Submitted:
05 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
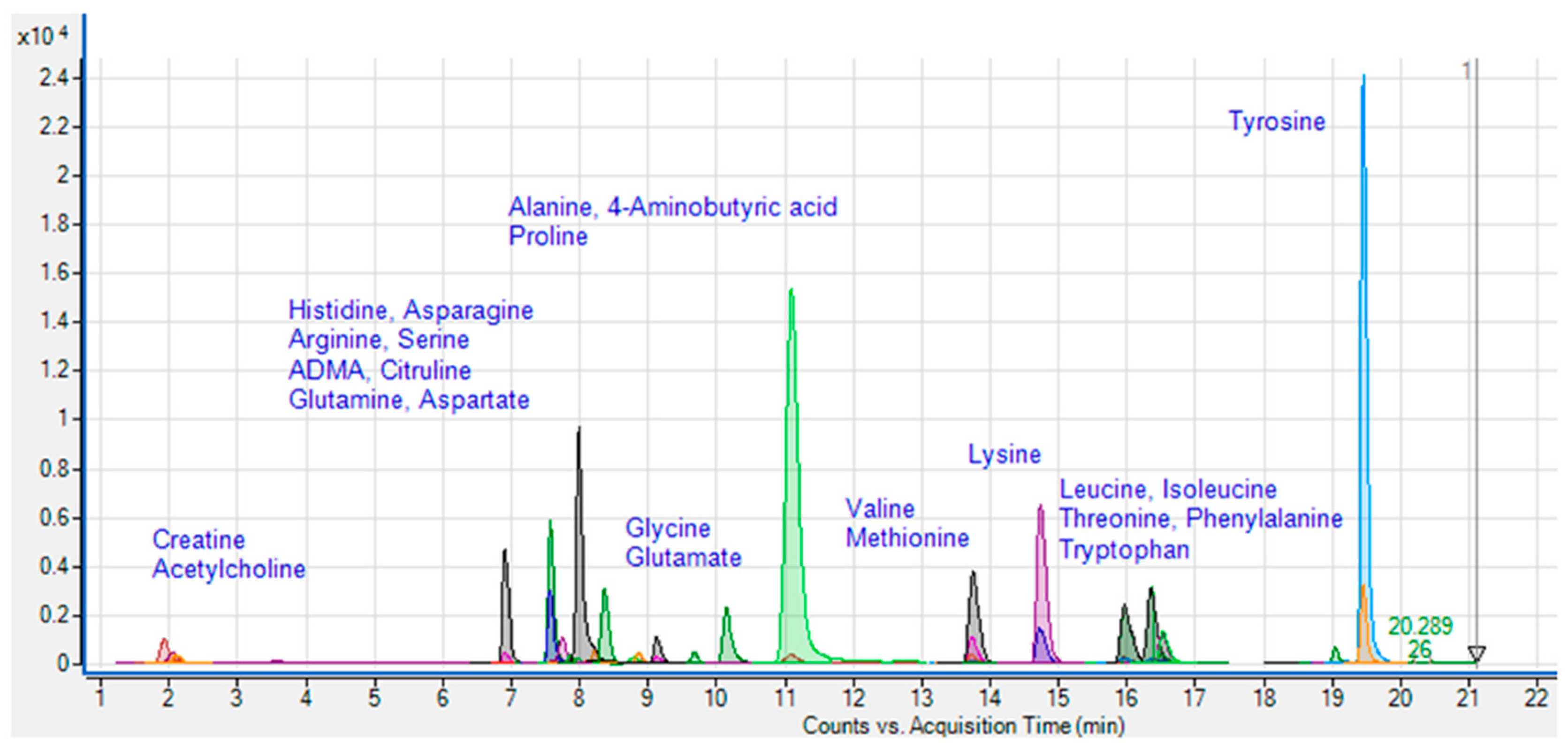
2.2. Sample collection and amines analyzed
2.3. Chemical and reagents
2.4. Sample preparation and LC/MS/MS analysis
2.5. Statistical analyses
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of amino acids and amines in plasma
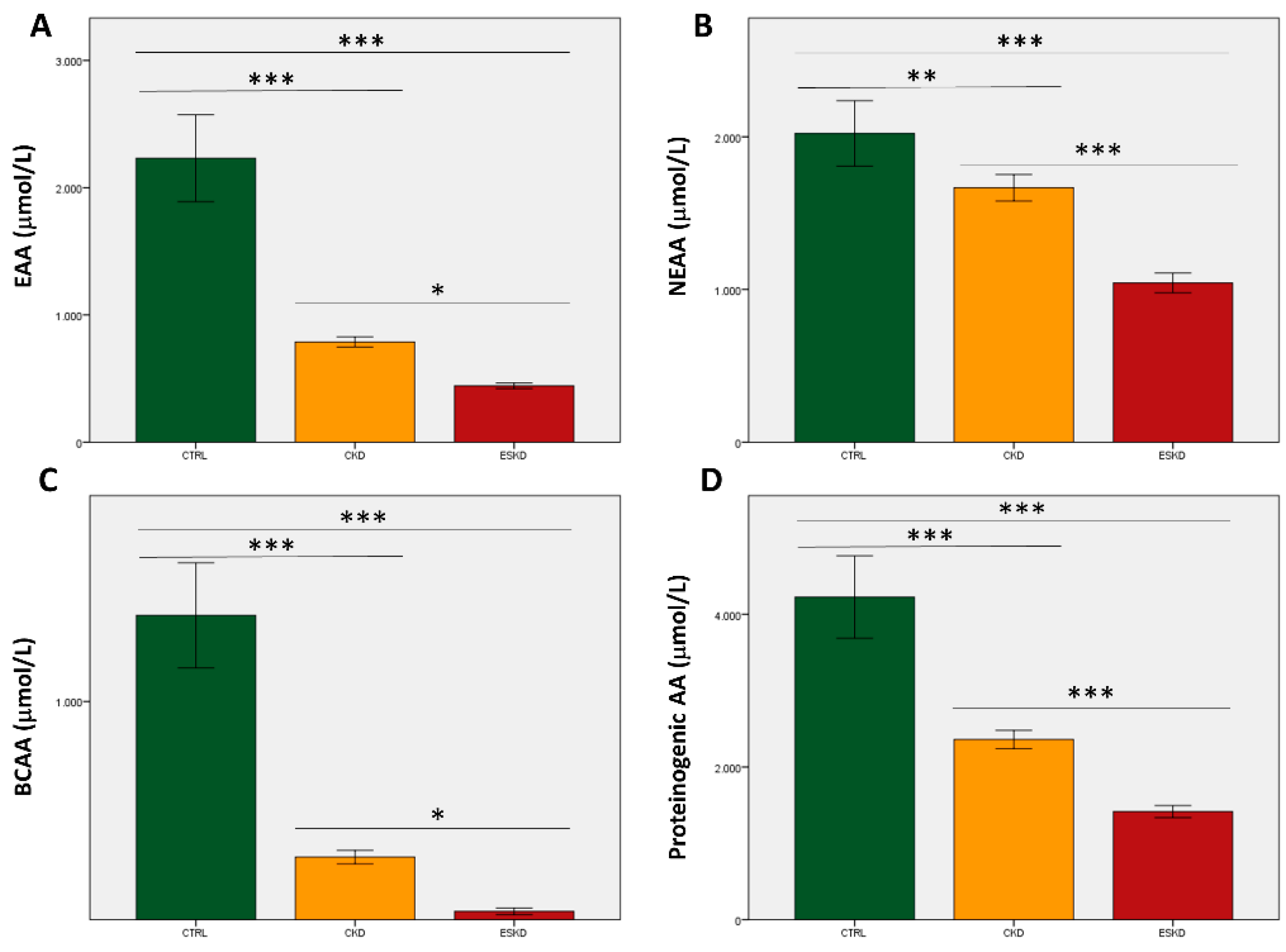
3.2. Amino acids total concentrations and ratios
| CTRL | CKD | ESKD | P-value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | Mean | SD | CKD/ESKD | |
| Alanine | 527.24 | 397.88 | 279.59 | 112.52 | 150.17 | 88.45 | <0.0001 |
| Arginine | 96.28 | 73.09 | 58.40 | 19.49 | 41.51 | 20.77 | <0.0001 |
| Asparagine | 23.34 | 27.69 | 1.23 | 0.55 | 0.77 | 0.31 | 1.000 |
| Aspartate | 32.90 | 50.38 | 3.18 | 1.96 | 2.12 | 1.05 | 1.000 |
| Citrulline | 27.33 | 11.49 | 93.45 | 42.29 | 70.09 | 48.87 | <0.0001 |
| Glycine | 49.60 | 56.69 | 101.82 | 58.36 | 101.62 | 78.18 | 1.000 |
| Glutamate | 150.35 | 133.99 | 57.01 | 36.94 | 37.73 | 23.87 | 0.016 |
| Glutamine | 226.53 | 123.81 | 769.87 | 393.51 | 415.60 | 254.99 | <0.0001 |
| Histidine | 71.72 | 59.13 | 108.59 | 42.72 | 54.26 | 34.46 | <0.0001 |
| Isoleucine | 110.40 | 131.03 | 74.14 | 29.25 | 50.62 | 19.27 | 0.001 |
| Leucine | 743.67 | 989.98 | 86.89 | 30.38 | 54.23 | 19.26 | 1.000 |
| Lysine | 134.94 | 165.88 | 50.36 | 24.83 | 30.67 | 16.16 | 0.051 |
| Methionine | 11.15 | 19.13 | 6.05 | 3.75 | 3.52 | 6.93 | 0.041 |
| Phenylalanine | 318.80 | 1232.85 | 60.20 | 19.32 | 43.20 | 19.31 | 1.000 |
| Proline | 301.09 | 266.91 | 238.12 | 107.00 | 194.28 | 225.01 | 0.054 |
| L-Serine | 59.21 | 61.87 | 2.81 | 3.02 | 1.63 | 1.38 | 1.000 |
| Tyrosine | 527.33 | 718.83 | 54.80 | 29.97 | 23.05 | 16.99 | 1.000 |
| Threonine | 240.18 | 226.74 | 52.20 | 13.80 | 40.39 | 13.11 | 0.865 |
| Tryptophan | 139.90 | 65.27 | 80.57 | 35.99 | 40.62 | 13.71 | <0.0001 |
| Valine | 462.07 | 482.30 | 268.64 | 135.06 | 125.82 | 78.09 | <0.0001 |
| Acetylcholine | 0.76 | 0.43 | 1.15 | 0.42 | 1.15 | 0.49 | 1.000 |
| D-Serine | 0.66 | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.30 | 0.70 | 0.29 | <0.0001 |
| Kynurenine | 1.98 | 0.78 | 2.44 | 1.20 | 3.38 | 1.39 | <0.0001 |
| Kynurenic acid | 1.96 | 0.81 | 1.52 | 1.01 | 1.03 | 0.19 | <0.0001 |
| ADMA | 0.84 | 0.33 | 0.38 | 0.19 | 0.26 | 0.19 | <0.0001 |
| Creatine | 20.52 | 10.92 | 11.91 | 9.40 | 9.03 | 10.62 | 0.004 |
| GABA | 0.22 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.11 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.739 |
| Serotonin | 0.63 | 0.25 | 0.16 | 0.17 | 0.14 | 0.03 | 0.762 |
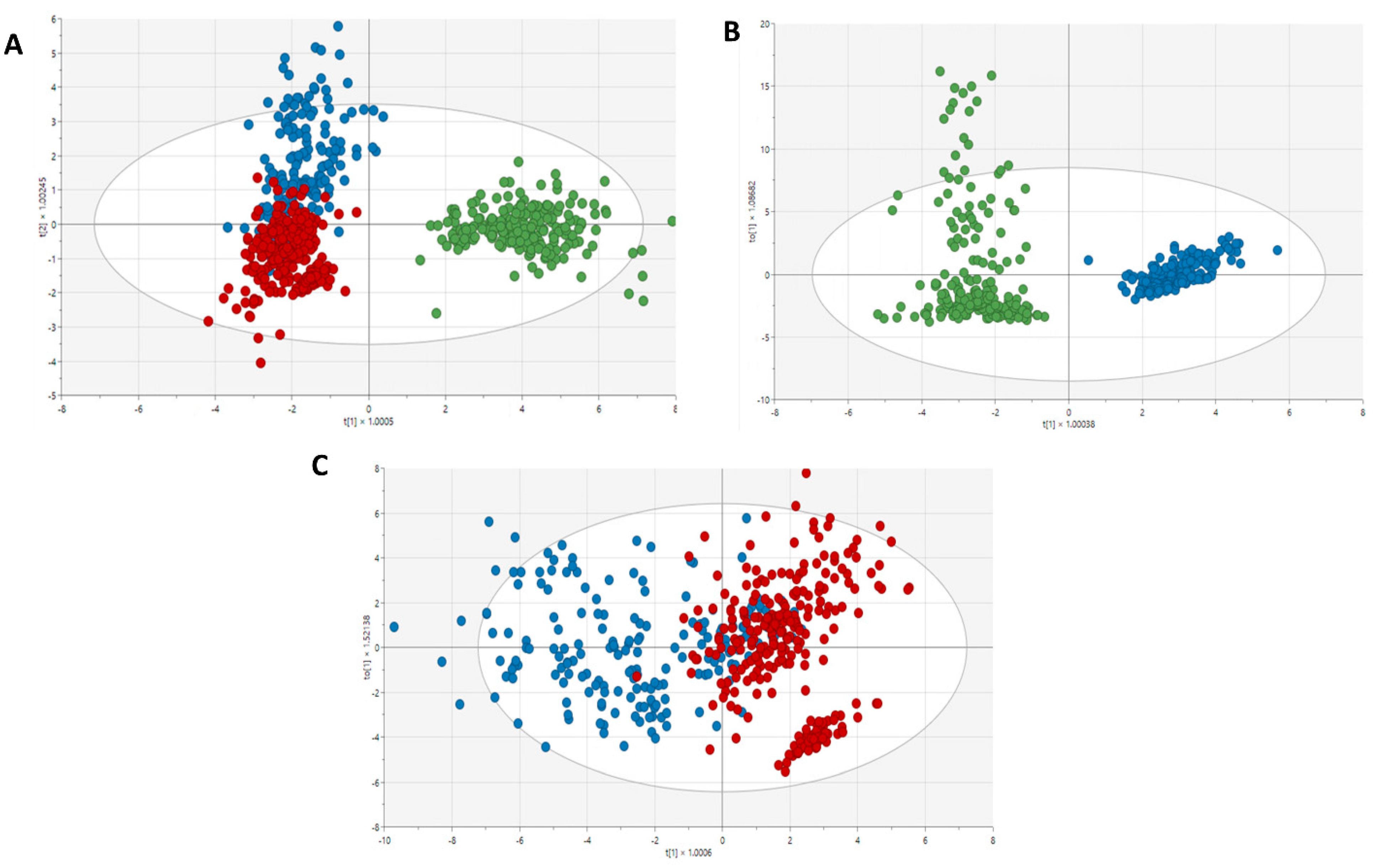
3.3. Metabolic profiles in the study groups
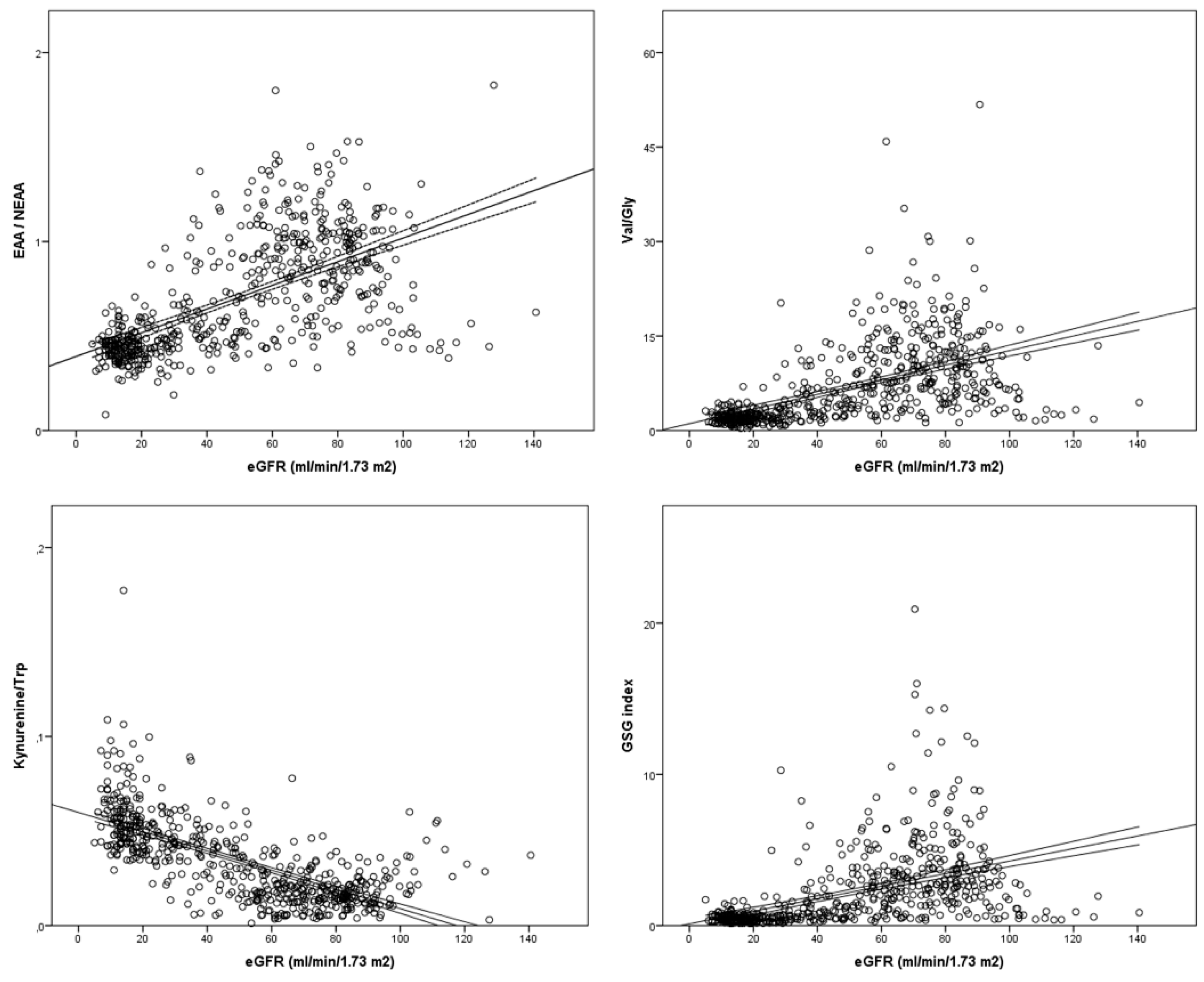
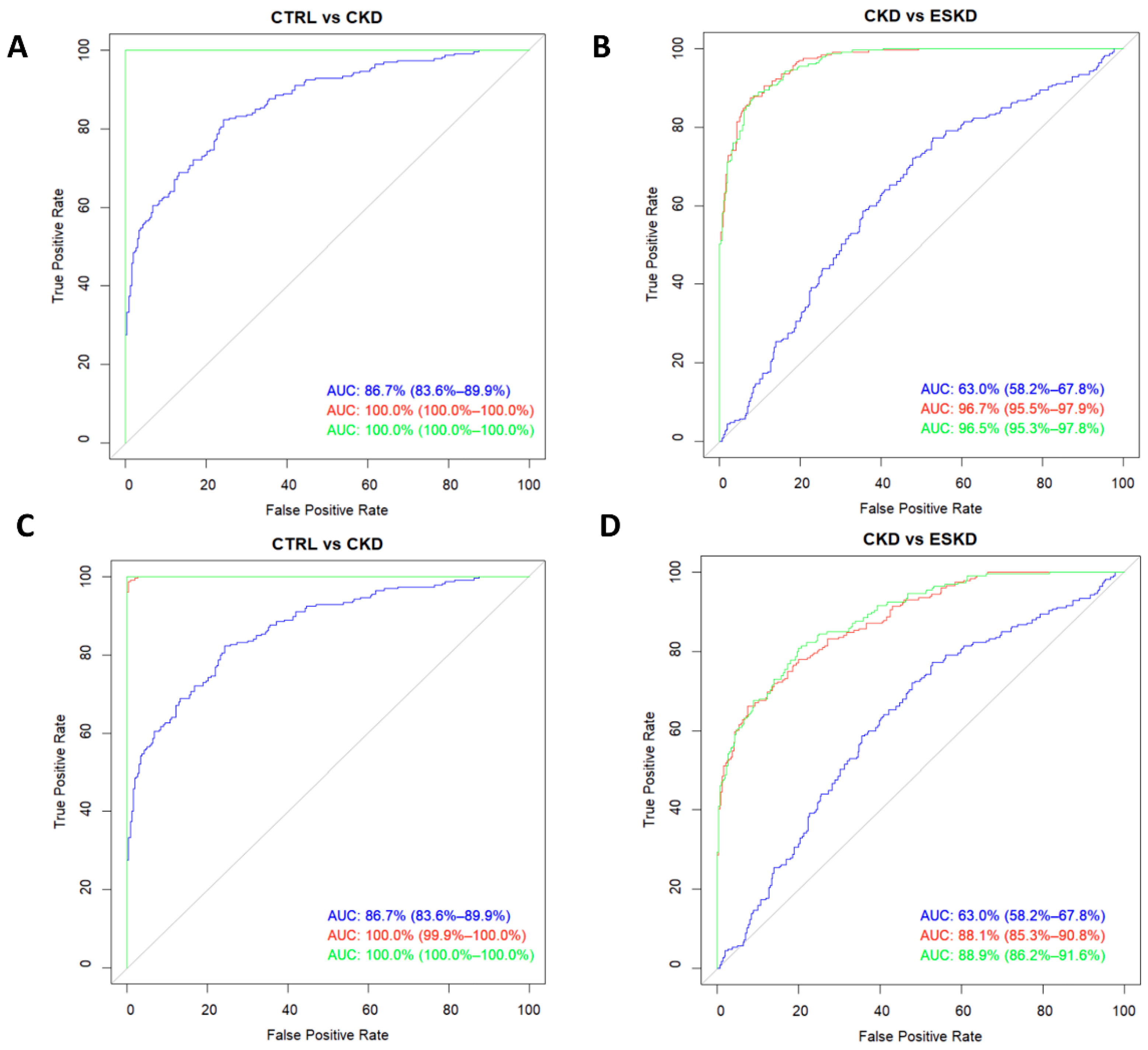
3.4. Amino acids and amines as biomarkers of renal impairment
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N.; McGaughey, M.; et al. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016-40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, A. RICORS2040: The need for collaborative research in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J 2022, 15, 372–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winearls, C.G.; Haynes, R.; Glassock, R. CKD staging--evolution not revolution. Nefrologia (Engl Ed) 2010, 30, 493–500. [Google Scholar]
- Garibotto, G.; Sofia, A.; Saffioti, S.; Bonanni, A.; Mannucci, I.; Verzola, D. Amino acid and protein metabolism in the human kidney and in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin Nutr 2010, 29, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, A.; Ng, A.; Kwan, T.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; Cowan, T.M. A rapid, sensitive method for quantitative analysis of underivatized amino acids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 2014, 944, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, S.; Sanchez-Ortega, A.; Unceta, N.; Goicolea, M.A.; Barrio, R.J. LC-QQQ-MS routine analysis method for new biomarker quantification in plasma aimed at early chronic kidney disease diagnosis. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2019, 169, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Dai, J.; Kang, H. The construction of a panel of serum amino acids for the identification of early chronic kidney disease patients. J Clin Lab Anal 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.E.; Baldim, J.L.; Chagas-Paula, D.A.; Soares, M.G.; Lago, J.H.G.; Goncalves, R.V.; et al. Predictive metabolomic signatures of end-stage renal disease: A multivariate analysis of population-based data. Biochimie 2018, 152, 14–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, F.; Lundin, U.; Gayrard, N.; Mischak, H.; Aparicio, M.; Mourad, G.; et al. Plasma and urinary amino acid metabolomic profiling in patients with different levels of kidney function. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2014, 9, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, S.E.; Abdel-Samiee, M.; El-Said, H.; Youssef, M.I.; ElZohry, H.A.; Abdelsameea, E.; et al. Evaluation of Amino Acids Profile as Non-Invasive Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Egyptians. Trop Med Infect Dis 2022, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonetti, S.; Herzog, R.I.; Caprio, S.; Santoro, N.; Trico, D. Glutamate-Serine-Glycine Index: A Novel Potential Biomarker in Pediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Children (Basel) 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.M.; Malec, P.A.; Mabrouk, O.S.; Ro, J.; Dus, M.; Kennedy, R.T. Benzoyl chloride derivatization with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for targeted metabolomics of neurochemicals in biological samples. J Chromatogr A 2016, 1446, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Mokdad, A.H.; Xian, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int 2018, 94, 567–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baigent, C.; Burbury, K.; Wheeler, D. Premature cardiovascular disease in chronic renal failure. Lancet 2000, 356, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Hare, A.M.; Bertenthal, D.; Walter, L.C.; Garg, A.X.; Covinsky, K.; Kaufman, J.S.; et al. When to refer patients with chronic kidney disease for vascular access surgery: Should age be a consideration? Kidney Int 2007, 71, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, E.P.; Clish, C.B.; Ghorbani, A.; Larson, M.G.; Elmariah, S.; McCabe, E.; et al. A combined epidemiologic and metabolomic approach improves CKD prediction. J Am Soc Nephrol 2013, 24, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Jang, H.B.; Yoo, M.G.; Park, S.I.; Lee, H.J. Amino Acid Metabolites Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease: An Eight-Year Follow-Up Korean Epidemiology Study. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levillain, O.; Hus-Citharel, A.; Morel, F.; Bankir, L. Localization of arginine synthesis along rat nephron. Am J Physiol 1990, 259, F916–F923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahabiyeh, L.A.; Nimer, R.M.; Sumaily, K.M.; Alabdaljabar, M.S.; Jacob, M.; Sabi, E.M.; et al. Metabolomics profiling distinctively identified end-stage renal disease patients from chronic kidney disease patients. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.O.; Townsend, R.R.; Feldman, H.I.; Pappan, K.L.; Kensicki, E.; Vander Jagt, D.L. Plasma metabolomic profiles in different stages of CKD. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2013, 8, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Banchaabouchi, M.; Marescau, B.; D'Hooge, R.; Engelborghs, S.; De Deyn, P.P. Consequences of renal mass reduction on amino acid and biogenic amine levels in nephrectomized mice. Amino Acids 2000, 18, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro, M. L-Arginine, Nitric Oxide, and Endothelial Dysfunction Underlying Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD). J Atheroscler Thromb 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goek, O.N.; Prehn, C.; Sekula, P.; Romisch-Margl, W.; Doring, A.; Gieger, C.; et al. Metabolites associate with kidney function decline and incident chronic kidney disease in the general population. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2013, 28, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, Y.; May, R.C.; Kelly, R.A.; Mitch, W.E. Acidosis, not azotemia, stimulates branched-chain, amino acid catabolism in uremic rats. Kidney Int 1987, 32, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holecek, M. Branched-chain amino acids in health and disease: Metabolism, alterations in blood plasma, and as supplements. Nutr Metab (Lond) 2018, 15, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, A.; Kalaska, B.; Pawlak, D. Kynurenine Pathway in Chronic Kidney Disease: What's Old, What's New, and What's Next? Int J Tryptophan Res 2020, 13, 1178646920954882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koenig, P.; Nagl, C.; Neurauter, G.; Schennach, H.; Brandacher, G.; Fuchs, D. Enhanced degradation of tryptophan in patients on hemodialysis. Clin Nephrol 2010, 74, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; Ding, J.; et al. Kynurenine regulates NLRP2 inflammasome in astrocytes and its implications in depression. Brain Behav Immun 2020, 88, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez Esquivel, D.; Ramirez-Ortega, D.; Pineda, B.; Castro, N.; Rios, C.; Perez de la Cruz, V. Kynurenine pathway metabolites and enzymes involved in redox reactions. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhary, G.; Sherchan, P.; Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Modification of kynurenine pathway via inhibition of kynurenine hydroxylase attenuates surgical brain injury complications in a male rat model. J Neurosci Res 2020, 98, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CTRL (n=264) | CKD (n=231) | ESKD (n=325) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean/N | SD/% | Mean/N | SD/% | Mean/N | SD/% | |
| Age | 75.92 | 7.10 | 65.91 | 12.83 | 68.79 | 13.20 |
| Sex | ||||||
| Men | 125 | 47.3% | 151 | 65.4% | 205 | 63.1% |
| Women | 139 | 52.7% | 80 | 34.6% | 120 | 36.9% |
| BMI | 27.64 | 4.01 | 30.14 | 5.54 | 28.44 | 5.89 |
| Serum creatinine (g/dL) | .93 | .25 | 2.09 | .91 | 5.50 | 1.93 |
| eGFR (ml/min/1.73 m2) | 71.47 | 40.32 | 11.36 | |||
| Proteins, 24 hrs | Na | 839.17 | 1404.27 | 1989.02 | 2053.95 | |
| Albumin, 24 hrs | Na | 574.87 | 1107.30 | 1387.46 | 1460.12 | |
| Creatinine, 24 hrs | Na | 1267.56 | 1072.39 | 863.01 | 350.54 | |
| ACR | Na | 520.14 | 951.91 | 1634.86 | 1601.60 | |
| Calcium (mg/dL) | 9.47 | 0.36 | 9.73 | 4.21 | 9.28 | 5.61 |
| Phosphorus (mg/dL) | 3.25 | 0.50 | 3.51 | 0.66 | 4.35 | 1.12 |
| PTH (pg/mL) | 66.84 | 31.94 | 173.88 | 143.61 | 333.64 | 244.53 |
| DM | ||||||
| No | 220 | 0.83 | 114 | 0.49 | 152 | 47.6% |
| Yes | 44 | 0.17 | 117 | 0.51 | 167 | 52.4% |
| Hypertension | ||||||
| No | 139 | 52.7% | 48 | 20.8% | 68 | 21.3% |
| Yes | 125 | 47.3% | 183 | 79.2% | 251 | 78.7% |
| Hyperlipidemia | ||||||
| No | 174 | 65.9% | 129 | 55.8% | 146 | 45.2% |
| Yes | 90 | 34.1% | 102 | 44.2% | 177 | 54.8% |
| Smoking | ||||||
| Nonsmoker | 188 | 72.9% | 102 | 44.2% | 166 | 51.9% |
| Smoker | 14 | 5.4% | 52 | 22.5% | 36 | 11.3% |
| Former smoker | 56 | 21.7% | 77 | 33.3% | 118 | 36.9% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





