Submitted:
02 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Metods
2.1. Setting and Population
2.2. Collection human milk samples
2.3. Activin A measurements
2.4. Statistical methods
3.Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Human Milk samples
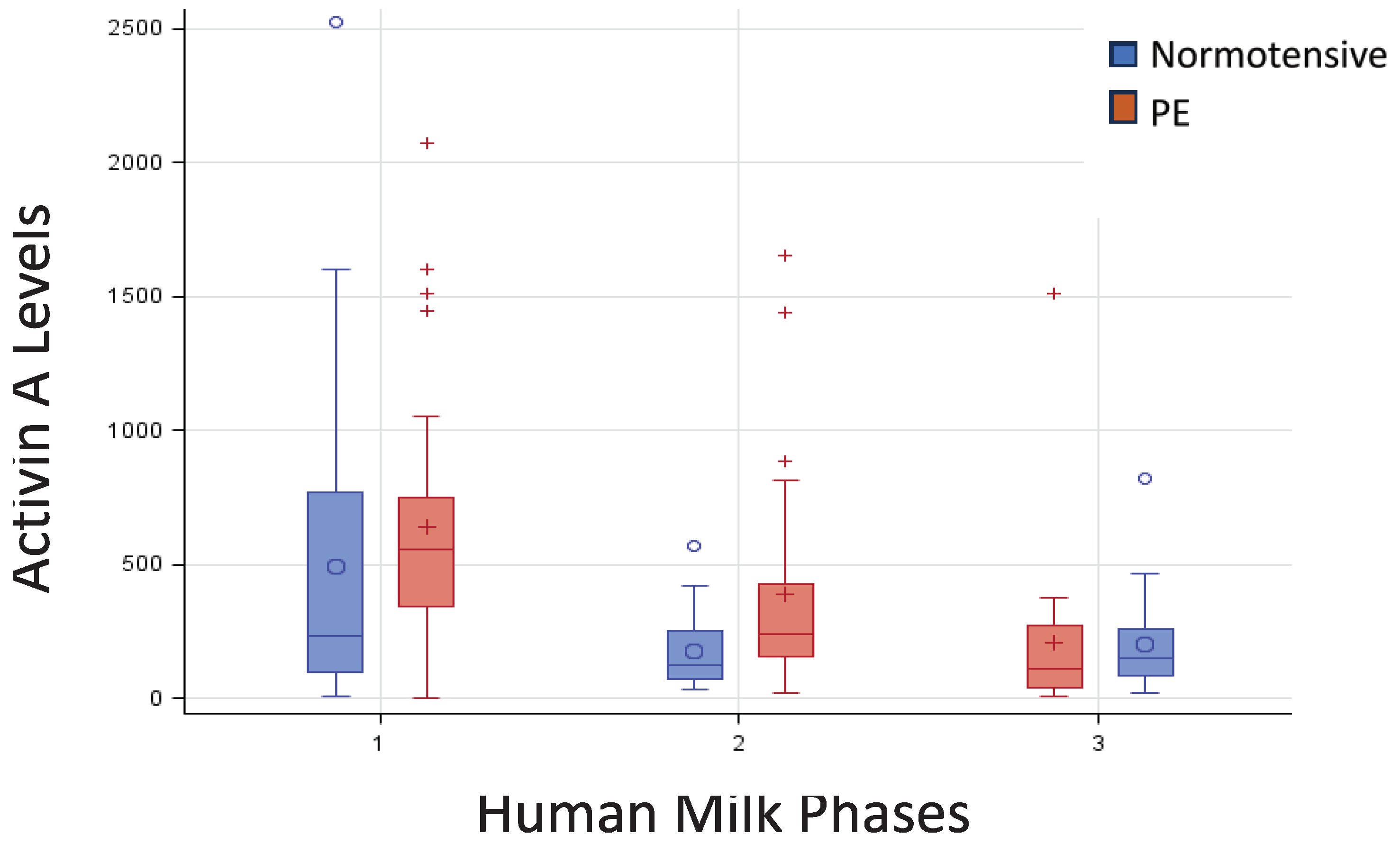
3.2. Activin A Concentrations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gestational Hypertension and Preeclampsia: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 222. Obstetrics & Gynecology 135(6):p e237-e260, June 2020. | . [CrossRef]
- Lisonkova S, Joseph KS. Incidence of preeclampsia: risk factors and outcomes associated with early- versus late-onset disease. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2013 Dec;209(6):544.e1-544.e12. Epub 2013 Aug 22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uzan J, Carbonnel M, Piconne O, Asmar R, Ayoubi JM. Pre-eclampsia: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011;7:467-74. Epub 2011 Jul 19. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hod T, Cerdeira AS, Karumanchi SA. Molecular Mechanisms of Preeclampsia. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2015 Aug 20;5(10):a023473. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Backes CH, Markham K, Moorehead P, Cordero L, Nankervis CA, Giannone PJ. Maternal preeclampsia and neonatal outcomes. J Pregnancy. 2011;2011:214365. Epub 2011 Apr 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Leitner Y, Harel S, Geva R, Eshel R, Yaffo A, Many A. The neurocognitive outcome of IUGR children born to mothers with and without preeclampsia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Nov;25(11):2206-8. Epub 2012 May 4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas NJ, Kampmann B, Mehring Le-Doare K. Human breast milk: A review on its composition and bioactivity. Early Hum Dev. 2015 Nov;91(11):629-35. Epub 2015 Sep 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gartner LM, Morton J, Lawrence RA, Naylor AJ, O'Hare D, Schanler RJ, Eidelman AI; American Academy of Pediatrics Section on Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding and the use of human milk. Pediatrics. 2005 Feb;115(2):496-506. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horta BL, and Victora CG. Long-term health effects of breastfeeding: a systematic review. World Health Organization 2013.
- Bar S, Milanaik R, Adesman A. Long-term neurodevelopmental benefits of breastfeeding. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2016 Aug;28(4):559-66. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peila C, Coscia A, Bertino E, Li Volti G, Galvano F, Barbagallo I, Visser GH, Gazzolo D. The Effect of Holder Pasteurization on Activin A Levels in Human Milk. Breastfeed Med. 2016 Nov;11:469-473. Epub 2016 Aug 16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luisi S, Calonaci G, Florio P, Lombardi I, De Felice C, Bagnoli F, Petraglia F. Identification of activin A and follistatin in human milk. Growth Factors. 2002 Sep;20(3):147-50. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzolo D, Abella R, Frigiola A, Giamberti A, Tina G, Nigro F, Florio P, Colivicchi M, Temporini F, Ricotti A, Li Volti G, Galvano F. Neuromarkers and unconventional biological fluids. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2010 Oct;23 Suppl 3:66-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tretter YP, Hertel M, Munz B, ten Bruggencate G, Werner S, Alzheimer C. Induction of activin A is essential for the neuroprotective action of basic fibroblast growth factor in vivo. Nat Med. 2000 Jul;6(7):812-5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Playford RJ, Macdonald CE, Johnson WS. Colostrum and milk-derived peptide growth factors for the treatment of gastrointestinal disorders. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000 Jul;72(1):5-14. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertino E, Di Nicola P, Varalda A, Occhi L, Giuliani F, Coscia A. Neonatal growth charts. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012 Apr;25 Suppl 1:67-9. Epub 2012 Mar 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir D., Demirel Sezer E, Turan V., Ozturk S., Canbay E. and E. Yıldırım Sozmen E. How Preeclampsia Affects Oxidant Status and Antiiflammatory Potential of Breast Milk? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2016; 100:S59 . [CrossRef]
- Duley L. The global impact of pre-eclampsia and eclampsia. Semin Perinatol. 2009 Jun;33(3):130-7. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangat K, Kilari A, Mehendale S, Lalwani S, Joshi S. Higher levels of brain derived neurotrophic factor but similar nerve growth factor in human milk in women with preeclampsia. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013 May;31(3):209-13. Epub 2013 Jan 18. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cekmen MB, Balat A, Balat O, Aksoy F, Yurekli M, Erbagci AB, Sahinoz S. Decreased adrenomedullin and total nitrite levels in breast milk of preeclamptic women. Clin Biochem. 2004 Feb;37(2):146-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbağci AB, Cekmen MB, Balat O, Balat A, Aksoy F, Tarakçioğlu M. Persistency of high proinflammatory cytokine levels from colostrum to mature milk in preeclampsia. Clin Biochem. 2005 Aug;38(8):712-6. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas NA, Santiago LTC, Kurokawa CS, Meira Junior JD, Corrente JE, Rugolo LMSS. Effect of preeclampsia on human milk cytokine levels. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2019 Jul;32(13):2209-2213. Epub 2018 Jan 25. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangat K, Upadhyay D, Kilari A, Sharma U, Kemse N, Mehendale S, Lalwani S, Wagh G, Joshi S, Jagannathan NR. Altered breast milk components in preeclampsia; An in-vitro proton NMR spectroscopy study. Clin Chim Acta. 2016 Dec 1;463:75-83. Epub 2016 Oct 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangat KD, Mehendale SS, Yadav HR, Kilari AS, Kulkarni AV, Taralekar VS, Joshi SR. Long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid composition of breast milk in pre-eclamptic mothers. Neonatology. 2010;97(3):190-4. Epub 2009 Oct 28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peila C, Bertino E, Cresi F, Coscia A. Interactions between preeclampsia and composition of the human milk: what do we know? J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2021 Jun 13:1-7. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y, Sun X, Jin L, Stringfield T, Lin L, Chen Y. Expression profiles of adiponectin receptors in mouse embryos. Gene Expr Patterns. 2005 Jun;5(5):711-5. [CrossRef]
- Saito S, Sakai M, Sasaki Y, Tanebe K, Tsuda H, Michimata T. Quantitative analysis of peripheral blood Th0, Th1, Th2 and the Th1:Th2 cell ratio during normal human pregnancy and preeclampsia. Clin Exp Immunol. 1999 Sep;117(3):550-5. [CrossRef]
- Jonsson Y, Rubèr M, Matthiesen L, Berg G, Nieminen K, Sharma S, Ernerudh J, Ekerfelt C. Cytokine mapping of sera from women with preeclampsia and normal pregnancies. J Reprod Immunol. 2006 Jun;70(1-2):83-91. [CrossRef]
- Dangat K, Kilari A, Mehendale S, Lalwani S, Joshi S. Preeclampsia alters milk neurotrophins and long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2014 Apr;33:115-21. Epub 2013 Dec 25. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpero LD, Frigiola A, Gazzolo D. Human milk and formulae: neurotrophic and new biological factors. Early Hum Dev. 2012 Mar;88 Suppl 1:S9-12. Epub 2012 Jan 17. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luisi S, Florio P, Reis FM, Petraglia F. Expression and secretion of activin A: possible physiological and clinical implications. Eur J Endocrinol. 2001 Sep;145(3):225-36. [CrossRef]
- Schubert D, Kimura H, LaCorbiere M, Vaughan J, Karr D, Fischer WH. Activin is a nerve cell survival molecule. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):868-70. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto M, Kondo S, Sakurai T, Etoh Y, Shibai H, Muramatsu M. Activin/EDF as an inhibitor of neural differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 30;173(1):193-200. [CrossRef]
- Schubert D, Kimura H. Substratum-growth factor collaborations are required for the mitogenic activities of activin and FGF on embryonal carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):841-6. [CrossRef]
- Iwahori Y, Saito H, Torii K, Nishiyama N. Activin exerts a neurotrophic effect on cultured hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. 1997 Jun 20;760(1-2):52-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu DD, Lai M, Hughes PE, Sirimanne E, Gluckman PD, Williams CE. Expression of the activin axis and neuronal rescue effects of recombinant activin A following hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in the infant rat. Brain Res. 1999 Jul 24;835(2):369-78. [CrossRef]
- Tretter YP, Hertel M, Munz B, ten Bruggencate G, Werner S, Alzheimer C. Induction of activin A is essential for the neuroprotective action of basic fibroblast growth factor in vivo. Nat Med. 2000 Jul;6(7):812-5. [CrossRef]
- Krieglstein K, Suter-Crazzolara C, Fischer WH, Unsicker K. TGF-beta superfamily members promote survival of midbrain dopaminergic neurons and protect them against MPP+ toxicity. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):736-42. [CrossRef]
- Hughes PE, Alexi T, Williams CE, Clark RG, Gluckman PD. Administration of recombinant human Activin-A has powerful neurotrophic effects on select striatal phenotypes in the quinolinic acid lesion model of Huntington's disease. Neuroscience. 1999;92(1):197-209. [CrossRef]
- Duman RS, Monteggia LM. A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 2006 Jun 15;59(12):1116-27. Epub 2006 Apr 21. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpero LD, Bellissima V, Colivicchi M, Sabatini M, Frigiola A, Ricotti A, Ghiglione V, Strozzi MC, Li Volti G, Galvano F, Gazzolo D. Next generation biomarkers for brain injury. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013 Oct;26 Suppl 2:44-9. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedger MP, Phillips DJ, de Kretser DM. Divergent cell-specific effects of activin-A on thymocyte proliferation stimulated by phytohemagglutinin, and interleukin 1beta or interleukin 6 in vitro. Cytokine. 2000 Jun;12(6):595-602. [CrossRef]
- Schultz Jel J, Witt SA, Glascock BJ, Nieman ML, Reiser PJ, Nix SL, Kimball TR, Doetschman T. TGF-beta1 mediates the hypertrophic cardiomyocyte growth induced by angiotensin II. J Clin Invest. 2002 Mar;109(6):787-96. [CrossRef]
- Giguère Y, Charland M, Bujold E, Bernard N, Grenier S, Rousseau F, Lafond J, Légaré F, Forest JC. Combining biochemical and ultrasonographic markers in predicting preeclampsia: a systematic review. Clin Chem. 2010 Mar;56(3):361-75. Epub 2009 Dec 31. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Normotensive N=46 |
Preeclamptic N=39 |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Maternal characteristics | |||
| Age (years) | median [IQR] | 33.5 [31,32,33,34,35,36,37] | 35 [31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38] |
| Italian | n (%) | 35 (76.1) | 31 (79.5) |
| Caesarian Section | n (%) | 25 (54.4) | 28 (71.8) |
| Weight gain (kg) | mean (SD) | 10.9 (4.75) | 10.4 (5.65) |
| Primigravida | n (%) | 29 (63.0) | 25 (64.0) |
| Smoker | n (%) | 6 (13.0) | 2 (5.1) |
| Newborn characteristics | |||
| Singleton | n (%) | 38 (82.6) | 36 (92.3) |
| IUGR | n (%) | 2 (4.4) | 16 (41.0) |
| GA (weeks) | median [IQR] | 37 [31;39] | 32 [29,30,31,32,33,34,35] |
| Girls | n (%) | 19 (41.3) | 19 (48.7) |
| Birth weight (g) | mean (SD) | 2345 (1028) | 1542 (720) |
| Birth weight (z-score) | mean (SD | -0.21 (0.934) | -1.16 (0.810) |
| SGA | n (%) | 6 (13.0) | 19 (50.0) |
| LGA | n (%) | 2 (4.4) | 0 (0.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





