Submitted:
06 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Ethanol Consumption: A Risk Factor for Arterial Hypertension
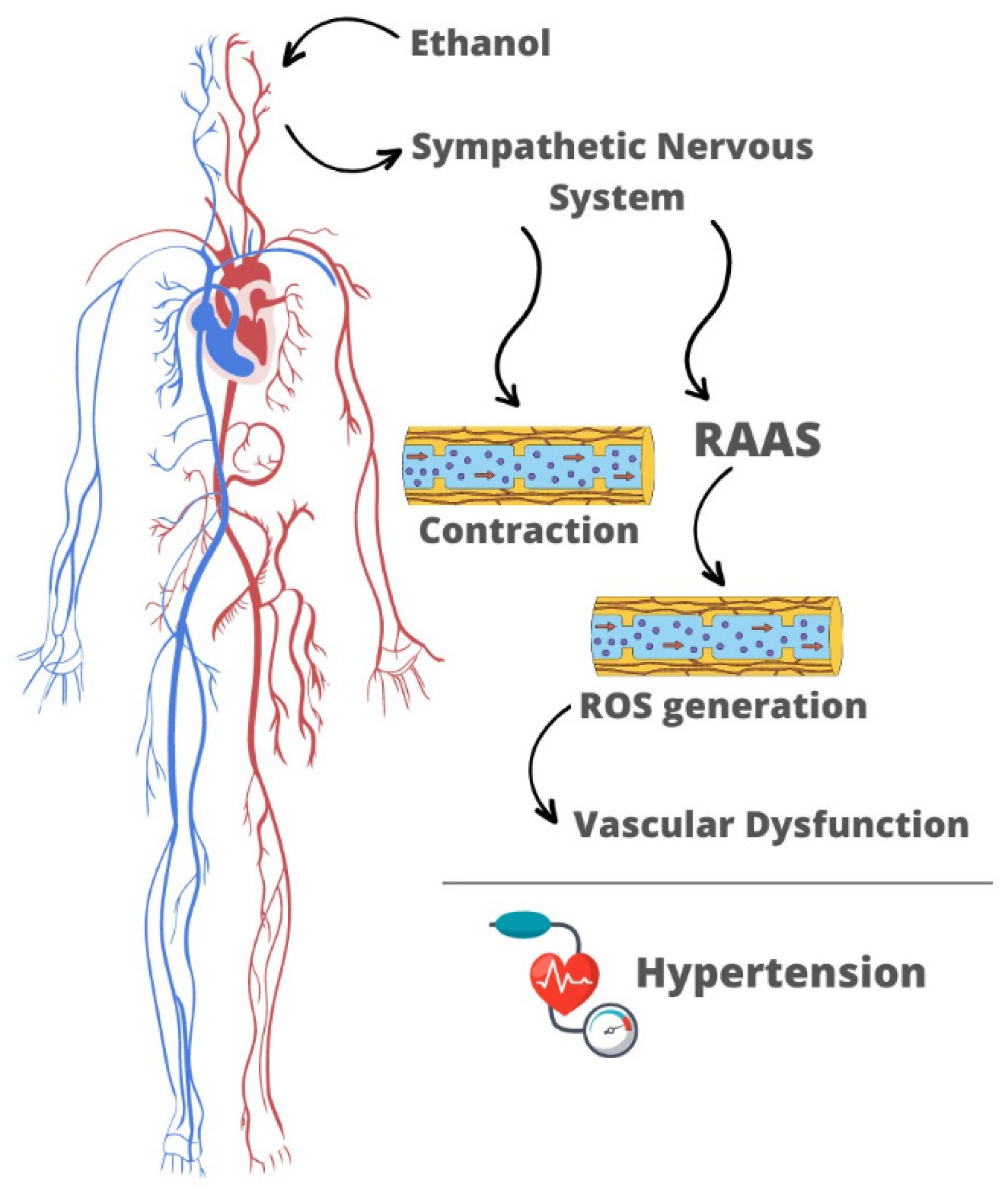
3. Mechanisms Underlying Ethanol-Induced Hypertension: The Neuroendocrine and Myogenic Theories
3.1. Neuroendocrine Changes
3.2. The Myogenic Theory
4. Interplay of Neuroendocrine and Myogenic Changes in Mediating the Pressor Effects of Ethanol
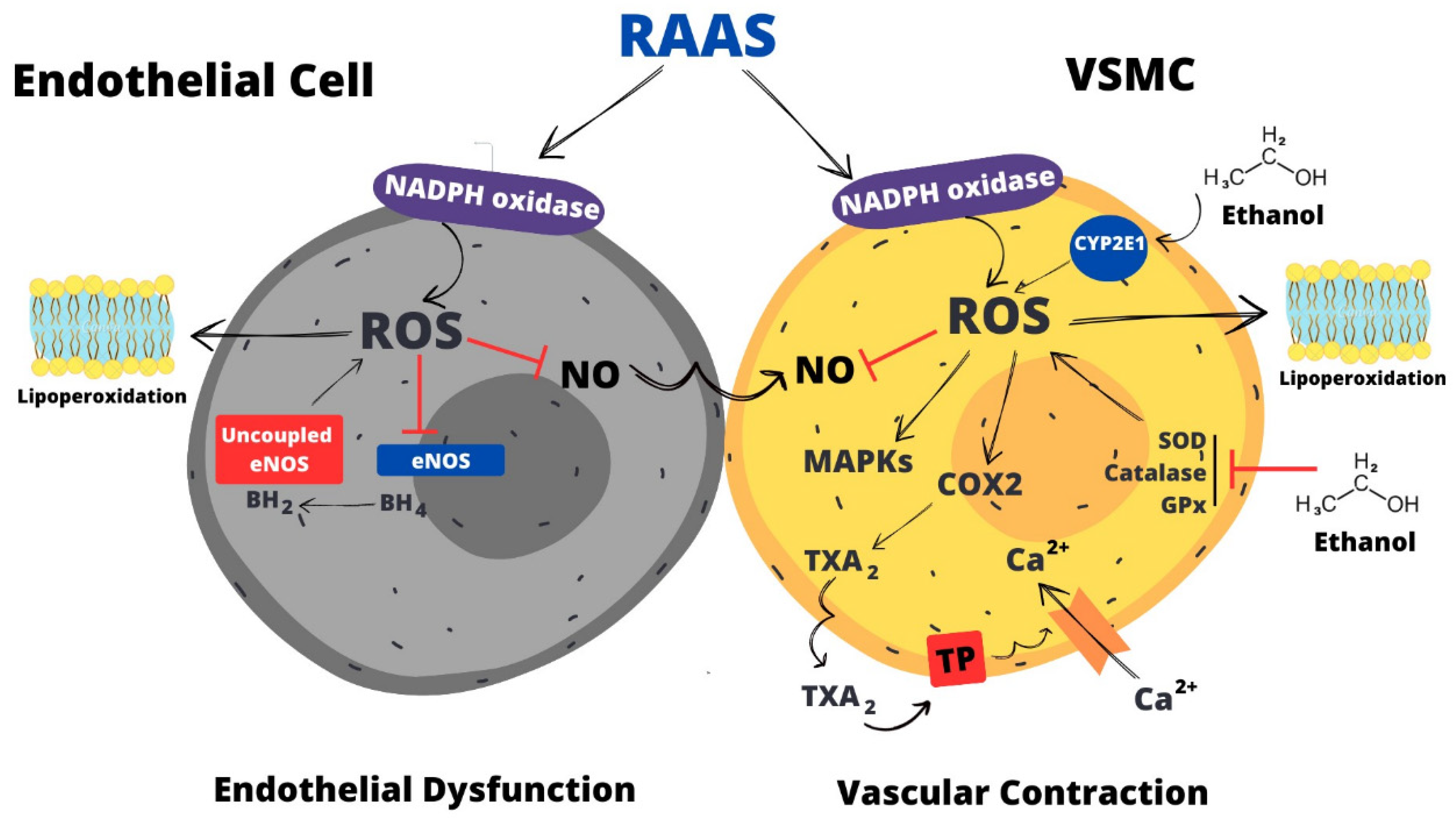
5. Oxidative Stress: The Major Mediator of Vascular Dysfunction Induced by Ethanol
5.1. NADPH Oxidase is a Major Mediator of ROS Generation in Response to Ethanol
5.2. Other Sources of Ethanol-Induced ROS Generation in the Vasculature
5.3. Impairment of Antioxidant Systems May Contribute to Ethanol-Induced ROS Accumulation
5.4. Ethanol-Induced Oxidative Stress Leads to Ca2+ ion Accumulation in the Vasculature
5.5. Role of ROS in Endothelial Dysfunction Induced by Ethanol
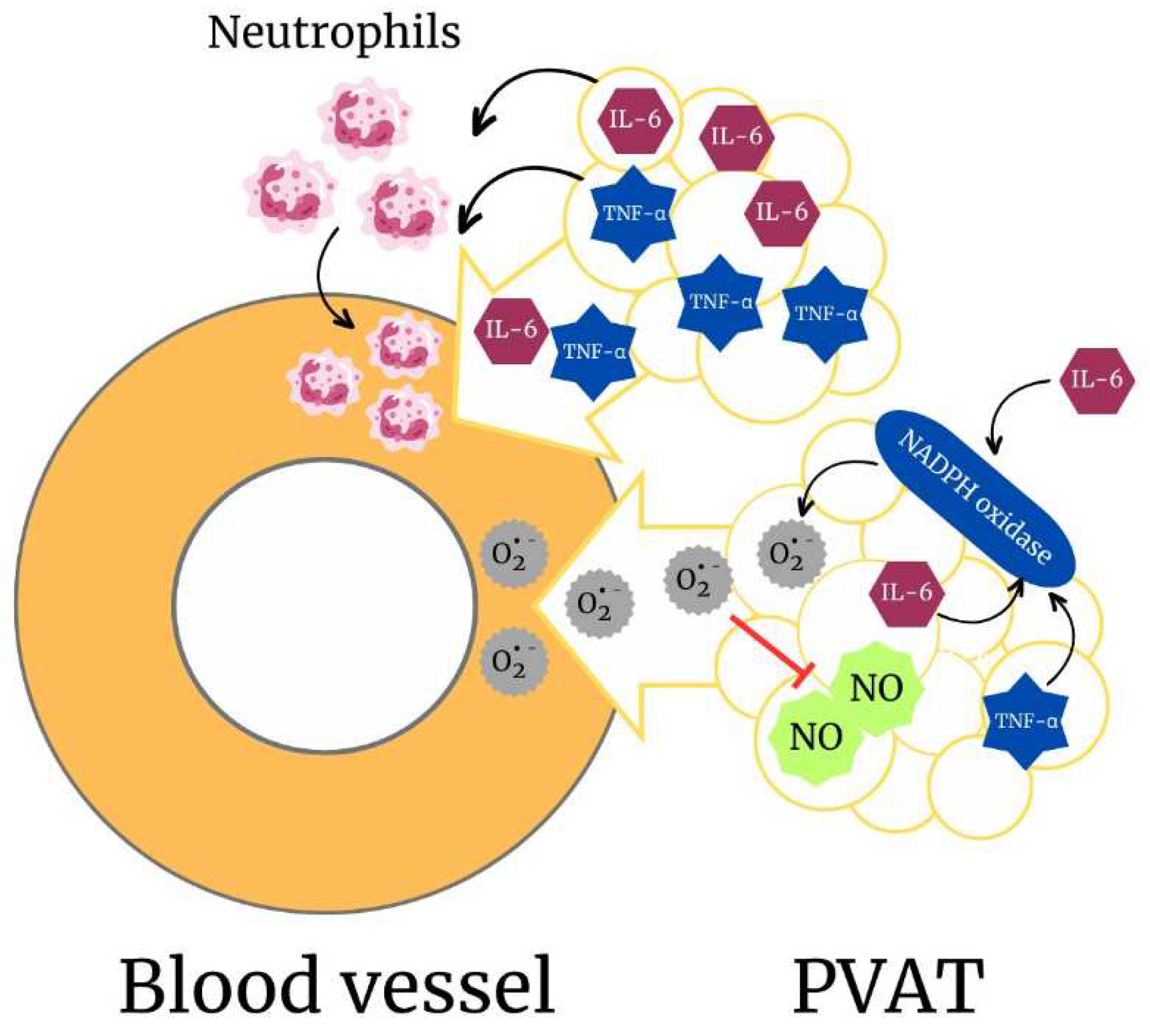
5.6. Perivascular Adipose Tissue (PVAT) and Its Role in Ethanol-Induced ROS Production
6. Conclusion
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MacMahon, S. Alcohol consumption and hypertension. Hypertension 1987, 9, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatsky, A.L.; Friedman, G.D.; Siegelaub, A.B.; Gérard, M.J. Alcohol Consumption and Blood Pressure. New Engl. J. Med. 1977, 296, 1194–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, V.A.; Chapman, J.M.; Coulson, A.H. Effects of various factors on systolic and diastolic blood pressure in the Los Angeles heart study. J. Chronic Dis. 1967, 20, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyntelberg, F.; Meyer, J. Relationship between blood pressure and physical fitness, smoking and alcohol consumption in copenhagen males aged 40–59. Acta Medica Scand. 1974, 195, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, A.R.; Stamler, J.; Paul, O.; Berkson, D.M.; Lepper, M.H.; McKean, H.; Shekelle, R.B.; A Lindberg, H.; Garside, D. Alcohol consumption, cardiovascular risk factors, and mortality in two Chicago epidemiologic studies. Circulation 1977, 56, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkwright, P.D.; Beilin, L.J.; Rouse, I.; Armstrong, B.K.; Vandongen, R. Effects of alcohol use and other aspects of lifestyle on blood pressure levels and prevalence of hypertension in a working population. Circulation 1982, 66, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkola, J.; Fyhrquist, F.; Ylikahri, R. Renin, aldosterone and Cortisol during ethanol intoxication and hangover. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1979, 106, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen, H.; Christensen, N.J.; Rasmussen, S.; Hollnagel, H.; Nielsen, M.D.; Giese, J. The Influence of Chronic High Alcohol Intake on Blood Pressure, Plasma Noradrenaline Concentration and Plasma Renin Concentration. Clin. Sci. 1981, 61, 377s–379s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, J.; Beevers, D. Pressor effect of alcohol in hypertension. Lancet 1984, 323, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, L.G.; Reid, J.L. Changes in plasma free 3,4-dihydroxyphenylethylene glycol and noradrenaline levels after acute alcohol administration. Clin. Sci. 1985, 69, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.C.; Sutter, M.C. Ethanol consumption and blood pressure. Life Sci. 1983, 33, 1965–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinardi, G.; Brieva, C.; Vinet, R.; Penna, M. Effects of chronic ethanol consumption on α-adrenergic-induced contractions in rat thoracic aorta. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1992, 23, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.A.; Osborn, K.; Hwang, C.-L.; Sabbahi, A.; Piano, M.R. Ethanol Induced Oxidative Stress in the Vasculature: Friend or Foe. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2020, 16, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceron, C.S.; Marchi, K.C.; Muniz, J.J.; Tirapelli, C.R. Vascular oxidative stress: a key factor in the development of hypertension associated with ethanol consumption. Curr. Hypertens. Rev. 2015, 10, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, L.N.; Gonzaga, N.A.; Simplicio, J.A.; Vale, G.T.D.; Carballido, J.M.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Tirapelli, C.R. Pharmacological characterization of the mechanisms underlying the vascular effects of succinate. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 789, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simplicio, J.A.; Dourado, T.M.; Awata, W.M.; Vale, G.T.D.; Dias, V.R.; Barros, P.R.; de Martinis, B.S.; Tostes, R.C.; Tirapelli, C.R. Ethanol consumption favors pro-contractile phenotype of perivascular adipose tissue: A role for interleukin-6. Life Sci. 2023, 319, 121526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Dinh Cat, A.; Montezano, A.C.; Burger, D.; Touyz, R.M. , Angiotensin II, NADPH Oxidase, and Redox Signaling in the Vasculature. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatsky, A.L.; Friedman, G.D.; A Armstrong, M.; Y, O.; T, S.; F, I.; K, Y.; H, I.; H, W.; T, M.; et al. The relationships between alcoholic beverage use and other traits to blood pressure: a new Kaiser Permanente study. Circulation 1986, 73, 628–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, J.D. Alcohol Usage as a Possible Explanation for Socio-economic and Occupational Differentials in Mortality from Hypertension and Coronary Heart Disease in England and Wales*. Aust. New Zealand J. Med. 1976, 6, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMahon, S.W.; Blacket, R.B.; Macdonald, G.J.; Hall, W. Obesity, Alcohol Consumption and Blood Pressure in Australian Men and Women The National Heart Foundation of Australia Risk Factor Prevalence Study. J. Hypertens. 1984, 2, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milon, H.; Froment, A.; Gaspard, P.; Guidollet, J.; Ripoll, J.P. Alcohol consumption and blood pressure in a French epidemiological study. Eur. Hear. J. 1982, 3, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harburg, E.; Ozgoren, F.; Hawthorne, V.M.; A Schork, M. Community norms of alcohol usage and blood pressure: Tecumseh, Michigan. Am. J. Public Heal. 1980, 70, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, J.F.; Watson, R.D.; Skan, W.; Beevers, D.G. The pressor and metabolic effects of alcohol in normotensive subjects. Hypertension 1986, 8, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seppä, K.; Sillanaukee, P. Binge Drinking and Ambulatory Blood Pressure. Hypertension 1999, 33, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosito, G.A.; Fuchs, F.D.; Duncan, B.B. Dose-dependent biphasic effect of ethanol on 24-h blood pressure in normotensive subjects. Am. J. Hypertens. 1999, 12, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, T.A.; Burke, V.; Beilin, L.J.; Puddey, I.B.; Stranges, S.; Wu, T.; Dorn, J.M.; Freudenheim, J.L.; Muti, P.; Farinaro, E.; et al. Randomized Controlled Intervention of the Effects of Alcohol on Blood Pressure in Premenopausal Women. Hypertension 2015, 66, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilkens, R.R.; Burke, V.; Hodgson, J.M.; Barden, A.; Beilin, L.J.; Puddey, I.B. Red Wine and Beer Elevate Blood Pressure in Normotensive Men. Hypertension 2005, 45, 874–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briasoulis, A.; Agarwal, V.; Messerli, F.H. Alcohol Consumption and the Risk of Hypertension in Men and Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2012, 14, 792–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.; Irving, H.M.; Baliunas, D.; Roerecke, M.; Patra, J.; Mohapatra, S.; Rehm, J. Alcohol and hypertension: gender differences in dose-response relationships determined through systematic review and meta-analysis. Addiction 2009, 104, 1981–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerecke, M.; Tobe, S.W.; Kaczorowski, J.; Bacon, S.L.; Vafaei, A.; Hasan, O.S.M.; Krishnan, R.J.; Raifu, A.O.; Rehm, J. Sex-Specific Associations Between Alcohol Consumption and Incidence of Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cohort Studies. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2018, 7, e008202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Abdel-Rahman, A.; Wooles, W.R. Ethanol-induced hypertension involves impairment of baroreceptors. Hypertension 1987, 10, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, J.A.; Wooles, W.R. Effect of acute and chronic ethanol on the agonist responses of vascular smooth muscle. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 152, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Rahman, A.R.; Dar, M.S.; Wooles, W.R. Effect of chronic ethanol administration on arterial baroreceptor function and pressor and depressor responsiveness in rats. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1985, 232. [Google Scholar]
- Resstel, L.B.; Tirapelli, C.R.; Lanchote, V.L.; Uyemura, S.A.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Corrêa, F.M. Chronic ethanol consumption alters cardiovascular functions in conscious rats. Life Sci. 2006, 78, 2179–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.C.; Godin, D.V.; Sutter, M.C. Erythrocyte membrane properties of the chronic alcoholic rat. Drug Alcohol Depend. 1983, 12, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, T.C.; A Wall, R.; Sutter, M.C.; M, E.-M.; A, A.-R.; S, V.; C, S.; V, P.; P, H.; P, R.; et al. Chronic ethanol consumption, stress, and hypertension. Hypertension 1985, 7, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkan, T.; Yildiz, F.; Ilbay, G.; Ozdemirci, S.; Erden, B.F.; Gacar, N.; Ulak, G. Blood pressure and vascular reactivity to endothelin-1, phenylephrine, serotonin, KCl and acetylcholine following chronic alcohol consumption in vitro. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2001, 15, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, A.L.; Ruginsk, S.G.; Uchoa, E.T.; Crestani, C.C.; Scopinho, A.A.; Correa, F.M.A.; De Martinis, B.S.; Elias, L.L.K.; Resstel, L.B.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J. Time-Course of Neuroendocrine Changes and Its Correlation with Hypertension Induced by Ethanol Consumption. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013, 48, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaglia, P.; Ceron, C.S.; Mecawi, A.S.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Coelho, E.B.; Tirapelli, C.R. Angiotensin type 1 receptor mediates chronic ethanol consumption-induced hypertension and vascular oxidative stress. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 74, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Brown, R.; Ilg, K.J.; Chen, A.F.; Ren, J. Dietary Mg2+ supplementation restores impaired vasoactive responses in isolated rat aorta induced by chronic ethanol consumption. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 442, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhofer, G.; Lambie, D.G.; Johnson, R.H. Effects of ethanol on plasma catecholamines and norepinephrine clearance. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1983, 34, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, M.A.; Vandongen, R.; Davidson, L.; Beilin, L.J.; Rouse, I.L. Acute effects of moderate alcohol consumption on blood pressure and plasma catecholamines. Clin. Sci. 1984, 66, 643–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, G.T.D.; Simplicio, J.A.; Gonzaga, N.A.; Yokota, R.; Ribeiro, A.A.; Casarini, D.E.; de Martinis, B.S.; Tirapelli, C.R. Nebivolol prevents vascular oxidative stress and hypertension in rats chronically treated with ethanol. Atherosclerosis 2018, 274, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkola, J.; Fyhrquist, F.; Nieminen, M.M.; Weber, T.H.; Tontti, K. Renin-Aldosterone Axis in Ethanol Intoxication and Hangover. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1976, 6, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddey, I.B.; Vandongen, R.; Beilin, L.J.; Rouse, I.L. Alcohol Stimulation of Renin Release in Man: Its Relation to the Hemodynamic, Electrolyte, and Sympatho-Adrenal Responses to Drinking*. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1985, 61, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.W.; Morseth, S.L.; Abhold, R.H.; Harding, J.W. Elevations in plasma angiotensin II with prolonged ethanol treatment in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1986, 24, 813–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, K.; Vazquez, M.; Ansari, R.A.; Malafa, M.P.; Lalla, J. Chronic alcohol-induced oxidative endothelial injury relates to angiotensin II levels in the rat. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 307, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dourado, T.M.; Assis, V.O.; Awata, W.M.; de Mello, M.M.; Cárnio, E.C.; Castro, M.M.; Tirapelli, C.R. Mineralocorticoid receptors contribute to ethanol-induced vascular hypercontractility through reactive oxygen species generation and up-regulation of cyclooxygenase 2. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 949, 175723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatton, D.C.; Bukoski, R.D.; Edgar, S.; McCarron, D.A. Chronic alcohol consumption lowers blood pressure but enhances vascular contractility in Wistar rats. J. Hypertens. 1992, 10, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.W.; Kennedy, R.H. Effects of chronic ethanol consumption on aortic constriction in male and female rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 366, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Al-Khoury, J.; Bkaily, G.; D'Orléans-Juste, P.; Lanchote, V.L.; Uyemura, S.A.; de Oliveira, A.M. Chronic Ethanol Consumption Enhances Phenylephrine-Induced Contraction in the Isolated Rat Aorta. Experiment 2005, 316, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Leone, A.F.C.; Coelho, E.B.; Resstel, L.B.M.; A Corrêa, F.M.; Lanchote, V.L.; A Uyemura, S.; Padovan, C.M.; de Oliveira, A.M. Effect of ethanol consumption on blood pressure and rat mesenteric arterial bed, aorta and carotid responsiveness. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2007, 59, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladipo, C.; Adigun, S.; Nwaigwe, C.; Adegunloye, B. Chronic Ethanol Consumption Alters Vascular Smooth Muscle Responses In Rats. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2002, 29, 707–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Legros, E.; Brochu, I.; Honoré, J.-C.; Lanchote, V.L.; A Uyemura, S.; De Oliveira, A.M.; D'Orléans-Juste, P. Chronic ethanol intake modulates vascular levels of endothelin-1 receptor and enhances the pressor response to endothelin-1 in anaesthetized rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Leone, A.F.C.; Yogi, A.; Tostes, R.C.; Lanchote, V.L.; A Uyemura, S.; Resstel, L.B.M.; A Corrêa, F.M.; Padovan, C.M.; de Oliveira, A.M.; et al. Ethanol consumption increases blood pressure and alters the responsiveness of the mesenteric vasculature in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2008, 60, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Casolari, D.A.; Montezano, A.C.; Yogi, A.; Tostes, R.C.; Legros, E.; D'Orléans-Juste, P.; Lanchote, V.L.; Uyemura, S.A.; de Oliveira, A.M. Ethanol Consumption Enhances Endothelin-1-Induced Contraction in the Isolated Rat Carotid. Experiment 2006, 318, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, L.N.; Lacchini, R.; Carnio, E.C.; Queiroz, R.H.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; de Oliveira, A.M.; Tirapelli, C.R. Ethanol Consumption Increases Endothelin-1 Expression and Reactivity in the Rat Cavernosal Smooth Muscle. Alcohol Alcohol. 2013, 48, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, K.C.; Ceron, C.S.; Muniz, J.J.; De Martinis, B.S.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Tirapelli, C.R. NADPH Oxidase Plays a Role on Ethanol-Induced Hypertension and Reactive Oxygen Species Generation in the Vasculature. Alcohol Alcohol. 2016, 51, 522–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, C.S.; Vale, G.T.D.; Simplicio, J.A.; Passaglia, P.; Ricci, S.T.; Tirapelli, C.R. Data on the effects of losartan on protein expression, vascular reactivity and antioxidant capacity in the aorta of ethanol-treated rats. Data Brief 2017, 11, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Agag, L.H.; Khoo, N.K.; Binsack, R.; White, C.R.; Darley-Usmar, V.; Grenett, H.E.; Booyse, F.M.; Digerness, S.B.; Zhou, F.; Parks, D.A. Evidence of cardiovascular protection by moderate alcohol: Role of nitric oxide. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipólito, U.V.; Rocha, J.T.; Martins-Oliveira, A.; Tirapelli, D.P.; Jacob-Ferreira, A.; Batalhão, M.E.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Carnio, E.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Queiroz, R.H.; et al. Chronic ethanol consumption reduces adrenomedullin-induced relaxation in the isolated rat aorta. Alcohol 2011, 45, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.T.; Hipólito, U.V.; Martins-Oliveira, A.; Tirapelli, D.P.; Batalhão, M.E.; Carnio, E.C.; Queiroz, R.H.; Coelho, E.B.; Cunha, T.M.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; et al. Ethanol Consumption Alters the Expression and Reactivity of Adrenomedullin in the Rat Mesenteric Arterial Bed. Alcohol Alcohol. 2011, 47, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champion, H.C.; Pierce, R.L.; Bivalacqua, T.J.; Murphy, W.A.; Coy, D.H.; Kadowitz, P.J. Analysis of responses to hAmylin, hCGRP, and hADM in isolated resistance arteries from the mesenteric vascular bed of the rat. Peptides 2001, 22, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simplicio, J.A.; Vale, G.T.D.; Gonzaga, N.A.; Leite, L.N.; Hipólito, U.V.; Pereira, C.A.; Tostes, R.C.; Tirapelli, C.R. Reactive oxygen species derived from NAD(P)H oxidase play a role on ethanol-induced hypertension and endothelial dysfunction in rat resistance arteries. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 73, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; A Casolari, D.; Yogi, A.; Montezano, A.C.; Tostes, R.C.; Legros, E.; D'Orléans-Juste, P.; De Oliveira, A.M. Functional characterization and expression of endothelin receptors in rat carotid artery: involvement of nitric oxide, a vasodilator prostanoid and the opening of K+channels in ETB-induced relaxation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, N.S.; Tostes, R.C.; Paradis, P.; Schiffrin, E.L. Aldosterone, Inflammation, Immune System, and Hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2020, 34, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascolo, A.; Scavone, C.; Rafaniello, C.; De Angelis, A.; Urbanek, K.; di Mauro, G.; Cappetta, D.; Berrino, L.; Rossi, F.; Capuano, A. The Role of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System in the Heart and Lung: Focus on COVID-19. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 667254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapp, A.D.; Gui, L.; Huber, M.J.; Liu, J.; Larson, R.A.; Zhu, J.; Carter, J.R.; Chen, Q.-H. Sympathoexcitation and pressor responses induced by ethanol in the central nucleus of amygdala involves activation of NMDA receptors in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H701–H709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, L. Reactive oxygen species: key regulators in vascular health and diseases. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 175, 1279–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.-M.; Hu, Y.-Y.; Yang, T.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.-N. Reactive Oxygen Species and Oxidative Stress in Vascular-Related Diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Cheng, C.K.; Zhang, C.-L.; Huang, Y. Interplay Between Oxidative Stress, Cyclooxygenases, and Prostanoids in Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2021, 34, 784–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedard, K.; Krause, K.-H. The NOX Family of ROS-Generating NADPH Oxidases: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2007, 87, 245–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; Anagnostopoulou, A.; Camargo, L.L.; Rios, F.J.; Montezano, A.C. Vascular Biology of Superoxide-Generating NADPH Oxidase 5—Implications in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Disease. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2019, 30, 1027–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermot, A.; Petit-Härtlein, I.; Smith, S.M.E.; Fieschi, F. NADPH Oxidases (NOX): An Overview from Discovery, Molecular Mechanisms to Physiology and Pathology. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.; Pritchard, M.T.; McMullen, M.R.; Wang, Q.; E Nagy, L.; Nagy, L.E. Chronic ethanol feeding increases activation of NADPH oxidase by lipopolysaccharide in rat Kupffer cells: role of increased reactive oxygen in LPS-stimulated ERK1/2 activation and TNF-α production. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 1348–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Minicis, S.; A Brenner, D. Oxidative stress in alcoholic liver disease: Role of NADPH oxidase complex. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, S98–S103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Crews, F.T. NADPH oxidase and reactive oxygen species contribute to alcohol-induced microglial activation and neurodegeneration. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 5–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeligar, S.M.; Harris, F.L.; Hart, C.M.; Brown, L.A.S. Ethanol Induces Oxidative Stress in Alveolar Macrophages via Upregulation of NADPH Oxidases. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3648–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, K.; Ferder, L.; A Ansari, R.; Lalla, J. Chronic ethanol ingestion induces aortic inflammation/oxidative endothelial injury and hypertension in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2010, 30, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, A.; Callera, G.E.; Mecawi, A.S.; Batalhão, M.E.; Carnio, E.C.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Queiroz, R.H.; Touyz, R.M.; Tirapelli, C.R. Acute ethanol intake induces superoxide anion generation and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation in rat aorta: A role for angiotensin type 1 receptor. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2012, 264, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, L.N.; Vale, G.T.D.; Simplicio, J.A.; De Martinis, B.S.; Carneiro, F.S.; Tirapelli, C.R. Ethanol-induced erectile dysfunction and increased expression of pro-inflammatory proteins in the rat cavernosal smooth muscle are mediated by NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 804, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceron, C.S.; Vale, G.T.D.; Simplicio, J.A.; Ricci, S.T.; De Martinis, B.S.; de Freitas, A.; Tirapelli, C.R. Chronic ethanol consumption increases vascular oxidative stress and the mortality induced by sub-lethal sepsis: Potential role of iNOS. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 825, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simplicio, J.A.; Gonzaga, N.A.; Nakashima, M.A.; De Martinis, B.S.; Cunha, T.M.; Tirapelli, L.F.; Tirapelli, C.R. Tumor necrosis factor-α receptor 1 contributes to ethanol-induced vascular reactive oxygen species generation and hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2017, 11, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, A.M.; Griendling, K.K. NADPH oxidases and angiotensin II receptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 302, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callera, G.E.; Touyz, R.M.; Tostes, R.C.; Yogi, A.; He, Y.; Malkinson, S.; Schiffrin, E.L.; L, C.; A, H.; F, R.; et al. Aldosterone Activates Vascular p38MAP Kinase and NADPH Oxidase Via c-Src. Hypertension 2005, 45, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmine, T.; Miwa, Y.; Takahashi-Yanaga, F.; Morimoto, S.; Maehara, Y.; Sasaguri, T. The involvement of aldosterone in cyclic stretch-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase in vascular smooth muscle cells. Hypertens. Res. 2009, 32, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, C.M.; Leandro, A.; Azul, L.; Seiça, R.; Perry, G. Vascular Oxidative Stress: Impact and Therapeutic Approaches. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Patel, K.P.; Mayhan, W.G. Impairment of neuronal nitric oxide synthase-dependent dilation of cerebral arterioles during chronic alcohol consumption. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Mayhan, W.G. Sex Difference in Nitric Oxide Synthase???Dependent Dilatation of Cerebral Arterioles During Long-Term Alcohol Consumption. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2005, 29, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.; Bian, J.; Thur, L.A.; Peters, T.A.; Piano, M.R.; Phillips, S.A. Tetrahydrobiopterin Restores Microvascular Dysfunction in Young Adult Binge Drinkers. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2019, 44, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchardt, M.; Herrmann, J.; Tolle, M.; Van Der Giet, M. Xanthine Oxidase and its Role as Target in Cardiovascular Disease: Cardiovascular Protection by Enzyme Inhibition? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 3391–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyanaraman, B. Teaching the basics of redox biology to medical and graduate students: Oxidants, antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2013, 1, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aberle, N.S.; Ren, J. Experimental assessment of the role of acetaldehyde in alcoholic cardiomyopathy. Biol. Proced. Online 2003, 5, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Kawase, T.; Alderman, J.; Inatomi, N.; Lieber, C.S. Role of xanthine oxidase in ethanol-induced lipid peroxidation in rats. Gastroenterology 1990, 98, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.F.; Matschinsky, F.M. Ethanol metabolism: The good, the bad, and the ugly. Med Hypotheses 2020, 140, 109638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haorah, J.; Knipe, B.; Leibhart, J.; Ghorpade, A.; Persidsky, Y. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress in brain endothelial cells causes blood-brain barrier dysfunction. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2005, 78, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haorah, J.; Knipe, B.; Gorantla, S.; Zheng, J.; Persidsky, Y. Alcohol-induced blood?brain barrier dysfunction is mediated via inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate receptor (IP3R)-gated intracellular calcium release. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotha, R.R.; Tareq, F.S.; Yildiz, E.; Luthria, D.L. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants—A Critical Review on In Vitro Antioxidant Assays. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, M.-R.; Hong, Y.-C.; Choquet, H.; Trapani, E.; Goitre, L.; Trabalzini, L.; Akers, A.; et al. Superoxide Dismutases: Role in Redox Signaling, Vascular Function, and Diseases. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rua, R.M.; Ojeda, M.L.; Nogales, F.; Rubio, J.M.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Funuyet, J.; Murillo, M.L.; Carreras, O. Serum selenium levels and oxidative balance as differential markers in hepatic damage caused by alcohol. Life Sci. 2014, 94, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Ahluwalia, P.; Kaur, P.; Sharma, J. Effect of monosodium glutamate on various lipid fractions and certain antioxidant enzymes in arterial tissue of chronic alcoholic adult male mice. Toxicol. Int. 2012, 19, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretón-Romero, R.; Lamas, S. Hydrogen peroxide signaling in vascular endothelial cells. Redox Biol. 2014, 2, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byon, C.H.; Heath, J.M.; Chen, Y. Redox signaling in cardiovascular pathophysiology: A focus on hydrogen peroxide and vascular smooth muscle cells. Redox Biol. 2016, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, C.; Calderon, P.B. Catalase, a remarkable enzyme: targeting the oldest antioxidant enzyme to find a new cancer treatment approach. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.-W.; Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. Ethanol-Induced Contractions in Cerebral Arteries. Stroke 2001, 32, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.-W.; Wang, J.; Zheng, T.; Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. Roles of tyrosine kinase–, 1-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–, and mitogen-activated protein kinase–signaling pathways in ethanol-induced contractions of rat aortic smooth muscle: possible relation to alcohol-induced hypertension. Alcohol 2002, 28, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, N.A.; Callera, G.E.; Yogi, A.; Mecawi, A.S.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Queiroz, R.H.; Touyz, R.M.; Tirapelli, C.R. Acute ethanol intake induces mitogen-activated protein kinase activation, platelet-derived growth factor receptor phosphorylation, and oxidative stress in resistance arteries. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 509–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, M.; Valdés, E.; Fernández, J.; Rodrigo, R. Effects of Chronic Ethanol Consumption on Extramitochondrial Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ethanol Metabolism by Rat Kidney. Gen. Pharmacol. Vasc. Syst. 1998, 30, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Pan, X.; Wei, G.; Hua, Y. Research progress of glutathione peroxidase family (GPX) in redoxidation. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1147414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, K.; Mejia, J.; Lalla, J.; Kazim, S. Time response of alcohol-induced alterations in blood pressure, nitric oxide and oxidant to antioxidant balance in the plasma of rats. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2004, 9, 229–34. [Google Scholar]
- Rendón-Ramírez, A.; Cortés-Couto, M.; Martínez-Rizo, A.B.; Muñiz-Hernández, S.; Velázquez-Fernández, J.B. Oxidative damage in young alcohol drinkers: A preliminary study. Alcohol 2013, 47, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasdev, S.; A Sampson, C.; Prabhakaran, V.M. Platelet-free calcium and vascular calcium uptake in ethanol-induced hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1991, 18, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altura, B.M.; Zhang, A.; Cheng, T.P.-O.; Altura, B.T. Exposure of piglet coronary arterial muscle cells to low alcohol results in elevation of intracellular free Ca2+: relevance to fetal alcohol syndrome. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1996, 314, R9–R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Cheng, T.P.-O.; Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. Chronic treatment of cultured cerebral vascular smooth cells with low concentration of ethanol elevates intracellular calcium and potentiates prostanoid-induced rises in [Ca2+]i: Relation to etiology of alcohol-induced stroke. Alcohol 1997, 14, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Li, W.; Zhang, A.; Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. α-Tocopherol prevents ethanol-induced elevation of [Ca2+]i in cultured canine cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 245, 17–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, W.; Altura, B.T.; Altura, B.M. Catalase prevents elevation of [Ca2+]i induced by alcohol in cultured canine cerebral vascular smooth muscle cells: Possible relationship to alcohol-induced stroke and brain pathology. Brain Res. Bull. 2003, 59, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, A.; Callera, G.E.; Hipólito, U.V.; Silva, C.R.; Touyz, R.M.; Tirapelli, C.R. Ethanol-induced vasoconstriction is mediated via redox-sensitive cyclo-oxygenase-dependent mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 2010, 118, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, S.T.; Sano, H.; Saito, K.; Kubota, Y.; Yokoyama, M.; L, R.; M, B.; L, D.; J, V.; J, N.; et al. Magnesium supplementation prevents the development of alcohol-induced hypertension. Hypertension 1992, 19, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasdev, S.; Gupta, I.P.; A Sampson, C.; Longerich, L.; Parai, S. Ethanol induced hypertension in rats: reversibility and role of intracellular cytosolic calcium. Artery 1993, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Tirapelli, C.R.; Fukada, S.Y.; Yogi, A.; Chignalia, A.Z.; Tostes, R.C.; Bonaventura, D.; Lanchote, V.L.; Cunha, F.Q.; de Oliveira, A.M. Gender-specific vascular effects elicited by chronic ethanol consumption in rats: a role for inducible nitric oxide synthase. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, M.; Kepinska, M. Human Nitric Oxide Synthase—Its Functions, Polymorphisms, and Inhibitors in the Context of Inflammation, Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Leyte, D.J.; Zepeda-García, O.; Domínguez-Pérez, M.; González-Garrido, A.; Villarreal-Molina, T.; Jacobo-Albavera, L. Endothelial Dysfunction, Inflammation and Coronary Artery Disease: Potential Biomarkers and Promising Therapeutical Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brizzolara, A.L.; Morris, D.G.; Burnstock, G. Ethanol affects sympathetic cotransmission and endothelium-dependent relaxation in the rat. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 254, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhan, W.G.; Didion, S.P. Effect of Chronic Alcohol Consumption on Responses of Cerebral Arterioles. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1996, 20, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayock, D.E.; Ness, D.; Mondares, R.L.; Gleason, C.A.; Sun, H.; Patel, K.P.; Mayhan, W.G. Responses of cerebral arterioles during chronic ethanol exposure. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 1992, 262, H787–H791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Mayhan, W.G.; Mayock, D.E.; Ness, D.; Mondares, R.L.; Gleason, C.A.; Faraci, F.M.; Patel, K.P. Temporal effect of alcohol consumption on reactivity of pial arterioles: role of oxygen radicals. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2001, 280, H992–H1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosentino, F.; Katusic, Z.S. Tetrahydrobiopterin and Dysfunction of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Coronary Arteries. Circulation 1995, 91, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piano, M.R.; Phillips, S.A.; Hwang, C.-L. The effects of alcohol consumption on flow-mediated dilation in humans: A systematic review. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e14872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thijssen, D.H.J.; Bruno, R.M.; Van Mil, A.C.C.M.; Holder, S.M.; Faita, F.; Greyling, A.; Zock, P.L.; Taddei, S.; Deanfield, J.E.; Luscher, T.; et al. Expert consensus and evidence-based recommendations for the assessment of flow-mediated dilation in humans. Eur. Hear. J. 2019, 40, 2534–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Gennaro, C.; Saccani-Jotti, G.; Pinelli, S.; Venturi, N.; Palombi, F.; Manfredi, G.; Pellegrino, A.; Bicchieri, L.; Sansoni, P.; Montanari, A. Endothelial Dysfunction and High Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Severe Alcoholics Improve Only Partially Following a Medium-Term Alcohol Withdrawal. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 36, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goslawski, M.; Piano, M.R.; Bian, J.-T.; Church, E.C.; Szczurek, M.; Phillips, S.A. Binge Drinking Impairs Vascular Function in Young Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Shen, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, G. Evaluation of the brachial artery endothelial function in chronic alcohol consumption among males by high-frequency ultrasonography. Echocardiography 2016, 34, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, N.; Kajikawa, M.; Maruhashi, T.; Kishimoto, S.; Yusoff, F.M.; Goto, C.; Nakashima, A.; Tomiyama, H.; Takase, B.; Yamashina, A.; et al. Endothelial function is preserved in light to moderate alcohol drinkers but is impaired in heavy drinkers in women: Flow-mediated Dilation Japan (FMD-J) study. PLOS ONE 2020, 15, e0243216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, Y.Z. Regional Heterogeneity of Perivascular Adipose Tissue: Morphology, Origin, and Secretome. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Bibi, A.; Valoti, M.; Fusi, F. Perivascular Adipose Tissue and Vascular Smooth Muscle Tone: Friends or Foes? Cells 2023, 12, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.K.; Ding, H.; Jiang, M.; Yin, H.; Gollasch, M.; Huang, Y. Perivascular adipose tissue: Fine-tuner of vascular redox status and inflammation. Redox Biol. 2023, 62, 102683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzaga, N.A.; Awata, W.M.; Vale, G.T.D.; Marchi, K.C.; Muniz, J.J.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Tirapelli, C.R. Perivascular adipose tissue protects against the vascular dysfunction induced by acute ethanol intake: Role of hydrogen peroxide. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2018, 111, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



