Submitted:
09 September 2023
Posted:
12 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
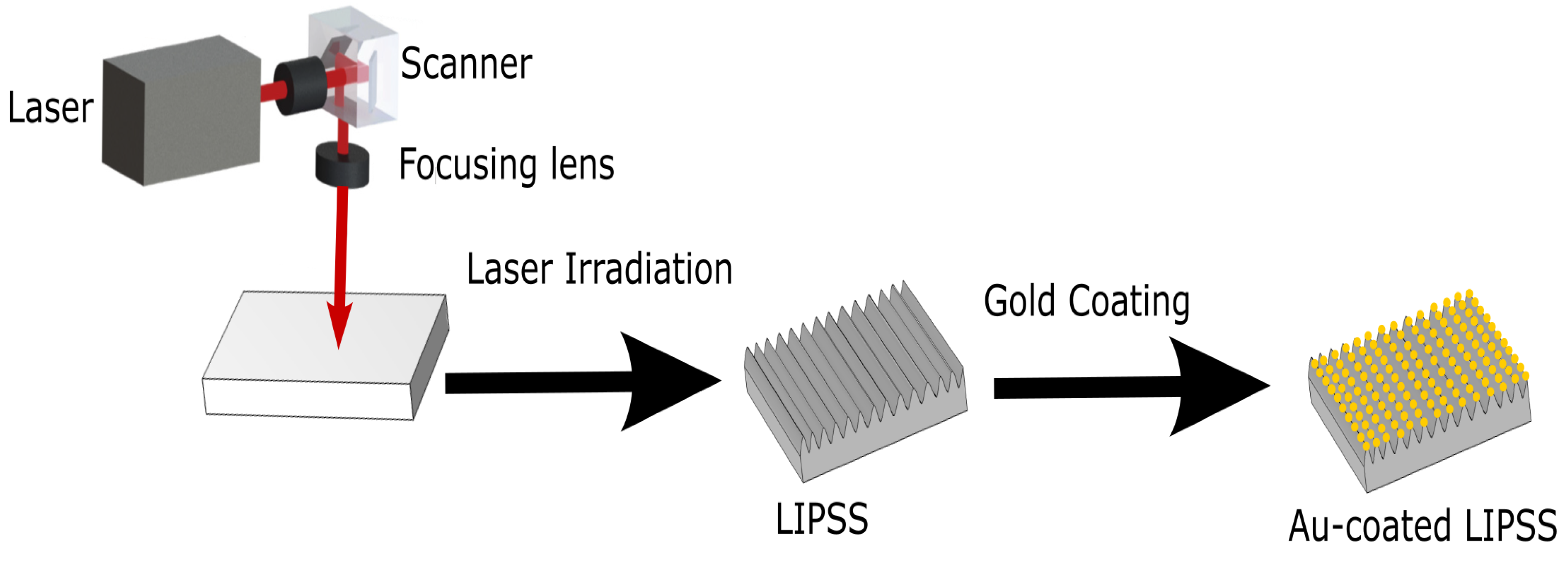
2. Experimental work and methodology
2.1. Fabrication of LIPSS on Silicon Substrates
2.2. Deposition of Gold Nanoparticles onto silicon Substrates
2.3. SERS experiments
3. Results and Discussion
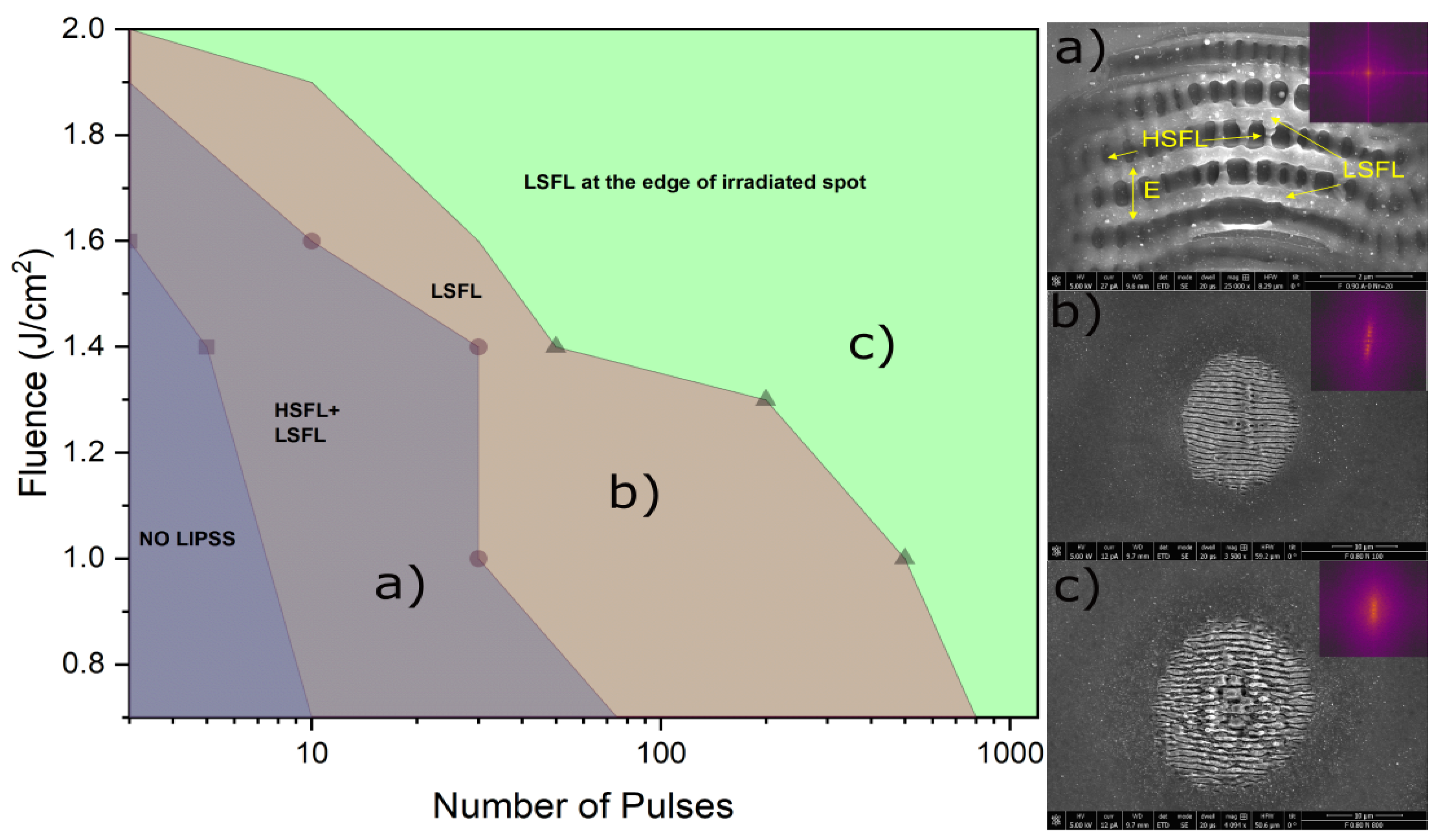
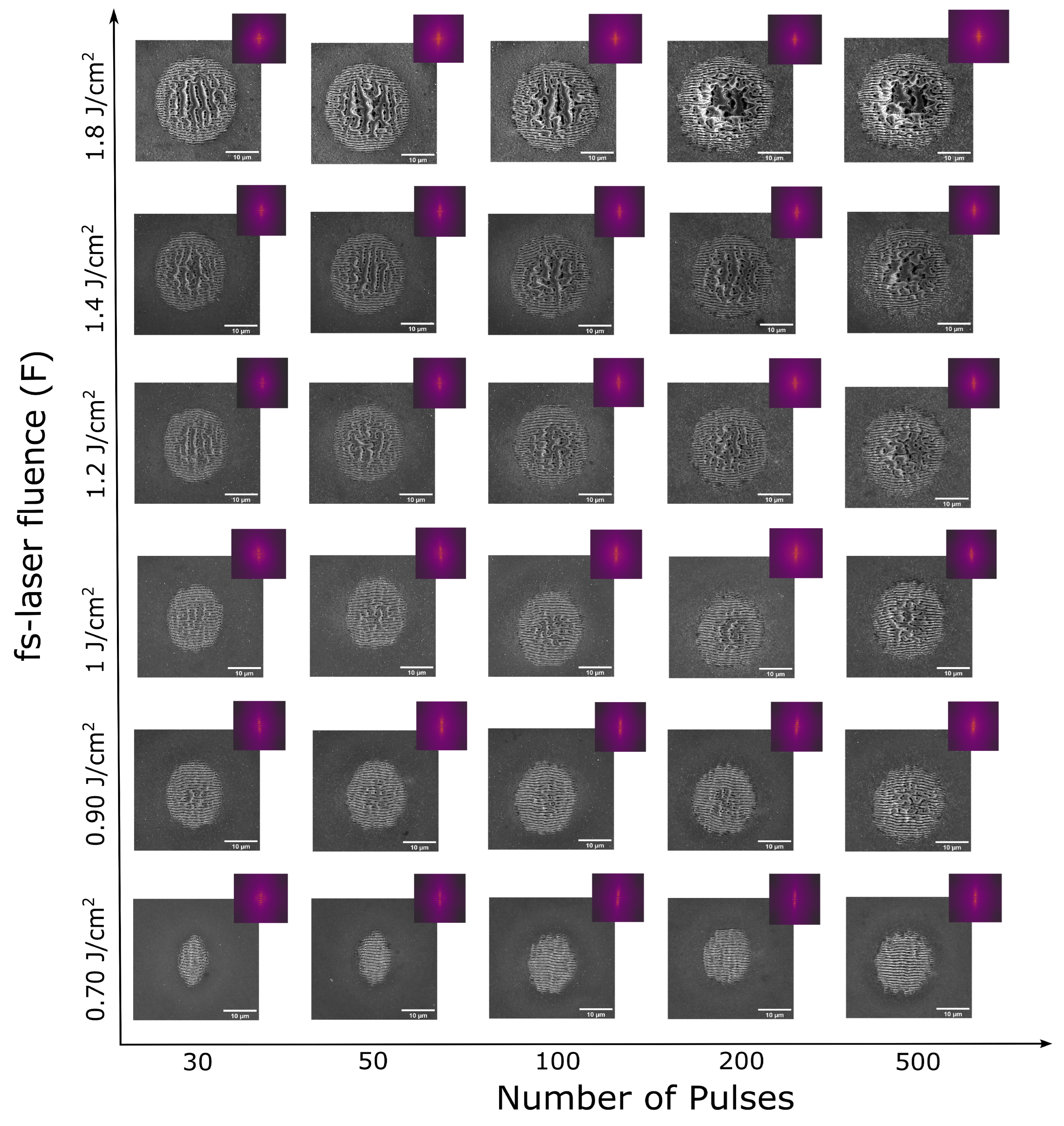
3.1. Evolution of LIPSS on silicon
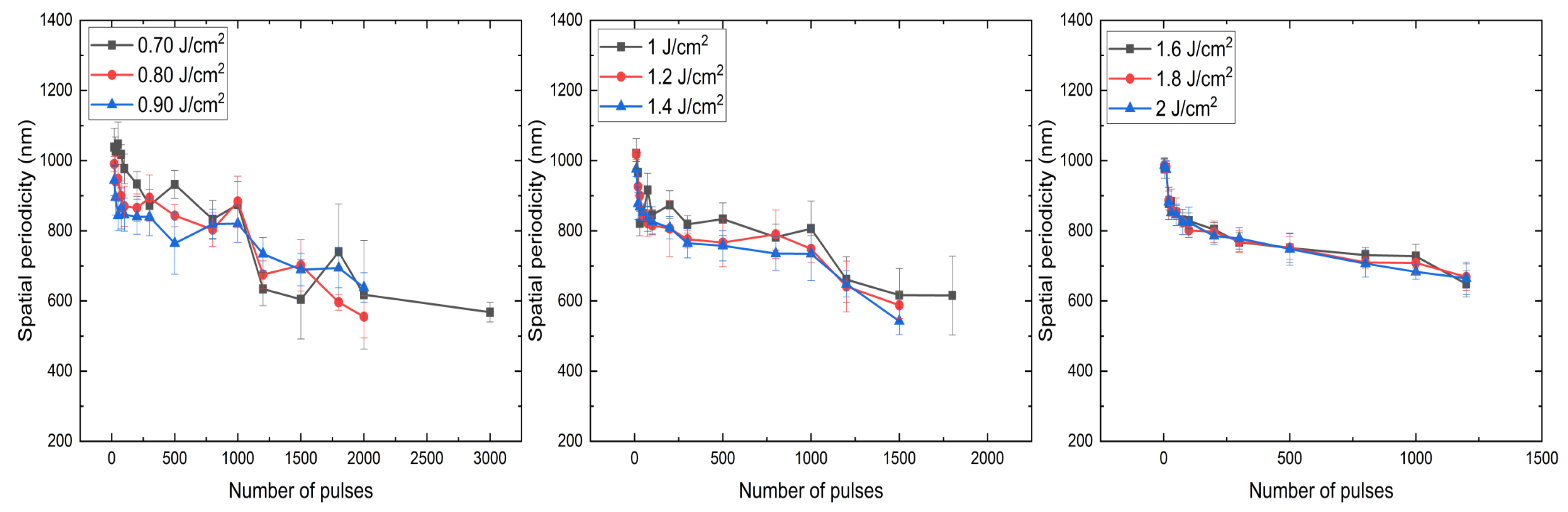
3.2. Periodicity Dependence on Fluence and Number of Pulses
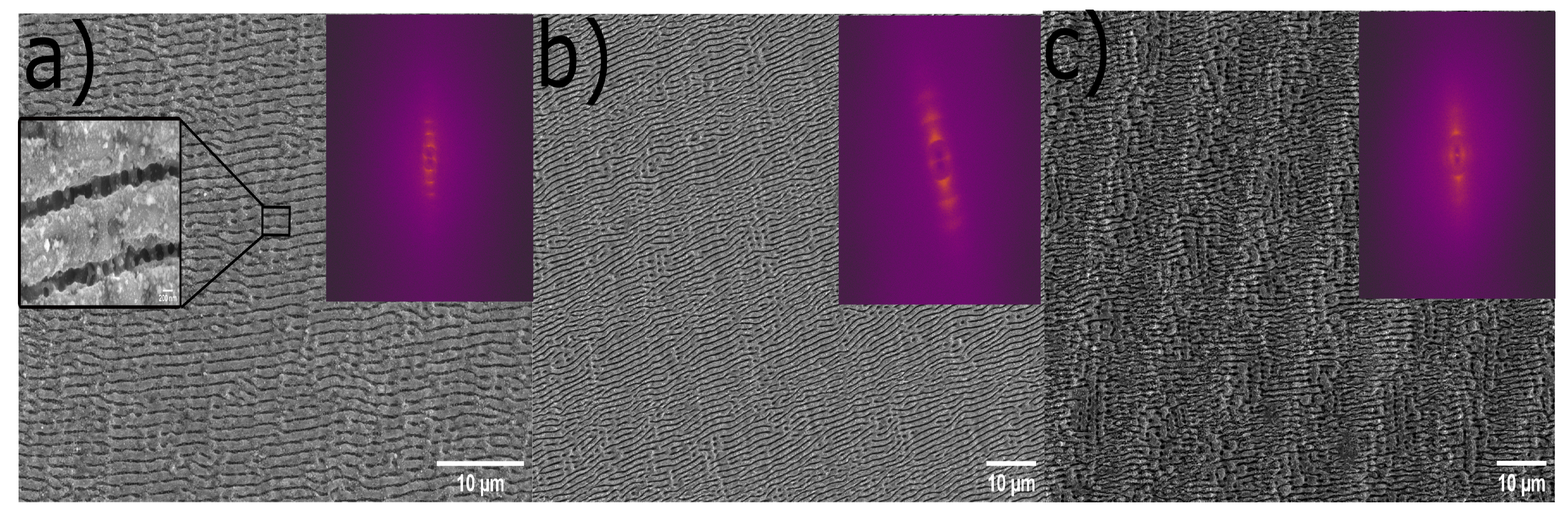
3.3. Fabrication of large area Si LIPSS and damage studies
3.4. SERS Outcomes Across LIPSS Stages
4. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gräf, S. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on different materials: Fundamentals, properties and applications. Advanced Optical Technologies 2020, 9, 11–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser & Photonics Reviews 2013, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar]
- Florian, C.; Kirner, S.V.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J. Surface functionalization by laser-induced periodic surface structures. Journal of Laser Applications 2020, 32, 022063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Kirner, S.V.; Krüger, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures (LIPSS). In Handbook of laser micro-and nano-engineering; 2020; pp. 1–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bonse, J. Quo vadis LIPSS?—recent and future trends on laser-induced periodic surface structures. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Xu, X. Laser fluence dependence of ripple formation on fused silica by femtosecond laser irradiation. Applied Physics A 2019, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. Journal of Applied Physics 2009, 106, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J. Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures: when Maxwell meets Marangoni 2022.
- Sipe, J.; Young, J.F.; Preston, J.; Van Driel, H. Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Physical Review B 1983, 27, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufft, D.; Rosenfeld, A.; Das, S.; Grunwald, R.; Bonse, J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures revisited: A comparative study on ZnO. Journal of Applied Physics 2009, 105, 034908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, A.; Haugen, H. Subwavelength ripple formation on the surfaces of compound semiconductors irradiated with femtosecond laser pulses. Applied Physics Letters 2003, 82, 4462–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varlamova, O.; Reif, J.; Varlamov, S.; Bestehorn, M. Self-organized surface patterns originating from laser-induced instability. In Progress in nonlinear nano-optics; 2015; pp. 3–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J. Pulse number dependence of laser-induced periodic surface structures for femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. Journal of Applied Physics 2010, 108, 034903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, W.; Hu, X.; Zhang, C. Functional performance of Silicon with periodic surface structures induced by femtosecond pulsed laser. Coatings 2022, 12, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, S.; Emory, S.R. Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. science 1997, 275, 1102–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uskoković-Marković, S.; Kuntić, V.; Bajuk-Bogdanović, D.; Holclajtner Antunović, I. Surface-enhanced raman scattering (SERS) biochemical applications. In Encyclopedia of spectroscopy and spectrometry; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Kosuda, K.; Bingham, J.; Wustholz, K.; Van Duyne, R.; Groarke, R. 4.06—nanostructures and surface-enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Comprehensive Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2016, 117–152. [Google Scholar]
- Kahraman, M.; Mullen, E.R.; Korkmaz, A.; Wachsmann-Hogiu, S. Fundamentals and applications of SERS-based bioanalytical sensing. Nanophotonics 2017, 6, 831–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, B.S.; Choi, S.; Choi, J.; Song, J.; Cho, S. Mn-doped V 2 VI 3 semiconductors: Single crystal growth and magnetic properties. Journal of applied physics 2005, 97, 10D324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Wang, R.; Wang, Q.; Xiang, Z.; Li, Z.; Gu, H.; Wang, X. An overview of surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates by pulsed laser deposition technique: fundamentals and applications. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials 2021, 4, 885–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.J.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Jia, L.; Kim, S.I.; Yoon, J.C.; Thomas, E.L.; Jang, J.H. An optimal substrate design for SERS: dual-scale diamond-shaped gold nano-structures fabricated via interference lithography. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 1836–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, G.; Chirumamilla, M.; Toma, A.; Gopalakrishnan, A.; Zaccaria, R.P.; Alabastri, A.; Leoncini, M.; Di Fabrizio, E. Plasmon based biosensor for distinguishing different peptides mutation states. Scientific reports 2013, 3, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Y.; Liao, J.D.; Ju, Y.H.; Chang, C.W.; Shiau, A.L. Focused ion beam-fabricated Au micro/nanostructures used as a surface enhanced Raman scattering-active substrate for trace detection of molecules and influenza virus. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 185308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Dai, Y.; Hu, Y.; Ni, J.; Ji, S.; Cai, Z.; Smith, Z.J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; et al. Nanogap plasmonic structures fabricated by switchable capillary-force driven self-assembly for localized sensing of anticancer medicines with microfluidic SERS. Advanced Functional Materials 2020, 30, 1909467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, V.; Kanaujia, P.K.; Bommali, R.K.; Prakash, G.V. Efficient Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering substrates from femtosecond laser based fabrication. Optical Materials 2017, 72, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebollar, E.; Sanz, M.; Perez, S.; Hernandez, M.; Martín-Fabiani, I.; Rueda, D.R.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Domingo, C.; Castillejo, M. Gold coatings on polymer laser induced periodic surface structures: assessment as substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2012, 14, 15699–15705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, P.; Shi, X.; Jiang, F.; Xu, X. Superhydrophobic nanostructured copper substrate as sensitive SERS platform prepared by femtosecond laser pulses. Applied Surface Science 2020, 501, 144269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.; Bharati Moram, S.S.; Yendeti, B.; Podagatlapalli, G.K.; Nageswara Rao, S.; Pathak, A.P.; Mohiddon, M.A.; Soma, V.R. Femtosecond laser-induced, nanoparticle-embedded periodic surface structures on crystalline silicon for reproducible and multi-utility SERS platforms. Acs Omega 2018, 3, 18420–18432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erkızan, S.N.; İdikut, F.; Demirtaş, Ö.; Goodarzi, A.; Demir, A.K.; Borra, M.; Pavlov, I.; Bek, A. LIPSS for SERS: Metal Coated Direct Laser Written Periodic Nanostructures for Surface Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy. Advanced Optical Materials 2022, 10, 2200233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Guan, K.; Lu, L.; Zhang, J.; Lu, N.; Guan, Y. Engineered functional surfaces by laser microprocessing for biomedical applications. Engineering 2018, 4, 822–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, J.E.; Santos, D.P.d.; Poppi, R.J. Fabrication of gold nanoparticle-coated paper and its use as a sensitive substrate for quantitative SERS analysis. Microchimica Acta 2016, 183, 2745–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xu, B.B.; Cao, X.W.; Li, Q.K.; Tian, W.J.; Chen, Q.D.; Juodkazis, S.; Sun, H.B. Competition between subwavelength and deep-subwavelength structures ablated by ultrashort laser pulses. Optica 2017, 4, 637–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Edfuf, Y.; Sánchez-Gil, J.A.; Garcia-Pardo, M.; Serna, R.; Tsibidis, G.D.; Giannini, V.; Solis, J.; Siegel, J. Tuning the period of femtosecond laser induced surface structures in steel: From angled incidence to quill writing. Applied Surface Science 2019, 493, 948–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, Z. Origin of Laser-Induced Near-Subwavelength Ripples: Interference between Surface Plasmons and Incident Laser. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Xu, L.; Lu, Y. Continuous modulations of femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures and scanned line-widths on silicon by polarization changes. Optics express 2013, 21, 15505–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamuro, K.; Hashida, M.; Miyasaka, Y.; Ikuta, Y.; Tokita, S.; Sakabe, S. Laser fluence dependence of periodic grating structures formed on metal surfaces under femtosecond laser pulse irradiation. Phys. Rev. B 2010, 82, 165417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Sub-100-nm laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of titanium by Ti: sapphire femtosecond laser pulses in air. Applied Physics A 2013, 110, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakabe, S.; Hashida, M.; Tokita, S.; Namba, S.; Okamuro, K. Mechanism for self-formation of periodic grating structures on a metal surface by a femtosecond laser pulse. Phys. Rev. B 2009, 79, 033409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, N.; Xu, Z. Origin of laser-induced near-subwavelength ripples: interference between surface plasmons and incident laser. ACS nano 2009, 3, 4062–4070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Munz, M.; Sturm, H. Structure formation on the surface of indium phosphide irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. Journal of Applied Physics 2005, 97, 013538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, W.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Lu, Y. Anisotropy modulations of femtosecond laser pulse induced periodic surface structures on silicon by adjusting double pulse delay. Optics express 2014, 22, 15820–15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Yao, J.W.; Liu, H.Y.; Dai, Q.F.; Wu, L.J.; Lan, S.; Trofimov, V.A.; Lysak, T.M. Colorizing silicon surface with regular nanohole arrays induced by femtosecond laser pulses. Optics letters 2012, 37, 1106–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.; Li, X. Optimal size of gold nanoparticles for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy under different conditions. Journal of nanomaterials 2013, 2013, 49–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlen, A.; Berthomieu, D.; Edely, M.; Rérat, M. Raman spectra and DFT calculations of thiophenol molecules adsorbed on a gold surface. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 2022, 24, 29505–29511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, R.L.; Farrar, L.W.; Greeneltch, N.G.; Van Duyne, R.P.; Polla, D.L. Measurement of the Raman line widths of neat benzenethiol and a self-assembled monolayer (SAM) of benzenethiol on a silver-coated surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate. Applied Spectroscopy 2012, 66, 740–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buividas, R.; Stoddart, P.R.; Juodkazis, S. Laser fabricated ripple substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Annalen der Physik 2012, 524, L5–L10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, G.; Brehm, G.; Schneider, S.; Graener, H.; Seifert, G.; Nielsch, K.; Choi, J.; Göring, P.; Gösele, U.; Miclea, P.; et al. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy employing monodisperse nickel nanowire arrays. Applied physics letters 2006, 88, 023106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

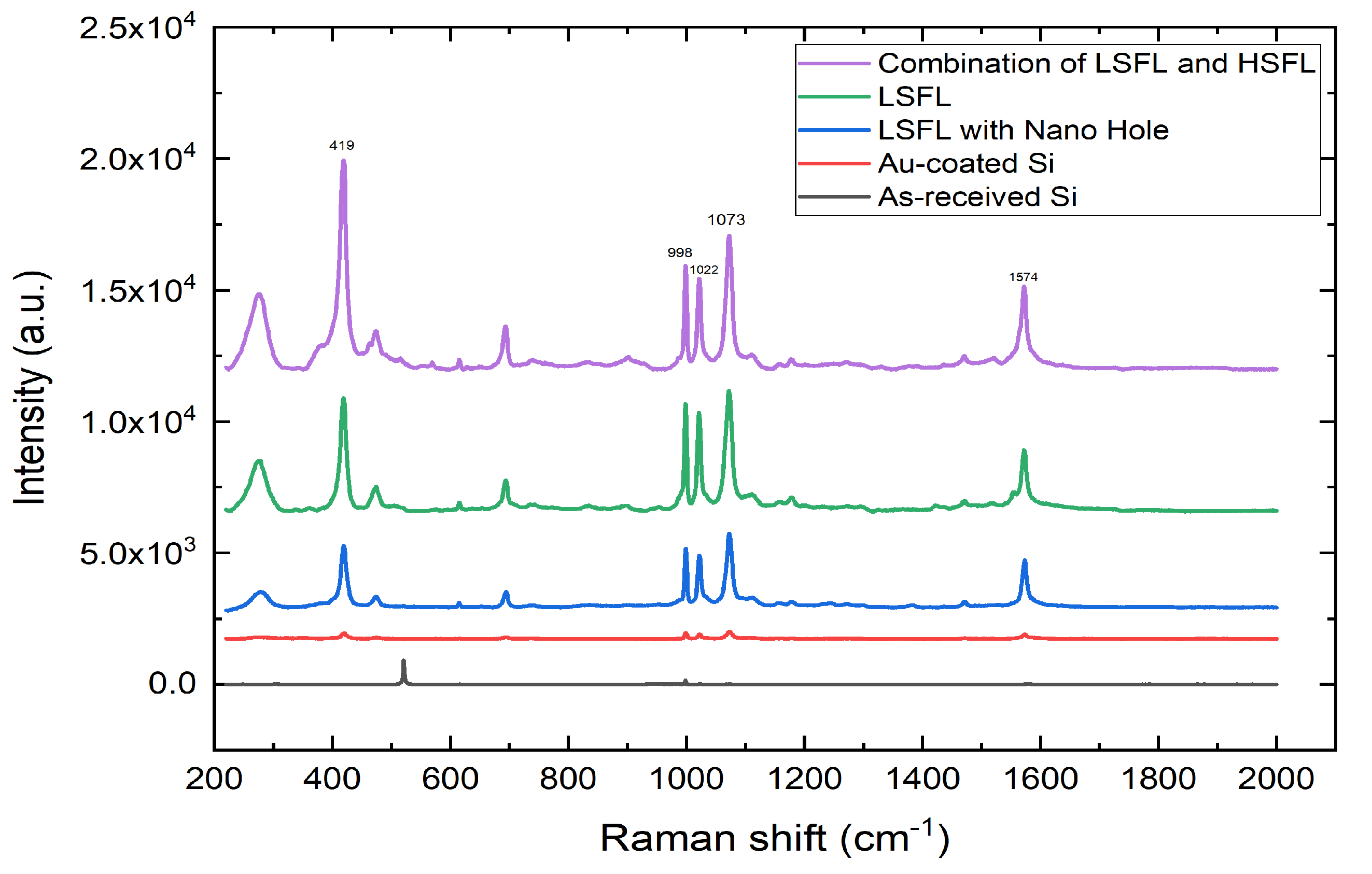
| Peak () | 419 | 998 | 1022 | 1073 | 1574 |
| Combination of LSFL and HSFL | |||||
| LSFL Structures | |||||
| LSFL with nano-hole structures |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





