Submitted:
05 September 2023
Posted:
07 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. AgNPs Suspension Preparation
2.3. İnvitro Establishment of Cultures
2.4. Growth Parameters
2.5. Physiological Parameters
2.6. Biochemical Parameters
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
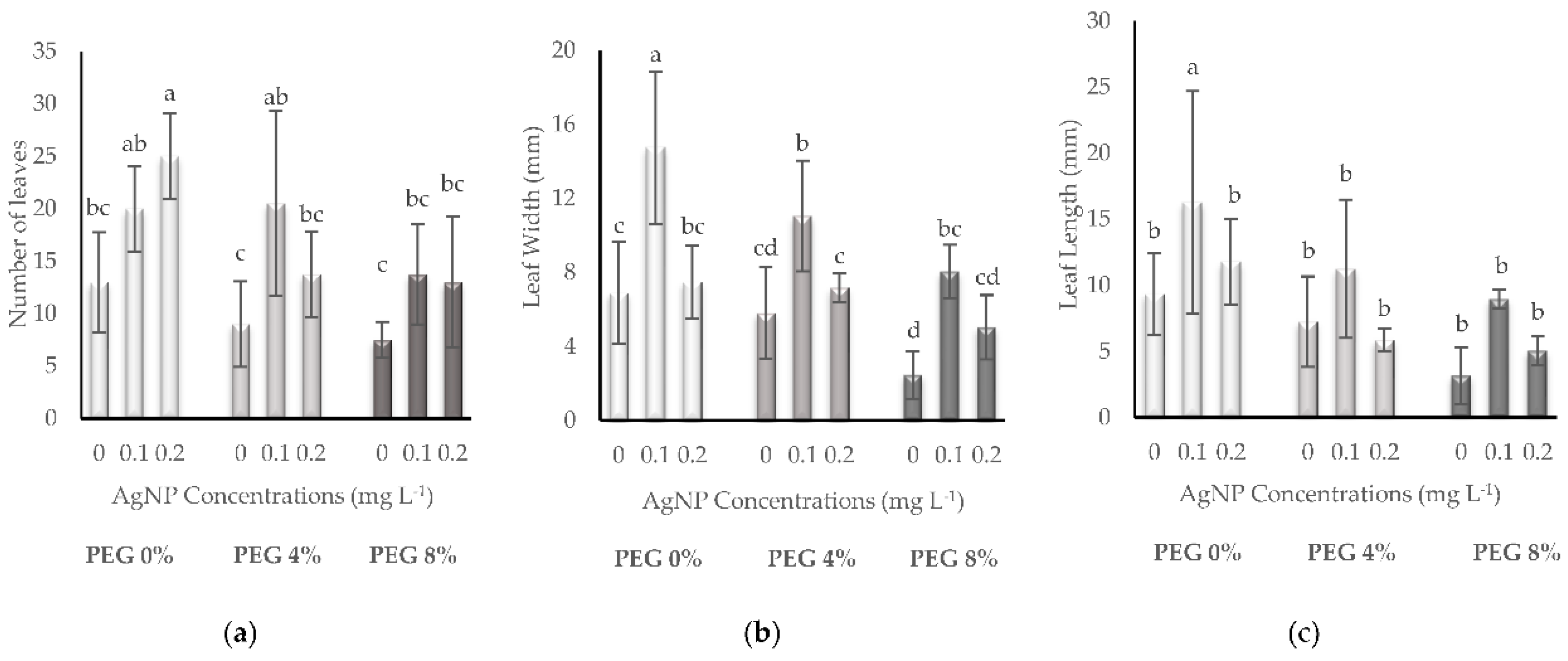
3.1. Growth Parameters
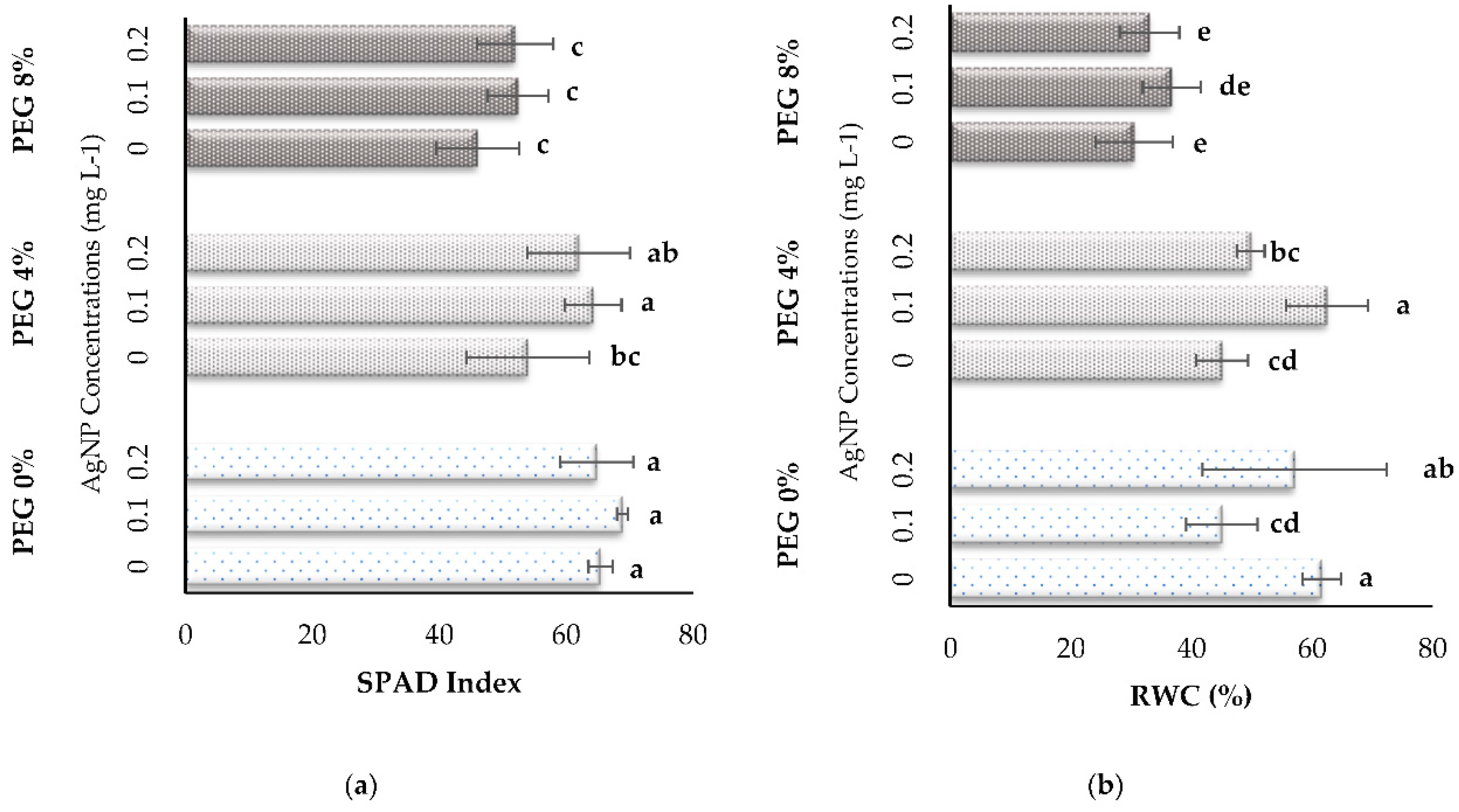
3.2. Physiological Parameters
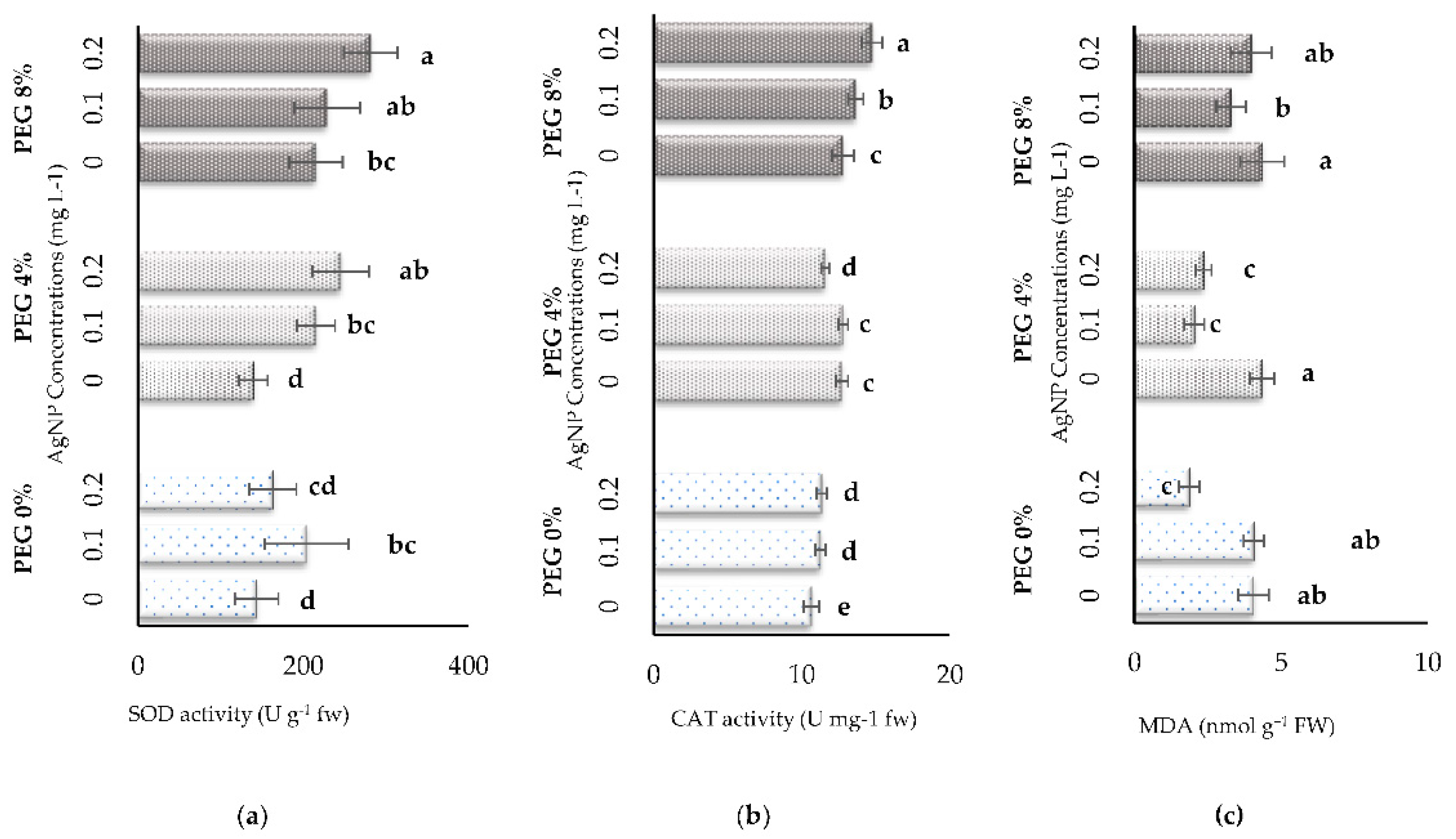
3.3. Biochemical Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolarević, T.; Milinčić, D.D.; Vujović, T.; Gašić, U.M.; Prokić, L.; Kostić, A.Ž.; Cerović, R.; Stanojevic, S.P.; Tešić, Ž.L.; Pešić, M.B. Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Properties of Field-Grown and In vitro Leaves, and Calluses in Blackberry and Blueberry. Horticulturae 2021, 7, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconeasa, Z.; Iuhas, C.I.; Ayvaz, H.; Rugină, D.; Stanilă, A.; Dulf, F.; Bunea, A.; Socaci, S.A.; Socaciu, C.; Pintea, A. Phytochemical characterization of commercial processed blueberry, blackberry, blackcurrant, cranberry, and raspberry and their antioxidant activity. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dewir, Y.H.; Al-Ali, A.M.; Rihan, H.Z.; Alshahrani, T.; Alwahibi, M.S.; Almutairi, K.F.; Naidoo, Y.; Fuller, M.P. Effects of Artificial Light Spectra and Sucrose on the Leaf Pigments, Growth, and Rooting of Blackberry (Rubus fruticosus) Microshoots. Agronomy 2023, 13, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paczkowska-Walendowska, M.; Gościniak, A.; Szymanowska, D.; Szwajgier, D.; Baranowska-Wójcik, E.; Szulc, P.; Dreczka, D.; Simon, M.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. Blackberry Leaves as New Functional Food? Screening Antioxidant, Anti-Inflammatory and Microbiological Activities in Correlation with Phytochemical Analysis. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, V.R.; Pereira, P.A.; da Silva, T.L.; de Oliveira Lima, L.C.; Pio, R.; Queiroz, F. Determination of the bioactive compounds, antioxidant activity and chemical composition of Brazilian blackberry, red raspberry, strawberry, blueberry and sweet cherry fruits. Food Chem. 2014, 156, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlemi, A.V.; Lamari, F.N. Berry leaves: An alternative source of bioactive natural products of nutritional and medicinal value. Antioxidants 2016, 5, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalefetoğlu, T.; Ekmekçi, Y. The effects of drought on plants and tolerance mechanisms. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. 2005, 18, 723–740.10. [Google Scholar]
- Sade, B.; Soylu, S.; Yetim, E. Drought and oxidative stress. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 11102–11109. [Google Scholar]
- Oguz, M.C.; Aycan, M.; Oguz, E.; Poyraz, I.; Yildiz, M. Drought stress tolerance in plants: Interplay of molecular, biochemical and physiological responses in important development stages. Physiologia 2022, 2, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, K.; Muneer, S. Drought Stress-Induced Physiological Mechanisms, Signaling Pathways and Molecular Response of Chloroplasts in Common Vegetable Crops. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2021, 41, 669–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marthandan, V.; Geetha, R.; Kumutha, K.; Renganathan, V.G.; Karthikeyan, A.; Ramalingam, J. Seed Priming: A Feasible Strategy to Enhance Drought Tolerance in Crop Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gelaw, T.A.; Sanan-Mishra, N. Non-coding RNAs in response to drought stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritts, M.P.; Langhans, R.W.; Whitlow, T.H.; Kelly, M.J.; Roberts, A. Winter raspberry production in greenhouses. Hort Technology 1999, 9, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGhie, T.K.; Hall, H.K.; Ainge, G.D.; Mowat, A.D. Breeding Rubus cultivars for high anthocyanin content and high antioxidant capacity. Acta Hortic. 2002, 585, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, S.; Duran, C.N. The effect of mycorrhiza applications and different irrigation regimes on growth and development characteristics of blackberry cuttings. Turkish J. Agric. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 8, 638–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, W.; Li, W.; Lyu, L. Drought-induced oxidative damage and antioxidant responses in blackberry cultivar ‘Hull Thornless’. Pak. J. Agric. Res 2019, 33, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlikowska, T.; Kucharska, D.; Horbowicz, M. The reaction of raspberry and blackberry cultivars to drought stress simulated in vitro by polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000. Acta Hortic. 2009, 839, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dascălu, M.; Istrate, M.; Grădinariu, G.; Zlati, C.; Bernardis, R.; Prodan, N.D.; Sfichi-Duke, L. Soil moisture study and its influences on blackberry culture for North East Moldova County. Lucrări Științifice, Universitatea de Științe Agricole Și Medicină Veterinară" Ion Ionescu de la Brad" Iași, Seria Horticultură 2013, 56, 185–188. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, H.; Wu, W.; Li, W. Effect of drought stress on physiological changes and leaf surface morphology in the blackberry. Braz. J. Bot. 2017, 40, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Wu, W.L.; Lyu, L.F. Influence of drought stress on the leaf morphology and physiological characteristics in blackberry (Rubus L.) seedlings. In XXX International Horticultural Congress IHC2018: III International Berry Fruit Symposium, İstanbul, Turkey, 2018 (12-16 August 2018).
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, W.; Li, W.; Wei, Y.; Dong, S. Physiological responses of blackberry cultivar ‘Ningzhi 1’ to drought stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 62, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Qiu, L.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Yan, D.; Zheng, B. Spermidine induces physiological and biochemical changes in southern highbush blueberry under drought stress. Braz. J. Bot. 2017, 40, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, S.M.; Hosseini, M.S.; Daneshvar Hakimi Meybodi, N.; Peijnenburg, W. Mitigation of the Effect of Drought on Growth and Yield of Pomegranates by Foliar Spraying of Different Sizes of Selenium Nanoparticles. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mozafari, A.A.; Havas, F.; Ghaderi, N. Application of iron nanoparticles and salicylic acid in in vitro culture of strawberries (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) to cope with drought stress. Plant. Cell, Tissue Organ. Cult. (PCTOC) 2018, 132, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohan-Baghkheirati, E.; Geisler-Lee, J. Gene expression, protein function and pathways of Arabidopsis thaliana responding to silver nanoparticles in comparison to silver ions, cold, salt, drought, and heat. Nanomaterials 2015, 5, 436–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Bhatt, D.; Zaidi, M.G.H.; Saradhi, P.P.; Khanna, P.K.; Arora, S. Silver nanoparticle-mediated enhancement in growth and antioxidant status of Brassica juncea. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2012, 167, 2225–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengottaiyan, A.; Mythili, R.; Selvankumar, T.; Aravinthan, A.; Kamala-Kannan, S.; Manoharan, K.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Govarthanan, M.; Kim, J.-H. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Solanum indicum L. and their antibacterial, splenocyte cytotoxic potentials. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 3095–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, H.M. Effects of silver nanoparticles in some crop plants, common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and corn (Zea mays L.). Int. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2012, 3, 190–197. [Google Scholar]
- Kaveh, R.; Li, Y.-S.; Ranjbar, S.; Tehrani, R.; Brueck, C.L.; Van Aken, B. Changes in Arabidopsis thaliana Gene Expression in Response to Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10637–10644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannini, C.; Domingo, G.; Onelli, E.; Prinsi, B.; Marsoni, M.; Espen, L.; Bracale, M. Morphological and proteomic responses of Eruca sativa exposed to silver nanoparticles or silver nitrate. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, M.; Naghdi Badi, H.; Ghorbanpour, M. Nano-elicitation of secondary pharmaceutical metabolites in plant cells: A review. J. Med. Plants 2019, 18, 6–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, F.; Javed, B.; Razzaq, A.; Mashwani, Z.U.R. Applications of copper and silver nanoparticles on wheat plants to induce drought tolerance and increase yield. IET Nanobiotechnology 2021, 15, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, M.; Saleem, M.F.; Ullah, N.; Khan, M.J.; Maqsood, H.; Ahmad, H.; Tanveer, A.; Shahid, M. Silver nanoparticles protect tillering in drought-stressed wheat by improving leaf water relations and physiological functioning. Funct. Plant Biol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabdallah, N.M.; Hasan, M.M.; Salih, A.M.; Roushdy, S.S.; Al-Shammari, A.S.; Alsanie, S.I.; El-Zaidy, M. Silver nanoparticles improve growth and protect against oxidative damage in eggplant seedlings under drought stress. Plant Soil Environ. 2021, 67, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavam, M. Effect of silver nanoparticles on tolerance to drought stress in Thymus daenensis Celak and Thymus vulgaris L. in germination and early growth stages. Environ. Stress. Crop. Sci. 2019, 12, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Akhoundnejad, Y.; Karakas, O.; Demirci, O. Response of Lettuce to Silver Nanoparticles Under Drought Conditions. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. A Sci. 2022, 46, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjat, S.S.; Ganjali, A. The effect of silver nanoparticle on lentil seed germination under drought stress. Int. J. Farm. Allied Sci. 2016, 5, 208–212. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, G.A.; Andersen, M.T.; Forster, R.L.S.; Braithwaite, M.; Hall, H.K. History of Boysenberry and Youngberry in New Zealand in relation to their problems with Boysenberry decline, the association of a fungal pathogen, and possibly a phytoplasma, with this disease. N. Zldn. J. Crop. Hortic. Sci. 1999, 27, 281–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Colman, B.P.; McGill, B.M.; Wright, J.P.; Bernhardt, E.S. Effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on germination and early growth of eleven wetland plants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şener, S.; Kurt, Z. The effects of Benzyl Amino Purine (BAP) and Indole Butyric Acid (IBA) on in vitro shoot proliferation and rooting of Boysenberry. COMU J. of Agr. F. 2022, 10, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, F.J.; de Andrés, E.F.; Tenorio, J.L.; Ayerbe, L. Growth of epicotyls, turgor maintenance and osmotic adjustment in pea plants (Pisum sativum L.) subjected to water stress. Field Crop. Res. 2004, 86, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakmak, I. Activity of ascorbate-dependent H2O2-scavenging enzymes and leaf chlorosis are enhanced in magnesium-and potassium-deficient leaves, but not in phosphorus-deficient leaves. J. Exp. Bot. 1994, 45, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oğuz, İ.; Oğuz, H.İ.; Kafkas, N.E. Strawberry cultivation techniques. In Recent Studies on Strawberries, 1st ed.; Editor N.E. Kafkas, IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022; pp. 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Şener, S. Abiotic stress factors and strawberry cultivation. Impact of Climate Change on Agriculture, 1. ed.; Akçal, A.; Çamoğlu G.; Tan, S.; Holistence Publications, Çanakkale, Turkey, 2021; pp.111-125.
- Debnath, S.C.; Goyali, J.C. In Vitro Propagation and Variation of Antioxidant Properties in Micropropagated Vaccinium Berry Plants—A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayğı, H. Adverse effects of climate Change on agriculture: An evaluation of fruit and honey bee farming. Asian J. Agric. Rural Dev. 2020, 10, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, S.; Clapa, D.; Mitre, V. Response of the Five Highbush Blueberry Cultivars to In Vitro Induced Drought Stress by Polyethylene Glycol. Agronomy 2022, 12, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurek, M.; Siekierzyńska, A.; Jacek, B.; Litwińczuk, W. Differences in response to drought stress among highbush blueberry plants propagated conventionally and by tissue culture. Plant Biosyst. 2021, 155, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, E.A.; El-Kerdany, A.Y.; Afifi, M.K. Effect of drought and salinity stresses on two strawberry cultivars during their regeneration in vitro. Int. J. Innov. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2017, 4, 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, V.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, A.; Mishra, A.; Rawat, S.; Shami, V.; Kaushik, P. Response of Wheat Genotypes to Drought Stress Stimulated by PEG. Stresses 2022, 2, 26–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajput, V.D.; Minkina, T.; Kumari, A.; Harish; Singh, V. K.; Verma, K.K.; Mandzhieva, S.; Sushkova, S.; Srivastava, S.; Keswani, C. Coping with the challenges of abiotic stress in plants: New dimensions in the field application of nanoparticles. Plants 2021, 10, 1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Tiwari, S.; Pandey, J.; Lata, C.; Singh, I.K. Role of nanoparticles in crop improvement and abiotic stress management. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 337, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faizan, M.; Yu, F.; Chen, C.; Faraz, A.; Hayat, S. Zinc oxide nanoparticles help to enhance plant growth and alleviate abiotic stress: A review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2020, 22, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.V.; Nguyen, H.M.; Le, N.T.; Nguyen, K.H.; Le, H.M.; Nguyen, A.T.; Dinh, N.T.T.; Hoang, S.A.; Ha, C.V. Copper Nanoparticle Application Enhances Plant Growth and Grain Yield in Maize under Drought Stress Conditions. Plant Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Alabdallah, N.M.; Hasan, M.; Hammami, I.; Alghamdi, A.I.; Alshehri, D.; Alatawi, H.A. Green synthesized metal oxide nanoparticles mediate growth regulation and physiology of crop plants under drought stress. Plants 2021, 10, 1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna; Ali, B. ; Azeem, M.A.; Qayyum, A., Mustafa, G., Ahmad, M.A., Javed, M.T., Eds.; Chaudhary, H.J. Bio-Fabricated Silver Nanoparticles: A Sustainable Approach for Augmentation of Plant Growth and Pathogen Control. In Sustainable Agriculture Reviews 53; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 345–371. [Google Scholar]
- Mahendran, D.; Geetha, N.; Venkatachalam, P. Role of silver nitrate and silver nano-particles on tissue culture medium and enhanced the plant growth and development. In Vitro Plant Breeding towards Novel Agronomic Traits: Biotic and Abiotic Stress Tolerance; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 59–74. ISBN 9789813298248. [Google Scholar]
- Jasim, B.; Thomas, R.; Mathew, J.; Radhakrishnan, E.K. Plant growth and diosgenin enhancement effect of silver nanoparticles in Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.). Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, H.T.; Thuong, T.T.; Cuong, D.M.; Luan, V.Q.; Hien, V.T.; Hieu, T.; Nam, N.B.; Phuong, H.T.N.; Van The Vinh, B.; Khai, H.D.; et al. Silver nanoparticles improved explant disinfection, in vitro growth, runner formation and limited ethylene accumulation during micropropagation of strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2021, 145, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezvani, N.; Sorooshzadeh, A.; Farhadi, N. Effect of nano-silver on growth of saffron in flooding stress. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2012, 6, 11–16. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.X.; Zhu, D.; Asghar, S. Response of strawberry cv. Toyonokain vitro to silver nitrate (AgNO3). Hortscience 2005, 40, 747–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentini, Z.; Mussell, H.; Mutschler, M.A.; Earle, E.D. Ethylene generation and reversal of ethylene effects during development in vitro of rapid-cycling Brassica campestris L. Plant Sci. 1988, 54, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roustan, J.P.; Latché, A.; Fallot, J. Inhibition of ethylene production and stimulation of carrot somatic embryogenesis by salicylic acid. Biol. Plant 1990, 32, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojjat, S.S.; Hojjat, H. Effect of Nano Silver on Seed Germination and Seedling Growth in Fenugreek Seed. ETP Int. J. Food Eng. 2015, 1, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharon, M.; Choudhary, A.K.; Kumar, R. Nanotechnology in a Gricultural Diseases and food safety. J. Phytol. 2010, 2, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zarei, S.; Ehsanpour, A.A. Ethylene inhibition with silver nitrate (AgNO3) and pyrazinamide (PZA) ameliorates in vitro salt tolerance of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L) plantlets. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC) 2023, 154, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Ali, S.; Jan, S.A.; Din, J.; Ali, G.M. Assessment of Silver Nitrate on Callus Induction and in Vitro Shoot Regeneration in Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum Mill.). Pak. J. Bot. 2014, 46, 2163–2172. [Google Scholar]
- Mohiuddin, A.; Chowdhury, M.; Abdullah, Z.C.; Napis, S. Influence of silver nitrate (ethylene inhibitor) on cucumber in vitro shoot regeneration. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1997, 51, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasaya, A.; Yasir, T.A.; Sarwar, N.; Farooq, O.; Sheikh, G.R.; Baloch, A.W. Improving growth and yield of mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) through foliar application of silver and zinc nanoparticles. Pure and Applied Biology (PAB) 2020, 9, 790–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejatzadeh-Barandozi, F.; Darvishzadeh, F.; Aminkhani, A. Effect of nano silver and silver nitrate on seed yield of (Ocimum basilicum L.). Org. Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 4, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnaraj, C.; Jagan, E.G.; Ramachandran, R.; Abirami, S.M.; Mohan, N.; Kalaichelvan, P.T. Effect of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles on Bacopa monnieri (Linn.) Wettst. plant growth metabolism. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.-S.; Li, M.; Chang, F.-Y.; Li, W.; Yin, L.-Y. Physiological analysis of silver nanoparticles and AgNO3 toxicity to Spirodela polyrhiza. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1880–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruyer, N.; Dorais, M.; Bastien, C.; Dassylva, N.; Triffault-Bouchet, G. Interaction between silver nanoparticles and plant growth. Acta Hortic. 2014, 1037, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syu, Y.; Hung, J.-H.; Chen, J.-C.; Chuang, H. Impacts of size and shape of silver nanoparticles on Arabidopsis plant growth and gene expression. Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 83, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.; Belozerova, I. Influence of metal nanoparticles on the soil microbial community and germination of lettuce seeds. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2009, 197, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.N.; Ho, C.M.; Chen, R.; He, Q.Y.; Yu, W.Y.; Sun, H.; Tam, P.K.H.; Chiu, J.F.; Che, C.M. Silver nanoparticles: Partial oxidation and antibacterial activities. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elzaawely, A.A.; Xuan, T.D.; Tawata, S. Changes in essential oil, kava pyrones and total phenolics of Alpinia zerumbet (Pers.) BL Burtt. & RM Sm. leaves exposed to copper sulphate. Environ. Exper. Bot. 2007, 59, 347–353. [Google Scholar]
- Heredia, J.B.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L. The effects of exogenous ethylene and methyl jasmonate on the accumulation of phenolic antioxidants in selected whole and wounded fresh produce. Food Chem. 2009, 115, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubashir, A.; Nisa, Z.U.; Shah, A.A.; Kiran, M.; Hussain, I.; Ali, N.; Zhang, L.; Madnay, M.; Alsiary, W.A.; Korany, S.M.; et al. Effect of foliar application of nano-nutrients solution on growth and biochemical attributes of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) under drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1066790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Tyagi, S.R.; Wani, M.R.; Ahmad, P. Drought Tolerance: Role of Organic Osmolytes, Growth Regulators, and Mineral Nutrients. In Physiological Mechanisms and Adaptation Strategies in Plants Under Changing Environment; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 25–55. [Google Scholar]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Agarwal, R.M. Potassium up-regulates antioxidant metabolism and alleviates growth inhibition under water and osmotic stress in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Protoplasma 2017, 254, 1471–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.; Jamei, R. Effect of silver nanoparticles and Pb(NO3)2 on the yield and chemical composition of Mung bean (Vigna radiata). J. Stress Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 10, 316–325. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaq, A.; Ammara, R.; Jhanzab, H.M.; Mahmood, T.; Hafeez, A.; Hussain, S. A novel nanomaterial to enhance growth and yield of wheat. J. Nanosci. Technol. 2016, 2, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.D.; Agarwal, A.; Pradhan, S. Phytostimulatory effect of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) on rice seedling growth: An insight from antioxidative enzyme activities and gene expression patterns. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami Mehrian, S.; Heidari, R.; Rahmani, F. Effect of silver nanoparticles on free amino acids content and antioxidant defense system of tomato plants. Indian J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 20, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nxele, X.; Klein, A.; Ndimba, B. Drought and salinity stress alters ROS accumulation, water retention, and osmolyte content in sorghum plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 108, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Toxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: Photosynthesis, oxidative stress, membrane permeability, and ultrastructure analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 15032–15042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimian, E.; Bybordi, A. Effect of salinity, salicylic acid, silicium and ascorbic acid on lipid peroxidation, antioxidant enzyme activity and fatty acid content of sunflower. African Journal of Agricultural Research 2012, 7, 3685–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.H.; Parvin, K.; Bhuiyan, T.F.; Anee, T.I.; Nahar, K.; Hossen, M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Alam, M.; Fujita, M. Regulation of ROS metabolism in plants under environmental stress: A review of recent experimental evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, G.; Yao, L.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Gao, W. Effects of metal nanoparticles and other preparative materials in the environment on plants: From the perspective of improving secondary metabolites. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2022, 70, 916–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genady, E.A.; Qaid, E.A.; Fahmy, A.H. Copper sulfate nanoparticales in vitro applications on Verbena bipinnatifida Nutt. Stimulating growth and total phenolic content increasments. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Allied Sci. 2016, 5, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanati, F.; Bakhtiarian, S. Effect of Methyl Jasmonate and Silver Nanoparticles on Production of Secondary Metabolites by Calendula officinalis L (Asteraceae). Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 13, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh Homaee, M.; Ehsanpour, A.A. Silver nanoparticles and silver ions: Oxidative stress responses and toxicity in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) grown in vitro. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2016, 57, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahanger, M.A.; Qi, M.; Huang, Z.; Xu, X.; Begum, N.; Qin, C.; Zhang, C.; Ahmad, N.; Mustafa, N.S.; Ashraf, M.; et al. Improving Growth and Photosynthetic Performance of Drought Stressed Tomato by Application of Nano-Organic Fertilizer Involves up-Regulation of Nitrogen, Antioxidant and Osmolyte Metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 216, 112195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteiza, P.I.; Erlejman, A.G.; Verstraeten, S.V.; Keen, C.L.; Fraga, C.G. Flavonoid-membrane interactions: A protective role of flavonoids at the membrane surface? Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2005, 12, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharibi, S.; Sayed Tabatabaei, B.E.; Saeidi, G.; Talebi, M.; Matkowski, A. The effect of drought stress on polyphenolic compounds and expression of flavonoid biosynthesis related genes in Achillea pachycephala Rech.f. Phytochemistry 2019, 162, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Cao, B. Regulation of flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene involved in the flavonoid biosynthesis pathway in response to UV-B radiation and drought stress in the desert plant, Reaumuria soongorica. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2013, 73, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Diao, J.; Ji, J.; Wang, G.; Guan, C.; Jin, C.; Wang, Y. Molecular cloning and identification of a flavanone 3-hydroxylase gene from Lycium chinense, and its overexpression enhances drought stress in tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 98, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
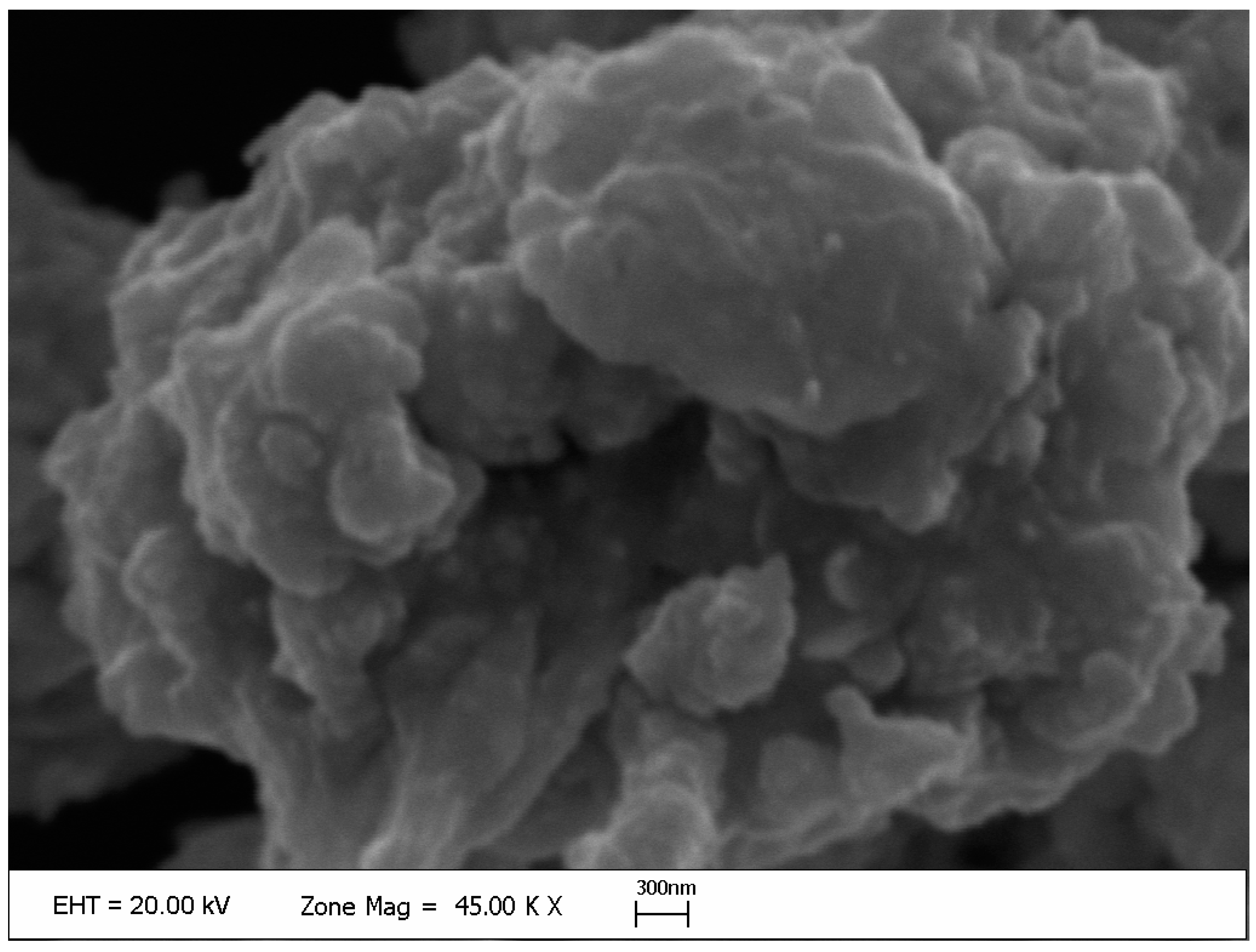

| PEG % | AgNP (mg L-1) | SFW (g) | SDW (g) | SL (mm) | SD (mm) | RFW (g) | RDW (g) | RL (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0.39 bc | 0.074 ab | 27.25 bcd | 1.23 cd | 0.053 b | 0.051 b | 15.93 bcd |
| 0.1 | 0.72 ab | 0.126 a | 44.53 a | 2.43 a | 0.285 a | 0.227 a | 26.78 ab | |
| 0.2 | 0.74 a | 0.078 ab | 34.13 ab | 2.13 ab | 0.194 ab | 0.070 b | 29.43 a | |
| 4 | 0 | 0.30 c | 0.027 b | 18.50 d | 1.40 bcd | 0.070 b | 0.029 b | 13.35 cd |
| 0.1 | 0.65 ab | 0.056 ab | 34.08 ab | 1.48 bcd | 0.129 ab | 0.045 b | 14.53 cd | |
| 0.2 | 0.56 abc | 0.058 ab | 26.65 bcd | 2.05 abc | 0.076 b | 0.058 b | 15.90 bcd | |
| 8 | 0 | 0.29 c | 0.035 b | 20.93 cd | 1.08 b | 0.050 b | 0.035 b | 11.93 d |
| 0.1 | 0.70 ab | 0.051 b | 31.28 bc | 1.83 abcd | 0.138 ab | 0.027 b | 25.13 abc | |
| 0.2 | 0.56 abc | 0.045 b | 24.63 bcd | 1.78 abcd | 0.027 b | 0.030 b | 16.58 bcd |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





