1. Introduction
The cervical vertebral foramina are the lateral canals where nerve roots exit the vertebral column. These foramina, located in a motion segment, can undergo degenerative changes over time, potentially leading to cervical foraminal stenosis [
1,
2]. Foraminal stenosis can also occur more rapidly in the case of disc herniation, trauma or tumor [
3]. Cervical foraminal stenosis with radiculopathy has a prevalence ranging from 121 to 507 per 100,000 individuals [
4].
A major challenge in diagnosing conditions in the cervical spine is the discrepancy between MRI findings and the clinical presentation. This can be attributed to the fact that MRI images are often obtained in a relaxed supine position, which may not fully capture the pathology present during functional positions since many patients experience aggravated radiculopathy in specific head movements and positions. The dynamic head movements can be used for differential diagnosis and identifying affected nerve roots through the Spurling test [
5]. The test is a diagnostic tool that utilizes cervical spine dynamics and is often used as a complement to the cervical MRI in the attempt to pinpoint in the source of the pain and find the narrow foramina [
6]. The Spurling test has previously shown to have a high specificity of 0.89–1.00 (95% CI 0.59–1.00) and a moderate sensitivity ranging from 0.38 to 0.97 (95% CI 0.21–0.99) to detect cervical foraminal stenosis [
7]. There are indications that the Spurling test may have a both higher sensitivity and specificity than generally anticipated, but what actually happens in the foramina has not been thoroughly investigated [
8].
In the lumbar spine, the value of pure axial loading during MRI acquisition has been reported and proven to change both central and foraminal properties, which can sharpen the diagnostics in cases when an unloaded MRI does not clearly correlate with the patient’s symptoms [
9,
10,
11]. Similar to situations encountered in the lumbar spine, when the suspected foramina is not clear, it rises the question if the pathology in the cervical spine is desguised because the diagnostic MRI is done in a relaxed supine position? If foramina could be visualized in a “Spurling like position” it could possibly aid, specifically in situations when there are more than one foraminal stenosis and difficulties to pinpoint where the symptoms arise from.
Previous attempts have been made to study the foramina in the cervical spine with the head in different static positions such as flexion and extension [
12], as well as in more complex combined movements [
13]. Some effects on the foraminal area have been observed. However, this previous work has primarily focused on healthy individuals. Furthermore, the techniques employed in these studies lacked the capability to dynamically adjust the positioning of the patient's head in response to their symptoms and to simultaneously provide feedback on the exacerbation of pain.
In a recent study involving 10 healthy participants, an MRI compatible device with MRI – referred to as the Dynamic MRI Compression System (DMRICS®) was used. This device has the capacity to gradually apply controlled axial forces at the four corners of a head plate with the patient in place in the MRI, and when symptoms occur acquire images. In this way the device assists in effectively simulating a Spurling test and has in healthy individuals been demonstrated to induce substantial alterations of the cervical foramina compared to relaxed images [
14].To our knowledge there are no other devices available for systematic position and force control of the cervical spine in an MRI gantry.
The aim of this study was to investigate the feasibility to use DMRICS in patients with intermittent arm radiculopathy and assess possible changes in cervical foramina, with both quantitative measurements and grading systems, on MRI during a simulated Spurling test.
2. Materials and Methods
Ten patients referred to our spine surgery unit between March and May 2022 for suspected cervical foraminal stenosis were consecutively included. The inclusion criteria were intermittent arm radiculopathy with a positive Spurling test, age between 20-60 years and a recently conducted MRI showing one or two ipsilateral stenotic foramina that might explain the symptoms. All patients underwent a new MRI scan in the DIMRICS, first in a relaxed supine position and thereafter with the neck in an extended and lateral flexed position with a slight rotation including an applied axial load, to simulate the position of a Spurling test [
6]. The position and load of the head/neck was slowly applied until a position where the patients experienced radiating arm pain or could not withstand more pressure. Two image acquisitions were obtained, first in the relaxed position and then in the finally reached provoked position. The Neck Disability Index (NDI) and EQ-5D 5L were collected right before the MRI. All participants filled out a Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) directly before and after the examination, reporting on neck and arm pain. Further, the patients answered if the possible change of pain during the examination was concordant with the pain experienced on a daily basis. All included patients signed a written informed consent before inclusion and the procedures were performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board in Gothenburg, Sweden (Dnr [574-18]).
2.1 The Compression Device
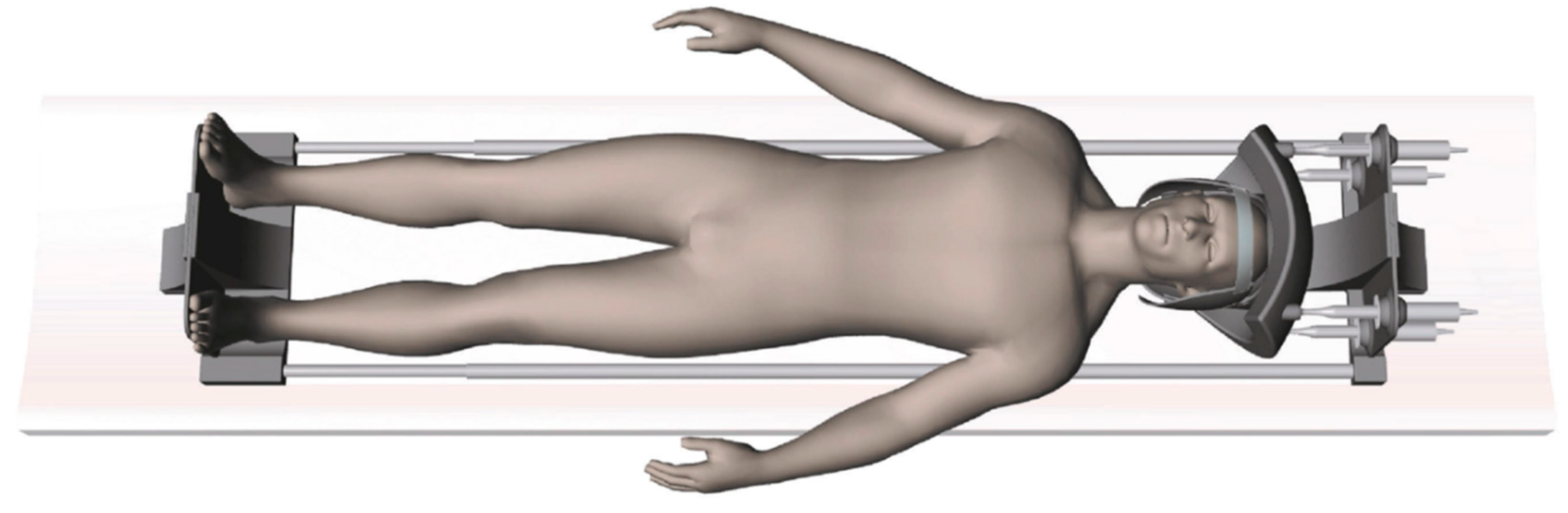
The Dynamic MRI Compression System (DMRICS), an MRI-compatible compression device, has previously been developed to apply controlled forces to the head and neck during image acquisition (
Figure 1). The device utilizes a water hydraulic system with four cylinders connected to a helmet-like structure on the patient’s head, which is linked to an adjustable footplate for varying patient heights. The helmet’s hydraulic cylinders connect to tubes leading to the control room cylinders, which are attached to linear actuators for real-time force control and monitoring. This enables flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation, and axial compression adjustments. To reach the Spurling position, force is applied to the posterior cylinders and the to the side that the head is flexed towards. A time-stamped log tracks all actions using a custom-developed software. During the compression, the relative forces exerted on each hydraulic cylinder was measured and the data was saved in the log. Instead of calibrating the forces applied in kilograms or pounds, it provides a relative force measurement during compression. The DMRICS has previously only been tested on healthy adults [
14].
2.2 Image Acquisition and Analysis
Using an MRI 3T scanner (GE 3T Architect Medical Systems, Waukesha, WI, USA) and an air coil, T2-weighted (T2w) fast spin echo images were obtained in the oblique sagittal plane (TR 3910 ms, TE 102 ms, FOV 27x27 cm2, matrix 280x280 and voxel size 1.0x1.0x1.0 mm3) and the axial plane (TR 1292 ms, TE 90.85 ms, FOV 26x26 cm2, matrix 400x280 and voxel size 0.6x0.9x5.0 mm3). The latest GE Software SW 29.1 was used. The images in the oblique sagittal plane were evaluated only on the symptomatic side. The exact same scan protocol was applied in both the relaxed supine position and in the subsequent provoked position. The angles for image caption of oblique sagittal and axial scans were chosen to target the foramina in the suspected level(s) as optimal as possible. Multiplanar reconstruction was used only to fine pitch the angles to find the best possible view. Standard protocols for images storage practices were employed throughout the process.
2.3 Measurements and Observers
A radiologist (>15 years of experience) assessed the foraminal properties of C4-C7 on the symptomatic side on images both in the relaxed and in the provoked position. All investigations were coded for blinding purposes. In all included patients, the assessed levels included the clinically suspected stenotic foramina (from the MRI at referral). Two quantitative measures were utilized: the smallest foraminal area on the oblique sagittal images and the foraminal cross-distance in the narrowest axial image plane. Additionally, the radiologist employed the Park and Kim grading systems [
15,
16] to classify foraminal stenosis in both image planes and the Pfirrmann classification system [
17] to grade disc degeneration for the discs levels at all examined foramina. The clinic's standard software, Agfa Enterprise Imaging, was used for all measurements and classifications. Intra- and inter reliability of the measurements has been tested in a previous pilot study of the DMRICS proving excellent intrarater reliability (> 0.98) and good interrater reliability (> 0.62) [
14].
2.4 Statistical Analysis
The Mann-Whitney U-test was used when comparing differences between groups. When comparing differences within groups, the Wilcoxon matched-pairs sign-rank test was used. The Spearman rank correlation was used to estimate the degree of association between quantitative and qualitative measures (Park and Kim). To estimate the effect size for differences in qualitative measures between groups, we estimated ordinal logistic regressions and reported odds ratios with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI). The significance level was set to 5%. The NDI was interpreted with guidance of Vernon et al. [
18] that suggest that a score between 0 and 4 represents no disability, 5 and 14 mild disability, 15 and 24 moderate disability, 25 and 34 severe disability, and greater than 35 complete disability. All analyses were done using SPSS software version 28 and Stata version 17.0.
3. Results
3.1 Baseline Data
The study population consisted of 10 patients resulting in 30 examined foramina. The baseline data and level of disc degeneration is displayed in
Table 1.
3.2 Compliance and Patient Experience of the DMRICS Equipment
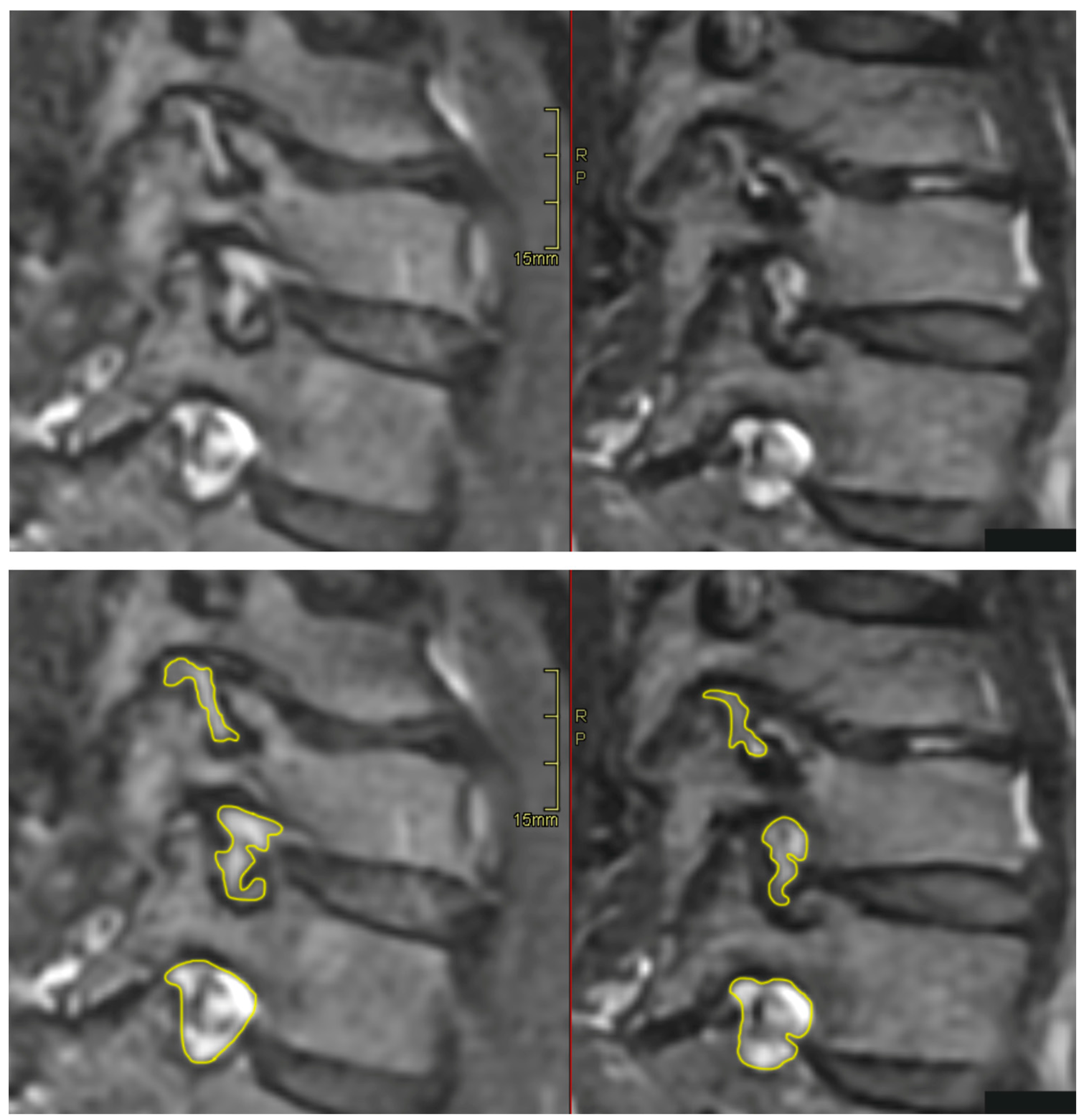
All patients were positioned without any complaints in the DMRICS apparatus, outside the MRI gantry. The patients were subsequently positioned within the MRI for a relaxed image acquisition. After successfully conducting the simulated Spurling test, immediate imaging was performed, which produced clinically acceptable image quality in 9 out of 10 patients in both relaxed and provoked position, as shown in
Figure 2.
3.3 Applied Force by DMRICS
In 7/9 patients there was 50% or stronger force applied to the ipsilateral posterior cylinder compared to the contralateral anterior cylinder to achieve a simulated Spurling test.
3.4 Changes of NRS Scores in Neck and Arm and If the Pain Was Concordant
During the simulated Spurling test, the neck pain NRS scores increased from 4.6 (SD: 1.84) to 6.8 (SD: 2.25, p = 0.011), and the arm pain NRS scores increased from 5.2 (SD: 2.94) to 6.7 (SD: 3.09, p = 0.017). Nine out of 10 of the patients reported that the arm pain experienced during the application of forces by the DMRICS was concordant with their ordinary intermittent arm pain symptoms.
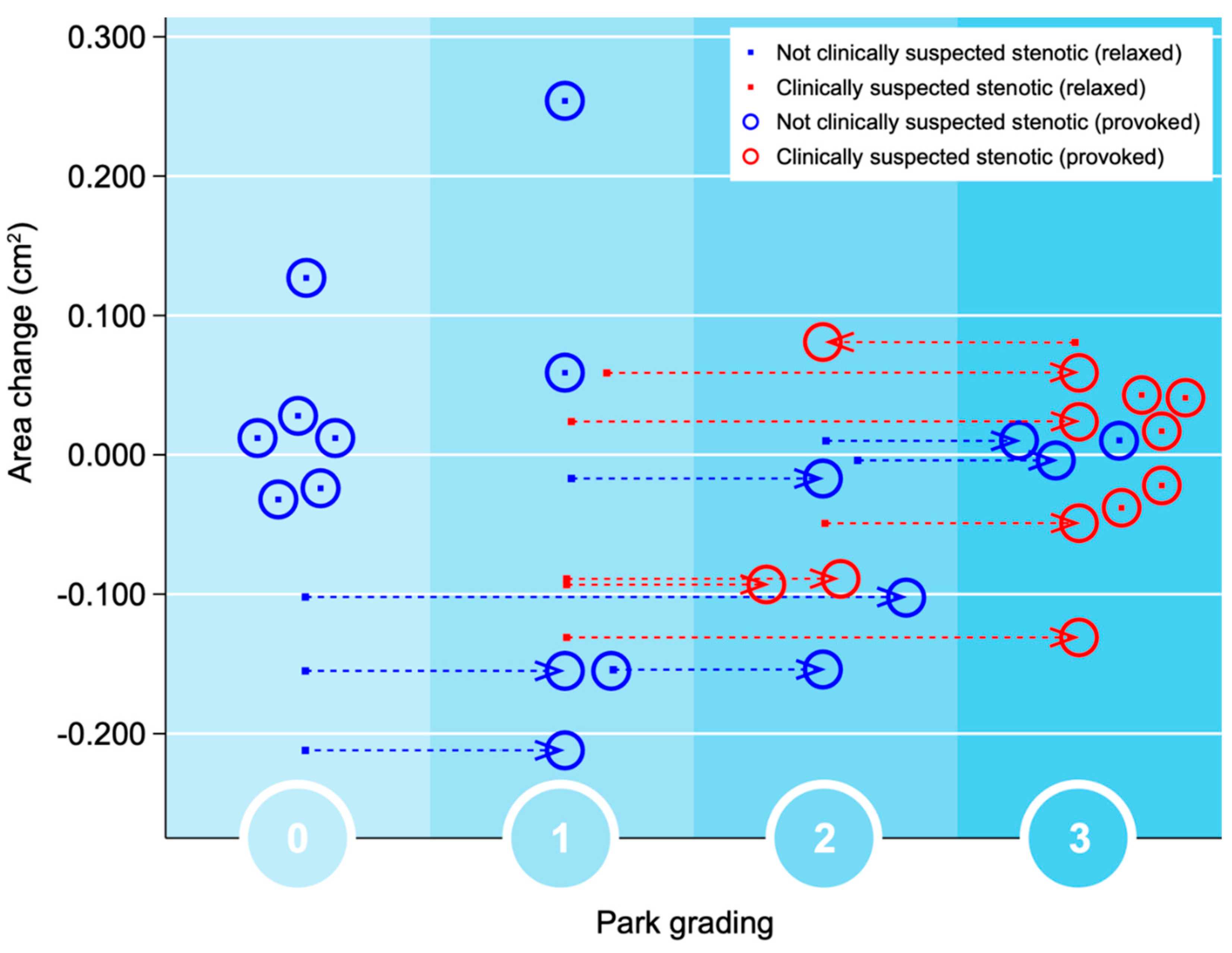
3.5 Qualitative Grading of Foramina in Relaxed and Provoked Position
Significant changes of gradings of Park and Kim classifications respectively after provocation (both p = 0.000) were seen. After applying the simulated Spurling test, all initially labeled stenotic foramina were classified as Park grade 2 or 3, with some moving up by 1 grade and others by 2 grades. In 13 out of 27 gradings by Park and 9 out of 27 gradings by Kim escalated to a higher grade after provocation. However, there were no significant alterations in the quantitative assessments. In foramina with high Park gradings (2 or 3) in the relaxed images, only minor area changes were observed, depicting that the degenerative segments are less dynamic, see
Figure 3.
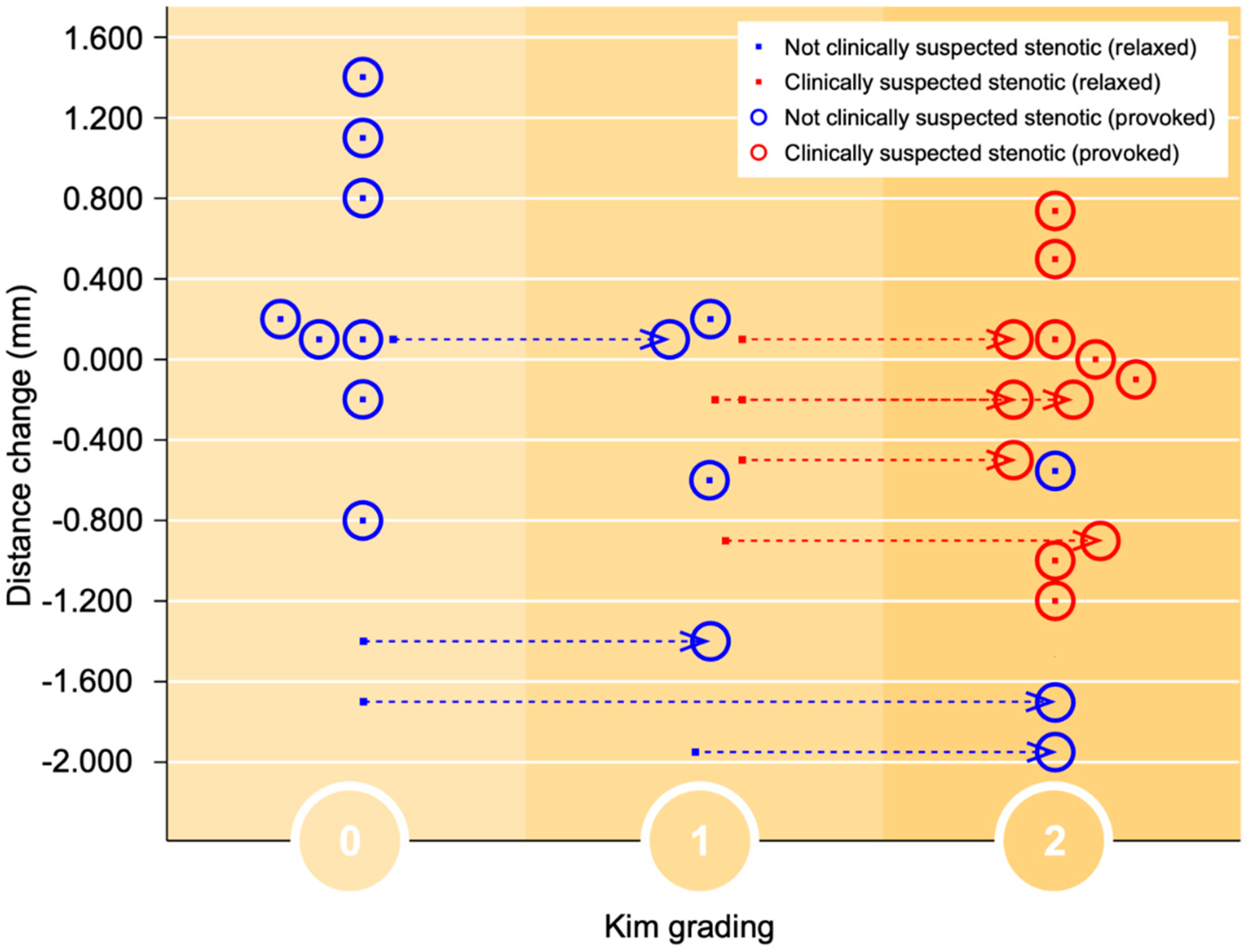
In accordance with the foraminal changes related to Park gradings during provocation, the foraminal Kim gradings during provocation were all assessed as grade 2, compared to 1 or 2 in the relaxed position, see
Figure 4.
3.6. Quantitative Measurements of Foramina in Relaxed and Provoked Position
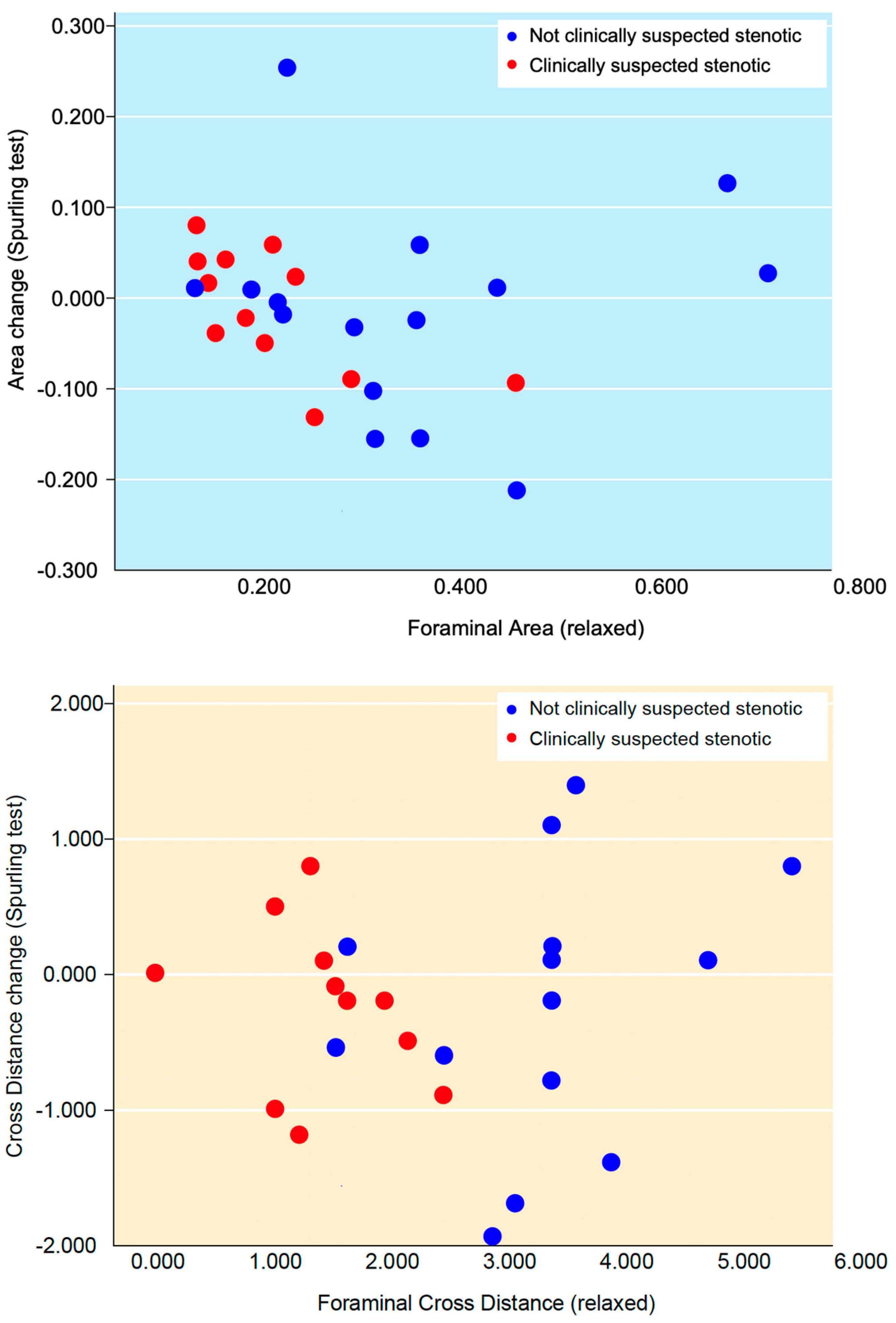
The changes of all foraminal area and cross distance measurements after the simulated Spurling test did not show any statistically significant difference, -0.013 cm2 (p > 0.503) and -0.21 mm (p > 0.260) respectively. Neither was any statistical differences found for area or cross distance changes in suspected nor for not suspected foramina when comparing measurements at rest and during provocation. The clinically suspected stenotic foramina (from MRI at referral) had lower values for both area and cross distance and also small alterations in area size and cross-distance after provocation, see
Figure 5.
3.7. Changes of Foramina in Relation to Disc Degeneration
In the simulated Spurling test, 12/18 foramina adjacent to discs with Pfirrmann grades 2 or 3 exhibited a reduction in measured area, while 7/9 foramina next to discs with Pfirrmann grades 4 or 5 increased in size. Furthermore, 11/18 foramina neighboring discs with Pfirrmann grades 2 or 3 showed a decrease in cross distance following the provocation. In contrast, foramina adjacent to discs with Pfirrmann grades 4 or 5 showed mixed results: 3 foramina increased, 5 decreased, and 1 remained unchanged in cross distance.
3.8. Qualitative Grading Systems in Relation to Suspected Levels and Area/Distance Measurements
If the pre-referral MRI indicated potential foraminal stenosis, the likelihood of being categorized in a more advanced Park classification was amplified by a factor of 18.6 (p = 0.002). Similarly, the probability of landing in a higher Kim classification increased by a factor of 19.6 (p = 0.032).
There was a strong association between the measured area as well as cross distances in relation to the assigned classification level for the Park (p= 0.000) and Kim (p = 0.000) systems, both during relaxed and provoked positions.
4. Discussion
This pilot study examined the feasibility of the DMRICS in patients with intermittent arm radiculopathy, showing that the device was well-tolerated by all patients with obtained images of diagnostic quality during provocation in all patients except one. The device was able to simulate the Spurling test resulting in a concordant pain in 9/10 of the patients and changes in nerve compromise grading but not quantitative measures of the foramina.
The significant increase of the qualitative gradings of the foramina, when comparing MRI before and during the simulated Spurling test, indicate that a Spurling test leads to higher Park and Kim grades. This offers not only insights into the variations of the often-employed clinical Spurling test but also proposes a possible clinical utility for dynamic MRI. The method could help in determining the severity of foraminal stenosis and identifying the impacted nerve roots if they are not distinctly discernible in a routine, relaxed MRI. Especially when several foramina are narrow on a routine MRI and the symptoms and clinical examination can´t discriminate which nerve root(s) that are giving rise to the experienced pain. However, for the foraminal area and cross-distance measures no significant changes were detected in the present work. The reason for these contradictory findings may be that the foraminal shape shifts with compression and thereby the nerve compression may increase even if the overall area is not changed or even increases, see
Figure 2. Further, the magnitude of measurement error in such small structures, especially for the axial-cross distance measurements may also play a role here.
In previous work with the cervical spine in different positions during MRI Bartlett and colleagues [
19] provided empirical evidence illustrating foraminal changes in images captured during both flexion and extension. Subsequently, a more comprehensive study conducted by Muhle et al [
12] expanded upon these findings. Muhle's research included not only images taken in flexion and extension, but also those captured during rotation, thereby demonstrating foraminal area changes across various positions on the oblique image plane. In this study, the research team employed an MRI-compatible head fixation device, which facilitated the accurate positioning of the head during image acquisition. This device was however a fixed construct placing the head and cervical spine in a static unloaded position and the included individuals were healthy subjects without any neck or arm pain.
More similar to what was performed in our study Takasaki and colleagues [
13] conducted MRI scans in various static head positions, including during a simulated Spurling test. However, this was also performed on a healthy group of individuals (23 participants, average age 24.5 years). A reduction of the foraminal area on the ipsilateral side of the executed Spurling test, was observed on the oblique sagittal image plane. In our study, wherein we focused on patients experiencing intermittent radiculopathy, averaging 44.5 years in age, we found no such measurable area reduction. Differences in the biomechanical properties of the cervical spine and intervertebral discs under varying degrees of degenerations may be a reason for this, with possible more changes of the foraminal form than the area in patients with more degeneration. This may explain the somewhat conflicting findings between the present study on patients with known degeneration and previous studies on healthy subjects regarding quantitative measurements as in opposition to individuals with less degenerated higher discs. This was supported by our findings that foramina adjacent to discs with lower Pfirrmann grades (2 or 3) showed a reduction in area and cross-distance following the simulated Spurling test, while foramina next to discs with higher Pfirrmann grades (4 or 5) exhibited mixed results. These findings are in accordance with findings in the lumbar spine where degenerative motion segments had a smaller range of motion compared to less degenerated segments [
20].
There were conceptional differences between our study and previous studies. Instead of using a static position, we progressively applied the Spurling test, akin to how it’s done in a clinical setting. During the change of head/cervical position the patients were asked to communicate their discomfort threshold, and the provocation was stopped, and images were acquired at that precise position. It was only in one out of ten patients that the images taken during the simulated test did not reach good quality (caused by motion artifacts). However, the obtained sequences were captured in a relatively short time frame, less than 3 minutes, which probably contributed to the good acceptance among these patients.
In both the initial MRI scans at referral and the new relaxed MRI scans in this study, we found a strong correlation between the severity of foraminal stenosis (quantified through measurements) and the Park and Kim classification systems. These findings align with previous studies [
21,
22]. Notably, images taken during provocation showed even higher scores in the Park and Kim classifications, reinforcing the reliability of these systems. This suggests the potential clinical utility of imaging in a provoked position for more accurate diagnosis.
4.1. Clinical Relevance and Future Perspective
The DMRICS may help to identify the specific nerve roots responsible for the patient's symptoms if this is clinically not obvious, which could facilitate more targeted treatment approaches, such as selective nerve root blocks or addressing limited number of levels during surgery. The study also considered the patient experience during the use of the DMRICS device, as well as changes in pain levels before and after the simulated Spurling test, thereby providing insights into the potential clinical applicability of the device.
Future research is warranted to validate present findings in larger cohorts and investigate the diagnostic accuracy of the DMRICS in differentiating between nerve roots signaling pain due to compression and nerve roots without pain signaling, but located in a narrow foramina, in patients with cervical radiculopathy.
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
The strengths of this study include its novelty, as it utilizes a newly developed MRI-compatible compression device to simulate the Spurling test during MRI acquisition. Furthermore, the study employs a thorough and well-defined methodology, including the use of multiple quantitative and qualitative measures for assessing cervical foramina.
A limitation is that the present study is a pilot study including only a small sample size, with low statistical power. This may have the reduced possibility to detect small differences in quantitative measurements of the foraminal area and cross distance, especially for the degenerated symptomatic levels. Moreover, the limited resolution of conventional MRIs can pose challenges in accurately assessing area and cross-distance measurements due to the substantial influence of partial volume effects. These imperfections in the images may be less consequential when performing qualitative evaluations as opposed to precise quantitative measurements.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, our pilot study demonstrates the potential value of the DMRICS device in simulating the Spurling test in supine position and assessing cervical foraminal changes in patients with intermittent arm radiculopathy. The device may enhance the diagnostic accuracy of cervical radiculopathy by providing additional information on the biomechanical behavior of the cervical spine and foraminal dimensions during provocation. Further research with larger sample sizes and diverse patient populations is warranted to validate the clinical utility of the DMRICS in the diagnosis and management of cervical radiculopathy.
6. Patents
Patent of DMRICS is pending (no 2251201-6).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, John Hutchins, Hanna Hebelka, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby; Formal analysis, John Hutchins and Tor Åge Myklebust; Funding acquisition, Helena Brisby; Investigation, John Hutchins, Hanna Hebelka, Pär-Arne Svensson, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby; Methodology, John Hutchins, Hanna Hebelka, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby; Project administration, John Hutchins and Helena Brisby; Resources, Helena Brisby; Supervision, Hanna Hebelka, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby; Validation, Hanna Hebelka, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby; Visualization, John Hutchins; Writing – original draft, John Hutchins; Writing – review & editing, John Hutchins, Hanna Hebelka, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby.
Funding
This research was funded by grants from the Swedish state under an agreement between the Swedish government and the county councils, the ALF agreement, grant number: ALFGBG-965910(HB), from AFA Insurance Foundation Sweden and from King Gustav V’s and Queen Victoria’s Freemason Foundation. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Gothenburg Regional Ethics Committee, Dnr 574-18.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The measurement data details are available upon request from the corresponding author. The MRI data are not publicly available due to ethical and privacy policy reasons.
Conflicts of Interest
John Hutchins, Hanna Hebelka, Kerstin Lagerstrand and Helena Brisby have partial ownership in patent holding company of the DMRICS compressive device.
References
- Holck P (2010) [Anatomy of the cervical spine]. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 130:29-32. [CrossRef]
- Hoy D, March L, Woolf A, Blyth F, Brooks P, Smith E, Vos T, Barendregt J, Blore J, Murray C, Burstein R, Buchbinder R (2014) The global burden of neck pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Annals of the rheumatic diseases 73:1309-1315. [CrossRef]
- Rao R (2002) Neck Pain, Cervical Radiculopathy, and Cervical Myelopathy: Pathophysiology, Natural History, and Clinical Evaluation. Journal of bone and joint surgery American volume 84:1872-1881. [CrossRef]
- Mansfield M, Smith T, Spahr N, Thacker M (2020) Cervical spine radiculopathy epidemiology: A systematic review. Musculoskeletal care. [CrossRef]
- Jones SJ, Miller JMM (2022) Spurling Test. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. Copyright © 2022, StatPearls Publishing LLC., Treasure Island (FL).
- Tong HC, Haig AJ, Yamakawa K (2002) The Spurling test and cervical radiculopathy. Spine 27:156-159. [CrossRef]
- Thoomes EJ, van Geest S, van der Windt DA, Falla D, Verhagen AP, Koes BW, Thoomes-de Graaf M, Kuijper B, Scholten-Peeters WGM, Vleggeert-Lankamp CL (2018) Value of physical tests in diagnosing cervical radiculopathy: a systematic review. Spine J 18:179-189. [CrossRef]
- Shabat S, Leitner Y, David R, Folman Y (2012) The correlation between Spurling test and imaging studies in detecting cervical radiculopathy. J Neuroimaging 22:375-378. [CrossRef]
- Danielson BI, Willen J, Gaulitz A, Niklason T, Hansson TH (1998) Axial loading of the spine during CT and MR in patients with suspected lumbar spinal stenosis. Acta Radiol 39:604-611. [CrossRef]
- Michelini G, Corridore A, Torlone S, Bruno F, Marsecano C, Capasso R, Caranci F, Barile A, Masciocchi C, Splendiani A (2018) Dynamic MRI in the evaluation of the spine: state of the art. Acta Biomed 89:89-101. [CrossRef]
- Hansson T, Suzuki N, Hebelka H, Gaulitz A (2009) The narrowing of the lumbar spinal canal during loaded MRI: the effects of the disc and ligamentum flavum. Eur Spine J 18:679-686. [CrossRef]
- Muhle C, Resnick D, Ahn JM, Südmeyer M, Heller M (2001) In Vivo Changes in the Neuroforaminal Size at Flexion-Extension and Axial Rotation Of The Cervical Spine In Healthy Persons Examined Using Kinematic Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Spine 26:e287-e293. [CrossRef]
- Takasaki H, Hall T, Jull G, Kaneko S, Iizawa T, Ikemoto Y (2009) The influence of cervical traction, compression, and spurling test on cervical intervertebral foramen size. Spine 34:1658-1662. [CrossRef]
- Hutchins J, Lagerstrand K, Stävlid E, Svensson PA, Rennerfelt K, Hebelka H, Brisby H (2023) MRI evaluation of foraminal changes in the cervical spine with assistance of a novel compression device. Sci Rep 13:11508. [CrossRef]
- Park HJ, Kim SS, Lee SY, Park NH, Chung EC, Rho MH, Kwon HJ, Kook SH (2013) A practical MRI grading system for cervical foraminal stenosis based on oblique sagittal images. Br J Radiol 86:20120515. [CrossRef]
- Kim S, Lee JW, Chai JW, Yoo HJ, Kang Y, Seo J, Ahn JM, Kang HS (2015) A New MRI Grading System for Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Based on Axial T2-Weighted Images. Korean Journal of Radiology 16:1294-1302. [CrossRef]
- Pfirrmann CWA, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N (2001) Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Spine 26:1873-1878.
- Vernon H (2000) Assessment of Self-Rated Disability, Impairment, and Sincerity of Effort in Whiplash-Associated Disorder. Journal of Musculoskeletal Pain 8:155-167. [CrossRef]
- Bartlett RJ, Hill CA, Rigby AS, Chandrasekaran S, Narayanamurthy H (2012) MRI of the cervical spine with neck extension: is it useful? Br J Radiol 85:1044-1051. [CrossRef]
- Vaisy M, Gizzi L, Petzke F, Consmüller T, Pfingsten M, Falla D (2015) Measurement of Lumbar Spine Functional Movement in Low Back Pain. The Clinical Journal of Pain 31:876-885. [CrossRef]
- Park HJ, Kim SS, Lee SY, Park NH, Chung EC, Rho MH, Kwon HJ, Kook SH (2013) A practical MRI grading system for cervical foraminal stenosis based on oblique sagittal images. British Journal of Radiology 86:20120515. [CrossRef]
- Kim S, Lee JW, Chai JW, Yoo HJ, Kang Y, Seo J, Ahn JM, Kang HS (2015) A New MRI Grading System for Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Based on Axial T2-Weighted Images. Korean J Radiol 16:1294-1302. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).