1. Introduction
In recent years, significant research attention has been focused on metasurfaces [
1,
2,
3,
4]. These surfaces are usually composed of artificial electromagnetic materials made from subwavelength-scale dielectric nanostructures. Metasurfaces have the ability to manipulate light efficiently and flexibly, thus bringing new design possibilities and methods to the optics field. All-dielectric metasurfaces in particular offer advantages that include low losses, high efficiency, and ease of integration, making these surfaces highly promising for a variety of applications, including optical imaging [
5,
6,
7,
8], optical information processing [
9], and optoelectronic devices [
10,
11]. However, the limited nonlinear optical coefficients of traditional optical materials such as silicon have hindered the development progress of nonlinear optics in all-dielectric metasurfaces [
12]. To enhance the nonlinear effects in these all-dielectric metasurfaces, one effective method is to use bound states in the continuum (BICs) to achieve high-Q resonances. Unlike conventional bound states, BICs are in a continuous spectrum, can coexist with extended waves, and remain completely bound without any radiation [
13,
14,
15,
16]. Based on BICs, a high level of localized electromagnetic field enhancement can be generated in all-dielectric metasurfaces, thus improving the efficiency of nonlinear processes significantly.
In addition, these metasurfaces can support Mie resonances [
17,
18], including electric dipole (ED), magnetic dipole (MD), and toroidal dipole (TD) resonances. A TD can be regarded as a circular arrangement of MDs or EDs that are compressed into a point and then connected head-to-tail, and an almost unknown third type of electromagnetic multipole, i.e., the toroidal multipole, is required, along with familiar magnetic multipoles and electric multipoles, to form a complete multipole representation of any radiating or nonradiating source [
19,
20]. It should be noted that the TD resonance in metal metasurfaces is relatively weak and it is often masked by stronger electric and magnetic multipoles [
21]. However, the all-dielectric metasurface proposed in this paper enables observation and detection of the TD response. By providing a reasonable design for the super-material unit structure, generation of the TDs can be achieved. The TD resonance in metasurfaces provides new opportunities for development of optical devices such as high-sensitivity sensors [
22,
23,
24], and optical modulators and switches [
25]. Furthermore, recent reports have revealed a strong connection between the TD resonance and the BICs, allowing high Q and a strong electromagnetic field enhancement.
In this paper, we present the design of a novel silicon-based all-dielectric metasurface structure that breaks the in-plane symmetry of the metasurface structure by arranging high-resistivity silicon disks that contain a pair of orthogonal slits into clusters. Using this structure, the prominent feature of the BIC–Fano resonance can be observed in the transmission spectrum. Through analysis of the multipole expansion of the microscopic scattered power and the electromagnetic field modulus distribution, we demonstrate the existence of a TD-BIC in this structure, and also achieve continuous tuning of the Fano resonance via adjustment of the geometric parameters. This work provides a novel and effective scheme for nonlinear optics design in all-dielectric metasurfaces.
2. Materials and Methods
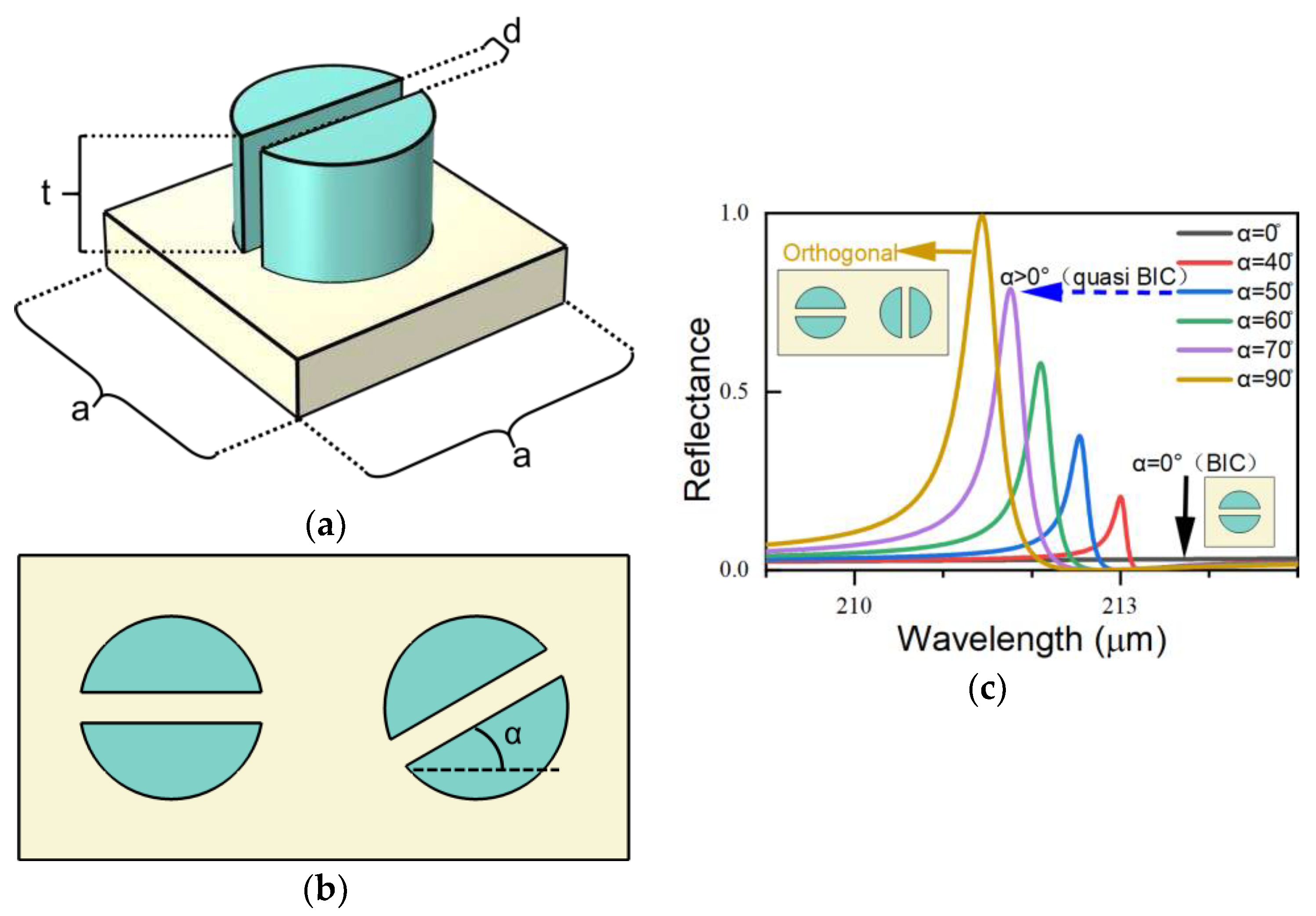
Figure 1 shows the proposed all-dielectric metasurface, which is composed of resonant units consisting of slit silicon disks deposited on a quartz substrate (where the refractive index of silicon is n=11.7). The silicon disks are distributed in a square lattice with a period of 100 μm (p). The disks have a radius of 30 μm (r), a thickness of 40 μm (t), and a gap width of 10 μm (d). The electromagnetic properties and the spectral response of the all-dielectric metasurface were simulated numerically using COMSOL Multiphysics software, where periodic boundary conditions were applied on the four sides of the resonant unit and perfectly matched layers were added at the top and the bottom. The excitation field is an x-polarized plane wave propagating along the z-axis.
3. Results
To initiate the BICs, we rotated adjacent silicon disk slits by an angle α, thus breaking the in-plane symmetry of the metasurface. As α changes, the metasurface transforms from BICs into quasi-BICs. When α=0°, the metasurface is at BICs that cannot be excited by external fields and are unobservable. As α increases, a sharp asymmetric Fano line shape then appears and is accompanied by a blue shift in the resonance center and an increase in the modulation depth until α=90°, when the adjacent silicon disk slits are distributed orthogonally and the modulation depth reaches a maximum. To ensure maximum reflectance, we studied the case of the orthogonal slit distribution.
Figure 1c shows the reflection spectrum of the orthogonal distribution structure, as fitted using the Fano formula [
26]:
In the equation,
is the Fano fitting parameter that determines the asymmetry of the curve.
and
are coupling parameters.
represents the resonance peak wavelength and
represents the resonance linewidth. Therefore,
. The resonance peak wavelength and resonance linewidth are 211.43 μm and 0.44 μm for this resonance, respectively, resulting in a Q factor of 480. To enable further quantitative analysis of the microscopic aspects of the multipole properties of the resonance, we also calculate the multipole expansion of the scattered power of this resonance in Cartesian coordinates as follows [
27,
28].
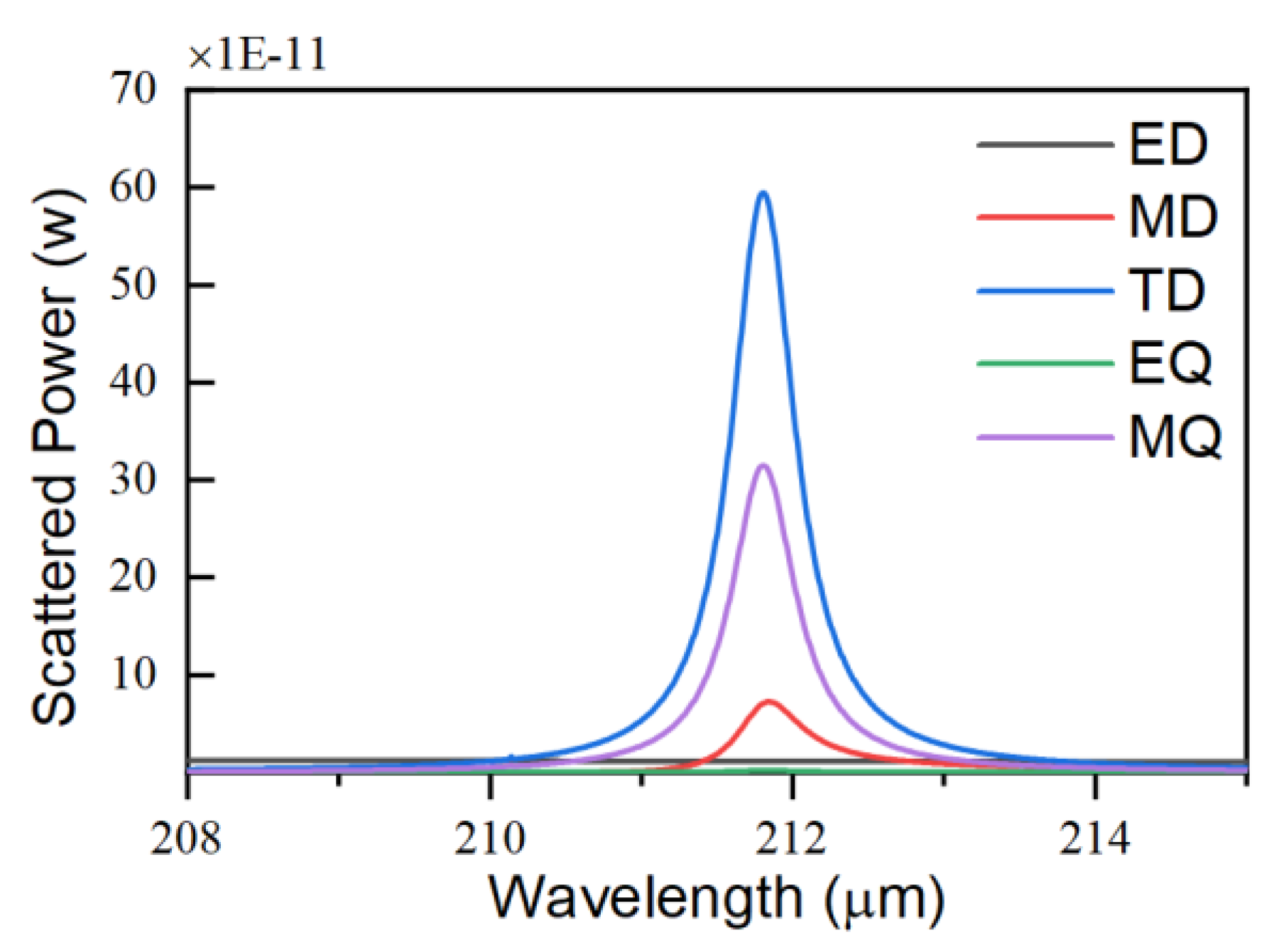
Figure 2 illustrates the scattering powers of the ED, the MD, the TD, the electric quadrupole (Qe), and the magnetic quadrupole (Qm). From
Figure 2, it is evident that the TD is dominant in resonance, followed by the Qm. The scattering power of the Qm is less than half that of the TD. Simultaneously, the ED, the MD, and the Qe are suppressed strongly. To explore the mechanism of this TD-BIC, we analyze it from the perspective of its electromagnetic field and current profile. As shown in
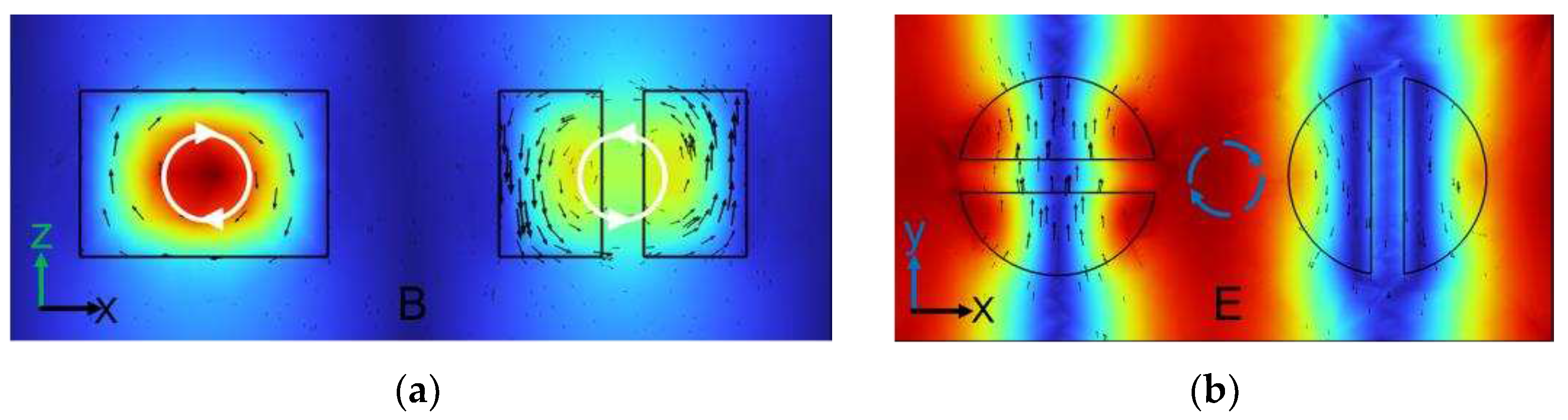
Figure 3, the displacement current forms two reversed loops in the x-z plane and the magnetic field forms a clockwise loop in the x-y plane, indicating that this is a TD resonance pattern along the negative z-direction.
4. Discussion
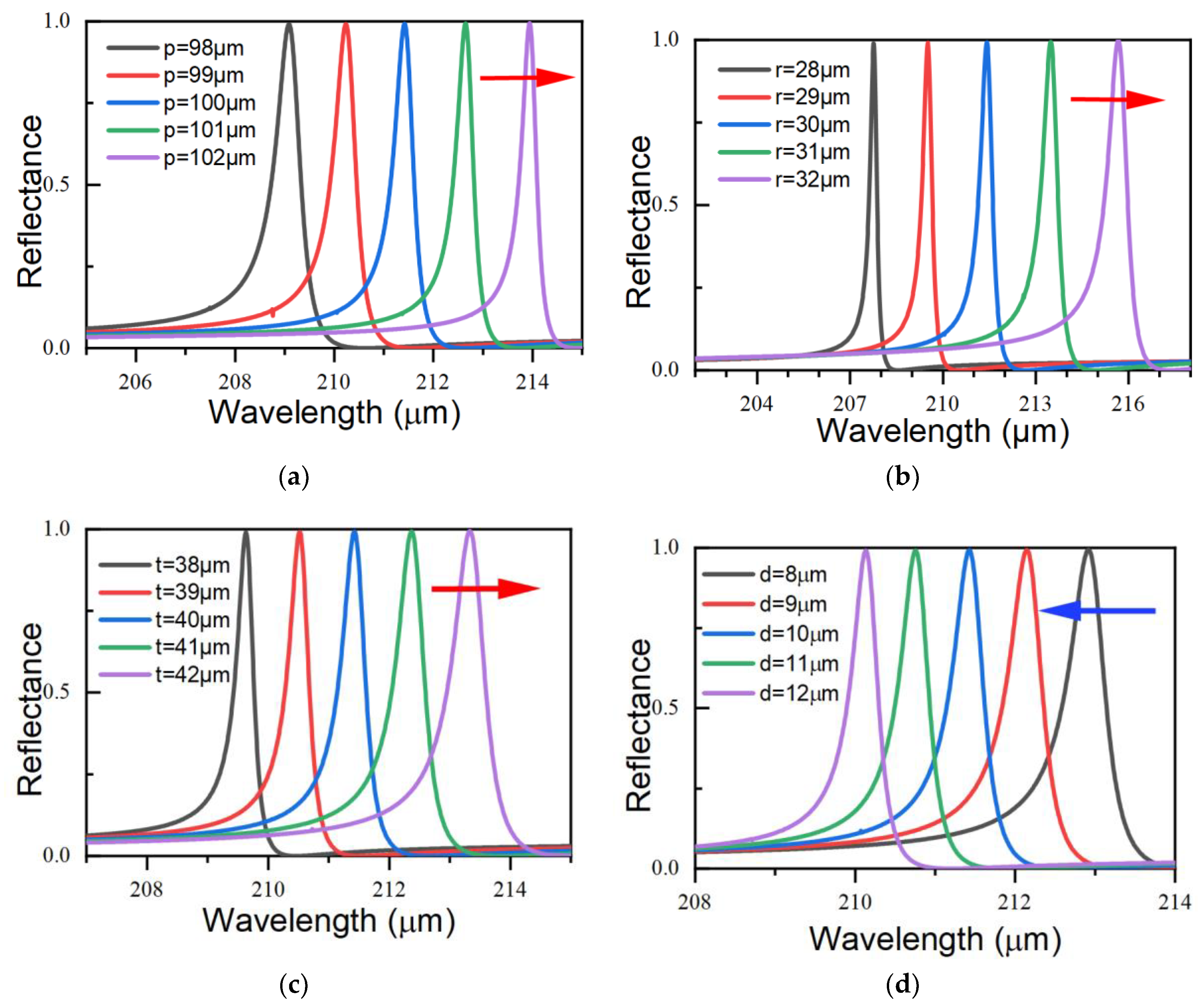
We investigated the reflectance spectra of the asymmetric metasurface structures with various geometric parameters. All geometric parameters were varied in steps of 1 μm, with only one parameter being varied in each figure, while the other parameters were maintained at their corresponding values in
Figure 1. The results are shown in
Figure 4. When the period, radius, and thickness of the unit structure were varied, a redshift in the resonance was observed. The linewidth increased slightly with increasing thickness. The redshift was more pronounced with increasing radius than it was with changing thickness, and increasing the radius also led to a larger linewidth and a reduced Q-factor. The linewidth decreased and the Q-factor increased when the period increased. In contrast, increasing the gap width caused a blueshift in the resonance with almost no change observed in the linewidth. By comparing the effects of these different geometric parameters on the reflection spectra of the asymmetric metasurface structures, we found that the Fano resonance was more sensitive to radius than to the other parameters because the TD mode was a complex collective response that was more dependent on the radius than on the other geometric parameters. Based on these results, we can adjust the TD resonances of the asymmetric metasurface structures easily by changing the different geometric parameters.
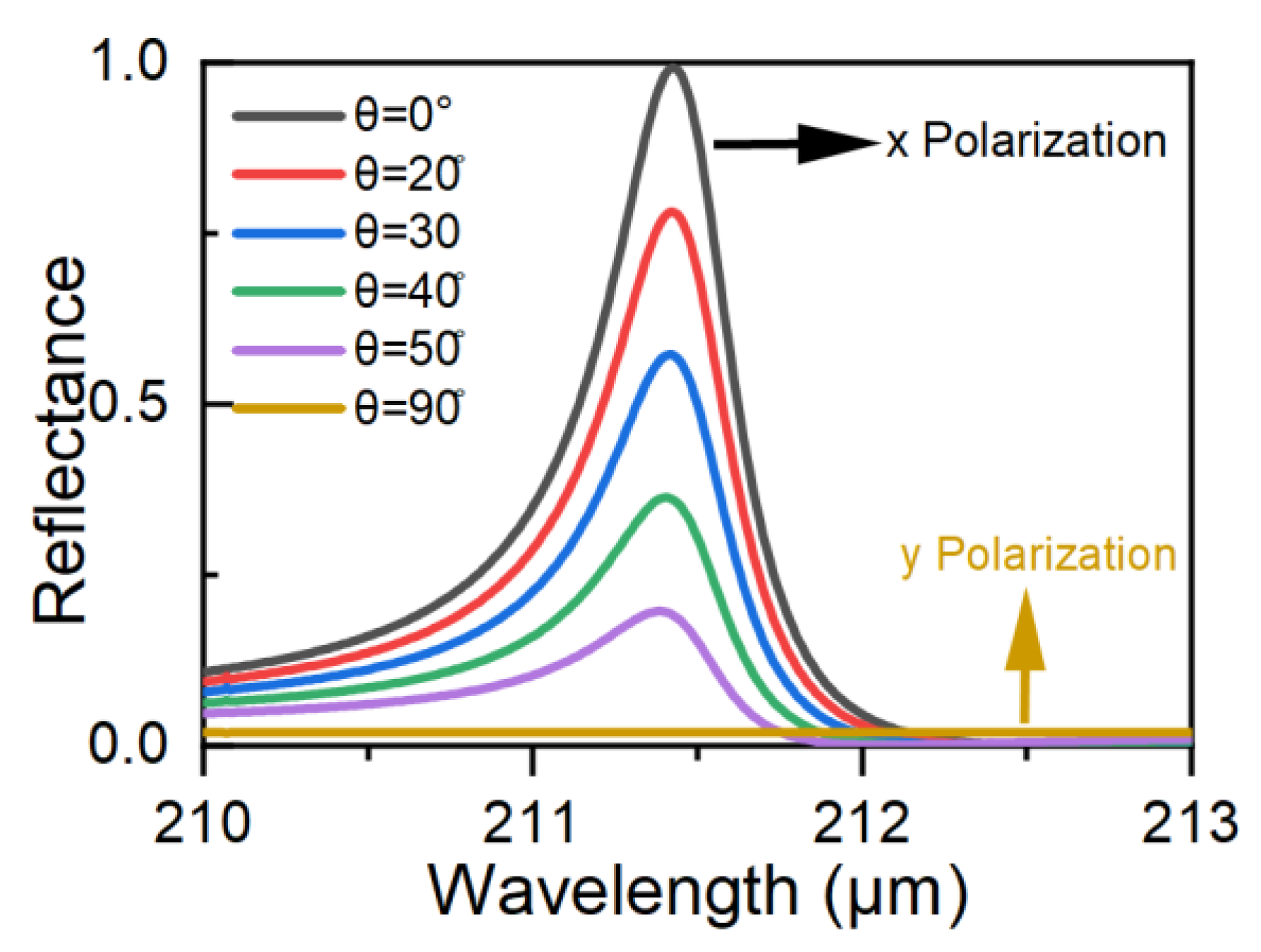
We also studied the effect of the incident light’s polarization angle on the resonance, with results as shown in
Figure 5. The results demonstrate that the reflection spectrum’s modulation depth reaches a maximum when the incident light is polarized along the x direction, but the resonance disappears when the incident light is polarized along the y direction. This occurs because the designed metasurface structure only breaks the symmetry along the x direction, and periodic translational symmetry is maintained along the y direction. Optical switching may be achieved using this feature. When θ=0°, electromagnetic waves at the resonance peak are reflected completely, and this state can be considered to be “off”. When θ increases, the reflectivity then decreases, and this can be considered to be “on”. The transmitted light intensity can then be modulated by simply changing θ.
In summary, we have designed a TD-BIC metasurface structure that can achieve continuous tuning of the Fano resonance by adjusting its geometric parameters. We revealed the mechanism of the TD-BIC by analyzing multipole decomposition of the scattered power, along with the electromagnetic field and the polarization current. Additionally, our design and fabrication methods are universal and can easily be extended to different wavelengths. Furthermore, the designed metasurface structure can be applied to optical devices, including optical switches and high-sensitivity refractive index sensors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J. J.; methodology, J. J. and X. L.; software, J. J.; validation, J. J.; formal analysis, J. J.; investigation, J. J., X. L. and X. Y.; resources, X. L. and Y. G.; data curation, J. J.; writing—original draft preparation, J. J.; writing—review and editing, X. L. and Y. G.; visualization, J. J.; supervision, X. L., Y. G. and X. Y.; project administration, X. L. and Y. G.; funding acquisition, X. L. and Y. G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 51862027 and the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia, grant number 2022QN01005.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available on
reasonable request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Yu, N.; Genevet, P.; Kats, M.A.; Aieta, F.; Tetienne, J.-P.; Capasso, F.; Gaburro, Z. Light Propagation with Phase Discontinuities: Generalized Laws of Reflection and Refraction. Science 2011, 334, 333–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overvig, A.C.; Shrestha, S.; Malek, S.C.; Lu, M.; Stein, A.; Zheng, C.; Yu, N. Dielectric Metasurfaces for Complete and Independent Control of the Optical Amplitude and Phase. Light Sci Appl 2019, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Lei, L.; Xie, M.; Xu, P.; Xu, S. High-Performance Metamaterial Light Absorption from Visible to Near-Infrared Assisted by Anti-Reflection Coating. Photonics 2023, 10, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhang, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Fu, M.; Yang, J. Design of Reflective Tunable Structural Color Metasurface Based on Guided-Mode Resonance Filter and Sb2S3. Photonics 2023, 10, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlickriede, C.; Kruk, S.S.; Wang, L.; Sain, B.; Kivshar, Y.; Zentgraf, T. Nonlinear Imaging with All-Dielectric Metasurfaces. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4370–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.; Li, X.; Pu, M.; Ma, X.; Zhang, F.; Gao, P.; Liu, K.; Luo, X. Midinfrared Real-Time Polarization Imaging with All-Dielectric Metasurfaces. Applied Physics Letters 2019, 114, 161904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Suen, J.Y.; Liu, X.; Padilla, W.J. All-Dielectric Metasurface Absorbers for Uncooled Terahertz Imaging. Optica 2017, 4, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zou, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, H.; Fu, Q. Hierarchical Feature Enhancement Algorithm for Multispectral Infrared Images of Dark and Weak Targets. Photonics 2023, 10, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Ou, X.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Ping Yang; Wang, S. ; Duan, H. All-Dielectric Metasurfaces for Polarization Manipulation: Principles and Emerging Applications. Nanophotonics 2020, 9, 3755–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Luo, H.; Li, Q.; Pei, X.; Du, K.; Qiu, M. Near-Infrared Super-Absorbing All-Dielectric Metasurface Based on Single-Layer Germanium Nanostructures. Laser & Photonics Reviews 2018, 12, 1800076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhara, E.; Ghobadi, A.; Ozbay, E. An All-Dielectric Metasurface Coupled with Two-Dimensional Semiconductors for Thermally Tunable Ultra-Narrowband Light Absorption. Plasmonics 2021, 16, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, Q.; Piredda, G.; Boyd, R.W.; Agrawal, G.P.; Fauchet, P.M. Anisotropic Nonlinear Response of Silicon in the Near-Infrared Region. Appl. Phys. Lett.
- Hsu, C.W.; Zhen, B.; Lee, J.; Chua, S.-L.; Johnson, S.G.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Soljačić, M. Observation of Trapped Light within the Radiation Continuum. Nature 2013, 499, 188–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, H.; Wintgen, D. Interfering Resonances and Bound States in the Continuum. Phys. Rev. A 1985, 32, 3231–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carletti, L.; Koshelev, K.; De Angelis, C.; Kivshar, Y. Giant Nonlinear Response at the Nanoscale Driven by Bound States in the Continuum. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2018, 121, 033903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.W.; Zhen, B.; Stone, A.D.; Joannopoulos, J.D.; Soljačić, M. Bound States in the Continuum. Nat Rev Mater 2016, 1, 16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, F.; Lippens, D. Mie Resonance-Based Dielectric Metamaterials. Materials Today 2009, 12, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivshar, Y.; Miroshnichenko, A. Meta-Optics with Mie Resonances. Opt. Photonics News 2017, 28, 24–31; [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savinov, V.; Papasimakis, N.; Tsai, D.P.; Zheludev, N.I. Optical Anapoles. Commun Phys 2019, 2, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miroshnichenko, A.E.; Evlyukhin, A.B.; Yu, Y.F.; Bakker, R.M.; Chipouline, A.; Kuznetsov, A.I.; Luk’yanchuk, B.; Chichkov, B.N.; Kivshar, Y.S. Nonradiating Anapole Modes in Dielectric Nanoparticles. Nat Commun 2015, 6, 8069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaelberer, T.; Fedotov, V.A.; Papasimakis, N.; Tsai, D.P.; Zheludev, N.I. Toroidal Dipolar Response in a Metamaterial. Science 2010, 330, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zheng, L.; Xiong, L.; Qi, J.; Li, B. High Q-factor multiple Fano resonances for high-sensitivity sensing in all-dielectric metamaterials. OSA Continuum 2019, 2, 2818–2829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, Z.; Du, Y.; Qin, J. Ultrasensitive Terahertz Sensing with High- Q Toroidal Dipole Resonance Governed by Bound States in the Continuum in All-Dielectric Metasurface. Nanophotonics 2021, 10, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, A.; Bu, P.; Cheng, L.; Hu, C.; Mahapatra, R. High-Sensitivity Sensor Based on Diametrical Graphene Strip Plasma-Induced Transparency. Photonics 2023, 10, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, J.; Zheng, C.; Yue, Z.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, J. Active Controllable Spin-Selective Terahertz Asymmetric Transmission Based on All-Silicon Metasurfaces. Applied Physics Letters 2021, 118, 221110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fano, U. Effects of Configuration Interaction on Intensities and Phase Shifts. Physical Review 1961, 124, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evlyukhin, A.B.; Fischer, T.; Reinhardt, C.; Chichkov, B.N. Optical Theorem and Multipole Scattering of Light by Arbitrarily Shaped Nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 205434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radescu, E.E.; Vaman, G. Exact Calculation of the Angular Momentum Loss, Recoil Force, and Radiation Intensity for an Arbitrary Source in Terms of Electric, Magnetic, and Toroid Multipoles. Phys. Rev. E 2002, 65, 046609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).