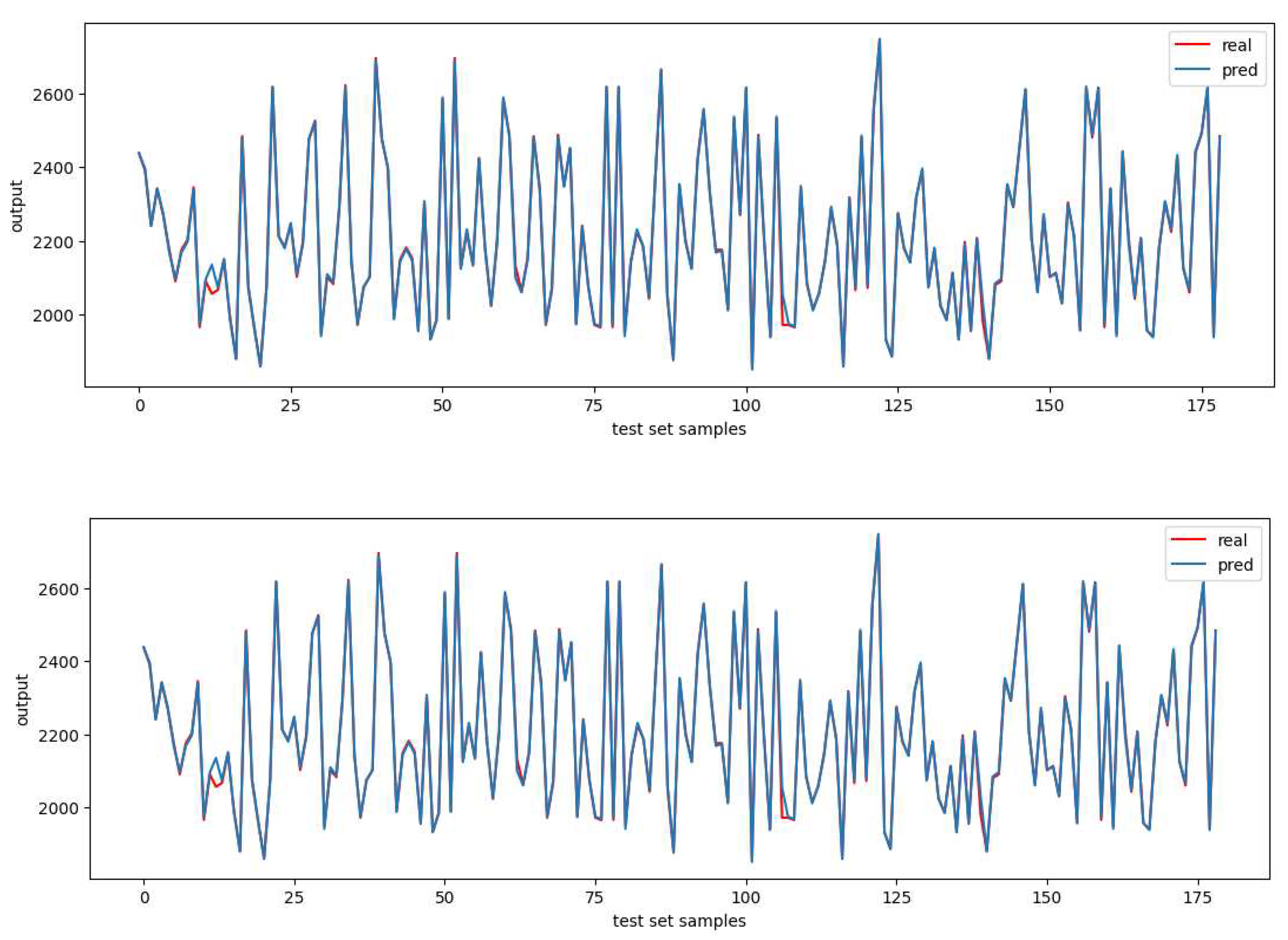
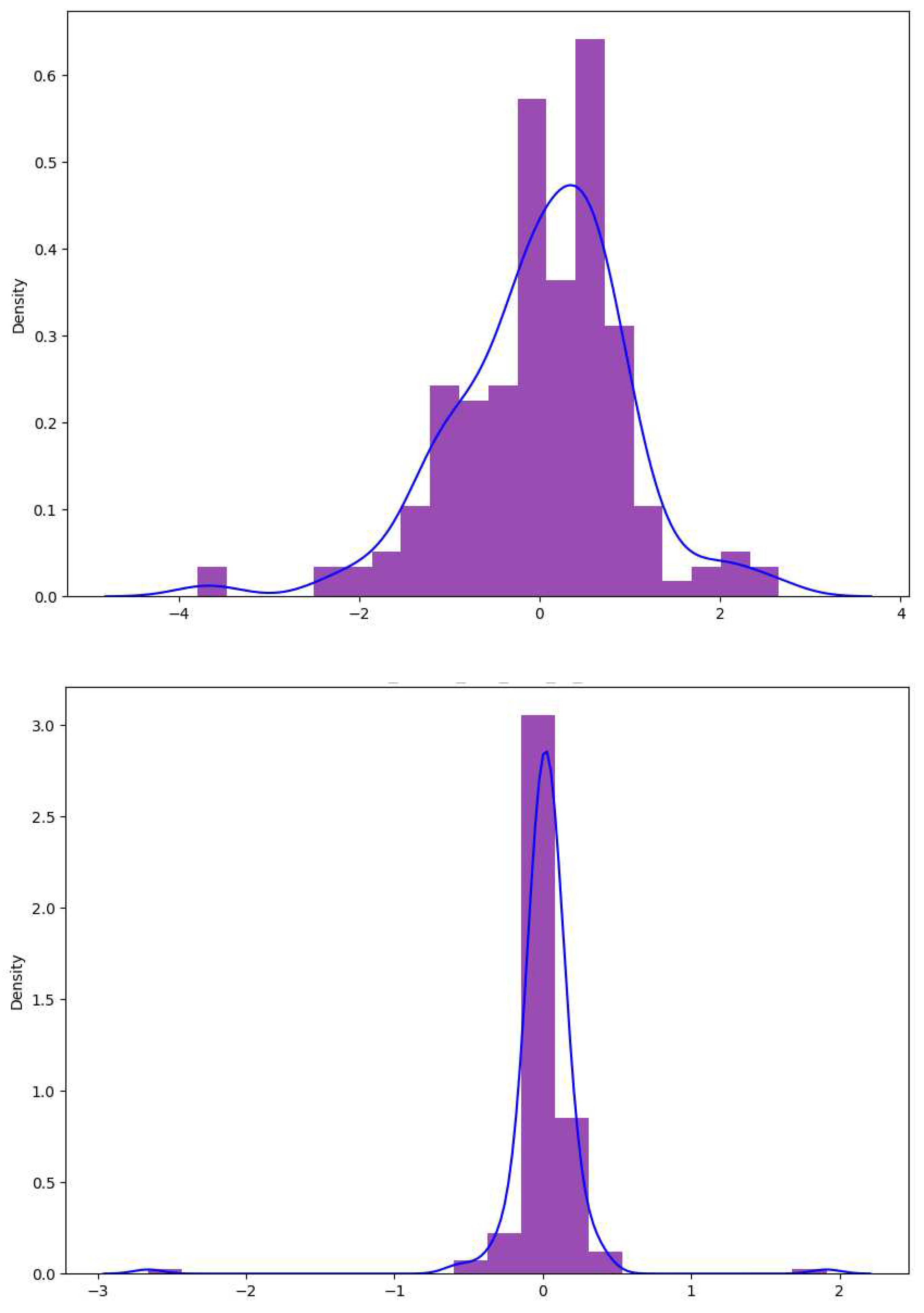
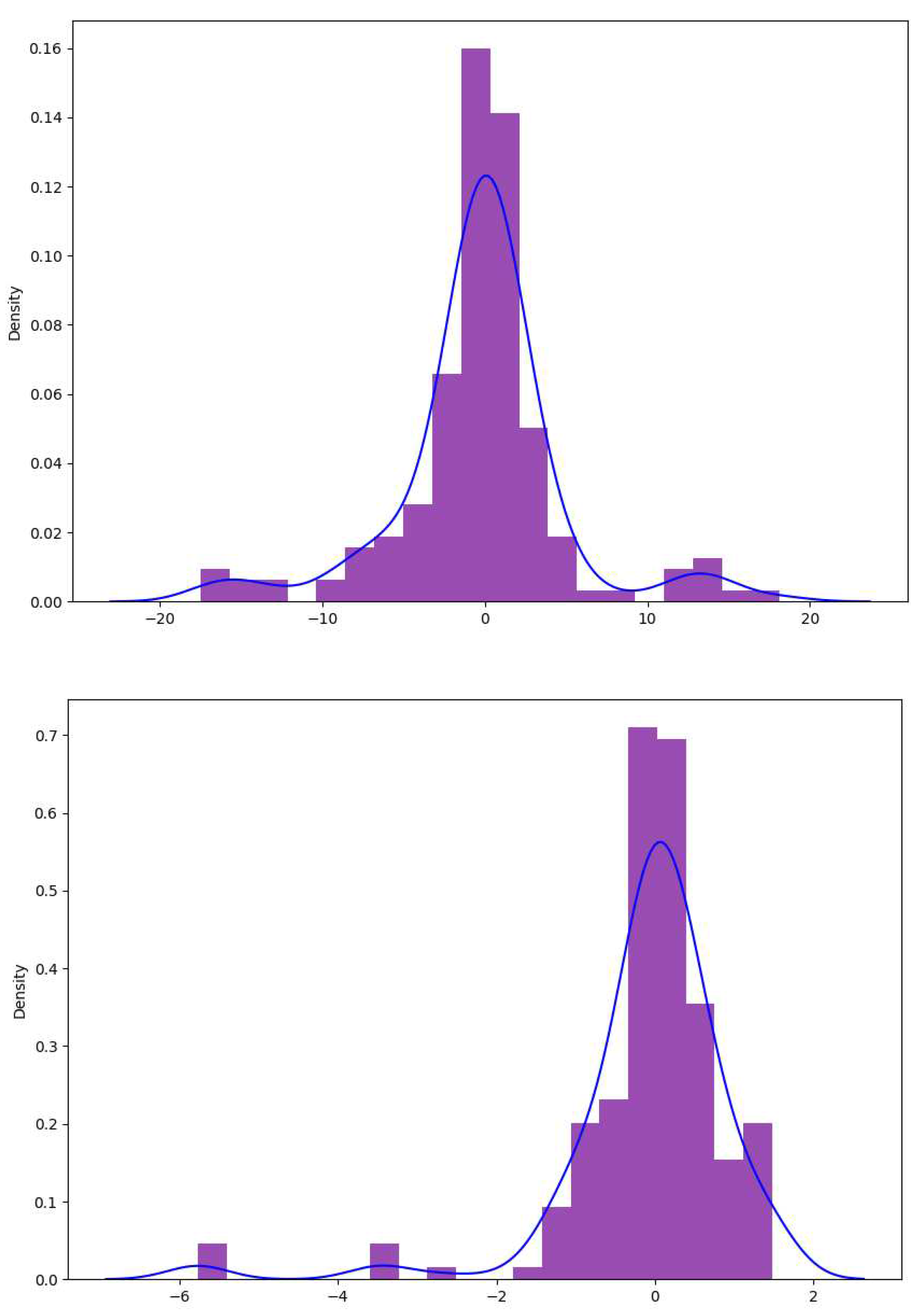
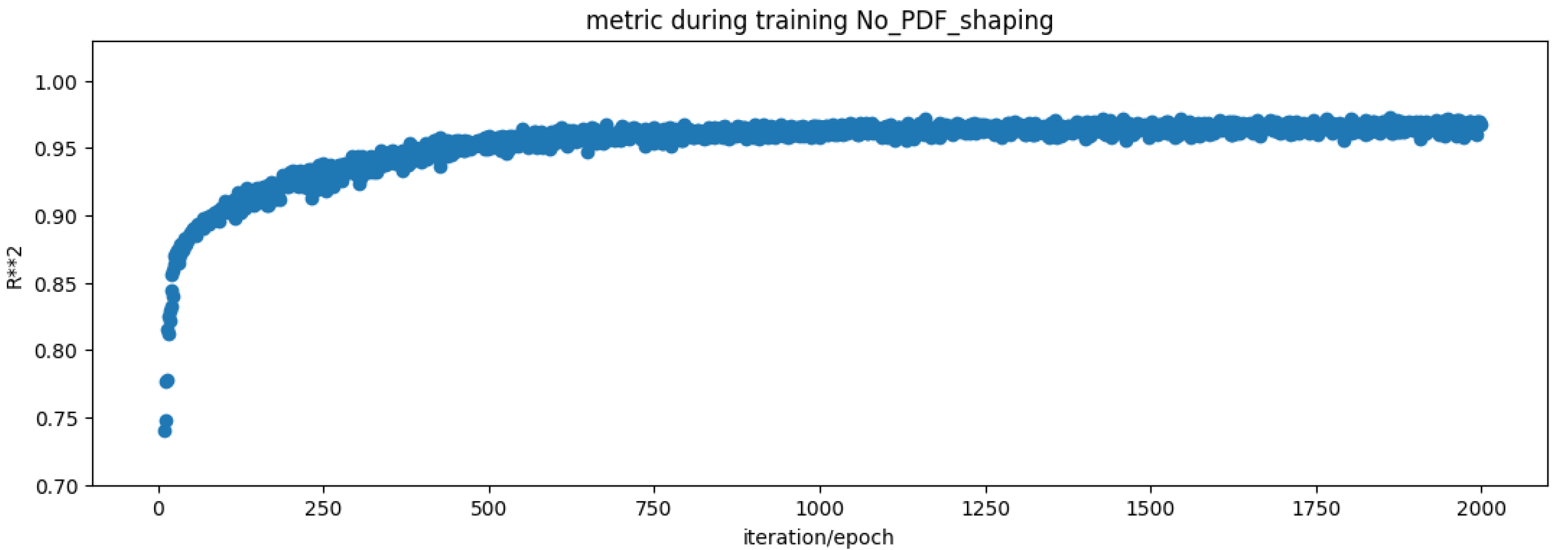
In statistics, the question of how well a model performs for the data is sometimes described in terms of bias and variance. In this context, bias means that the model cannot learn the true relationship in the data. For example, a linear regression cannot fit a curve. So, it has bias. Neural network–based models, for instance, can fit the training data so well that they can prove unable to adapt upon encountering new, unseen data. This is called overfitting. This difference in fitting between the train set and the test set is sometimes called the variance in the context of overfitting. So, an overfitted model on the train set may have higher variance because it does not generalize well to the test set. Therefore, the goal when building a regression model for your data is to have both good bias and variance in the context of fitting the data.
There are several approaches to fit models to regression data. Three important ones are linear regression, regression trees, and neural networks. The next sections discuss neural network–based regression and regression trees leading up to XGBoost.
2.1.1. Regression Trees
As previously indicated, regression trees can fit nonlinear data. Regression trees are a type of decision tree in which the predicted values are not discrete classes but instead are real valued numbers. The key concept here is to use the features from the samples to build a tree. The nodes in the tree are decision points leading to leaves. The leaves contain values that are used to determine the final predicted regression value.
For example, if a selected feature ranges from 0 to 255, a threshold value, such as 115, can be selected to decide which child node of the parent node should be moved to. In the simplest case, each parent node in a regression tree has two child nodes. Once the selected feature’s threshold is established, this cut off is used to help select the output regression value. In the simplest case, the child node on the left can accumulate all the output values that correspond to the values below the threshold for the given feature. Concurrently, the right node collects those above the threshold. Simply averaging values in each node can give an initial predicted value. However, this method is not the best solution. The goal in training regression trees is to try multiple thresholds and select the ones that provide the best results. Through iterative optimization and comparison of predicted values to real values, optimal regression trees can be obtained.
Regression trees start from the top and work their way down to the leaf nodes. Leaf nodes are used to select output values. Nonleaf nodes are typically decision nodes based on the optimal threshold for the range of values in that feature. The key question is how to select the optimal features to use and their optimal threshold value for a given node.
How are features and thresholds selected? One simple way is to iteratively try different thresholds and then try predicting an output value with each regression tree model candidate. For each predicted output for a given tree candidate, the approach compares the predicted value to the real value and selects the candidate that minimizes the errors. In the context of regression trees, the difference between the real and the predicted values is called the residual. This loss function is very similar to the minimum squared errors (MSE) loss function. In this case, the objective goal is to minimize these residuals.
Given a set of output values in a node, each will be tried iteratively, and the sum of squares residual will be calculated for all the threshold candidates. Once the optimized threshold is calculated, the process can be repeated by adding new nodes. When a node can no longer be split, the process stops, and it is called a leaf. Overfitting can be an issue with regression trees. To reduce the possibility of overfitting, rules are used to stop adding nodes once some criteria have been met. As an example, if a node does not have enough samples to calculate an average, perhaps if there are less that 30 samples for this node, the nodes will stop splitting.
Another key question is the selection of features to use for the decision node. Intuitively, the process is fairly logical and simple. For each feature, the optimal threshold will be calculated as previously described. Then, of the n feature candidates, the one that minimizes the residuals will be selected.
2.1.2. AdaBoost
AdaBoost (Adaptive Boosting) is a more advanced version of the standard regression trees algorithm. In AdaBoost, trees are created with a fixed size, which are called stumps. They can be restricted to stumps of just two levels. Some stumps have more weight than others when predicting the final value. Order is important in AdaBoost. One important characteristic in AdaBoost is that errors are considered and given more importance when creating subsequent stumps.
In AdaBoost, the training samples have weights to indicate importance. As the process advances, the weights are updated. Initially, all samples have the same weight, and all weights add up to one. During training, the weight for the stump is calculated by determining the accuracy between the predicted and the real values. The stump weight is the sum of the weights of all the poorly predicted samples. The weight importance is also known as the
amount of say (
) and is calculated as follows:
where
represents the total number of errors.
In the next iteration, the data sample weights need to be adjusted. Samples that have caused errors in the model have their weights increased. The other samples get their weights decreased.
The formula to increase the weights for error samples is as follows:
To decrease the weights for nonerror samples is as follows:
After updating the weights for the data samples, the weights are normalized to add up to 1.
In the next iteration, a new data set is created that contains more copies of the samples that have the highest error weights. These samples can be duplicated. A special random selection algorithm is used to select these samples. Although random, the algorithm favors the selection of samples with higher error weights.
Once the new training data set is created, weights are reassigned to each sample of the new data set. The new data set is the same size as the original data set. All the weights are set to be the same again, and the process begins again. The point is that penalized samples in the previous iteration are duplicated more in the new data set.
This method is how a user learns the AdaBoost stumps and their weights. Then, the user can predict with all these stumps, but the learned weights are considered when making a prediction.
2.1.3. Gradient Boost
AdaBoost, as previously described, builds small stumps with weights. Gradient boost (as compared with AdaBoost) builds subtrees that can have one node or more. But, the nodes are added iteratively. The final gradient boost tree is a linear combination of subtrees.
The first node in the linear combination of subtrees is simply one node that predicts the average of all regression outputs for the training data. The algorithm then continues additively adding subtrees. The next subtree is based on the errors from the first tree, such as the errors made in the tree that only has one node predicting the average of the y output values in the training data.
The errors are the differences between predicted and real output values. As previously described, the gradient boost tree is a linear combination of subtrees (see Equation 5). The first node predicts the average regression output, but subsequent subtrees predict residuals. These residuals are added to the initial average node and adjust the output value. The residuals are differences between predicted and real values. Similar to previously described regression trees, the residuals are assigned to nodes in the tree based on how they minimize errors.
where
predicts the average output, and all other subtrees predict residuals.
To prevent overfitting, a learning rate ( ) is assigned (which is a scaling factor) to the subtrees to control the effect of the residuals on the final regression output.
Every iteration, the new tree is used to predict new output values, and these values are compared with the real values. The difference is the residuals. These residuals are used to create the new subtree for the next iteration. Once the residuals for an iteration are calculated, a new subtree can be created. The process involves ranking the residuals. This process continues until a stopping criteria is reached. The learning rate is usually 0.1.
2.1.4. XGBoost
XGBoost [
6] is an improvement on gradient boosting. It has new algorithms and approaches for creating the regression tree. It also has optimizations to improve the performance and speed by which it can learn and process data.
XGBoost has some similar characteristics to gradient boosting. The first node always predicts 0.5 instead of the average, as with gradient boosting. Also similar to gradient boosting, XGBoost fits a regression tree to calculate residuals with each subtree. Unlike gradient boosting, XGBoost has its own algorithm to build the regression tree. Formally, XGBoost [
6] can be defined as follows.
For a given data set, a tree ensemble model uses
K additive functions to predict the output.
where
. The symbol
F is the space of regression trees. Each
corresponds to an independent subtree. Each regression subtree contains an output value on each leaf. This value is represented by
w. For a given sample, the decision rules in the tree are used to find the respective leaves and calculate the final prediction. This prediction is obtained by summing up the output values in the corresponding leaves. To learn the set of functions used in the regression tree, the following loss function must be minimized.
where
is a type of MSE measuring the difference between the real and predicted values, and the term
is used to control the number of terminal nodes. This process is called pruning, and it is part of the optimization objective. The term
is a regularization parameter. It represents the output value
w and helps to smooth the learned values. Also,
is a scaling factor. Setting the regularization parameters to zero makes the loss become the same as the traditional gradient tree boosting.
The tree ensemble model includes functions as parameters and cannot be optimized using traditional optimization methods. Instead, the model is trained in an additive manner. Formally, let
be the prediction of the instance
i at iteration
t. The new
(i.e., subtree) will need to be added to minimize the loss as follows:
This means that an must be added greedily, which results in the most improvement to this model based on the loss. So, in XGBoost, given a node with residuals, the goal is to find output values for this node that create a subtree that minimizes the loss function. The term can be written as . The term represents the output value.
Optimization in XGBoost is a bit different in practice from neural networks. In neural networks, derivatives are taken for gradients during the epochs in the training process, and they do back propagation. In contrast, in XGBoost, a loss has to be calculated and minimized theoretically, but in practice, the derivatives (gradients) are always the general equation of adding the residuals and dividing by the total. So, notably, no derivative calculation occurs during training. Unlike neural networks, XGBoost uses the same overall design for every single model, and the user only has to calculate the derivative once (on paper) and know that it will work for all of the models created. In contrast, every neural network has a different design (e.g., different number of hidden layers, different loss functions, different number of weights), so the user always has to calculate the gradient for each model. In general, by minimizing the loss function with the derivative, general equations are obtained, which are used to build the tree. So, this derivation gives the general formulas. This objective can be optimized in a general setting. Derivation and simplification give general equations.
In normal circumstances, it is not possible to enumerate all the possible tree structures. Instead, a greedy algorithm that starts from a single leaf and iteratively adds branches to the tree is used. As such, the process to create the tree is as follows.
In essence, different subtree candidates must be tried, and the one that optimizes the loss function should be selected. During the learning process, the tree starts with one node and tries to add more subtrees with optimal node and threshold configurations. The user needs a way to score the subtree candidates to select the best one. Each subtree gets scored using the gain value. The gain value for a subtree candidate is calculated from other values associated with each of the nodes that make up that subtree candidate. Once similarity scores for each node in the subtree candidate are obtained, they are used to calculate the gain of that particular split of the nodes in the subtree. This gain equation is used to evaluate the split candidates. For example, assuming nodes left and right for a root node, the gain can be calculated as follows:
The gain score helps to determine the correct threshold. For other threshold cutoffs, other gains can be calculated and the optimal one selected. So, the threshold that gave the largest gain is used. If a node only has one residual, then that is it, and it is a leaf.
The gain depends on similarity scores. The process to create a set of subtree candidates needs these similarity scores and is as follows. For each node in a subtree candidate, a quality score or similarity score is calculated from all the residuals in the node. The similarity score function is as follows:
where the residuals are summed first and then squared. The symbol
is a regularization parameter.
Once the similarity score is calculated, the node should be split into two child nodes. The residuals are grouped into these nodes. Because the threshold for the node is not known, the feature is iteratively split from its lowest value to its highest values in the range. Here, however, XGBoost uses an optimized technique called percent quantiles to select the threshold. Residuals that belong to less than the threshold go on the left node, and residuals that belong to more than the threshold go on the right node. Once again, the similarity scores are calculated for each of the two left and right nodes.
The optimal subtree candidate is selected using the similarity score and the gain score as previously described. Once the best candidate is selected, the next step is to calculate its output values for the leaf nodes. The output values are also governed by the loss function, and the formula for them can be derived from it, as shown in Equation 11. So, for a given subtree structure, the optimal
of leaf
j can be computed as
This step completes the tree building process. Now, the tree can be used to predict
y similarly to how this is done with gradient boosting.
where
predicts 0.5, and all other subtrees predict residuals that get added together but are scaled based on the learning rate
.