Submitted:
06 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Objectives
2. Bibliometric Analysis
3.1. Methods for Retrieving Water Quality
3.1.1. Analytical Methods
3.1.2. Semi-Analytical Methods
3.1.3. Empirical Methods
3.1.4. Semi-Empirical Methods
3.1.5. Artificial Intelligence/Machine Learning (AI/ML) Methods
3.2. Parameters
3.2.1. Chlorophyll-α (chl-α)
3.2.2. Total Suspended Matter (TSM) and Turbidity (TUR)
3.2.3. Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) and Total Organic Carbon (TOC)
3.2.4. Water Transparency (Secchi Disk Depth (SDD))
3.2.5. Water Temperature
3.2.6. Surface Salinity
3.2.7. Electrical Conductivity (EC)
3.3. Sensors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dudgeon, D.; Arthington, A.H.; Gessner, M.O.; Kawabata, Z.-I.; Knowler, D.J.; Lévêque, C.; Naiman, R.J.; Prieur-Richard, A.-H.; Soto, D.; Stiassny, M.L.J.; et al. Freshwater Biodiversity: Importance, Threats, Status and Conservation Challenges. Biol. Rev. 2006, 81, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global Lake Responses to Climate Change. Nat Rev Earth Environ 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stendera, S.; Adrian, R.; Bonada, N.; Cañedo-Argüelles, M.; Hugueny, B.; Januschke, K.; Pletterbauer, F.; Hering, D. Drivers and Stressors of Freshwater Biodiversity Patterns across Different Ecosystems and Scales: A Review. Hydrobiologia 2012, 696, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; McDonald, C.; de Hoyos, C.; Mischke, U.; Phillips, G.; Borics, G.; Poikane, S.; Skjelbred, B.; Solheim, A.L.; Van Wichelen, J.; et al. Sustaining Recreational Quality of European Lakes: Minimizing the Health Risks from Algal Blooms through Phosphorus Control. J Appl Ecol 2013, 50, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.T.; Goethals, P.L.M. Opportunities and Challenges for the Sustainability of Lakes and Reservoirs in Relation to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Water 2019, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J. Limnology and Oceanography: Two Estranged Twins Reuniting by Global Change. Inland Waters 2014, 4, 215–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.C.; Michalak, A.M.; Pahlevan, N. Widespread Global Increase in Intense Lake Phytoplankton Blooms since the 1980s. Nature 2019, 574, 667–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adrian, R.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Zagarese, H.; Baines, S.B.; Hessen, D.O.; Keller, W.; Livingstone, D.M.; Sommaruga, R.; Straile, D.; Van Donk, E.; et al. Lakes as Sentinels of Climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2283–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brönmark, C.; Hansson, L.-A. Environmental Issues in Lakes and Ponds: Current State and Perspectives. Environ Conserv 2002, 29, 290–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cai, Z.; Chen, L.; Ruan, J. Assessment on the Water Quality Influenced by Large-Scale Controlled Planting of Water Hyacinth in the Dianchi Lake.; Zhao, J., Iranpour, R., Li, X., Jin, B., Eds.; 2013; Vol. 726–731, pp. 1782-+.
- Moss, B. Cogs in the Endless Machine: Lakes, Climate Change and Nutrient Cycles: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 434, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poikane, S.; Birk, S.; Böhmer, J.; Carvalho, L.; de Hoyos, C.; Gassner, H.; Hellsten, S.; Kelly, M.; Lyche Solheim, A.; Olin, M.; et al. A Hitchhiker’s Guide to European Lake Ecological Assessment and Intercalibration. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 52, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, D.; Borja, A.; Carstensen, J.; Carvalho, L.; Elliott, M.; Feld, C.K.; Heiskanen, A.-S.; Johnson, R.K.; Moe, J.; Pont, D.; et al. The European Water Framework Directive at the Age of 10: A Critical Review of the Achievements with Recommendations for the Future. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 4007–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum The Global Risks Report 2023; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023; p. 97.
- Meerhoff, M.; Jeppesen, E. Shallow Lakes and Ponds. In Encyclopedia of Inland Waters; Elsevier, 2009; pp. 645–655 ISBN 978-0-12-370626-3.
- Postel, S.L.; Carpenter, S.R. Freshwater Ecosystem Services. In Nature’s Services Societal Dependence on Natural Ecosystems; Island Press: Covelo, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 195–214. ISBN 1-55963-475-8. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffer, M. Ecology of Shallow Lakes; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2004; ISBN 978-1-4020-2306-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Leavitt, P.R.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B. Anthropogenic Eutrophication of Shallow Lakes: Is It Occasional? Water Res. 2022, 221, 118728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearing, J.A.; Acma, B.; Bub, S.; Chambers, F.M.; Chen, X.; Cooper, J.; Crook, D.; Dong, X.H.; Dotterweich, M.; Edwards, M.E.; et al. Social-Ecological Systems in the Anthropocene: The Need for Integrating Social and Biophysical Records at Regional Scales. Anthr. Rev. 2015, 2, 220–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Binding, C.; Brockmann, C.; Dekker, A.G.; DiGiacomo, P.; Greb, S.; Griffith, D.; Groom, S.; Hestir, E.; Hunter, P.; et al. Earth Observations in Support of Global Water Quality Monitoring; Reports and Monographs of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group; International Ocean-Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG): Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2018; Vol. IOCCG report 17, ISBN 978-1-896246-67-3. [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer, B.A.; Schaeffer, K.G.; Keith, D.; Lunetta, R.S.; Conmy, R.; Gould, R.W. Barriers to Adopting Satellite Remote Sensing for Water Quality Management. Int J Remote Sens 2013, 34, 7534–7544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brivio, P.A.; Giardino, C.; Zilioli, E. Validation of Satellite Data for Quality Assurance in Lake Monitoring Applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresciani, M.; Stroppiana, D.; Odermatt, D.; Morabito, G.; Giardino, C. Assessing Remotely Sensed Chlorophyll-a for the Implementation of the Water Framework Directive in European Perialpine Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 3083–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Puijenbroek, P.J.T.M.; Evers, C.H.M.; van Gaalen, F.W. Evaluation of Water Framework Directive Metrics to Analyse Trends in Water Quality in the Netherlands. Sustain. Water Qual. Ecol. 2015, 6, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyjol, Y.; Argillier, C.; Bonne, W.; Borja, A.; Buijse, A.D.; Cardoso, A.C.; Daufresne, M.; Kernan, M.; Ferreira, M.T.; Poikane, S.; et al. Assessing the Ecological Status in the Context of the European Water Framework Directive: Where Do We Go Now? Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497–498, 332–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Remote Sensing Techniques to Assess Water Quality. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparslan, E.; Aydöner, C.; Tufekci, V.; Tüfekci, H. Water Quality Assessment at Ömerli Dam Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 135, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anding, D.; Kauth, R. Estimation of Sea Surface Temperature from Space. Remote Sens Environ 1970, 1, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G. Satellite Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Estimating Estuarine and Coastal Water Quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Din, M.S.; Gaber, A.; Koch, M.; Ahmed, R.S.; Bahgat, I. Remote Sensing Application for Water Quality Assessment in Lake Timsah, Suez Canal, Egypt. J. remote sens. technol. 2013, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Cazzaniga, I.; Schenk, K.; Rieger, P.; Braga, F.; Matta, E.; Brando, V. Evaluation of Multi-Resolution Satellite Sensors for Assessing Water Quality and Bottom Depth of Lake Garda. Sensors 2014, 14, 24116–24131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjimitsis, D.G.; Clayton, C. Assessment of Temporal Variations of Water Quality in Inland Water Bodies Using Atmospheric Corrected Satellite Remotely Sensed Image Data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 159, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellweger, F.L.; Schlosser, P.; Lall, U.; Weissel, J.K. Use of Satellite Imagery for Water Quality Studies in New York Harbor. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyev, K.Ya.; Pozdnyakov, D.V.; Pettersson, L.H. Water Quality Remote Sensing in the Visible Spectrum. Int J Remote Sens 1998, 19, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, S.; Pulliainen, J.; Kallio, K.; Hallikainen, M. Lake Water Quality Classification with Airborne Hyperspectral Spectrometer and Simulated MERIS Data. Remote Sens Environ 2002, 79, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, P.; Pinheiro Santos, N.A. A Spatial-Statistical Approach for Modeling the Effect of Non-Point Source Pollution on Different Water Quality Parameters in the Velhas River Watershed – Brazil. J. Environ. Manage. 2008, 86, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of Variations in Ocean Color. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakov, D.; Shuchman, R.; Korosov, A.; Hatt, C. Operational Algorithm for the Retrieval of Water Quality in the Great Lakes. Remote Sens Environ 2005, 97, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, E.; Dekker, A. Application of Remote Sensing Techniques for Water Quality Monitoring. Hydrobiological Bulletin 1986, 20, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usali, N.; Ismail, M.H. Use of Remote Sensing and GIS in Monitoring Water Quality. J Sustain Dev 2010, 3, p228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Ma, T. Application of Remote Sensing Techniques in Monitoring and Assessing the Water Quality of Taihu Lake. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 2001, 67, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Ekroos, A.; Hallikainen, M. The Role of Remote Sensing Technology in the EU Water Framework Directive (WFD). Environ Sci Policy 2004, 7, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and Reservoirs as Sentinels, Integrators, and Regulators of Climate Change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birk, S.; Ecke, F. The Potential of Remote Sensing in Ecological Status Assessment of Coloured Lakes Using Aquatic Plants. Ecol. Indic. 2014, 46, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Trinanes, J.; Muller-Karger, F.E.; Ambo-Rappe, R.; Boström, C.; Buschmann, A.H.; Byrnes, J.; Coles, R.G.; Creed, J.; et al. Toward a Coordinated Global Observing System for Seagrasses and Marine Macroalgae. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, F.; Wallis, C.; Sinnott, A.M. Optical Remote Sensing of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation: Opportunities for Shallow Clearwater Streams. Limnologica 2013, 43, 388–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, G.; Bresciani, M.; Trodd, W.; Tierney, D.; O’Boyle, S.; Plant, C.; Deakin, J. Estimation of Lake Ecological Quality from Sentinel-2 Remote Sensing Imagery. Hydrobiologia 2020, 847, 1423–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, V.; Serôdio, J.; Lillebø, A.I.; Sousa, A.I. Use of Hyperspectral Reflectance to Non-Destructively Estimate Seagrass Zostera Noltei Biomass. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 107018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Zamurović-Nenad, Ž.; Hoogenboom, H.J.; Peters, S.W.M. Remote Sensing, Ecological Water Quality Modelling and in Situ Measurements: A Case Study in Shallow Lakes. Hydrol Sci J 1996, 41, 531–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, S.; Brabyn, L.; Hicks, B.J.; Collier, K. Satellite Remote Sensing for Mapping Vegetation in New Zealand Freshwater Environments: A Review. N Z Geog 2010, 66, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalacska, M.; Chmura, G.L.; Lucanus, O.; Bérubé, D.; Arroyo-Mora, J.P. Structure from Motion Will Revolutionize Analyses of Tidal Wetland Landscapes. Remote Sens Environ 2017, 199, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, D.S.; Kim, Y.D.; Kang, B.; Kim, D. Applications of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles in Fluvial Remote Sensing: An Overview of Recent Achievements. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 22, 588–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Villa, P.; Martinelli, A. Application of Remote Sensing in Water Resource Management: The Case Study of Lake Trasimeno, Italy. Water Resour. Manag. 2010, 24, 3885–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, D.Z.; Wang, L.; Huang, F.R. Advance in Remote Sensing of Water Quality. Marine Environmental Science 2012, 31, 285–288. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, M.; Melesse, A.; Reddi, L. A Comprehensive Review on Water Quality Parameters Estimation Using Remote Sensing Techniques. Sensors 2016, 16, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, W. Water Quality Monitoring and Evaluation Using Remote Sensing Techniques in China: A Systematic Review. ECOSYST HEALTH SUST 2019, 5, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, G.; Nolè, A.; Urbano, V.; Amato, M.; Ferrara, A. Assessing Water Quality by Remote Sensing in Small Lakes: The Case Study of Monticchio Lakes in Southern Italy. iForest 2009, 2, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Han, L.; Kung, H. -T.; Van Arsdale, R.B. Applications of Landsat-5 TM Imagery in Assessing and Mapping Water Quality in Reelfoot Lake, Tennessee. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2006, 27, 5269–5283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinska-Skotak, K.; Kruk, M.; Mróz, M. The Spatial Diversification of Lake Water Quality Parameters in Mazurian Lakes in Summertime. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 26th EARSeL Symposium on New Developments and Challenges in Remote Sensing; Millpress: Warsaw, Poland, 2007; pp. 591–602.
- Keith, D.J.; Schaeffer, B.A.; Lunetta, R.S.; Gould, R.W.; Rocha, K.; Cobb, D.J. Remote Sensing of Selected Water-Quality Indicators with the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean (HICO) Sensor. Int J Remote Sens 2014, 35, 2927–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.; Bowles, J.; Corson, M. Expected Improvements in the Quantitative Remote Sensing of Optically Complex Waters with the Use of an Optically Fast Hyperspectral Spectrometer—A Modeling Study. Sensors 2015, 15, 6152–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Verdú, A.; Domínguez-Gómez, J.-A.; Peña-Martínez, R. Use of CHRIS for Monitoring Water Quality in Rosarito Reservoir. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 3rd CHRIS/Proba Workshop; Frascati, Italy, March 21 2005; p. 26.
- Gitelson, A.A.; Dall’Olmo, G.; Moses, W.; Rundquist, D.C.; Barrow, T.; Fisher, T.R.; Gurlin, D.; Holz, J. A Simple Semi-Analytical Model for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Turbid Waters: Validation. Remote Sens Environ 2008, 112, 3582–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.J.; Barrow, T. A Bio-Optical Algorithm for the Remote Estimation of the Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Case 2 Waters. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilerson, A.A.; Gitelson, A.A.; Zhou, J.; Gurlin, D.; Moses, W.; Ioannou, I.; Ahmed, S.A. Algorithms for Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Coastal and Inland Waters Using Red and near Infrared Bands. Opt. Express 2010, 18, 24109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Satellite Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration Using the Red and NIR Bands of MERIS—The Azov Sea Case Study. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sensing Lett. 2009, 6, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, K.; Kutser, T.; Hannonen, T.; Koponen, S.; Pulliainen, J.; Vepsäläinen, J.; Pyhälahti, T. Retrieval of Water Quality from Airborne Imaging Spectrometry of Various Lake Types in Different Seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 59–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olmo, G.; Gitelson, A.A. Effect of Bio-Optical Parameter Variability and Uncertainties in Reflectance Measurements on the Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters: Modeling Results. Appl. Opt. 2006, 45, 3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, D.J.; Milstead, B.; Walker, H.; Snook, H.; Szykman, J.; Wusk, M.; Kagey, L.; Howell, C.; Mellanson, C.; Drueke, C. Trophic Status, Ecological Condition, and Cyanobacteria Risk of New England Lakes and Ponds Based on Aircraft Remote Sensing. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2012, 6, 063577–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddick, K.G.; Gons, H.J.; Rijkeboer, M.; Tilstone, G. Optical Remote Sensing of Chlorophyll a in Case 2 Waters by Use of an Adaptive Two-Band Algorithm with Optimal Error Properties. Appl. Opt. 2001, 40, 3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogenboom, H.J.; Dekker, A.G.; Althuis, Ij.A. Simulation of AVIRIS Sensitivity for Detecting Chlorophyll over Coastal and Inland Waters. Remote Sens Environ 1998, 65, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Li, Y.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, C.; Lu, H. A Four-Band Semi-Analytical Model for Estimating Chlorophyll a in Highly Turbid Lakes: The Case of Taihu Lake, China. Remote Sens Environ 2009, 113, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Tedesco, L.P.; Li, S.; Duan, H.; Liu, D.; Hall, B.E.; Du, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, K.; et al. Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll-a in Turbid Inland Waters: Three-Band Model versus GA-PLS Model. Remote Sens Environ 2013, 136, 342–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiemann, S.; Kaufmann, H. Lake Water Quality Monitoring Using Hyperspectral Airborne Data—A Semiempirical Multisensor and Multitemporal Approach for the Mecklenburg Lake District, Germany. Remote Sens Environ 2002, 81, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.M.; Rundquist, D.; Schalles, J.; Ramirez, L. Application of Hyperspectral Remotely Sensed Data for Water Quality Monitoring: Accuracy and Limitation. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 9th International Symposium on Spatial Accuracy Assessment in Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences; International Spatial Accuracy Research Association (ISARA): Leicester, UK, July 20, 2010; pp. 349–352. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, P.D.; Tyler, A.N.; Carvalho, L.; Codd, G.A.; Maberly, S.C. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Cyanobacterial Pigments as Indicators for Cell Populations and Toxins in Eutrophic Lakes. Remote Sens Environ 2010, 114, 2705–2718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menken, K.D.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Influence of Chlorophyll and Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) on Lake Reflectance Spectra: Implications for Measuring Lake Properties by Remote Sensing. Lake Reserv Manag 2006, 22, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Martínez, R.; Ruiz-Verdú, A.; Domínguez-Gómez, J.A. Mapping of Photosynthetic Pigments in Spanish Inland Waters Using MERIS Imagery. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2004 Envisat & ERS Symposium; Salzburg, Austria, September 6 2004.
- Le, C.; Hu, C.; Cannizzaro, J.; English, D.; Muller-Karger, F.; Lee, Z. Evaluation of Chlorophyll-a Remote Sensing Algorithms for an Optically Complex Estuary. Remote Sens Environ 2013, 129, 75–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Perk, R.L.; Gurlin, D.; Rundquist, D.C.; Leavitt, B.C.; Barrow, T.M.; Brakhage, P. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Productive Waters Using Airborne Hyperspectral Data. Water Res. 2012, 46, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, J.A.D.; Alonso, C.A.; García, A.A. Remote Sensing as a Tool for Monitoring Water Quality Parameters for Mediterranean Lakes of European Union Water Framework Directive (WFD) and as a System of Surveillance of Cyanobacterial Harmful Algae Blooms (SCyanoHABs). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 181, 317–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soomets, T.; Uudeberg, K.; Jakovels, D.; Brauns, A.; Zagars, M.; Kutser, T. Validation and Comparison of Water Quality Products in Baltic Lakes Using Sentinel-2 MSI and Sentinel-3 OLCI Data. Sensors 2020, 20, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Brando, V.E.; Dekker, A.G.; Strömbeck, N.; Candiani, G. Assessment of Water Quality in Lake Garda (Italy) Using Hyperion. Remote Sens Environ 2007, 109, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Anderson, A.I.; Griffin, R.; Dix, M.; Romero-Oliva, C.S.; Ochaeta, G.; Skinner-Alvarado, J.; Ramirez Moran, M.V.; Hernandez, B.; Cherrington, E.; Page, B.; et al. Hyperspectral Satellite Remote Sensing of Water Quality in Lake Atitlán, Guatemala. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.; Davis, C.; Tufillaro, N.; Kudela, R.; Gao, B.-C. Application of the Hyperspectral Imager for the Coastal Ocean to Phytoplankton Ecology Studies in Monterey Bay, CA, USA. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1007–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, J.E.; Maritorena, S.; Siegel, D.A.; O’Brien, M.E.; Toole, D.; Mitchell, B.G.; Kahru, M.; Chavez, F.P.; Strutton, P.; Cota, G.F.; et al. Ocean Color Chlorophyll a Algorithms for SeaWiFS, OC2 and OC4: Version 4. In SeaWiFS Postlaunch Calibration and Validation Analyses; 2000.
- Chao Rodríguez, Y.; el Anjoumi, A.; Domínguez Gómez, J.A.; Rodríguez Pérez, D.; Rico, E. Using Landsat Image Time Series to Study a Small Water Body in Northern Spain. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, M.G.; Hicks, B.J.; Brabyn, L. Remote Sensing of Water Quality in the Rotorua Lakes; Environment Bay of Plenty: Whakatāne, New Zealand, 2007; p. 27. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Jordan, K.J. Estimating and Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Pensacola Bay, Florida Using Landsat ETM+ Data. Int J Remote Sens 2005, 26, 5245–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, A.M.; Rundquist, D.C.; Nasu, S.; Takagi, M. Assessing the Potential of Remotely Sensed Data for Water Quality Monitoring of Coastal and Inland Waters 2008.
- Zhang, C.; Han, M. Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Laizhou Bay Using Landsat 8 OLI Data. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 36th IAHRWorld Congress; Hague, The Netherlands, June 28 2015.
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Valentini, E.; Gasperini, L.; Bolpagni, R.; Brando, V.E. Airborne Hyperspectral Data to Assess Suspended Particulate Matter and Aquatic Vegetation in a Shallow and Turbid Lake. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 157, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Luo, D. Application of MODIS Satellite Data in Monitoring Water Quality Parameters of Chaohu Lake in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2009, 148, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osińska-Skotak, K.; Kruk, M.; Mróz, M.; Szumilo, M. Chris/Proba Superspectral Data for Inland Water Quality Studies. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of 4th EARSeL Workshop on Imaging Spectroscopy; Warsaw, Poland, 2005; pp. 317–325.
- Dekker, A.G.; Peters, S.W.M. The Use of the Thematic Mapper for the Analysis of Eutrophic Lakes: A Case Study in the Netherlands. Int J Remote Sens 1993, 14, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, D.G. The Airborne Remote Sensing of Phytoplankton Chlorophyll in the Lakes and Tarns of the English Lake District. Int J Remote Sens 1997, 18, 1961–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekercin, S. Water Quality Retrievals from High Resolution IKONOS Multispectral Imagery: A Case Study in Istanbul, Turkey. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2007, 183, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Chen, J. Water Quality Monitoring in a Slightly-Polluted Inland Water Body through Remote Sensing — Case Study of the Guanting Reservoir in Beijing, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Engin. China 2008, 2, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Choi, M. Assessment of Water Quality Based on Landsat 8 Operational Land Imager Associated with Human Activities in Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudheer, K.P.; Chaubey, I.; Garg, V. Lake Water Quality Assessment from Landsat Thematic Mapper Data Using Neural Network: An Approach to Optimal Band Combination Selection. J Am Water Resour Assoc 2006, 42, 1683–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torbick, N.; Hession, S.; Hagen, S.; Wiangwang, N.; Becker, B.; Qi, J. Mapping Inland Lake Water Quality across the Lower Peninsula of Michigan Using Landsat TM Imagery. Int J Remote Sens 2013, 34, 7607–7624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezonik, P.; Menken, K.D.; Bauer, M. Landsat-Based Remote Sensing of Lake Water Quality Characteristics, Including Chlorophyll and Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM). Lake Reserv Manag 2005, 21, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Pepe, M.; Brivio, P.A.; Ghezzi, P.; Zilioli, E. Detecting Chlorophyll, Secchi Disk Depth and Surface Temperature in a Sub-Alpine Lake Using Landsat Imagery. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Blackwell, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, G. Water Quality Monitoring Using Landsat Themate Mapper Data with Empirical Algorithms in Chagan Lake, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boucher, J.; Weathers, K.C.; Norouzi, H.; Steele, B. Assessing the Effectiveness of Landsat 8 Chlorophyll a Retrieval Algorithms for Regional Freshwater Monitoring. Ecol Appl 2018, 28, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Hunter, P.D.; Lankester, T.; Hubbard, S.; Spyrakos, E.; N. Tyler, A.; Présing, M.; Horváth, H.; Lamb, A.; Balzter, H.; et al. Validation of Envisat MERIS Algorithms for Chlorophyll Retrieval in a Large, Turbid and Optically-Complex Shallow Lake. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 157, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannheim, S.; Segl, K.; Heim, B.; Kaufmann, H. Monitoring of Lake Water Quality Using Hyperspectral CHRIS/Proba Data. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2nd CHRIS/Proba Workshop; Frascati, Italy, April 28 2004.
- Qi, L.; Hu, C.; Duan, H.; Barnes, B.; Ma, R. An EOF-Based Algorithm to Estimate Chlorophyll a Concentrations in Taihu Lake from MODIS Land-Band Measurements: Implications for near Real-Time Applications and Forecasting Models. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10694–10715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparslan, E.; Coskun, H.G.; Alganci, U. Water Quality Determination of Küçükçekmece Lake, Turkey by Using Multispectral Satellite Data. The Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansaray, A.S.; Dzialowski, A.R.; Martin, M.E.; Wagner, K.L.; Gholizadeh, H.; Stoodley, S.H. Comparing PlanetScope to Landsat-8 and Sentinel-2 for Sensing Water Quality in Reservoirs in Agricultural Watersheds. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blix, K.; Pálffy, K.; Tóth, V.; Eltoft, T. Remote Sensing of Water Quality Parameters over Lake Balaton by Using Sentinel-3 OLCI. Water 2018, 10, 1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W.; Bernard, S.; Winter, K. Remote Sensing of Cyanobacteria-Dominant Algal Blooms and Water Quality Parameters in Zeekoevlei, a Small Hypertrophic Lake, Using MERIS. Remote Sens Environ 2010, 114, 2070–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciel, D.A.; Novo, E.M.L.D.M.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Martins, V.S.; Flores Júnior, R.; Oliveira, A.H.; Sander De Carvalho, L.A.; Lobo, F.D.L. Evaluating the Potential of CubeSats for Remote Sensing Reflectance Retrieval over Inland Waters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2020, 41, 2807–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allee, R.J.; Johnson, J.E. Use of Satellite Imagery to Estimate Surface Chlorophyll a and Secchi Disc Depth of Bull Shoals Reservoir, Arkansas, USA. Int J Remote Sens 1999, 20, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Finlay, J.C.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of Landsat 8 and Landsat 7 for Regional Measurements of CDOM and Water Clarity in Lakes. Remote Sens Environ 2016, 185, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, B.J.; Stichbury, G.A.; Brabyn, L.K.; Allan, M.G.; Ashraf, S. Hindcasting Water Clarity from Landsat Satellite Images of Unmonitored Shallow Lakes in the Waikato Region, New Zealand. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 7245–7261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewidar, Kh.; Khedr, A. Water Quality Assessment with Simultaneous Landsat-5 TM at Manzala Lagoon, Egypt. Hydrobiologia 2001, 457, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Brooks, C.; French, N.; Shuchman, R. Remote Sensing of Lake Clarity; Michigan Tech Research Institute: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Choubey, V.K. Laboratory Experiment, Field and Remotely Sensed Data Analysis for the Assessment of Suspended Solids Concentration and Secchi Depth of the Reservoir Surface Water. Int J Remote Sens 1998, 19, 3349–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E.; Brezonik, P.L. A 20-Year Landsat Water Clarity Census of Minnesota’s 10,000 Lakes. Remote Sens Environ 2008, 112, 4086–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Lou, L.; Chen, Y. Empirical Estimation of Total Phosphorus Concentration in the Mainstream of the Qiantang River in China Using Landsat TM Data. Int J Remote Sens 2010, 31, 2309–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Application of Landsat Imagery to Regional-Scale Assessments of Lake Clarity. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E. A Procedure for Regional Lake Water Clarity Assessment Using Landsat Multispectral Data. Remote Sens Environ 2002, 82, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, K.E.; Olmanson, L.G.; Heinert, N.J.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Extending Satellite Remote Sensing to Local Scales: Land and Water Resource Monitoring Using High-Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens Environ 2003, 88, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriwongsitanon, N.; Surakit, K.; Thianpopirug, S. Influence of Atmospheric Correction and Number of Sampling Points on the Accuracy of Water Clarity Assessment Using Remote Sensing Application. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenstein, E.M.; Park, M.-H. Assessment of Nutrient Distributions in Lake Champlain Using Satellite Remote Sensing. J Environ Sci (China) 2014, 26, 1831–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutser, T.; Pierson, D.C.; Kallio, K.Y.; Reinart, A.; Sobek, S. Mapping Lake CDOM by Satellite Remote Sensing. Remote Sens Environ 2005, 94, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Tranvik, L.; Pierson, D.C. Variations in Colored Dissolved Organic Matter between Boreal Lakes Studied by Satellite Remote Sensing. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2009, 3, 033538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Pierson, D.C.; Tranvik, L.; Reinart, A.; Sobek, S.; Kallio, K. Using Satellite Remote Sensing to Estimate the Colored Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption Coefficient in Lakes. Ecosystems (N. Y., Print) 2005, 8, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.P.; Shanmugam, P. An Optical Model for the Remote Sensing of Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter in Coastal/Ocean Waters. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2011, 93, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toming, K.; Kutser, T.; Laas, A.; Sepp, M.; Paavel, B.; Nõges, T. First Experiences in Mapping Lake Water Quality Parameters with Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, I.D.; D’Sa, E.J.; Osburn, C.L.; Bianchi, T.S.; Ko, D.S.; Oviedo-Vargas, D.; Arellano, A.R.; Ward, N.D. Assessing Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) Distribution, Stocks, and Fluxes in Apalachicola Bay Using Combined Field, VIIRS Ocean Color, and Model Observations. Remote Sens Environ 2017, 191, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, W.-N.; Tian, Y.Q.; Yu, Q. Estimation of Colored Dissolved Organic Matter from Landsat-8 Imagery for Complex Inland Water: Case Study of Lake Huron. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 2201–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T. The Possibility of Using the Landsat Image Archive for Monitoring Long Time Trends in Coloured Dissolved Organic Matter Concentration in Lake Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 123, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johannessen, S.; Miller, W.; Cullen, J. Calculation of UV Attenuation and Colored Dissolved Organic Matter Absorption Spectra from Measurements of Ocean Color. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.H.; Shanmugam, P.; Moon, J.E.; Ryu, J.H. Satellite Remote Sensing of a Low-Salinity Water Plume in the East China Sea. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 2019–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Retuerta, E.; Siegel, D.A.; Nelson, N.B.; Duarte, C.M.; Reche, I. Observations of Chromophoric Dissolved and Detrital Organic Matter Distribution Using Remote Sensing in the Southern Ocean: Validation, Dynamics and Regulation. J Mar Syst 2010, 82, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paavel, B.; Arst, H.; Metsamaa, L.; Toming, K.; Reinart, A. Optical Investigations of CDOM-Rich Coastal Waters in Pärnu Bay. Estonian J. Earth Sci. 2011, 60, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiorani, L.; Fantoni, R.; Lazzara, L.; Nardello, I.; Okladnikov, I.; Palucci, A. Lidar Calibration of Satellite Sensed CDOM in the Southern Ocean. In Proceedings of the EARSeL eProceedings; 2006; Vol. 5; pp. 89–99. [Google Scholar]
- Georgas, N.; Li, W.; Blumberg, A.F. Investigation of Coastal CDOM Distributions Using In-Situ and Remote Sensing Observations and a Predictive CDOM Fate and Transport Model; Center for Maritime Systems, Davidson Laboratory, Stevens Institute of Technology: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2009; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- D’Alimonte, D.; Zibordi, G.; Berthon, J.-F. Determination of CDOM and NPPM Absorption Coefficient Spectra from Coastal Water Remote Sensing Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tehrani, N.; D’Sa, E.; Osburn, C.; Bianchi, T.; Schaeffer, B. Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter and Dissolved Organic Carbon from Sea-Viewing Wide Field-of-View Sensor (SeaWiFS), Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) and MERIS Sensors: Case Study for the Northern Gulf of Mexico. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1439–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, T.; Brando, V.; Cherukuru, N.; Clementson, L.; Blondeau-Patissier, D.; Dekker, A.; Schaale, M.; Fischer, J. Remote Sensing of Apparent and Inherent Optical Properties of Tasmanian Coastal Waters: Application to MODIS Data. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the XIX Ocean Optics Conference; Barga, Italy, October 6 2008; pp. 6–10.
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Loiselle, S.A.; Shen, Q.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Y. Optical Characterization of Black Water Blooms in Eutrophic Waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 482–483, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, F.; Giardino, C.; Bassani, C.; Matta, E.; Candiani, G.; Strömbeck, N.; Adamo, M.; Bresciani, M. Assessing Water Quality in the Northern Adriatic Sea from HICOTM Data. Remote Sens Lett 2013, 4, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishino, M.; Tanaka, A.; Ishizaka, J. Retrieval of Chlorophyll a, Suspended Solids, and Colored Dissolved Organic Matter in Tokyo Bay Using ASTER Data. Remote Sens Environ 2005, 99, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Gege, P.; Pflug, B.; Oppelt, N. Mapping Indicators of Lake Ecology at Lake Starnberg, Germany—First Results of Sentinel-2A. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of Living Planet Symposium 2016; Ouwehand, L., Ed.; Prague, Czech Republic, 2016; Vol. SP-740, pp. 1–8.
- Mohamed, H.M.; Khalil, M.T.; El-Kafrawy, S.B.; El-Zeiny, A.M.; Khalifa, N.; Emam, W.W.M. Can Statistical Remote Sensing Aid in Predicting the Potential Productivity of Inland Lakes? Case Study: Lake Qaroun, Egypt. Stoch Environ Res Risk Assess 2022, 36, 3221–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, F.; Nee Lala, M.G. Remote Estimation of Water Quality Parameters of Himalayan Lake (Kashmir) Using Landsat 8 OLI Imagery. Geocarto International 2017, 32, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmalik, K.W. Role of Statistical Remote Sensing for Inland Water Quality Parameters Prediction. Egypt. J. Remote. Sens. Space Sci. 2018, 21, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdous, J.; Rahman, M.T.U. Developing an Empirical Model from Landsat Data Series for Monitoring Water Salinity in Coastal Bangladesh. J. Environ. Manage. 2020, 255, 109861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Márquez, L.C.; Torres-Bejarano, F.M.; Torregroza-Espinosa, A.C.; Hansen-Rodríguez, I.R.; Rodríguez-Gallegos, H.B. Use of LANDSAT 8 Images for Depth and Water Quality Assessment of El Guájaro Reservoir, Colombia. J South Am Earth Sci 2018, 82, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Márquez, L.C.; Torres-Bejarano, F.M.; Rodríguez-Cuevas, C.; Torregroza-Espinosa, A.C.; Sandoval-Romero, J.A. Estimation of Water Quality Parameters Using Landsat 8 Images: Application to Playa Colorada Bay, Sinaloa, Mexico. Appl Geomat 2018, 10, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, J.; Hasan, M.A.; Alashker, Y.; Ahmed, M. Bathymetric and Geochemical Analysis of Lake Al-Saad, Abha, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia Using Geoinformatics Technology. J. geogr. inf. syst. 2014, 06, 440–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papoutsa, C.; Retalis, A.; Toulios, L.; Hadjimitsis, D.G. Defining the Landsat TM/ETM+ and CHRIS/PROBA Spectral Regions in Which Turbidity Can Be Retrieved in Inland Waterbodies Using Field Spectroscopy. Int J Remote Sens 2014, 35, 1674–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Song, K.; Wen, Z.; Liu, G.; Shang, Y.; Lyu, L.; Du, J.; Yang, Q.; Li, S.; Tao, H.; et al. Remote Sensing of Turbidity for Lakes in Northeast China Using Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning Algorithms. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observations Remote Sensing 2021, 14, 9132–9146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barre, H.M.J.P.; Duesmann, B.; Kerr, Y.H. SMOS: The Mission and the System. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.A.; Torres, F.; Corbella, I.; Colliander, A. SMOS Calibration. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 646–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Camps, A.; Borges, A.; Martin-Neira, M.; Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Kerr, Y.H.; Hahne, A.; Mecklenburg, S. SMOS: The Challenging Sea Surface Salinity Measurement from Space. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE; May 5 2010; Vol. 98, pp. 649–665.
- Zine, S.; Boutin, J.; Font, J.; Reul, N.; Waldteufel, P.; Gabarro, C.; Tenerelli, J.; Petitcolin, F.; Vergely, J.-L.; Talone, M.; et al. Overview of the SMOS Sea Surface Salinity Prototype Processor. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2008, 46, 621–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Lagerloef, G.S.E.; Le Vine, D.M.; Camps, A.; Zanife, O.-Z. The Determination of Surface Salinity with the European SMOS Space Mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Tenerelli, J.; Chapron, B.; Vandemark, D.; Quilfen, Y.; Kerr, Y. SMOS Satellite L-Band Radiometer: A New Capability for Ocean Surface Remote Sensing in Hurricanes. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2012, 117, n. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Boutin, J.; Reul, N.; Spurgeon, P.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Chuprin, A.; Gabarró, C.; Gourrion, J.; Guimbard, S.; Hénocq, C.; et al. SMOS First Data Analysis for Sea Surface Salinity Determination. Int J Remote Sens 2013, 34, 3654–3670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.T.; Ponte, R.M. Assessing Temporal Aliasing in Satellite-Based Surface Salinity Measurements. J Atmos Ocean Technol 2012, 29, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vine, D.M.; Lang, R.; Utku, C.; Tarkocin, Y. Remote Sensing of Salinity: The Dielectric Constant of Sea Water. In Proceedings of the 2011 XXXth URSI General Assembly and Scientific Symposium; IEEE: Istanbul, Türkiye, August, 2011; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, J.L.; Goodberlet, M. Development and Applications of STARRS: A next Generation Airborne Salinity Imager. Int J Remote Sens 2004, 25, 1319–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemas, V. Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Salinity: An Overview with Case Studies. J Coast Res 2011, 276, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, T.; Wesson, J.C.; Burrage, D. Airborne Remote Sensing of the Plata Plume Using STARRS. Sea Technol. 2006, 47, 31–34. [Google Scholar]
- Burrage, D.; Wesson, J.; Martinez, C.; Pérez, T.; Möller, O.; Piola, A. Patos Lagoon Outflow within the Río de La Plata Plume Using an Airborne Salinity Mapper: Observing an Embedded Plume. Cont Shelf Res 2008, 28, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Heron, M.L.; Prytz, A.; Ridd, P.V.; Steinberg, C.R.; Hacker, J.M. Evaluation of a New Airborne Microwave Remote Sensing Radiometer by Measuring the Salinity Gradients across the Shelf of the Great Barrier Reef Lagoon. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.L.; Goodberlet, M.; Zaitzeff, J.B. Airborne Salinity Mapper Makes Debut in Coastal Zone. Eos Trans. AGU 1998, 79, 173–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrage, D.; Heron, M.; Hacker, J.; Miller, J.; Stieglitz, T.; Steinberg, C.; Prytz, A. Structure and Influence of Tropical River Plumes in the Great Barrier Reef: Application and Performance of an Airborne Sea Surface Salinity Mapping System. Remote Sens Environ 2003, 85, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, M.L.; Prytz, A.; Stieglitz, T.; Burrage, D.M. Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Salinity: A Case Study in the Burdekin River, North-Eastern Australia. Gayana (Concepc) 2004, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, W.J.; Yueh, S.H.; Li, F.K.; Dinardo, S.; Chao, Y.; Koblinsky, C.; Lagerloef, G.; Howden, S. Ocean Surface Salinity Remote Sensing with the JPL Passive/Active L-/S-Band (PALS) Microwave Instrument. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the IEEE 2001 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium; IEEE: Sydney, Australia, July 9 2001; Vol. 2, pp. 937–939.
- Li, F.K.; Wilson, W.J.; Yueh, S.H.; Dinardo, S.J.; Howden, S. Passive Active L/S-Band Microwave Aircraft Sensor for Ocean Salinity Measurements. In Proceedings of the IGARSS 2000. IEEE 2000 International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium. Taking the Pulse of the Planet: The Role of Remote Sensing in Managing the Environment. Proceedings (Cat. No.00CH37120); IEEE: Honolulu, HI, USA, 2000; Vol. 6, pp. 2540–2542.
- Wilson, W.J.; Yueh, S.H.; Dinardo, S.J.; Chazanoff, S.L.; Kitiyakara, A.; Li, F.K.; Rahmat-Samii, Y. Passive Active L- and S-Band (PALS) Microwave Sensor for Ocean Salinity and Soil Moisture Measurements. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Vine, D.M.; Haken, M.; Wang, J.R. Rfi at L-Band in Synthetic Aperture Radiometers. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium; Toulouse, France, July 21 2003; pp. 1742–1744.
- Le Vine, D.; Kao, M.; Garvine, R.; Sanders, T. Remote Sensing of Ocean Salinity: Results from the Delaware Coastal Current Experiment. J Atmos Ocean Technol 1998, 15, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Boutin, J.; Hauser, D.; Reverdin, G.; Pardé, M.; Zribi, M.; Fanise, P.; Chanut, J.; Lazure, P.; Tenerelli, J.; et al. Remote Sensing of Sea Surface Salinity from CAROLS L-Band Radiometer in the Gulf of Biscay. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 50, 1703–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.S.; Kwan, S.; Young, J.; Nichol, J.; Zhangging, L.; Emerson, N. Modeling of Suspended Solids and Sea Surface Salinity in Hong Kong Using Aqua/MODIS Satellite Images. KJRS 2007, 23, 161–169. [Google Scholar]
- Reul, N.; Saux-Picart, S.; Chapron, B.; Vandemark, D.; Tournadre, J.; Salisbury, J. Demonstration of Ocean Surface Salinity Microwave Measurements from Space Using AMSR-E Data over the Amazon Plume. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L13607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Castaing, P. A Reflectance Band Ratio Used to Estimate Suspended Matter Concentrations in Sediment-Dominated Coastal Waters. Int J Remote Sens 2002, 23, 5079–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirabumi, P.; Wicaksono, P.; Kamal, M.; Ridwansyah, I.; Subehi, L.; Dianto, A. Spatial Distribution Analysis of Total Suspended Solid (TSS) Using PlanetScope Data in Menjer Lake, Wonosobo Regency. J. appl. geospatial inf. 2020, 4, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binding, C.E.; Jerome, J.H.; Bukata, R.P.; Booty, W.G. Suspended Particulate Matter in Lake Erie Derived from MODIS Aquatic Colour Imagery. Int J Remote Sens 2010, 31, 5239–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, I.; Morris, E.P.; Ruiz, J.; Navarro, G. Assessment of Suspended Solids in the Guadalquivir Estuary Using New DEIMOS-1 Medium Spatial Resolution Imagery. Remote Sens Environ 2014, 146, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, Q.; Shi, T.; Hu, S.; Wu, G.; Zhou, Q. Application of Sentinel 2 MSI Images to Retrieve Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations in Poyang Lake. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, F.L.; Costa, M.P.F.; Novo, E.M.L.M. Time-Series Analysis of Landsat-MSS/TM/OLI Images over Amazonian Waters Impacted by Gold Mining Activities. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 157, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.L.; McKee, B.A. Using MODIS Terra 250 m Imagery to Map Concentrations of Total Suspended Matter in Coastal Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2004, 93, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondrusek, Michael. ; Stengel, Eric.; Kinkade, Christopher.S.; Vogel, Ronald.L.; Keegstra, Phillip.; Hunter, Craig.; Kim, Chunai. The Development of a New Optical Total Suspended Matter Algorithm for the Chesapeake Bay. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 119, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Quan, W.; Cui, T.; Song, Q. Estimation of Total Suspended Matter Concentration from MODIS Data Using a Neural Network Model in the China Eastern Coastal Zone. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2015, 155, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Vos, R.J.; Peters, S.W.M. Analytical Algorithms for Lake Water TSM Estimation for Retrospective Analyses of TM and SPOT Sensor Data. Int J Remote Sens 2002, 23, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Chen, S.; Li, D.; Wang, D.; Liu, J. The Spatial and Temporal Variation of Total Suspended Solid Concentration in Pearl River Estuary during 1987–2015 Based on Remote Sensing. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 618, 1125–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handcock, R.N.; Gillespie, A.R.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Kay, J.E.; Burges, S.J.; Kampf, S.K. Accuracy and Uncertainty of Thermal-Infrared Remote Sensing of Stream Temperatures at Multiple Spatial Scales. Remote Sens Environ 2006, 100, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, R.N.; Tormos, T.; Danis, P.-A. Retrieving Water Surface Temperature from Archive LANDSAT Thermal Infrared Data: Application of the Mono-Channel Atmospheric Correction Algorithm over Two Freshwater Reservoirs. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 2014, 30, 247–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.; Mustard, J.F. High Spatial Resolution Sea Surface Climatology from Landsat Thermal Infrared Data. Remote Sens Environ 2004, 90, 293–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.-H.; Shanmugam, P.; Lee, J.-H.; Kang, Y.Q. Application of Satellite Infrared Data for Mapping of Thermal Plume Contamination in Coastal Ecosystem of Korea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2006, 61, 186–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.E.; Kampf, S.K.; Handcock, R.N.; Cherkauer, K.A.; Gillespie, A.R.; Burges, S.J. Accuracy of Lake and Stream Temperatures Estimated from Thermal Infrared Images. J Am Water Resour Assoc 2005, 41, 1161–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trisakti, B.; Sulma, S.; Budhiman, S. Study of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) Using Landsat-7/ETM (in Comparison with Sea Surface Temperature of Noaa-12 AVHRR). In Proceedings of the Proceedings the 13thWorkshop of OMISAR (WOM-13) on Validation and Application of Satellite Data for Marine Resources Conservation; Denpasar, Indonesia, September 7 2004; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Wloczyk, C.; Richter, R.; Borg, E.; Neubert, W. Sea and Lake Surface Temperature Retrieval from Landsat Thermal Data in Northern Germany. Int J Remote Sens 2006, 27, 2489–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Byrne, D.; Weatherbee, R. Coastal Sea Surface Temperature Variability from Landsat Infrared Data. Remote Sens Environ 2002, 81, 262–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, V.E.; Braga, F.; Zaggia, L.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Matta, E.; Bellafiore, D.; Ferrarin, C.; Maicu, F.; Benetazzo, A.; et al. High-Resolution Satellite Turbidity and Sea Surface Temperature Observations of River Plume Interactions during a Significant Flood Event. Ocean Sci. 2015, 11, 909–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politi, E.; Cutler, M.E.J.; Rowan, J.S. Using the NOAA Advanced Very Highresolution Radiometer to Characterise Temporal and Spatial Trends in Watertemperature of Large European Lakes. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 126, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, P.; Hook, S.J. Space Observations of Inland Water Bodies Show Rapidsurface Warming since 1985. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcântara, E.H.; Stech, J.L.; Lorenzzetti, J.A.; Bonnet, M.P.; Casamitjana, X.; Assireu, A.T.; Novo, E.M.L. de M. Remote Sensing of Water Surface Temperature and Heat Flux over a Tropical Hydroelectric Reservoir. Remote Sens Environ 2010, 114, 2651–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Boschetti, L. Multi-temporal assessment of bio-physical parameters in lakes Garda and Trasimeno from MODIS and MERIS. ItJRS 2011, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sima, S.; Ahmadalipour, A.; Tajrishy, M. Mapping Surface Temperature in a Hyper-Saline Lake and Investigating the Effect of Temperature Distribution on the Lake Evaporation. Remote Sens Environ 2013, 136, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, E.; Kondrik, D.; Fedorova, A.; Pozdnyakov, D.; Tang, D.L.; Pettersson, L. A Spaceborne Assessment of Cyclone Impacts on Barents Sea Surface Temperature and Chlorophyll. Int J Remote Sens 2015, 36, 1921–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierman, P.E. Remote Sensing to Monitor Interactions Between Aquaculture and the Environment of Spencer Gulf, South Australia. PhD Thesis, University of Adelaide: Adelaide, Australia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Syariz, M.A.; Jaelani, L.M.; Subehi, L.; Pamungkas, A.; Koenhardono, E.S.; Sulisetyono, A. Retrieval of Sea Surface Temperature over Poteran Island Water of Indonesia with Landsat 8 Tirs Image: A Preliminary Algorithm. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. - ISPRS Arch. 2015, XL-2/W4, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wan, Z.; Wang, P.; Sparrow, M.; Liu, J.; Zhou, X.; Haginoya, S. Estimation of Surface Long Wave Radiation and Broadband Emissivity Using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Land Surface Temperature/Emissivity Products. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, I.J. Improving Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Temperature Accuracies Using Water Vapor Profile Data. J Atmos Ocean Technol 2011, 28, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinart, A.; Reinhold, M. Mapping Surface Temperature in Large Lakes with MODIS Data. Remote Sens Environ 2008, 112, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour Kheyrollah, H.; Rontu, L.; Duguay, C.; Eerola, K.; Kourzeneva, E. Impact of Satellite-Based Lake Surface Observations on the Initial State of HIRLAM. Part II: Analysis of Lake Surface Temperature and Ice Cover. Tellus A: Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2014, 66, 21395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrigley, R.C.; Horne, A.J. Remote Sensing and Lake Eutrophication. Nature 1974, 250, 213–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpace, F.; Holmquist, K.; Fisher, L. Landsat Analysis of Lake Quality. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 1979, 45, 623–633. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, M.W. A Current Review of Empirical Procedures of Remote Sensing in Inland and Near-Coastal Transitional Waters. Int J Remote Sens 2011, 32, 6855–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odermatt, D.; Gitelson, A.; Brando, V.E.; Schaepman, M. Review of Constituent Retrieval in Optically Deep and Complex Waters from Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 118, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Islam, M.A.; Gao, J. Quantification of Shallow Water Quality Parameters by Means of Remote Sensing. PPG: Earth and Environment 2003, 27, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topp, S.N.; Pavelsky, T.M.; Jensen, D.; Simard, M.; Ross, M.R.V. Research Trends in the Use of Remote Sensing for Inland Water Quality Science: Moving towards Multidisciplinary Applications. Water 2020, 12, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörnhöfer, K.; Oppelt, N. Remote Sensing for Lake Research and Monitoring – Recent Advances. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 105–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; Masek, J.G.; Cohen, W.B.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E. Opening the Archive: How Free Data Has Enabled the Science and Monitoring Promise of Landsat. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 122, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestir, E.L.; Brando, V.E.; Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Matta, E.; Villa, P.; Dekker, A.G. Measuring Freshwater Aquatic Ecosystems: The Need for a Hyperspectral Global Mapping Satellite Mission. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 167, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.E. Marginalia: Eutrophication: The Scientific Background of a Contemporary Practical Problem. Am. Sci. 1973, 61, 269–279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Tian, Y.Q.; Becker, B.L.; Siqueira, P.; Torbick, N. Spatio-Temporal Variations of CDOM in Shallow Inland Waters from a Semi-Analytical Inversion of Landsat-8. Remote Sens Environ 2018, 218, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, K. Remote Sensing as a Tool for Monitoring Lake Water Quality. In Water Quality Measurements; Heinonen, P., Ziglio, G., Van Der Beken, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 237–245. ISBN 978-0-470-51112-1. [Google Scholar]
- Morel, A. Bio-Optical Models. In Encyclopedia of Ocean Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Ouma, Y.O.; Waga, J.; Okech, M.; Lavisa, O.; Mbuthia, D. Estimation of Reservoir Bio-Optical Water Quality Parameters Using Smartphone Sensor Apps and Landsat ETM+: Review and Comparative Experimental Results. J. Sensors 2018, 2018, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagan, V.; Peterson, K.T.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Sidike, P.; Sloan, J.; Greeling, B.A.; Maalouf, S.; Adams, C. Monitoring Inland Water Quality Using Remote Sensing: Potential and Limitations of Spectral Indices, Bio-Optical Simulations, Machine Learning, and Cloud Computing. Earth Sci Rev 2020, 205, 103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Politi, E.; Cutler, M.E.J.; Rowan, J.S. Evaluating the Spatial Transferability and Temporal Repeatability of Remote-Sensing-Based Lake Water Quality Retrieval Algorithms at the European Scale: A Meta-Analysis Approach. Int J Remote Sens 2015, 36, 2995–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Oggioni, A.; Bresciani, M.; Yan, H. Remote Sensing of Suspended Particulate Matter in Himalayan Lakes: A Case Study of Alpine Lakes in the Mount Everest Region. Mt Res Dev 2010, 30, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, D.J.; Carpenter, S.M. Modeling Inland Water Quality Using Landsat Data. Remote Sens Environ 1983, 13, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.M.; Johnson, W.L.; Deuell, R.L.; Lindstrom, O.M.; Meisner, D.E. Use of Landsat Data to Predict the Trophic State of Minnesota Lakes. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 1983, 49, 219–229. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote Sensing of Inland Waters: Challenges, Progress and Future Directions. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, P.A. Imaging Spectroscopy of Lake Water Quality Parameters; Remote Sensing Laboratories, Department of Geography, University of Zürich: Zürich, Switzerland, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Kong, J.; Hu, H.; Du, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, F. A Review of Remote Sensing for Water Quality Retrieval: Progress and Challenges. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Method of Water Quality Remote Sensing and Its Application. Energy Environ. 2009, 5, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Han, X.; Chen, X.; Qi, L. Long-Term Distribution Patterns of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake: MERIS Full-Resolution Observations with a Practical Approach. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 275–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyhun, Ö.; Yalçın, A. Remote Sensing of Water Depths in Shallow Waters via Artificial Neural Networks. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2010, 89, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Roberts, D.A.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Tang, L. Estimation of Higher Chlorophylla Concentrations Using Field Spectral Measurement and HJ-1A Hyperspectral Satellite Data in Dianshan Lake, China. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 88, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynne, T.T.; Stumpf, R.P.; Tomlinson, M.C.; Warner, R.A.; Tester, P.A.; Dyble, J.; Fahnenstiel, G.L. Relating Spectral Shape to Cyanobacterial Blooms in the Laurentian Great Lakes. Int J Remote Sens 2008, 29, 3665–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roesler, C.S.; Perry, M.J.; Carder, K.L. Modeling in Situ Phytoplankton Absorption from Total Absorption Spectra in Productive Inland Marine Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989, 34, 1510–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Garbuzov, G.; Szilagyi, F.; Mittenzwey, K.-H.; Karnieli, A.; Kaiser, A. Quantitative Remote Sensing Methods for Real-Time Monitoring of Inland Waters Quality. Int J Remote Sens 1993, 14, 1269–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gons, H.J. Optical Teledetection of Chlorophyll a in Turbid Inland Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, W.J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Berdnikov, S.; Povazhnyy, V. Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Case II Waters Using MODIS and MERIS Data—Successes and Challenges. Environ. Res. Lett. 2009, 4, 045005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neville, R.A.; Gower, J.F.R. Passive Remote Sensing of Phytoplankton via Chlorophyll α Fluorescence. J. Geophys. Res. 1977, 82, 3487–3493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dierberg, F.E.; Carriker, N.E. Field Testing Two Instruments for Remotely Sensing Water Quality in the Tennessee Valley. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 28, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, M.W.; Odermatt, D. Improved Algorithm for Routine Monitoring of Cyanobacteria and Eutrophication in Inland and Near-Coastal Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 156, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafique, N.A.; Fulk, F.; Autrey, B.C.; Flotemersch, J. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Water Quality Parameters for Large Rivers in the Ohio River Basin. In Proceedings of the First Interagency Conference on Research in the Watershed; Benson, AZ, USA; 2003; pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Lacaux, J.P.; Tourre, Y.M.; Vignolles, C.; Ndione, J.A.; Lafaye, M. Classification of Ponds from High-Spatial Resolution Remote Sensing: Application to Rift Valley Fever Epidemics in Senegal. Remote Sens Environ 2007, 106, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helms, J.R.; Stubbins, A.; Ritchie, J.D.; Minor, E.C.; Kieber, D.J.; Mopper, K. Absorption Spectral Slopes and Slope Ratios as Indicators of Molecular Weight, Source, and Photobleaching of Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2008, 53, 955–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twardowski, M.S.; Boss, E.; Sullivan, J.M.; Donaghay, P.L. Modeling the Spectral Shape of Absorption by Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter. Mar Chem 2004, 89, 69–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I. O.C.C.G. Remote Sensing of Ocean Colour in Coastal, and Other Optically-Complex, Waters; Sathyendranath, S., Ed.; Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG); International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group (IOCCG): Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mobley, C. Chapter 3: Optical Properties of Water. In Light and Water: Radiative Transfer in Natural Waters; Handbook of Optics: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1994; Vol. 1, pp. 60–144. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Ma, R.; Duan, H.; Jiang, G.; Shang, L.L. Remote Sensing Retrieval for Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Turbid Case II Waters(I): The Optimal Model. J INFRARED MILLIM W 2011, 30, 531–536. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, G.; Wang, X.; Chen, X. Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a Concentration with Multi-Sensor Data by GSM01 Merging Algorithm. Journal of Geo-Information Science 2013, 15, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B. Inversion of Water Quality Parameters and Evaluation of Eutrophication in Inland Lakes. Master’s Thesis, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China: Sichuan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Giardino, C.; Brando, V.E.; Gege, P.; Pinnel, N.; Hochberg, E.; Knaeps, E.; Reusen, I.; Doerffer, R.; Bresciani, M.; Braga, F.; et al. Imaging Spectrometry of Inland and Coastal Waters: State of the Art, Achievements and Perspectives. Surv. Geophys. 2019, 40, 401–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.Y.; Gordon, H.R. Report of the Working Group on Water Color. Boundary Layer Meteorol 1980, 18, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobley, C.D. A Numerical Model for the Computation of Radiance Distributions in Natural Waters with Wind-roughened Surfaces. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1989, 34, 1473–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Candiani, G.; Bresciani, M.; Lee, Z.; Gagliano, S.; Pepe, M. BOMBER: A Tool for Estimating Water Quality and Bottom Properties from Remote Sensing Images. Comput Geosci 2012, 45, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gege, P. WASI-2D: A Software Tool for Regionally Optimized Analysis of Imaging Spectrometer Data from Deep and Shallow Waters. Comput Geosci 2014, 62, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Vos, R.J.; Peters, S.W.M. Comparison of Remote Sensing Data, Model Results and in Situ Data for Total Suspended Matter (TSM) in the Southern Frisian Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 268, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Malthus, T.J.; Seyhan, E. Quantitative Modeling of Inland Water Quality for High-Resolution MSS Systems. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1991, 29, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Arst, H. Remote Sensing Reflectance Model of Optically Active Components of Turbid Waters. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the SPIE 2319, Oceanic Remote Sensing and Sea Ice Monitoring; Johannessen, J.A., Guymer, T.H., Eds.; Rome, Italy, December 21 1994; Vol. 2319, pp. 85–91.
- Heege, T.; Kiselev, V.; Wettle, M.; Hung, N.N. Operational Multi-Sensor Monitoring of Turbidity for the Entire Mekong Delta. Int J Remote Sens 2014, 35, 2910–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, V.; Silvestri, S.; Marani, M. Remote Sensing Retrieval of Suspended Sediment Concentration in Shallow Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2011, 115, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lymburner, L.; Botha, E.; Hestir, E.; Anstee, J.; Sagar, S.; Dekker, A.; Malthus, T. Landsat 8: Providing Continuity and Increased Precision for Measuring Multi-Decadal Time Series of Total Suspended Matter. Remote Sens Environ 2016, 185, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Retrieval of Suspended Sediment Concentration in the Yangtze Estuary and Its Spatiotemporal Dynamics Analysis Based on GOCI Image Data. Master’s Thesis, University of Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Le, C.F.; Li, Y.M.; Zha, Y.; Sun, D.; Yin, B. Validation of a Quasi-Analytical Algorithm for Highly Turbid Eutrophic Water of Meiliang Bay in Taihu Lake, China. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2492–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J. The Elements of Statistical Learning; Springer Series in Statistics; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-387-84857-0. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.P.; Basant, N.; Gupta, S. Support Vector Machines in Water Quality Management. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 703, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q. A Unified Model for Remotely Estimating Chlorophyll a in Lake Taihu, China, Based on SVM and in Situ Hyperspectral Data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Kawamura, K.; Sakuno, Y.; Fan, X.; Gong, Z.; Lim, J. Retrieval of Chlorophyll-a and Total Suspended Solids Using Iterative Stepwise Elimination Partial Least Squares (ISE-PLS) Regression Based on Field Hyperspectral Measurements in Irrigation Ponds in Higashihiroshima, Japan. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, A.; Han, L.; Li, Y.; Xie, Y. Monitoring Urban Black-Odorous Water by Using Hyperspectral Data and Machine Learning. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, R.; Huang, J.-T.; Gong, Y. Learning Small-Size DNN with Output-Distribution-Based Criteria. In Proceedings of the Fifteenth annual conference of the international speech communication association; 2014; pp. 1910–1914. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, Z.; Zhong, P.; Yu, Y.; Hu, W.; Li, S. A CNN with Multiscale Convolution and Diversified Metric for Hyperspectral Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 3599–3618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, G.; Zhang, F.; Du, Q. Hyperspectral Image Classification Using Deep Pixel-Pair Features. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 55, 844–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Du, B. Deep Learning for Remote Sensing Data: A Technical Tutorial on the State of the Art. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2016, 4, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidike, P.; Sagan, V.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Maimaitiyiming, M.; Shakoor, N.; Burken, J.; Mockler, T.; Fritschi, F.B. DPEN: Deep Progressively Expanded Network for Mapping Heterogeneous Agricultural Landscape Using WorldView-3 Satellite Imagery. Remote Sens Environ 2019, 221, 756–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, J.E.; Anderson, D.T.; Chan, C.S. Comprehensive Survey of Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: Theories, Tools, and Challenges for the Community. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Hasan, M.; Van Essen, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.S.; Asari, V.K. A State-of-the-Art Survey on Deep Learning Theory and Architectures. Electronics 2019, 8, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ye, Y.; Yin, G.; Johnson, B.A. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing Applications: A Meta-Analysis and Review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2019, 152, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Cox, A.; Martinez, M. Suspended Sediment Concentration Estimation from Landsat Imagery along the Lower Missouri and Middle Mississippi Rivers Using an Extreme Learning Machine. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Hao, S.; Liu, Y. Deep Learning–Based Remote Sensing Estimation of Water Transparency in Shallow Lakes by Combining Landsat 8 and Sentinel 2 Images. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 4401–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartling, S.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Maimaitijiang, M.; Carron, J. Urban Tree Species Classification Using a WorldView-2/3 and LiDAR Data Fusion Approach and Deep Learning. Sensors 2019, 19, 1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaitijiang, M.; Sagan, V.; Sidike, P.; Hartling, S.; Esposito, F.; Fritschi, F.B. Soybean Yield Prediction from UAV Using Multimodal Data Fusion and Deep Learning. Remote Sens Environ 2020, 237, 111599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Smith, B.; Schalles, J.; Binding, C.; Cao, Z.; Ma, R.; Alikas, K.; Kangro, K.; Gurlin, D.; Hà, N.; et al. Seamless Retrievals of Chlorophyll-a from Sentinel-2 (MSI) and Sentinel-3 (OLCI) in Inland and Coastal Waters: A Machine-Learning Approach. Remote Sens Environ 2020, 240, 111604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, W.; Li, H. Hyperspectral Image Reconstruction by Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Classification. Pattern Recognit 2017, 63, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tan, K.; Du, Q.; Chen, Y.; Du, P. Caps-TripleGAN: GAN-Assisted CapsNet for Hyperspectral Image Cassification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 7232–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Tan, K.; Jia, X.; Wang, X. Deep Learning Based Regression for Optically Inactive Inland Water Quality Parameter Estimation Using Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 286, 117534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Rao, R.S.P.; Salvato, F.; Havelund, J.F.; Møller, I.M.; Thelen, J.J.; Xu, D. MU-LOC: A Machine-Learning Method for Predicting Mitochondrially Localized Proteins in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shi, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Fei, T.; Wu, G. Improving Spectral Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Content through Semi-Supervised Regression. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.H.; Sayers, M.; Dehm, D.; Shuchman, R.; Quintero, K.; Bosse, K.; Sawtell, R. Unmanned Aerial System Based Spectroradiometer for Monitoring Harmful Algal Blooms: A New Paradigm in Water Quality Monitoring. J. Great Lakes Res. 2019, 45, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebud, Y.; Naja, G.M.; Rivero, R.G.; Melesse, A.M. Water Quality Monitoring Using Remote Sensing and an Artificial Neural Network. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 4875–4887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakili, T.; Amanollahi, J. Determination of Optically Inactive Water Quality Variables Using Landsat 8 Data: A Case Study in Geshlagh Reservoir Affected by Agricultural Land Use. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 247, 119134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-C.; Son, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Khim, J.S.; Nam, J.; Chang, W.K.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.-H.; Ryu, J. Remote Sensing and Water Quality Indicators in the Korean West Coast: Spatio-Temporal Structures of MODIS-Derived Chlorophyll-a and Total Suspended Solids. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 121, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems; 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994.
- Mouw, C.B.; Greb, S.; Aurin, D.; DiGiacomo, P.M.; Lee, Z.; Twardowski, M.; Binding, C.; Hu, C.; Ma, R.; Moore, T.; et al. Aquatic Color Radiometry Remote Sensing of Coastal and Inland Waters: Challenges and Recommendations for Future Satellite Missions. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 160, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G.; Brando, V.E.; Anstee, J.M.; Pinnel, N.; Kutser, T.; Hoogenboom, E.J.; Peters, S.; Pasterkamp, R.; Vos, R.; Olbert, C.; et al. Imaging Spectrometry of Water. In Imaging Spectrometry; Meer, F.D. van der, Jong, S.M.D., Eds.; Remote Sensing and Digital Image Processing; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2002; Vol. 4, pp. 307–359; ISBN 978-1-4020-0194-9.
- Wang, S.; Garcia, M.; Bauer-Gottwein, P.; Jakobsen, J.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Bandini, F.; Paz, V.S.; Ibrom, A. High Spatial Resolution Monitoring Land Surface Energy, Water and CO2 Fluxes from an Unmanned Aerial System. Remote Sens Environ 2019, 229, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Qiu, Z.; Li, Y.; Shi, K.; Gong, S. Detection of Total Phosphorus Concentrations of Turbid Inland Waters Using a Remote Sensing Method. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharaf El Din, E.; Zhang, Y.; Suliman, A. Mapping Concentrations of Surface Water Quality Parameters Using a Novel Remote Sensing and Artificial Intelligence Framework. Int J Remote Sens 2017, 38, 1023–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Merzlyak, M.N. Remote Estimation of Chlorophyll Content in Higher Plant Leaves. Int J Remote Sens 1997, 18, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Liu, H.; Beck, R.; Lekki, J.; Yang, B.; Shu, S.; Liu, Y.; Benko, T.; Anderson, R.; Tokars, R.; et al. Regionally and Locally Adaptive Models for Retrieving Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Inland Waters from Remotely Sensed Multispectral and Hyperspectral Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2019, 57, 4758–4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Q.; Tian, Y.Q.; Becker, B.L. Remote Sensing Estimation of Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Optically Shallow Waters. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 128, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Lyu, H.; Mu, M.; Miao, S.; et al. An Approach for Retrieval of Horizontal and Vertical Distribution of Total Suspended Matter Concentration from GOCI Data over Lake Hongze. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 700, 134524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Evaluation of Medium to Low Resolution Satellite Imagery for Regional Lake Water Quality Assessments. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Son, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, W. Remote Sensing of Water Optical Property for China’s Inland Lake Taihu Using the SWIR Atmospheric Correction with 1640 and 2130 Nm Bands. IEEE J Sel Top Appl Earth Obs Remote Sens 2013, 6, 2505–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W.; Bernard, S.; Robertson Lain, L. An Algorithm for Detecting Trophic Status (Chlorophyll-a), Cyanobacterial-Dominance, Surface Scums and Floating Vegetation in Inland and Coastal Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 124, 637–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, R.H.; Sultan, M.I.; Boyer, G.L.; Twiss, M.R.; Konopko, E. Mapping Cyanobacterial Blooms in the Great Lakes Using MODIS. J. Great Lakes Res. 2009, 35, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Nim, C.J.; Son, S.; Shi, W. Characterization of Turbidity in Florida’s Lake Okeechobee and Caloosahatchee and St. Lucie Estuaries Using MODIS-Aqua Measurements. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5410–5422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaf El Din, E.; Zhang, Y. Estimation of Both Optical and Nonoptical Surface Water Quality Parameters Using Landsat 8 OLI Imagery and Statistical Techniques. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2017, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quibell, G. The Effect of Suspended Sediment on Reflectance from Freshwater Algae. Int J Remote Sens 1991, 12, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, S.J.; Moore, G.F.; Bale, A.J.; Dyer, K.R.; Aiken, J. An Operational Approach to Determining Suspended Sediment Distributions in the Humber Estuary by Airborne Multi-Spectral Imagery. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1st International Airborne Remote Sensing Conference and Exhibition; 1994; Vol. 3, pp. 10–20.
- Han, L.; Rundquist, D.C. Spectral Characterization of Suspended Sediments Generated from Two Texture Classes of Clay Soil. Int J Remote Sens 1996, 17, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Cooper, C.M.; Schiebe, F.R. The Relationship of MSS and TM Digital Data with Suspended Sediments, Chlorophyll, and Temperature in Moon Lake, Mississippi. Remote Sens Environ 1990, 33, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.A.; Schiebe, F.R.; Nix, J.F. Remote Sensing of Lake Chicot, Arkansas: Monitoring Suspended Sediments, Turbidity, and Secchi Depth with Landsat MSS Data. Remote Sens Environ 1992, 39, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Fu, J.; Sheng, G. Water Quality Change in Reservoirs of Shenzhen, China: Detection Using LANDSAT/TM Data. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 328, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichot, C.G.; Downing, B.D.; Bergamaschi, B.A.; Windham-Myers, L.; Marvin-DiPasquale, M.; Thompson, D.R.; Gierach, M.M. High-Resolution Remote Sensing of Water Quality in the San Francisco Bay–Delta Estuary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, E.; van der Meer, F.; van Ruitenbeek, F.; van der Werff, H.; de Smeth, B.; Kim, K.-W. Mapping of Heavy Metal Pollution in Stream Sediments Using Combined Geochemistry, Field Spectroscopy, and Hyperspectral Remote Sensing: A Case Study of the Rodalquilar Mining Area, SE Spain. Remote Sens Environ 2008, 112, 3222–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmanson, L.G.; Brezonik, P.L.; Bauer, M.E. Airborne Hyperspectral Remote Sensing to Assess Spatial Distribution of Water Quality Characteristics in Large Rivers: The Mississippi River and Its Tributaries in Minnesota. Remote Sens Environ 2013, 130, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Li, L.; Li, S.; Tedesco, L.; Hall, B.; Li, L. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing of Total Phosphorus (TP) in Three Central Indiana Water Supply Reservoirs. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 1481–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiner, L.E. Estimating Oceanic Chlorophyll Concentrations with Neural Networks. Int J Remote Sens 1999, 20, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, S.E.; Jones, C.T.; Li, W.K.W.; Lazin, G.; Horne, E.; Caverhill, C.; Cullen, J.J. Deriving Optical Metrics of Coastal Phytoplankton Biomass from Ocean Colour. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 119, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, D.; Sur, P.; Mandai, S.; Saha, T.; Kole, R. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Water. Int J Environ Sci Technol (Tehran) 2008, 5, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyche-Solheim, A.; Feld, C.K.; Birk, S.; Phillips, G.; Carvalho, L.; Morabito, G.; Mischke, U.; Willby, N.; Søndergaard, M.; Hellsten, S.; et al. Ecological Status Assessment of European Lakes: A Comparison of Metrics for Phytoplankton, Macrophytes, Benthic Invertebrates and Fish. Hydrobiologia 2013, 704, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svirčev, Z.; Simeunović, J.; Subakov-Simić, G.; Krstić, S.; Pantelić, D.; Dulić, T. Cyanobacterial Blooms and Their Toxicity in Vojvodina Lakes, Serbia. Int J Environ Res 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Climate Change: A Catalyst for Global Expansion of Harmful Cyanobacterial Blooms. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, M.W. Eutrophication and Cyanobacterial Blooms in South African Inland Waters: 10 Years of MERIS Observations. Remote Sens Environ 2014, 155, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Qin, B.; Brookes, J.D.; Shi, K.; Zhu, G.; Zhu, M.; Yan, W.; Wang, Z. The Influence of Changes in Wind Patterns on the Areal Extension of Surface Cyanobacterial Blooms in a Large Shallow Lake in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Shang, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, S.; Feng, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Shan, K. Distinguishing Two Phenotypes of Blooms Using the Normalised Difference Peak-Valley Index (NDPI) and Cyano-Chlorophyta Index (CCI). Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 628–629, 848–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierssen, H.M.; Kudela, R.M.; Ryan, J.P.; Zimmerman, R.C. Red and Black Tides: Quantitative Analysis of Water-Leaving Radiance and Perceived Color for Phytoplankton, Colored Dissolved Organic Matter, and Suspended Sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2646–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.F.R.; Doerffer, R.; Borstad, G.A. Interpretation of the 685nm Peak in Water-Leaving Radiance Spectra in Terms of Fluorescence, Absorption and Scattering, and Its Observation by MERIS. Int J Remote Sens 1999, 20, 1771–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.; Mayo, M.; Yacobi, Y.Z.; Parparov, A.; Berman, T. The Use of High-Spectral-Resolution Radiometer Data for Detection of Low Chlorophyll Concentrations in Lake Kinneret. J. Plankton Res. 1994, 16, 993–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gower, J.F.R.; Brown, L.; Borstad, G.A. Observation of Chlorophyll Fluorescence in West Coast Waters of Canada Using the MODIS Satellite Sensor. Can. J. Remote. Sens. 2004, 30, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, J.; Repic, R. Hyperspectral and Video Remote Sensing of Oklahoma Lakes. In Proceedings of the Papers and Proceedings of Applied Geography Conferences; Denton, TX, USA, 1995; Vol. 18, pp. 79–86.
- Brivio, P.A.; Giardino, C.; Zilioli, E. Determination of Chlorophyll Concentration Changes in Lake Garda Using an Image-Based Radiative Transfer Code for Landsat TM Images. Int J Remote Sens 2001, 22, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukata, R.P.; Jerome, J.H.; Kondratyev, A.S.; Pozdnyakov, D.V. Optical Properties and Remote Sensing of Inland and Coastal Waters; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 0-8493-4754-8. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; 7th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 978-1-118-34328-9.
- Zhang, Y.; Pulliainen, J.; Koponen, S.; Hallikainen, M. Application of an Empirical Neural Network to Surface Water Quality Estimation in the Gulf of Finland Using Combined Optical Data and Microwave Data. Remote Sens Environ 2002, 81, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- French Water Partnership Better Knowledge for Better Management: Complementarity between Field Data and Satellite Data 2019.
- Myint, S.W.; Walker, N.D. Quantification of Surface Suspended Sediments along a River Dominated Coast with NOAA AVHRR and SeaWiFS Measurements: Louisiana, USA. Int J Remote Sens 2002, 23, 3229–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, K.A.; Wetzel, R.L.; Orth, R.J. Seasonal Pulses of Turbidity and Their Relations to Eelgrass (Zostera Marina L.) Survival in an Estuary. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 1997, 215, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havens, K.E. Submerged Aquatic Vegetation Correlations with Depth and Light Attenuating Materials in a Shallow Subtropical Lake. Hydrobiologia 2003, 493, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Shi, K. Fifteen-Year Monitoring of the Turbidity Dynamics in Large Lakes and Reservoirs in the Middle and Lower Basin of the Yangtze River, China. Remote Sens Environ 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilotta, G.S.; Brazier, R.E. Understanding the Influence of Suspended Solids on Water Quality and Aquatic Biota. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2849–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kefford, B.J.; Zalizniak, L.; Dunlop, J.E.; Nugegoda, D.; Choy, S.C. How Are Macroinvertebrates of Slow Flowing Lotic Systems Directly Affected by Suspended and Deposited Sediments? Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novo, E.M.M.; Hansom, J.D.; Curran, P.J. The Effect of Sediment Type on the Relationship between Reflectance and Suspended Sediment Concentration. Int J Remote Sens 1989, 10, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrakos, E.; O’Donnell, R.; Hunter, P.D.; Miller, C.; Scott, M.; Simis, S.G.H.; Neil, C.; Barbosa, C.C.F.; Binding, C.E.; Bradt, S.; et al. Optical Types of Inland and Coastal Waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2018, 63, 846–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.; Li, Y.; Li, L.; Lu, H. Absorption Characteristics of Optically Complex Inland Waters: Implications for Water Optical Classification. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 860–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Lavender, S.; Castaing, P. Spectral Signature of Highly Turbid Waters: Application with SPOT Data to Quantify Suspended Particulate Matter Concentrations. Remote Sens Environ 2002, 81, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and Validation of a Generic Multisensor Algorithm for Mapping of Total Suspended Matter in Turbid Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on Total Suspended Matters in the Yangtze Estuary and Its Adjacent Coastal Waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens Environ 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telmer, K.; Costa, M.; Simões Angélica, R.; Araujo, E.S.; Maurice, Y. The Source and Fate of Sediment and Mercury in the Tapajós River, Pará, Brazilian Amazon: Ground- and Space-Based Evidence. J. Environ. Manage. 2006, 81, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaza, A.; Buzzi, J.; García-Meléndez, E.; Vázquez, I.; Bellido, E.; Carrère, V.; Müller, A. Pyrite Mine Waste and Water Mapping Using Hymap and Hyperion Hyperspectral Data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 1957–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rügner, H.; Schwientek, M.; Beckingham, B.; Kuch, B.; Grathwohl, P. Turbidity as a Proxy for Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and Particle Facilitated Pollutant Transport in Catchments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrabadi, T.; Ruegner, H.; Sirdari, Z.Z.; Schwientek, M.; Grathwohl, P. Using Total Suspended Solids (TSS) and Turbidity as Proxies for Evaluation of Metal Transport in River Water. Appl. Geochemistry 2016, 68, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julian, J.P.; Doyle, M.W.; Stanley, E.H. Empirical Modeling of Light Availability in Rivers. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, G03022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendonça, R.; Müller, R.A.; Clow, D.; Verpoorter, C.; Raymond, P.; Tranvik, L.J.; Sobek, S. Organic Carbon Burial in Global Lakes and Reservoirs. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiken, G.R.; McKnight, D.M.; Wershaw, R.L.; MacCarthy, P. Humic Substances in Soil, Sediment, And Water: Geochemistry, Isolation and Characterization; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kritzberg, E.S.; Cole, J.J.; Pace, M.L.; Granéli, W.; Bade, D.L. Autochthonous versus Allochthonous Carbon Sources of Bacteria: Results from Whole-Lake 13 C Addition Experiments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2004, 49, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Finlay, J.C.; Bauer, M.E. Factors Affecting the Measurement of CDOM by Remote Sensing of Optically Complex Inland Waters. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 157, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle-Newall, E.J.; Fisher, T.R. Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter and Dissolved Organic Carbon in Chesapeake Bay. Mar Chem 2002, 77, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houser, J.N. Water Color Affects the Stratification, Surface Temperature, Heat Content, and Mean Epilimnetic Irradiance of Small Lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 2447–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Alikas, K.; Kothawala, D.N.; Köhler, S.J. Impact of Iron Associated to Organic Matter on Remote Sensing Estimates of Lake Carbon Content. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 156, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbett, C.A. Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) Workshop Summary; University of South Florida: Tampa, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X.; Mannino, A.; Russ, M.E.; Hooker, S.B. Remote Sensing of the Absorption Coefficients and Chlorophyll a Concentration in the United States Southern Middle Atlantic Bight from SeaWiFS and MODIS-Aqua. J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113, C11022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo, C.E.; Miller, R.L. On the Use of Ocean Color Remote Sensing to Measure the Transport of Dissolved Organic Carbon by the Mississippi River Plume. Remote Sens Environ 2008, 112, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Tian, Y.Q.; Chen, R.F.; Liu, A.; Gardner, G.B.; Zhu, W. Functional Linear Analysis of in Situ Hyperspectral Data for Assessing CDOM in Rivers. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 2010, 76, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, G.M.; Hoepffner, N.; Mingazzini, M. Optical Properties of the Water in a Deltaic Environment: Prospective Tool to Analyze Satellite Data in Turbid Waters. Remote Sens Environ 1996, 58, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Castillo, C.E.; Gilbes, F.; Coble, P.G.; Müller-Karger, F.E. On the Dispersal of Riverine Colored Dissolved Organic Matter over the West Florida Shelf. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stedmon, C.A.; Markager, S.; Søndergaard, M.; Vang, T.; Laubel, A.; Borch, N.H.; Windelin, A. Dissolved Organic Matter (DOM) Export to a Temperate Estuary: Seasonal Variations and Implications of Land Use. Estuaries Coast 2006, 29, 388–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, R.G.M.; Ahad, J.M.E.; Baker, A.; Cowie, G.L.; Ganeshram, R.; Upstill-Goddard, R.C.; Uher, G. The Estuarine Mixing Behaviour of Peatland Derived Dissolved Organic Carbon and Its Relationship to Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter in Two North Sea Estuaries (U.K.). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2007, 74, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignudelli, S.; Santinelli, C.; Murru, E.; Nannicini, L.; Seritti, A. Distributions of Dissolved Organic Carbon (DOC) and Chromophoric Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM) in Coastal Waters of the Northern Tyrrhenian Sea (Italy). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 60, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguy-Robertson, A.; Li, L.; Tedesco, L.P.; Wilson, J.S.; Soyeux, E. Determination of Absorption Coefficients for Chlorophyll a, Phycocyanin, Mineral Matter and CDOM from Three Central Indiana Reservoirs. J. Great Lakes Res. 2013, 39, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Luo, L.; Wang, X.C.; Song, J.; Han, J.; Ao, D. A Novel Index for Assessing the Water Quality of Urban Landscape Lakes Based on Water Transparency. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 735, 139351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teubner, K.; Teubner, I.; Pall, K.; Kabas, W.; Tolotti, M.; Ofenböck, T.; Dokulil, M.T. New Emphasis on Water Transparency as Socio-Ecological Indicator for Urban Water: Bridging Ecosystem Service Supply and Sustainable Ecosystem Health. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 573724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, J.E. The Secchi Disc. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1968, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowers, D.G.; Roberts, E.M.; Hoguane, A.M.; Fall, K.A.; Massey, G.M.; Friedrichs, C.T. Secchi Disk Measurements in Turbid Water. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2020, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, M.; He, J.; Shi, K.; Wang, M.; Yu, Z. Thermal Structure and Response to Long-Term Climatic Changes in Lake Qiandaohu, a Deep Subtropical Reservoir in China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2014, 59, 1193–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernand, M.R. On the History of the Secchi Disc. J. Eur. Opt. Society-Rapid Publ. 2010, 5, 10013s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, J.T.O. Light and Photosynthesis in Aquatic Ecosystems; 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; ISBN 0-521-15175-9.
- Lee, Z.; Shang, S.; Hu, C.; Du, K.; Weidemann, A.; Hou, W.; Lin, J.; Lin, G. Secchi Disk Depth: A New Theory and Mechanistic Model for Underwater Visibility. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 169, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vundo, A.; Matsushita, B.; Jiang, D.; Gondwe, M.; Hamzah, R.; Setiawan, F.; Fukushima, T. An Overall Evaluation of Water Transparency in Lake Malawi from MERIS Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hou, X.; Zheng, Y. Monitoring and Understanding the Water Transparency Changes of Fifty Large Lakes on the Yangtze Plain Based on Long-Term MODIS Observations. Remote Sens Environ 2019, 221, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhellemont, Q.; Ruddick, K. Atmospheric Correction of Metre-Scale Optical Satellite Data for Inland and Coastal Water Applications. Remote Sens Environ 2018, 216, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Maier, P.; Riese, F.; Norra, S.; Holbach, A.; Börsig, N.; Wilhelms, A.; Moldaenke, C.; Zaake, A.; Hinz, S. Hyperspectral Data and Machine Learning for Estimating CDOM, Chlorophyll a, Diatoms, Green Algae and Turbidity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamun, M.; Kim, J.-J.; Alam, M.A.; An, K.-G. Prediction of Algal Chlorophyll-a and Water Clarity in Monsoon-Region Reservoir Using Machine Learning Approaches. Water 2019, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Duan, H.; Cao, Z.; Xue, K.; Qi, T.; Ma, J.; Liu, D.; Song, K.; Huang, C.; Song, X. Sentinel-3 OLCI Observations of Water Clarity in Large Lakes in Eastern China: Implications for SDG 6.3.2 Evaluation. Remote Sens Environ 2020, 247, 111950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.X.; Tuia, D.; Mou, L.; Xia, G.-S.; Zhang, L.; Xu, F.; Fraundorfer, F. Deep Learning in Remote Sensing: A Comprehensive Review and List of Resources. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Mag. 2017, 5, 8–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, I.; Shin, J.; Lee, H.; Park, S.; Nam, G.; Kang, T.; Cho, K.H.; Cha, Y. Deep Learning-Based Retrieval of Cyanobacteria Pigment in Inland Water for in-Situ and Airborne Hyperspectral Data. Ecological Indicators 2020, 110, 105879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheela, A.M.; Letha, J.; Joseph, S.; Ramachandran, K.K.; S. P., S. Trophic State Index of a Lake System Using IRS (P6-LISS III) Satellite Imagery. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 177, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham, S.D.; Chipman, J.W.; Lillesand, T.M.; Dodson, S.I. Alternate Stable States and the Shape of the Lake Trophic Distribution. Hydrobiologia 2006, 571, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A Trophic State Index for Lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megard, R.O.; Settles, J.C.; Boyer, H.A.; Combs, W.S. Light, Secchi Disks, and Trophic States. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1980, 25, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCullough, I.M.; Loftin, C.S.; Sader, S.A. Combining Lake and Watershed Characteristics with Landsat TM Data for Remote Estimation of Regional Lake Clarity. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 123, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baban, S.M.J. Detecting Water Quality Parameters in the Norfolk Broads, U.K., Using Landsat Imagery. Int J Remote Sens 1993, 14, 1247–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.C.; Greb, S.R.; Diebel, M.; Turner, M.G. Annual Precipitation Regulates Spatial and Temporal Drivers of Lake Water Clarity. Ecol Appl 2017, 27, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, S.A.C.; Soranno, P.A.; Cheruvelil, K.S.; Batzli, S.A.; Skole, D.L. Regional Assessment of Lake Water Clarity Using Satellite Remote Sensing. J Limnol 2003, 62, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayley, S.E.; Creed, I.F.; Sass, G.Z.; Wong, A.S. Frequent Regime Shifts in Trophic States in Shallow Lakes on the Boreal Plain: Alternative “Unstable” States? Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2002–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; De Leeuw, J.; Skidmore, A.K.; Prins, H.H.T.; Liu, Y. Comparison of MODIS and Landsat TM5 Images for Mapping Tempo–Spatial Dynamics of Secchi Disk Depths in Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Int J Remote Sens 2008, 29, 2183–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdin, J.P. Bureau of Reclamation Monitoring Water Quality Conditions in a Large Western Reservoir with Landsat Imagery (USA). Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 1985, 51, 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.L.; Knuteson, R.O.; Revercomb, H.E.; Feltz, W.; Howell, H.B.; Menzel, W.P.; Nalli, N.R.; Brown, O.; Brown, J.; Minnett, P.; et al. Observations of the Infrared Radiative Properties of the Ocean–Implications for the Measurement of Sea Surface Temperature via Satellite Remote Sensing. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society 1996, 77, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vesecky, J.F.; Onstott, R.G.; Wang, N.-Y.; Lettvin, E.; Slawski, J.; Shuchman, R.A. Water Surface Temperature Estimates Using Active and Passive Microwave Remote Sensing: Preliminary Results from an Outdoor Wind-Wave Tank. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of IGARSS ’94 - 1994 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium; IEEE: Pasadena, CA, USA, 1994; Vol. 2, pp. 1021–1023. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, N.-B.; Imen, S.; Vannah, B. Remote Sensing for Monitoring Surface Water Quality Status and Ecosystem State in Relation to the Nutrient Cycle: A 40-Year Perspective. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 2015, 45, 101–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haakstad, M.; Kogeler, J.W.; Dahle, S. Studies of Sea Surface Temperatures in Selected Northern Norwegian Fjords Using Landsat TM Data. Polar Res 1994, 13, 95–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgrien, D.W.; Brooks, A.S. Analysis of Thermal Features of Lake Michigan from AVHRR Satellite Images. J. Great Lakes Res. 1992, 18, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeDrew, E.; Franklin, S. The Use of Thermal Infrared Imagery in Surface Current Analysis of a Small Lake. Photogramm Eng Remote Sensing 1985, 51, 565–573. [Google Scholar]
- Crosman, E.T.; Horel, J.D. MODIS-Derived Surface Temperature of the Great Salt Lake. Remote Sens Environ 2009, 113, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, W.D.; Mann, K.H. Inland Water Ecosystem Available online:. Available online: https://www.britannica.com/science/inland-water-ecosystem/Permanent-bodies-of-standing-fresh-water (accessed on 29 August 2023).
- Martin, S. An Introduction to Remote Sensing; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- European Space Agency Esa’sWater Mission SMOS Available online: https://www.esa.int/Applications/Observing_the_Earth/FutureEO/SMOS.
- NASA Aquarius Yields NASA’s First Global Map of Ocean Salinity Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/aquarius/news/aquarius20110922.html.
- Boutin, J.; Martin, N. ARGO Upper Salinity Measurements: Perspectives for L-Band Radiometers Calibration and Retrieved Sea Surface Salinity Validation. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sensing Lett. 2006, 3, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topliss, B.J.; Gower, J.F.R.; Helbig, J.A.; Isenor, A.W. Sea Surface Salinity from Space: A Canadian Perspective; Fisheries and Oceans: Sarnia, ON, Canada, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Elachi, C.; Van Zyl, J.J. Introduction to the Physics and Techniques of Remote Sensing; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Vol. 28. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, M. Oceanographic Applications of Remote Sensing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995; ISBN 0-8493-4525-1. [Google Scholar]
- Klein, L.; Swift, C.T. An Improved Model for the Dielectric Constant of Sea Water at Microwave Frequencies. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 1977, 25, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagerloef, G.; Swift, C.; Le Vine, D. Sea Surface Salinity: The next Remote Sensing Challenge. oceanog 1995, 8, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, C.; Behringer, D. Using Satellite-Derived Sea Level and Temperature Profiles for Determining the Salinity Variability: A New Approach. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2000, 105, 8537–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, C.T. Passive Microwave Remote Sensing of the Ocean—A Review. Boundary Layer Meteorol 1980, 18, 25–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Pan, D.; Cai, W.-J.; He, X.; Wang, D.; Tao, B.; Zhu, Q. Remote Sensing of Salinity from Satellite-Derived CDOM in the Changjiang River Dominated East China Sea. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, Z.; Clayton, T.D.; Swarzenski, P.; Brock, J.C.; Muller–Karger, F.E. Assessment of Estuarine Water-Quality Indicators Using MODIS Medium-Resolution Bands: Initial Results from Tampa Bay, FL. Remote Sens Environ 2004, 93, 423–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United States Environmental Protection Agency Conductivity Available online:. Available online: https://archive.epa.gov/water/archive/web/html/vms59.html (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Miller, R.L.; Bradford, W.L.; Peters, N.E. Specific Conductance: Theoretical Considerations and Application to Analytical Quality Control; 1988.
- Hayashi, M.; Vogt, T.; Mächler, L.; Schirmer, M. Diurnal Fluctuations of Electrical Conductivity in a Pre-Alpine River: Effects of Photosynthesis and Groundwater Exchange. J. Hydrol. 2012, 450–451, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr, S.U.; Van der Zande, D.; Staehr, P.A.U.; Markager, S. Suitability of Multisensory Satellites for Long-Term Chlorophyll Assessment in Coastal Waters: A Case Study in Optically-Complex Waters of the Temperate Region. Ecological Indicators 2022, 134, 108479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Holbach, A.; Wilhelms, A.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zou, H.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Norra, S. Highly Time-Resolved Analysis of Seasonal Water Dynamics and Algal Kinetics Based on in-Situ Multi-Sensor-System Monitoring Data in Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.G. Detection of Optical Water Quality Parameters for Eutrophic Waters by High Resolution Remote Sensing. PhD Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, X.; Tian, L.; Huang, J.; Feng, L. Improved Capabilities of the Chinese High-Resolution Remote Sensing Satellite GF-1 for Monitoring Suspended Particulate Matter (SPM) in Inland Waters: Radiometric and Spatial Considerations. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppelt, N.; Scheiber, R.; Gege, P.; Wegmann, M.; Taubenböck, H.; Berger, M. Fundamentals of Remote Sensing for Terrestrial Applications: Evolution, Current State-of-the-Art and Future Possibilities. In Remotely Sensed Data Characterization, Classification, and Accuracies; Thenkabail, P.S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; p. 24. ISBN 978-0-429-08939-8. [Google Scholar]
- Pyo, J.; Ligaray, M.; Kwon, Y.; Ahn, M.-H.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.; Kang, T.; Cho, S.; Park, Y.; Cho, K. High-Spatial Resolution Monitoring of Phycocyanin and Chlorophyll-a Using Airborne Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wass, P.D.; Marks, S.D.; Finch, J.W.; Leeks, G.J.L.; Ingram, J.K. Monitoring and Preliminary Interpretation of In-River Turbidity and Remote Sensed Imagery for Suspended Sediment Transport Studies in the Humber Catchment. Sci. Total Environ. 1997, 194–195, 263–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.; Duan, H.; Baek, S.; Kim, M.S.; Jeon, T.; Kwon, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Cho, K.H. A Convolutional Neural Network Regression for Quantifying Cyanobacteria Using Hyperspectral Imagery. Remote Sens Environ 2019, 233, 111350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Li, J. Can MODIS Land Reflectance Products Be Used for Estuarine and Inland Waters? Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 3583–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byfield, V. Optical Remote Sensing of Marine, Coastal, and Inland Waters. In Handbook of Optoelectronics; Applied Optical Electronics; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017; p. Vol. 3, pp. 103–114. ISBN 978-1-315-10361-7. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Pulliainen, J.T.; Koponen, S.S.; Hallikainen, M.T. Water Quality Retrievals from Combined Landsat TM Data and ERS-2 SAR Data in the Gulf of Finland. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linchant, J.; Lisein, J.; Semeki, J.; Lejeune, P.; Vermeulen, C. Are Unmanned Aircraft Systems (UASs) the Future of Wildlife Monitoring? A Review of Accomplishments and Challenges. Mamm Rev 2015, 45, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.; Gaston, K.J. Lightweight Unmanned Aerial Vehicles Will Revolutionize Spatial Ecology. Front Ecol Environ 2013, 11, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Xia, K.; Huang, X.; Feng, H.; Yang, Y.; Du, X.; Huang, L. Evaluation of Water Quality Based on UAV Images and the IMP-MPP Algorithm. Ecol Inform 2021, 61, 101239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.H.; Chan, S.N.; Lee, J.H.W. Remote Sensing of Coastal Algal Blooms Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 152, 110889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcilwaine, B.; Rivas Casado, M.; Leinster, P. Using 1st Derivative Reflectance Signatures within a Remote Sensing Framework to Identify Macroalgae in Marine Environments. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, A.C.; Ambrosia, V.G.; Hinkley, E.A. Unmanned Aircraft Systems in Remote Sensing and Scientific Research: Classification and Considerations of Use. Remote Sens. 2012, 4, 1671–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.-B.; Vannah, B.W.; Yang, Y.J.; Elovitz, M. Integrated Data Fusion and Mining Techniques for Monitoring Total Organic Carbon Concentrations in a Lake. Int J Remote Sens 2014, 35, 1064–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Helmer, E.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, D.; Chen, J.; Lefsky, M.A. A Flexible Spatiotemporal Method for Fusing Satellite Images with Different Resolutions. Remote Sens Environ 2016, 172, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Atkinson, P.M. Spatio-Temporal Fusion for Daily Sentinel-2 Images. Remote Sens Environ 2018, 204, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, B.P.; Olmanson, L.G.; Mishra, D.R. A Harmonized Image Processing Workflow Using Sentinel-2/MSI and Landsat-8/OLI for Mapping Water Clarity in Optically Variable Lake Systems. Remote Sens Environ 2019, 231, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.T.; Sagan, V.; Sloan, J.J. Deep Learning-Based Water Quality Estimation and Anomaly Detection Using Landsat-8/Sentinel-2 Virtual Constellation and Cloud Computing. GIsci Remote Sens 2020, 57, 510–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Masek, J.; Schwaller, M.; Hall, F. On the Blending of the Landsat and MODIS Surface Reflectance: Predicting Daily Landsat Surface Reflectance. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2207–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Göttsche, F.-M. Integrated Fusion of Multi-Scale Polar-Orbiting and Geostationary Satellite Observations for the Mapping of High Spatial and Temporal Resolution Land Surface Temperature. Remote Sens Environ 2015, 156, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvestro, F.B. Remote Sensing Analysis of Water Quality. J Water Pollut Control Fed 1970, 42, 553–561. [Google Scholar]
- Barnes, B.B.; Hu, C.; Bailey, S.W.; Pahlevan, N.; Franz, B.A. Cross-Calibration of MODIS and VIIRS Long near Infrared Bands for Ocean Color Science and Applications. Remote Sens Environ 2021, 260, 112439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, C.; Braga, F.; Zaggia, L.; Brando, V.E.; Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Bassani, C. Spatio-Temporal Analysis of Prodelta Dynamics by Means of New Satellite Generation: The Case of Po River by Landsat-8 Data. Int J Appl Earth Obs Geoinf 2018, 66, 210–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Qin, B. Monitoring Water Quality Using Proximal Remote Sensing Technology. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, H.; Ma, R.; Hu, C. Evaluation of Remote Sensing Algorithms for Cyanobacterial Pigment Retrievals during Spring Bloom Formation in Several Lakes of East China. Remote Sens Environ 2012, 126, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- I.O.C.C.G. Atmospheric Correction for Remotely-Sensed Ocean-Colour Products. In Reports of the International Ocean Colour Coordinating Group; Wang, M., Ed.; Dartmouth, NS, Canada, 2010.
- Wendel, A.; Underwood, J. Illumination Compensation in Ground Based Hyperspectral Imaging. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2017, 129, 162–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schläpfer, D.; Richter, R. Geo-Atmospheric Processing of Airborne Imaging Spectrometry Data. Part 1: Parametric Orthorectification. Int J Remote Sens 2002, 23, 2609–2630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, F.; Schläpfer, D.; Nieke, J.; Itten, K. Sensor Performance Requirements for the Retrieval of Atmospheric Aerosols by Airborne Optical Remote Sensing. Sensors 2008, 8, 1901–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cillero Castro, C.; Domínguez Gómez, J.A.; Delgado Martín, J.; Hinojo Sánchez, B.A.; Cereijo Arango, J.L.; Cheda Tuya, F.A.; Díaz-Varela, R. An UAV and Satellite Multispectral Data Approach to Monitor Water Quality in Small Reservoirs. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostater, C.R.Jr.; Ghir, T.; Bassetti, L.; Hall, C.; Reyeier, E.; Lowers, R.; Holloway-Adkins, K.; Virnstein, R. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Protocol Development for Submerged Aquatic Vegetation in Shallow Waters. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the SPIE—The International Society for Optical Engineering; Bostater, C.R.Jr., Santoleri, R., Eds.; SPIE: Barcelona, Spain, February 26 2004; Vol. 5233, pp. 199–215.
- O’Neill, J.D.; Costa, M. Mapping Eelgrass (Zostera Marina) in the Gulf Islands National Park Reserve of Canada Using High Spatial Resolution Satellite and Airborne Imagery. Remote Sens Environ 2013, 133, 152–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.; Hedley, J.; Lavender, S. Sun Glint Correction of High and Low Spatial Resolution Images of Aquatic Scenes: A Review of Methods for Visible and near-Infrared Wavelengths. Remote Sens. 2009, 1, 697–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, J.E.; Bright, E.A.; Ferguson, R.L.; Field, D.W.; Wood, L.L.; Haddad, K.D.; Iredale, H., III; Jensen, J.R.; Klemas, V.V.; Orth, R.J.; et al. NOAA Coastal Change Analysis Program (C-Cap): Guidance for Regional Implementation; NOAA: Washington, DC, USA, 1995; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Rowan, G.S.L.; Kalacska, M. A Review of Remote Sensing of Submerged Aquatic Vegetation for Non-Specialists. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyzenga, D.R. Passive Remote Sensing Techniques for Mapping Water Depth and Bottom Features. Appl. Opt. 1978, 17, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
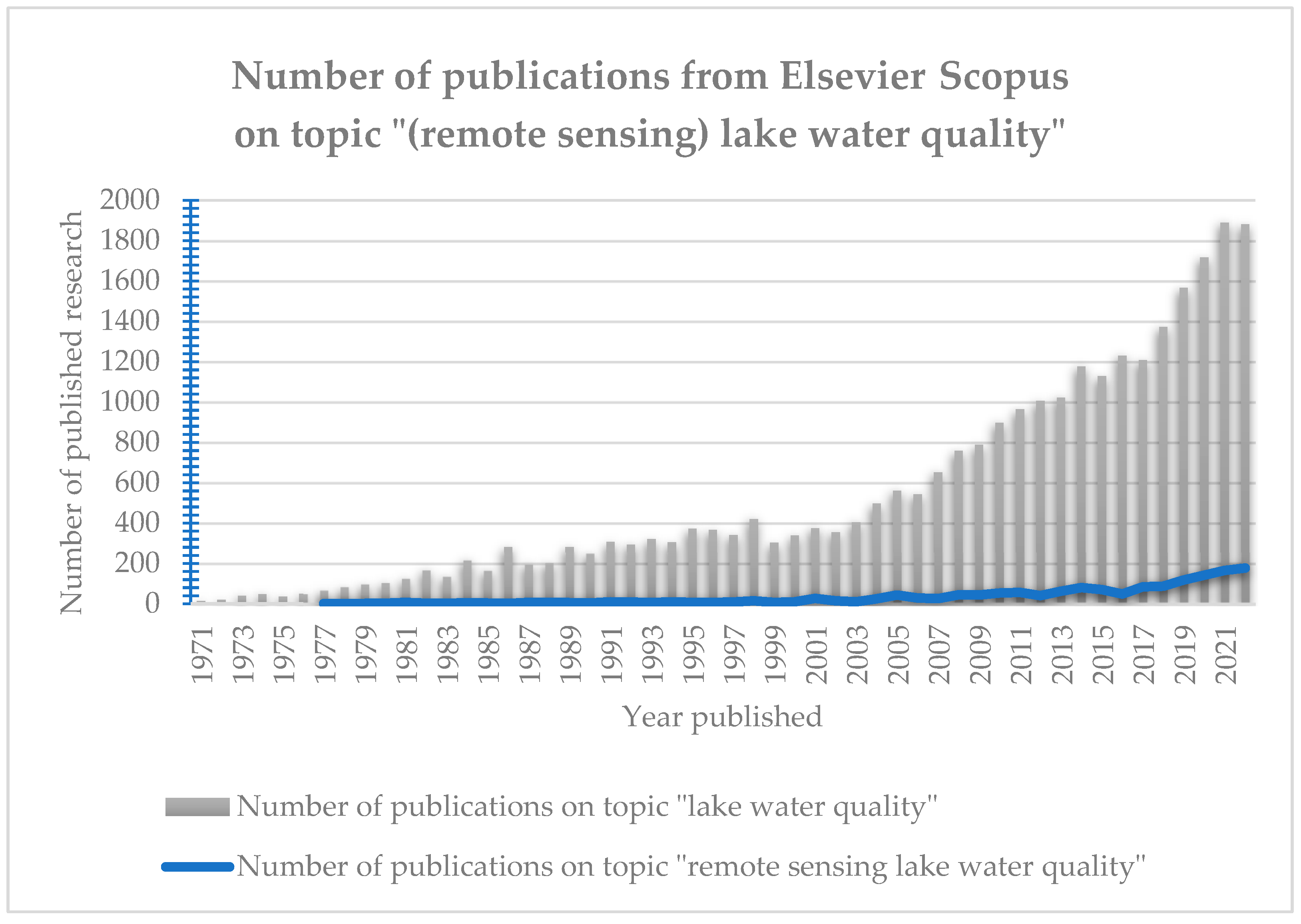
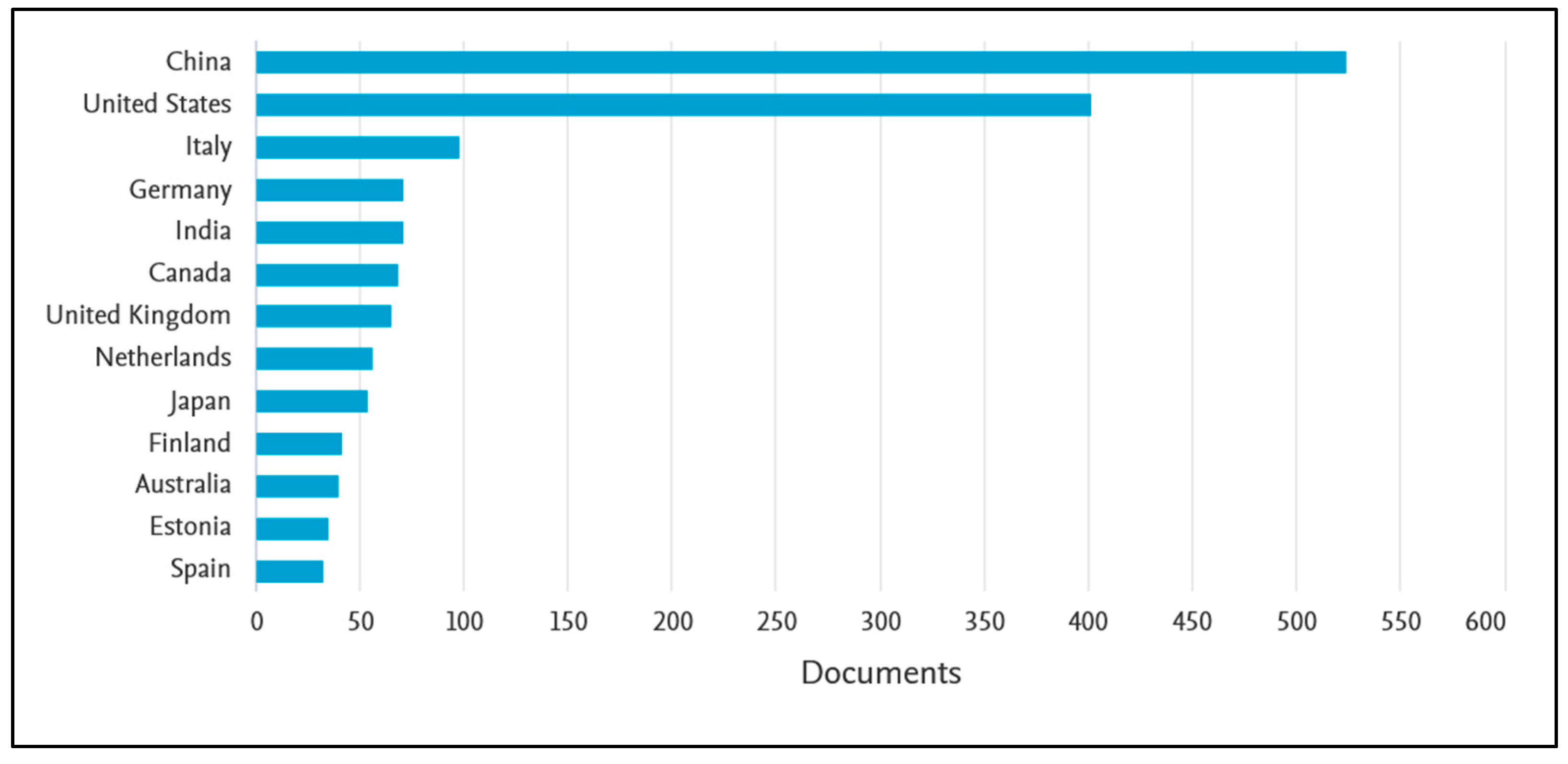
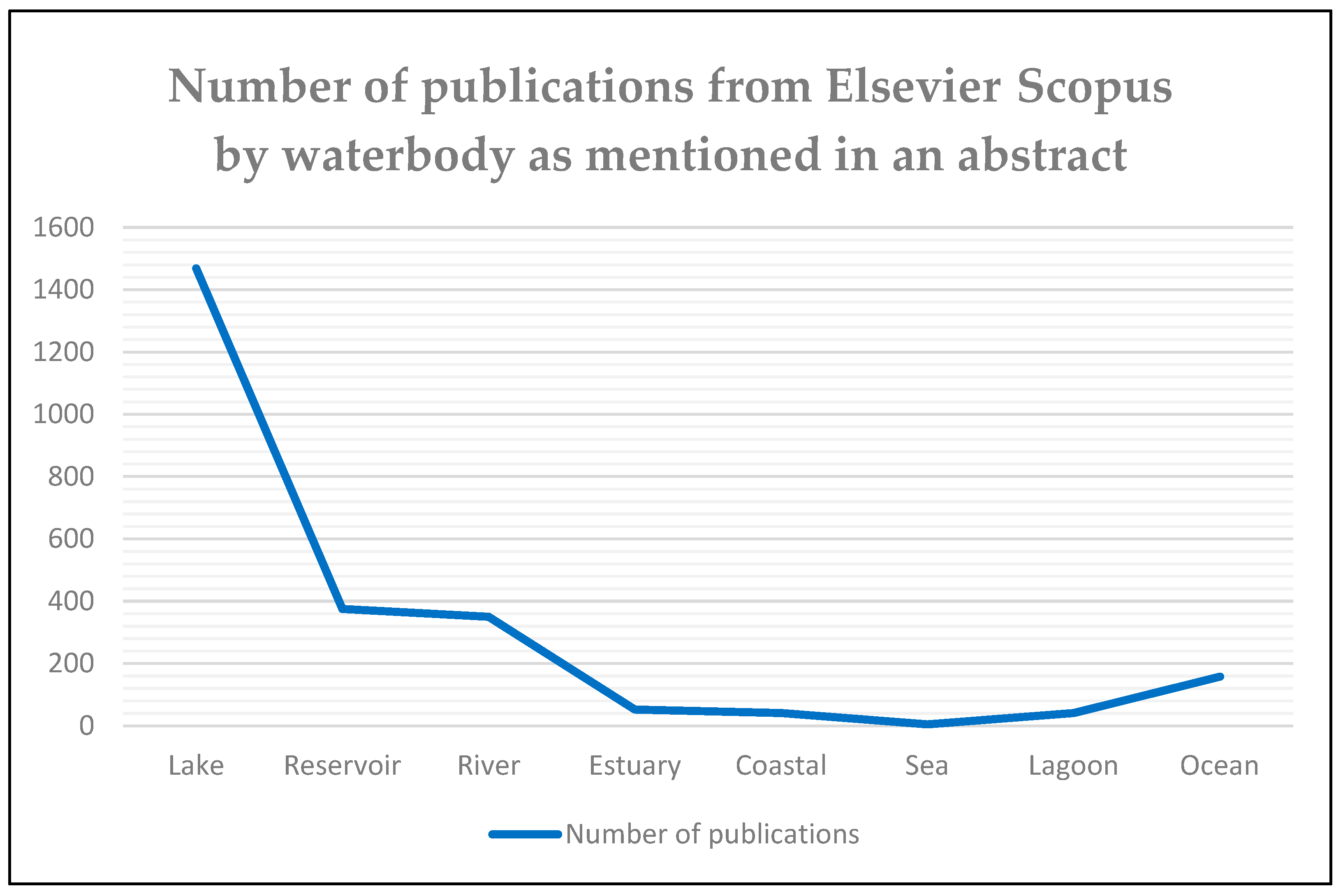
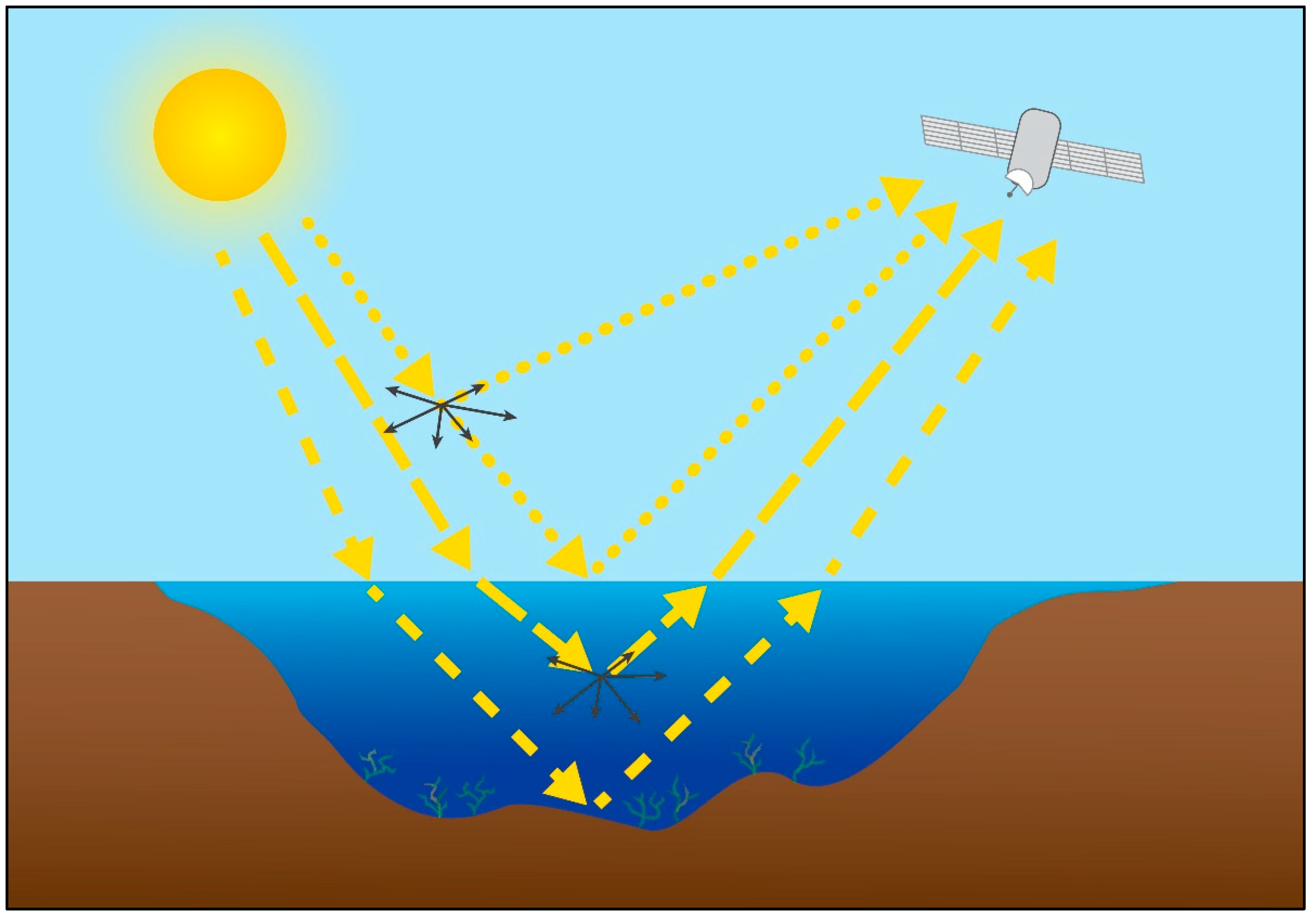
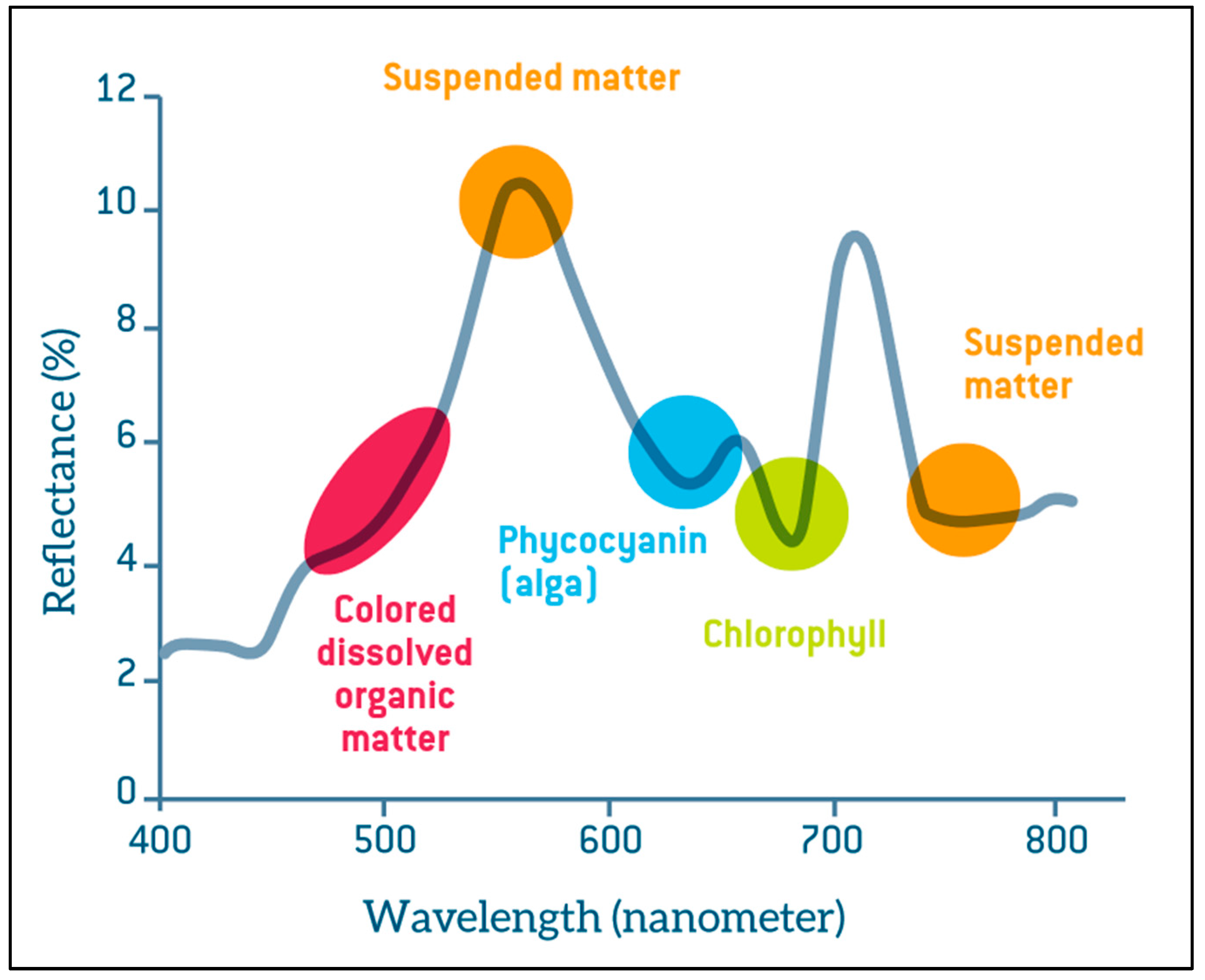
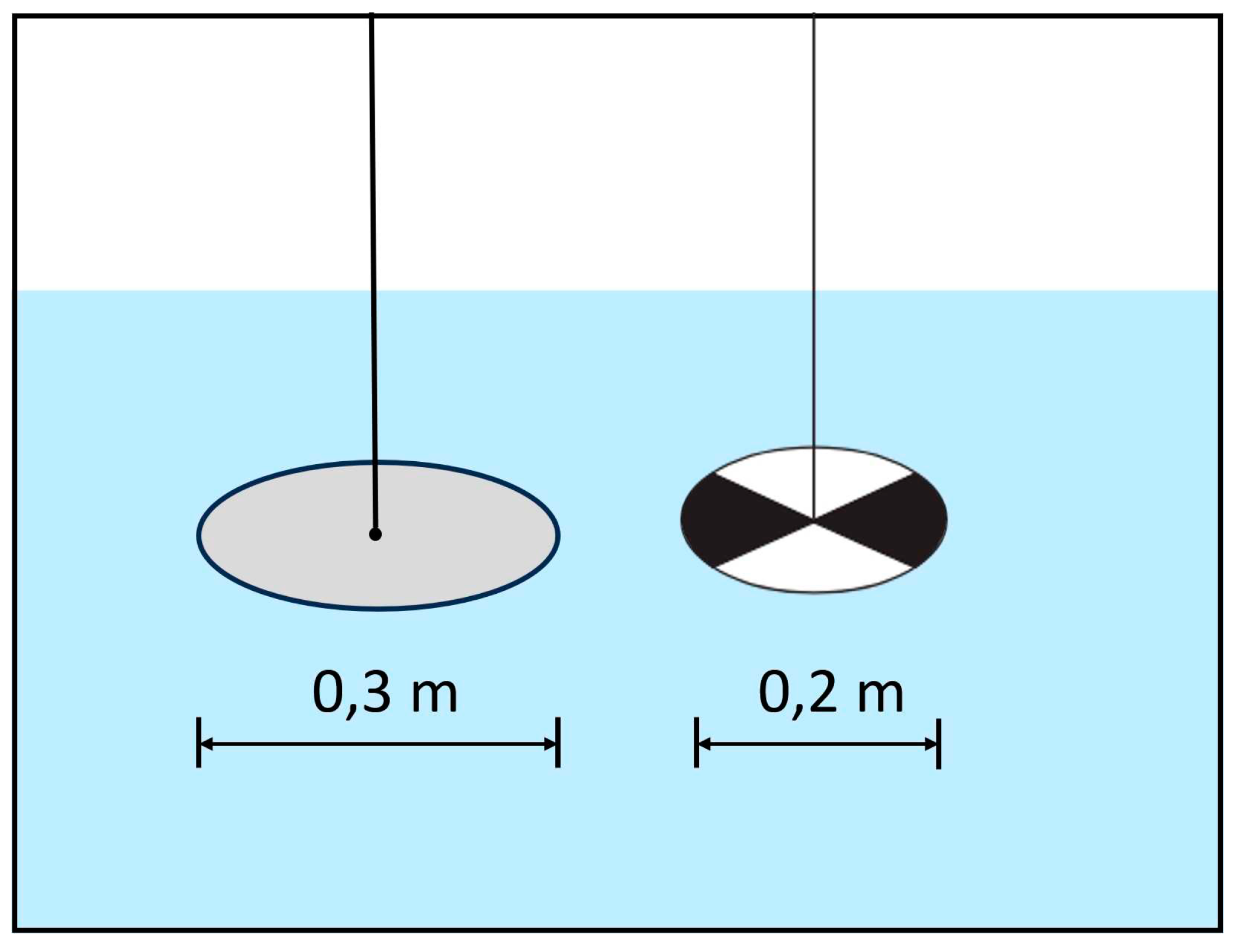
| Water Quality Parameter | Abbreviation | Units | Optical Activity | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll-α | chl-α | mg/L | Active | Biological |
| Transparency (Secchi Disk Depth) | SDD | m | Active | Physical |
| Colored Dissolved Organic Matters | CDOM | mg/L | Active | Physical |
| Electrical Conductivity | EC | µS/cm | Active | Physical |
| Turbidity | TUR | NTU | Active | Physical |
| Surface Salinity | SS | PSU | Active | Physical |
| Total Suspended Matters | TSM | mg/L | Active | Physical |
| Water temperature | WT | °C | Active | Physical |
| pH | pH | - | Active | Chemical |
| Total Organic Carbon | TOC | mg/L | Active | Chemical |
| Dissolved Oxygen | DO | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
| Chemical Oxygen Demand | COD | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
| Biochemical Oxygen Demand | BOD | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
| Total Nitrogen | TN | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
| Ammonia Nitrogen | NH3-N | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
| Total Phosphorus | TP | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
| Orthophosphate | PO4 | mg/L | Inactive | Chemical |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




