Submitted:
06 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
| A. Headache that meets the criteria for medication-overuse headache. B. Regular use of (ergotamine, triptans, common analgesics, acetil-salicil acid, paracetamol (acetaminofen), non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), opioids, combined analgetics, and other* for 10 or more days per month for a period of more than 3 months. |
Epidemiology
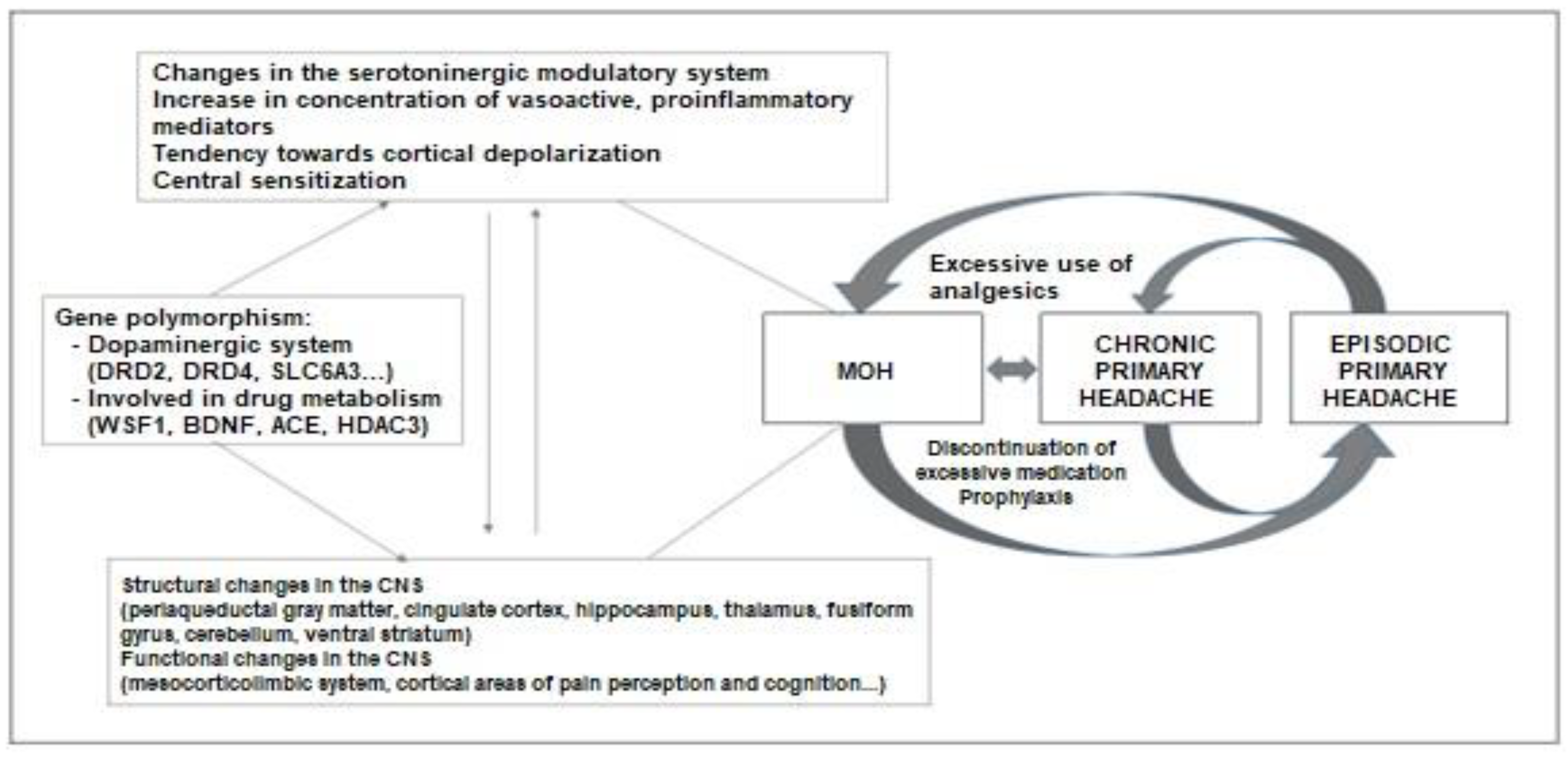
Pathophysiology
Risk Factors
Type of excessively used therapy
Impact of medication overuse headache (MOH)
Comorbidities
Diagnosis
Headache of excessive use of ergotamine
Headache of excessive use of triptans
Headache due to overuse of common analgesics.
Headache due to overuse of opioids
Headache due to overuse of combined analgetics
Medication overuse headache attributed to multiple classes of drugs, rather than individual overuse
Medication overuse headache attributed to unverified overuse of various classes of drugs
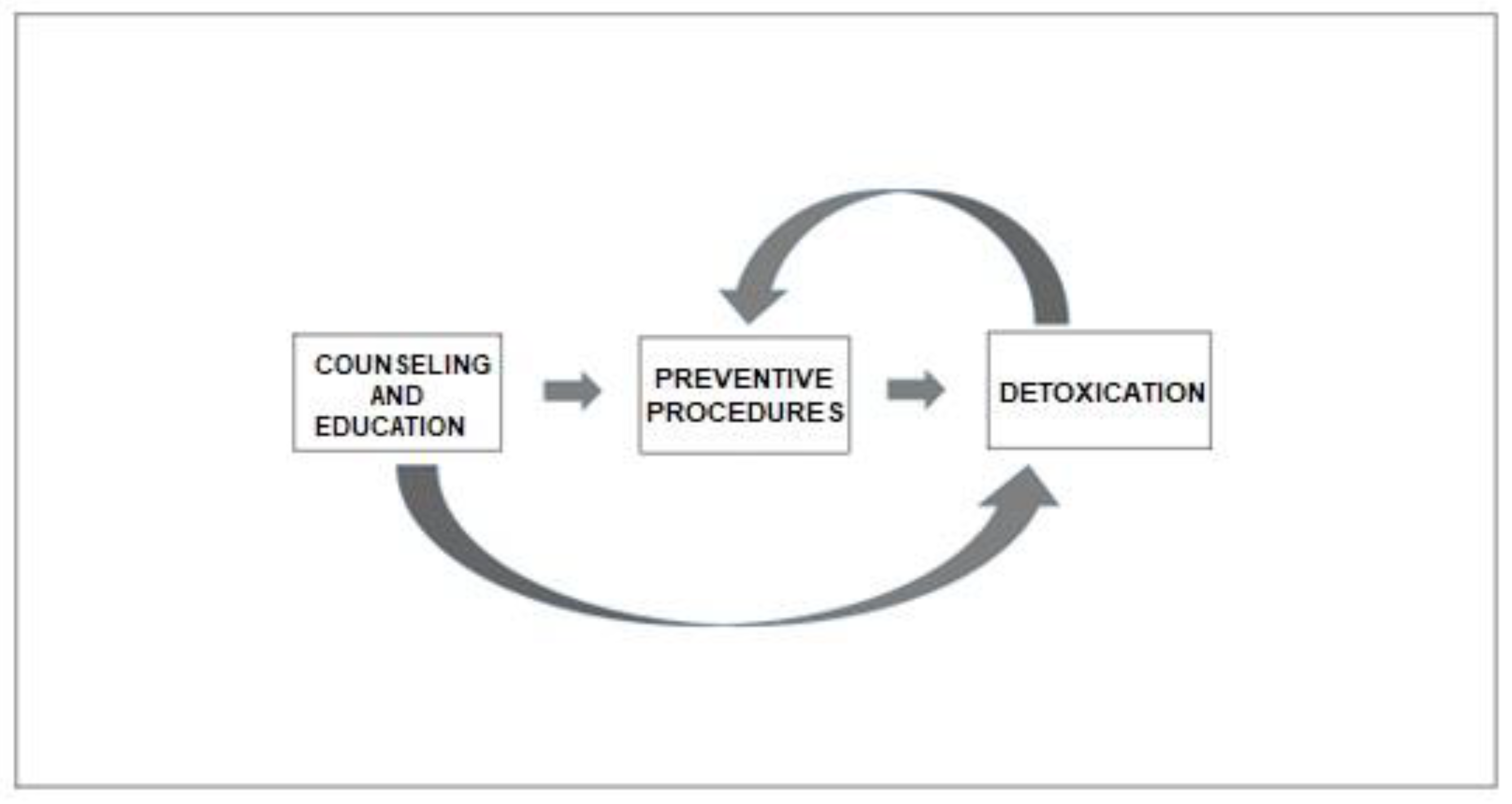
Therapy
Bridging therapy
Discontinuation of medications overused medications and preventive therapy
The treatment of medication overuse
Patient education and multidisciplinary care
Clinical monitoring and prognosis
Personal experience
Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
Clinical Implications
References
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017, 390, 1211–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization, Lifting The Burden. Atlas of headache disorders and resources in the world. WHO, Geneva: 2011.
- Saylor, D. , and Steiner, TJ. The Global Burden of Headache. Semin Neurol 2018, 38, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kristoffersen ES, Lundqvist C. Medication-overuse headache: epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2014, 5, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, ME. , and Lipton, RB. Migraine chronification. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2011, 11, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenbussche, N. , Paemeleire, K., Katsarava, Z. The Many Faces of Medication-Overuse Headache in Clinical Practice. Headache, 1111. [Google Scholar]
- Diener, HC. , Antonaci, F., Braschinsky, M., et al.. European Academy of Neurology guideline on the management of medication-overuse headache Eur J Neurol. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jonsson, P. , Jakobsson, A., Hensing, G., et al. Holding on to the indispensable medication – A grounded theory on medication use from the perspective of persons with medication overuse headache. J Headache Pain 2013.
- Westergaard, ML. , Munksgaard, SB., Bendtsen, L., et al. Medication-overuse headache: a perspective review. Ther Adv Drug Saf 2016, 7, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbussche,,N. , Laterza, D., Lisicki, M., et al. Medication-overuse headache: A widely recognized entity amidst ongoing debate. J Headache Pain 2018, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, HC. , Dodick, D., Evers, S., et al.,Pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment of medication overuse headache. Lancet Neurol 2019, 18, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, AD. , Burdine, D., Kabbouche, MA., et al. Genomic expression patterns in medication overuse headaches. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwedt, TJ. , and Chong, CD. Medication overuse headache: pathophysiological insights from structural and functional brain MRI research. Headache 2017, 57, 1173–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikiatkhachorn, A. , Le Grand, SM., Supornsilpchai, W., et al. Pathophysiology of medication overuse headache– An update. Headache 2014, 54, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supornsilpchai,W. , Maneesri Le Grand, S., Srikiatkhachorn, A. Cortical hyperexcitability and mechanism of medication-overuse headache. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongsebandhu-Phubhakdi, S. , and Srikiatkhachorn,A.. Pathophysiology of medication-overuse headache: implications from animal studies. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2012, 16, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, A. , Gu, P., De Felice, M., et al.. Increased susceptibility to cortical spreading depression in an animal model of medication-overuse headache. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belanger, S. , Ma, W., Chabot, J-G., et al.. Expression of calcitonin gene-related peptide, substance P and protein kinase C in cultured dorsal root ganglion neurons following chronic exposure to mu, delta and kappa opiates. Neuroscience 2002, 115, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Felice, M. , Ossipov, MH., Wang, R., et al. Triptan-induced enhancement of neuronal nitric oxide synthase in trigeminal ganglion dural afferents underlies increased responsiveness to potential migraine triggers. Brain 2010, 133, 2475–2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada-Ogawa, A. , Porreca, F., Meng,ID.. Sustained morphine-induced sensitization and loss of diffuse noxious inhibitory controls (DNIC) in durasensitive medullary dorsal horn neurons. J Neurosci 2009, 29, 15828–15835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasuntronwong, A. , J ansri,U., Srikiatkhachorn, A. Neural hyperactivity in the amygdala induced by chronic treatment of rats with analgesics may elucidate the mechanisms underlying psychiatric comorbidities associated with medication-overuse headache. BMC Neurosci 2017, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikiatkhachorn,A. , Tarasub, N., Govitrapong,P. Effect of chronic analgesic exposure on the central serotonin system: a possible mechanism of analgesic abuse headache. Headache 2000, 40, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tohyama,Y. , Yamane, F., Merid, MF., et al. Effects of selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonists on regional serotonin synthesis in the rat brain: an autoradiographic study with alpha-[14C] methyl-L-tryptophan. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2001, 11, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, CF. , Tohyama, Y., Diksic, M., et al. Effects of acute or chronic administration of anti-migraine drugs sumatriptan and zolmitriptan on serotonin synthesis in the rat brain. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikiatkhachorn, A. , and Anthony, M.. Platelet serotonin in patients with analgesic-induced headache. Cephalalgia 1996, 16, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolf, CJ. Central sensitization: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 2012, 152, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G. , Curra,A., Di Lorenzo, C., et al. Abnormal cortical responses to somatosensory stimulation in medication-overuse headache. BMC,Neurol 2010, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curra,A. , Coppola, G., Gorini, M., et al. Drug-induced changes in cortical inhibition in medication overuse headache. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munksgaard, SB. , Bendtsen, L., Jensen, RH.. Modulation of central sensitisation by detoxification in MOH: results of a 12-month detoxification study. Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riederer, F. , Marti, M., Luechinger, R., et al.. Grey matter changes associated with medication-overuse headache: correlations with disease related disability and anxiety. World J Biol Psychiatry 2012, 13, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, L. , Christidi, F., Steiger, VR., et al. Pain modulation is affected differently in medication-overuse headache and chronic myofascial pain – a multimodal MRI study. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 764–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Wilcke, T. , Leinisch, E., Straube, A., et al. Gray matter decrease in patients with chronic tension type headache. Neurology 2005, 65, 1483–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanraud, S. , Di Scala, G., Dilharreguy, B., et al.. Brain functional connectivity and morphology changes in medication-overuse headache: clue for dependence-related processes? Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, S. , Grazzi, L., Muffatti, R., et al.. In medication-overuse headache, fMRI shows long-lasting dysfunction in midbrain areas. Headache 2012, 52, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torta, DM. , Costa, T., Luda, E., et al. Nucleus accumbens functional connectivity discriminates medication-overuse headache. NeuroImage Clin 2016, 11, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumal, A. , Laureys, S., Di Clemente, L., et al.. Orbitofrontal cortex involvement in chronic analgesic-overuse headache evolving from episodic migraine. Brain 2006, 129, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riederer, F. , Gantenbein, AR., Marti, M., et al.. Decrease of gray matter volume in the midbrain is associated with treatment response in medication-o,veruse headache: possible influence of orbitofrontal cortex. J Neurosci 2013, 33, 15343–15349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlund, K. , Sun-Edelstein, C., Druyts, E., et al.. Risk of medication overuse headache across classes of treatments for acute migraine. J Headache Pain 2016, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigal, ME. , Serrano, D., Buse, D., et al. (2008). Acute migraine medications and evolution from episodic to chronic migraine: A longitudinal population-based study. Headache 2008, 48, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, SM. , Becker, WJ., Heine, JA.. Opiate use to control bowel motility may induce chronic daily headache in patients with migraine. Headache 2001, 41, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahra, A. , Walsh, M., Menon, S., et al. Does chronic daily headache arise de novo in association with regular use of analgesics? Headache 2003, 43, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, K. , Albretsen, C., Vilming, ST., et al.. A 4-year follow-up of patients with medication-overuse headache previously included in a randomized multicenter study. J Headache Pain 2011, 12, 315–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevoli, S. , Sancisi, E., Grimaldi, D., et al. Family history for chronic headache and drug overuse as a risk factor for headache chronification. Headache 2009, 49, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmroth, V. , Katsarava, Z., Fritsche, G., et al.. Features of m;edication overuse headache following overuse of different acute headache drugs. Neurology 2002, 59, 1011–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starling, AJ. , Hoffman-Snyder, C., Halker, RB., et al. Risk of development of medication overuse headache with nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory drug therapy for migraine: A critically appraised topic. Neurologist 2011, 17, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diener, HC. , and Limmroth, V. Medication-overuse headache: A worldwide problem. Lancet Neurol 2004, 3, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashina, S. , Serrano, D., Lipton, RB., et al.. Depression and risk of transformation of episodic to chronic migraine. J Headache Pain 2012, 13, 615–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, S. , Paolucci, M., Quintiliani, L., et al. Psychopathological profile of medication overuse headache patients, drug assumption and degree of disability. Neurol Sci 2018, 39, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ljubisavljevic, M. (2020). Ruminativni stil mišljenja, depresivnost, anksioznost, stres i kvalitet života kod pacijenata sa glavoboljom prekomerne upotrebe medikamenata. Master degree. 2020; Faculty for Phylosophy Nis.
- Ljubisavljevic, M. , Ignjatovic, A., Djordjevic, V., et al. Depression, Anxiety, Stress and Health Related Quality of Life among Patients with Medication Overuse Headache in Tertiary Headache Center: A Cross Sectional Study. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 2020.
- Ljubisavljevic, M. , Ignjatovic, A., Ljubisavljevic, S. The ruminative thought style with associated anxiety influence the occurrence of medication overuse headache, 2021; unpublished.
- Sarchielli, P. , Corbelli, I., Messina, P., et al.. Psychopathological comorbidities in medication-overuse headache: A multicentre clinical study. Eur J Neurol 2016, 23, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mose, LS. , Pedersen, SS., Jensen,RH., et al.. Personality traits in migraine and medication-overuse headache: A comparative study. Acta Neurol Scand 2019, 140, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbelli, I. , Caproni, S., Eusebi, P., et al.. Drug-dependence behavior and outcome of medication-overuse headache after treatment. J Headache Pain 2012, 13, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, F. , Tanzilli, A., Simonelli, A., et al.. Personality and personality disorders in medication-overuse headache: A controlled study by SWAP-200. Pain Res Manag, 2019; 1874078. [Google Scholar]
- Sances, G. , Galli, F., Ghiotto, N., et al. Factors associated with a negative outcome of medication-overuse headache: A 3-year follow-up (the ‘CARE’ protocol). Cephalalgia 2013, 33, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanteri-Minet, M. , Duru, G., Mudge, M., et al. Quality of life impairment, disability and economic burden associated with chronic daily headache, focusing on chronic migraine with or without medication overuse: A systematic review. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 837–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, M. , De Icco, R., Allena, M., et al. Clinical subtypes of medication overuse headache – Findings from a large cohort. Headache 2019, 59, 1481–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehuys, E. , Paemeleire, K., Crombez, G., et al. The heterogeneity of headache patients who self-medicate: A cluster analysis approach. Pain 2016, 157, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pini, LA. , Cicero, AF., Sandrin,i M. Long-term follow-up of patients treated for chronic headache with analgesic overuse. Cephalalgia 2001, 21, 878–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saper,JR. , and Lake, AE. Medication overuse headache: Type I and type II. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munksgaard, SB. , Jensen, RH. Medication overuse headache. Headache 2014, 54, 1251–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, C. , Wessely, P., Bingol, C., et al. Longterm prognosis of analgesic withdrawal in patients with drug-induced headaches. Headache 1989, 29, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendtsen, L. , Munksgaard, S., T assorelli, C., et al. Disability, anxiety and depression associated with medication-overuse headache can be considerably reduced by detoxification and prophylactic treatment. Results from a multicentre, multinational study (COMOESTAS project). Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 426–433. [Google Scholar]
- Lampl, C. , Thomas, H., Tassorelli,C., et al. Headache, depression and anxiety: associations in the Eurolight project. J Headache Pain 2016, 17, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cupini, LM. , Murtas,MD., Costa, C., et al. Obsessive-compulsive disorder and migraine with medication-overuse headache: research submission. Headache 2009, 49, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curone, M. , Tullo, V., Mea, E., et al. Psychopathological profile of patients with chronic migraine and medication overuse: study and findings in 50 cases. Neurol Sci 2011, 32, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radat, F. , and Lanteri-Minet, M. What is the role of dependence-related behavior in medication-overuse headache? Headache 2010, 50, 1597–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, F. , Pozzi,G., Frustaci, A., et al. Differences in the personality profile of medication-overuse headache sufferers and drug addict patients: a comparative study using MMPI-2. Headache 2011, 51, 1212–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scher, AI. , Stewart, WF., Ricci, JA., et al. Factors associate,d with the onset and remission of chronic daily headache in a population-based study. Pain 2003, 106, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigal, ME. , Liberman, JN., Lipton, RB.. Obesity and migraine: a population study. Neurology 2006, 66, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershey, AD. , Powers, SW., Nelson, TD. al. Obesity in the pediatric headache population: a multicenter study. Headache 2009, 49, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakalnis, A. , and Kring, D. Chronic daily headache, medication overuse, and obesity in children and adolescents. J Child Neurol 2012, 27, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancisi, E. , Cevoli, S., Vignatelli, L., et al. Increased prevalence of sleep disorders in chronic headache: a case-control study. Headache 2010, 50, 1464–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarava, Z. , Fritsche, G., Muessig, M., et al.. Clinical features of ;withdrawal headache following overuse of triptans and other headache drugs. Neurology 2001, 57, 1694–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuh, JL. , Wang, SJ., Lu, SR., et al. Does medication overuse headache represent a behavior of dependence? Pain, 2005; 119, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bigal, ME. , Rapoport, AM., Sheftell, FD., et al. Transformed migraine and Medication overuse in a tertiary headache centre - Clinical characteristics and treatment outcomes. Cephalalgia 2004, 24, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, RB. , Aaseth, K., Saltyte Benth, J., et al. The severity of dependence scale detects people with medication overuse: The Akershus study of chronic headache. J Neurol Neurosurg 2009, 80, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, G. , Frettloh, J., Huppe, M., et al. Prevention of medication overuse in patients with migraine. Pain 2010, 151, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grande, RB. , Aaseth, K., Benth, JS., et al. Reduction in medication-overuse headache after short information. The Akershus study of chronic headache. Eur J Neurol 2011, 18, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, C. , Grande, RB., Aaseth, K., et al. The severity of dependence scale predicts prognosis of medication overuse headache. The Akershus study of chronic headache. Pain 2012, 153, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, J. , and Berciano, J. Daily chronic headache in patients with migraine induced by abuse of ergotamine-analgesics: Response due to a protocol of outpatient treatment. Neurologia 1993, 8, 212–215. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, P. , Di Lorenzo, C., Faroni, J., et al. Advice alone vs. structured detoxification programmes for medication overuse headache: A prospective, randomized, open-label trial in transformed migraine patients with low medical needs. Cephalalgia 2006, 26, 1097–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersen, ES. , Straand,J., Vetvik, KG., et al.. Brief intervention by general practitioners for medication-overuse headache, followup after 6 months: a pragmatic cluster-randomised controlled trial. J Neurol 2016, 263, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersen, ES. , Straand,J., Vetvik, KG., et al. Brief intervention for medication- overuse headache in primary care. The BIMOH study: a double-blind pragmatic cluster randomized parallel controlled trial. J Neurol Neurosurg Ps 2015, 86, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristoffersen,ES. , Straand, J., Russell, MB., et al. Lasting improvement of medication-overuse headache after brief intervention – a long-term follow-up in primary care. Eur J Neurol 2017, 24, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creac’h, C. , Frappe, P., Cancade, M., et al. In-patient versus outpatient withdrawal programmes for medication overuse headache: A 2-year randomized trial. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhr, B. , Evers, S., Bauer, B., et al. Drug-induced headache: Long-term results of stationary versus ambulatory withdrawal therapy. Cephalalgia 1999, 19, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frich, JC. , Kristoffersen, ES., Lundqvist,C. GPs’ experiences with brief intervention for medication-overuse headache: A qualitati,ve study in general practice. Br J Gen Pract 2014, 64, e525–e531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paemeleire, K. , Crevits, L., Goadsby, PJ., et al. Practical management of medication-overuse headache. Acta Neurol Belg 2006, 106, 43–51. [Google Scholar]
- Trucco, M. , Meineri, P., Ruiz, L., et al. Medication overuse headache: Withdrawal and prophylactic therapeutic regimen. Headache 2010, 50, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obermann, M. , and Katsarava, Z. Management of medication-overuse headache. Expert Rev Neurother 2007, 7, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, SJ. Medication-overuse headache. Continuum (Minneapolis, Minn) 2012, 18, 807–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnider, P. , Aull, S., Baumgartner, C., et al. Long-term outcome of patients w;ith, headache and drug abuse after inpatient withdrawal: Five-year follow-up. Cephalalgia 1996, 16, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelstoft, IMS. , Carlsen, LN., Munksgaard, SB., et al. Complete withdrawal is the most feasible treatment for medication-overuse headache: A randomized controlled open-label trial. Eur J Pain 2019, 23, 1162–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, M. , Carlsen, LN., Munksgaard, SB., et al. Complete withdrawal is the most effective approach to reduce disability in patients ;with medication-overuse headache: A randomized controlled open-label trial. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarava,Z. , and Diener,HC. Medication overuse headache in Germany. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 1221–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limmroth, V. , Biondi, D,. Pfeil, J., et al. T Dopiramate in patients with episodic migraine: reducing the risk for chronic forms of headache. Headache 2007, 47, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hashel, JY. , Ahmed, SF., Alroughani, R. Prevalence of primary headache disorders in Kuwait. Neuroepidemiology 2017, 48, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westergaard,ML. , Lau, CJ., Allesoe, K., et al. Monitoring chronic headache and medication-overuse headache prevalence in Denmark. Cephalalgia 2020, 40, 6–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, MB. Epidemiology and management of medication-overuse headache in the general population. Neurol Sci, 2019; 40, (Suppl. 1), 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Dodick, D. , and Freitag, F. Evidence-based understanding of medication- overuse headache: Clinical implications. Headache, S: 4).
- Williams, DR. , and Stark, RJ. Intravenous lignocaine (lidocaine) infusion for the treatment of chronic daily headache with substantial medication overuse. Cephalalgia 2003, 23, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil-Gouveia, R. , and Goadsby, PJ. Neuropsychiatric side-effects of lidocaine: Examples from the treatment of headache and a review. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afridi, SK. , Shields, KG., Bhola, R., et al. Greater occipital nerve injection in primary headache syndromes – Prolonged effects from a single injection. Pain 2006, 122, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karadas, O. , Ozon, AO., Ozcelik, F., et al. Greater occipital nerve block in the treatment of triptan-overuse headache: A randomized comparative study. Acta Neurol Scand 2017, 135, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J. Detoxification for medication overuse headache is the primary task. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeberg, P. , Olesen, J., Jensen, R. Efficacy of multidisciplinary treatment in a tertiary referral headache centre. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P. , Faroni, JV., Nappi, G. Short-term effectiveness of simple advice as a withdrawal strategy in simple and complicated medication overuse headache. Eur J Neurol 2011, 18, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 111. Bendtsen ,L., Birk, S., Kasch, H., et al. Reference programme: diagnosis and treatment of headache disorders and facial pain. Danish Headache Society, 2nd Edition, 2012. J Headache Pain, 2012; 13, (Suppl. 1), S1–S29.
- Pijpers, JA. , Wiendels, NJ., Koppen, H., Ferrari, MD., Haan, J., Terwindt, GM. Medication-overuse headache. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2018, 162, 1749. [Google Scholar]
- 113. Radat F, Lanteri-Minet M. What is the role of dependence-related behavior in medication-overuse headache? Headache, 2010; 50, 1597–1611.
- Tassorelli, C. , Jensen, R., Allena, M., et al. A consensus protocol for the management of medication-overuse headache: Evaluation in a multicentric, multinational study. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlsen, LN. , Munksgaard, SB., Jensen, RH., et al. (2018). Complete detoxification is the most effective treatment of medication-overuse headache: A randomized controlled open-label trial. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellestad, PL. , Carlsen, LN. , Westergaard, ML., et al. Economic benefits of treating medication-overuse headache - results from the multicenter COMOESTAS project. Cephalalgia 2018, 39, 274–285. [Google Scholar]
- Bottiroli,S. , Allena, M., Sances, G., et al. (2018). Changes in anxiety and depression symptoms associated to the outcome of MOH: a post-hoc analysis of the Comoestas Project. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A. , Fantini, J., Monti, F., et al. (2019). Dramatic placebo effect of high frequency repetitive TMS in treatment of chronic migraine and medication overuse headache. J Clin Neurosci 2019, 60, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidverc-Trajkovic, J. , Pekmezovic, T., Jovanovic, Z., et al. Medication overuse headache: Clinical features predicting treatment outcome at 1-year follow-up. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, K. , Albretsen, C., Vilming, ST., et al. Management of medication overuse headache: 1-year randomized multicentre open-label trial. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener, HC. , Bussone, G., Van Oene, JC., et al. Topiramate reduces headache days in chronic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Cephalalgia 2007, 27, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein,SD. , Lipton, RB., Dodick, DW., et al. Efficacy and safety of topiramate for the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Headache 2007, 47, 170–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diener,HC. , Dodick, DW., Goadsby, PJ., et al.. Utility of topiramate for the treatment of patients with chronic migraine in the presence or absence of acute medication overuse. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarchielli, P. , Messina, P., Cupini, LM., et al. Sodium valproate in migraine without aura and medication overuse headache: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2014, 24, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodick, DW. , Turkel, CC., DeGryse, RE., et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: Pooled results from the double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled phases of the PREEMPT clinical program. Headache 2010, 50, 921–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, SD. , Blumenfeld, AM., Cady, RK., et al. OnabotulinumtoxinA for treatment of chronic migraine: PREEMPT 24-week pooled subgroup analysis of patients who had acute headache medication overuse at baseline. J Neurol Sci 2013, 331, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, A. , Curto, M., Lionetto, L., et al. A two years open-label prospective study of OnabotulinumtoxinA 195 U in medication overuse headache: a real-world experience. J Headache Pain 2015, 17, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandrini, G. , Perrotta, A., Tassorell, C., et al. Botulinum toxin type-A in the prophylactic treatment of medication-overuse headache: A multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel group study. J Headache Pain 2011, 12, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijpers,JA. , Kies, DA., Louter, MA., et al. Acute withdrawal and botulinum toxin A in chronic migraine with medication overuse: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Brain 2019, 142, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dressler, D. OnabotulinumtoxinA should be considered in medication overuse withdrawal in patients with chronic migraine. Brain 2020, 143, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiseo, C. , Ornello, R., Pistoia, F., et al. How to integrate monoclonal antibodies targeting the calcitonin gene-related peptide or its receptor in daily clinical practice. J Headache Pain 2019, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tepper, S. , Lipton, RB., Silberstein, S., et al. Long-term efficacy of erenumab in chronic migraine patients with acute medication overuse. Poster PF 109LB and E-Poster presentation, 60th American Headache Society Scientific Meeting, San Francisco, Headache 58 (Suppl. 2): 160-162.
- Silberstein, S. , Ashina, S., Katsarava, Z., et al. (2018). The impact of fremanezumab on medication overuse in patients with chronic migraine. J Headache Pain 2018, 19, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, CC. , Schwedt, TJ., Wang, SJ., et al. Treatment of medication-overuse headache: a systematic review. Cephalalgia 2015, 36, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, MD. , Carvalho, Dde S., Gabbai, AA., et al.. Amitriptyline and aerobic exercise or amitriptyline alone in the treatment of chronic migraine: a randomized comparative study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 2014, 72, 851–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hepp, Z. , Dodick, DW., Varon, SF., et al. Persistence and switching patterns of oral migraine prophylactic medications among patients with chronic migraine: A retrospective claims analysis. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedenrud, T. , Babic, N., Jonsson, P.. Medication overuse headache: self-perceived and actual knowledge among pharmacy staff. Headache 2014, 54, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, JJY. , and Chan, YC. Medical undergraduate survey on headache education in Singapore: knowledge, perceptions, and assessment of unmet needs. Headache 2017, 57, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsen, LN. , Westergaard, ML., Bisgaard, M., et al. National awareness campaign to prevent medication-overuse headache in Denmark. Cephalalgia 2017, 38, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scher, AI. , Stewart,WF., Lipton, RB. Caffeine as a risk factor for chronic daily headache: A population-based study. Neurology 2004, 63, 2022–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, AN. , and Lake, AE. 3rd. Clinical aspects of medication overuse headaches. Headache 2014, 54, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Goffau,MJ. , Klaver, AR., Willemsen, MG., et al. The effectiveness of treatments for patients with medication overuse headache; A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Pain 2017, 18, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, SJ. , Stillman, MJ., Tepper, DE., et al. A prospective cohort study of outpatient interdisciplinary rehabilitation of chronic headache patients. Headache 2017, 57, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaul, C. , van Doorn, C., Webering, N., et al. Clinical outcome of a headache-specific multidisciplinary treatment program and adherence to treatment recommendations in a tertiary headache center: An observational study. J Headache Pain. 2011, 12, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J. , Hayes, J., Pakalnis, A. A randomized trial of telephone- based motivational interviewing for adolescent chronic headache with medication overuse. Cephalalgia 2014, 34, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rausa, M. , Palomba, D., Cevoli, S., et al. Biofeedback in the prophylactic treatment of medication overuse headache: A pilot randomized controlled trial. J Headache Pain 2016, 17, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazzi, L. , Andrasik, F., D’Amico, D., et al. Behavioral and pharmacologic ;treatment of transformed migraine with analgesic overuse: Outcome at 3 years. Headache 2002, 42, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jellestad, PL. , Carlsen, LN., Westergaard, ML., et al. Economic benefits of treating medication-overuse headache – Results from the multicenter COMOESTAS project. Cephalalgia 2019, 39, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, CC. , Schwedt,TJ., Wang, SJ., et al. Treatment of medication-overuse headache: A systematic review. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, AJ. , and Shevell, M. Chronic daily headaches in pediatric neurology practice. J Child Neurol 2004, 19, 925–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand,AA. , and Goadsby, PJ. Medication overuse in children and adolescents. Curr Pain Headache Rep 2014, 18, 428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritsche, G. , Eberl, A., Katsarava, Z., et al. Druginduced headache: Long-term follow-up of withdrawal therapy and persistence of drug misuse. Eur Neurol 2001, 45, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarava, Z. , Limmroth,V., Finke,M., et al. Rates and predictors for relapse in medication overuse headache: A 1-year prospective study. Neurology 2003, 60, 1682–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altieri, M. , Di, GR., Di, CL., et al. Combined pharmacological and short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy for probable medication overuse headache: a pilot study. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valguarnera, F. , and Tanganelli, P. The efficacy of withdrawal therapy in subjects with chronic daily headache and medication overuse following prophylaxis with topiramate and amitriptyline. Neurol Sci, 2010; 31, (Suppl. 1), S175–S177. [Google Scholar]
- Grazzi, L. , Sansone, E., Raggi, A., et al. Mindfulness and pharmacological prophylaxis after withdrawal from medication overuse in patients with chronic migraine: an effectiveness trial with a one-year follow-up. Headache Pain 2017, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boe,MG. , Thortveit, E., Vatne, A., et al. Chronic headache with medication overuse: Long-term prognosis after withdrawal therapy. Cephalalgia 2017, 37, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerzoni, S. , Pellesi, L., Baraldi, C., et al. Long-term treatment benefits and prolonged efficacy of onabotulinumtoxina in patients affected by chronic migraine and medication overuse headache over 3 years of therapy. Front Neurol 2017, 8, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsarava, Z. , Muessig, M., Dzagnidze, A., et al. Medication overuse headache: rates and predictors for relapse in a 4-year prospective study. Cephalalgia 2005, 25, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zidverc-Trajkovic, JJ. , Pekmezovic, T., Jovanovic, Z., et al. Long-term predictors of remission in patients treated for medication-overuse headache at a specialized headache center: A prospective cohort study. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, P. , Faroni, JV., Nappi, G. Medication overuse headache: Predictors and rates of relapse in migraine patients with low medical needs. A 1-year prospective study. Cephalalgia 2008, 28, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, A. , Giovannetti, AM., Leonardi, M., et al. Predictors of 12-months relapse after withdrawal treatment in hospitalized patients with chronic migraine associated with medication overuse: a longitudinal observational study. Headache 2017, 57, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sances, G. , Ghiotto, N., Galli, F., et al. Risk factors in medication-overuse headache: a 1-year follow-up study (care II protocol). Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




