1. Introduction
With the increasing need for downsizing in the electronics industry, the development of molecular electronic devices presents a promising solution to overcome the limitations imposed by silicon-based electronics[
1,
2]. The conventional silicon electronics has relied on lithographic patterning of polymer resists at progressively smaller lengths to scale down device dimensions. However, this approach has its limitations. In response, numerous fabrication techniques have been explored to create molecular electronic devices, resulting in significant advancements in fabrication, characterization, and application within this field[
3,
4,
5].
One of the hottest topics is to recognize and manipulate the functions and lateral structures of molecules at the nanoscale during two-dimensional (2D) supramolecular self-assembly process[
6]. Molecular self-assembly is a spontaneous process[
7,
8,
9], during which, molecules are held together into ordered structures via intra- and intermolecular non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding[
10,
11], van der Waals force[
12], π-π stacking[
13,
14] and electrostatic force[
15,
16]. In assistance of an atomically-flat substrate, 2D self-assembled networks can be stabilized on the surface of substrate based on the noncovalent interactions between molecules and substrates under thermodynamic control. In order to tune the functions and structures, the ordered 2D patterns can go through a structural and functional transition into another one with external stimuli, such as solvents[
17,
18,
19], thermal treatment[
20,
21], varying concentrations[
22,
23], light irradiation[
24], electric field[
25,
26], guest-molecule-induced co-adsorption and desorption processes[
27,
28].
Since its invention by in 1981, scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) has proven as a powerful technique for visualizing 2D materials and molecular networks, providing direct proofs for the way of molecular bonding and phase transition at the solid-liquid interface[
29]. Owing to this significant contribution, Gerd Binning and Heinrich Rohrer were awarded with the Nobel Prize of Physics in 1986. The principle of STM is simple. When an atomically-sharp conductive STM tip is close enough to a conductive substrate, a tunneling current is generated through the tip and the substrate upon applying a sufficient voltage in between. The tunneling current exponentially changes with the distance between the tip apex and the measured atom on the substrate. Based on the relationship between the tunneling current and the distance, a STM image with atomic resolution can be generated when the tip is scanning over the substrate. Therefore, STM can be very useful to monitor the molecular structure formed during self-assembly, molecular dynamics under thermodynamics and surface chirality. Furthermore, external forces from the STM tip or flow can also be applied to trigger the phase transition process of self-assembled molecular networks.
In this contribution, we focus on the recent progress of controlling the external stimuli to achieve state-of-the-art manipulation of phase transition of 2D molecular networks probed by STM at the solid-liquid interface, including temperature, electric field, photo-irradiation, shear-flow, and tip induction.
2. Thermal treatment
As molecular self-assembly process is governed under thermodynamic control[
30,
31,
32], thermal treatment is also a critical factor to manipulate the phase transition process of 2D molecular networks. Moreover, thermal treatment is a widely recognized process that can lead to the creation of an organized adlayer or the development of a new thermodynamically stable structure, or result in the expansion of the domain size[
33]. Azzam et al. demonstrated a continuous decrease of the surface coverage of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) of terphenylethanethiol on Au (111) and dramatic alterations in the substrate morphology caused by the partial desorption of molecules with elevated temperatures[
34]. Interestingly, the SAMs of terphenylethanethiol experienced a consecutive α-β-γ-δ phase transitions upon thermal annealing from the room temperature up to 468 K. At the room temperature, a densely packed α phase with
structure was observed on the Au (111) substrate, while it changed to β phase with
structure, associated with the appearance of irregular gold islands, up on annealing at 333K. Further annealing to 373K promoted the formation of γ phase with (2
structure. A final δ phase (2
appeared upon annealing at the temperature higher than 468K. The packing density of the molecules continuously decreased with the phase transition at higher temperatures due to the thermal-induced partial desorption of molecules.
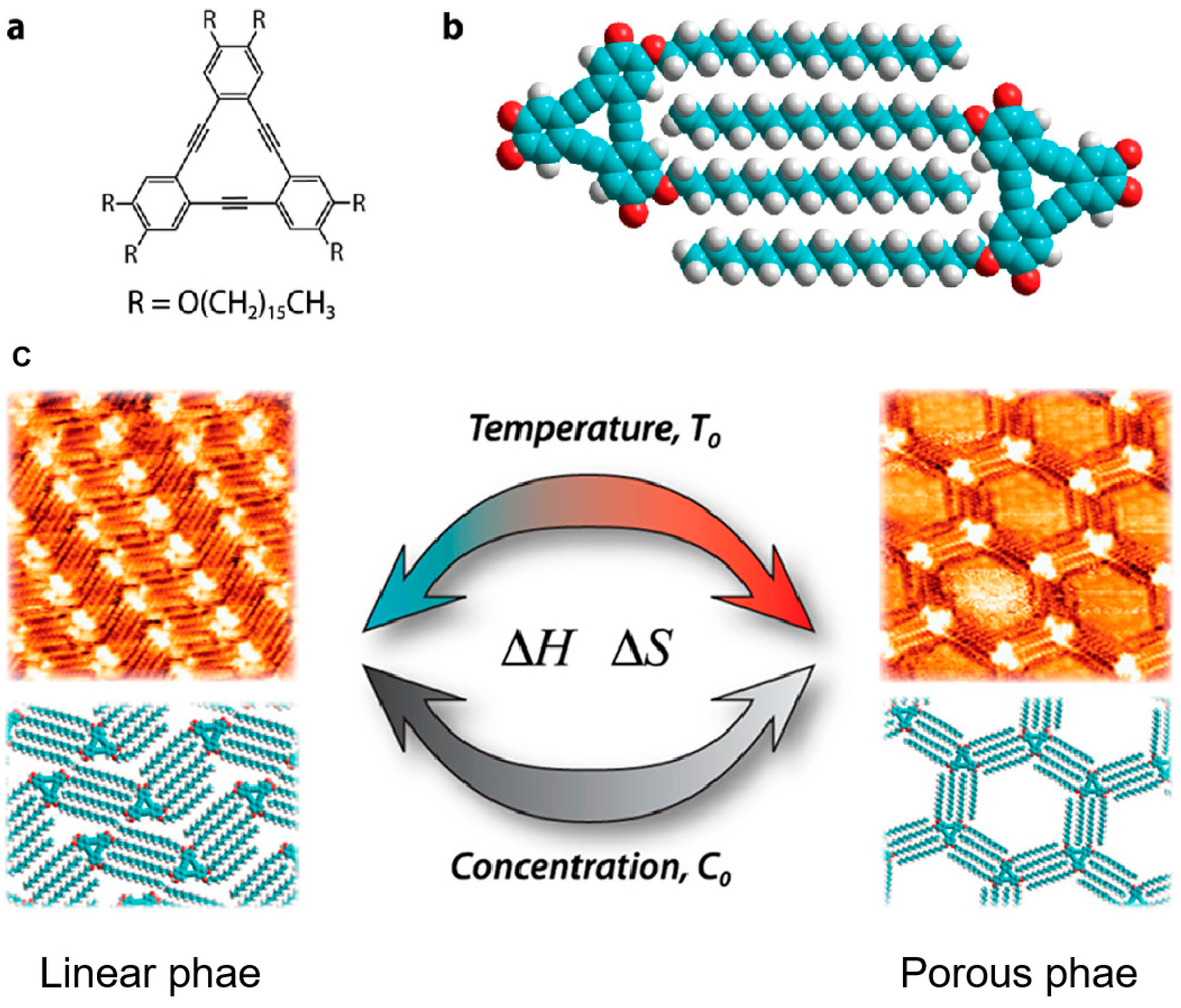
Similarly, De Feyter et al. realized the temperature-induced structural phase transition between a closely arranged linear and a loosely packed porous phase of SAMs of alkylated dehydrobenzo[
12]annulene (DBA) derivative on a graphite substrate.
Figure 1a,b showed the chemical structure of DBA-OC16 and the corresponding molecular model of the interlocking arrangement of alkoxy chains between neighboring DBA-OC16 molecules. Following this way, the DBA-OC16 molecules were expected to form linear and porous phases on a flat substrate. At the room temperature, the DBA molecules were co-adsorbed with solvent molecules (1,2,4-trichlorobenzene) as the guests on graphite surface and arranged into porous structure[
20]. Based on thermal annealing up to 353 K, the solvent molecules were evaporated from the pores and the structure were stabilized as a closely packed linear phase under entropic and enthalpic control. Furthermore, thermal treatment also can help induce the switch of chirality of SAMs. At the room temperature high concentration of chiral DBA(S) molecules appeared on the graphite surface with the co-existence of 81% clockwise (CW) and 19% counter-clockwise (CCW) porous patterns. However, annealing at 80 ℃ converted the original phases to a homochiral SAMs of CCW pattern by coalescence of domains through a ripening process, which is because that the guests DBA(S) molecules acting as guests preferentially stayed in CCW pores to form stable host-guest system[
35]. Besides, thermal annealing can also help conduct the trans-cis transformation of SAMs. Wan et al. investigated the temperature effect on the self-assembly behavior of bis(4,4’-(m,m’-di(dodecyloxy)phenyl)-2,2’-difluoro-1,3,2-dioxaborine) on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite (HOPG)[
36]. Firstly, a lamellar structure with trans conformation was observed on the HOPG surface at the room temperature with two dioxaborine (DOB) moieties aligned in a dihedral angle of 180 degree. When the temperature was lifted to 100 ℃, the quality of the SAMs was improved with long-range ordering of molecular arrays. Heating at 130 ℃ triggered the trans-cis transformation and a small region with hexagonal structure of cis isomer of the molecules was observed. When heating at 150 ℃, the domain of hexagonal structure of cis isomers expanded and eventually accomplished the complete trans-cis transformation by covering the entire surface. Furthermore, thermal annealing was feasible for the promotion of on-surface synthesis process to form 2D covalent organic frameworks (COFs)[
37,
38] and graphene nanoribbons (GNRs)[
39,
40,
41].
3. Photo-Induction
Recently, surface photochemistry has been intensively studied, due to its powerful function for tunning SAMs’ ordering and initiating on-surface polymerization, including photoisomerization[
42,
43], photopolymerization[
44,
45] and photocycloaddition[
46,
47]. The SAM adlayer normally experiences significant structural changes as a result of surface photochemical reactions, primarily due to the substantial structural disparity between the photo-active molecules before and after the photo-induction. Pace et al. observed the light-induced SAM phase transition of azobenzene molecules on Au (111) substrate with STM images. The transformation of the trans-form of SAM to the cis-form was promoted by 360 nm light irradiation, while the reversed transition was performed by 450 nm light irradiation[
48].
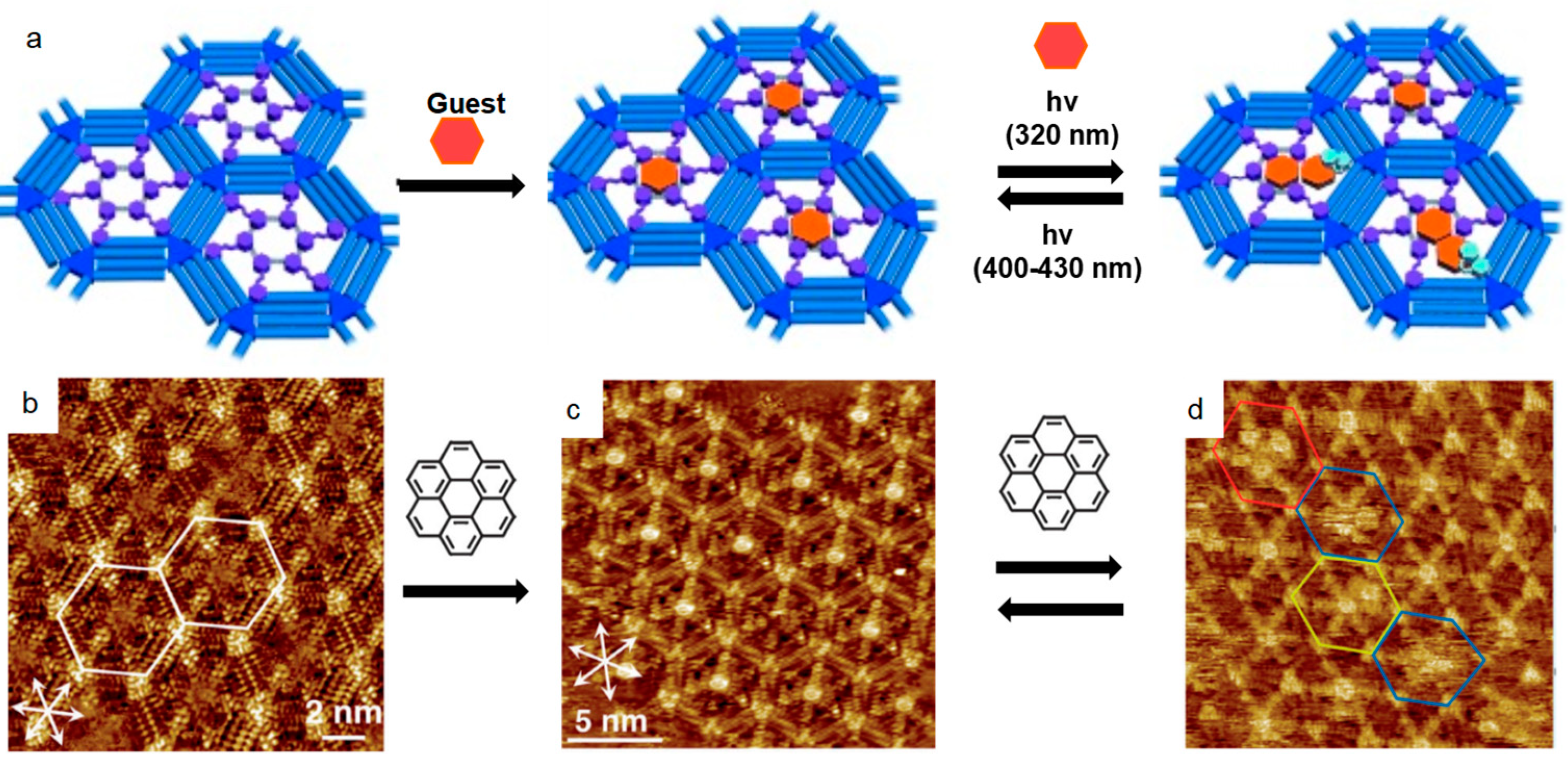
Later, Tahara et al. investigated the photo-induced phase transition of SAMs in a more complex system, involving a photo-induced guest adsorption and desorption process[
49]. The schematic illustration clearly demonstrated the photo-induced guest adsorption and desorption process in DBA pores,
Figure 2a. Firstly, the trans-form azobenzene-functionalized DBA self-assembled into hexagonal porous structure at the1-octanoicacid/graphite interface,
Figure 2b. After adding the coronene guest molecules into the system, one of each coronene molecule was immobilized in one pore formed by the trans-azobenzene-functionalized DBA,
Figure 2c. Upon light-irradiation at 320 nm, the trans-to-cis transformation occurred with desorption of one or two azobenzene units from the substrate surface, which left sufficient space for the accommodation of additional coronene guest molecules in the pores,
Figure 2d. Reversely, applying a light-irradiation at 400-430 nm initiated the cis-to-trans transformation, which promoted the re-adsorption of the trans-molecules onto the substrate surface and excluded the extra guest molecules. Yokoyama et al. demonstrated the investigation of photo-activated structural switch behavior of a photochromic terthiophene derivative with STM at the solid-liquid interface[
50]. No ordered structure was observed for the closed-ring phase of terthiophene derivative, while it underwent a phase transition to two ordered phases (α-ordering and β-ordering) due to the visible-light-induced ring opening of the terthiophene derivative. When UV light was used for the photo-induction, a third ordered phase (γ-ordering) appeared due to the formation of the annulated isomer. It is also possible to control the conductance of molecular electronics via light-irradiation induced opening and closing of the ring of the thiophene unit of SAM on Au substrate. A reversible conversion between two distinguishable conductance states can be controlled via photoisomerisation of the switches by using alternative irradiation with UV (λ=313 nm) or visible (λ> 420 nm) light to achieve on-state and off-state, respectively. This transition process was clearly probed by the STM images, showing the distinct height difference between the one-state (0.4–0.6 nm) and off-state of the molecules (0–0.1 nm)[
51].
4. Voltage Induction
Electric field is an efficient way to control the surface self-assembly process of molecules. The surface structural transition influenced by the electric field is indicative of the modulation of the interaction between the substrate and the molecule, as well as potential changes in intermolecular interactions., which normally leads to the order-disorder transition, surface coverage manipulation and polymorph switch. Lee et al. reported that a reversible transition between low-density porous and high-density nonporous SAM networks of 1,3,5-tris(4-carboxyphenyl)-benzene (BTB) molecules was successfully achieved by applying bias voltage with opposite signs through STM, due to the protonation or deprotonation process of the BTB molecules[
52]. Based on this porous-nonporous structure transition, a controlled capturing and releasing of guest molecules was accomplished at the solution-solid interface. Besides, the voltage induction was also feasible to initiate the phase transformation between the SAMs and covalent organic frameworks (COFs). Cai et al. formed a SAM of 1,3,5-tris(4-biphenylboronic acid)benzene (TBPBA) on HOPG with a closely packed structure under ambient conditions with a positive bias voltage applied to the substrates and the molecules[
53]. When the substrate and the molecules were applied with negative bias voltage, the noncovalently bonded TBPBA molecules were arranged into loosely packed porous structure with the co-adsorption of 1-octanoic acid solvent molecules as the guests inside the cores and more interestingly the boronic acid groups of each TBPBA molecule formed covalent bonds with the three adjacent molecules. The electric field-induced phase transition between the SAM and COF was totally reversable in dependent of the polarity of the applied bias voltage. However, this method was just able to control the local structure of molecules around the STM tip. Luckily, applying an electrochemical STM (EC-STM) system, which allows to independently control the tip and substrate voltage, can globally control the phase transition process over the entire substrate. Wen et al. reported a sequential control of the polymorph change of SAM of nitrobenzene and picric acid on Au (111) substrate in in 0.1 M HClO
4, which was recorded by an EC-STM[
54]. At surface potential of 550 mV, nitrobenzene molecules formed a well-ordered SAM in a (
×
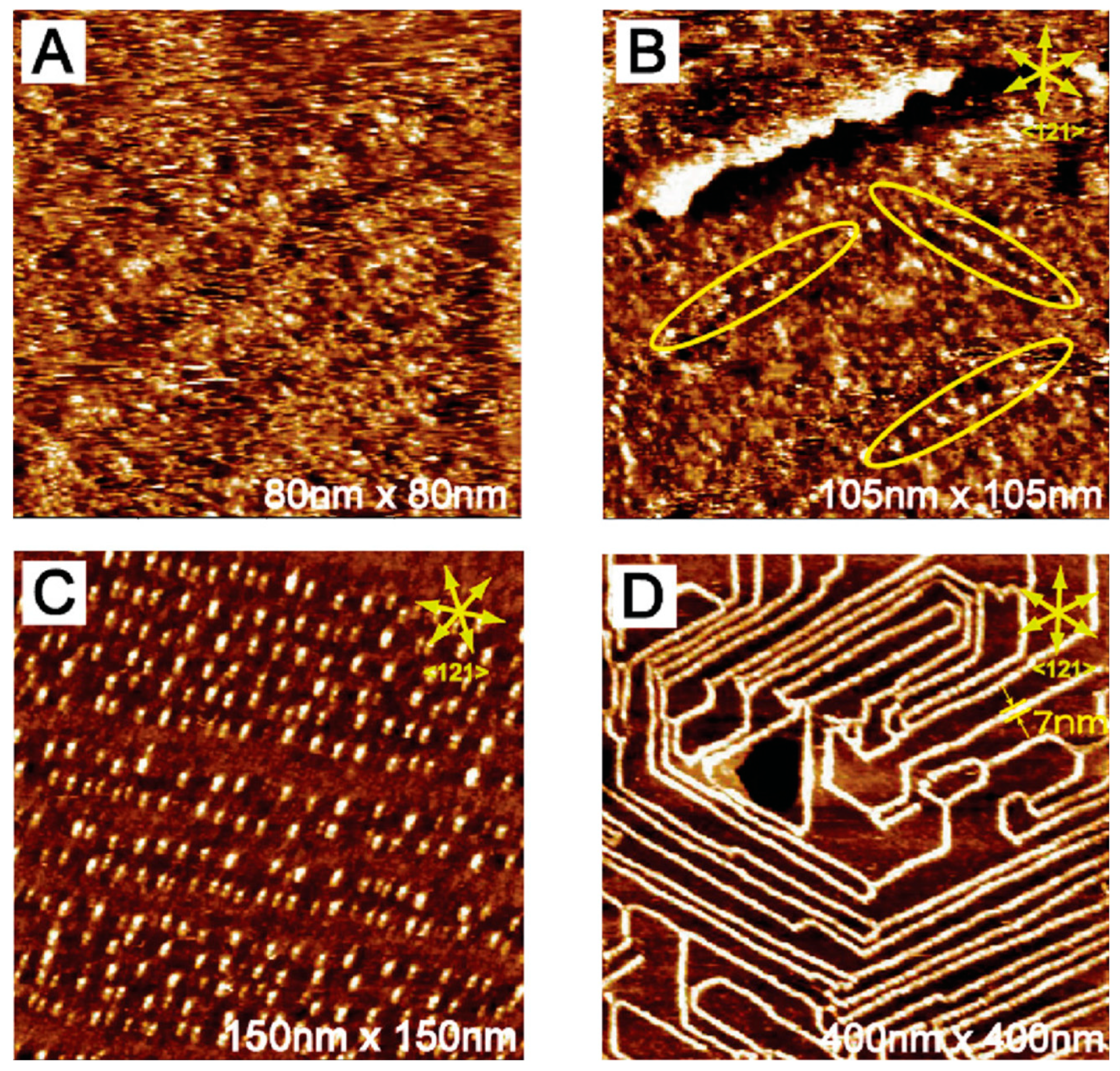
) organization. The molecules started to nucleate into organic islands at 300 mV and further transformed into 1D molecular wires at 220 mV. By holding such substrate potential for 4h, the density and continuity of the molecular wires expanded. This phase transition was caused by the irreversible reduction of the nitro groups into hydroxyamino and amine groups depending on the applied substrate potential. In contrast, picric acid formed disordered phase at 500 mV (
Figure 3a), and bright clusters started to appear at 360 mV (
Figure 3b). More clusters grew by shifting the substrate potential to 250 mV and they were aligned following preferred directions,
Figure 3c. Finally, at 200 mV, the aligned clusters were connected into molecular wires along the reconstruction lines of Au (111),
Figure 3d.
Besides the electrochemically responsive molecules, charged molecules can also be induced by the substrate voltage to form transformable SAM. Cui et al. investigated the self-assembly behavior of 9-phenylbenzo[
1,
2]quinolizino-[3,4,5,6-fed]phenanthridinylium perchlorate (PQPClO
4) on Au(111) in 0.1M HClO
4[
55]. When the substrate potential is much more positive at 800 mV, the adlayer of PQP amorphized due to the strong repulsive force between the accumulated positive charge on the substrate and the positive charged molecules. When the substrate is less densely charged at 600 mV, an ordered porous structure was observed in the STM image and the PQP cations rotated by 90
o in order to enlarge the pore size for the accommodation of an extra PQP cation as the guest into the pores at 400 mV. When the substrate voltage was negatively shifted to 150 mV, a completely different polymorph was observed in the STM image. The PQP cations were arranged into high-density linear structure with additional PQP cations forming double rows in a second layer. Other than alteration of the surface charge density, it is also possible to tune the charge density of the molecules for the voltage induced phase transition by an EC-STM. Sagara et al. demonstrated the faradaic phase transition of SAM of dibenzyl viologen (dBV) molecules on HOPG upon voltage induced redox process in which the potential driven transition between dBV
•+ and dBV
2+ was achieved by adjusting the potential more negative or positive than the redox peaks[
56]. The EC-STM image showed that the 2D linear pattern of the reduced form dBV
•+ was formed at substrate potential of -0.38V following the three main symmetric axes of HOPG, while the oxidized form dBV
2+ formed gas-like adsorption layer at the potential regions more positive than the cathodic transition potentials due to the mobility of the molecules caused by the intermolecular electrostatic repulsion and adsorption-desorption dynamic equilibrium. Later, Huynh et al. investigated the same system on HOPG and graphene substrates in more depth by identifying three different redox states of dBV rather than the two states observed by Sagara[
57]. Similarly, a mobile phase of dBV
2+ was formed by controlling the substrate potential to the more positive regions than the redox peaks, while a condensed linear stacking phase (dBV
0) was observed at the substrate potential more negative than the redox peaks. Surprisingly, a dimer phase was identified at the potential regions in between the two redox peaks.
5. Flow-Induction
The manipulation of the spatial organization of molecular components on surfaces is a crucial aspect in the bottom-up approach for the development of nanotechnologies. Supramolecular self-assembly process offers a promising method for constructing ordered patterns through the spontaneous arrangement of specifically designed molecular building blocks. However, this process involves intricate intermolecular, intramolecular, and molecule-substrate interactions, which are challenging to control. As a result, it often leads to the formation of polycrystalline or amorphous structures at the sub-micrometer scale. Recently, shear flow method was introduced to align macromolecules and liquid crystalline polymers[
58,
59,
60]. Inspired by this, Lee et al. introduced an applicable shear-flow method for globally guiding the self-assembly behavior of building blocks by dragging the building block containing solution with a piece of ultra-clean tissue following certain direction to induce the long-range alignment of 2D nanopatterns of SAM of 3,6,11,14-tetradodecyloxydibenzo[g,p]-chrysene (DBC)[
61]. Before shear-treatment, the DBC molecules formed a typical face-on orientation for polyaromatic molecules, while it transformed into an edge-on orientation with the molecules aligned following the [01?10] direction of the HOPG substrate. This transition can be clearly indicated by the alteration of the lattice parameters of adlayer and the spacing reduction on the neighboring molecules from 1.7 to 0.5 nm. Remarkably, this method allows the formation of DBC molecules with singular domain yup to ∼7 mm. Dragging the solution along the direction parallel to the unit cell vectors of HOPG is critical to fabricate such large domain with unique alignment, otherwise multiple small domains can be formed following the three main symmetric axes of HOPG due to the strong molecule-substrate interactions. Furthermore, the aligned SAM was able to maintain its arrangement by overcoming the local defects on the substrate such as step-edges. However, the existence of many defective areas within the long-range ordered SAM remained as a big issue, which determined the quality of the SAM based molecular electronics. The Authors optimized the SAM quality using a different molecular system, in which the oligomer molecules self-assembled in the solution phase into ordered 1D chains following the main symmetric axes of the substrate due to the strong molecule-substrate interactions[
62]. While shear-flow treatment converted the directional multiple domains into unidirectionally singular domain following the flow direction with ultra-low defective areas less than 0.5%, compared to that of 5% without the treatment. The spatial ordering control was further extended to the third dimension by controlling the alignment of multilayer molecular assembly process.
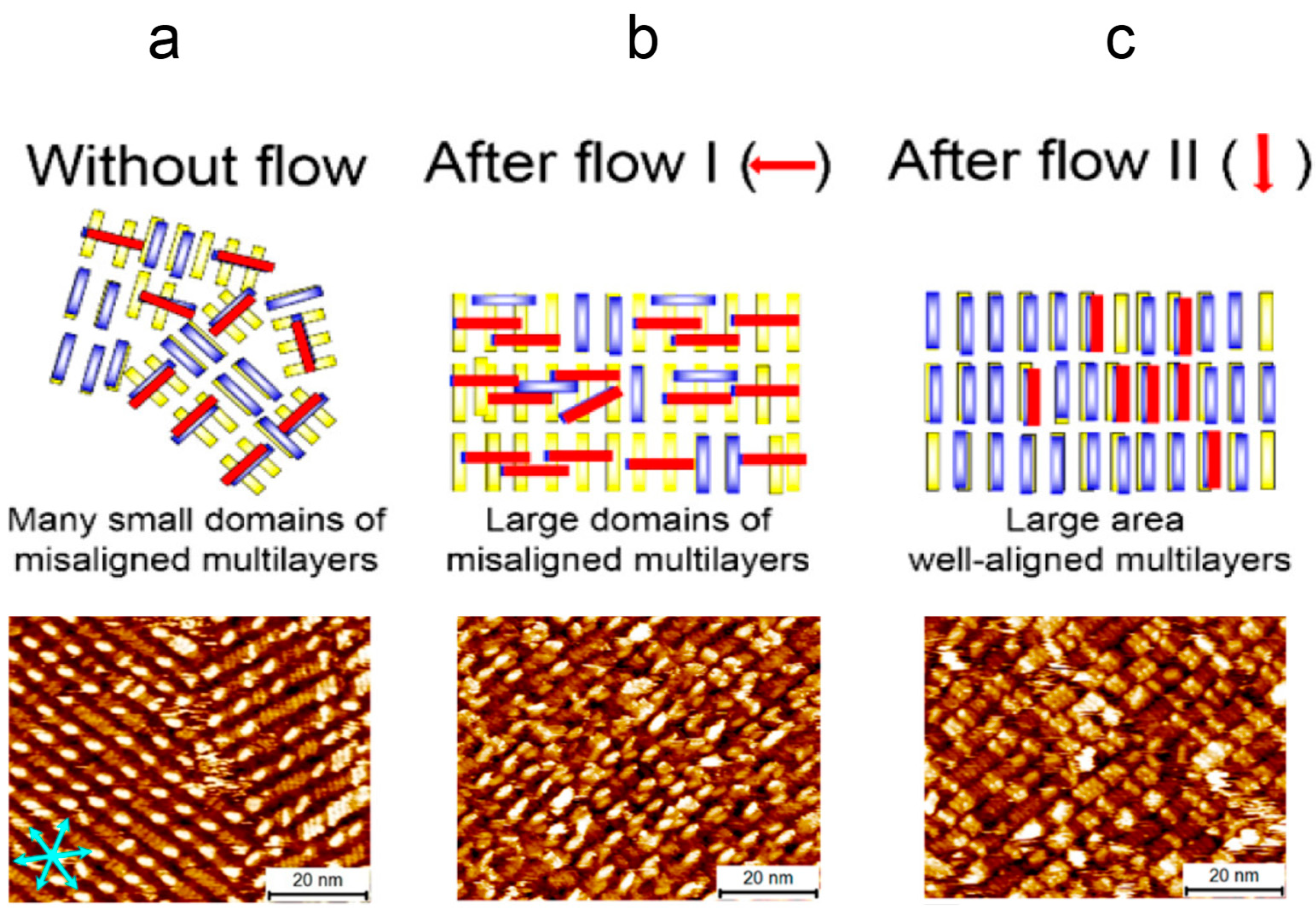
Lee et al. used SAM of hexarylene diimide(HDI) as an example for demonstrating the multilayer alignment via shear flow[
63]. Without any external induction, HDI formed a linear structure with many small domains on the first layer following the three main symmetric axes of HOPG and misaligned multilayers,
Figure 4a. With the first-step shear flow treatment with the flow direction perpendicular to the linear rods, the small domains on the first layer merged as a large and unidirectional domain with the molecules on the multilayer remaining misaligned,
Figure 4b. Following the second-step shear flow treatment with the flow direction parallel to the linear rods, the molecules on the multilayers were also unidirectional aligned according to the flow directions,
Figure 4c. Surprisingly, Elemans et al. also managed to form well-ordered SAM of porphyrin trimers with an ultra-large domain size in millimeter scale, upon applying macroscopic dewetting of solvent to create a flow force for the guidance of the porphyrin macrocycles SAM alignment[
64]. This method was proven effective for directing the formation of large-domain liquid crystals.
6. Tip Induction
STM is a powerful tool for the direct visualization of the structure and the lattice parameters of the SAMs at the atomic resolution. Meanwhile, its tip, which is normally used for the surface structure probing, can also be useful for the manipulation of the adlayer structure of SAMs. Initially, short-period voltage by the pulse function was applied to the adlayer molecules to tune their local electronic states through the STM tip for the induction of the structural transition of adlayer. Alemani et al. observed the transformation between the trans- and cis- phase of 3,3′,5,5′-tetra-tert-butylazobenzene (TBA) on Au (111) substrate under ultra-high vacuum conditions[
65]. At first, a thermodynamically favorable trans-isomer of TBA spontaneously adsorbed on Au (111), arranging into ordered islands with parallel rows. By applying a 2V voltage pulse on the adlayer, the trans-isomer of TBA molecule can be converted to the cis-isomer and the precisely reverse induction can be achieved by applying another 2V voltage pulse on the same molecule due to the voltage induced shift of molecular lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LOMO). Similarly, Mali et al. found a tip-pulse induced phase transition behavior between the hexagonal motif (α phase) of SAM of PQPClO
4 and the self-host-guest structure (β phase) with one extra PQPClO
4 molecule located in the core formed by the α phase[
66]. The energy provided through the STM tip pulsing was responsible for the transformation of SAM configurations. Recently, STM tip has been used as a nanolithography tool to remove certain grafted defects on substrates for the selective mergence and alignment of SAM molecular domains. Bragança et al. observed the phenomena that the large domains of SAM of 5-octadecyloxy-isophthalic acid (ISA-OC18) on HOPG were interrupted into small pieces by the covalently grafted low-density diazonium molecules[
67]. These grafted molecules worked as domain boundaries for the containment of the domain size of SAM. The selective Ostwald ripening process, characterized by the growth of larger domains at the expense of smaller ones, was achieved by precisely removing specific grafted molecules located on the boundaries of the domains using STM tip. Following a similar strategy, a fully grafted substrate was nano-shaved by STM tip to create nano-corrals for further space-confined self-assembly process. The tip-induced confinement effect has a significant impact on the self-assembly behavior of molecules, including the alignment of domains, selective chirality and phase transition of SAMs. For example, Verstraete et al. used HOPG with high-density grafting of diazonium molecules as a template, on which well-defined and stable patterns can be formed for studying the ex-situ and in-situ self-assembly behavior of molecules via nano-shaving with the STM tip[
68]. The categorization of ex-situ and in-situ were defined by the absence or presence of PCDA solution on the substrate surface during the nano-shaving process. On a pristine HOPG (unconfined), the 10,12-pentacosadiynoic acid (PCDA) molecules formed linear structure following the three main symmetric axes of HOPG with multiple domains, as expected. In an ex-situ corral with 180 nm × 180 nm size, the self-assembly behavior of PCDA is similar to that on the unconfined HOPG and no alignment effect was observed. For comparison, the PCDA molecules aligned unidirectionally following their molecular long axis to form a large domain in the in-situ corral.
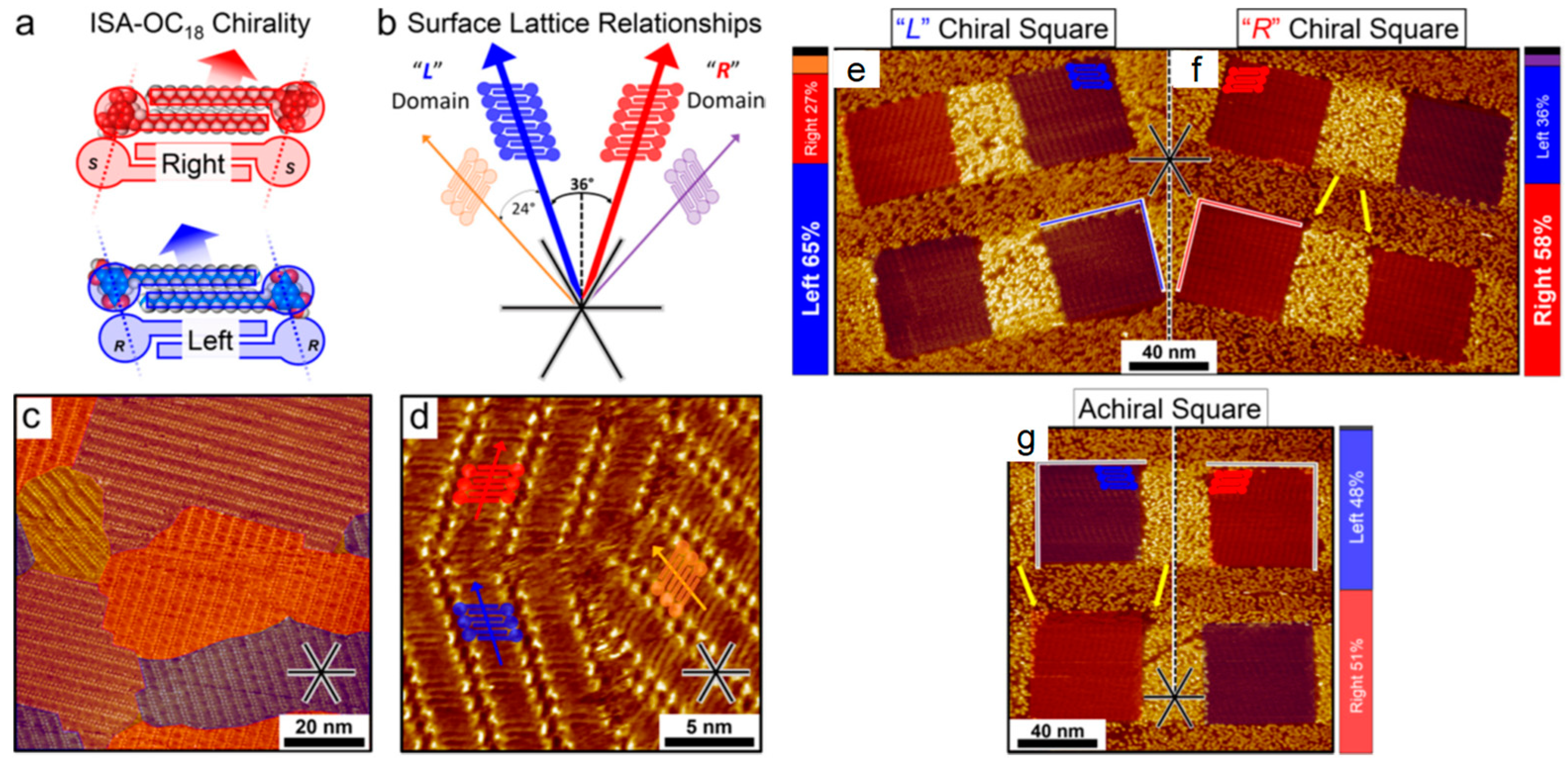
Additionally, the tip-created chirality in these nano-corrals were useful to build chiral surfaces for biasing the enantiomorphic assembly of a prochiral molecule during the self-assembly process. In
Figure 5, Seibel et al. demonstrated the possibility of using nanoconfined corrals with different chirality for the induction of selective adsorption of chiral polymorphs[
69].
Figure 5a showed that self-assembly of a prochiral 5-octadecyloxy-isophthalic acid (ISA-OC18) molecules into chiral lamellae with interdigitated alkyl-chains was observed with S (left) or R (right) chirality according to their tilt direction. These chiral lamellae preferentially adsorb on the HOPG surface to form L or R domains, which can be classified by the tilt direction with respect to the [210] surface direction of HOPG,
Figure 5b. The large-area and small-area STM images in
Figure 5c,d showed an equivalent adsorption of L and R domains on the surface without any confinement.
Figure 5g showed that no chiral biasing effect was observed during the self-assembly of ISA-OC18 in achiral nano-corrals based on a large number of statistical analyses. However, when the nano-corrals were created with different chirality by adjusting their tilt angles of 18° left and right with respect to the [210] surface direction of HOPG substrate, the preferential adsorption of enantiomorph was observed in those chiral nano-corrals. In the nano-corrals designed for left-handed enantiomorphs, a majority of 65% exhibited a preference for adsorption,
Figure 5e. However, this preference decreased to 36% in the right-handed nano-corrals,
Figure 5f. In contrast, only 27% right-handed enantiomorphs tended to adsorb in the left-handed nano-corrals, which increased to 58% in the right-handed ones.
7. Conclusions
Self-assembly is a widely observed and significant phenomenon in the natural world. The study of adsorption and self-assembly at surfaces and interfaces is a crucial area of investigation in physical chemistry, as it is closely linked to various fundamental and practical scientific inquiries such as chirality, host-guest chemistry, and molecular electronics. In the field of nanoscience and nanotechnology, self-assembly is increasingly recognized as a prominent method in the "bottom-up" approach for constructing molecular nanostructures. The advent of STM has provided researchers with “visible” evidence in studying the self-assembly process. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the underlying physical chemistry mechanisms involved in adsorption and self-assembly on surfaces and interfaces is a crucial initial step in the development of controllable processes. It is widely recognized that surface self-assembly is influenced by the interplay between the interactions of molecules with the substrate and with each other. The molecule-substrate interaction plays a role in determining the orientation of molecules in the adlayer, while intermolecular interactions are responsible for the formation of ordered molecular nanostructures in two dimensions. A thorough comprehension of the driving forces behind the self-assembly process enables the customization of this process. This can be achieved through external stimuli, such as, temperature, electric field, photo-irradiation, shear flow, tip induction and other factors. In the realm of nanotechnology applications, surface 2D ordered structures hold significant perspectives for nanopatterning and high-density data storage. The utilization of self-assembly techniques in nanolithography offers several desirable attributes, including inexpensiveness, rapid processing, and high resolution. However, one of the primary challenges that must be addressed is the compatibility of these techniques with existing lithography methods. Nevertheless, we maintain a positive outlook on the future of self-assembly techniques in nanofabrication applications. For example, creation of nanoconfined spaces for further self-assembly upon the employment of STM tip can open up possibilities for the development of innovative engineered materials with nanometer precision. The integration of lithographic and self-assembly methods can lead to the development of a diverse array of directed assembly techniques that possess enhanced capabilities beyond those of their individual components.
Author Contributions
writing—original draft preparation, Zhi Li.; writing—review and editing, YaNan Li; and ChengJie Yin.; project administration, ChengJie Yin. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by Scientific Research Foundation for High-level Talents of Anhui University of Science and Technology (2022yjrc50), Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2208085QB45).
Conflicts of Interest
“The authors declare no conflict of interest.”
References
- Chen, H.; Stoddart, J. From Molecular to Supramolecular Electronics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 804-828. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, X.; Soni, S.; Chiechi, R. Charge Transport through Molecular Ensembles: Recent Progress in Molecular Electronics. Chem. Phys. Rev. 2021, 2, 021303. [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; Tong, Z.; Ma, L.; Zhu, W.-H.; Wu, W.; Xie, Y. Molecular Engineering Strategies for Fabricating Efficient Porphyrin-Based Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 13, 1617-1657. [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Li, T.; Hu, W.; Fuchs, H. Recent Progress in Aromatic Polyimide Dielectrics for Organic Electronic Devices and Circuits. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806070. [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, T. Recent Progress in the Development of Molecular-Scale Electronics Based on Photoswitchable Molecules. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 821-848. [CrossRef]
- Ariga, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Mori, T.; Takeya, J.; Shrestha, L. K.; Hill, J. Self-Assembly as a Key Player for Materials Nanoarchitectonics. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2019, 20, 51-95. [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G. M.; Mathias, J. P.; Seto, C. Molecular Self-Assembly and Nanochemistry: A Chemical Strategy for the Synthesis of Nanostructures. Science 1991, 254, 1312-1319. [CrossRef]
- Pochan, D.; Scherman, O. Introduction: Molecular Self-Assembly. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13699-13700. [CrossRef]
- Otero, R.; Gallego, J. M.; de Parga, A. L. V.; Martín, N.; Miranda, R. Molecular Self-Assembly at Solid Surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5148-5176. [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Cheng, Z.; Kariuki, M.; Hall, S. C.; Hill, S. K.; Rho, J. Y.; Perrier, S. Molecular Self-Assembly and Supramolecular Chemistry of Cyclic Peptides. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 13936-13995. [CrossRef]
- Lei, P.; Ma, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Gan, L.; Deng, K.; Duan, W.; Li, W.; Zeng, Q. The Self-Assembly and Structural Regulation of a Hydrogen-Bonded Dimeric Building Block Formed by Two NH··· O Hydrogen Bonds on HOPG. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 108005. [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.-Y.; Wagner, H.; Held, P. A.; Du, S.; Gao, H.-J.; Studer, A.; Fuchs, H. In-Plane Van Der Waals Interactions of Molecular Self-Assembly Monolayer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2015, 106, 081606. [CrossRef]
- Bera, S.; Basu, S.; Jana, B.; Dastidar, P. Real-Time Observation of Macroscopic Helical Morphologies under Optical Microscope: A Curious Case of π-π Stacking Driven Molecular Self-Assembly of an Organic Gelator Devoid of Hydrogen Bonding. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202216447. [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gao, S.; Fang, Y.; Lin, X.; Jin, X.; Wang, X.; Ke, L.; Shi, K. The π–π Stacking-Guided Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Nanomedicine for Effective Delivery of Antineoplastic Therapies. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 3159-3177. [CrossRef]
- Halter, M.; Liao, Y.; Plocinik, R. M.; Coffey, D. C.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Mazur, U.; Simpson, G. J.; Robinson, B. H.; Keller, S. Molecular Self-Assembly of Mixed High-Beta Zwitterionic and Neutral Ground-State NLO Chromophores. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1778-1787. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Miao, K.; Zha, B.; Xu, L.; Miao, X.; Deng, W. Fabrication of Chiral Networks for a Tri-Substituted Anthraquinone Derivative Using Molecular Self-Assembly. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 13164-13168. [CrossRef]
- Sirtl, T.; Song, W.; Eder, G.; Neogi, S.; Schmittel, M.; Heckl, W. M.; Lackinger, M. Solvent-Dependent Stabilization of Metastable Monolayer Polymorphs at the Liquid–Solid Interface. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6711-6718. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Yan, X.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J. Solvent-Induced Structural Transition of Self-Assembled Dipeptide: From Organogels to Microcrystals. Chem. Eur J. 2010, 16, 3176-3183. [CrossRef]
- Katsonis, N.; Xu, H.; Haak, R. M.; Kudernac, T.; Tomović, Ž.; George, S.; Van der Auweraer, M.; Schenning, A. P.; Meijer, E. W.; Feringa, B. Emerging Solvent-Induced Homochirality by the Confinement of Achiral Molecules against a Solid Surface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 4997-5001. [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M. O.; Adisoejoso, J.; Tahara, K.; Katayama, K.; Van der Auweraer, M.; Tobe, Y.; De Feyter, S. Temperature-Induced Structural Phase Transitions in a Two-Dimensional Self-Assembled Network. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12068-12075. [CrossRef]
- Gutzler, R.; Sirtl, T.; Dienstmaier, J.; Mahata, K.; Heckl, W. M.; Schmittel, M.; Lackinger, M. Reversible Phase Transitions in Self-Assembled Monolayers at the Liquid− Solid Interface: Temperature-Controlled Opening and Closing of Nanopores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5084-5090. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cao, K.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, G.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, W.; Bai, W.; Weng, X.; Chen, W. A General Strategy for Synthesizing Biomacromolecular Ionogel Membranes Via Solvent-Induced Self-Assembly. Nat. Synth. 2023, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wei, X.; Tan, P.; Yu, Y.; Yang, B.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, H.; Lin, H.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. Concentration-Controlled Reversible Phase Transitions in Self-Assembled Monolayers on HOPG Surfaces. Small 2015, 11, 2284-2290. [CrossRef]
- Fang, G.; Shi, Y.; Maclennan, J. E.; Clark, N. A.; Farrow, M. J.; Walba, D. Photo-Reversible Liquid Crystal Alignment Using Azobenzene-Based Self-Assembled Monolayers: Comparison of the Bare Monolayer and Liquid Crystal Reorientation Dynamics. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17482-17488. [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.-X.; Wang, H.; Duan, S.; Zhang, H.-M.; Xu, X.; Chi, L.-F. Potential-Induced Phase Transition of N-Isobutyryl-L-Cysteine Monolayers on Au (111) Surfaces. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2017, 33, 1010-1016. [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, A.; Zeng, X.; Saleemi, A. S.; Cheng, K.-Y.; Lee, S.-L. Electric-Field-Induced Supramolecular Phase Transitions at the Liquid/Solid Interface: Cat-Assembly from Solvent Additives. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 8790-8793. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Wang, Z. X.; Han, X. B.; Sun, Y.-L.; Pryor, D. Orientational Ordering of Guest Induced Structural Phase Transition Coupled with Switchable Dielectric Properties in a Host–Guest Crystal: Bis(Thiourea) Thiazolium Chloride. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 108028-108033. [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-W.; Adisoejoso, J.; Plas, J.; Hong, J.; Müllen, K.; De Feyter, S. Self-Assembly Behavior of Alkylated Isophthalic Acids Revisited: Concentration in Control and Guest-Induced Phase Transformation. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15206–15211. [CrossRef]
- Binning, G.; Rohrer, H.; Gerber, C.; Weibel, E. Surface Studies by Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 57-61. [CrossRef]
- Williams, R. J.; Smith, A. M.; Collins, R.; Hodson, N.; Das, A. K.; Ulijn, R. Enzyme-Assisted Self-Assembly under Thermodynamic Control. Nature Nanotech. 2009, 4, 19-24. [CrossRef]
- Packwood, D. M.; Han, P.; Hitosugi, T. Chemical and Entropic Control on the Molecular Self-Assembly Process. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14463. [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Li, X.; Yu, H. Thermodynamic Phase-Like Transition Effect of Molecular Self-Assembly. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 12, 126-131. [CrossRef]
- Su, G. J.; Aguilar-Sanchez, R.; Li, Z.; Pobelov, I.; Homberger, M.; Simon, U.; Wandlowski, T. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy and Spectroscopy Studies of 4-Methyl-4'-(N-Mercaptoalkyl) Biphenyls on Au (111)-(1×1). Chem. Eur. J. 2007, 8, 1037-1048. [CrossRef]
- Azzam, W.; Al-Rashdi, A.; Subaihi, A.; Rohwerder, M.; Zharnikov, M.; Bashir, A. Annealing Effect for Self-Assembled Monolayers Formed from Terphenylethanethiol on Au (111). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2020, 22, 13580-13591. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ghijsens, E.; Ivasenko, O.; Cao, H.; Noguchi, A.; Mali, K. S.; Tahara, K.; Tobe, Y.; De Feyter, S. Dynamic Control over Supramolecular Handedness by Selecting Chiral Induction Pathways at the Solution–Solid Interface. Nature Chem. 2016, 8, 711-717. [CrossRef]
- Rohde, D.; Yan, C. J.; Yan, H. J.; Wan, L. J. From a Lamellar to Hexagonal Self-Assembly of Bis (4, 4'-(M, M'-Di (Dodecyloxy) Phenyl)-2, 2'-Difluoro-1, 3, 2-Dioxaborin) Molecules: A Trans-to-Cis-Isomerization-Induced Structural Transition Studied with STM. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 118, 4100-4104. [CrossRef]
- Shi, K. J.; Zhang, X.; Shu, C. H.; Li, D. Y.; Wu, X. Y.; Liu, P. Ullmann Coupling Reaction of Aryl Chlorides on Au (111) Using Dosed Cu as a Catalyst and the Programmed Growth of 2D Covalent Organic Frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8726-8729. [CrossRef]
- Dienstmaier, J. r. F.; Gigler, A. M.; Goetz, A. J.; Knochel, P.; Bein, T.; Lyapin, A.; Reichlmaier, S.; Heckl, W. M.; Lackinger, M. Synthesis of Well-Ordered Cof Monolayers: Surface Growth of Nanocrystalline Precursors Versus Direct on-Surface Polycondensation. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9737-9745. [CrossRef]
- Ruffieux, P.; Wang, S.; Yang, B.; Sánchez-Sánchez, C.; Liu, J.; Dienel, T.; Talirz, L.; Shinde, P.; Pignedoli, C. A.; Passerone, D. On-Surface Synthesis of Graphene Nanoribbons with Zigzag Edge Topology. Nature 2016, 531, 489-492. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Narita, A.; Müllen, K. Graphene Nanoribbons: On-Surface Synthesis and Integration into Electronic Devices. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001893. [CrossRef]
- Zuzak, R.; Castro-Esteban, J.; Engelund, M.; Pérez, D.; Peña, D.; Godlewski, S. On-Surface Synthesis of Nanographenes and Graphene Nanoribbons on Titanium Dioxide. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 2580-2587. [CrossRef]
- Toyoda, R.; Hoang, N. V.; Moghaddam, K. G.; Crespi, S.; Pooler, D. R.; Faraji, S.; Pshenichnikov, M. S.; Feringa, B. Synergistic Interplay between Photoisomerization and Photoluminescence in a Light-Driven Rotary Molecular Motor. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5765. [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.-Y.; Niu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lu, M.; Zhang, M.; Shi, J.-W.; Liu, J.; Yan, Y.; Li, S.-L.; Lan, Y.-Q. Interpenetrating 3D Covalent Organic Framework for Selective Stilbene Photoisomerization and Photocyclization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 8860-8870. [CrossRef]
- Gan, Y.; Yin, J.; Jiang, X. Self-Wrinkling Induced by the Photopolymerization and Self-Assembly of Fluorinated Polymer at Air/Liquid Interface. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18574-18582. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wong, K. M.-C.; Wong, H.-L.; Yam, V. W.-W. Interfaces, Helical Self-Assembly and Photopolymerization Properties of Achiral Amphiphilic Platinum (Ii) Diacetylene Complexes of Tridentate 2, 6-Bis (1-Alkylpyrazol-3-Yl) Pyridines. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17445-17453. [CrossRef]
- Gromov, S. P.; Vedernikov, A. I.; Lobova, N. A.; Kuz'mina, L. G.; Basok, S. S.; Strelenko, Y. A.; Alfimov, M. V.; Howard, J. Controlled Self-Assembly of Bis (Crown) Stilbenes into Unusual Bis-Sandwich Complexes: Structure and Stereoselective [2+2] Photocycloaddition. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 724-737. DO. [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, K. M.; Rival, J. V.; Sreeraj, P.; Nambiar, S. R.; Jeyabharathi, C.; Nonappa; Shibu, E. Precision Nanocluster-Based Toroidal and Supertoroidal Frameworks Using Photocycloaddition-Assisted Dynamic Covalent Chemistry. Small 2023, 19, 2207119. [CrossRef]
- Pace, G.; Ferri, V.; Grave, C.; Elbing, M.; von Hänisch, C.; Zharnikov, M.; Mayor, M.; Rampi, M. A.; Samorì, P. Cooperative Light-Induced Molecular Movements of Highly Ordered Azobenzene Self-Assembled Monolayers. PNAS 2007, 104, 9937-9942. [CrossRef]
- Tahara, K.; Inukai, K.; Adisoejoso, J.; Yamaga, H.; Balandina, T.; Blunt, M. O.; De Feyter, S.; Tobe, Y. Tailoring Surface-Confined Nanopores with Photoresponsive Groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 125, 8531-8534. [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, S.; Hirose, T.; Matsuda, K. Photoinduced Four-State Three-Step Ordering Transformation of Photochromic Terthiophene at a Liquid/Solid Interface Based on Two Principles: Photochromism and Polymorphism. Langmuir 2015, 31, 6404-6414. [CrossRef]
- Pijper, T. C.; Kudernac, T.; Katsonis, N.; van der Maas, M.; Feringa, B. L.; van Wees, B. Reversible Light Induced Conductance Switching of Asymmetric Diarylethenes on Gold: Surface and Electronic Studies. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9277-9282. DO. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-L.; Fang, Y.; Velpula, G.; Cometto, F. P.; Lingenfelder, M.; Mullen, K.; Mali, K. S.; De Feyter, S. Reversible Local and Global Switching in Multicomponent Supramolecular Networks: Controlled Guest Release and Capture at the Solution/Solid Interface. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 11608-11617. [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.-F.; Zhan, G.; Daukiya, L.; Eyley, S.; Thielemans, W.; Severin, K.; De Feyter, S. Electric-Field-Mediated Reversible Transformation between Supramolecular Networks and Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 11404-11408. [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.; Pan, G.-B.; Wan, L.-J. Oriented Organic Islands and One-Dimensional Chains on a Au (111) Surface Fabricated by Electrodeposition: An Stm Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 12123-12127. [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Mali, K. S.; Ivasenko, O.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Walter, M.; Müllen, K.; De Feyter, S.; Mertens, S. Squeezing, Then Stacking: From Breathing Pores to Three-Dimensional Ionic Self-Assembly under Electrochemical Control. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 12951-12954. [CrossRef]
- Higashi, T.; Shigemitsu, Y.; Sagara, T. Faradaic Phase Transition of Dibenzyl Viologen on an HOPG Electrode Surface Studied by in Situ Electrochemical Stm and Electroreflectance Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2011, 27, 13910-13917. [CrossRef]
- Thi, M. T. H.; Thanh, H. P.; De Feyter, S. Surface Engineering of Graphite and Graphene by Viologen Self-Assembling: From Global to Local Architectures. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 6413-6419. [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, E.; Li, G.; Lam, J. W. Y.; Tang, B. Shear Induced Molecular Alignments of a Side-Chain Liquid Crystalline Polyacetylene Containing Biphenyl Mesogens. Polymer 2003, 44, 8095-8102. [CrossRef]
- Rozman, M.; Urbakh, M.; Klafter, J.; Elmer, F. Atomic Scale Friction and Different Phases of Motion of Embedded Molecular Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 1998, 102, 7924-7930. [CrossRef]
- Hoogboom, J.; Garcia, P. M.; Otten, M. B.; Elemans, J. A.; Sly, J.; Lazarenko, S. V.; Rasing, T.; Rowan, A. E.; Nolte, R. Tunable Command Layers for Liquid Crystal Alignment. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 11047-11052. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-L.; Chi, C.-Y. J.; Huang, M.-J.; Chen, C.-h.; Li, C.-W.; Pati, K.; Liu, R.-S. Shear-Induced Long-Range Uniaxial Assembly of Polyaromatic Monolayers at Molecular Resolution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10454-10455. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S. L.; Lin, N. T.; Liao, W. C.; Chen, C. h.; Yang, H. C.; Luh, T. Oligomeric Tectonics: Supramolecular Assembly of Double-Stranded Oligobisnorbornene through π-π Stacking. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 11594-11600. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-L.; Yuan, Z.; Chen, L.; Mali, K. S.; Müllen, K.; De Feyter, S. Forced to Align: Flow-Induced Long-Range Alignment of Hierarchical Molecular Assemblies from 2D to 3D. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4117-4120. [CrossRef]
- Van Hameren, R.; Schön, P.; Van Buul, A. M.; Hoogboom, J.; Lazarenko, S. V.; Gerritsen, J. W.; Engelkamp, H.; Christianen, P. C.; Heus, H. A.; Maan, J. Macroscopic Hierarchical Surface Patterning of Porphyrin Trimers Via Self-Assembly and Dewetting. Science 2006, 314, 1433-1436. [CrossRef]
- Alemani, M.; Peters, M. V.; Hecht, S.; Rieder, K.-H.; Moresco, F.; Grill, L. Electric Field-Induced Isomerization of Azobenzene by STM. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 14446-14447. [CrossRef]
- Mali, K. S.; Wu, D.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K.; Van der Auweraer, M.; De Feyter, S. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy-Induced Reversible Phase Transformation in the Two-Dimensional Crystal of a Positively Charged Discotic Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5686-5688. [CrossRef]
- Bragança, A. M.; Greenwood, J.; Ivasenko, O.; Phan, T. H.; Müllen, K.; De Feyter, S. The Impact of Grafted Surface Defects and Their Controlled Removal on Supramolecular Self-Assembly. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 7028-7033. [CrossRef]
- Verstraete, L.; Greenwood, J.; Hirsch, B. E.; De Feyter, S. Self-Assembly under Confinement: Nanocorrals for Understanding Fundamentals of 2D Crystallization. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10706-10715. [CrossRef]
- Seibel, J.; Verstraete, L.; Hirsch, B. E.; Braganca, A. M.; De Feyter, S. Biasing Enantiomorph Formation Via Geometric Confinement: Nanocorrals for Chiral Induction at the Liquid–Solid Interface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 11565-11568. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).