Submitted:
01 September 2023
Posted:
06 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Acetic acid production from lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis
2.1. Pyrolysis reactions and multiphase behaviour of bio-oil
2.2. Chemical Conversion of the Main Biomass Constituents
2.3. Operating conditions of pyrolysis influencing the yield of acetic acid
2.3.1. The composition of the raw materials
2.3.2. Biomass Particle Size
2.3.3. Moisture Content
2.3.4. Pretreatment of biomass
2.3.4.1. Chemical pretreatments
2.3.4.2. Physical Pretreatments
2.3.4.3. Biological Pretreatments
2.3.5. Catalysts
2.3.6. Reactors
2.3.7. Temperature of pyrolysis
2.3.8. Carrier Gas Flow Rate
2.3.9. Residence Time
2.3.10. Heating Rate
3. Membrane filtration
3.1. Overview of Membrane Processes
3.2. Operating conditions for the separation of acetic acid
3.2.1. Pressure
3.2.2. Feed Solution
3.2.3. Boundary Layer
3.2.4. Effect of Time on Membrane Separation
3.2.5. Membranes
3.2.6. Temperature
3.2.7. Charge Characteristics
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rafione, T., Développement d’une bioraffinerie forestière intégrée et verte. 2014, École Polytechnique de Montréal.
- Laurent, P., et al., Le bioraffinage, une alternative prometteuse à la pétrochimie. BASE, 2011.
- Ballerini, D., Les biocarburants: répondre aux défis énergétiques et environnementaux des transports. 2011: Editions Technip.
- Studer, M. and P. Poldervaart, Nouvelles voies dans le bioraffinage du bois.
- Alauddin, Z.A.B.Z., P. Lahijani, M. Mohammadi, and A.R. Mohamed, Gasification of lignocellulosic biomass in fluidized beds for renewable energy development: A review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2010. 14(9): p. 2852-2862. [CrossRef]
- Jones, M., A. Gandia, S. John, and A. Bismarck, Leather-like material biofabrication using fungi. Nature Sustainability, 2021. 4(1): p. 9-16. [CrossRef]
- Venderbosch, R. and W. Prins, Fast pyrolysis technology development. Biofuels, bioproducts and biorefining, 2010. 4(2): p. 178-208. [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., M. Wu, and C. Wu, Application of biomass fast pyrolysis part I: Pyrolysis characteristics and products. Energy, 2014. 66: p. 162-171. [CrossRef]
- Grams, J., Chromatographic analysis of bio-oil formed in fast pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass. Reviews in Analytical Chemistry, 2020. 39(1): p. 65-77. [CrossRef]
- Demirbas, A., Biorefineries: Current activities and future developments. Energy conversion and management, 2009. 50(11): p. 2782-2801. [CrossRef]
- Vidra, A. and Á. Németh, Bio-produced acetic acid: A review. Periodica Polytechnica Chemical Engineering, 2018. 62(3): p. 245-256.
- Joachim, U.d.M.b., M.N. Thaddée, and M. Lelo, Inhibition du développement de l’Aspergillus flavus par l’acide acétique: Analyse de trois expériences réalisées à Kinshasa-RD Congo. 2020.
- Ivany, J.A., Acetic acid for weed control in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Canadian Journal of Plant Science, 2010. 90(4): p. 537-542. [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.-L., W.-T. Liu, and T. Zhou, Fumigation of sweet cherries with thymol and acetic acid to reduce postharvest brown rot and blue mold rot. Fruits, 2001. 56(2): p. 123-130. [CrossRef]
- Merli, G., A. Becci, A. Amato, and F. Beolchini, Acetic acid bioproduction: The technological innovation change. Science of the Total Environment, 2021. 798: p. 149292. [CrossRef]
- Kumbhar, G., et al., DIFFERENT ROUTES FOR PRODUCTION OF ACETIC ACID–A CASE STUDY. 2019.
- Hidalgo, C., et al., Effect of barrel design and the inoculation of Acetobacter pasteurianus in wine vinegar production. International Journal of Food Microbiology, 2010. 141(1-2): p. 56-62. [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-J., G.-G. Choi, and J.-S. Kim, Production of acetic acid-rich bio-oils from the fast pyrolysis of biomass and synthesis of calcium magnesium acetate deicer. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2017. 124: p. 122-129. [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-J., S. Ramaswamy, U. Tschirner, and B. Ramarao, A review of separation technologies in current and future biorefineries. Separation and purification technology, 2008. 62(1): p. 1-21. [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-H., et al., Separation of furans and carboxylic acids from sugars in dilute acid rice straw hydrolyzates by nanofiltration. Bioresource technology, 2010. 101(13): p. 4889-4894. [CrossRef]
- Pinelo, M., G. Jonsson, and A.S. Meyer, Membrane technology for purification of enzymatically produced oligosaccharides: molecular and operational features affecting performance. Separation and Purification Technology, 2009. 70(1): p. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.-H., et al., Separation of acetic acid from xylose by nanofiltration. Separation and Purification Technology, 2009. 67(1): p. 95-102. [CrossRef]
- Baker, R.W., Membrane technology and applications. 2012: John Wiley & Sons.
- Bellona, C., J.E. Drewes, P. Xu, and G. Amy, Factors affecting the rejection of organic solutes during NF/RO treatment—a literature review. Water research, 2004. 38(12): p. 2795-2809. [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A., Principles and practice of biomass fast pyrolysis processes for liquids. Journal of analytical and applied pyrolysis, 1999. 51(1-2): p. 3-22. [CrossRef]
- Bridgwater, A.V., D. Meier, and D. Radlein, An overview of fast pyrolysis of biomass. Organic geochemistry, 1999. 30(12): p. 1479-1493. [CrossRef]
- Morf, P., P. Hasler, and T. Nussbaumer, Mechanisms and kinetics of homogeneous secondary reactions of tar from continuous pyrolysis of wood chips. Fuel, 2002. 81(7): p. 843-853. [CrossRef]
- Van de Velden, M., et al., Fundamentals, kinetics and endothermicity of the biomass pyrolysis reaction. Renewable energy, 2010. 35(1): p. 232-242.
- Garcia-Perez, M., et al., Effects of temperature on the formation of lignin-derived oligomers during the fast pyrolysis of Mallee woody biomass. Energy & Fuels, 2008. 22(3): p. 2022-2032. [CrossRef]
- Oasmaa, A., et al., Pyrolysis oil multiphase behavior and phase stability: a review. Energy & Fuels, 2016. 30(8): p. 6179-6200. [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D., C.U. Pittman Jr, and P.H. Steele, Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: a critical review. Energy & fuels, 2006. 20(3): p. 848-889. [CrossRef]
- Vitasari, C.R., G.W. Meindersma, and A.B. De Haan, Water extraction of pyrolysis oil: The first step for the recovery of renewable chemicals. Bioresource technology, 2011. 102(14): p. 7204-7210. [CrossRef]
- Collard, F.-X. and J. Blin, A review on pyrolysis of biomass constituents: Mechanisms and composition of the products obtained from the conversion of cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2014. 38: p. 594-608. [CrossRef]
- Bentsen, N.S., C. Felby, and B.J. Thorsen, Agricultural residue production and potentials for energy and materials services. Progress in energy and combustion science, 2014. 40: p. 59-73. [CrossRef]
- Lauri, P., et al., Woody biomass energy potential in 2050. Energy policy, 2014. 66: p. 19-31. [CrossRef]
- Konan, D., et al., An Overview of Extrusion as a Pretreatment Method of Lignocellulosic Biomass. Energies, 2022. 15(9). [CrossRef]
- Vorwerk, S., S. Somerville, and C. Somerville, The role of plant cell wall polysaccharide composition in disease resistance. Trends in plant science, 2004. 9(4): p. 203-209. [CrossRef]
- Aspinall, G.O., Chemistry of cell wall polysaccharides, in Carbohydrates: Structure and function. 1980, Elsevier. p. 473-500.
- Yang, H., et al., Characteristics of hemicellulose, cellulose and lignin pyrolysis. Fuel, 2007. 86(12-13): p. 1781-1788. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-r., T. Liang, B. Ru, and X.-j. Guo, Mechanism of xylan pyrolysis by Py-GC/MS. Chemical research in Chinese universities, 2013. 29: p. 782-787.
- Faravelli, T., A. Frassoldati, G. Migliavacca, and E. Ranzi, Detailed kinetic modeling of the thermal degradation of lignins. Biomass and bioenergy, 2010. 34(3): p. 290-301. [CrossRef]
- Jakab, E., O. Faix, and F. Till, Thermal decomposition of milled wood lignins studied by thermogravimetry/mass spectrometry. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1997. 40: p. 171-186. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D., et al., Advancing biomass pyrolysis by torrefaction pretreatment: Linking the productions of bio-oil and oxygenated chemicals to torrefaction severity. Fuel, 2022. 330: p. 125514. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S., et al., Structural characterization and pyrolysis behavior of cellulose and hemicellulose isolated from softwood Pinus armandii Franch. Energy & Fuels, 2016. 30(7): p. 5721-5728. [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.M., et al., Fast pyrolysis of oil mallee woody biomass: effect of temperature on the yield and quality of pyrolysis products. Industrial & engineering chemistry research, 2008. 47(6): p. 1846-1854.
- Duman, G., et al., The slow and fast pyrolysis of cherry seed. Bioresource technology, 2011. 102(2): p. 1869-1878. [CrossRef]
- Casoni, A.I., et al., Pyrolysis of sunflower seed hulls for obtaining bio-oils. Bioresource Technology, 2015. 177: p. 406-409. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, G., S. Wu, and H. Zhang, Estimation and comparison of bio-oil components from different pyrolysis conditions. Frontiers in Energy Research, 2015. 3: p. 28. [CrossRef]
- Lv, G. and S. Wu, Analytical pyrolysis studies of corn stalk and its three main components by TG-MS and Py-GC/MS. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2012. 97: p. 11-18. [CrossRef]
- Maschio, G., C. Koufopanos, and A. Lucchesi, Pyrolysis, a promising route for biomass utilization. Bioresource Technology;(United Kingdom), 1992. 42(3). [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-H., B.-S. Kang, and J.-S. Kim, Production of bio-oil from rice straw and bamboo sawdust under various reaction conditions in a fast pyrolysis plant equipped with a fluidized bed and a char separation system. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2008. 82(2): p. 240-247. [CrossRef]
- Martins, J.P.G., et al., Study of pequi peel pyrolysis: Thermal decomposition analysis and product characterization. Biomass and Bioenergy, 2021. 149: p. 106095. [CrossRef]
- Isahak, W.N.R.W., M.W. Hisham, M.A. Yarmo, and T.-y.Y. Hin, A review on bio-oil production from biomass by using pyrolysis method. Renewable and sustainable energy reviews, 2012. 16(8): p. 5910-5923. [CrossRef]
- Suriapparao, D.V. and R. Vinu, Effects of biomass particle size on slow pyrolysis kinetics and fast pyrolysis product distribution. Waste and biomass valorization, 2018. 9: p. 465-477. [CrossRef]
- Bridgeman, T., et al., Influence of particle size on the analytical and chemical properties of two energy crops. Fuel, 2007. 86(1-2): p. 60-72. [CrossRef]
- Luo, G., et al., Pyrolysis of whole wood chips and rods in a novel ablative reactor. Fuel, 2017. 194: p. 229-238. [CrossRef]
- Beaumont, O. and Y. Schwob, Influence of physical and chemical parameters on wood pyrolysis. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Process Design and Development, 1984. 23(4): p. 637-641.
- Zheng, A., et al., Quantitative comparison of different chemical pretreatment methods on chemical structure and pyrolysis characteristics of corncobs. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2018. 91(5): p. 676-682. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., et al., Properties and pyrolysis behavior of moso bamboo sawdust after microwave-assisted acid pretreatment. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2018. 129: p. 86-92. [CrossRef]
- Piskorz, J., D.S.A. Radlein, D.S. Scott, and S. Czernik, Pretreatment of wood and cellulose for production of sugars by fast pyrolysis. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 1989. 16(2): p. 127-142. [CrossRef]
- Ciolkosz, D. and R. Wallace, A review of torrefaction for bioenergy feedstock production. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2011. 5(3): p. 317-329. [CrossRef]
- Boateng, A. and C. Mullen, Fast pyrolysis of biomass thermally pretreated by torrefaction. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2013. 100: p. 95-102. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D., et al., Torrefaction of biomass stalk and its effect on the yield and quality of pyrolysis products. Fuel, 2015. 159: p. 27-32. [CrossRef]
- Stephanidis, S., et al., Catalytic upgrading of lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis vapours: Effect of hydrothermal pre-treatment of biomass. Catalysis Today, 2011. 167(1): p. 37-45. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y., et al., Novel micronized woody biomass process for production of cost-effective clean fermentable sugars. Bioresource technology, 2018. 260: p. 311-320. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z., et al., Effect of pretreatment with Phanerochaete chrysosporium on physicochemical properties and pyrolysis behaviors of corn stover. Bioresource Technology, 2022. 361: p. 127687. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y., et al., Improving the conversion of biomass in catalytic fast pyrolysis via white-rot fungal pretreatment. Bioresource technology, 2013. 134: p. 198-203. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, N., et al., Comparative analysis of the secretomes of Schizophyllum commune and other wood-decay basidiomycetes during solid-state fermentation reveals its unique lignocellulose-degrading enzyme system. Biotechnology for biofuels, 2016. 9: p. 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Xu, P., et al., Cadmium induced oxalic acid secretion and its role in metal uptake and detoxification mechanisms in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Applied microbiology and biotechnology, 2015. 99: p. 435-443. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X., et al., Effect of biopretreatment on thermogravimetric and chemical characteristics of corn stover by different white-rot fungi. Bioresource technology, 2010. 101(14): p. 5475-5479. [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-J., S.-H. Jung, and J.-S. Kim, Co-production of furfural and acetic acid from corncob using ZnCl2 through fast pyrolysis in a fluidized bed reactor. Bioresource technology, 2013. 144: p. 172-178. [CrossRef]
- Psarras, A., et al., Acetic acid conversion reactions on basic and acidic catalysts under biomass fast pyrolysis conditions. Molecular Catalysis, 2019. 465: p. 33-42. [CrossRef]
- Qi, W., et al., Catalytic pyrolysis of several kinds of bamboos over zeolite NaY. Green chemistry, 2006. 8(2): p. 183-190. [CrossRef]
- Adam, J., et al., Pyrolysis of biomass in the presence of Al-MCM-41 type catalysts. Fuel, 2005. 84(12-13): p. 1494-1502. [CrossRef]
- Patwardhan, P.R., J.A. Satrio, R.C. Brown, and B.H. Shanks, Influence of inorganic salts on the primary pyrolysis products of cellulose. Bioresource technology, 2010. 101(12): p. 4646-4655. [CrossRef]
- Lede, J., J. Panagopoulos, and J. Villermaux, Experimental Measurement of ablation rate of wood pieces, undergoing fast pyrolysis by contact with a heated wall. Prepr. Pap., Am. Chem. Soc., Div. Fuel Chem.;(United States), 1983. 38(CONF-830814-).
- Ahmed, A., et al., Sawdust pyrolysis from the furniture industry in an auger pyrolysis reactor system for biochar and bio-oil production. Energy Conversion and Management, 2020. 226: p. 113502. [CrossRef]
- Mabrouki, J., et al., Simulation of biofuel production via fast pyrolysis of palm oil residues. Fuel, 2015. 159: p. 819-827. [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.S., et al., Bio-oil production from fast pyrolysis of waste furniture sawdust in a fluidized bed. Bioresource technology, 2010. 101(1): p. S91-S96. [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q., X. Ma, and J. Dong, Preparation, chemical constituents and antimicrobial activity of pyroligneous acids from walnut tree branches. Journal of analytical and applied pyrolysis, 2010. 87(1): p. 24-28. [CrossRef]
- Uzun, B.B., A.E. Pütün, and E. Pütün, Fast pyrolysis of soybean cake: Product yields and compositions. Bioresource technology, 2006. 97(4): p. 569-576. [CrossRef]
- Laougé, Z.B., A.S. Çığgın, and H. Merdun, Optimization and characterization of bio-oil from fast pyrolysis of Pearl Millet and Sida cordifolia L. by using response surface methodology. Fuel, 2020. 274: p. 117842.
- Gupta, G.K. and M.K. Mondal, Bio-energy generation from sagwan sawdust via pyrolysis: product distributions, characterizations and optimization using response surface methodology. Energy, 2019. 170: p. 423-437. [CrossRef]
- Açıkalın, K., F. Karaca, and E. Bolat, Pyrolysis of pistachio shell: Effects of pyrolysis conditions and analysis of products. Fuel, 2012. 95: p. 169-177. [CrossRef]
- Ratanapisit, J., et al., Preliminary evaluation of production and characterization of wood vinegar from rubberwood. Songklanakarin Journal of Science & Technology, 2009. 31(3).
- Sarchami, T., N. Batta, and F. Berruti, Production and separation of acetic acid from pyrolysis oil of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Biofuels, Bioproducts and Biorefining, 2021. 15(6): p. 1912-1937. [CrossRef]
- Guo, W., H.-H. Ngo, and J. Li, A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresource technology, 2012. 122: p. 27-34. [CrossRef]
- Giorno, L., E. Drioli, and H. Strathmann, Characterization of Porous and Dense Membranes. Encyclopedia of Membranes, 2016: p. 362-372. [CrossRef]
- Espinasse, B., Approche théorique et expérimentale de la filtration tangentielle de colloïdes: flux critique et colmatage. 2003, Université Paul Sabatier-Toulouse III.
- Pontalier, P.-Y., A. Ismail, and M. Ghoul, Mechanisms for the selective rejection of solutes in nanofiltration membranes. Separation and purification technology, 1997. 12(2): p. 175-181. [CrossRef]
- Baruah, K. and S. Hazarika, Separation of acetic acid from dilute aqueous solution by nanofiltration membrane. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2014. 131(15). [CrossRef]
- Blatt, W.F., A. Dravid, A.S. Michaels, and L. Nelsen, Solute polarization and cake formation in membrane ultrafiltration: causes, consequences, and control techniques, in Membrane Science and Technology: Industrial, Biological, and Waste Treatment Processes. 1970, Springer. p. 47-97. [CrossRef]
- In, C., Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, ; Lide, DR, Ed. 2006, Taylor and Francis Group LLC: New York.
- Wu, H., et al., Performance characterization of nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, and ion exchange technologies for acetic acid separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 2021. 265: p. 118108. [CrossRef]
- Teella, A., G.W. Huber, and D.M. Ford, Separation of acetic acid from the aqueous fraction of fast pyrolysis bio-oils using nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2011. 378(1-2): p. 495-502. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S., T.E. Amidon, and C. David Wood, Membrane filtration: concentration and purification of hydrolyzates from biomass. Journal of biobased materials and bioenergy, 2008. 2(2): p. 121-134. [CrossRef]
- Gherasim, C.-V., J. Cuhorka, and P. Mikulášek, Analysis of lead (II) retention from single salt and binary aqueous solutions by a polyamide nanofiltration membrane: Experimental results and modelling. Journal of membrane science, 2013. 436: p. 132-144. [CrossRef]
- Chen, C., et al., A method for concentration of monosaccharide and removal of inhibitors during hydrolysate pretreatment for improved bioethanol production. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020. 260: p. 120999. [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, L., M.S. Jahan, and Y. Ni, Recovering/concentrating of hemicellulosic sugars and acetic acid by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis from prehydrolysis liquor of kraft based hardwood dissolving pulp process. Bioresource Technology, 2014. 155: p. 111-115. [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H., et al., Monophenols separation from monosaccharides and acids by two-stage nanofiltration and reverse osmosis in hydrothermal liquefaction hydrolysates. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016. 504: p. 141-152. [CrossRef]
- Pervez, M.N., et al., Factors influencing pressure-driven membrane-assisted volatile fatty acids recovery and purification-A review. Science of The Total Environment, 2022. 817: p. 152993.
- Jun, B.-M., S.H. Kim, S.K. Kwak, and Y.-N. Kwon, Effect of acidic aqueous solution on chemical and physical properties of polyamide NF membranes. Applied Surface Science, 2018. 444: p. 387-398. [CrossRef]
- Zacharof, M.-P., S.J. Mandale, P.M. Williams, and R.W. Lovitt, Nanofiltration of treated digested agricultural wastewater for recovery of carboxylic acids. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016. 112: p. 4749-4761. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q., et al., Study on the concentration of acrylic acid and acetic acid by reverse osmosis. Membranes, 2020. 10(7): p. 142. [CrossRef]
- Hoseinpour, H., M. Peyravi, A. Nozad, and M. Jahanshahi, Static and dynamic assessments of polysulfonamide and poly (amide-sulfonamide) acid-stable membranes. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2016. 67: p. 453-466. [CrossRef]
- Wei, X., et al., SiO2-modified nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes with high flux and acid resistance. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2019. 136(18): p. 47436. [CrossRef]
- Roy, Y. and D.M. Warsinger, Effect of temperature on ion transport in nanofiltration membranes: Diffusion, convection and electromigration. Desalination, 2017. 420: p. 241-257. [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, M., G. Trägårdh, and K. Östergren, The influence of pH, salt and temperature on nanofiltration performance. Journal of Membrane Science, 2008. 312(1-2): p. 97-106.
- Sharma, R.R., R. Agrawal, and S. Chellam, Temperature effects on sieving characteristics of thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes: pore size distributions and transport parameters. Journal of membrane science, 2003. 223(1-2): p. 69-87. [CrossRef]
- Han, I. and M. Cheryan, Nanofiltration of model acetate solutions. Journal of membrane science, 1995. 107(1-2): p. 107-113. [CrossRef]
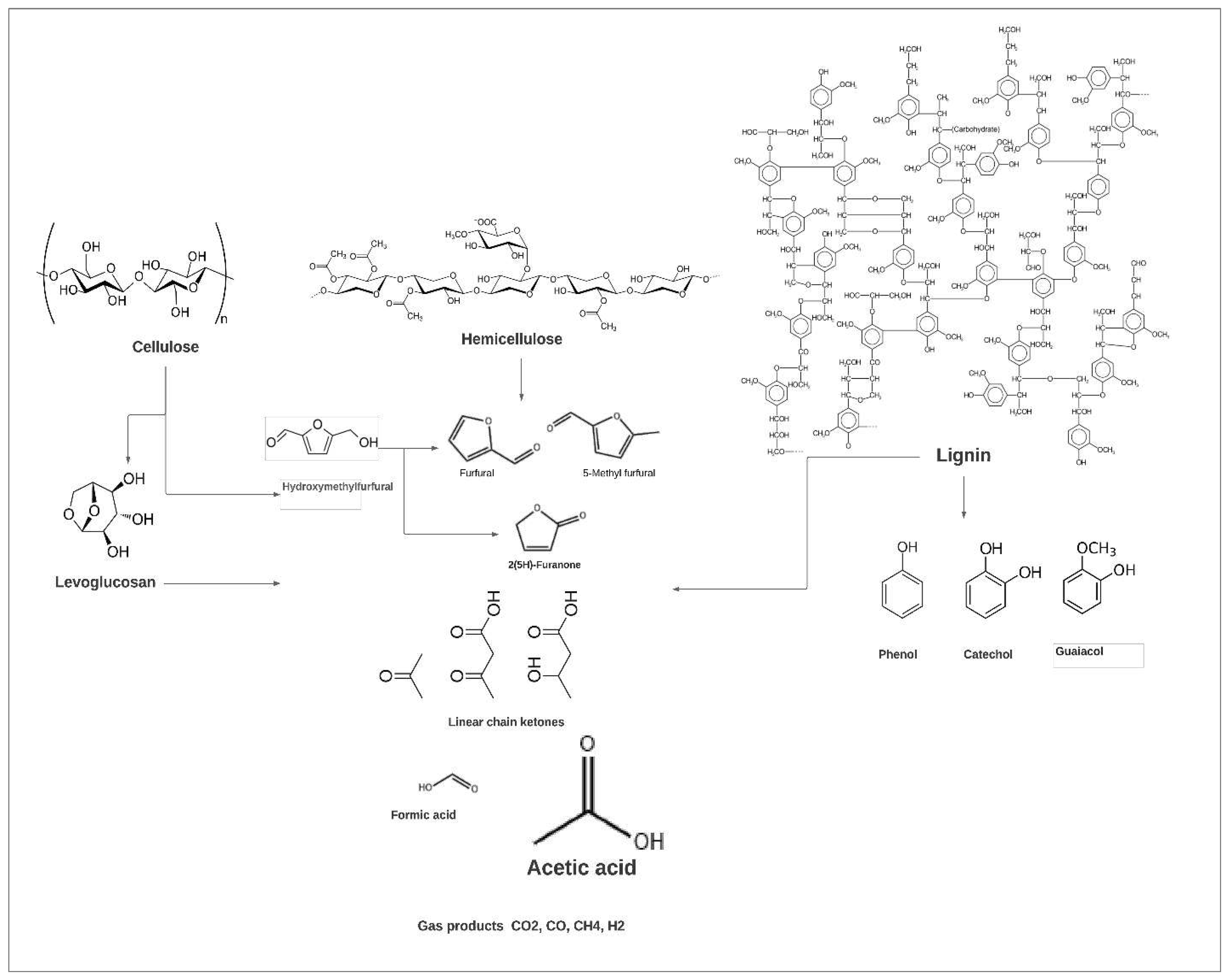
| Step | Temp. | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Char formation | < 773.15 k: | Generation of benzene rings and their subsequent amalgamation into a polycyclic structure referred to as ‘Char’ |
| Depolymerisation | 523.15 and 773.15 k | The cleavage of chemical bonds connecting the monomeric units within the polymer matrix. Production of volatile molecules |
| Fragmentation | > 873.15 k | Linkage of multiple covalent bonds of the polymer and the monomer units. Production of non-condensable gases and various low-molecular-weight organic compounds (CH3COOH) |
| Biomass | Cellulose (wt%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Lignin (%) | Acetic acid yield (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sunflower seed hulls | 40 | 18 | 20 | 60 | Casoni, Bidegain [47] |
| Bagasse | 45.9 | 28 | 20.7 | 4.8 wt. | Lyu, Wu and Zhang [48] |
| Spruce | 47.2 | 13.3 | 36 | 2.3 wt. | |
| Pine | 47 | 21.7 | 27.7 | 2.3 wt. | |
| Corn stalk | 42.4 | 29.6 | 21.7 | 35.9 | Lv and Wu [49] |
| Wood | 47.5 | 19.4 | 24 | Tar fraction : 4 – 5 wt. Aqueous fraction : 9.4 – 11.3 wt. |
Maschio, Koufopanos and Lucchesi [50] |
| Hazelnut shells | 27.5 | 24.1 | 40.7 | ||
| Corncobs | 51.2 | 31.8 | 14.8 | ||
| Olive husks | 22.2 | 21.1 | 45 | ||
| Wheat straw | 24.0 | 40 | 21 | ||
| Lucerne pressed cake | 13.7 | 45.5 | 21.3 | ||
| Rice straw | 37.8 | 25.3 | 23.3 | Upper phase: 5.73 | Jung, Kang and Kim [51] |
| Bamboo | 41 | 26.5 | 25.3 | Upper phase: 3.46 Lower phase: 1.07 |
|
| Pequi peel | 24.35 | 13.75 | 10.50 – 12.40 | Martins, Setter [52] | |
| Biomass | Reactor | Temp. | Carrier gas flow | Residence time | Heating rate | Particle size | Composition | Acetic acid yield (%) | References | ||
| Lignin | Cellulose | Hemicellulose | |||||||||
| Betula pubescens, Bambusa rigida and Dendrocalamus latiflorus | Fixed bed reactor | 773 K and 873 K | 28 ml.min-1 | 10 h | 10 K.min-1 | - | 11.9 – 21.7 | 28.8 – 44.8 | 10.5 – 21.8 | 15 – 38 (a) 54.6 – 100 (b) |
Qi, Hu [73] |
| Cedar sawdust | Fluidized bed reactor (40 × 400 mm) | 700 K | 30 L.min-1 | < 2 s | 10 K.min-1 | 0.5 – 1 mm | 31.45 | 48.34 | 11.3 | O.P: 0.25 (1)A.P : 0.39 (2) | Yang, Wu and Wu [8] |
| Cherry seed | Fixed bed | 300°C, 500°C | 25 ml.min-1 | 1 | 5°C.min-1 | < 2 mm | 29.08 | 32.06 | 28.59 | 26.51, 26.35 | Duman, Okutucu [46] |
| Cherry seed | Fluidized bed | 400°C, 600°C | 25 ml.min-1 | 1 – 2 | 5°C.min-1 | < 2 mm | 29.08 | 32.06 | 28.59 | 91.74, 5.63 | Duman, Okutucu [46] |
| Cherry seed shell (CSS) | Fixed bed | 300°C, 500°C | 25 ml.min-1 | 1 | 5°C.min-1 | < 2 mm | 36.90 | 27.19 | 31.93 | 42.47, 39.28, 74.5 | Duman, Okutucu [46] |
| Cherry seed shell (CSS) | Fluidized bed | 400°C, 500°C, 600°C | 25 ml.min-1 | 1 – 2 | 5°C.min-1 | < 2 mm | 36.90 | 27.19 | 31.93 | 64.07, 36.25 | Duman, Okutucu [46] |
| Coffee bean residue | Fluidized bed reactor (40 × 400 mm) | 700 K | 30 L.min-1 | < 2 s | 10 K.min-1 | 0.3 – 0.9 mm | 30.92 | 19.72 | 30.32 | O.P: 0.16 (1)A.P: 2.10 (2) | Yang, Wu and Wu [8] |
| Mallee woody biomass (eucalyptus Loxophleba, subspecies Lissophloia) | Fluidized-bed reactor | 350 °C – 580°C | 53 and 38 L.min-1 | 1.4 s and 0.7 s | - | 180 – 450 mm | - | - | - | 5.73 - 8.71 | Garcia, Wang [45] |
| Mixed wood sawdust | Pyroprobe® 5200 | 600 °C | - | 30 s | 10 000°C.s-1 | 26.5 µm – 925 µm | - | - | - | 0.49 – 3.76 | Suriapparao and Vinu [54] |
| Pearl Millet (PM) | - | 400 °C | 200 ml.min-1 | - | - | - | 15.75 | 48.93 | 3.16 | 7.04 |
Laougé, Çığgın and Merdun [82] |
| Pine pellets | Fluidized-bed reactor | 600°C | 53 and 38 L.min-1 | 1.4 s and 0.7 s | - | 450 – 600 mm | - | - | - | 2.66 | Garcia, Wang [45] |
| Pistachio shell | Fixed bed (102 ×4 cm) | 500 °C | 250 ml.min-1 | 40°C.min-1 | 1 – 2 mm | - | - | - | 9.68 |
Açıkalın, Karaca and Bolat [84] | |
| Rice straw | Fluidized bed reactor (40 × 400 mm) | 700 K | 30 L.min-1 | < 2 s | 10 K.min-1 | 2 – 5 mm | 12.66 | 36.78 | 31.67 | O.P 0.18 (1)A.P 2.92 (2) | Yang, Wu and Wu [8] |
| Rubberwood (Hevea brasiliensis) | Horizontal-cylindrical furnace (45×80 cm) | 400°C | - | - | 2.0°C.min-1 | 35 cm | - | - | - | 4.524 | Ratanapisit, Apiraksakul [85] |
| Rubberwood (Hevea brasiliensis) | Horizontal-cylindrical furnace (45×80 cm) | > 400°C | - | - | 2.0°C.min-1 | 35 cm | - | - | - | 4.259 | Ratanapisit, Apiraksakul [85] |
| Sagwan sawdust | Réacteur à lit fixe | 639.45°C | 181.59 ml.min-1 | - | 10°C.min-1 | 60 and 80 mesh | 24.7 | 51.1 | 12.9 | 3.611 |
Gupta and Mondal [83] |
| Sida cordifolia L. (Sida) | - | 400°C | 200 ml.min-1 | - | - | 1.5 mm | 12.04 | 49.17 | 21.91 |
7.73 |
Laougé, Çığgın and Merdun [82] |
| Walnut tree branches | Vertical pyrolytic (130 mm × 270 mm) | 450°C | - | - | 1°C.min-1 | 3 × 10 cm | 28.43 | 45.36 |
18.26 | 22.62 | Wei, Ma and Dong [80] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





