1. Introduction
Poly(lactic-
co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) has a series of properties (adjustable sizes, stability, biodegradability, the possibility of surface functionalization) that offers it numerous advantages already described that led to its extensive use as a drug delivery system [
1].
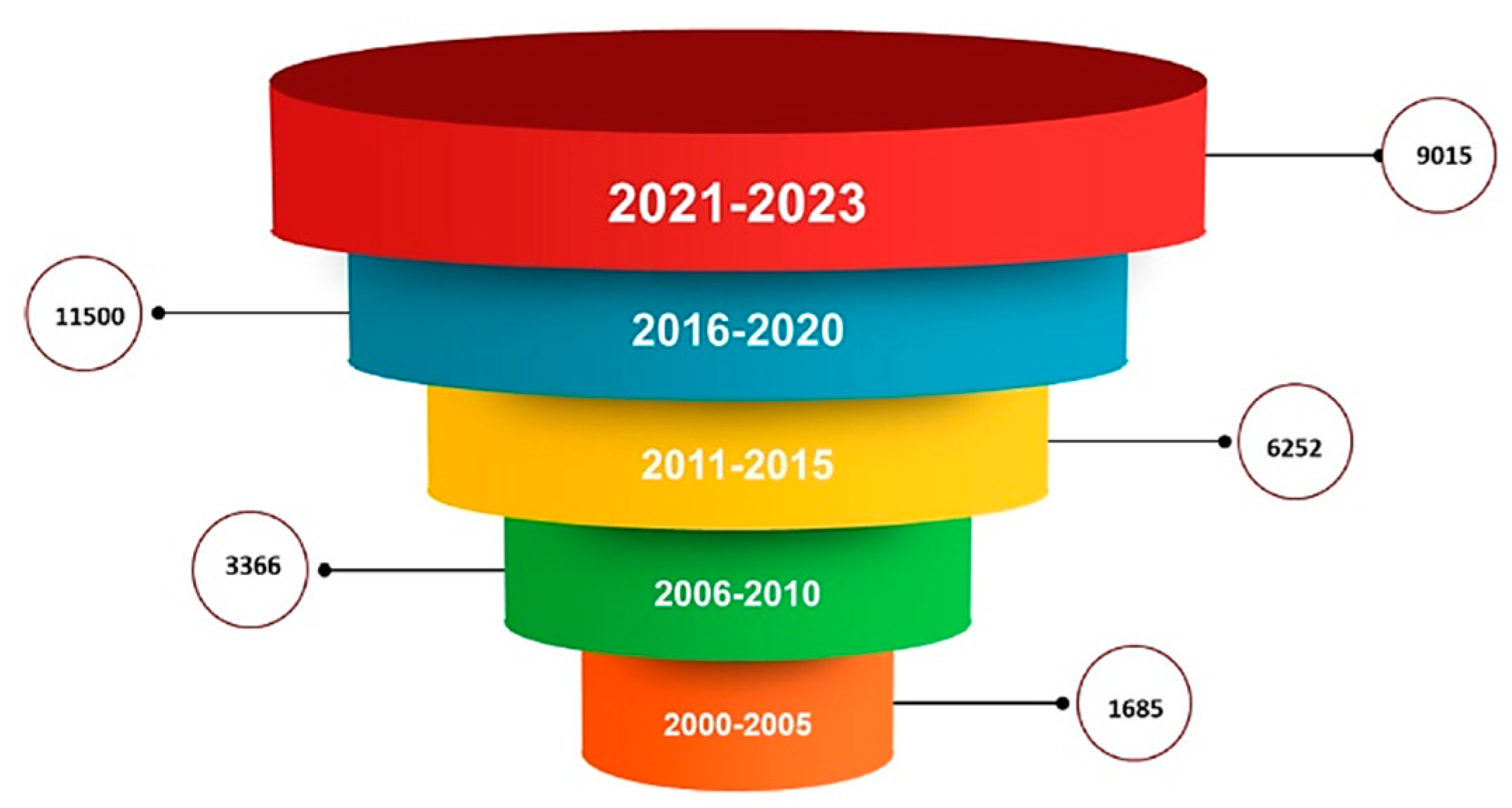
Analyzing Elsevier and Springer databases using keywords such as ‘PLGA’ (subject areas: material science, pharmaceutical science), we found a total number of 32 596 articles, including review and research articles between 2000 and 2023. Between 2000–2005, only 1685 articles were found, representing 5.16%. Between 2006–2010, the search returned double the number of articles, 3366 (10.32%). In the next five years, 2011–2015 has an impressive number of 6252 articles, representing 19.18%. Between 2015–2020, we found 11 500 (35.28%) articles. In the last three years, there are 9015 articles already published with PLGA, representing 27.65% of the total (
Figure 1).
The flexibility of degradation is an important factor that makes PLGA suitable to produce medical devices, such as nanoparticles, implants, or grafts. PLGA consists of a class of biodegradable polymers that are approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which gives them sustainability in terms of drug delivery. These polymers have been studied as vehicles for proteins, peptides, ribonucleic acid (RNA) or deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) [
2].
PLGA-based micro or nanoparticles represent most formulations on the pharmaceutical market, there are 14 products with PLGA clinically approved and currently used in medical practice (
e.g., Lupron
® – the oldest one, approved in 1989 [
3], Zilretta
® [
4], Bydureon
® [
5]) in diseases such as prostate cancer, osteoarthritis, diabetes, etc., and many other PLGA-based products in clinical trials [
6].
1.1. PLGA Structure and Physical Properties
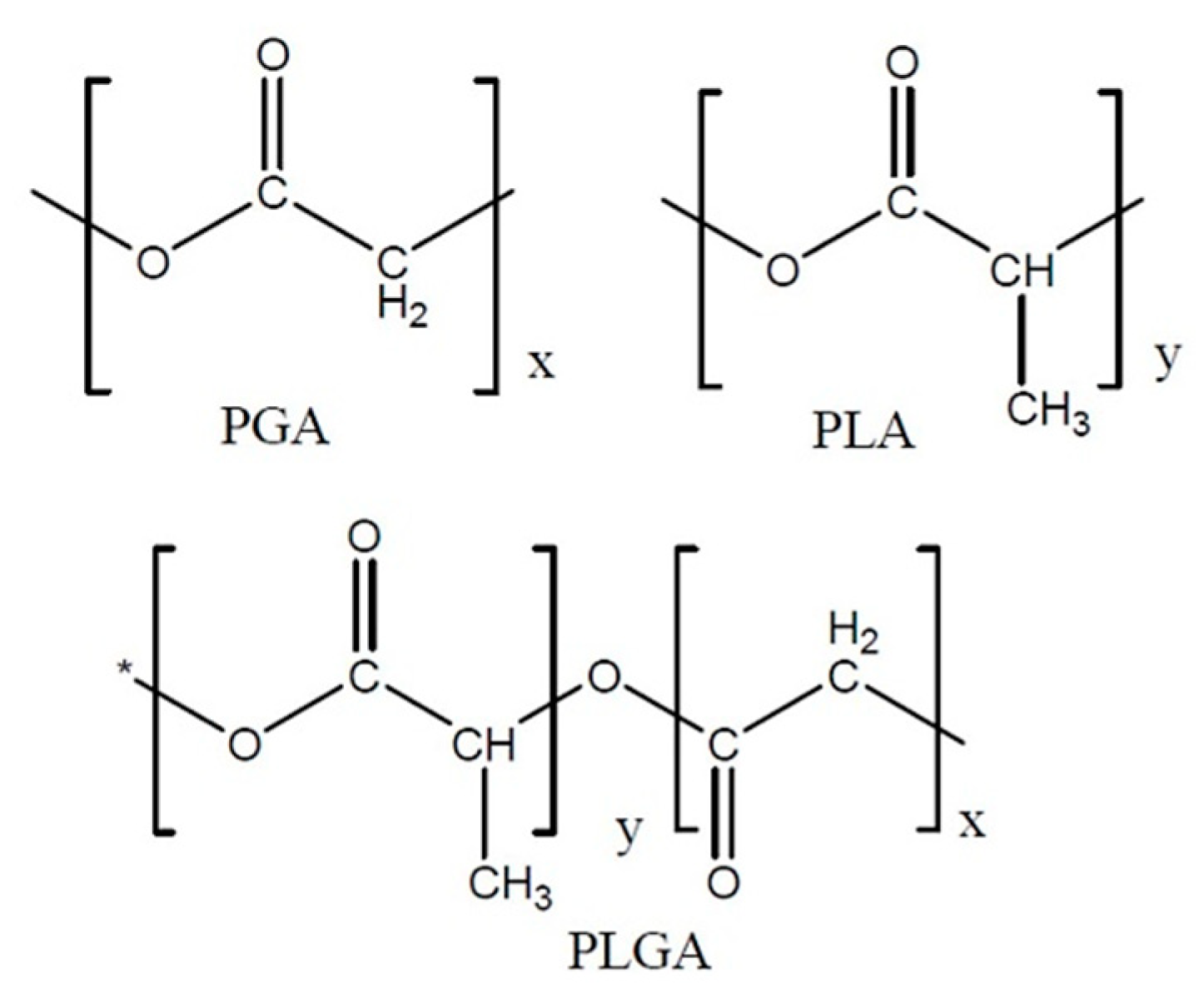
PLGA is a copolymer of polyglycolic acid (PGA) and polylactic acid (PLA). Several types of PLGA can be obtained depending on the molar ratio of PLA to PGA: 50/50, 65/35, 75/25 and 95/5 (
Figure 2). The molar ratio that also gives the degree of crystallinity of PLGA, which varies from amorphous to crystalline, and solubility also differs depending on the composition of the polymers: PLGA with a lot of PLA dissolves in chlorinated solvents, and that with a lot of PGA needs fluorinated solvents [
7].
1.2. PLGA in Living Tissues
PLGA is considered compatible with living tissues, meaning it does not elicit a significant immune response or toxic effects in living tissues. It has been extensively studied and used in preclinical and clinical settings. However, it is important to note that individual responses can vary, and careful consideration of factors, such as degradation rate, molecular weight, and specific application is necessary to ensure optimal biocompatibility.
In the body, PLGA undergoes a process of hydrolysis and forms lactic acid and glycolic acid [
8]. These original monomers of PLGA are secondary products of metabolic pathways in the human body. The human body can metabolize glycolic acid to toxic oxalic acid, but the amounts in typical applications are negligible and systemic toxicity is minimal [
9]. On the other hand, the acidic PLGA degradation medium can induce an autocatalytic environment because the local pH drops sufficiently for this to be possible. The autocatalytic capacities of PLGA are size dependent. The first surface that begins to degrade is the center of the PLGA matrix because this is where acidic oligomers accumulate. Thus, an acidic center is formed from which erosion begins.
Polymer–drug interaction was also observed in the studies, which gives PLGA a potential degree of toxicity in drug dose delivery. At the same time, toxicity can also be associated with the inconstant release of medicinal substances, but additional studies are needed to prove this aspect [
10].
1.3. Boron – An Essential Element
Boron (B) is an essential element, although it is required in small amounts compared to other essential elements. It plays important roles in various biological processes and is necessary for the growth and development of plants, animals, and humans [
11]. In plants, B is involved in cell wall formation, membrane integrity, carbohydrate metabolism, and the transport of nutrients [
12]. It also plays a role in pollen germination and fruit development. In animals and humans, B is involved in bone health, as it influences the metabolism and utilization of calcium, magnesium, and vitamin D. It also plays a role in brain function and cognitive performance.
B has a huge impact on the microbiota, particularly in the gastrointestinal tract [
13]. There are a few studies that suggest that it may have a modulatory role. One study published in the Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology investigated the influence of B on gut microbiota in rats. The results showed that B supplementation led to changes in the composition of the gut microbiota, including an increase in the abundance of certain bacterial species. Karatekeli
et al. (2023) showed that B exhibits hepatoprotective antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiapoptotic effect in rats exposed to aflatoxins [
14]. Arciniega-Martínez
et al. (2022) examined the effects of B on immune function [
15], showing that B-containing compounds induce an immune response on cells.
B was recently claimed as an essential element for the human host–microbiota healthy symbiosis and the effects of B deficiency in the microbiota could lead to: (
i)
dysbiosis (claimed to happen due to deficiency of the autoinducer-2–furanosyl borate diester (AI-2B) signaling molecule); and (
ii)
degradation of the mucus gel layer, due to the lack of B content in the mucin gel structure, which causes the interaction of the bacterial biofilm directly with the host cell membranes and therefore, their direct infection. Recent new insights into B’s mechanism of action are based on claims that: (
i) B is an essential element for the symbiosis between the commensal microorganisms in the microbiome and the human and animal host; (
ii) B is not required by the human cell, the human host cells do not need B nutritionally, this element being necessary only for a healthy symbiosis between the host organism and the various microbiomes of the gut, scalp, mouth, skin and vagina; (
iii) some naturally occurring prebiotic B compounds (PBCs) have recently been proven to be microbiota-accessible B compounds. More than that, PBCs, such as B-containing pectic polysaccharides (BPPs) and the recently discovered borate complexes of chlorogenic acid (diester chlorogenoborate – DCB), are indigestible compounds while B inorganics compounds, such as boric acid (BA) and borate salts, are digestible and, in certain circumstances, they can be toxic. These observations helped to formulate a new perspective on the essentiality of B in the animal kingdom, pretending that the signaling molecule AI-2B is actually able to modulate microbiota (composition, bacteria behavior and community dynamics) as well as the mucus gel layer under conditions of dysbiosis. The production of AI-2B by one phylum could influence the gene expression of other species and facilitate interspecies communication, making bacteria to change its behavior, especially luminescence, virulence, and formation of biofilm between various species. This characteristic determines AI-2B to turn into a very good candidate for regulating interactions between cells in the human gut and the microbiota, where hundreds of bacterial phyla live together and communicate. Recently, the AI-2B molecule has been proposed as a biomarker for dysbiosis [
16,
17]. In addition, B has recently been declared an essential element involved in the synthesis of the AI-2 quorum sensing system. At the same time, the active AI-2B is being generated by the addition of borate to the AI-2 precursor, being able to amplify the activity of AI-2 and support the secretion of extracellular polymeric substances.
Several natural organic B species have been detected in bacteria (borate polyketides, borate–siderophore complexes, AI-2B), fungi (borate esters of carbohydrates) and plants (rhamnogalacturonan II–borate complex (BPP), borate esters of carbohydrates, borate esters of organic acids,
bis-
N-acetyl serine, and borate complexes of phenolic acids, such as DCB). These organic B species are distinct from inorganic BA/borates, which aren’t prebiotic because they are digestible and could be toxic to the microbiota [
18,
19].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) 65:35, molecular weight (MW) 40 000–75 000, was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Taufkirchen, Germany). Dichloromethane (DCM), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) 8-88 (MW ~67 000), ammonium acetate and LiChrosolv® water and acetonitrile for chromatography were achieved from Merck Millipore (Darmstadt, Germany). For zinc–boron (Zn–B) complex synthesis, Zn powder, BA and fructose were purchased also from Merck Millipore.
2.2. Synthesis of Zn–B Complex
Zn–B complex was synthesized based on general methods used for the synthesis of various borate complexes with carbohydrates (fructose, sorbitol, mannitol) and B inorganic anions [
20,
21,
22,
23]. The optimization of Zn–B complex synthesis was made using a Büchi-type reactor made of steel, with a capacity of 300 mL, and which can withstand a pressure of up to 100 bar, equipped with temperature probe, pressure gauge, pneumatic connection, and safety valve. For the activation of metallic Zn, 9.146 g (70 mmol) of Zn powder and 300 mL of distilled water were added to a Büchi-type reactor, equipped with two necks, device for nitrogen admission and overpressure regulation, and with a thermometer. The air was gradually replaced, for 10–15 minutes, with inert gas (purging with nitrogen). The reaction mixture was heated to 140–150ºC, for three hours, under strong stirring (plate with electromagnetic stirrer), to activate metallic Zn. After three hours, the reaction mixture from the metallic Zn activation was cooled to 50–60ºC, then 12.412 g (68.95 mmol) of fructose and 2.137 g (34.47 mmol) of BA (in this order) were gradually added, while stirring. Next, the reaction mixture was kept under stirring for 60 minutes, at a temperature of 50–60ºC. After three hours, the reaction mixture has a temperature of 91.5ºC and a pH of 6.36. After another 60 minutes, the reaction mixture was filtered under vacuum to separate the excess of unreacted metallic Zn.
2.3. Synthesis of Zn–B–PLGA Biocomposite
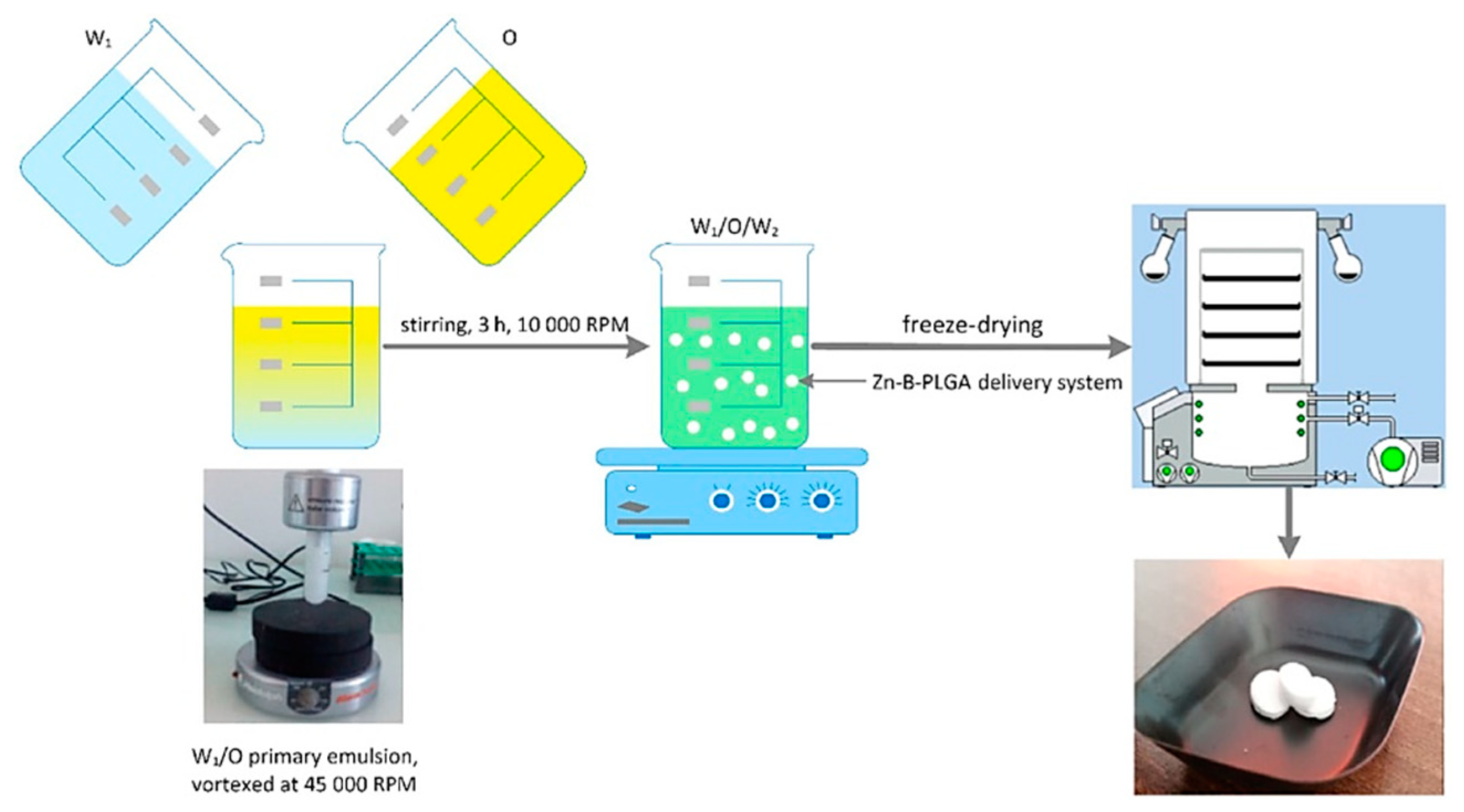
W1 aqueous phase: 50 mg of Zn–B complex were solubilized in 2 mL aqueous solution with 4% PVA 8-88 (w/v).
Oil phase O: 50–150 mg of PLGA 65:35 was dissolved in DCM. The two phases were brought into contact and mixed at 45000 rpm in a Heidolph Silent Crusher Vortex (Wood Dale, Illinois, USA) to obtain the primary emulsion W1/O.
W2 aqueous phase: 95 mL of aqueous solution with 1–4% PVA 8-88 as emulsifier (w/v). The primary emulsion was added dropwise to the secondary aqueous phase stirred at 1000 rpm for three hours to evaporate the DCM.
The particles were centrifuged at 11 000 rpm, washed and frozen overnight. The final suspension was subjected to a lyophilization process using an Alpha 1-2 LSCbasic freeze dryer (Martin Christ Gefriertrocknungsanlagen GmbH, Osterode am Harz, Germany), as follows: the suspended particles were frozen at -55°C overnight and at 0.02 mbar for 48 hours.
2.4. Design of Experiments Analysis
To solve design constraints and perform minimum experimental runs, we used design of experiments (DoE) by a systematic quality by design (QbD) approach. The details of the variables are described in
Table 1. The independent variables (factors) were the PVA concentration and the PLGA concentration, whereas the dependent variables (responses) were the size of the Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite and the
zeta potential (ZP). According to a full factorial (two levels) design, interaction model, we performed seven experiments, as in
Table 2. The model included only those terms for which the significance level was less than
p<0.05. We calculated
R2 (the fraction of the variation in the response explained by the model),
Q2 (the predictive power of the models),
F-value (the ratio of the mean regression), model validity (the extent to which the measurement corresponds to real-life situations), reproducibility (ability to produce the same output if the input is the same).
The experimental data obtained from the seven experiments were fitted to a polynomial model, allowing the prediction of the formulation variables on the Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite characteristics, using the MODDE for Windows software ver. 21.1 (Sartorius Stedim Data Analytics AB, Umeå, Sweden). In this mathematical approach, each response
Y can be represented by an equation:
where
X1,
X2 are the independent variables as in
Table 1, and the coefficients are as follows:
b1,
b2 represent the estimation of the main effects of the
X1,
X2 factors;
b12 represents the estimation of the interaction between
X1 and
X2 factors.
2.5. Morphological Aspects of Zn–B–PLGA Biocomposite
Micrographs were acquired using a high-resolution scanning electron microscope, FEI Inspect F50 (FEI Company, Hillsboro, Oregon, USA), at 30 keV and various magnifications.
2.6. Hydrodynamic Diameter of the Particles Determined by the DLS Technique
The numerical and volumetric distribution of the synthesized nanoparticles (hydrodynamic diameter) was measured by the dynamic light scattering (DLS) technique using a Brookhaven 90 Plus equipment (Brookhaven Instruments Corp., Austin, Texas, USA) provided with laser of 35 mW output power and 660 nm wavelength. The analysis of the Brownian motion of the particles brought into the liquid medium and dispersed (by ultrasonication) was correlated with the size of the particles by illuminating them with a laser and analyzing the intensity of the fluctuations of the scattered light.
2.7. Determination of Loading Efficiency by UHPLC/MS
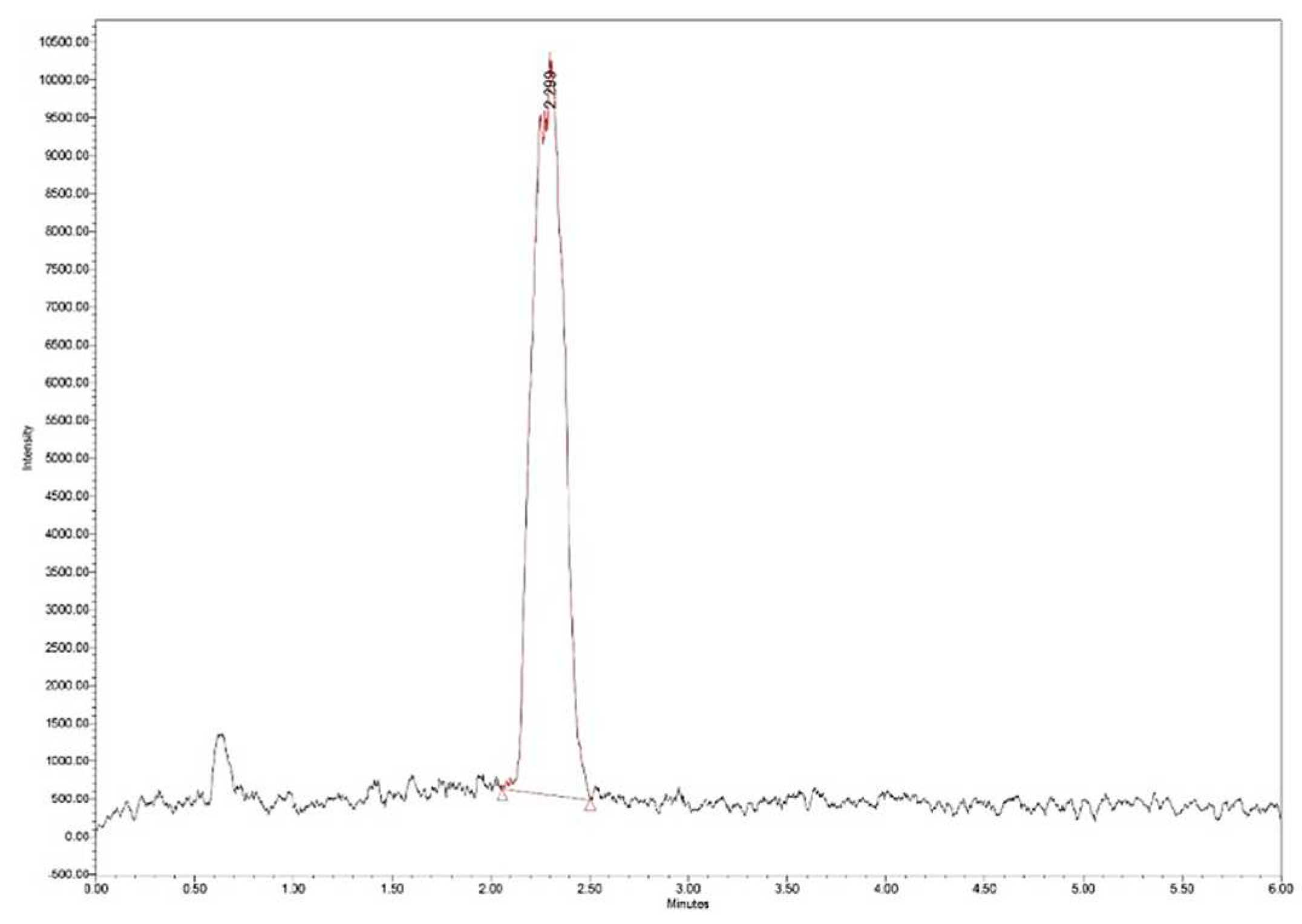
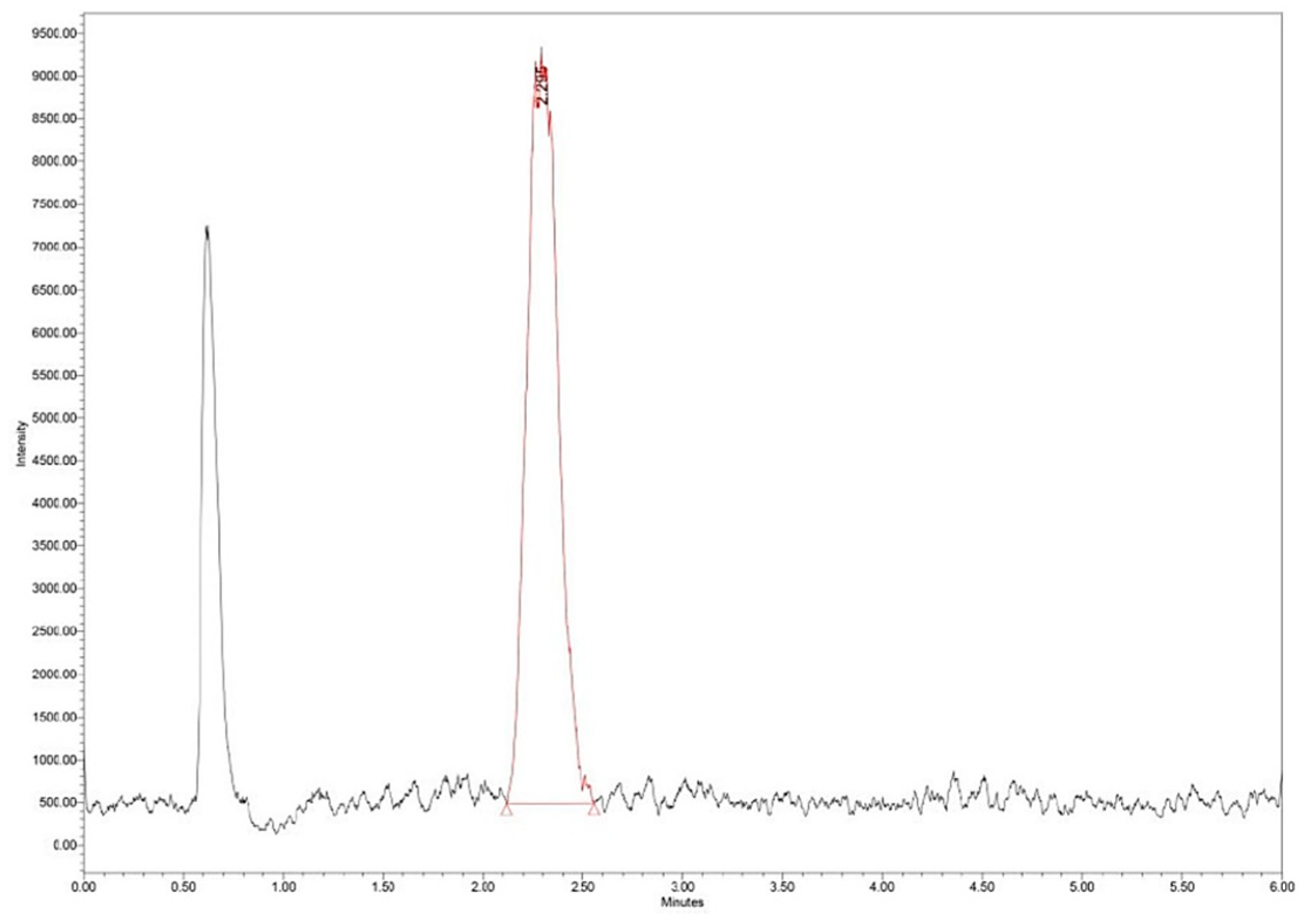
The loading efficiency (LE%) was determined by measuring 25 mg of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles in 2 mL of water. The dispersion was initially stirred under ultrasound and then left for 40 days for the complete release of the active principle and complete and complete hydrolysis of the polymer. The obtained solution was filtered, diluted 1:20 and subjected to ultra-high performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (UHPLC/MS) analysis (
Figure 3).
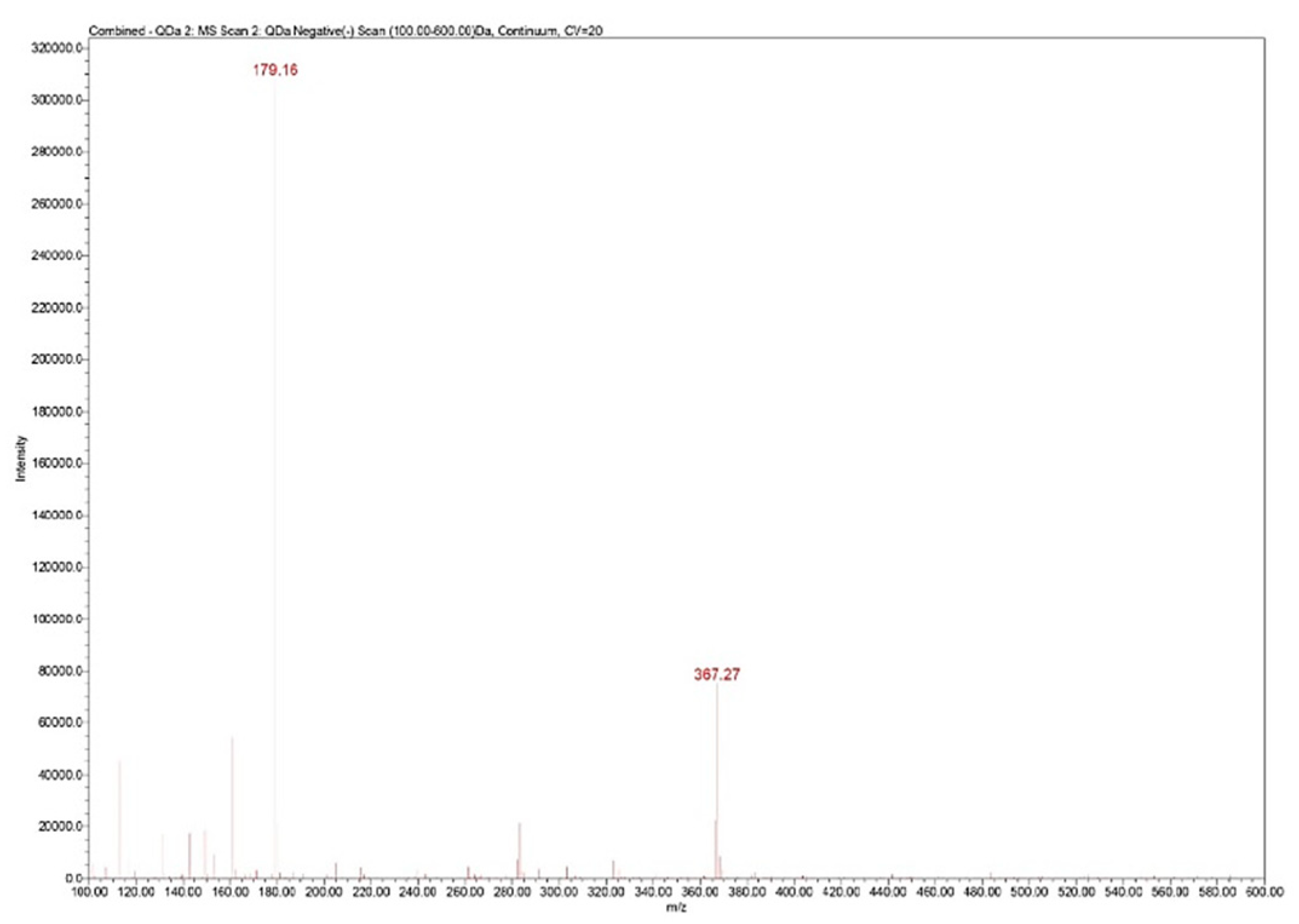
The UHPLC/MS analysis was performed on the Waters (Milford, Massachusetts, USA) Arc System coupled with a Waters QDa MS detector. The column was a Waters Atlantis Premier BEH Z-HILIC (2.1×100 mm, 2.5 μm) eluted with two solvents: A (10% ammonium acetate in water) and B (acetonitrile) in isocratic mode (25% A). The mobile phase had a flow rate set at 0.3 mL/min. The column temperature was equilibrated to 30°C. The injection volume was 5 μL. The QDa MS detector was set to negative mode at 0.8 kV for the capillary, 20 V for the cone voltage and 400°C for the capillary. The mass range was set at
m/z 100–600 for spectra collection and Selected Ion Recording (SIR) mode was used for quantification at
m/z 367 (
Figure 4).
LE% was calculated using formula:
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Zn–B–PLGA Biocomposite
The water/oil/water (W/O/W) double emulsion method [
24] is one of the most used methods for PLGA-based biomaterials due to the simplicity of the process, the low cost of the used instrumentation, and the easiness in parameters control [
25]. The method consists in adding the insoluble volatile organic phase (DCM) [
26] over the W
1 aqueous phase, which contains Zn–B complex dissolved in the aqueous phase, emulsifying at a high speed (45 000 rpm) with a homogenizer. The result is a water-in-oil primary emulsion that was added by continuous mixing to a very large amount of W
2 aqueous phase (95 mL) containing different surfactants, in our case PVA (1–4%,
w/v) forming a W/O/W double emulsion (
Figure 5). The concentration of the polymer was chosen between 50 and 150 mg. The use of DCM as organic solvent leads to Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite spheres of 15–450 nm size (as shown by DLS), while for the use of other type of organic solvent (acrylonitrile [
27], tetrahydrofuran [
28]) leads to obtaining smaller particles, with diameters less than 100 nm.
3.2. Design of Experiments Analysis
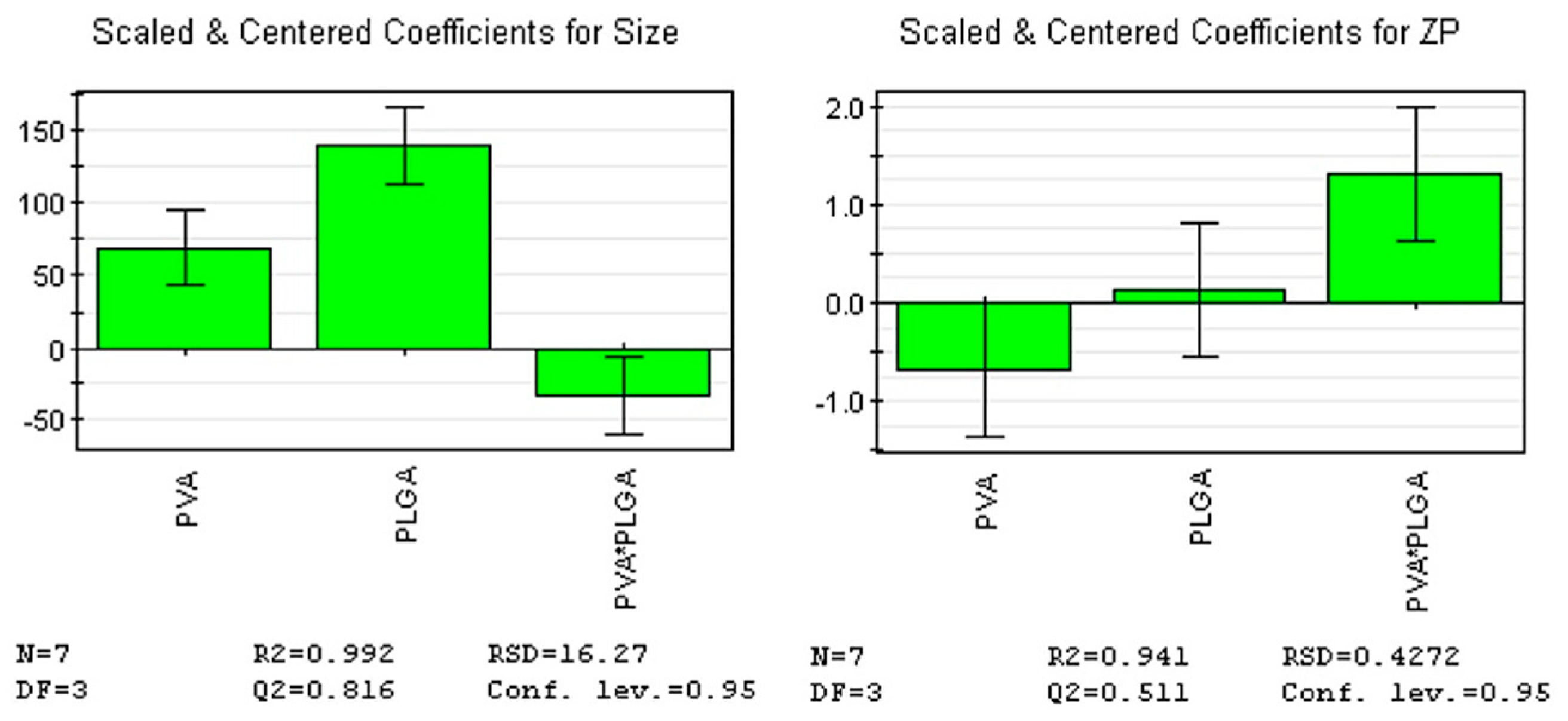
To determine the levels of factors that ensure optimal size and ZP, we fitted an initial model that explained over 99% of the size’s variation and over 94% of the ZP’s variation, indicating that all responses were well fitted by the model. The predictive power of the model was high for size (82%) and moderate for ZP (51%), indicating that all responses were well predicted by the model. Furthermore, model validity (0.62 for size and 0.86 for ZP) and reproducibility (0.99 for size and 0.86 for ZP) values were greater than 0.6 and 0.8, respectively, suggesting a reduced experimental error.
F-value for regression was 128.26 (
p-value = 0.001) for size, and 15.9 (
p-value = 0.024) for ZP, respectively (
Table 2;
Figure 6).
According to the coefficient list for designed model, as in
Figure 6, each response was represented by the equations:
The results of the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test showed not only the p-value was lower than 0.05 for all responses, but also p-value for the lack of fit was greater than 0.05 for all responses (F-value = 3.12, p-value = 0.219 for size, and F-value = 0.46, p-value = 0.566 for ZP), confirming that the proposed model is adequate, reliable, and has a good predictive power.
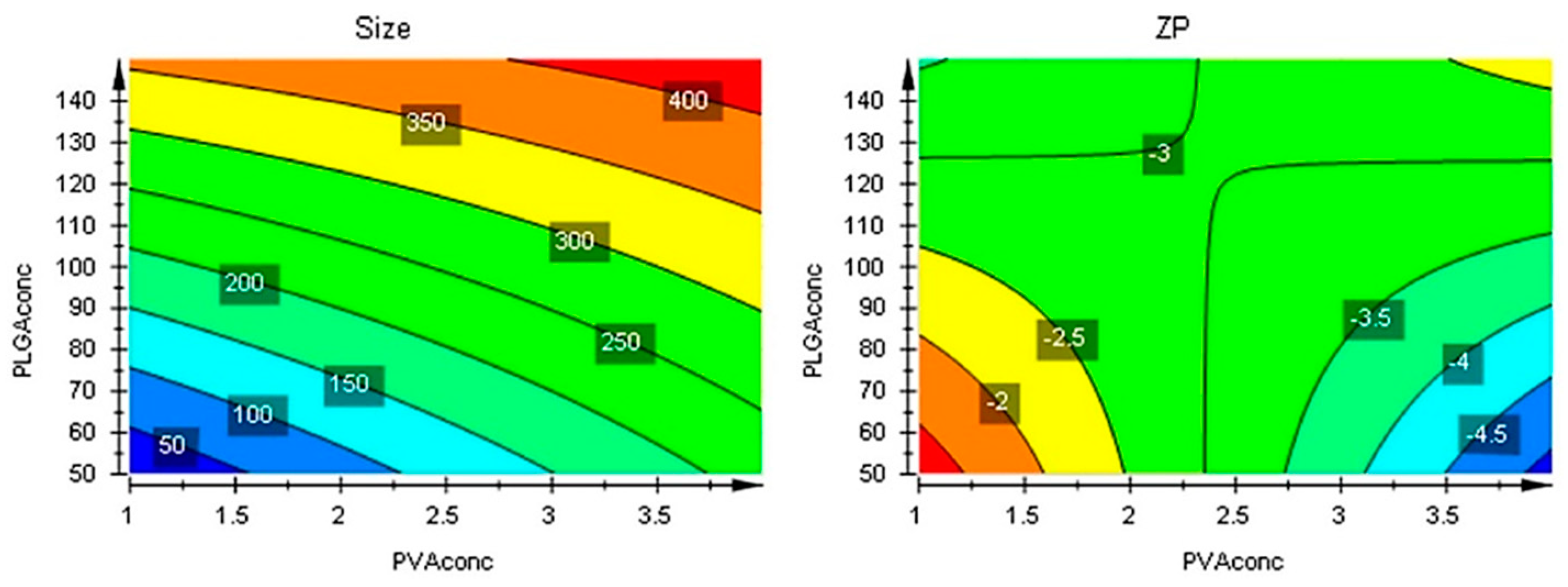
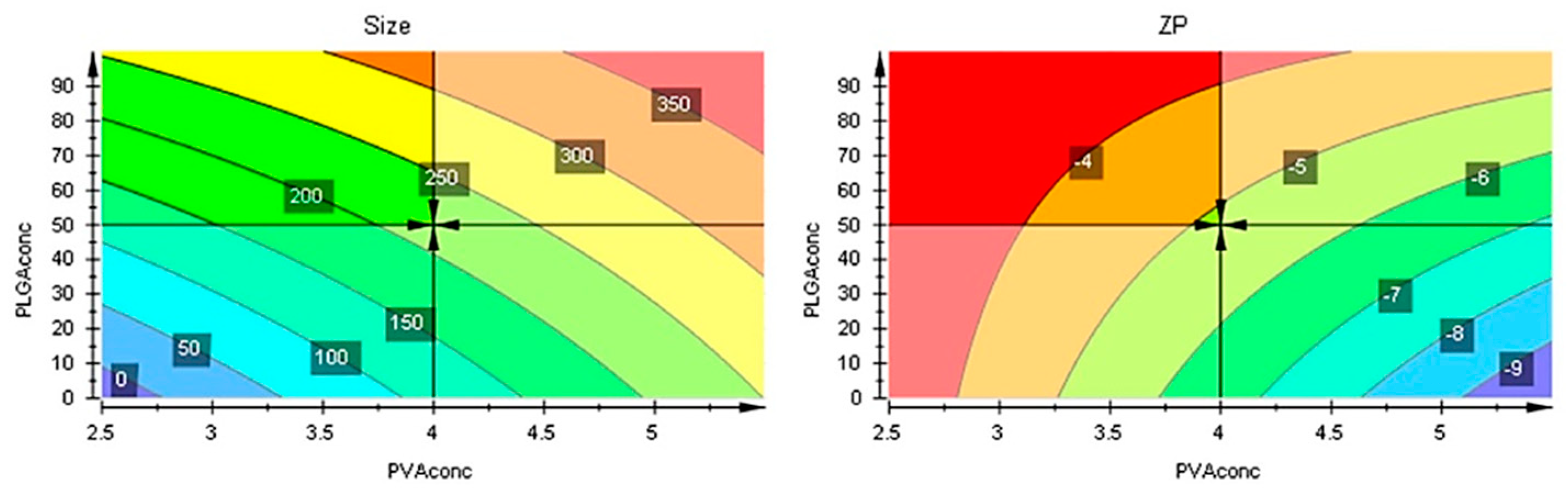
The responses contour plots illustrated the quantitative effect of the factors on the two responses, identifying the optime values for the two factors to obtain the expected responses, as in
Figure 7.
After performing optimizer within the design space with a target of 200 nm for size and minimize for ZP, the model proposed the
X1 = 4% and
X2 = 50 mg values. More, using prediction list outside the design space, as in
Figure 8, the characteristics of the optimum formulation could be obtained for
X1 = 5 and
X2 = 10 values, the model predicting the size = 221 nm (119 nm to 323 nm) and ZP = -8.3 (-11 to -5.7) values (
Figure 9).
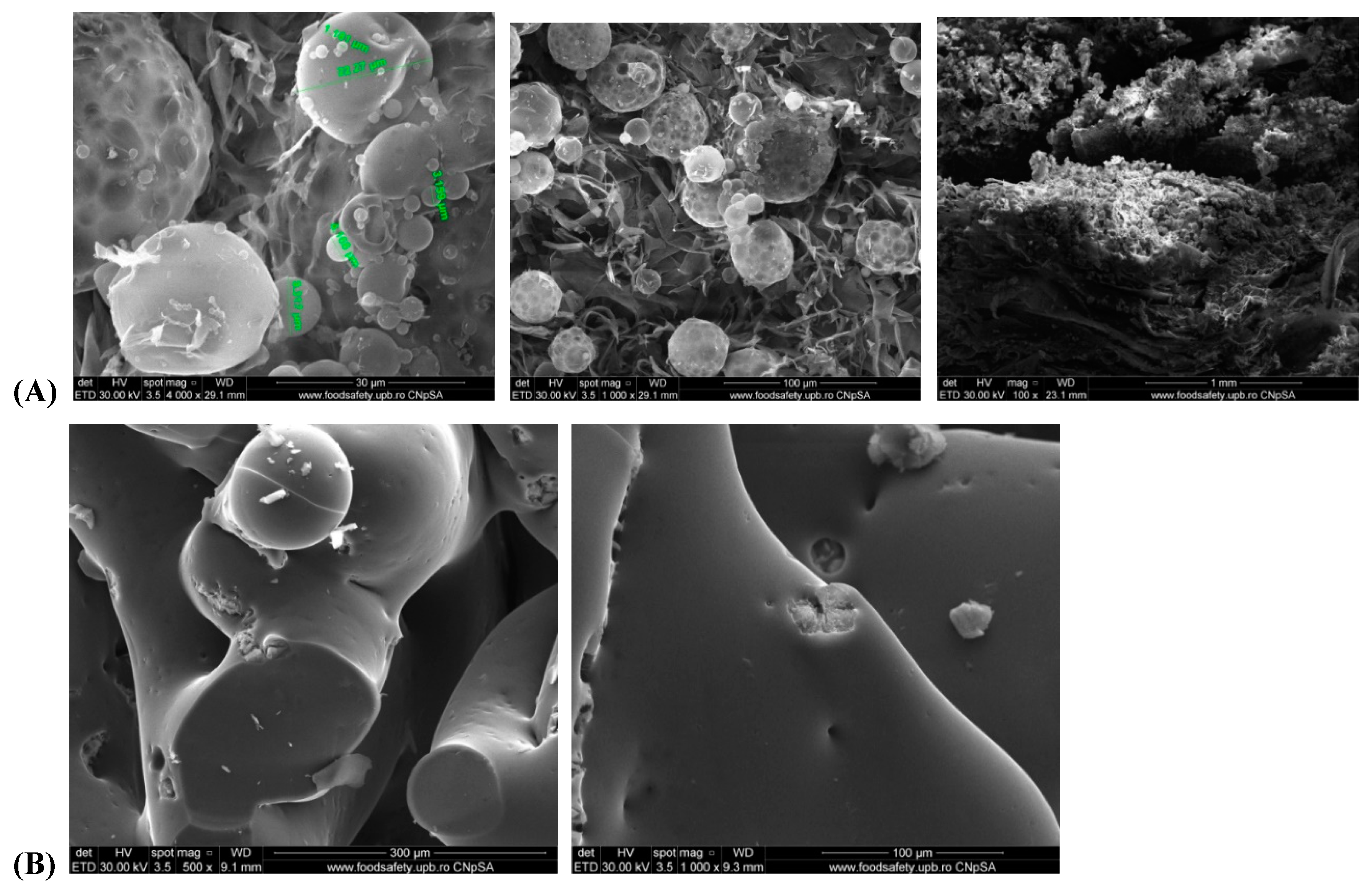
3.3. Morphological Aspects of Zn–B–PLGA Biocomposite
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) at different magnitudes revealed a porous material, the spherical shape of the particles of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite are well organized. The three-dimensional aspect of the lattice was also highlighted by SEM (
Figure 10, A and B).
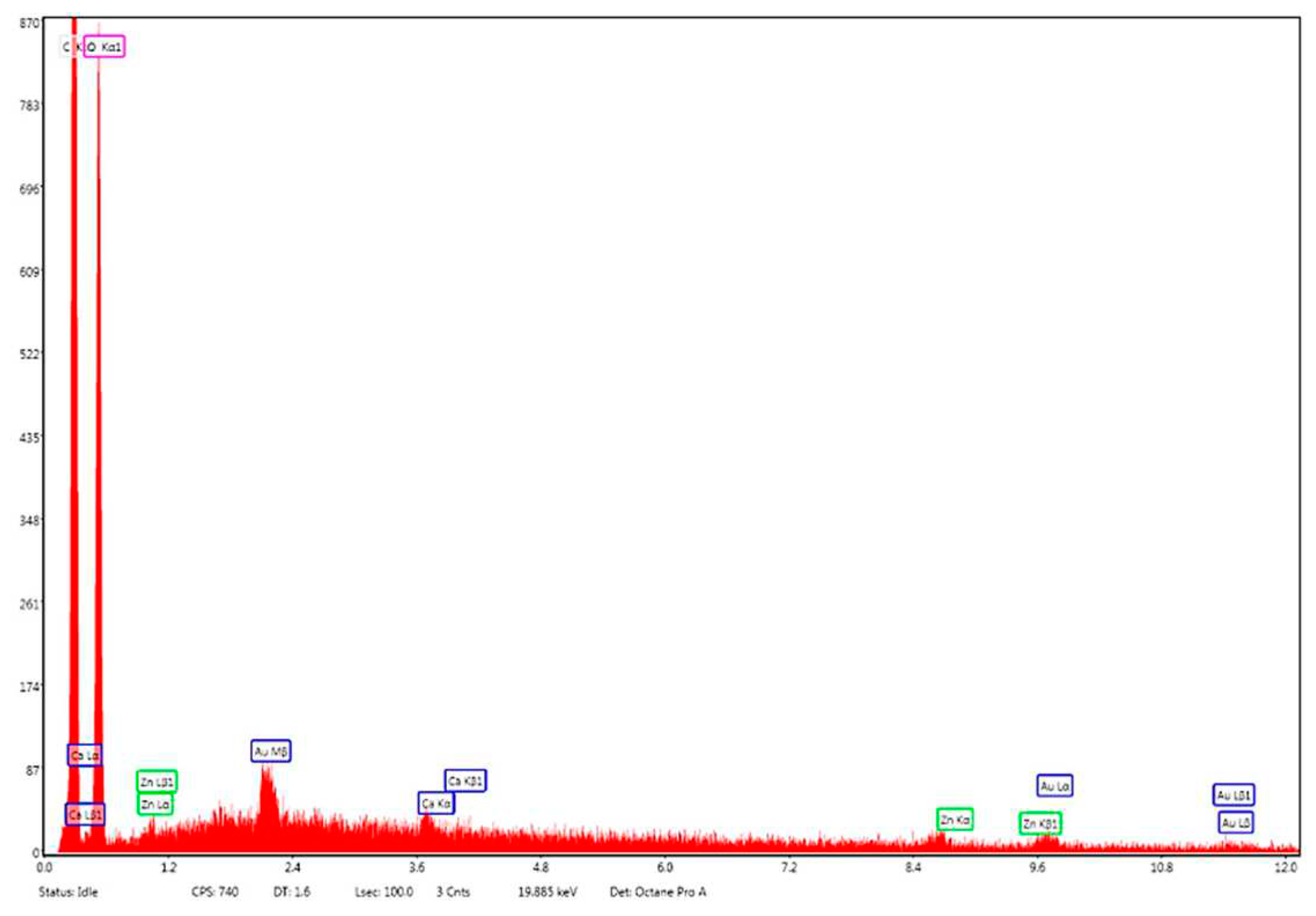
Energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis on the elemental composition of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite is shown in Figure 11. According to the EDX mapping, the predominant elements content in the Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite are C (56.33 wt%), O (43.46 wt%), Zn (0.21 wt%). Our EDX analyzer can detect elements with an atomic number from 11 (Na) upward, so B, our major interest element could not be detected by this method (
Figure 11).
3.4. Hydrodynamic Diameter of the Zn–B–PLGA Biocomposite Particles
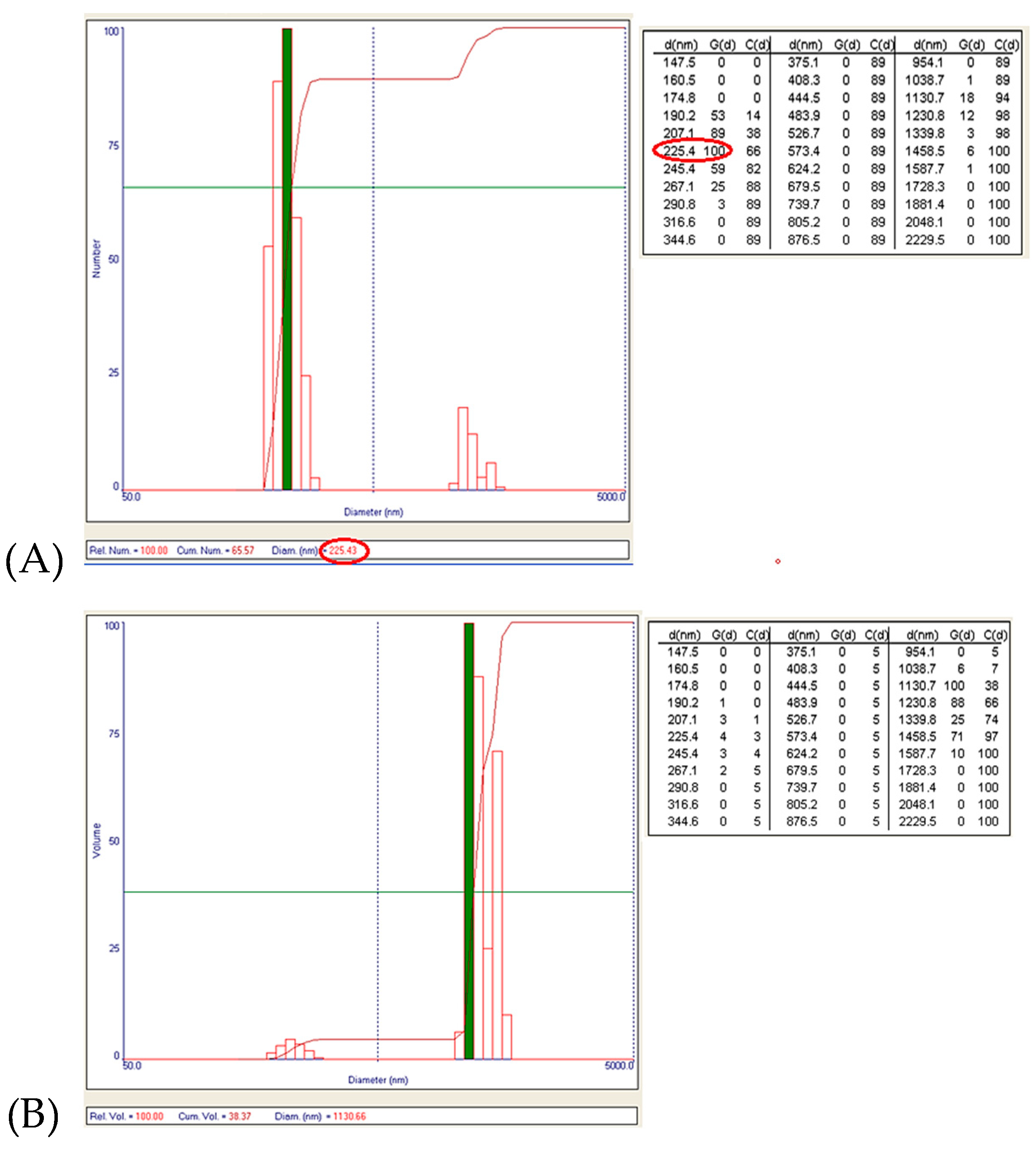
The obtained data showed the presence of two granulometric intervals: [190–291] nm and [1–1.6] μm, respectively. From the point of view of the numerical distribution, for N2 synthesis the largest number of particles have a size around 225 nm (
Figure 12A), and the particles that are the majority in the case of volume distribution (the largest volume being around the size of 1.1 μm,
Figure 12B) are just a few in number.
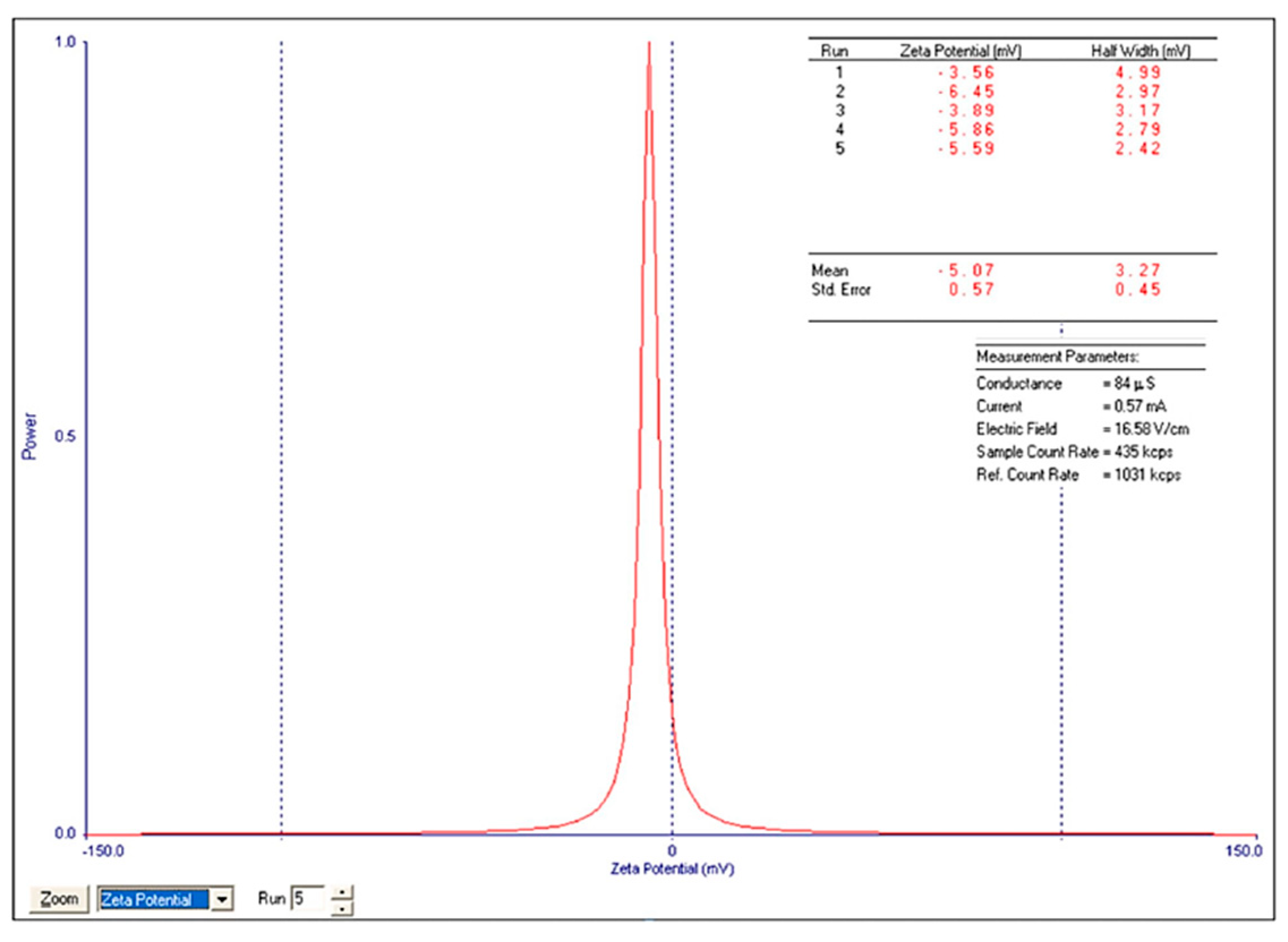
The ZP (-5.07±0.57 for
n=5,
Figure 13) was calculated by determining the electrophoretic mobility and applying the Henry equation.
3.5. Determination of Loading Efficiency by UHPLC/MS
LEs between 5–16% were obtained for different synthesis conditions.
Figure 14 shows a typical chromatogram for N5 synthesis with LE of 5%. The desired loading efficiency can widely vary [
29]. Through the double emulsion method, incorporation efficiencies of up to 30–35% are generally obtained. This percentage may vary depending on experimental variables (PLGA/Zn–B ratio, solvent, evaporation conditions), and in the synthesis process [
30]. Based on the intended therapeutic purpose and the nature of the active substance being encapsulated, there is no universally fixed minimum LE%. Our future analyzes will focus on maximizing the incorporation percentage by varying the synthesis conditions.
4. Discussion
The properties of PLGA biocomposites depend greatly on the lactic acid/glycolic acid (LA/GA) polymer ratio because GA has a low solubility in water while LA is extremely high soluble in water.
For our synthesis, with Zn–B complex-loaded PLGA nanoparticles as potential oral delivery system, we preferred to use PLGA with the ratio of copolymers 65:35, which is known to have a slower degradation time (2–3 months) and implicitly the release of the active principle (1–2 months) slower than PLGA 50:50 but not so great as that of PLGA 85:15 [
31].
Since Zn–B complex is hydrophilic, the W/O/W double emulsion was successfully used, evaporating the organic solvent (DCM), which could have raised the issue of high toxicity [
32].
We used PVA as a non-ionic surfactant [
33] in the aqueous phase which has hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail ([CH
2CH(OH)]
n), which is considered a critical double emulsion-stabilizing surfactant, although there are studies that consider that an increased concentration of it can affect the encapsulation efficiency [
34]. Since in our previous studies of experimental design we found that the stirring speed had no major impact on efficiency or particle size, therapeutic agent encapsulation efficiency increase with concentration and pH, and decrease with PLGA concentration [
35,
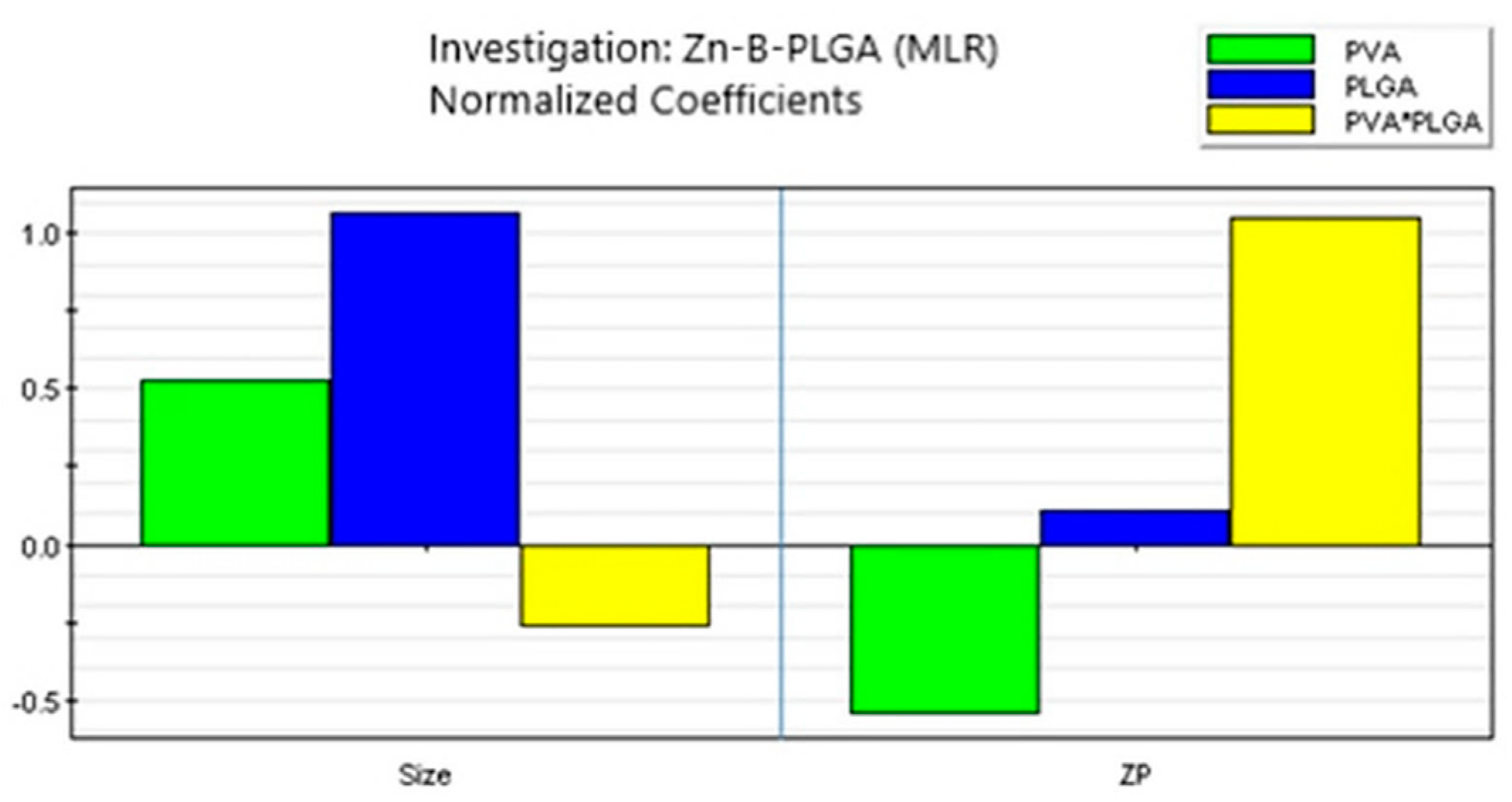
36], we chose to investigate how other parameters influence the size of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite, such as the amount of polymer added in the synthesis process and the concentration of the emulsifying agent. Our findings confirm that the size of the particles increase with increasing amounts of PLGA and PVA.
4.1. Morphology
At higher magnifications, a fibrillar interpenetrated structure can be noted with the appearance of a folded sheet. Furthermore, the SEM micrographs showed pore channels, which are characteristic to W/O/W double emulsion, the inner water droplets tend to come out through a diffusion process during the volatilization process of the organic solvent, as the polymer precipitates and encapsulates the active principle from W
1 aqueous phase [
37]. The addition of Zn–B complex does not substantially change the morphology of the material, the active substance being most likely absorbed inside the pores and just a smaller amount may be on the surface of the particles.
4.2. DLS Measurements
PLGA is extremely safe as a drug delivery system for micro/nanoparticles, but nanoparticles of any biocomposite material have specific biodistribution, with toxic effects depending on the size [
38]. Even if nanoparticles with larger sizes can incorporate a larger amount of drug, those with smaller sizes have a better penetration of biological barriers and the arrival of the drug at the site of action.
Our goal was to vary the synthesis parameters to obtain particles with dimensions of 100–200 nm, because cellular uptake is deeply affected by the size of the nanoparticle [
39]. When we obtained Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles as targeted drug delivery, we also considered that the active principle loading capacity increases with size.
4.3. Zeta Potential
Information regarding ZP for biopolymeric nanocomposites is very limited. The data provided by our study is novel in this field. When immersed in water, Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite exhibits a negative ZP. The obtained negative charge is attributed to dissociation of carboxylic groups on the particle surface [
40]. Also, the ZP (-5 mV) after lyophilization is not in the stability range [-25 mV; +25 mV], the literature mentions that particles with negative charges have colloid stability. Our other ZP studies on nanocomposites with PLGA showed that the centrifuged particles exhibit a much lower potential (-42 mV) compared to the lyophilized ones [
41].
5. Conclusions
The Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite represents a novel delivery system for Zn and B as active principles. Its applicability will be further analyzed, and the synthesis parameters will be adjusted to better use of PLGA as novel Zn–B complex carrier. The obtained material is stable and functional, being able to combine the desired properties of the carrier material and the encapsulated Zn–B complex in future pharmaceutical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.V.C., I.R.S. and A.T.Ş.; formal analysis, G.R. and A.B.; investigation, V.L.E., A.S. and C.N.; resources, I.R.S., A.B. and J.N.; writing—original draft preparation, M.V.C., A.B., I.R.S. and G.D.M.; writing—review and editing, I.R.S. and G.D.M.; visualization, I.R.S., A.T.Ş. and G.D.M.; supervision, I.R.S., J.N. and G.D.M.; funding acquisition, I.R.S. and J.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant of the Ministry of Research, Innovation and Digitization, CCCDI–UEFISCDI, project number PN-III-P2-2.1-PED-2021-0804, within PNCDI III.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The manuscript does not contain experiments on laboratory animals.
Informed Consent Statement
The manuscript does not contain clinical studies or patient data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funder had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Danhier F, Ansorena E, Silva JM, Coco R, Le Breton A, Préat V (2012) PLGA-based nanoparticles: an overview of biomedical applications. J Control Release, 161(2):505–522. [CrossRef]
- Nie H, Lee LY, Tong H, Wang CH (2008) PLGA/chitosan composites from a combination of spray drying and supercritical fluid foaming techniques: new carriers for DNA delivery. J Control Release 129(3):207–214. [CrossRef]
- Anselmo AC, Mitragotri S (2014) An overview of clinical and commercial impact of drug delivery systems. J Control Release 190:15–28. [CrossRef]
- Molavi F, Barzegar-Jalali M, Hamishehkar H (2020) Polyester based polymeric nano and microparticles for pharmaceutical purposes: a review on formulation approaches. J Control Release 320:265–282. [CrossRef]
- Zhong H, Chan G, Hu Y, Hu H, Ouyang D (2018) A comprehensive map of FDA-approved pharmaceutical products. Pharmaceutics 10(4):263. [CrossRef]
- Wan B, Bao Q, Burgess D (2023) Long-acting PLGA microspheres: advances in excipient and product analysis toward improved product understanding. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 198:114857. [CrossRef]
- Chen X, Bai L, Tian J, Zhou H, Zhou M, Xiao J, Li Y (2021) Effect of glycolide dosage on molecular weight of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid). IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 692:032107. [CrossRef]
- Andhariya JV, Jog R, Shen J, Choi S, Wang Y, Zou Y, Burgess DJ (2019) In vitro–in vivo correlation of parenteral PLGA microspheres: effect of variable burst release. J Control Release 314:25–37. [CrossRef]
- Miao Y, Cui H, Dong Z, Ouyang Y, Li Y, Huang Q, Wang Z (2021) Structural evolution of polyglycolide and poly(glycolide-co-lactide) fibers during in vitro degradation with different heat-setting temperatures. ACS Omega 6(43):29254–29266. [CrossRef]
- Proikakis CS, Tarantili PA, Andreopoulos AG (2006) The role of polymer/drug interactions on the sustained release from poly(DL-lactic acid) tablets. Eur Polym J 42(12):3269–3276. [CrossRef]
- Kim HJ, Furukawa Y, Kakegawa T, Bita A, Scorei R, Benner SA (2016) Evaporite borate-containing mineral ensembles make phosphate available and regiospecifically phosphorylate ribonucleosides: borate as a multifaceted problem solver in prebiotic chemistry. Angew Chemie Int Ed Engl 55(51):15816–15820. [CrossRef]
- Uluisik I, Karakaya HC, Koc A (2018) The importance of boron in biological systems. J Trace Elem Med Biol 45:156–162. [CrossRef]
- Biţă A, Scorei IR, Bălşeanu TA, Ciocîlteu MV, Bejenaru C, Radu A, Bejenaru LE, Rău G, Mogoşanu GD, Neamţu J, Benner SA (2022) New insights into boron essentiality in humans and animals. Int J Mol Sci 23(16):9147. [CrossRef]
- Karatekeli S, Demirel HH, Zemheri-Navruz F, Ince S (2023) Boron exhibits hepatoprotective effect together with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic pathways in rats exposed to aflatoxin B1. J Trace Elem Med Biol 77:127127. [CrossRef]
- Arciniega-Martínez IM, Romero-Aguilar KS, Farfán-García ED, García-Machorro J, Reséndiz-Albor AA, Soriano-Ursúa MA (2022) Diversity of effects induced by boron-containing compounds on immune response cells and on antibodies in basal state. J Trace Elem Med Biol 69:126901. [CrossRef]
- Biţă A, Scorei IR, Rangavajla N, Bejenaru LE, Rău G, Bejenaru C, Ciocîlteu MV, Dincă L, Neamţu J, Bunaciu A, Rogoveanu OC, Pop MI, Mogoşanu GD (2023) Diester chlorogenoborate complex: a new naturally occurring boron-containing compound. Inorganics 11(3):112. [CrossRef]
- Mitruţ I, Scorei IR, Manolea HO, Biţă A, Mogoantă L, Neamţu J, Bejenaru LE, Ciocîlteu MV, Bejenaru C, Rău G, Mogoşanu GD (2022) Boron-containing compounds in Dentistry: a narrative review. Rom J Morphol Embryol 63(3):477–483. [CrossRef]
- Donoiu I, Militaru C, Obleagă O, Hunter JM, Neamţu J, Biţă A, Scorei IR, Rogoveanu OC (2018) Effects of boron-containing compounds on cardiovascular disease risk factors – a review. J Trace Elem Med Biol 50:47–56. [CrossRef]
- Hunter DJ, March L, Chew M (2020) Osteoarthritis in 2020 and beyond: a Lancet Commission. Lancet 396(10264):1711–1712. [CrossRef]
- Scorei IR (2011) Calcium fructoborate: plant-based dietary boron as potential medicine for cancer therapy. Front Biosci (Schol Ed) 3(1):205–215. [CrossRef]
- Hunter JM (2015) Compositions and methods for borocarbohydrate complexes. United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), Patent No. 9102700 B1 from 08/11/2015. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/US9102700.
- Hubbard SA (1998) Comparative toxicology of borates. Biol Trace Elem Res 66(1–3):343–357. [CrossRef]
- Korolenko SE, Avdeeva VV, Malinina EA, Kuznetsov NT (2021) Zinc(II) and cadmium(II) coordination compounds with boron cluster anions: classification of compounds depending on strength of metal–boron cage interaction and analysis of structures (review). Russ J Inorg Chem 66(9):1350–1373. [CrossRef]
- Kamaly N, Yameen B, Wu J, Farokhzad OC (2016) Degradable controlled-release polymers and polymeric nanoparticles: mechanisms of controlling drug release. Chem Rev 116(4):2602–2663. [CrossRef]
- Silva ATCR, Cardoso BCO, Silva MESR, Freitas RFS, Sousa RG (2015) Synthesis, characterization, and study of PLGA copolymer in vitro degradation. J Biomater Nanobiotechnol 6(1):8–19. [CrossRef]
- Ciocîlteu MV, Podgoreanu P, Delcaru C, Chifiriuc MC, Manda CV, Biţă A, Popescu M, Amzoiu E, Croitoru O, Bleotu C, Bostan M, Neamţu J (2019) PLGA–gentamicin biocomposite materials with potential antimicrobial applications in orthopedics. Farmacia 67(4):580–586. [CrossRef]
- Huang W, Zhang C (2018) Tuning the size of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) nanoparticles fabricated by nanoprecipitation. Biotechnol J 13(1):1700203. [CrossRef]
- Prakapenka AV, Bimonte-Nelson HA, Sirianni RW (2017) Engineering poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) micro- and nano-carriers for controlled delivery of 17β-estradiol. Ann Biomed Eng 45(7):1697–1709. [CrossRef]
- Sun SB, Liu P, Shao FM, Miao QL (2015) Formulation and evaluation of PLGA nanoparticles loaded capecitabine for prostate cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(10):19670–19681. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. 4694.
- Huang WF, Tsui GCP, Tang CY, Yang M (2018) Optimization strategy for encapsulation efficiency and size of drug loaded silica xerogel/polymer core-shell composite nanoparticles prepared by gelation-emulsion method. Polym Eng Sci 58(5):742–751. [CrossRef]
- Houchin ML, Topp EM (2009) Physical properties of PLGA films during polymer degradation. J Appl Polym Sci 114(5):2848–2854. [CrossRef]
- Kluin OS, van der Mei HC, Busscher HJ, Neut D (2013) Biodegradable vs non-biodegradable antibiotic delivery devices in the treatment of osteomyelitis. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 10(3):341–351. [CrossRef]
- Hariharan S, Bhardwaj V, Bala I, Sitterberg J, Bakowsky U, Ravi Kumar MN (2006) Design of estradiol loaded PLGA nanoparticulate formulations: a potential oral delivery system for hormone therapy. Pharm Res 23(1):184–195. [CrossRef]
- Arriaga LR, Datta SS, Kim SH, Amstad E, Kodger TE, Monroy F, Weitz DA (2014) Ultrathin shell double emulsion templated giant unilamellar lipid vesicles with controlled microdomain formation. Small 10(5):950–956. [CrossRef]
- Turcu-Ştiolică A, Ciocîlteu MV, Podgoreanu P, Neacşu I, Ionescu (Filip) OL, Nicolicescu C, Neamţu J, Amzoiu E, Amzoiu E, Manda CV (2022) PLGA–gentamicin and PLGA–hydroxyapatite–gentamicin microspheres for medical applications. Pharm Chem J 56(5):645–653. [CrossRef]
- Ciocilteu MV, Nicolaescu OE, Mocanu AG, Nicolicescu C, Rau G, Neamtu J, Amzoiu E, Amzoiu E, Oancea C, Turcu-Stiolică A (2021) Process optimization using quality by design (QBD) approach of a gentamicin loaded PLGA biocomposite. J Sci Arts 4(57):1069–1080. [CrossRef]
- Mezzenga R, Folmer BM, Hughes E (2004) Design of double emulsions by osmotic pressure tailoring. Langmuir 20(9):3574–3582. [CrossRef]
- Berchane NS, Carson KH, Rice-Ficht AC, Andrews MJ (2007) Effect of mean diameter and polydispersity of PLG microspheres on drug release: experiment and theory. Int J Pharm 337(1–2):118–126. [CrossRef]
- He C, Hu Y, Yin L, Tang C, Yin C (2010) Effects of particle size and surface charge on cellular uptake and biodistribution of polymeric nanoparticles. Biomaterials 31(13):3657–3666. [CrossRef]
- Kadri R, Elkhoury K, Ben Messaoud G, Kahn C, Tamayol A, Mano JF, Arab-Tehrany E, Sánchez-González L (2021) Physicochemical interactions in nanofunctionalized alginate/GelMA IPN hydrogels. Nanomaterials (Basel) 11(9):2256. [CrossRef]
- Postelnicu RA, Ciocîlteu MV, Neacşu IA, Nicolicescu C, Costachi A, Amzoiu M, Neamţu J, Pisoschi CG, Mocanu AG, Rău G, Amzoiu E (2023) PLGA–bisphosphonates conjugated nanoparticles: synthesis and morphological characterization. Farmacia 71(1):83–90. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Distribution by year of articles written with PLGA from 2000 to the present, analyzing two databases: Springer and Elsevier. PLGA: Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid).
Figure 1.
Distribution by year of articles written with PLGA from 2000 to the present, analyzing two databases: Springer and Elsevier. PLGA: Poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid).
Figure 2.
Polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic acid (PLA) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) structures.
Figure 2.
Polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic acid (PLA) and poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) structures.
Figure 3.
Zn–B complex UHPLC chromatogram for a standard solution of 25 μg/mL. UHPLC: Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography.
Figure 3.
Zn–B complex UHPLC chromatogram for a standard solution of 25 μg/mL. UHPLC: Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography.
Figure 4.
Zn–B complex mass spectrum: m/z 179 fructose fragment; m/z 367 Zn from Zn–B complex.
Figure 4.
Zn–B complex mass spectrum: m/z 179 fructose fragment; m/z 367 Zn from Zn–B complex.
Figure 5.
Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite delivery system synthesis flow, W/O/W double emulsion followed by lyophilization. O: Oil; W: Water.
Figure 5.
Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite delivery system synthesis flow, W/O/W double emulsion followed by lyophilization. O: Oil; W: Water.
Figure 6.
Regression coefficients plots showing the scaled and centered coefficients for the two responses. Conf. lev.: Confidence level; DF: Degrees of freedom; N: No. of experiments; RSD: Residual standard deviation; ZP: Zeta potential.
Figure 6.
Regression coefficients plots showing the scaled and centered coefficients for the two responses. Conf. lev.: Confidence level; DF: Degrees of freedom; N: No. of experiments; RSD: Residual standard deviation; ZP: Zeta potential.
Figure 7.
Coefficient overview plot for both responses. MLR: Multiple linear regression.
Figure 7.
Coefficient overview plot for both responses. MLR: Multiple linear regression.
Figure 8.
Contour plots showing the effect of the interaction between factors on the two responses.
Figure 8.
Contour plots showing the effect of the interaction between factors on the two responses.
Figure 9.
Contour plots with optimizer showing the effect of the interaction between factors on the two responses beyond the initial intervals.
Figure 9.
Contour plots with optimizer showing the effect of the interaction between factors on the two responses beyond the initial intervals.
Figure 10.
Morphology of the Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles. SEM micrographs at different magnitudes: (A) Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite; (B) Zn–B complex. SEM: Scanning electron microscopy.
Figure 10.
Morphology of the Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles. SEM micrographs at different magnitudes: (A) Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite; (B) Zn–B complex. SEM: Scanning electron microscopy.
Figure 11.
EDX mapping analysis of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite. EDX: Energy dispersive X-ray.
Figure 11.
EDX mapping analysis of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite. EDX: Energy dispersive X-ray.
Figure 12.
(A) Numerical distribution of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles – maximum number of particles at 225.43 nm for N2 synthesis according to experimental design model (highlighted in red); (B) Volumetric distribution of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles for N2 synthesis.
Figure 12.
(A) Numerical distribution of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles – maximum number of particles at 225.43 nm for N2 synthesis according to experimental design model (highlighted in red); (B) Volumetric distribution of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles for N2 synthesis.
Figure 13.
ZP of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles for N2 synthesis.
Figure 13.
ZP of Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite particles for N2 synthesis.
Figure 14.
Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite UHPLC chromatogram for N2 synthesis according to experimental design model.
Figure 14.
Zn–B–PLGA biocomposite UHPLC chromatogram for N2 synthesis according to experimental design model.
Table 1.
Independent variables (factors) and their levels.
Table 1.
Independent variables (factors) and their levels.
| Independent variable |
Symbol |
Levels |
| -1 |
0 |
+1 |
| PVA concentration [%] |
X1 |
1 |
2.5 |
4 |
| PLGA concentration [mg] |
X2 |
50 |
100 |
150 |
Table 2.
Experimental design matrix of responses.
Table 2.
Experimental design matrix of responses.
| Experiment |
PVA concentration [%] |
PLGA concentration [mg] |
Particle size [nm] |
ZP [mV] |
| N1 |
1 |
50 |
17.7±0.071 |
-1.11±0.55 |
| N2 |
4 |
50 |
225±0.912 |
-5.07±0.57 |
| N3 |
1 |
150 |
365.7±0.05 |
3.45±2.49 |
| N4 |
4 |
150 |
435.2±0.079 |
-2.19±0.64 |
| N5 |
2.5 |
100 |
232.9±0.411 |
-3.71±1.69 |
| N6 |
2.5 |
100 |
241.9±0.04 |
-3.11±0.45 |
| N7 |
2.5 |
100 |
257.5±0.246 |
-2.78±0.33 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).