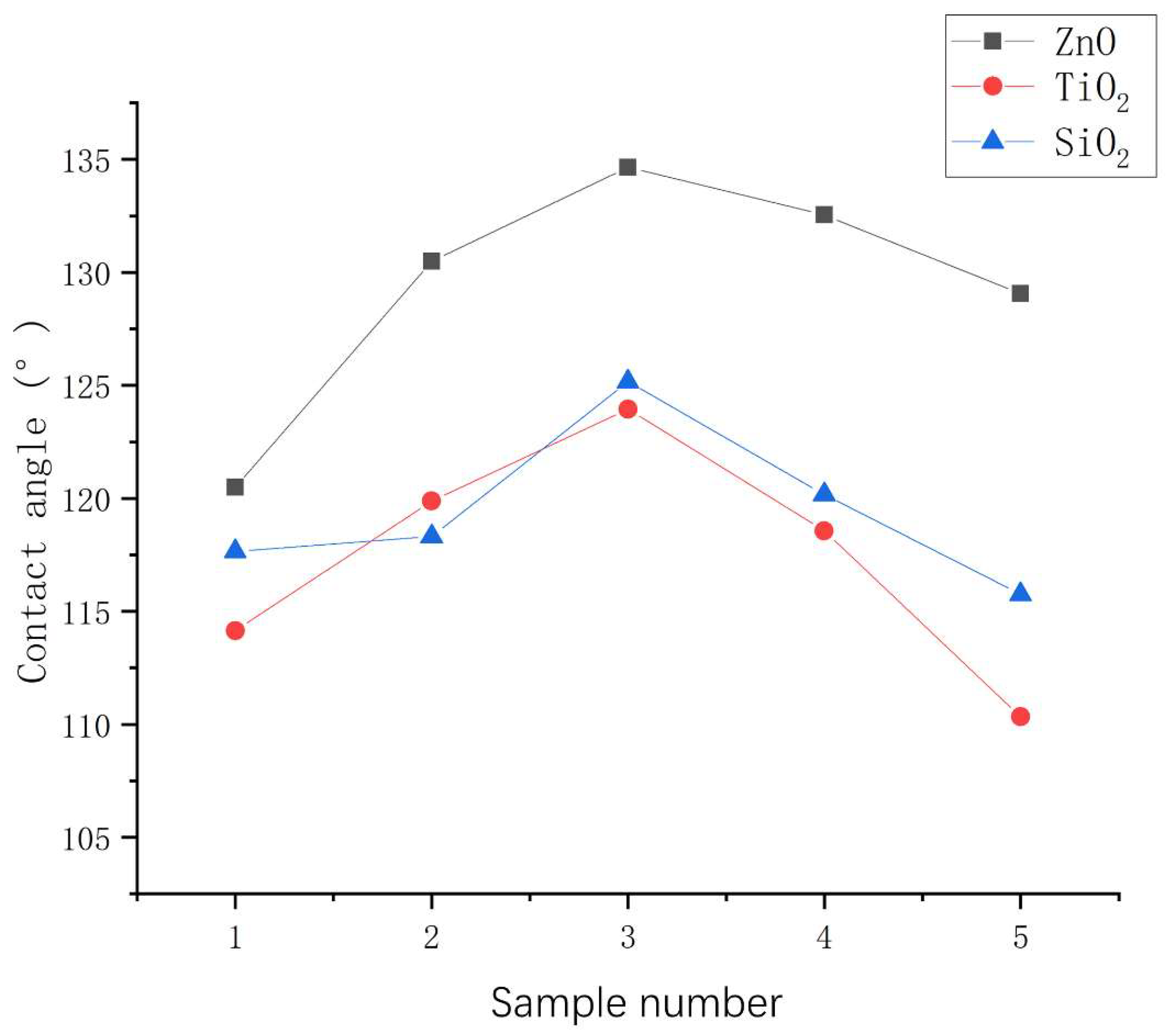
3.2. Contact angles of asphalt concrete with nanocomposite coatings
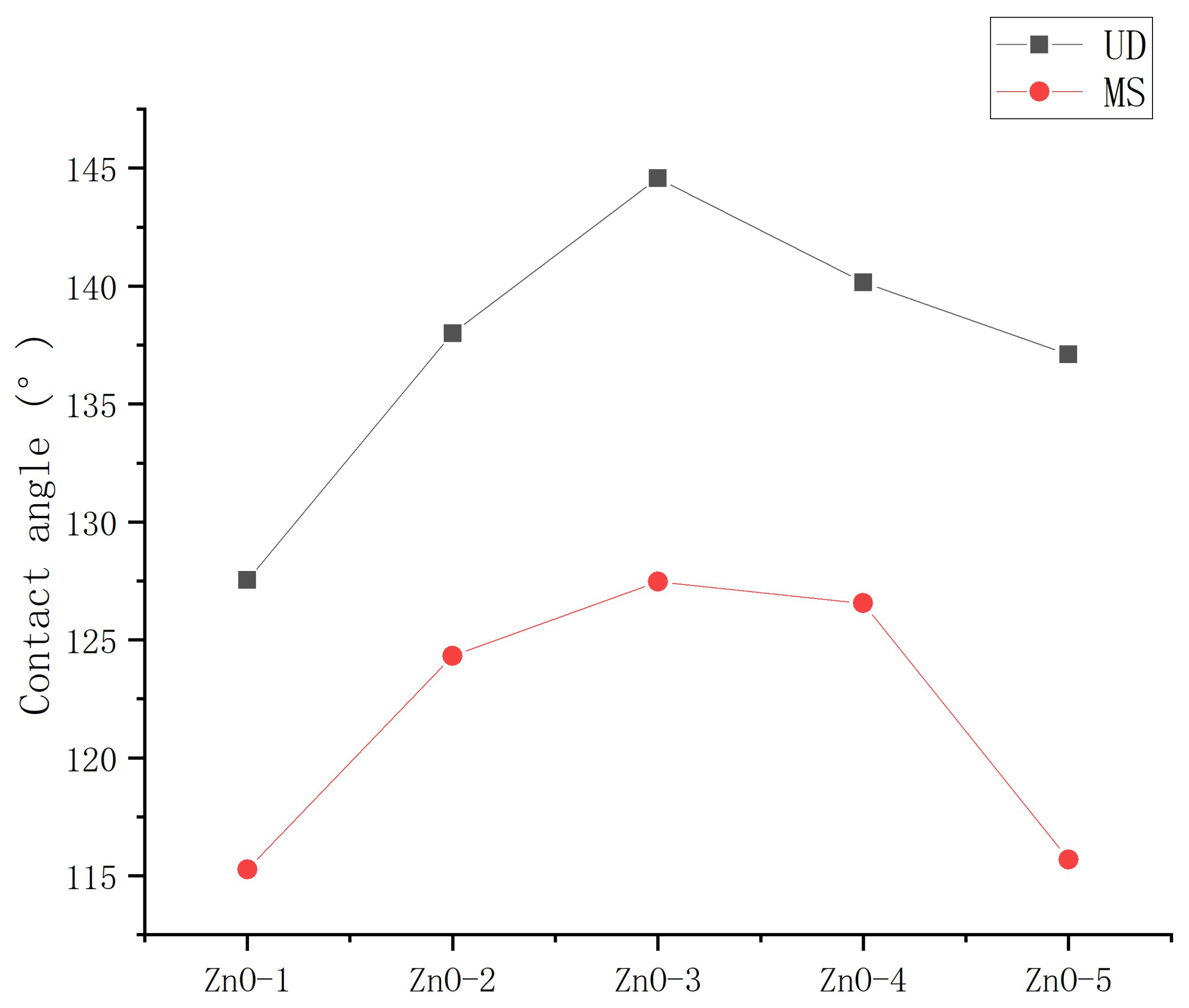
3.2.1. Influence of mass ratio of nanoparticles to stearic acid on contact angle
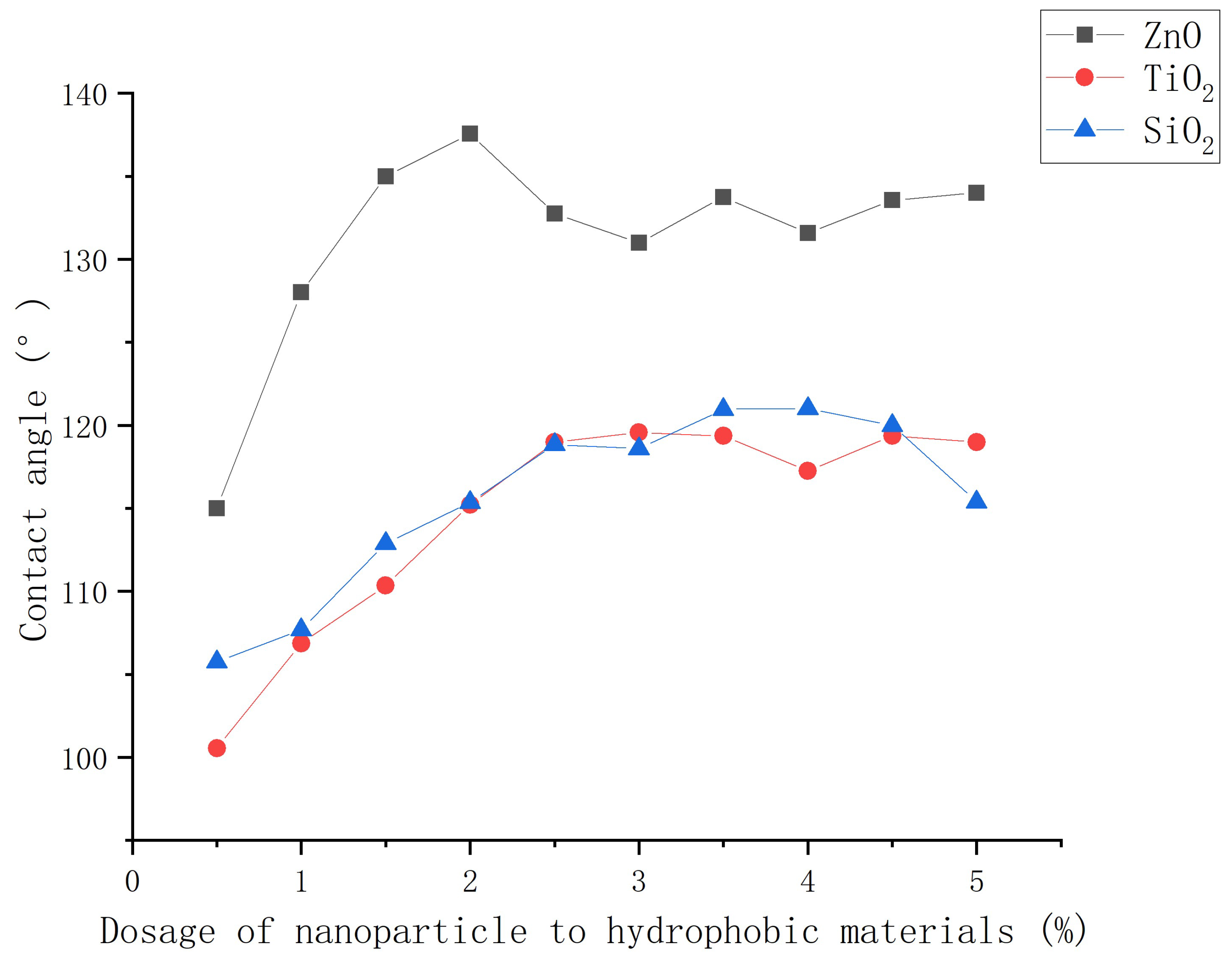
3.2.2. Influence of dosage of nanoparticle to hydrophobic materials on contact angle
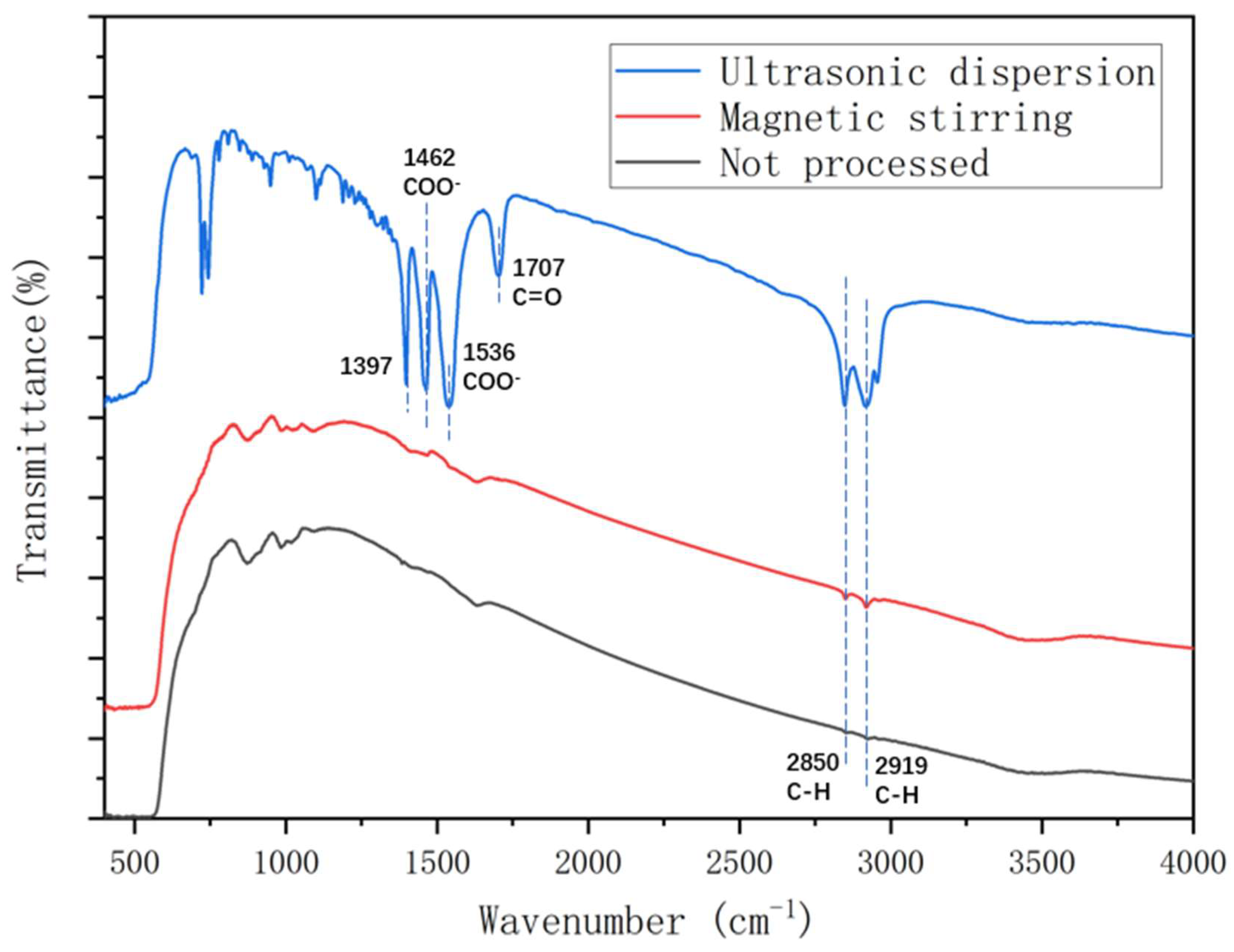
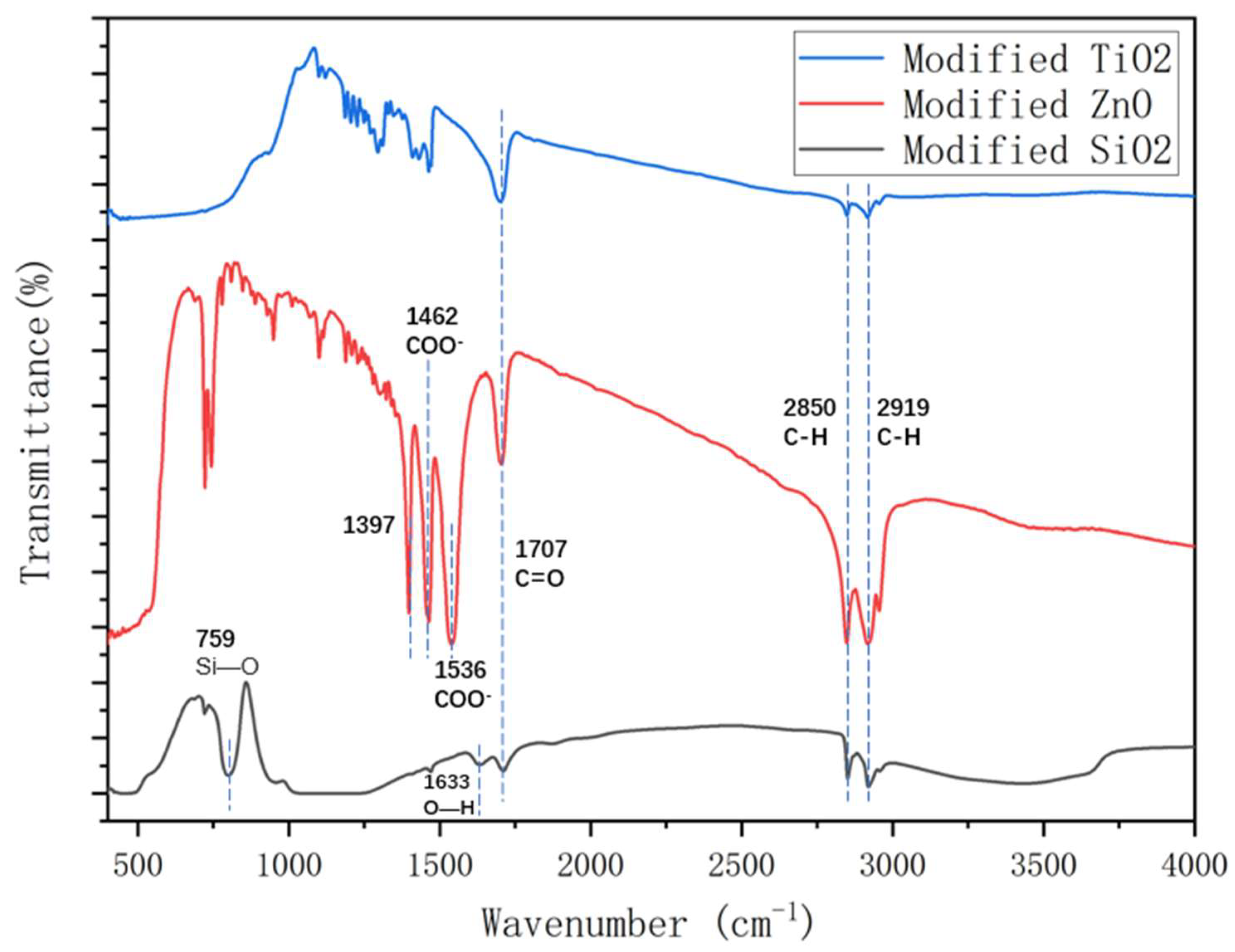
3.3. Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy analysis
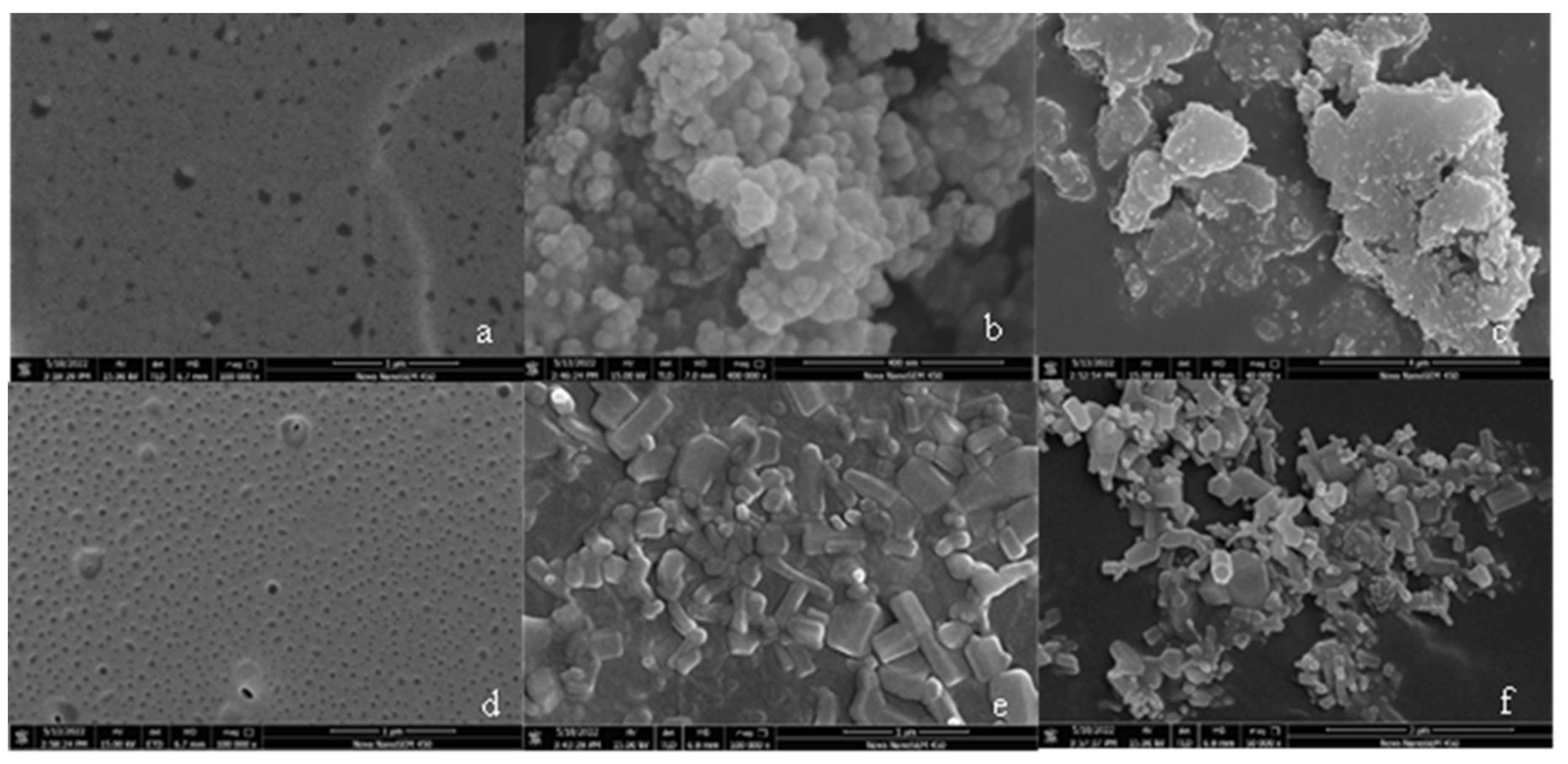
3.4. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis
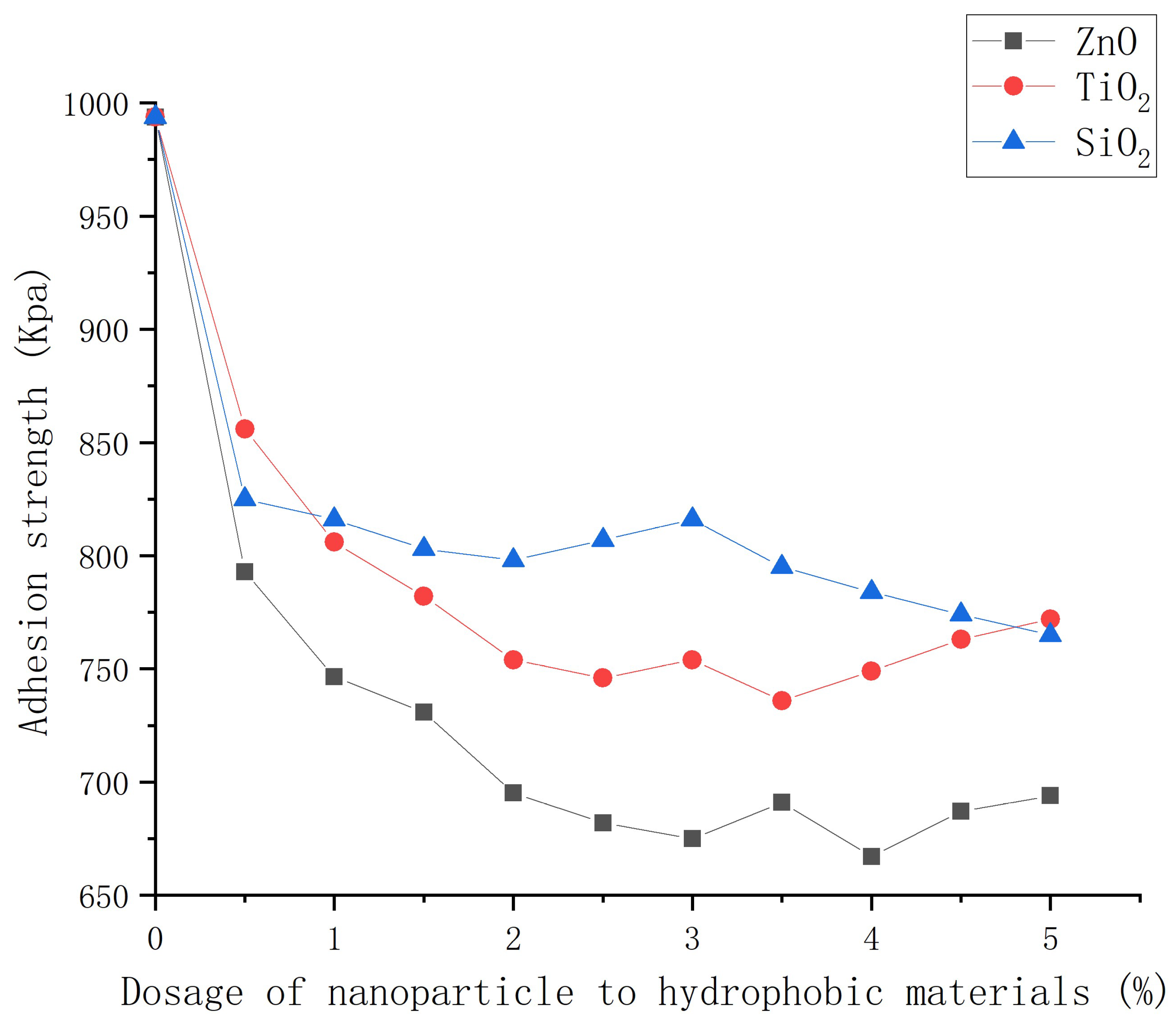
3.5. Ice adhesion force of asphalt concrete with nanocomposite coatings
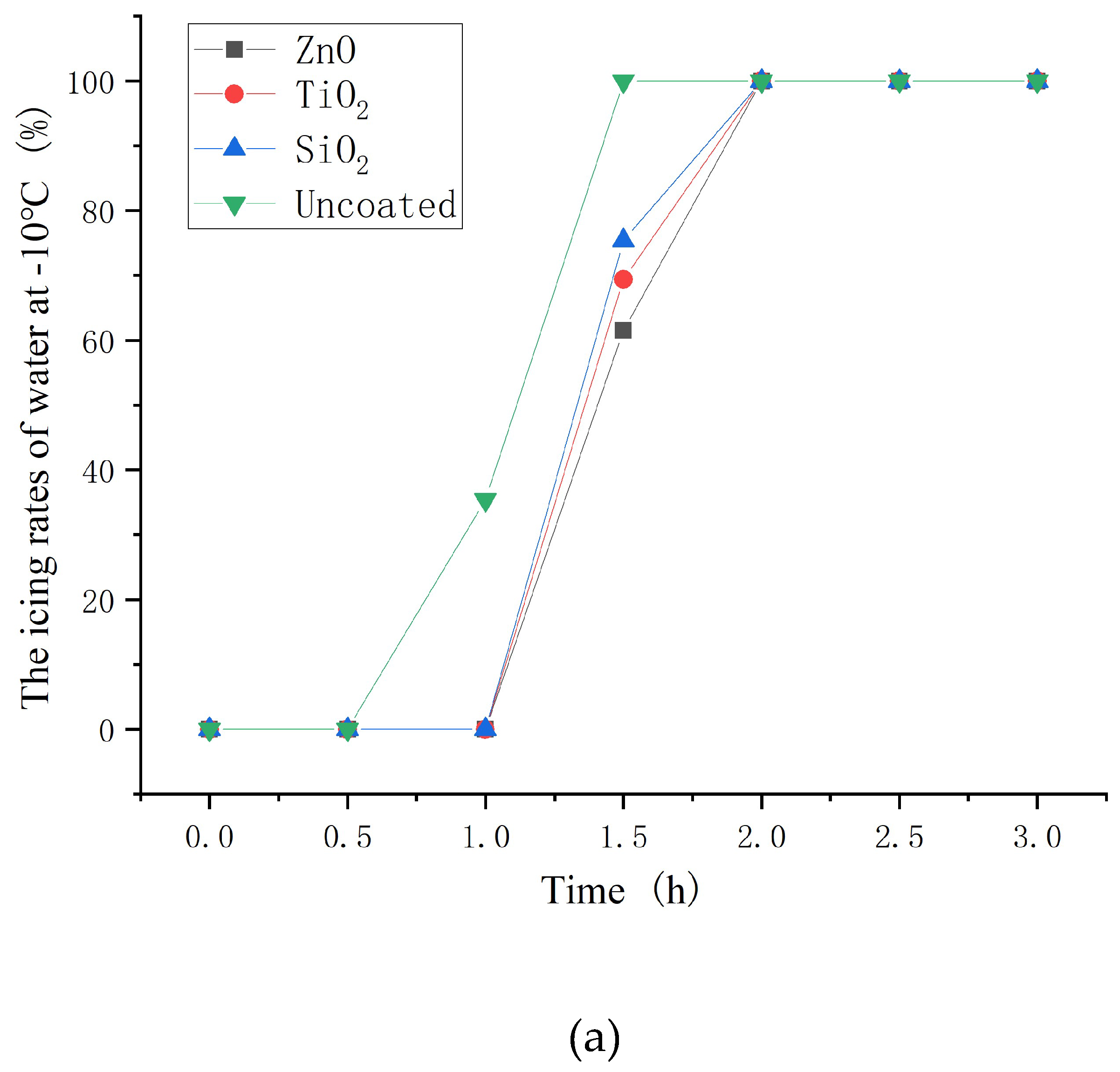
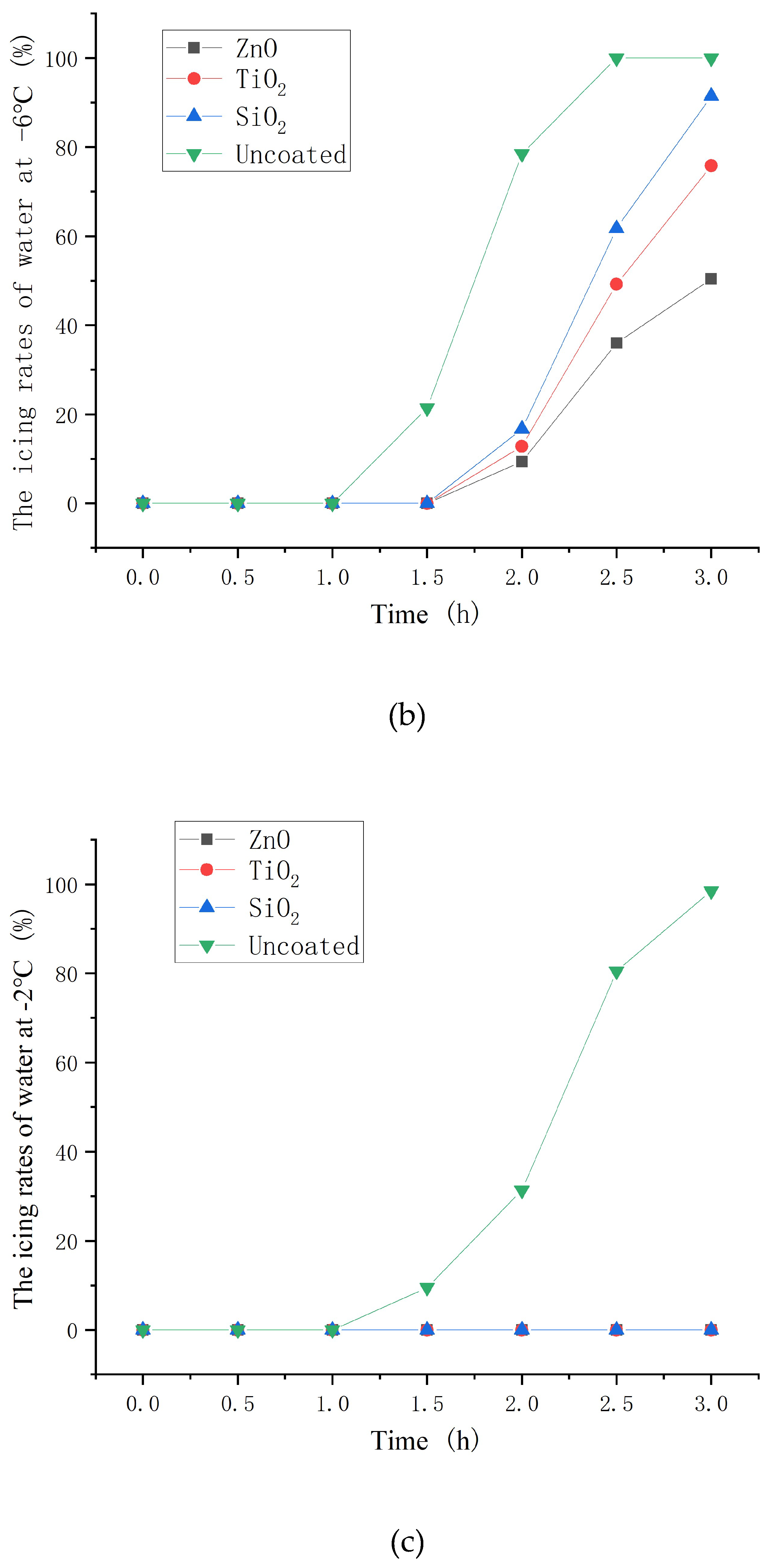
3.6. Icing rate of asphalt concrete with nanoparticle coatings
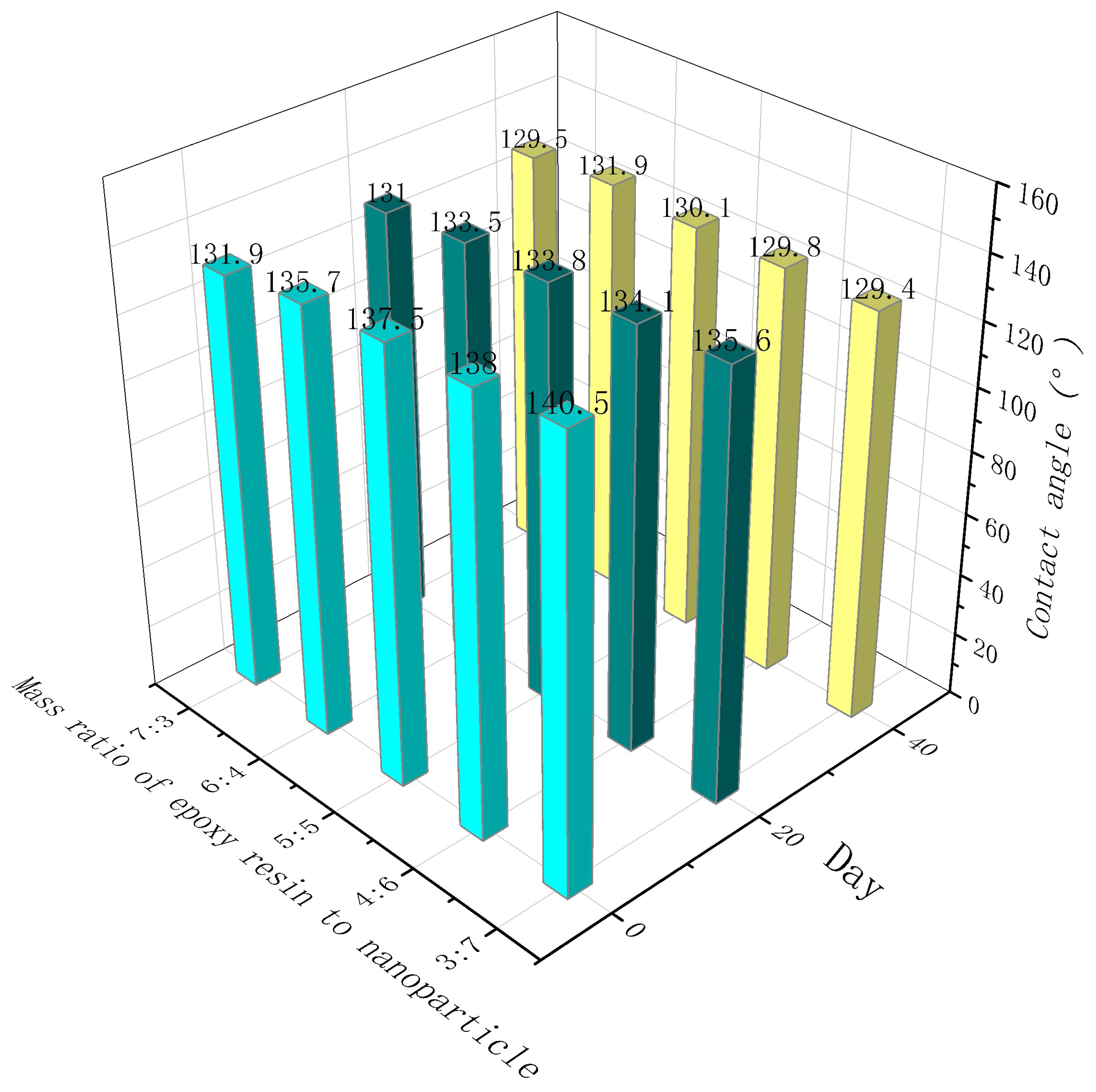
3.7. Contact angle attenuation of coatings with different epoxy resin contents
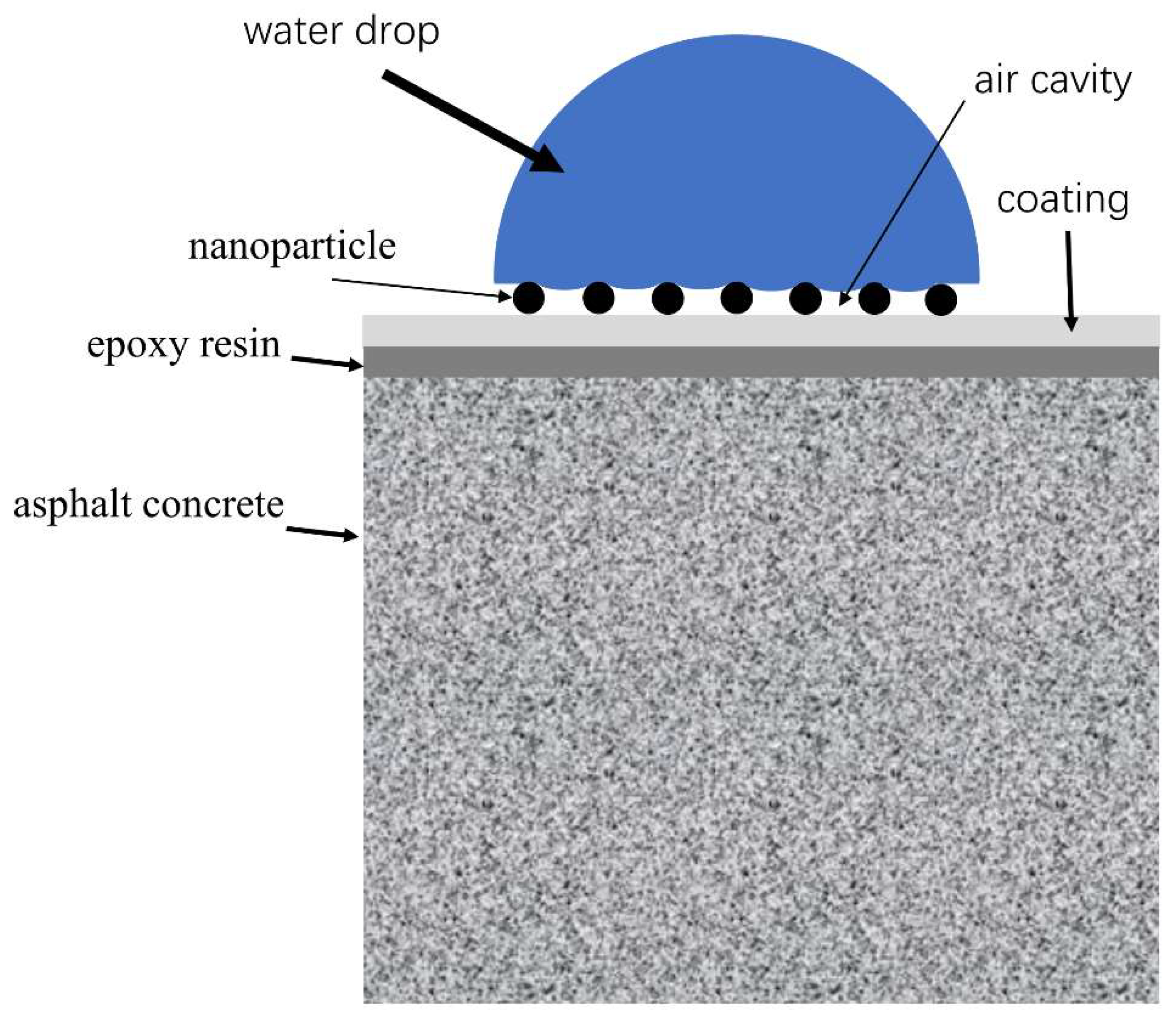
3.8. Mechanism of modified nanoparticles and epoxy resin
4. Conclusions
- Nano-ZnO, TiO2 and SiO2 particles can be modified into hydrophobicity by stearic acid. The optimum preparation method of nanoparticle/epoxy coating is: ultrasonic dispersion and layered spraying.
- The mass ratio of nanoparticles to stearic acid and dosage of nanoparticle to hydrophobic materials have a significant impact on the contact angle of hydrophobic coating. The contact angle increases first and then decreases with the increase of stearic acid. The contact angle increases first and then decreases with the increase of nanoparticle dosage.
- The FTIR test shows that during the chemical reactions of zinc oxide with stearic acid, the carboxyl group in stearic acid was esterified with the hydroxyl group in zinc oxide, which made ZnO nanoparticles disperse more efficiently. In addition, ultrasonic dispersion could increase the reaction degree significantly. The reaction degree of TiO2 and SiO2 with stearic acid was lower than that of ZnO, which could explain the poor hydrophobicity of TiO2 and SiO2 coatings.
- The SEM test shows that the surface of coating is covered with nanoparticles, which are interlaced with each other to form a rough hydrophobic surface. In addition, the ZnO/epoxy layered coating have a layered structure. The lower layer of epoxy resin solution can enhance the durability of the coating, and the upper layer of zinc oxide solution can form a rough hydrophobic surface.
- The hydrophobic coating can reduce the adhesion strength of ice and asphalt concrete, which decreases with the increase of nanoparticle dosage. ZnO, TiO2 and SiO2 coatings can help reduce the adhesion strength by 32.4%, 25.4%, and 22.6% compared with that of ordinary asphalt concrete.
- The hydrophobic coating has a good inhibiting effect on icing. Moreover, the inhibiting effect on icing of ZnO, TiO2 and SiO2 hydrophobic coating decrease in turn. In the environment of −10 and −2°C, hydrophobic coating delayed the beginning icing time by up to 30min and at least 2 hours, respectively.
- 7. The contact angle decreased with the increased dosage of the mass ratio of epoxy resin to nanoparticle, indicating that the epoxy resin significantly improved the durability of the coating. However, coatings with higher dosages of epoxy resin had smaller contact angles. Possibly, with increasing dosage of epoxy resin, epoxy resin fills the gap between nanoparticles and water droplets, reducing the hydrophobicity of the coating.
Acknowledgments
References
- Boinovich, L.B.; Emelyanenko, A.M. Anti-icing Potential of Superhydrophobic Coatings. Mendeleev Communications 2013, 23, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforte, J.L.; Allaire, M.A.; Laflamme, J. Wind tunnel evaluation of a rime metering device using a magnetostrictive sensor. Atmospheric Research 1995, 36, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, H.; Gao, X. Subcooled-Water Nonstickiness of Condensate Microdrop Self-Propelling Nanosurfaces. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015, 7, 26391–26395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Guo, Z.G. Fundamentals of icing and common strategies for designing biomimetic anti-icing surfaces. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2018, 6, 13549–13581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Zheng, Y.M.; Wen, M.X.; Song, C.; Lin, Y.C.; Jiang, L. Icephobic/Anti-Icing Properties of Micro/Nanostructured Surfaces. Advanced Materials 2012, 24, 2642–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.H.; Chen, Z. A mechanically robust transparent coating for anti-icing and self-cleaning applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2018, 6, 16043–16052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Huang, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, S.; Lai, Y.K. Liquid mobility on superwettable surfaces for applications in energy and the environment. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2019, 7, 38–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.H.; Zhao, X.; Ho, J.W.C.; Chen, Z. Design and durability study of environmental-friendly room-temperature processable icephobic coatings. Chemical Engineering Journal 2019, 355, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barthlott, W.; Neinhuis, C. Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 1997, 202, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laforte, C.; Laforte, J.; Carrière, J. How a solid coating can reduce the adhesion of ice on a structure. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the international workshop on atmospheric icing of structures (IWAIS); 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Arabzadeh, A.; Ceylan, H.; Kim, S.; Gopalakrishnan, K.; Sassani, A. Superhydrophobic Coatings on Asphalt Concrete Surfaces: Toward Smart Solutions for Winter Pavement Maintenance. Transportation Research Record 2016, 2551, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, M.; Li, W.; Wang, B.; Deng, B.; Ma, F.; Yu, Z. Preparation and anti-icing behavior of superhydrophobic surfaces on aluminum alloy substrates. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8482–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Li, W. Preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces on Al substrates and the anti-icing behavior. Journal of Alloys and Compounds 2013, 576, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonini, C.; Innocenti, M.; Horn, T.; Marengo, M.; Amirfazli, A. Understanding the effect of superhydrophobic coatings on energy reduction in anti-icing systems. Cold regions science and technology 2011, 67, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, A.; Dodiuk, H.; Laforte, C.; Kenig, S. The relationship between water wetting and ice adhesion. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 2009, 23, 1907–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Yue, J.; Guo, C.; Ji, Y. Influences of modified nanoparticles on hydrophobicity of concrete with organic film coating. Construction and Building Materials 2018, 169, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Hu, Y.; You, Z.; Yang, H.; Nie, Y.; Wu, T.; Yang, H.; Ou, R. Preparation and anti-icing performance of acrylic superhydrophobic asphalt pavement coating with microwave heating function. Construction and Building Materials 2022, 344, 128289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Wang, L.; Qian, H.; Li, X. Superhydrophobic surfaces for corrosion protection: a review of recent progresses and future directions. Journal of Coatings Technology and Research 2016, 13, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Dang, H. Surface-modification in situ of nano-SiO2 and its structure and tribological properties. Applied Surface Science 2006, 252, 7856–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, D.F.; Giannelis, E.P. Silicate Dispersion and Mechanical Reinforcement in Polysiloxane/Layered Silicate Nanocomposites. Chemistry of Materials 2010, 22, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.Q.; Zhao, Y.P. Growth of ZnO nanotetrapods with hexagonal crown. Applied Physics Letters 2006, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Feng, J.-T.; Zhao, Y.-P.; Yu, T.X. Fabrication of Novel Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Water Droplet Bouncing Behavior — Part 1: Stable ZnO–PDMS Superhydrophobic Surface with Low Hysteresis Constructed Using ZnO Nanoparticles. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 2010, 24, 2693–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.B.; Zhao, Y.P.; Yu, T.X. Fabrication of Novel Superhydrophobic Surfaces and Droplet Bouncing Behavior - Part 2: Water Droplet Impact Experiment on Superhydrophobic Surfaces Constructed Using ZnO Nanoparticles. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology 2011, 25, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Ogawa, T.; Kim, J.; Fujimoto, K.; Shiratori, S. Fabrication of a super-hydrophobic nanofibrous zinc oxide film surface by electrospinning. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, Z. A mechanically robust transparent coating for anti-icing and self-cleaning applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2018, 6, 16043–16052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Y.; Håkonsen, V.; He, Z.; Xiao, S.; He, J.; Zhang, Z. Enhancing the Mechanical Durability of Icephobic Surfaces by Introducing Autonomous Self-Healing Function. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces 2018, 10, 11972–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.H.; Ma, X.Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.C.; Zhu, Y.C. The influence of surface modification on the structure and properties of a zinc oxide-filled poly(ethylene terephthalate). Polymer International 2013, 62, 432–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.K.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication and characterization of superhydrophobicity ZnO nanoparticles with two morphologies by using stearic acid. Materials Research Express 2019, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Chen, S.; Liu, P.; Geng, F.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; He, D.; Pan, D. Improvement of β-TCP/PLLA biodegradable material by surface modification with stearic acid. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2016, 62, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfaoui, M.A.; Dolez, P.I.; Dube, M.; David, E. Development and characterization of a hydrophobic treatment for jute fibres based on zinc oxide nanoparticles and a fatty acid. Applied Surface Science 2017, 397, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Cheng, Y.M.; Wei, Q.B.; Li, X.H.; Zhang, Z.J. Suspension of surface-modified nano-SiO2 in partially hydrolyzed aqueous solution of polyacrylamide for enhanced oil recovery. Colloids and Surfaces a-Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2017, 524, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, W.; Tuteja, A.; Mabry, J.M.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H. A modified Cassie–Baxter relationship to explain contact angle hysteresis and anisotropy on non-wetting textured surfaces. Journal of colloid and interface science 2009, 339, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassie, A.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Transactions of the Faraday society 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreder, M.J.; Alvarenga, J.; Kim, P.; Aizenberg, J. Design of anti-icing surfaces: smooth, textured or slippery? Nature Reviews Materials 2016, 1, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | nanoparticle(g) | Stearic acid (g) | Anhydrous ethanol (ml) | Epoxy resin(g) | |
| ZnO-1 | ZnO(g) | 5 | 0.30 | 100 | 5 |
| ZnO-2 | 5 | 0.40 | 100 | 5 | |
| ZnO-3 | 5 | 0.50 | 100 | 5 | |
| ZnO-4 | 5 | 0.60 | 100 | 5 | |
| ZnO-5 | 5 | 0.70 | 100 | 5 | |
| SiO2-1 | SiO2(g) | 5 | 0.6 | 100 | 5 |
| SiO2-2 | 5 | 0.7 | 100 | 5 | |
| SiO2-3 | 5 | 0.8 | 100 | 5 | |
| SiO2-4 | 5 | 0.9 | 100 | 5 | |
| SiO2-5 | 5 | 1.00 | 100 | 5 | |
| TiO2-1 | TiO2(g) | 5 | 0.25 | 100 | 5 |
| TiO2-2 | 5 | 0.50 | 100 | 5 | |
| TiO2-3 | 5 | 0.75 | 100 | 5 | |
| TiO2-4 | 5 | 1.00 | 100 | 5 | |
| TiO2-5 | 5 | 1.25 | 100 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





