Introduction
In the contemporary age, Type A acute aortic dissection (TAAAD) persists as a clinicopathological entity that poses a life-threatening risk coupled with a substantial possibility of mortality and morbidity. Fifty per cent of patients with TAAAD die within 24 hours. Estimates indicate that up to another 50% pass away before reaching a referral centre specialised in aortic surgery. (1–8) The optimum treatment option for such patients is timely surgical repair. Thanks to greater clinical awareness, diagnostic techniques, and inceptive management, (9) there has been a rise in the number of cases diagnosed promptly and undergoing TAAAD repair in the previous decade. However, despite reports of lower operative mortality rates not exceeding 7% (15–18), survival rates following surgical procedures remain suboptimal, with high rates of in-hospital mortality (16–18%) (1–3, 7, 10–14). The implementation of appropriate interventions for specific patient populations has led to improved operative mortality and postoperative complication rates. A controversy remains surrounding which determinants to prioritise in preoperative assessment and decision-making to improve efficacy. Improved assessment of these factors may eliminate ambiguity regarding the risks of the procedural approach taken and predict operative mortality. The consideration of the impact of various surgical strategies on outcomes requires more reliable data. Similarly, further analysis is needed on the impact of the volume-outcome ratio of the surgeon or center on mortality, which is poorly understood at present. (1,2,7,13–15,22) In this context, a greater comprehension of the factors influencing patient outcomes during surgical interventions can provide significant assistance to the decision-making process. This understanding can assist in guiding the selection of the most appropriate surgical option and ultimately improve the outcomes of those who reach specialist referral centers for the treatment of TAAAD. Additionally, accurate risk stratification can offer improved clinical assistance to patients and enable surgeons who treat patients during hospitalization to be benchmarked. As there is limited information available in TAAAD literature on the effects of serum lactate concentration, the current study seeks to examine this predictor in relation to the most frequently evaluated outcome predictors in individuals undergoing surgery for TAAAD. Specifically, we assessed whether preoperative arterial lactate levels elevate the risk of operative mortality in patients with acute type A aortic dissection (TAAAD), considering clinical, perioperative variables, and surgical approach type.
Methods
This research is a component of a study approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB ID 202201173) and is recognised by the NCT 05927090. Patient agreement has been revoked following research guidance. This study complies with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data extraction and cleaning
Comprehensive analysis of prospectively collected data from three cardiovascular centres (Centre Cardiologique du Nord, Henri Mondor University Hospital, and the University of Genova) was conducted. The Central Cardiac Database, which combines three independent databases for cardiovascular outcomes research, was retrospectively analysed in the DISC Department at the University of Genoa. The registry prospectively gathers demographic information, along with pre- and postoperative clinical data, encompassing mortality, for all TAAAD procedures carried out in three adult cardiac surgery centres in France and Italy. Previous reports have detailed the flow of data from input by surgeons to analysis, including different surgical approaches (7,23–25). To summarise, the data was inputted locally and checked at the unit level by database managers before being uploaded to a single database for analysis. Reports were then generated for primary variables such as EuroSCORE risk factors, patient identifiers, and outcome data. The data was transferred to an academic health informatics department for data cleansing. A second statistician re-analysed the entire data collection process. Duplicate recordings were removed, transcriptional discrepancies recoded, and clinical and temporal conflicts resolved. The missing data were resolved during the data transfer validation phases from the individual centres.
Study endpoints.
The primary endpoint was set as operative mortality, defined as mortality within 30 days and during hospitalization, alongside secondary endpoints including stroke, mesenteric ischemia, paraplegia, sepsis, dialysis, atrial fibrillation, reoperation for bleeding, deep sternal wound infection-mediastinitis and VA ECMO. The presence of elevated arterial lactates was included as an additional secondary endpoint. The operative strategy is reported in the supplementary material (1,7).
Statistical analysis
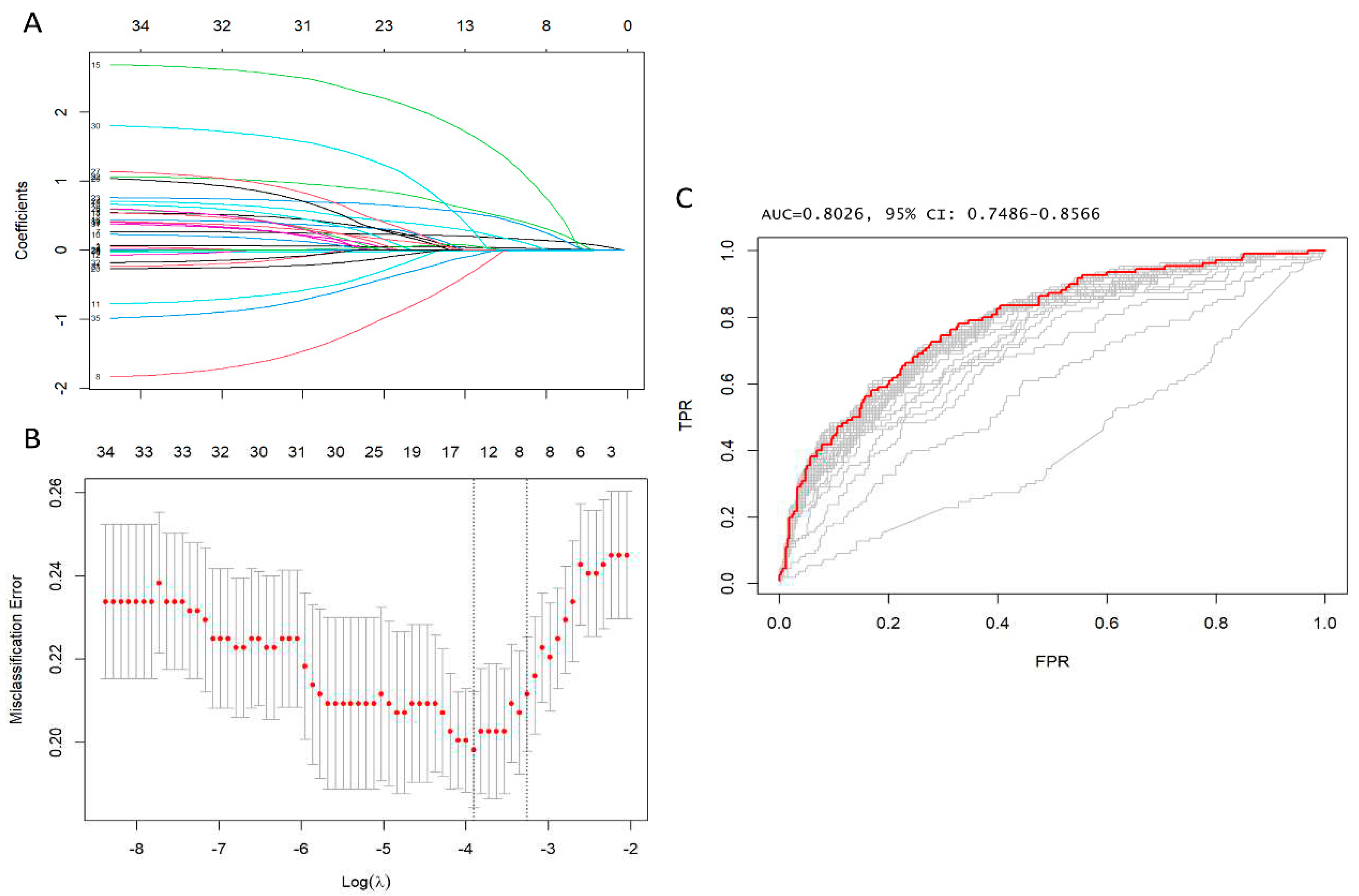
Categorical data were displayed as frequencies and percentages, then compared utilizing the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test where suitable. Continuous variables were expressed as mean and standard deviation (SD), or median and interquartile range (IQR) if presenting normal or non-normal distribution. These variables were compared using a 2-tailed t-test or Mann-Whitney test. Imputation was performed if missing values were below 20%. We utilized predictive mean matching for the imputation of numerical features, and logistic regression for binary variables. LASSO regression was applied to ascertain factors linked to early postoperative mortality, with an aim to minimize the possible collinearity of over-fitting variables and variables assessed from the same patient. The R package "glmnet" was employed for carrying out the LASSO regression. This is a logistic regression model that penalises the absolute size of the coefficients of a regression model using the value of λ. As the penalties increase, the estimates of weaker factors tend to shrink to zero, leaving only the strongest predictors in the model. The covariates with the most significant predictive power were chosen based on the λ (λ = Lambda.1se). Subsequently, variables identified through LASSO regression analysis were included in logistic regression models utilizing stepwise variable selection based on the Akaike information criterion (AIC), and those that remained consistently statistically significant were used to formulate the risk model. The variance inflation factor (VIF) was used to check for collinearity among the independent variables. Discrimination was evaluated through the use of the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve and the area under the curve (AUC). Calibration was determined by comparing predicted mortality rates from the final model to actual observed rates. The R package "cutpointr" was utilised to calculate the "optimal" cutpoint (cutpoint estimation method maximising the metric function after spline smoothing and using 1000 bootstraps) of arterial lactate in forecasting initial mortality. Outcomes were categorized according to the cutpoint and adjusted for age, gender, renal function, hypertension, diabetes, peripheral arteriopathy, pulmonary disease, preoperative stroke, prior cardiac surgery, recent myocardial infarction, left ventricular ejection fraction, and family history of aortic diseases. Odds ratio, risk ratio, and risk difference were then calculated. To determine the risk factors associated with elevated arterial lactates, we conducted a thorough analysis to identify the most appropriate independent variables for predicting increased arterial lactates in multiple linear regression. The entire statistical analysis was carried out using R Statistical Software (version 4.3.1; R Foundation for Statistical Computing in Vienna, Austria).
Results
Of the 633 consecutive patients operated on for type A acute aortic dissection from January 2005 to December 2022, 449 patients with preoperative arterial lactate data were chosen for the present study's patient population. The selection criteria included adults (aged > 18 years) who underwent TAAAD or intramural hematoma surgery. The inclusion criteria stipulated the involvement of the lesion in the ascending aorta, occurrence of symptoms within seven days of surgery, and referral of patients for primary surgical repair of TAAAD in accordance with recommendations. Furthermore, other significant cardiac surgical procedures required during TAAAD and retrograde extension of TAAAD were taken into account. Patients under 18 years old, those with previous TAAAD procedures, delayed presentation (acute aortic syndrome >7 days prior), traumatic aortic dissections, and endocarditis were all excluded. 304 patients (67.6%) were male, and the mean age was 64 years. See
Table 1 for complete demographic and clinical characteristics of the patients.
All patients underwent aortic hemiarch replacement with an open distal anastomosis at a minimum. Primary entry tears occurred in 283 cases (63.0%) in the ascending aorta, 115 (25.6%) in the aortic root, and 59 (13.1%) in the aortic arch. Of the patients, 102 (22.7%) underwent total or partial arch repair. Preoperative blood lactate levels were 1.40 mmol/L [IQR 1.00, 2.80], and 131 (29.2%) had malperfusion syndrome before surgery. The patients were categorised into five groups by increasing haemodynamic severity. For those needing "urgent" intervention, the procedure was conducted within 24 hours of admission during their initial hospital stay. Patients in this group had few symptoms with stable haemodynamics and no signs of malperfusion. Patients in the "emergency 1" group had symptoms, however, were stable from a haemodynamic perspective. They showed no indications of malperfusion or rupture, and surgery was advised within hours of being admitted. The “Emergency 2” grouping comprised of patients who necessitated prompt intervention immediately after hospitalization, or those who quickly worsened clinically. These patients exhibited haemodynamic instability that was not responsive to the administration of inotropes and/or malperfusion. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation is required for such categories of patients. "Salvage 1" and "Salvage 2" categories encompassed patients who required cardiopulmonary resuscitation with external chest compressions and/or open cardiac massage and were hospitalized as a result. These patients were in critical condition and were induced and initiated on cardiopulmonary bypass. "Salvage 1" patients underwent timely surgical procedures with cardiopulmonary bypass initiation due to worsening clinical conditions after anesthesia induction. They may have suffered from a cardiac tamponade, acute heart failure, or sudden rupture of the aorta. In the case of "Salvage 2" patients, cardiopulmonary resuscitation with external chest compressions was necessary during transport to the operating room, or prior to anesthesia induction. Swift initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass was necessary, often preceded by cardiac massage after median sternotomy. The surgical procedure was completed without prior knowledge of genuine aortic rupture or severe organ damage.
Predictors of early postoperative mortality
The operative mortality rate was 24.5% (110 out of 449 patients). No noteworthy difference in mortality rates was observed when comparing surgery with or without partial or total arch repair [83 out of 347 patients (23.9%) vs. 27 out of 102 patients (26.5%), p=0.69], or aortic root replacement [26 out of 109 patients (23.9%) vs. 84 out of 340 patients (24.7%), p=0.96]. In contrast, a significant difference was noted in cases where patients suffered from malperfusion [48 out of 131 patients (36.6%) vs. 62 out of 318 patients (19.5%), p<0.001]. Preoperative arterial lactates showed a statistically significant increase amongst patients with malperfusion [2.00 mmol/L (IQR 1.20, 3.20 mmol/L) compared to 1.20 mmol/L (IQR 0.90, 2.20 mmol/L), p <0.001]. No significant difference in early postoperative mortality was found when comparing patients who underwent surgery in the 1st half versus the 2nd half of the study period [26.0% (57 out of 219 patients) between 2005 to 2013 versus 23.0% (53 out of 230 patients) between 2015 to 2022, χ2 statistic = 0.54; P = 0.46]. 36 variables measured at baseline (i.e., hospital admission) (
Table 1) were included in the LASSO regression analysis. After LASSO regression selection (
Figure 1,
Supplementary Table S1,2), the following 14 variables remained significant predictors of early postoperative mortality, including age, eGFR, arterial lactate, family history of aortic dissection or aneurysm, poor mobility, left ventricular ejection fraction, cardiac tamponade, preoperative intubation, and malperfusion, cardiopulmonary bypass time, bicuspid aortic valve, antegrade cerebral perfusion, retrograde cerebral perfusion, and urgency of the procedure - Salvage grade 1 (procedure carried out in patients requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation with external chest compressions and/or open-chest cardiac massage between the induction of anaesthesia and the initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass).
These 14 variables were included in the logistic regression model, and 8 variables were identified as noteworthy independent predictors of operative mortality. These variables included age, eGFR, arterial lactate, family history of aortic dissection or aneurysm, poor mobility, cardiac tamponade, preoperative intubation and, cardiopulmonary bypass time (
Table 2).
Furthermore, the area under the ROC was curve 0.84 (95% CI: 0.79–0.88), Hosmer–Lemeshow’s test p value was 0.48 and, VIF was <1.5 indicating no collinearity amongst all the independent variables (
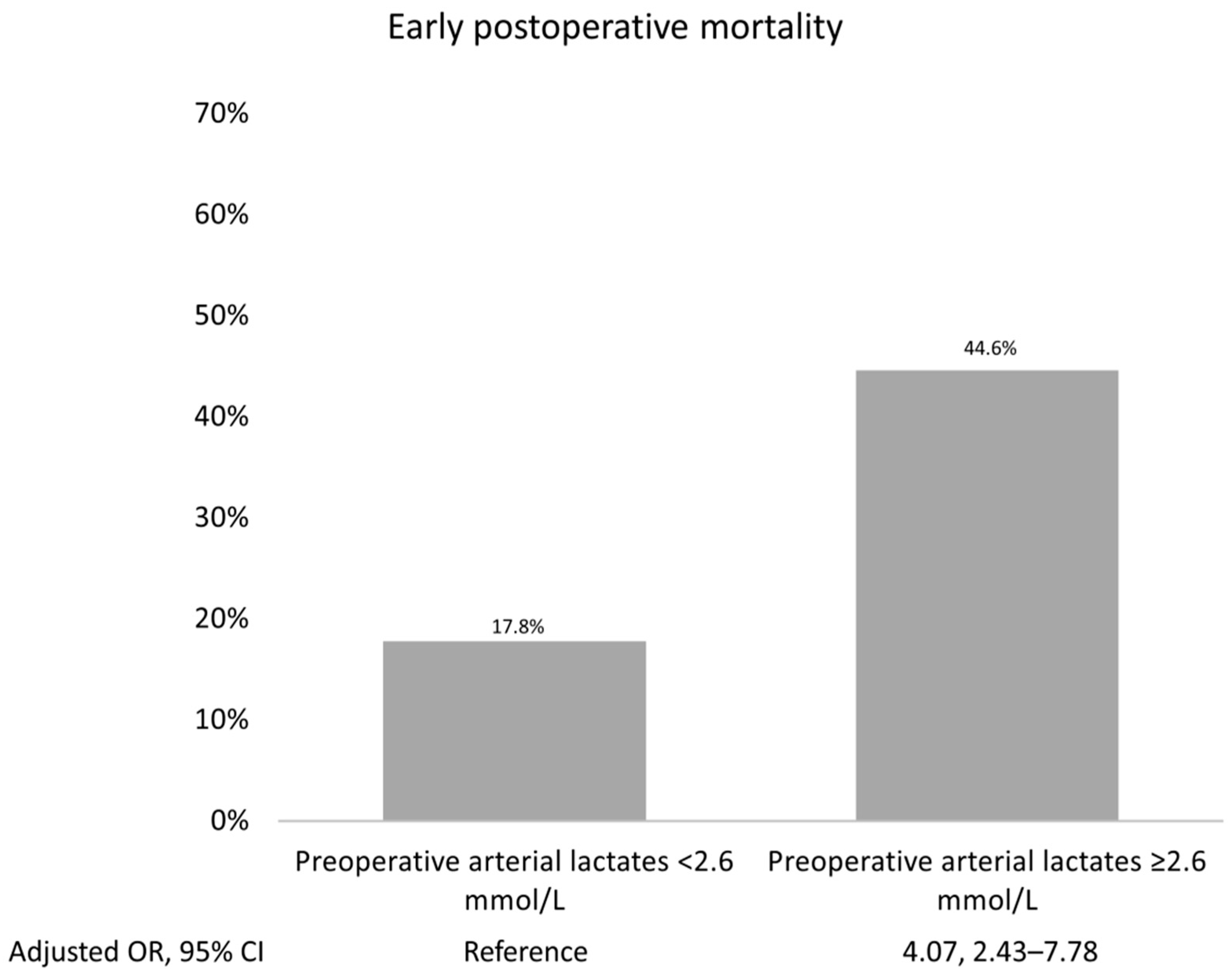
Supplementary Table S3). The most accurate prognostic cut-off level of arterial lactate for forecasting early postoperative mortality was determined to be ≥2.6 mmol/L, with an ROC curve value of 0.67. A sensitivity of 45%, specificity of 38%, and an Adjusted OR of 4.07 (95% CI 2.43, 7.78; P <0.001) were noted. The results are illustrated in the prognostic ROC curves (
Supplementary Figure S1 and Supplementary best cut-off statistics,
Table 3).
Figure 2 shows the highest early postoperative mortality rate that occurred when arterial lactates exceeded their prognostic cut-offs.
Early postoperative outcomes
Table 3 presents a breakdown of early adverse outcomes following surgery based on the preoperative arterial lactate cut-off (≥2.6 mmol/L). In addition to a higher early postoperative mortality, elevated lactate levels result in increased crude rates of postoperative mesenteric ischemia (11% vs 3.9%, p=0.03), sepsis (33.9% vs 21.4%, p=0.01), (12.5% vs 2.7%, p<0.001). After adjusting for baseline characteristics, it was confirmed that preoperative arterial lactates ≥ 2.6 mmol/L were associated with postoperative dialysis and the need for VA ECMO implantation. The adjusted risk difference was 9.3% and 7%, respectively.
Predictors of increased preoperative arterial lactates
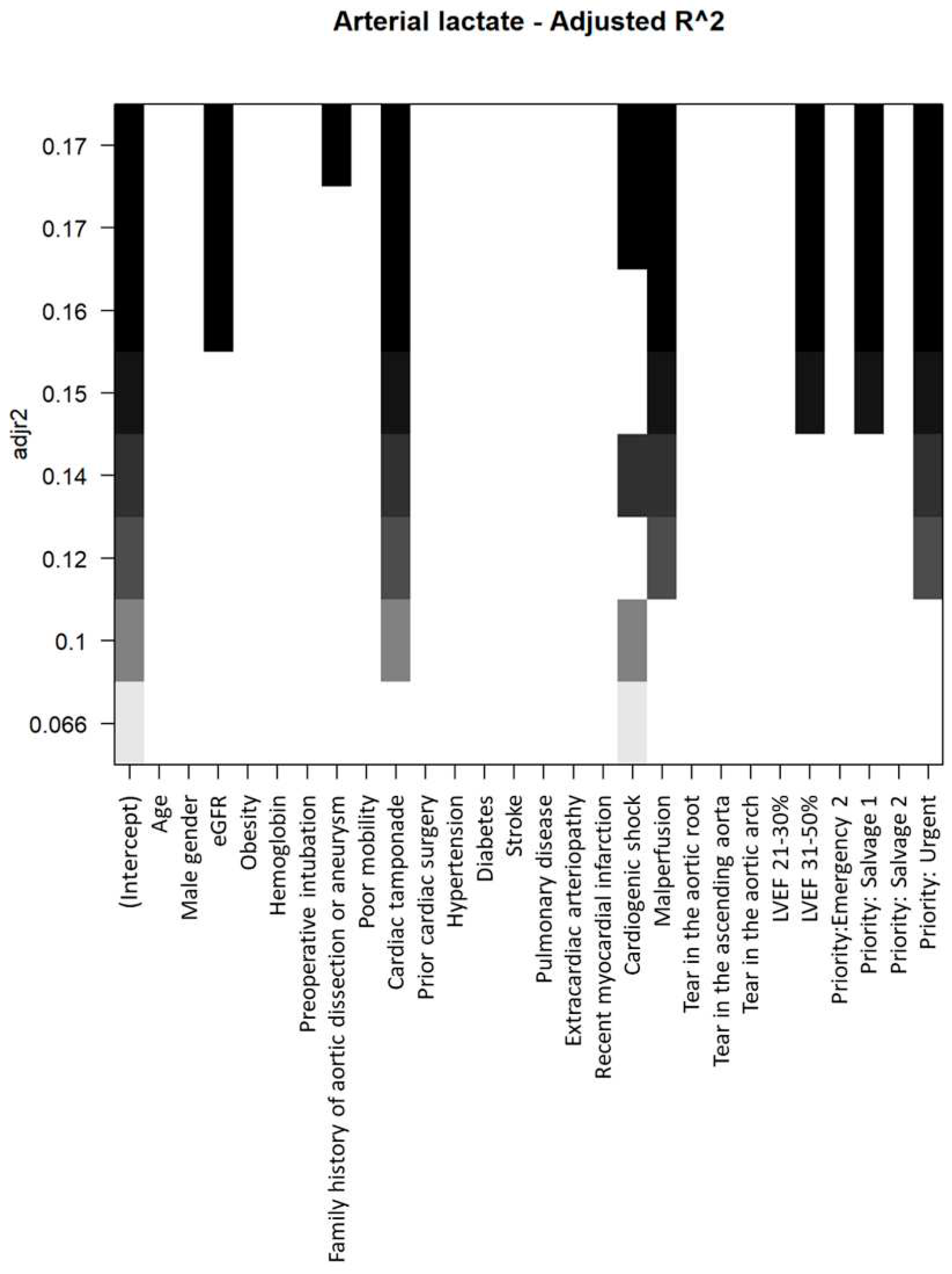
The process of selecting baseline variables to be incorporated into multivariable models for elevating preoperative arterial lactates is illustrated in
Figure 3.
Within the multivariable model, eGFR, cardiac tamponade, cardiogenic shock, LVEF 31–50%, and the urgency of the procedure (urgent and salvage grade 1) were identified as independent factors associated with increased preoperative arterial lactates (refer to
Table 4).
Discussion
Significant progress has been made in improving the diagnosis using imaging modalities and the medical treatment of TAAAD since its inception. The introduction of drug therapy, including the application of β-blockers, as well as the emergence of sophisticated and diverse cardiovascular, vascular, and hybrid surgical alternatives, have propelled the care process for patients with TAAAD forward. (3,29–31) In this detailed analysis, we assessed the survival rates post-surgical repair for acute type A aortic dissection in patients with malperfusion and raised serum lactate levels. The study is founded upon a 17-year span (2005–2022) of amassed data from a multi-centred registry comprised of three esteemed centres.
Our findings demonstrate that for patients with TAAAD, the unadjusted operative mortality rate was 24.5%, showing no significant variation between those who received partial or total arch repair or aortic root replacement. Our 17-year analysis reveals that the surgical approach to TAAAD continues to result in high mortality, as indicated by multiple multi-centred registries; however, the mortality rate is gradually decreasing (3,8,10–12). Furthermore, we have identified eight distinct risk factors linked to early mortality: age, arterial lactate, eGFR, family history of aortic dissection or aneurysm malperfusion, cardiac tamponade, preoperative intubation, cardiopulmonary bypass time and poor mobility. These factors have been incorporated into a bedside risk scoring tool primarily based on arterial lactate serum levels.
A surgical strategy for TAAAD has been associated with reduced rates of operative mortality. This ranges from 16–18% for patients who received root-sparing AAR using Dacron graft interposition with or without hemiarch repair (3, 8, 10, 11), to 26.9% for those who underwent TARP (12). However, various centres report varying percentages for lower operative mortality. The initial 48 hours following the emergence of clinical symptoms associated with aortic dissection marks a critical period for those suffering from TAAAD due to their increased susceptibility to malperfusion. Such individuals may exhibit high levels of serum lactate linked to malperfusion prior to their admission to hospital or even before the diagnosis of aortic dissection is made.
The findings detailed in this report align with a notable rise in patient mortality rates, particularly in those with elevated preoperative serum lactate levels. To ensure the accuracy of the study, we established five distinct categories of heightened hemodynamic severity (28), factoring in the time of the initial aortic dissection and subsequent hospitalization. By doing so, we were able to group patients according to arterial lactate value increments and assess mortality rates. For these patients, all of whom were considered candidates for surgery, it was observed that in the presence of high arterial lactate levels, the difference in risk mortality increased significantly by 23.4%. Furthermore, the risk mortality rate remained disappointingly high with an arterial lactate cut-off of ≥ 2.6 mmol/L (13.8% vs 32.9%; p<0.00
Our findings indicate that the mortality rate of the patient within the first 48 hours after the surgery, as well as the complications arising during ICU surveillance within the initial days following surgery, were consistent with higher preoperative arterial lactate levels. Alongside the risk of operative mortality, elevated arterial lactate levels are correlated with a substantial post-operative increase in the likelihood of VA ECMO (7%; p<0.001) and the need for dialysis. (9,3%; P = 0.003). The results indicate that age, cardiac tamponade (p<0.0116), and preoperative intubation due to hemodynamic instability and hypotension (p=0.005) were significant predictors of mortality following surgery. While the mortality rate for surgical procedures has significantly decreased in recent years, the estimate for in-hospital mortality in patients who receive optimal medical treatment (OMT) or suffer from malperfusion-related clinical complications remains constantly high. Patients undergoing OMT have a mortality rate greater than 50% (34), whereas patients with arterial lactate cut-off ≥ 2.6 mmol/L have a mortality rate of 32.9% as observed in this study (p<0.001). For individuals diagnosed with TAAAD, it is important to consider both the in-hospital mortality rate and the mortality rate in the wider population. It is worth noting that our study's findings only account for patients who died whilst in the tertiary care centre, and do not include those who died before arriving at the centre, including those transferred from other hospitals. Our findings correspond with those reported in the IRAD registry (3) and the UK National Adult Cardiac Surgical Audit (8). The mortality rate for TAAAD in the wider population is substantially higher (6).
Malperfusion Management Subgroup.
There exists a subgroup of patients deemed to carry an unmanageable degree of risk for operative mortality and post-operative complications that are serious and irreversible. This assessment is established purely on the grounds of evidence provided by various stakeholders, namely physicians/surgeons, patients, and family members. This diverse cohort includes elderly individuals, those with significant coexisting conditions, and those who only satisfy emergent clinical criteria for TAAAD repair. (1,20) Our appraisal of the IRAD registry demonstrated an upward trend in surgical interventions, with 90% of patients currently undergoing TAAAD repair. Importantly, a segment of this group of individuals declined to undergo surgical intervention. (3,34–36) As in prior studies, we found a subgroup of patients who initially presented with indications of cerebrovascular, mesenteric, and peripheral ischemia tied to acute and severe clinical situations, where the urgency of the procedure was deemed necessary. Along with advanced age and previous cardiac surgery, malperfusion findings are well-established markers of escalated operative risk and determine the decision-making process that guides TAAD repair. (1,15,36,37)
There is a strong link between malperfusion and a potential rise in arterial lactate levels. It is important to note that the definition of malperfusion can differ depending on the assessed registers. In our analysis, we grouped patients who experienced mesenteric malperfusion, renal malperfusion, cardiogenic shock (including cardiac tamponade and low cardiac output), any pulse deficit/limb ischemia, and cerebral perfusion deficit (recent cerebrovascular accident) as having organ malperfusion. We reported a rate that was comparable to that described in the GERAADA database (8) in the UK and higher than that reported in the NORCAAD registry (11). In our study, although an aortic tear was found in all patients, only 30.5% of cases presented subclinical or symptomatic malperfusion due to the static or dynamic behavior of the aortic tear. This led to multi-organ ischemia with increased arterial lactate and systemic metabolic damage. (1, 3, 35, 38)
Malperfusion persists when the true lumen of a vessel originating from the aortic conduit is obstructed by the expansion of a haematoma or thrombosis in the false lumen or by the action of the dissecting membrane itself. In such circumstances, timely and effective recanalisation is essential. It is possible that persistent poor dynamic perfusion could result in a vicious cycle that ultimately leads to a high lactate cutoff. In these situations, the membrane hovers in front of the aortic branch or protrudes into a branch, causing obstructive dynamics and consequent pressure fluctuations in the genuine and fake lumens during the cardiac cycle. We noticed a rise in raw rates of mesenteric postoperative ischemia (11% vs. 3.9%, p=0.03) because of the continual disruption of regional circulation in patients whose arterial lactate exceeded 2.6 mmol/L; this may be linked to continual branch thrombosis caused by low flow and embolism resulting in malperfusion. In our analysis, we noted that arterial lactate levels were elevated in cases of renal malperfusion (p=0.009) along with cardiac tamponade (p<0.0001), cardiogenic shock (p=0.05), LVEF (p=0.014), and priority urgency procedures (salvage 1 p=0.05; urgent p=0.0001). Therefore, after determining preoperative risks, a meticulous clinical examination, as well as surgical center proficiency, becomes particularly crucial in high-risk cases (8,24,30).
Although strong evidence has established that TAAAD repair may be a viable surgical option for high-risk groups such as octogenarians, offering TAAAD repair to these patients requires a balance between increased operative risks and high mortality rates. Rapid and informed decision-making should be made in the presence of malperfusion associated with higher lactate cut-offs, while considering patients and their families. (1, 30, 39) On the contrary, the cut-off for serum lactate below 2.6 mmol/L appears to substantiate the findings of past studies, which recorded a lower mortality rate that did not surpass 7% (15–18), approximately half that of the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection, German Registry for Acute Aortic Dissection Type A, Nordic Consortium for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection and UK National Adult Cardiac Surgical Audit (3,8,10,11). It is possible that these patients were not referred for TAAAD repair despite worsening organ malperfusion, which may have eliminated the molecular impacts of heightened arterial lactate concentration on OM and postoperative outcomes.
Surgical Repair in Patients with Higher Lactate
The optimal treatment plan for TAAAD in patients with heightened arterial lactate must balance the need for low operative mortality during the index procedure with minimal risk of future reoperation. However, if the ideal surgical option requires increased procedural complexity, it must be carefully considered as this may lead to prolonged periods of cardiac and organ ischemia during surgery. Our research suggests that the duration of cardiopulmonary bypass is a contributing factor to the heightened occurrence of OM (p=0.0011), evidenced by the significant coefficient in the LASSO logistic regression model for OM (So=0.0023). Therefore, when monitoring TAAAD repair, it is advisable to keep the arterial lactate level below the cut-off, as this is identified as an additional risk factor that can lead to multi-organ failure. This notion is supported by aggregated multicentre data. For instance, data published by the Society of Thoracic Surgeons for the period between 2014 and 2016 showed an overall mortality (OM) rate of 26.9% among recipients of total arch replacement, in comparison to an OM rate of 16.3% in patients who underwent hemi-arch repair (40). In a secondary report utilizing pooled meta-analytical data, a comparison was made between proximal conservative repair and extended arch repair. The analysis revealed that in the former approach, the risk of early mortality was reduced (relative risk, 0.69) in comparison to the likelihood of requiring a distal reoperation (relative risk, 3.14).
To the best of our knowledge, this is the most extensive evaluation of factors that affect outcomes following surgical repair for TAAAD and establish a threshold for the arterial lactate. Although arterial lactate is an indicator of tissue ischemia, there is a lack of data regarding the determination of the arterial lactate threshold in the scientific literature on TAAAD, and no assessment is reported on the relationship between arterial lactate fluctuations and organ malperfusion, which requires significant attention.
This issue contributes to the uncertainty surrounding the inconsistent outcomes regarding operative mortality as seen in numerous single-centre studies. It is possible that this result is caused by the worsening clinical status of patients due to malperfusion and multi-organ systemic metabolic damage. In one study, it was suggested that there was an increase in operative mortality for patients undergoing TAAAD repair, with the ascending aorta having a mortality rate of 9.8%, the hemiarch having a mortality rate of 21.6%, and TARP having a mortality rate of 28.6%. In contrast, another study reported slightly lower rates of OM (13.4% vs 9.7%) in recipients of hemiarch repair compared to those who received total arch replacement. However, the authors noted a significantly higher incidence of cerebral malperfusion and permanent neurological deficit in the total arch replacement group (22.7% vs 6.3%).
In our study, the majority of patients underwent limited replacement of the ascending aorta using an interposition graft, with or without hemiarch repair. This surgical approach was succeeded by aortic root replacement, whereas only a minor proportion of cases had TARP performed. The mortality rate showed no significant variation post-surgery, whether it included partial or total arch repair (p=0.69) or aortic root replacement (p=0.96). However, it was observed that the operative mortality was likely influenced by independent predictors such as cardiopulmonary bypass time and antegrade cerebral perfusion.
These findings support the theory that a total aortic arch replacement, which entails an extended period of ischemia, should only be carried out after evaluating the patient's preoperative state, monitoring arterial lactate levels, and reviewing surgical outcomes. Likewise, supporters of conservative surgery recommend complete removal of the intimal lesion along with the implant of a Dacron prosthesis to replace the ascending aorta with or without hemiarch. These options are still considered to be the most commonly used surgical techniques for TAAAD, as confirmed by sources 3, 8, 10–12, and 15.
In this study, the surgical repair extent (ascending aorta, hemiarch, total arch replacement) mainly addressed critical clinical conditions upon admission, such as malperfusion and arterial lactate concentration, and the characteristics of the aortic lesion, to minimise the risks of operative mortality and postoperative complications. The primary purpose remains the surgical repair of the entry tear of the dissection. Therefore, for patients with an entry tear that affected the lesser curvature of the aortic arch, we opted for the conservative surgical approach with the use of a Dacron prosthesis and hemiarch repair. Additional surgical options may have to be considered in cases of entrance lesions near the supra-aortic branches, in line with the degree of aortic arch involvement and preoperative patient conditions. These options may include more extensive arch surgery, as appropriate.
In recent years, there has been significant progress in providing aortic pathology services as a subspecialty. Advancements in surgical techniques, cerebral protection and the introduction of new technologies have encouraged extensive surgery for TAAAD repair. This involves replacing the aortic arch with potential extensions into the proximal descending aorta, along with hybrid procedures. The advantages of expanding the initial TAAAD operation to encompass treating extra dissected aortic portions become apparent through a higher level of risk reduction in the advancement of aortic dilation and rupture of the resected aortic aorta by means of second-phase endovascular treatment alternatives. However, although this anticipated medium and long-term advantage has been noticed for extensive repairs, it is imperative to carefully consider the risk of potentially higher mortality and morbidity resulting from the greater complexity of the initial procedure. Moreover, there is further evidence of percentage disparities in the outcomes for TAAAD repair in patients undergoing TARP or TARP plus FET. Proponents of more extensive surgical options compared recipients of conservative repair with those who underwent the extended TARP procedure. The incidence of OM (24.1% vs 22.6%) and PND (9.1% vs 7.5%) was found to be similar in both groups (44). It was also suggested that there were no differences in operative mortality (5.4% vs. 5.7%) or PND (1.4% vs. 2.3%) between conservative isolated hemiarch repair and FET (45). However, there were concerns about a higher incidence of OM. In actuality, few centres support a more conventional surgical approach or the adoption of aggressive methods such as TAR, antegrade stent graft, or FET, which have consistently reported mortality rates below 10% (15–18,43). However, TAR combined with FET constitutes a feasible strategy for mending the aortic arch and deserves consideration when analysing the outcomes emphasised by Sun and colleagues (18), who advocate strongly for this more comprehensive surgical approach in repairing TAAAD. They presented impressive findings from a cohort of 148 patients diagnosed with ruptured arch, arch aneurysm, or Marfan syndrome complicated by TAAAD who received TARP alongside FET. There was no significant difference in in-hospital mortality (4.7% vs. 6.1%; p=0.74), stroke (2.7% vs. 1.5%; p=1), and spinal cord injury (1.4% vs. 0; p=1) when comparing TARP plus FET and hemiarch substitution. Additionally, the FET group exhibited an improvement in false lumen thrombosis and a decrease in the need for reoperations (1 vs 4 patients; p=0.03).
Our analysis found that patients who underwent total replacement of the aortic arch faced a higher probability of stroke when their arterial lactate cut-off was ≥2.6 mmol/L (9.2% vs 14.3%; risk ratio 1.465), and a greater risk of operative mortality at Lasso logistic regression in patients who needed antegrade cerebral perfusion (s0=0.0498). Total aortic arch replacement has been proven to be a secure surgical choice in elective surgery. However, there is still debate around its impact on surgical mortality and morbidity, and its long-term benefits in TAAAD repair. (46) Our results reinforce the hypothesis that TARP is a surgical option that requires assessment depending on the patient's preoperative condition, given good surgical outcomes and a lower risk of postoperative complications. However, there is still debate around its impact on surgical mortality and morbidity, and its long-term benefits in TAAAD repair. (46)
The procedure involving complete replacement of the aortic root was carried out in 24.3% of patients in our case series, without affecting the recorded mortality rate. Aortic root surgery in the context of TAAAD is technically complex and increases the risk of surgery. Patients in need of this more complicated procedure experience much longer bypass and cross-clamp times in comparison to those who undergo ascending aortic replacement with preservation of the root. In particular, the delicacy of the dissected aortic tissue may complicate the reimplantation procedure of the dissected coronary buttons. Furthermore, there is potential for postoperative bleeding and ischemia from coronary button malposition, which can be fatal. In cases of extensive root destruction, concomitant root aneurysm, bicuspid aortopathy, or a history of connective tissue disease, we have performed root replacement with equivalent operative outcomes, as reported in other studies (3, 7, 10, 46–48).
Processes of Care and Aortic Centers
The group of patients with malperfusion and elevated arterial lactate concentrations requiring critical hospitalization for surgery underlines the significance of expediting TAAAD identification and patient transfer to surgery. (30) The study IRAD demonstrates ongoing delays in TAAAD recognition and treatment, with an average diagnosis time of 2.5 hours and surgery time of 3.5 hours following presentation. A timeframe of 6 hours is generally needed from arrival in the emergency department to surgery. Additionally, some patients unfortunately pass away before undergoing surgery, with a median estimated time (IQR) from admission to death of 8.9 hours (4–32). At our centre, there is frequently no need for interhospital transfer, which limits therapeutic delays due to the implementation of a regional transfer process in Ile de France. This process entails the patient being transported directly to the operating theatre upon arrival.
The regional care model, which highlights diagnosis and treatment protocols, requires evaluation to demonstrate reduced diagnosis and treatment times. Chikwe and colleagues (50) claim that improved aortic dissection survival can be attributed to both surgeon and centre volume. Therefore, prompt referral to aortic centres with cardiovascular and vascular specialists, and anaesthetists adept in intricate aortic surgery, cerebral safeguarding, and methods to tackle malperfusion are vital for these patients. Several studies have reported that transfer to high-volume specialised aortic centres reduces malperfusion complications and mortality (21,51–53). Although hospital care system factors are critical for prompt diagnosis and treatment, it is equally important to consider the time from patient symptom onset to presentation, with a median time of 1.5 hours [0, 8-3,3] (IQR). Therefore, it is vital to educate patients so that those who are at risk can identify the symptoms of TAAAD, report quickly to the emergency department, and request targeted aortic testing where necessary. (49,54)
Limitations
Although this study is the most comprehensive and up-to-date assessment of operative mortality and postoperative complication rates caused by increased arterial lactate concentrations in TAAAD patients, it has certain limitations which must be considered. The retrospective nature of the analysis and the incomplete or missing event information should be taken into account. Furthermore, the recorded survival rates based on arterial lactate levels are only applicable after TAAAD malperfusion recognition and referral for surgery. As Howard et al. (6) demonstrate, a significant proportion of patients with TAAD do not survive their hospital stay. While malperfusion is identified as an independent risk factor in most registries, the exact arterial lactate thresholds are not reported. Therefore, the early mortality rates for patients undergoing TAAAD repair who are referred to tertiary centers are not known, and this is linked with multi-organ metabolic damage induced by malperfusion and sustained by the high concentration of arterial lactates. Finally, given the retrospective nature of the analysis, it is difficult to determine whether high arterial lactate values may be associated with the observed postoperative complications and mortality depending on the type of surgical option used which dictated a conservative approach or an extensive approach.
Conclusion
Patients with a recognized TAAAD in contemporary times exhibit a mortality rate of 0.12% per hour during the first 48 hours. (34) Despite significant advancements in surgery, medical care, and imaging over the past 60 years, leading to a substantial decline in mortality rates, the severe clinical status of patients sustained by systemic malperfusion results in the remaining high mortality rate. The arterial lactate concentration of patients referred for TAAAD repair is an independent factor influencing operative mortality and postoperative complications. Considering an arterial lactate threshold of 2.6 mmol/L, mortality increases by 23.4% for higher levels (risk ratio 2.264; 1.660–3.082). In addition to surgical mortality, the risk of VA ECMO and the need for dialysis is significant in patients who have an upper arterial lactate threshold of ≥2.6 mmol/L within 48 hours after surgery. As arterial lactate, cardiopulmonary bypass, and anterograde cerebral perfusion are all independent factors that increase operative mortality, a tailored approach should be considered for patients with a higher arterial lactate cut-off of ≥2.6 mmol/L. This approach should dictate a more conservative option. These findings serve as a reminder that malperfusion in TAAAD requires more robust efforts to improve recognition, early initiation of transfer, and the surgical treatment protocol.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.N.; methodology, F.N., A.A., A S. ; software, A.S., A.A., G.P.; validation, F.N.; A.A.,A.S., I.G.; formal analysis, S.A., I.G., G.P; investigation, F.N, A.A., SS.AS., P.M; T.S., P.D.; data curation, F.N., A.A., A.S., F.S., N.NB and P.L.; writing— original draft preparation, F.N.; writing—review and editing, F.N., A.A., A.S., SS.AS, A.F.; visualization, F.N., F.A., F.S., P.M.,T.S., P.D., N.B. and P.L.; supervision; F.N., A.F., F.S., P.M., T.S., P.D., N.B. and P.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Institutional Review Board 202201173; initial approval date July 12, 2022
Informed Consent Statement
written informed consent was provided by all patients.
Data Availability Statement
Drs Nappi, Salsano, and Fiore were granted complete access to all data in the study and acknowledge their responsibility for the data's integrity and accuracy of the data analysis. Requests for the data supporting this article will be fulfilled upon reasonable inquiry to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Biancari, F.; Juvonen, T.; Fiore, A.; Perrotti, A.; Hervé, A.; Touma, J.; Pettinari, M.; Peterss, S.; Buech, J.; Dell’aquila, A.M.; et al. Current Outcome after Surgery for Type A Aortic Dissection. Ann. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nappi, F.; Petiot, S.; Salsano, A.; Singh, S.S.A.; Berger, J.; Kostantinou, M.; Bonnet, S.; Gambardella, I.; Biancari, F.; Almazil, A.; et al. Sex-Based Difference in Aortic Dissection Outcomes: A Multicenter Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, A.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Bossone, E.; Gleason, T.G.; Di Eusanio, M.; Sechtem, U.; Ehrlich, M.P.; Trimarchi, S.; Braverman, A.C.; Myrmel, T.; et al. Insights From the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection. Circulation 2018, 137, 1846–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braverman, A.C. Acute Aortic Dissection. Circulation 2010, 122, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahase, E. Half of patients with acute aortic dissection in England die before reaching a specialist centre. BMJ 2020, 368, m304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, D.P.; Banerjee, A.; Fairhead, J.F.; Perkins, J.; Silver, L.E.; Rothwell, P.M.; D, M.; F, R.; K, T.; D, G.; et al. Population-Based Study of Incidence and Outcome of Acute Aortic Dissection and Premorbid Risk Factor Control. Circulation 2013, 127, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nappi, F.; Singh, S.S.A.; Gambardella, I.; Alzamil, A.; Salsano, A.; Santini, F.; Biancari, F.; Schoell, T.; Bonnet, N.; Folliguet, T.; et al. Surgical Strategy for the Repair of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: A Multicenter Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2023, 10, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, U.; Dimagli, A.; Kaura, A.; Sinha, S.; Mariscalco, G.; Krasopoulos, G.; Moorjani, N.; Field, M.; Uday, T.; Kendal, S.; et al. Determinants of outcomes following surgery for type A acute aortic dissection: the UK National Adult Cardiac Surgical Audit. Eur. Hear. J. 2021, 43, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossone, E.; Gorla, R.; LaBounty, T.M.; Suzuki, T.; Gilon, D.; Strauss, C.; Ballotta, A.; Patel, H.J.; Evangelista, A.; Ehrlich, M.P.; et al. Presenting Systolic Blood Pressure and Outcomes in Patients With Acute Aortic Dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, 1432–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conzelmann, L.O.; Weigang, E.; Mehlhorn, U.; Abugameh, A.; Hoffmann, I.; Blettner, M.; Etz, C.D.; Czerny, M.; Vahl, C.F. Mortality in patients with acute aortic dissection type A: analysis of pre- and intraoperative risk factors from the German Registry for Acute Aortic Dissection Type A (GERAADA). Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2015, 49, e44–e52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geirsson, A.; Shioda, K.; Olsson, C.; Ahlsson, A.; Gunn, J.; Hansson, E.C.; Hjortdal, V.; Jeppsson, A.; Mennander, A.; Wickbom, A.; et al. Differential outcomes of open and clamp-on distal anastomosis techniques in acute type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 157, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’hara, D.; McLarty, A.; Sun, E.; Itagaki, S.; Tannous, H.; Chu, D.; Egorova, N.; Chikwe, J. Type-A Aortic Dissection and Cerebral Perfusion: The Society of Thoracic Surgeons Database Analysis. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2020, 110, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbel, R.; Aboyans, V.; Boileaul, C.; Bossone, E.; Bartolomeo, R.D.; Eggebrecht, H.; Evangelista, A.; Falk, V.; Frank, H.; Gaemperli, O.; et al. ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document Covering Acute and Chronic Aortic Diseases of the Thoracic and Abdominal Aorta of the Adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 2873–2926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frankel, W.C.; Green, S.Y.; Orozco-Sevilla, V.; Preventza, O.; Coselli, J.S. Contemporary Surgical Strategies for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2020, 32, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, C.; Robinson, N.B.; Farrington, W.J.; Rahouma, M.; Gambardella, I.; Gaudino, M.; Girardi, L.N. A tailored strategy for repair of acute type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2021, 164, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Norton, E.L.; Hobbs, R.; Farhat, L.; Wu, X.; Hornsby, W.E.; Kim, K.M.; Patel, H.J.; Deeb, G.M. Short- and long-term outcomes of aortic root repair and replacement in patients undergoing acute type A aortic dissection repair: Twenty-year experience. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 157, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, A.; Miyahara, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Matsumori, M.; Okada, K.; Okita, Y. Early and late outcomes of repaired acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection after graft replacement. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 151, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun L, Qi R, Zhu J, Liu Y, Zheng J. Total arch replacement combined with stented elephant trunk implantation: a new “standard” therapy for type a dissection involving repair of the aortic arch? Circulation. 2011; 123:971-8.
- Rylski, B.; Milewski, R.K.; Bavaria, J.E.; Vallabhajosyula, P.; Moser, W.; Szeto, W.Y.; Desai, N.D. Long-term results of aggressive hemiarch replacement in 534 patients with type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 2981–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, H.-H.; Richardt, D.; Diwoky, M.; Auer, C.; Bucsky, B.; Nasseri, B.; Klotz, S. Survival and reoperation after valve-sparing root replacement and root repair in acute type A dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 156, 2076–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.D.; Ganapathi, A.M.; Hanna, J.M.; Williams, J.B.; Gaca, J.G.; Hughes, G.C. Outcomes of Acute Type A Dissection Repair Before and After Implementation of a Multidisciplinary Thoracic Aortic Surgery Program. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1796–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawton, J.S.; Liu, J.; Kulshrestha, K.; Moon, M.R.; Damiano, R.J.; Maniar, H.; Pasque, M.K. The impact of surgical strategy on survival after repair of type A aortic dissection. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2015, 150, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juvonen, T.; Jormalainen, M.; Mustonen, C.; Demal, T.; Fiore, A.; Perrotti, A.; Hervé, A.; Mazzaro, E.; Gatti, G.; Pettinari, M.; et al. Direct Aortic Versus Supra-Aortic Arterial Cannulation During Surgery for Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Mol. Med. 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancari, F.; Dell’aquila, A.M.; Gatti, G.; Perrotti, A.; Hervé, A.; Touma, J.; Pettinari, M.; Peterss, S.; Buech, J.; Wisniewski, K.; et al. Interinstitutional analysis of the outcome after surgery for type A aortic dissection. Eur. J. Trauma Emerg. Surg. 2023, 49, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancari, F.; Pettinari, M.; Mariscalco, G.; Mustonen, C.; Nappi, F.; Buech, J.; Hagl, C.; Fiore, A.; Touma, J.; Dell’aquila, A.M.; et al. Outcome after Surgery for Iatrogenic Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grembi, J.A.; McQuade, E.T.R. Introducing riskCommunicator: An R package to obtain interpretable effect estimates for public health. PLOS ONE 2022, 17, e0265368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Variable selection with stepwise and best subset approaches. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 136–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biancari, F.; Mariscalco, G.; Yusuff, H.; Tsang, G.; Luthra, S.; Onorati, F.; Francica, A.; Rossetti, C.; Perrotti, A.; Chocron, S.; et al. European registry of type A aortic dissection (ERTAAD) - rationale, design and definition criteria. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2021, 16, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiratzka, L.F.; Bakris, G.L.; Beckman, J.A.; Bersin, R.M.; Carr, V.F.; Casey, D.E.; Eagle, K.A.; Hermann, L.K.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Kazerooni, E.A.; et al. 2010 ACCF/AHA/AATS/ACR/ASA/SCA/SCAI/SIR/STS/SVM Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Patients With Thoracic Aortic Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 55, e27–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonser, R.S.; Ranasinghe, A.M.; Loubani, M.; Evans, J.D.; Thalji, N.M.; Bachet, J.E.; Carrel, T.P.; Czerny, M.; Di Bartolomeo, R.; Grabenwöger, M.; et al. Evidence, Lack of Evidence, Controversy, and Debate in the Provision and Performance of the Surgery of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 2455–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassar, A.S.; Sundt, T.M. How should we manage type A aortic dissection? Gen. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2018, 67, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, A.E.; Johns, V.J.; Kime, S.W. DISSECTING ANEURYSM OF THE AORTA. Medicine 1958, 37, 217–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.; Thordsen, S.; Thomas, T.; Mackey-Bojack, S.M.; Duncanson, E.R.; Nwuado, D.; Garberich, R.F.; Harris, K.M. Clinical and pathologic findings of aortic dissection at autopsy: Review of 336 cases over nearly 6 decades. Am. Hear. J. 2018, 209, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Nienaber, C.A.; Peterson, M.D.; Woznicki, E.M.; Braverman, A.C.; Trimarchi, S.; Myrmel, T.; Pyeritz, R.; Hutchison, S.; Strauss, C.; et al. Early Mortality in Type A Acute Aortic Dissection. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 1009–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pape, L.A.; Awais, M.; Woznicki, E.M.; Suzuki, T.; Trimarchi, S.; Evangelista, A.; Myrmel, T.; Larsen, M.; Harris, K.M.; Greason, K.; et al. Presentation, Diagnosis, and Outcomes of Acute Aortic Dissection. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, A.; Montgomery, D.; Brinster, D.R.; Gilon, D.; Upchurch, G.R.; Gleason, T.G.; Estrera, A.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Eagle, K.A.; Hughes, G.C. Predicting In-Hospital Survival in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection Medically Treated. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1360–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampoldi, V.; Trimarchi, S.; Eagle, K.A.; Nienaber, C.A.; Oh, J.K.; Bossone, E.; Myrmel, T.; Sangiorgi, G.M.; De Vincentiis, C.; Cooper, J.V.; et al. Simple Risk Models to Predict Surgical Mortality in Acute Type A Aortic Dissection: The International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection Score. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 83, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.C.; Beaulieu, R.J.; A Ehlert, B.; Ratchford, E.V.; Black, I.J.H. Malperfusion syndromes in aortic dissections. Vasc. Med. 2016, 21, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimarchi, S.; Eagle, K.A.; Nienaber, C.A.; Rampoldi, V.; Jonker, F.H.; De Vincentiis, C.; Frigiola, A.; Menicanti, L.; Tsai, T.; Froehlich, J.; et al. Role of age in acute type A aortic dissection outcome: Report from the International Registry of Acute Aortic Dissection (IRAD). J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2010, 140, 784–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helder, M.R.; Schaff, H.V.; Day, C.N.; Pochettino, A.; Bagameri, G.; Greason, K.L.; Lansman, S.L.; Girardi, L.N.; Storlie, C.B.; Habermann, E.B. Regional and Temporal Trends in the Outcomes of Repairs for Acute Type A Aortic Dissections. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2019, 109, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylski, B.; Beyersdorf, F.; Kari, F.A.; Schlosser, J.; Blanke, P.; Siepe, M. Acute type A aortic dissection extending beyond ascending aorta: Limited or extensive distal repair. J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 148, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.B.; Chung, C.H.; Moon, D.H.; Ha, G.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Jung, S.H.; Choo, S.J.; Lee, J.W. Total arch repair versus hemiarch repair in the management of acute DeBakey type I aortic dissection☆. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2011, 40, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolomeo, R.; Leone, A.; Di Marco, L.; Pacini, D. When and how to replace the aortic arch for type A dissection. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Eusanio, M.; Berretta, P.; Cefarelli, M.; Jacopo, A.; Murana, G.; Castrovinci, S.; Di Bartolomeo, R. Total Arch Replacement Versus More Conservative Management in Type A Acute Aortic Dissection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2015, 100, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Lang, X.; Lu, F.; Song, Z.; Wang, J.; Han, L.; Xu, Z. Acute type A dissection without intimal tear in arch: Proximal or extensive repair? J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2014, 147, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leshnower, B.G.; Chen, E.P. When and how to replace the aortic root in type A aortic dissection. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geirsson, A.; Bavaria, J.E.; Swarr, D.; Keane, M.G.; Woo, Y.J.; Szeto, W.Y.; Pochettino, A. Fate of the Residual Distal and Proximal Aorta After Acute Type A Dissection Repair Using a Contemporary Surgical Reconstruction Algorithm. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007, 84, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berretta, P.; Patel, H.J.; Gleason, T.G.; Sundt, T.M.; Myrmel, T.; Desai, N.; Korach, A.; Panza, A.; Bavaria, J.; Khoynezhad, A.; et al. IRAD experience on surgical type A acute dissection patients: results and predictors of mortality. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.M.; Strauss, C.E.; Eagle, K.A.; Hirsch, A.T.; Isselbacher, E.M.; Tsai, T.T.; Shiran, H.; Fattori, R.; Evangelista, A.; Cooper, J.V.; et al. Correlates of Delayed Recognition and Treatment of Acute Type A Aortic Dissection. Circulation 2011, 124, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikwe, J.; Cavallaro, P.; Itagaki, S.; Seigerman, M.; DiLuozzo, G.; Adams, D.H. National Outcomes in Acute Aortic Dissection: Influence of Surgeon and Institutional Volume on Operative Mortality. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 95, 1563–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.D.; Benrashid, E.; Ross, A.K.; Pickett, L.C.; Smith, P.K.; Daneshmand, M.A.; Schroder, J.N.; Gaca, J.G.; Hughes, G.C. The utility of the aortic dissection team: outcomes and insights after a decade of experience. Ann. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2016, 5, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaja, R.; Talukder, S.; Norkunas, M.; Hoffman, R.; Nienaber, C.; Pepper, J.; Rosendahl, U.; Asimakopoulos, G.; Quarto, C. Impact of a streamlined rotational system for the management of acute aortic syndrome: sharing is caring†. Eur. J. Cardio-Thoracic Surg. 2018, 55, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstone, A.B.; Chiu, P.; Baiocchi, M.; Lingala, B.; Lee, J.; Rigdon, J.; Fischbein, M.P.; Woo, Y.J. Interfacility Transfer of Medicare Beneficiaries With Acute Type A Aortic Dissection and Regionalization of Care in the United States. Circulation 2019, 140, 1239–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helliker K, Burton T. Medical ignorance contributes to toll from aortic illness. The Wall Street Journal. , 2003. 4 November.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).