Submitted:
09 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Fe-bentonite and Al-bentonite
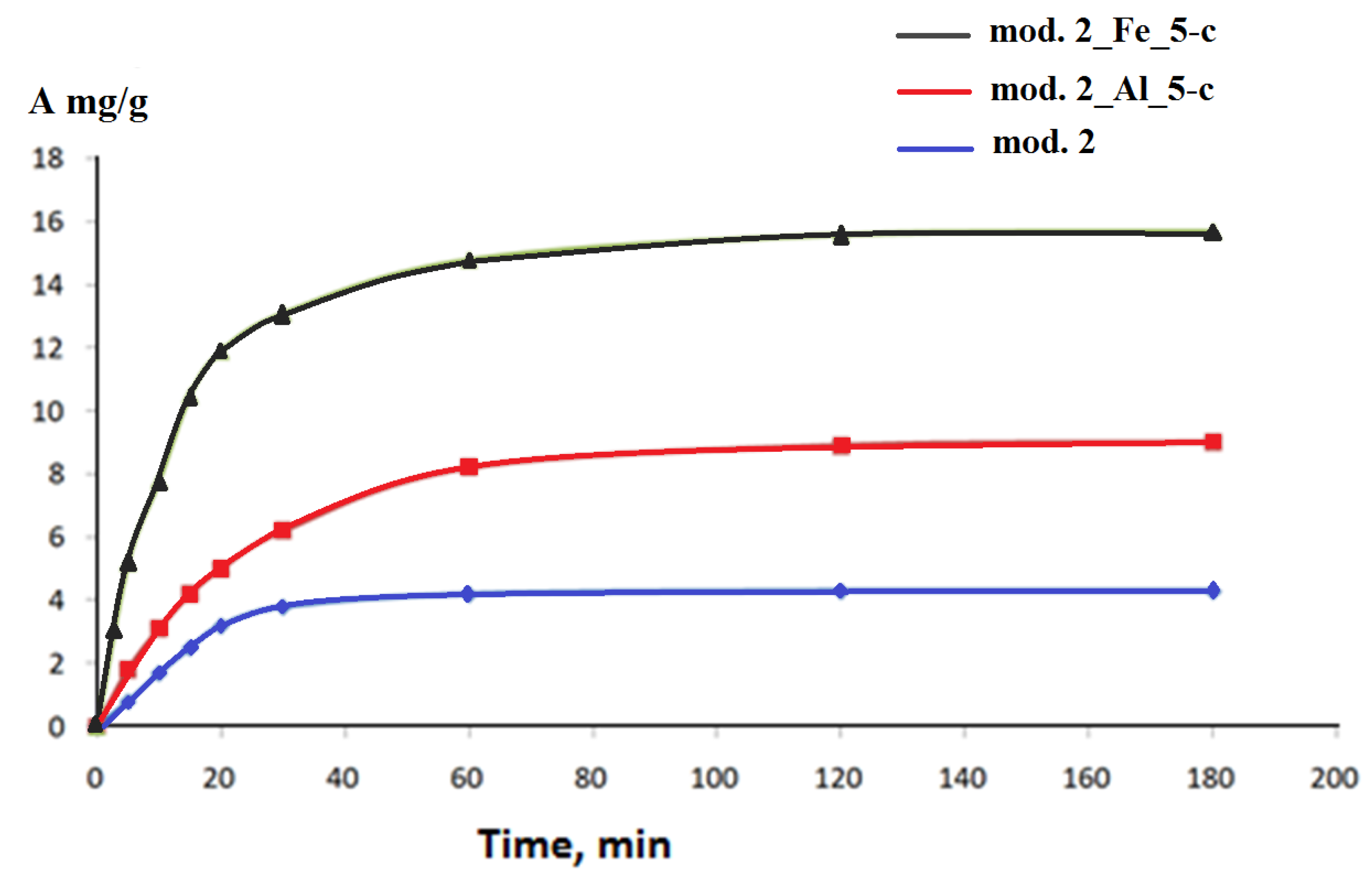
2.2. Adsorption studies
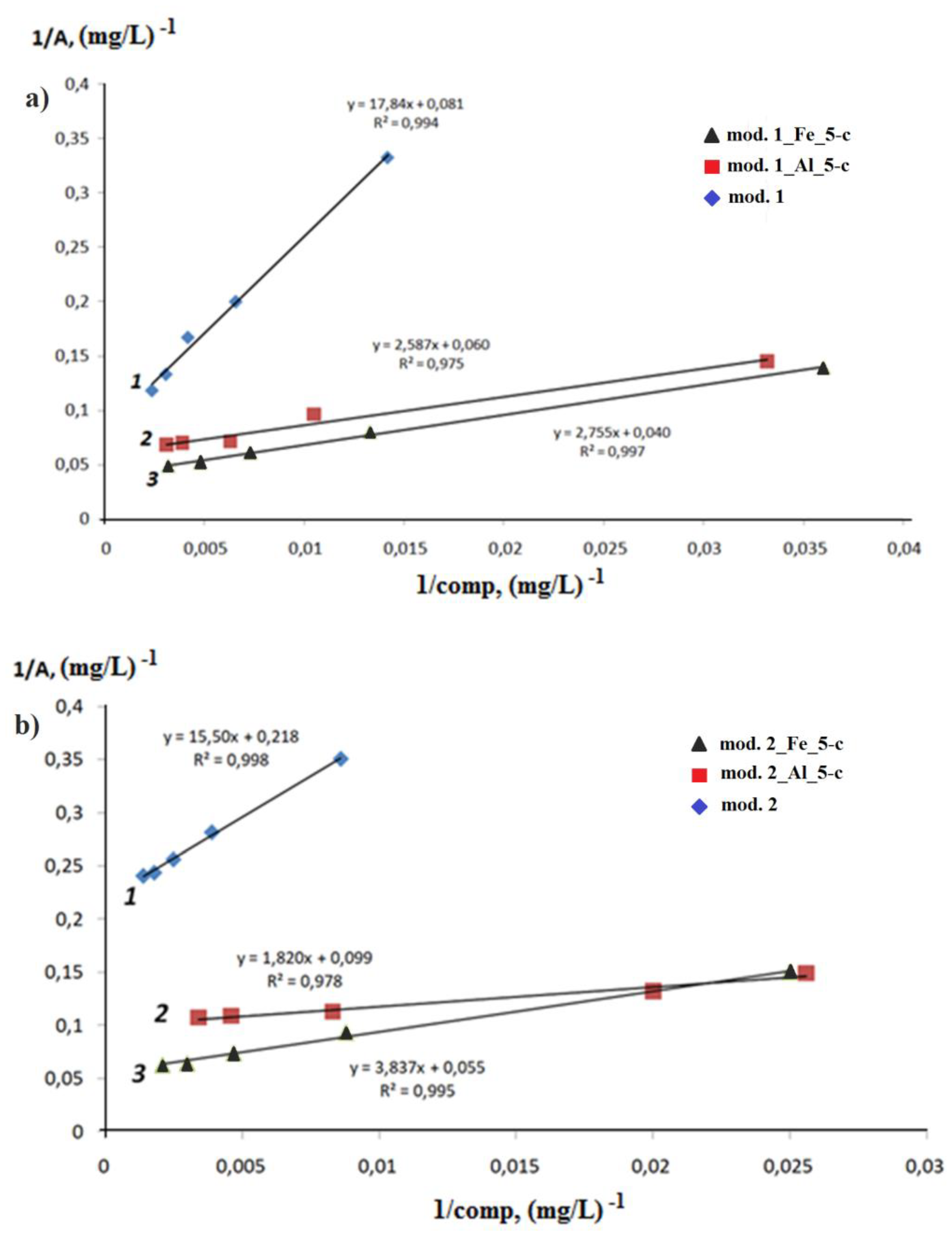
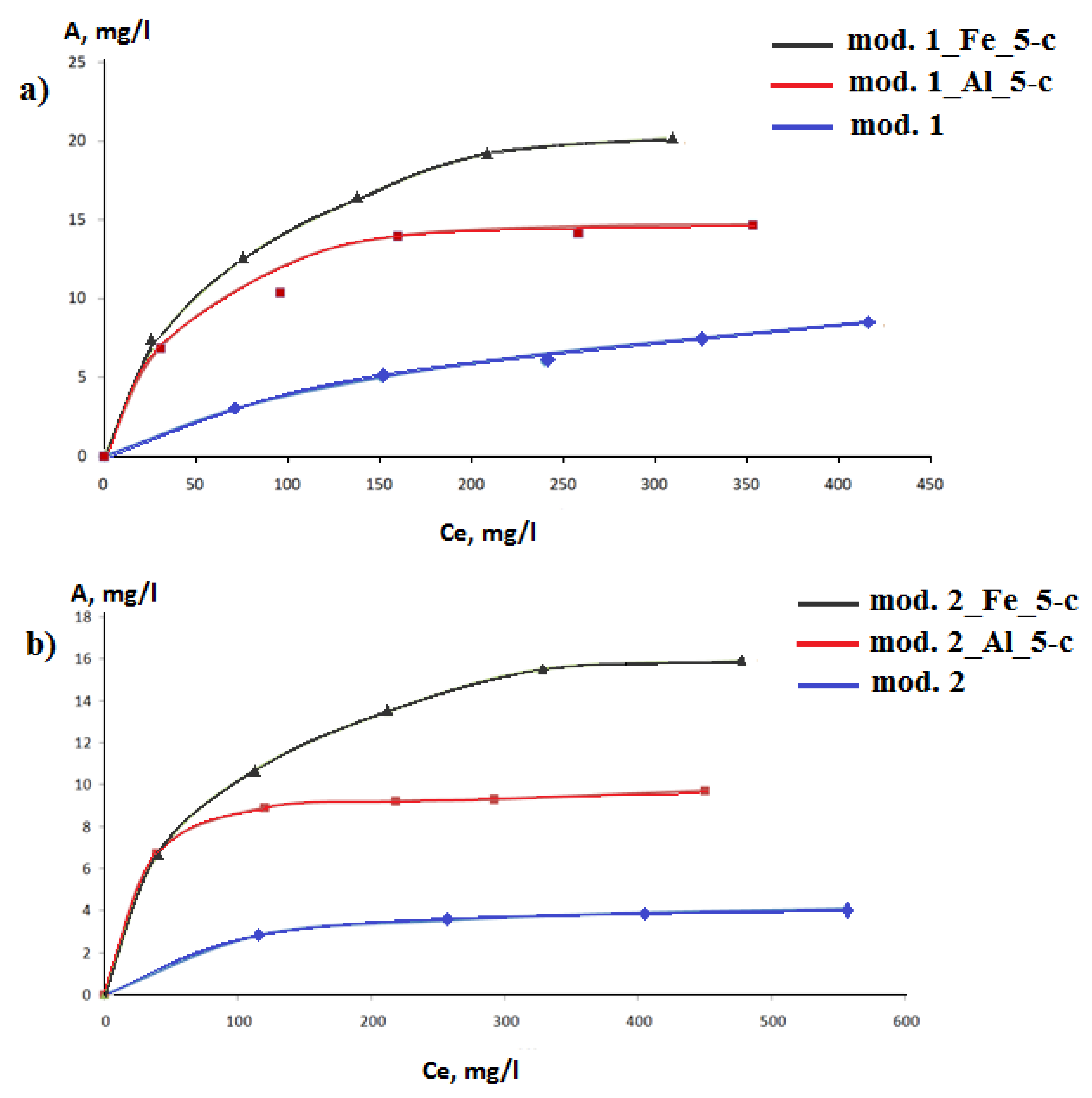
3. Results and Discussion
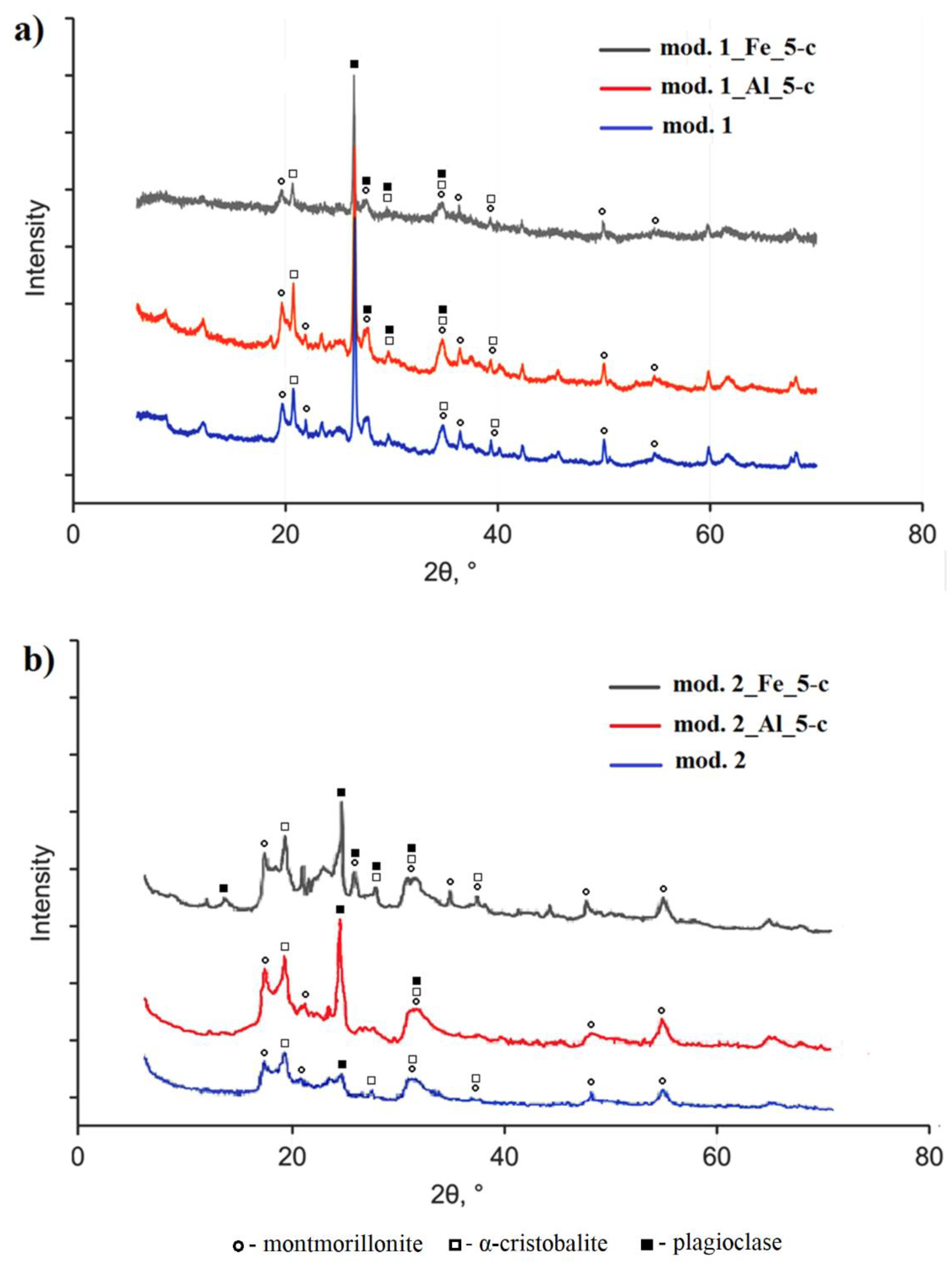
3.1. Characteization of the adsorbent
3.1.1. Elemental composition of the studied sorbents
3.2. Adsoption study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Choudhary, M.; Peter, C.N.; Shukla, S.K.; Govender, P.P.; Joshi, G.M.; Wang, R. Environmental Issues: A Challenge for Wastewater Treatment; 2020; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Gautam, R.K.; Sharma, S.K.; Mahiya, S.; Chattopadhyaya, M.C. CHAPTER 1. Contamination of Heavy Metals in Aquatic Media: Transport, Toxicity and Technologies for Remediation. In Heavy Metals In Water; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, 2014; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Kudaibergenova, R.; Ualibek, O.; Sugurbekov, E.; Demeuova, G.; Frochot, C.; Acherar, S.; Sugurbekova, G. Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Superhydrophobic Magnetic Nanomaterial as High Selective and Recyclable Sorbent for Oil/Organic Solvent Wastewater Treatment. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology 2022, 19, 8491–8506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Ramontja, J. Recent Modifications of Bentonite Clay for Adsorption Applications. Focus on Sciences 2016, 2, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marouf, R.; Dali, N.; Boudouara, N.; Ouadjenia, F.; Zahaf, F. Study of Adsorption Properties of Bentonite Clay. In Montmorillonite Clay; IntechOpen, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Novikova, L.; Belchinskaya, L. Adsorption of Industrial Pollutants by Natural and Modified Aluminosilicates. In Clays, Clay Minerals and Ceramic Materials Based on Clay Minerals; InTech, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xie, B.; Qin, Y. Effect of Bentonite on the Pelleting Properties of Iron Concentrate. J Chem 2017, 2017, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, A.; Zhuldu, K.; Serge, B. Use of Sorbents to Improve Water Quality in the Production of Reconstituted Dairy Products. Emir J Food Agric 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamzina Zhulduz Bazaralievna Patent for Utility Model. Method for Water Treatment for Producing Dairy Products from Regenerated Milk. 2023.
- My Linh, N. Le; Hoang Van, D.; Duong, T.; Tinh, M.X.; Quang Khieu, D. Adsorption of Arsenate from Aqueous Solution onto Modified Vietnamese Bentonite. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering 2019, 2019, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ani, F.; Al-Kindi, G. Suitability of the Iraqi Natural Clay for the Preparation of Al-Fe Pillared-Clays. MATEC Web of Conferences 2018, 162, 05017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnasri-Ghnimi, S.; Frini-Srasra, N. Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions by Adsorption Using Single and Mixed Pillared Clays. Appl Clay Sci 2019, 179, 105151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaya, R.R.; Juwono, A.L.; Rinaldi, N. Bentonite Modification with Pillarization Method Using Metal Stannum; 2017; p. 020010.
- Carriazo, J.; Guélou, E.; Barrault, J.; Tatibouët, J.M.; Molina, R.; Moreno, S. Synthesis of Pillared Clays Containing Al, Al-Fe or Al-Ce-Fe from a Bentonite: Characterization and Catalytic Activity. Catal Today 2005, 107–108, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitina, N. V.; Lamikhova, A.P.; Nikitina, N. V.; Kazarinov, I.A. Adsorption of Organic Reagents by Natural Bentonites Modified with Aluminum and Iron (III) Polyhydroxocations. Izvestiya of Saratov University. New Series. Series: Chemistry. Biology. Ecology 2021, 21, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izosimova, Y.; Gurova, I.; Tolpeshta, I.; Karpukhin, M.; Zakusin, S.; Zakusina, O.; Samburskiy, A.; Krupskaya, V. Adsorption of Cs(I) and Sr(II) on Bentonites with Different Compositions at Different PH. Minerals 2022, 12, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.R.; Lalhmunsiama; Bajaj, H. C.; Lee, S.-M. Activated Bentonite as a Low-Cost Adsorbent for the Removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions: Batch and Column Studies. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2016, 34, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, H.; Anoop Krishnan, K.; Pillai, R.R.; Sudhakaran, S. Stirring-Ageing Technique to Develop Zirconium-Pillared Bentonite Clay along with Its Surface Profiling Using Various Spectroscopic Techniques. Research on Chemical Intermediates 2020, 46, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belchinskaya, L.; Novikova, L.; Khokhlov, V.; Ly Tkhi, J. Contribution of Ion-Exchange and Non-Ion-Exchange Reactions to Sorption of Ammonium Ions by Natural and Activated Aluminosilicate Sorbent. Journal of Applied Chemistry 2013, 2013, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Samples of sorbents | The content of the element, wt. % | ||||||
| Al | Fe | Si | Ca | K | Ni | Ti | |
| mod. 1 | 7 | 47 | 14 | 2 | 13 | 20 | 2.5 |
| mod. 1_Fe_5-с | 7 | 71 | 8 | 0.6 | 4 | 14 | 0.7 |
| mod. 1_Al_5-с | 15 | 46 | 11 | 1 | 8 | 16 | 2 |
| mod. 2 | 8 | 23 | 44 | 17 | 5 | - | 2 |
| mod. 2_Fe_5-с | 6 | 57 | 31 | 2 | 2 | - | 1 |
| mod. 2_Al_5-с | 16 | 17 | 47 | 12 | 5 | - | 2 |
| Sample | Specific surface area, m2/g | Porevolume, cm3/g |
Distribution of pores by radius, % | |||
| 1.5 – 2.0 nm | 2.0 – 4.0 nm | 4.0 – 8.0 nm | more than 8.0 nm | |||
| mod. 1 | 37 | 0.054 | 8 | 15 | 20 | 56 |
| mod. 1_Fe_5-с | 91 | 0.101 | 13 | 27 | 17 | 43 |
| mod. 1_Al_5-с | 120 | 0.073 | 16 | 38 | 14 | 32 |
| mod. 2 | 51 | 0.061 | 9 | 21 | 21 | 49 |
| mod. 2_Fe_5-с | 86 | 0.125 | 22 | 46 | 19 | 13 |
| mod. 2_Al_5-с | 172 | 0,122 | 23 | 47 | 18 | 12 |
| Sorbentsample | Maximum adsorption, mg/g |
| mod. 1 | 12,3±0,6 |
| mod. 1_Fe_5-c | 16,7±0,9 |
| mod. 1_Al_5-c | 25,0±0,9 |
| mod. 2 | 4,6±0,2 |
| mod. 2_Fe_5-с | 10,1±0,5 |
| mod. 2_Al_5-с | 18,2±0,8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





