Submitted:
31 August 2023
Posted:
05 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- An efficient one-stage inpainting framework with effective modules is proposed to reduce the number of model parameters and computational costs to mitigate the overfitting problem when trained on small datasets, with potential applications in various environments.
- Qualitative and quantitative evaluations conducted on different public datasets demonstrate the excellent performance of our method compared with state-of-the-art models.
2. Related Works
2.1. Image Inpainting by Patch-Based Methods
2.2. Image Inpainting by Deep Generative Methods
2.3. Conditional Normalization
2.4. Neural Networks with Lightweight Architecture
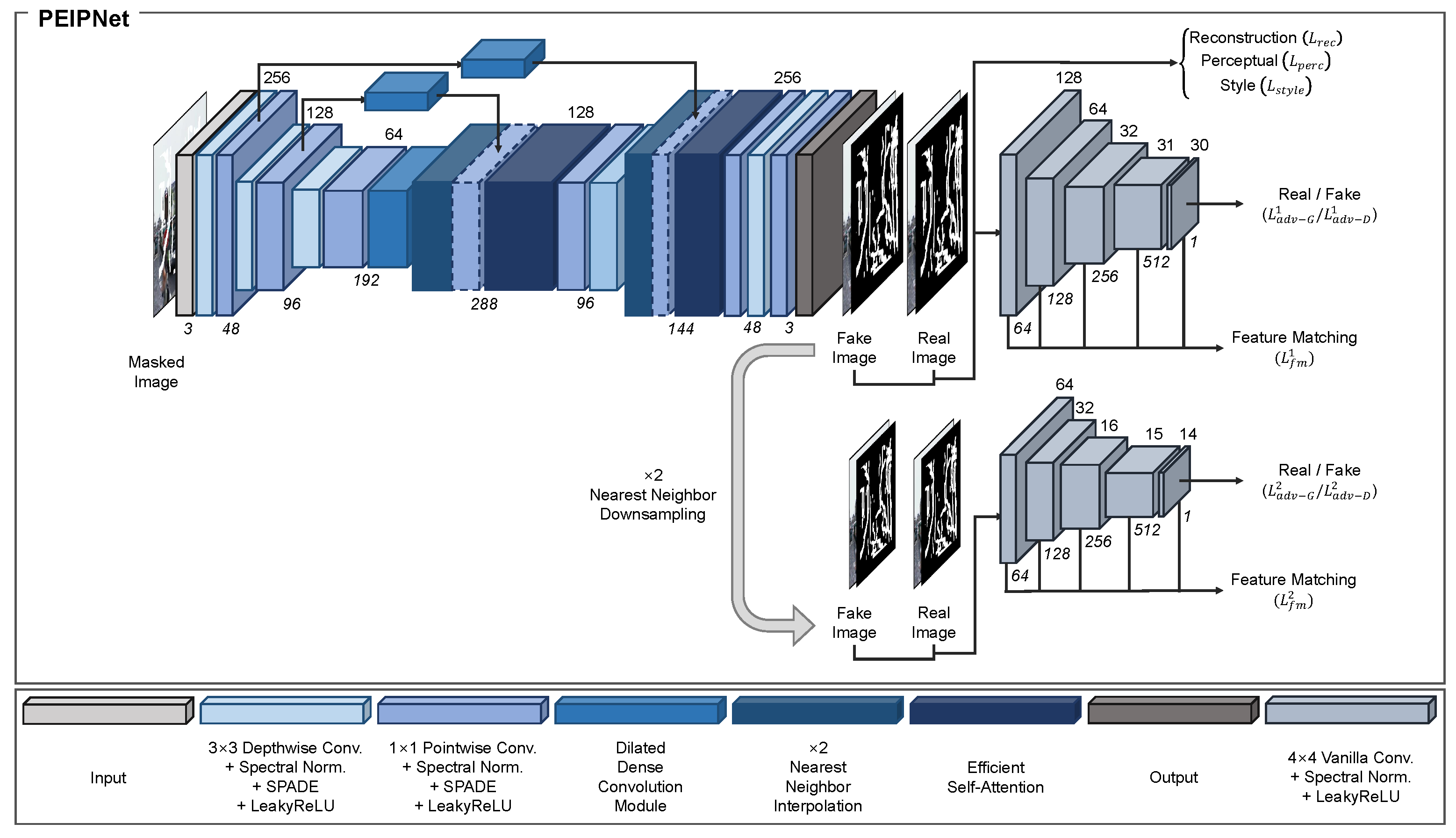
3. Methodology
3.1. Generator Architecture
3.1.1. Spatially-Adaptive Denormalization
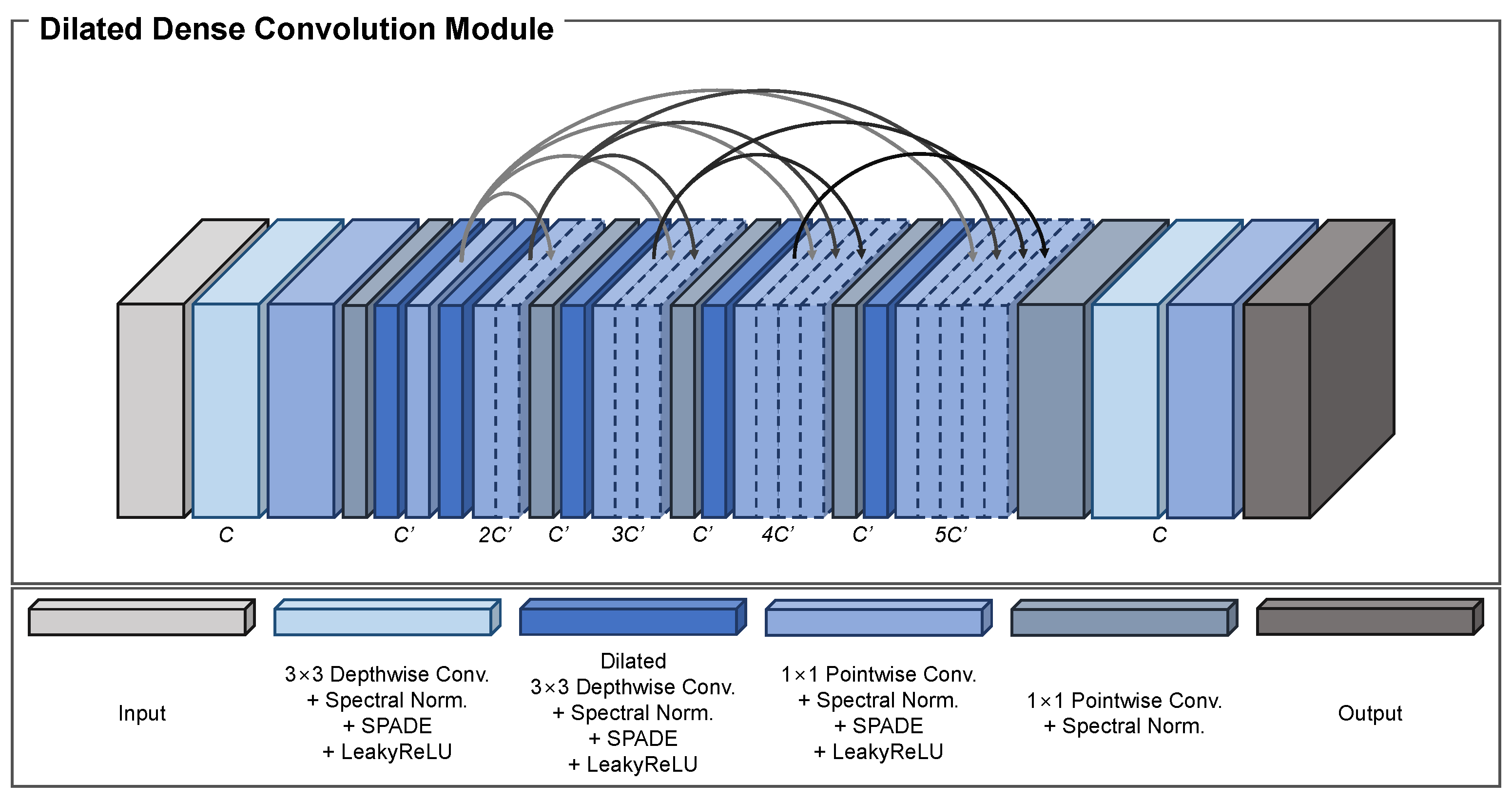
3.1.2. Dense Dilated Convolution Module
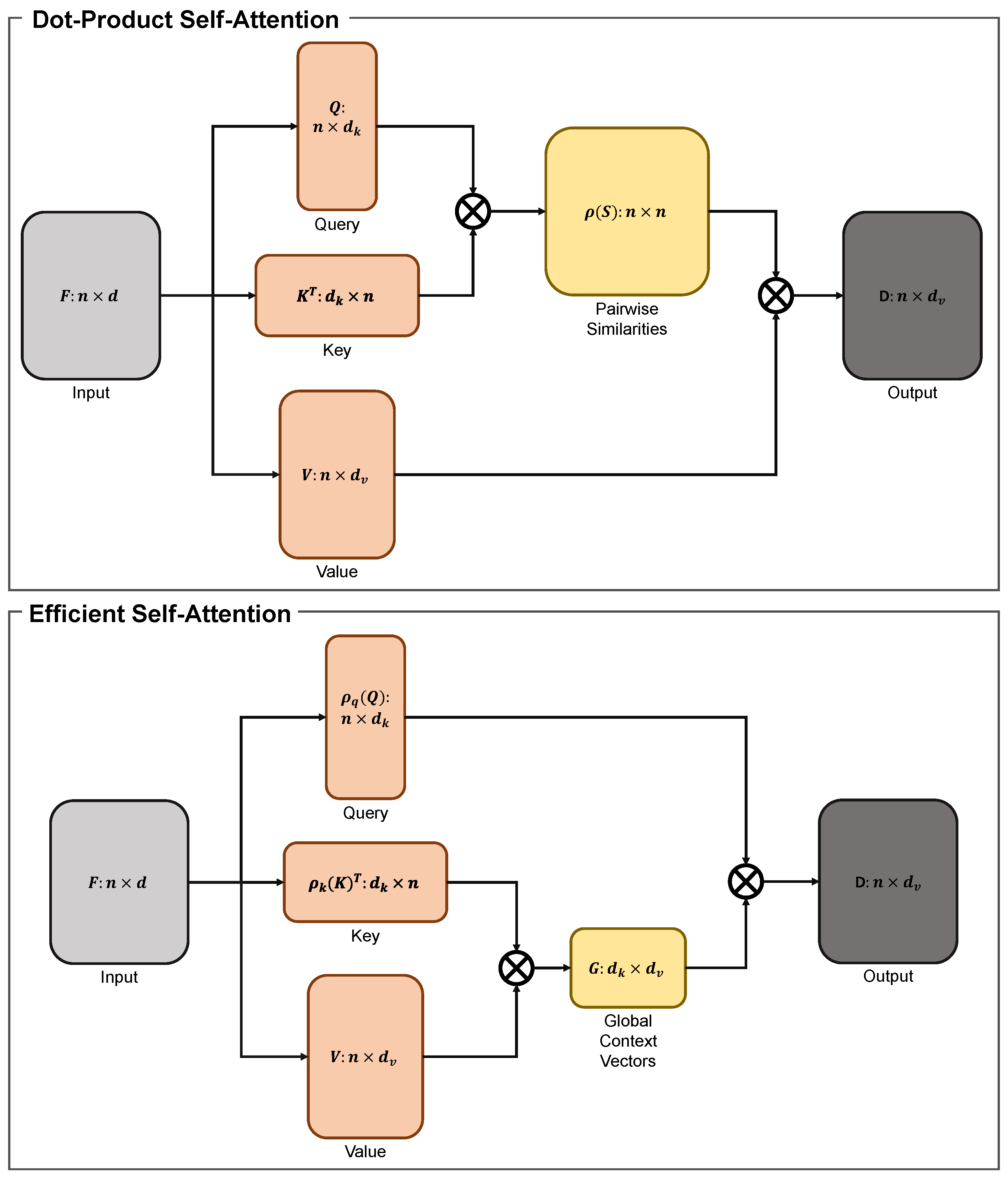
3.1.3. Efficient Self-Attention
3.2. Discriminator Architecture
3.3. Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Compared Methods
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Analysis of Model Complexity
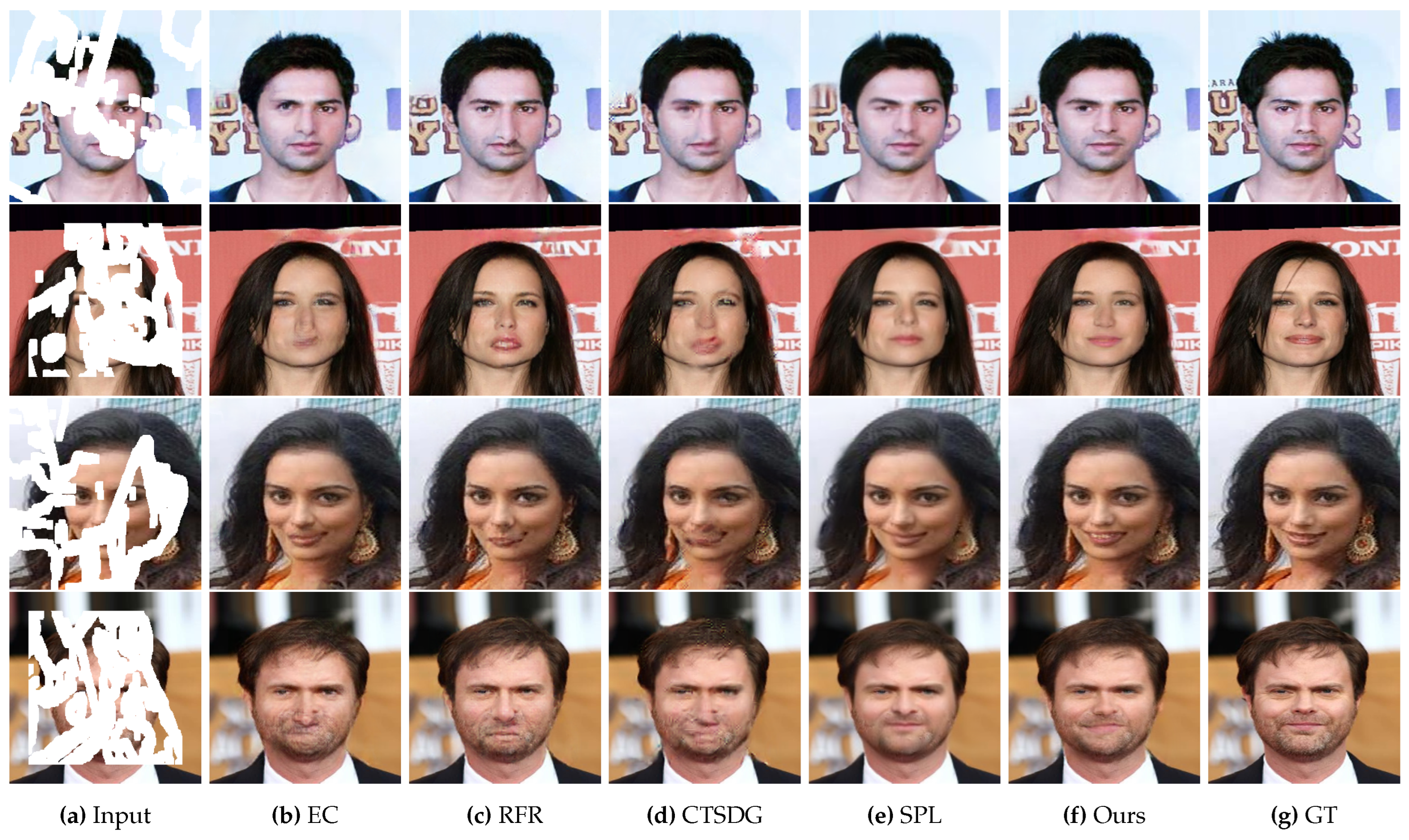
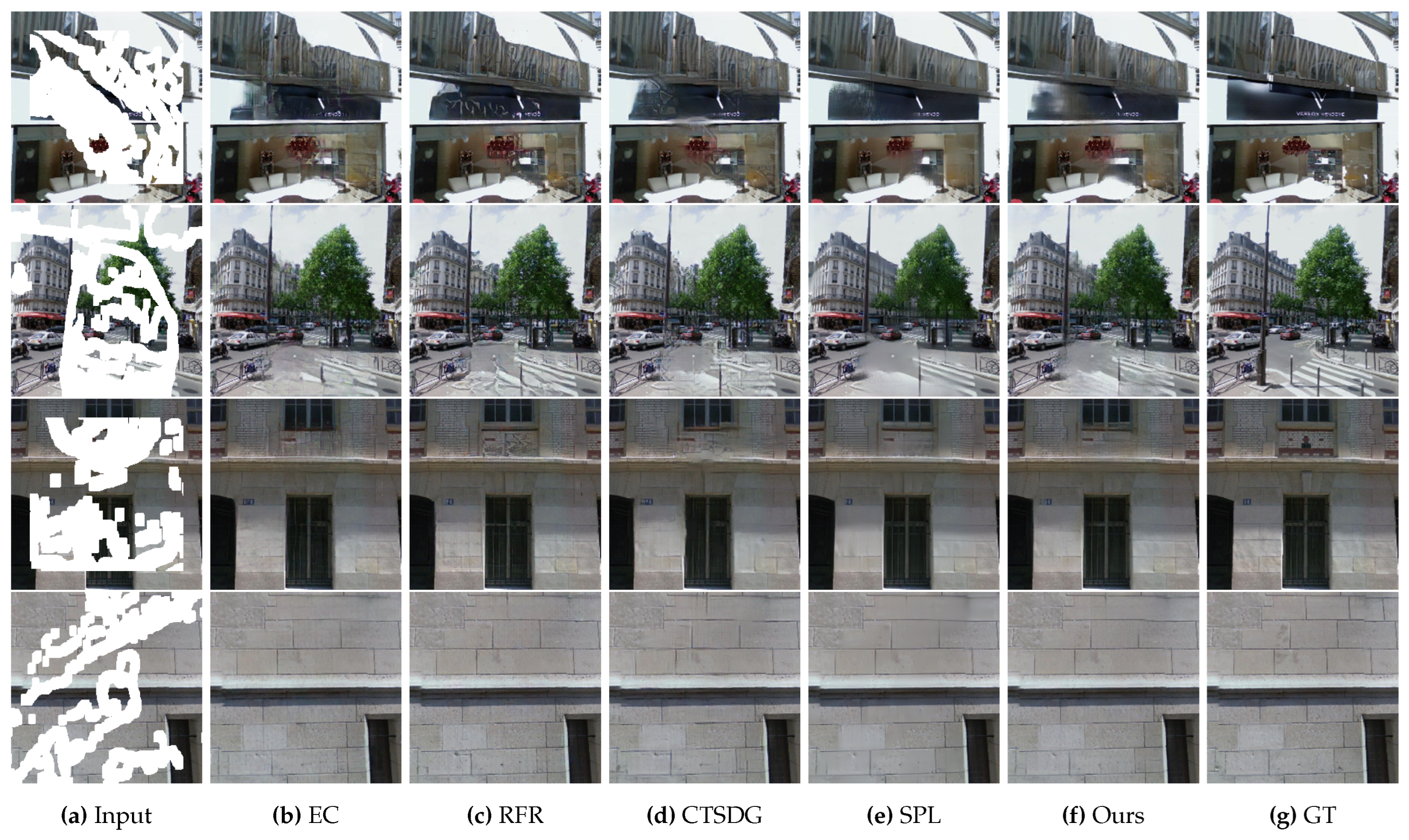
4.5. Qualitative Evaluations
4.6. Quantitative Evaluations
4.7. Ablation Studies
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Efros, A.A.; Leung, T.K. Texture synthesis by non-parametric sampling. seventh IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV). IEEE, 1999, Vol. 2, pp. 1033–1038.
- Ballester, C.; Bertalmio, M.; Caselles, V.; Sapiro, G.; Verdera, J. Filling-in by joint interpolation of vector fields and gray levels. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2001, 10, 1200–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efros, A.A.; Freeman, W.T. Image Quilting for Texture Synthesis and Transfer. 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, 2001, p. 341–346.
- Bertalmio, M.; Vese, L.; Sapiro, G.; Osher, S. Simultaneous structure and texture image inpainting. IEEE transactions on image processing 2003, 12, 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Criminisi, A.; Perez, P.; Toyama, K. Region filling and object removal by exemplar-based image inpainting. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2004, 13, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, F.; Ying, Y.; Wang, J.; Peng, Q. A Novel Texture Synthesis Based Algorithm for Object Removal in Photographs. Advances in Computer Science - ASIAN 2004. Higher-Level Decision Making, 2005, pp. 248–258.
- Cheng, W.H.; Hsieh, C.W.; Lin, S.K.; Wang, C.W.; Wu, J.L. Robust algorithm for exemplar-based image inpainting. International Conference on Computer Graphics, Imaging and Visualization, 2005, pp. 64–69.
- Simakov, D.; Caspi, Y.; Shechtman, E.; Irani, M. Summarizing visual data using bidirectional similarity. 2008 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition. IEEE, 2008, pp. 1–8.
- Barnes, C.; Shechtman, E.; Finkelstein, A.; Goldman, D.B. PatchMatch: A randomized correspondence algorithm for structural image editing. ACM Trans. Graph. 2009, 28, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D.; Krahenbuhl, P.; Donahue, J.; Darrell, T.; Efros, A.A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2016, pp. 2536–2544.
- Yu, F.; Koltun, V. Multi-Scale Context Aggregation by Dilated Convolutions. 4th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2016.
- Iizuka, S.; Simo-Serra, E.; Ishikawa, H. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Transactions on Graphics (ToG) 2017, 36, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Ram, S.; Rodríguez, J.J. Image inpainting using nonlocal texture matching and nonlinear filtering. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing 2018, 28, 1705–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Reda, F.A.; Shih, K.J.; Wang, T.C.; Tao, A.; Catanzaro, B. Image Inpainting for Irregular Holes Using Partial Convolutions. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 89–105.
- Wang, Y.; Tao, X.; Qi, X.; Shen, X.; Jia, J. Image inpainting via generative multi-column convolutional neural networks. Advances in neural information processing systems 2018, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, M.; Zuo, W.; Shan, S. Shift-net: Image inpainting via deep feature rearrangement. European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 1–17.
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T.S. Generative image inpainting with contextual attention. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2018, pp. 5505–5514.
- Li, J.; He, F.; Zhang, L.; Du, B.; Tao, D. Progressive reconstruction of visual structure for image inpainting. IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), 2019, pp. 5962–5971.
- Goodfellow, I.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.; Bengio, Y. Generative Adversarial Nets. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2014, Vol. 27.
- Liu, H.; Jiang, B.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, C. Coherent semantic attention for image inpainting. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019, pp. 4170–4179.
- Sagong, M.c.; Shin, Y.g.; Kim, S.w.; Park, S.; Ko, S.j. Pepsi: Fast image inpainting with parallel decoding network. IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2019, pp. 11360–11368.
- Zeng, Y.; Fu, J.; Chao, H.; Guo, B. Learning pyramid-context encoder network for high-quality image inpainting. IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2019, pp. 1486–1494.
- Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Shen, X.; Lu, X.; Huang, T.S. Free-form image inpainting with gated convolution. IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision (ICCV), 2019, pp. 4471–4480.
- Nazeri, K.; Ng, E.; Joseph, T.; Qureshi, F.; Ebrahimi, M. EdgeConnect: Structure Guided Image Inpainting using Edge Prediction. The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, 2019.
- Ren, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhang, R.; Li, T.H.; Liu, S.; Li, G. Structureflow: Image inpainting via structure-aware appearance flow. IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, 2019, pp. 181–190.
- Xiong, W.; Yu, J.; Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Lu, X.; Barnes, C.; Luo, J. Foreground-aware image inpainting. IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2019, pp. 5840–5848.
- Yang, J.; Qi, Z.; Shi, Y. Learning to incorporate structure knowledge for image inpainting. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence (AAAI), 2020, pp. 12605–12612.
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. 2017, arXiv:cs.CV/1704.04861. [Google Scholar]
- Park, T.; Liu, M.Y.; Wang, T.C.; Zhu, J.Y. Semantic Image Synthesis With Spatially-Adaptive Normalization. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019.
- Huang, G.; Liu, Z.; van der Maaten, L.; Weinberger, K.Q. Densely Connected Convolutional Networks. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017.
- Shen, Z.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, H.; Yi, S.; Li, H. Efficient Attention: Attention With Linear Complexities. IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2021, pp. 3531–3539.
- Telea, A. An image inpainting technique based on the fast marching method. Journal of graphics tools 2004, 9, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. seventh IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), 1999, Vol. 2, pp. 1150–1157.
- Ioffe, S.; Szegedy, C. Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift. 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2015, Vol. 37, pp. 448–456.
- Ulyanov, D.; Vedaldi, A.; Lempitsky, V. Instance Normalization: The Missing Ingredient for Fast Stylization. 2016, arXiv:cs.CV/1607.08022. [Google Scholar]
- Ba, J.L.; Kiros, J.R.; Hinton, G.E. Layer Normalization. 2016, arXiv:stat.ML/1607.06450. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; He, K. Group normalization. European conference on computer vision (ECCV), 2018, pp. 3–19.
- Dumoulin, V.; Shlens, J.; Kudlur, M. A Learned Representation For Artistic Style. 2017, arXiv:cs.CV/1610.07629. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, X.; Belongie, S. Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization. IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), 2017, pp. 1501–1510.
- De Vries, H.; Strub, F.; Mary, J.; Larochelle, H.; Pietquin, O.; Courville, A.C. Modulating early visual processing by language. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2017, Vol. 30.
- Yu, T.; Guo, Z.; Jin, X.; Wu, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, S. Region normalization for image inpainting. AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2020, pp. 12733–12740.
- Sifre, L. Rigid-motion scattering for image classification. Ph. D. thesis 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, J.; Dundar, A.; Culurciello, E. Flattened Convolutional Neural Networks for Feedforward Acceleration. 2015, arXiv:cs.NE/1412.5474. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Liu, B.; Foroosh, H. Factorized convolutional neural networks. IEEE international conference on computer vision workshops (CVPR), 2017, pp. 545–553.
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions. IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2017, pp. 1251–1258.
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016.
- Iandola, F.N.; Han, S.; Moskewicz, M.W.; Ashraf, K.; Dally, W.J.; Keutzer, K. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size. 2016, arXiv:cs.CV/1602.07360. [Google Scholar]
- Sindhwani, V.; Sainath, T.; Kumar, S. Structured transforms for small-footprint deep learning. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2015.
- Yang, Z.; Moczulski, M.; Denil, M.; De Freitas, N.; Smola, A.; Song, L.; Wang, Z. Deep fried convnets. IEEE international conference on computer vision (ICCV), 2015, pp. 1476–1483.
- Miyato, T.; Kataoka, T.; Koyama, M.; Yoshida, Y. Spectral Normalization for Generative Adversarial Networks. International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), 2018.
- Wang, X.; Girshick, R.; Gupta, A.; He, K. Non-Local Neural Networks. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018.
- Isola, P.; Zhu, J.Y.; Zhou, T.; Efros, A.A. Image-To-Image Translation With Conditional Adversarial Networks. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2017.
- Wang, T.C.; Liu, M.Y.; Zhu, J.Y.; Tao, A.; Kautz, J.; Catanzaro, B. High-Resolution Image Synthesis and Semantic Manipulation With Conditional GANs. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018.
- Johnson, J.; Alahi, A.; Fei-Fei, L. Perceptual Losses for Real-Time Style Transfer and Super-Resolution. European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2016, pp. 694–711.
- Gatys, L.A.; Ecker, A.S.; Bethge, M. Image Style Transfer Using Convolutional Neural Networks. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016.
- Lim, J.H.; Ye, J.C. Geometric GAN. 2017, arXiv:stat.ML/1705.02894. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very Deep Convolutional Networks for Large-Scale Image Recognition. 2014, arXiv:cs.CV/1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009, pp. 248–255. [CrossRef]
- Doersch, C.; Singh, S.; Gupta, A.; Sivic, J.; Efros, A.A. What makes Paris look like Paris? Communications of the ACM 2015, 58, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Deep Learning Face Attributes in the Wild. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2015.
- Zhou, B.; Lapedriza, A.; Khosla, A.; Oliva, A.; Torralba, A. Places: A 10 Million Image Database for Scene Recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 2018, 40, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, L.; Du, B.; Tao, D. Recurrent Feature Reasoning for Image Inpainting. IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020.
- Zeng, Y.; Lin, Z.; Lu, H.; Patel, V.M. CR-Fill: Generative Image Inpainting With Auxiliary Contextual Reconstruction. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021, pp. 14164–14173.
- Guo, X.; Yang, H.; Huang, D. Image Inpainting via Conditional Texture and Structure Dual Generation. IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021, pp. 14134–14143.
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.; Tai, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chu, W.; Ni, B.; Wang, C.; Yang, X. Context-Aware Image Inpainting with Learned Semantic Priors. IJCAI, 2021, pp. 1323–1329.
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. 2017, arXiv:cs.LG/1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts. 2016, arXiv:cs.LG/1608.03983. [Google Scholar]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; Desmaison, A.; Kopf, A.; Yang, E.; DeVito, Z.; Raison, M.; Tejani, A.; Chilamkurthy, S.; Steiner, B.; Fang, L.; Bai, J.; Chintala, S. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2019, Vol. 32, p. 8026–8037.
- Sajjadi, M.S.M.; Scholkopf, B.; Hirsch, M. EnhanceNet: Single Image Super-Resolution Through Automated Texture Synthesis. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017.
- Heusel, M.; Ramsauer, H.; Unterthiner, T.; Nessler, B.; Hochreiter, S. GANs Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Local Nash Equilibrium. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2017, Vol. 30.
- Zhang, R.; Isola, P.; Efros, A.A.; Shechtman, E.; Wang, O. The Unreasonable Effectiveness of Deep Features as a Perceptual Metric. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018.
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS), 2012, Vol. 25.




| Method | Number of Model Parameters | Operational Memory | Parameter Difference Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 21,535,684 | 2,291.2 | 23.91 |
| RFR | 31,224,064 | 2,119.5 | 34.66 |
| CR-Fill | 4,052,478 | 2,075.5 | 4.50 |
| CTSDG | 52,147,787 | 2,118.2 | 57.89 |
| SPL | 45,595,431 | 2,107.5 | 50.61 |
| Ours | 900,875 | 301.4 | 1 |
| Dataset | Paris Streetview | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask Ratio | (0.1,0.2] | (0.2,0.3] | (0.3,0.4] | (0.4,0.5] | |
| FID (↓) | EC | 18.5194 | 29.1657 | 41.9956 | 57.1491 |
| RFR | 16.6533 | 24.3895 | 34.3220 | 47.7101 | |
| CTSDG | 18.8494 | 30.4578 | 46.1283 | 63.7335 | |
| SPL | 17.7120 | 28.6431 | 44.2332 | 58.4954 | |
| Ours | 14.8024 | 23.5567 | 38.1458 | 54.1898 | |
| LPIPS (↓) | EC | 0.0375 | 0.0663 | 0.102 | 0.1479 |
| RFR | 0.0337 | 0.0598 | 0.0896 | 0.1302 | |
| CTSDG | 0.0373 | 0.0693 | 0.11 | 0.1606 | |
| SPL | 0.0367 | 0.068 | 0.1084 | 0.1571 | |
| Ours | 0.0301 | 0.0559 | 0.0943 | 0.1428 | |
| SSIM (↑) | EC | 0.9397 | 0.8946 | 0.8405 | 0.7764 |
| RFR | 0.9468 | 0.9052 | 0.8533 | 0.7911 | |
| CTSDG | 0.9471 | 0.9035 | 0.8469 | 0.7826 | |
| SPL | 0.9578 | 0.923 | 0.877 | 0.8209 | |
| Ours | 0.9522 | 0.9123 | 0.8605 | 0.8012 | |
| PSNR (↑) | EC | 30.9867 | 28.1855 | 25.749 | 23.8551 |
| RFR | 31.76 | 28.866 | 26.2591 | 24.4081 | |
| CTSDG | 31.8254 | 28.8162 | 26.0823 | 24.2014 | |
| SPL | 33.3091 | 30.226 | 27.3961 | 25.5072 | |
| Ours | 32.4553 | 29.4006 | 26.6137 | 24.7842 | |
| Dataset | CelebA | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask Ratio | (0.1,0.2] | (0.2,0.3] | (0.3,0.4] | (0.4,0.5] | |
| FID (↓) | EC | 2.0626 | 2.8117 | 4.0842 | 6.0656 |
| RFR | 3.2892 | 4.8099 | 6.9820 | 9.8065 | |
| CTSDG | 3.9021 | 6.7093 | 10.5437 | 15.1646 | |
| SPL | 2.2515 | 3.1305 | 4.5734 | 6.3852 | |
| Ours | 2.3552 | 3.1706 | 4.6410 | 7.1648 | |
| LPIPS (↓) | EC | 0.026 | 0.0468 | 0.0721 | 0.1032 |
| RFR | 0.0232 | 0.0416 | 0.0641 | 0.0908 | |
| CTSDG | 0.0293 | 0.0551 | 0.0858 | 0.1208 | |
| SPL | 0.0359 | 0.0578 | 0.0839 | 0.1142 | |
| Ours | 0.0195 | 0.0385 | 0.0638 | 0.0962 | |
| SSIM (↑) | EC | 0.952 | 0.9148 | 0.8712 | 0.821 |
| RFR | 0.9583 | 0.923 | 0.8813 | 0.834 | |
| CTSDG | 0.9533 | 0.9146 | 0.8697 | 0.8199 | |
| SPL | 0.9632 | 0.9358 | 0.9022 | 0.8624 | |
| Ours | 0.9613 | 0.9285 | 0.8892 | 0.8445 | |
| PSNR (↑) | EC | 32.0645 | 28.6826 | 26.1033 | 24.0045 |
| RFR | 32.8072 | 29.2923 | 26.6869 | 24.6201 | |
| CTSDG | 31.996 | 28.4897 | 25.9326 | 23.9307 | |
| SPL | 33.7915 | 30.611 | 28.0283 | 25.8719 | |
| Ours | 33.356 | 29.7005 | 26.9822 | 24.8199 | |
| Dataset | Places2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask Ratio | (0.1,0.2] | (0.2,0.3] | (0.3,0.4] | (0.4,0.5] | |
| FID (↓) | EC | 1.4810 | 3.3814 | 6.2819 | 10.7867 |
| CTSDG | 1.1672 | 3.3474 | 7.3858 | 14.0385 | |
| CR-Fill | 0.9558 | 2.2416 | 4.3691 | 7.7783 | |
| SPL | 0.6680 | 1.8749 | 4.0821 | 7.7864 | |
| Ours | 0.6796 | 1.9225 | 4.8417 | 10.5155 | |
| LPIPS (↓) | EC | 0.0515 | 0.0897 | 0.1323 | 0.1804 |
| CTSDG | 0.048 | 0.0925 | 0.1444 | 0.2021 | |
| CR-Fill | 0.0444 | 0.0808 | 0.1219 | 0.1689 | |
| SPL | 0.0373 | 0.0726 | 0.114 | 0.1618 | |
| Ours | 0.0365 | 0.0709 | 0.1139 | 0.1657 | |
| SSIM (↑) | EC | 0.9225 | 0.8654 | 0.8039 | 0.737 |
| CTSDG | 0.935 | 0.8795 | 0.8186 | 0.7522 | |
| CR-Fill | 0.9325 | 0.8784 | 0.8193 | 0.7542 | |
| SPL | 0.9547 | 0.9128 | 0.8643 | 0.8089 | |
| Ours | 0.9419 | 0.8929 | 0.8378 | 0.777 | |
| PSNR (↑) | EC | 27.9966 | 24.9664 | 22.826 | 21.1286 |
| CTSDG | 29.0271 | 25.6747 | 23.3848 | 21.6154 | |
| CR-Fill | 28.5685 | 25.1761 | 22.8066 | 20.95 | |
| SPL | 31.2566 | 27.7344 | 25.2727 | 23.3253 | |
| Ours | 29.8566 | 26.4925 | 24.1477 | 22.3093 | |
| Dataset | Paris Streetview | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDCM | ESA |
Average FID (↓) |
Average LPIPS (↓) |
Average SSIM (↑) |
Average PSNR (↑) |
|
| Dilated Conv. | Dense Block | |||||
| ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 42.6749 | 0.1005 | 0.8690 | 27.5524 |
| ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 41.1195 | 0.0971 | 0.8713 | 27.6425 |
| ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | 40.8669 | 0.0971 | 0.8717 | 27.6685 |
| ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 39.8682 | 0.0963 | 0.8740 | 27.7794 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 39.4503 | 0.0920 | 0.8737 | 27.8604 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 38.8718 | 0.0911 | 0.8745 | 27.9010 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 38.0788 | 0.0903 | 0.8771 | 28.0407 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 35.7588 | 0.0869 | 0.8796 | 28.1083 |
| DDCM | ESA | Number of Model Parameters |
Operational Memory |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dilated Conv. | Dense Block | |||
| ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | 418,763 | 286.1 |
| ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | 695,243 | 300.9 |
| ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | 624,395 | 287.4 |
| ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | 900,875 | 301.2 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | 418,763 | 287 |
| ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | 695,243 | 300.8 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | 624,395 | 287.8 |
| ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | 900,875 | 301.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





