1. Introduction
Curcumin, also known as diferuloylmethane, is composed of two molecules of ferulic acid and is the primary yellow pigment found in turmeric rhizomes (
Curcuma longa Linn). Curcumin has been used both as a coloring agent and a traditional remedy for various ailments throughout India and Southeast Asia [
1,
2]. The biological activities of curcumin have been extensively studied. These activities include antioxidant [
3,
4,
5], anti-cancer [
6,
7,
8], and anti-inflammatory [
3,
9,
10] properties. Various molecular mechanisms have been reported to be involved in the bioactive properties of curcumin. Curcumin scavenges DPPH, ABTS, superoxide anion radicals, and nitric oxide [
11,
12,
13]. Cell shrinkage, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and activation of caspase in curcumin-treated cells were observed as the induction of apoptosis, or programmed cell death [
14,
15]. Apoptosis induction in several types of cancer cells [
16] is suggested to be caused by the rapid generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) from curcumin in a cell culture system. It was also observed that curcumin inhibits the activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) signaling [
17,
18]. Moreover, curcumin treatment was found to induce the expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) [
19,
20,
21] and growth arrest and DNA damage-inducible (GADD) genes [
22,
23].
Curcumin contains a bis-α,β-unsaturated group with an electrophilic carbon center, a diketone moiety, and two hydroxyl methoxyphenyl groups [
19,
24]. Curcuminoids that contain a similar structure include demethoxycurcumin (DMC) and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BMC) [
25]. Both DMC and BMC are naturally occurring curcumin analogues that lack one or two methoxy groups on the ring structure of curcumin, respectively [
26]. These two compounds are also reported to have a potential role in health benefit effects such as antioxidant activity [
25,
27,
28]. Curcuminoids are not chemically stable due to the highly reactive functional groups. Their chemical stability can be greatly affected by a variety of physical and chemical factors including pH, temperature, and light [
29,
30,
31]. Curcumin is relatively stable under acidic conditions, but its stability is reduced at alkaline pHs [
32,
33].
Curcumin exhibits both anti- and pro-oxidizing properties [
34,
35]. ROS are highly reactive molecules derived from oxygen, including as superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical, and singlet oxygen. Previous studies have shown that the bioactivities induced by curcumin treatment in cells were eliminated in the presence of antioxidants such as
N-acetylcysteine (NAC) [
36,
37] and glutathione (GSH) [
38]. One suggestion is that the cellular events induced by curcumin occur through the generation of ROS. Yet the relationship between the cellular events induced by curcumin in an experimental system and ROS-dependent mechanism has not been clarified. Curcumin is a reactive compound that can potentially interact with various types of chemicals including antioxidants. Therefore, it remains to be determined whether the suppression of curcumin bioactivities by certain antioxidants is a result of ROS elimination or the direct modification of curcumin structure by these antioxidants.
In the present study, the effects of thiol and non-thiol antioxidants on the stability and bioactivities of curcumin were examined. We also tested different concentrations of thiol antioxidants to investigate their direct interaction with curcumin. Additionally, the stabilities of both DMC and BMC were tested when incubated with antioxidants, allowing speculation on the potential sites of interaction between the antioxidant and curcumin. The present results indicate that thiol groups interact with the a,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety of curcumin and suggest that these interactions may have a significant impact on the chemical stability and the bioactivity of curcumin and its related compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Changes in curcumin stability by different types of antioxidants
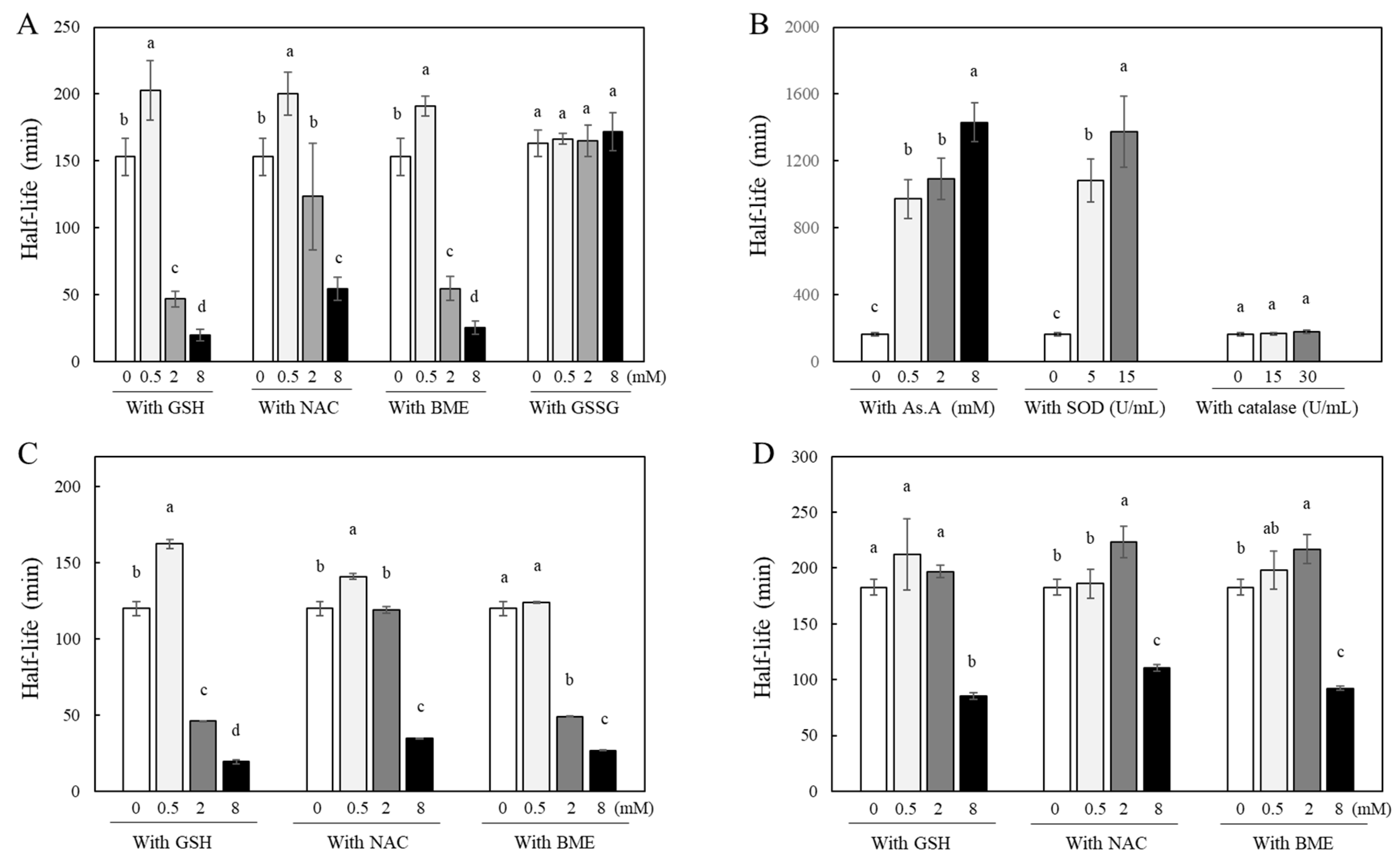
Curcumin is a yellowish hydrophobic compound and is unstable in aqueous systems causing decolorization. Our previous studies have confirmed that it was from the instability of curcumin, evidenced by changes in its absorbance at 405 nm [
33,
39,
40]. Since the degree of curcumin’s stability correlates directly with the absorbance at 405 nm, changes in curcumin stability in the presence of various antioxidants were measured by detecting absorbance at 405 nm. A solution containing 40 µM of curcumin was incubated at room temperature in the absence or presence of thiol antioxidants, and half-life was calculated. Incubation of curcumin with higher concentrations of GSH, NAC, and β-mercaptoethanol (BME) such as 2 and 8 mM induced rapid decolorization with similar or significantly shorter half-lives than those of curcumin alone, 153 ± 14 min. This suggests that curcumin became less stable in the presence of high concentrations of thiol antioxidants. In contrast, incubation with lower concentrations (0.5 mM) of GSH, NAC, and BME showed significantly longer half-lives, 200 ± 16, 191 ± 8, and 202 ± 22 min, respectively, compared to the curcumin alone (
Figure 1A). Curcumin clearly showed a biphasic effect on its stability; low concentrations (submillimolar levels at 0.5 mM) of thiol antioxidants improved its stability, whereas higher concentrations (>2 mM) of thiol antioxidants accelerated degradation of curcumin. L-glutathione oxidized (GSSG), in which two molecules of GSH are linked by a disulfide bond, is produced through the oxidation of GSH thiol groups in the cellular environment [
41]. Interestingly, the stability of curcumin was not affected when incubated with varying concentrations of GSSG such as 0.5, 2, and 8 mM. Half-lives of curcumin were not significantly different in all the conditions with and without GSSG (
Figure 1A).
To determine whether the antioxidant action contributes to the stability of curcumin, the effects of ascorbic acid (AS. A) as a non-thiol antioxidant and antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase on curcumin stability were analyzed (
Figure 1B). The half-life significantly increased when curcumin incubated with As.A in a concentration-dependent manner (971 ± 118, 1092 ± 125, and 1430 ± 115 min for 0.5, 2, and 8 mM As.A, respectively) compared to curcumin alone (163 ± 10 min). When incubated with SOD, curcumin exhibited a stability pattern similar to the condition incubated with As.A. At both 5 and 15 U/mL, SOD made curcumin more stable, resulting in longer half-lives. When incubated with catalase, no significant changes in half-lives were observed. These results reveal that non-thiol antioxidants affect curcumin's stability differently than thiol antioxidants, either causing no significant change or enhancing stability regardless of concentration.
The stability of both DMC (
Figure 1C) and BMC (
Figure 1D) was also examined in the absence or presence of thiol antioxidants, GSH, NAC, and BME. When DMC was incubated with low concentration of GSH or NAC (0.5 mM), half-lives of curcumin absorbance at 405 nm showed an increase compared to DMC alone, indicating enhanced stability induced by thiol-antioxidants. However, when incubated with 0.5 mM BME, the stability of DMC remained unchanged compared to DMC alone. GSH, NAC, and BME at higher concentrations such as 2 and 8 mM either maintained or decreased half-lives of DMC compared to DMC alone. In summary, the effect of thiol-antioxidants to DMC stability is similar to their effect on curcumin. BMC which lacks two methoxy groups on the ring structure in curcumin was more stable than curcumin or DMC with longer half-life of 182.9 ± 7.1 min. Incubation with low concentrations of thiol-antioxidants (0.5 mM) did not change BMC's stability significantly. Incubation with 2 mM of NAC or BME except GSH showed increased half-lives compared to BMC alone indicating enhanced stability of BMC. However, at the highest concentration of these three thiol antioxidants (8 mM), the half-life of BMC was significantly reduced, indicating accelerated degradation of BMC structure.
While there were minor variances among curcumin, DMC, and BMC, it is evident that thiol antioxidants modulates the chemical stability of curcuminoids with a common a,β-unsaturated carbonyl structure in a biphasic pattern; at a low concentration of thiol-antioxidant, the stability of curcuminoids improved, but at a higher concentration (8 mM), it decreased consistently. Non-thiol antioxidants solely contribute to the stabilization of curcumin regardless of concentration, suggesting a possible direct interaction between the thiol group and curcumin. The structural difference between curcumin, DMC, and BMC is the number of methoxy groups on their ring structures; the site of interaction with the thiol group does not appear to be the methoxy phenyl moiety.
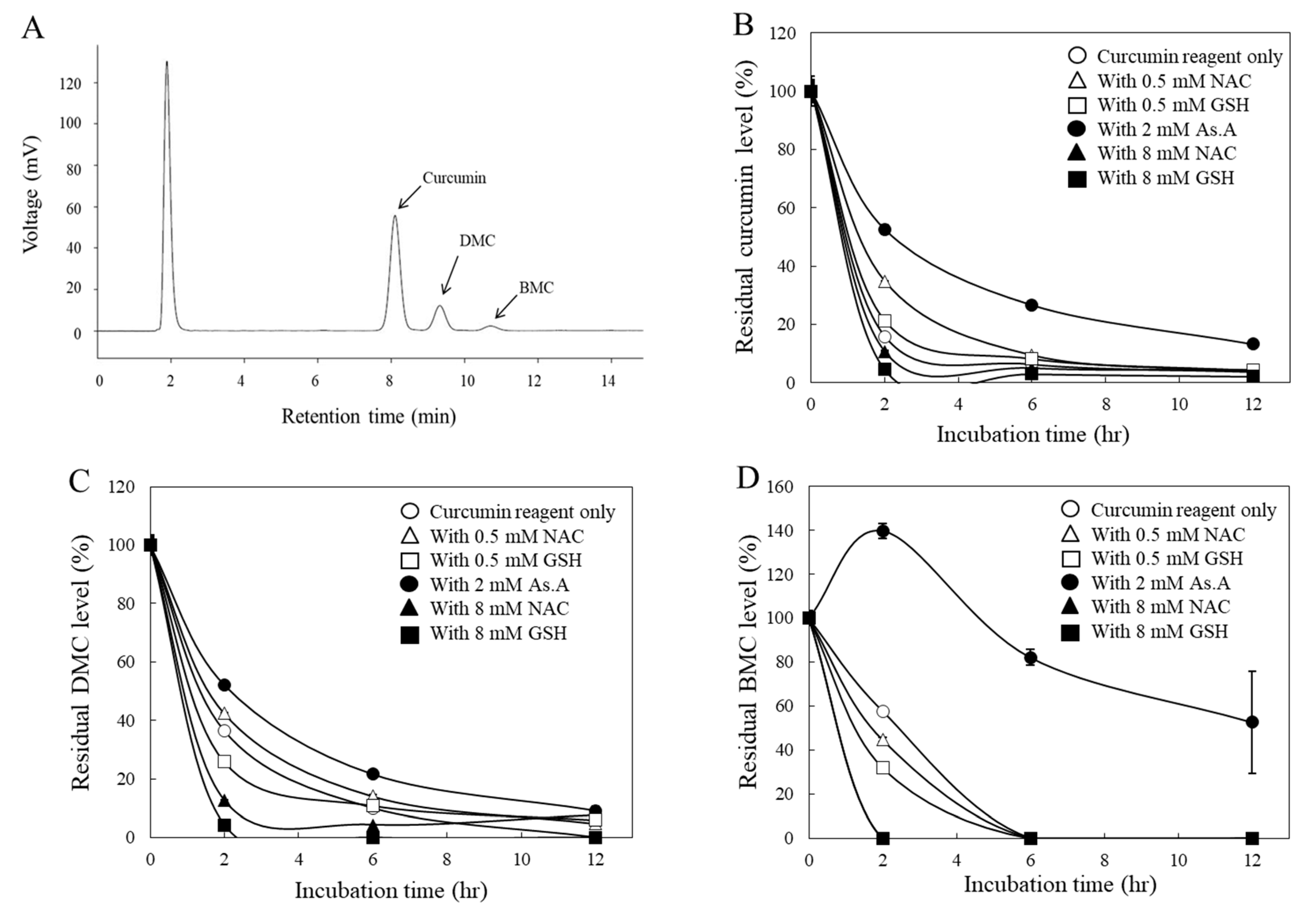
2.2. Changes in curcumin stability by antioxidants in a cell culture condition
Several ROS-dependent mechanisms of curcumin have been reported from the studies based on cell culture systems using antioxidants such as NAC [
36,
37] and GSH [
38]. To determine whether antioxidants also affect the stability of curcumin under the cell culture conditions, the residual levels of each curcuminoid in the medium were analyzed by HPLC after being treated to HeLa cells. In the current HPLC system, three distinctive peaks representing curcumin, DMC, and BMC were observed, and their compositions of the curcumin reagent used in this study were 79.4, 16.8, and 3.8% (w/w/w), respectively (
Figure 2A), which is consistent with other studies [
25].
All three curcuminoids including curcumin (
Figure 2B), DMC (
Figure 2C), and BMC (
Figure 2D) were unstable in a cell culture medium, with noticeable reductions in their concentrations within the initial 2 hr. For instance, when curcumin was incubated with a higher concentration (8 mM) of thiol-antioxidants, GSH and NAC, the residual levels of curcumin in the medium decreased more rapidly (
Figure 2B). Conversely, a lower concentration (0.5 mM) of them left more curcumin in the medium. Similarly, non-thiol antioxidant, As.A (8 mM) also resulted in more curcumin remaining in the medium. These results are consistent with the half-life data measured by detecting absorbance at 405 nm (
Figure 1A) and the idea that low concentration of thiol-antioxidants increased curcumin stability.
DMC (
Figure 2C) showed similar results to the curcumin (
Figure 2B), except for the low concentration (0.5 mM) of GSH, which exhibited slightly lower amounts in the medium compared to the DMC alone after a 2 hr incubation. Regarding BMC (
Figure 2D), neither low concentration (0.5 mM) of GSH nor NAC increased the residual amounts of BMC in the medium compared to BMC alone after 2 hr incubation. This is also consistent with
Figure 1D, which suggests that the low concentration of thiol-oxidants was unable to modulate the stability of BMC. However, As.A (2 mM) stabilized DMC and BMC in a cell culture medium, and residual levels of DMC and BMC were markedly higher than control (
Figure 2C and D).
Taken together, both non-thiol antioxidant and low concentration of thiol-antioxidants stabilized curcumin and DMC, whereas high concentration of thiol-antioxidants consistently reduced stability of all curcuminoids. In case of BMC, only non-thiol antioxidant, As.A, enhanced its stability. Although there was an exception, these findings still suggest that the thiol-group in thiol-antioxidant may directly interact with curcuminoids. Additionally, the methoxy group in their structure seems not important for their interaction with thiol group, considering all three curcuminoids showed a similar response to thiol group interaction.
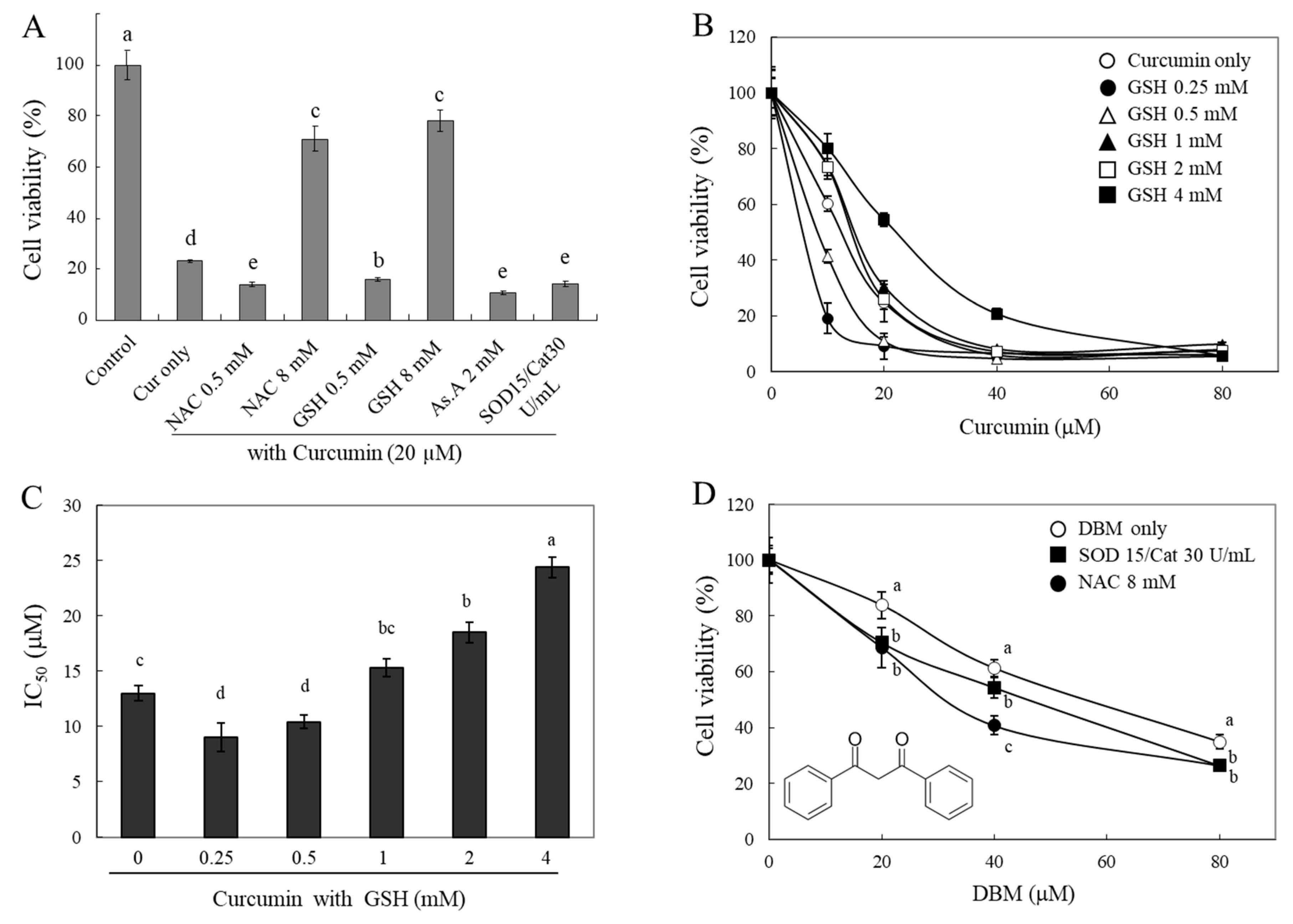
2.3. Changes in curcumin cytotoxicity by antioxidants
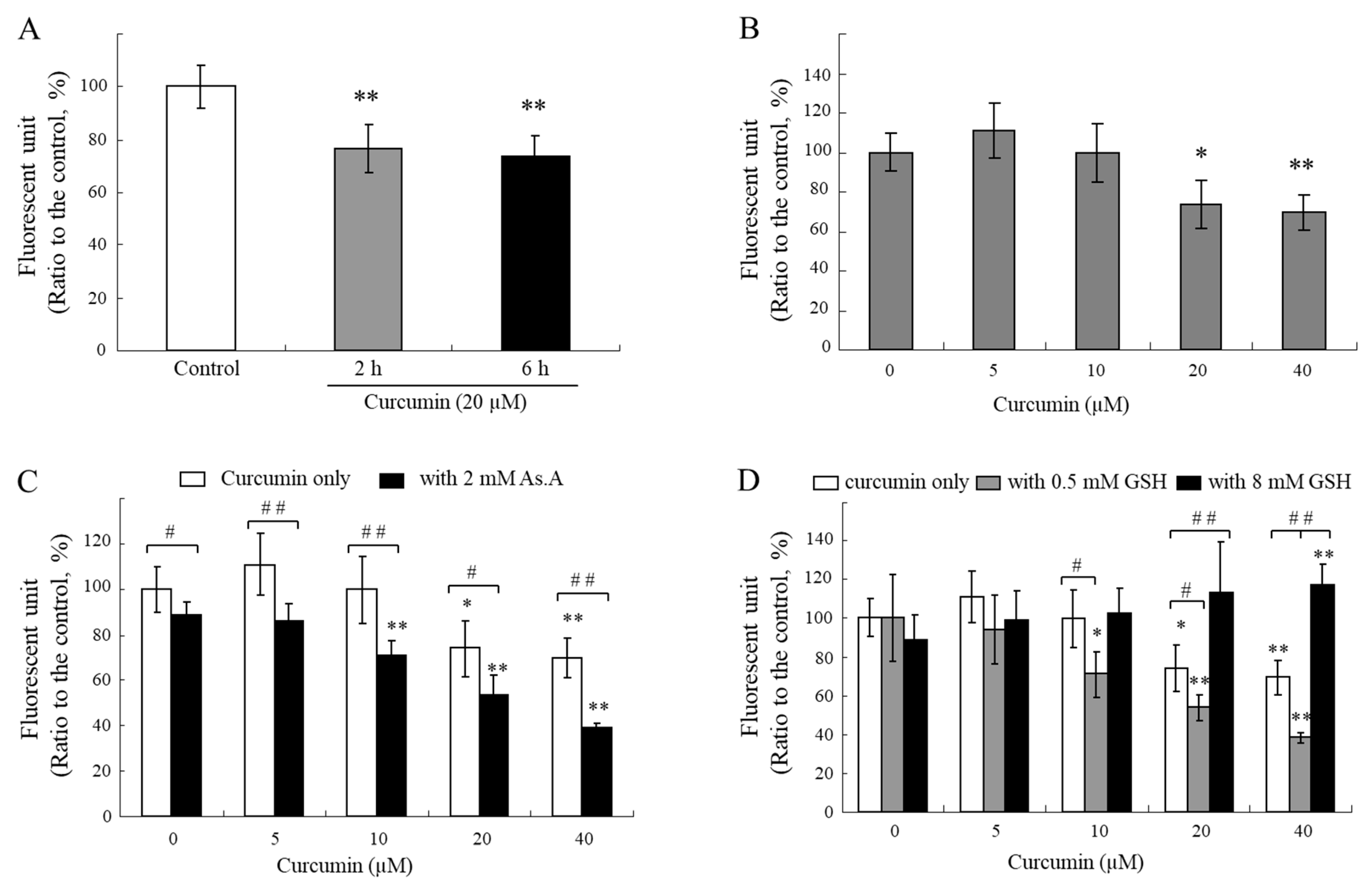
If a thiol group of antioxidants directly interacts with curcuminoids and degrades their structures, then their bioactivities, e.g. curcumin-induced cytotoxicity, can be modulated by the thiol-antioxidants. To test this hypothesis, we investigated changes in the cytotoxicity of curcumin in the presence of different types of antioxidants (
Figure 3A). A strong cytotoxic effect of curcumin (20 µM) on HeLa cells was observed. Presence of thiol-antioxidants, GSH and NAC (each 8 mM), were found to significantly reduce the cytotoxic effect of curcumin. Furthermore, there was a significant increase in the cytotoxic effect of curcumin in the presence of 0.5 mM GSH and NAC, 2 mM As.A, and 15 and 30 units/mL of SOD/catalase. The results demonstrate that modulation of curcumin cytotoxicity by thiol-antioxidants shows similar biphasic effects to those seen in curcumin stability (
Figure 1 and 2). Although lower concentrations of thiol-antioxidants increased curcumin-induced cell cytotoxicity, higher concentrations of GSH and NAC induced the opposite effect, reduction in curcumin cytotoxicity. These results also reveal that non-thiol antioxidants or antioxidant enzymes can improve curcumin stability and increase its cytotoxicity.
To better understand the action of GSH, we measured the cytotoxicity of curcumin against HeLa cells in the presence of different concentrations of GSH (0.25 - 4 mM,
Figure 3B). Both 0.25 mM and 0.5 mM GSH potentiated cytotoxicity induced by curcumin on HeLa cells. The cell viabilities were 19 ± 5% and 41 ± 2%, respectively, compared to 10 μM curcumin alone (60 ± 3%). In contrast, higher concentrations of GSH (2 and 4 mM) decreased cytotoxicity that was induced by curcumin and the cell viabilities were 73 ± 3%, and 81 ± 5%, respectively, compared to curcumin alone (60 ± 3%). The IC
50 was calculated and displayed in
Figure 3C. As shown in
Figure 3B, incubation of curcumin with lower concentrations of GSH (0.25 and 5 mM) decreased the IC
50 to 9.0 ± 1.3 and 10.4 ± 0.6 µM, respectively, compared to curcumin alone (13 ± 0.7 µM). As anticipated, higher concentrations of GSH (2 and 4 mM) caused an increase in the IC
50 of curcumin up to 24.4 ± 0.9 µM. The concentration-dependent IC
50 of GSH showed a U-shape, indicating a biphasic effect on curcumin-induced cell cytotoxicity. These findings also indicate that lower concentrations of thiol antioxidants may increase the stability of curcumin, whereas higher concentrations of thiol group directly impact its structure and result in decrease of curcumin bioactivities in a thiol concentration-dependent manner.
Dibenzoylmethane (DBM), which lacks an α,β-unsaturated moiety, was also used for cytotoxicity evaluation to understand an exact reactive site of curcumin with thiol groups. Cytotoxic effects of DBM were significantly enhanced in the presence of 15 and 30 units/mL of SOD/catalase or 8 mM of NAC (
Figure 3D). While 8 mM of NAC significantly reduced the stability and bioactivity of curcumin, this phenomenon was not observed in case of DBM and its cytotoxicity was rather enhanced. NAC might be involved only in stabilizing DBM structures; thiol groups are likely reactive with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl structure rather than diketone moiety. The precise characterization for chemical modification of curcumin and related α,β-unsaturated diketone derivatives by thiol compounds needs to be explored further.
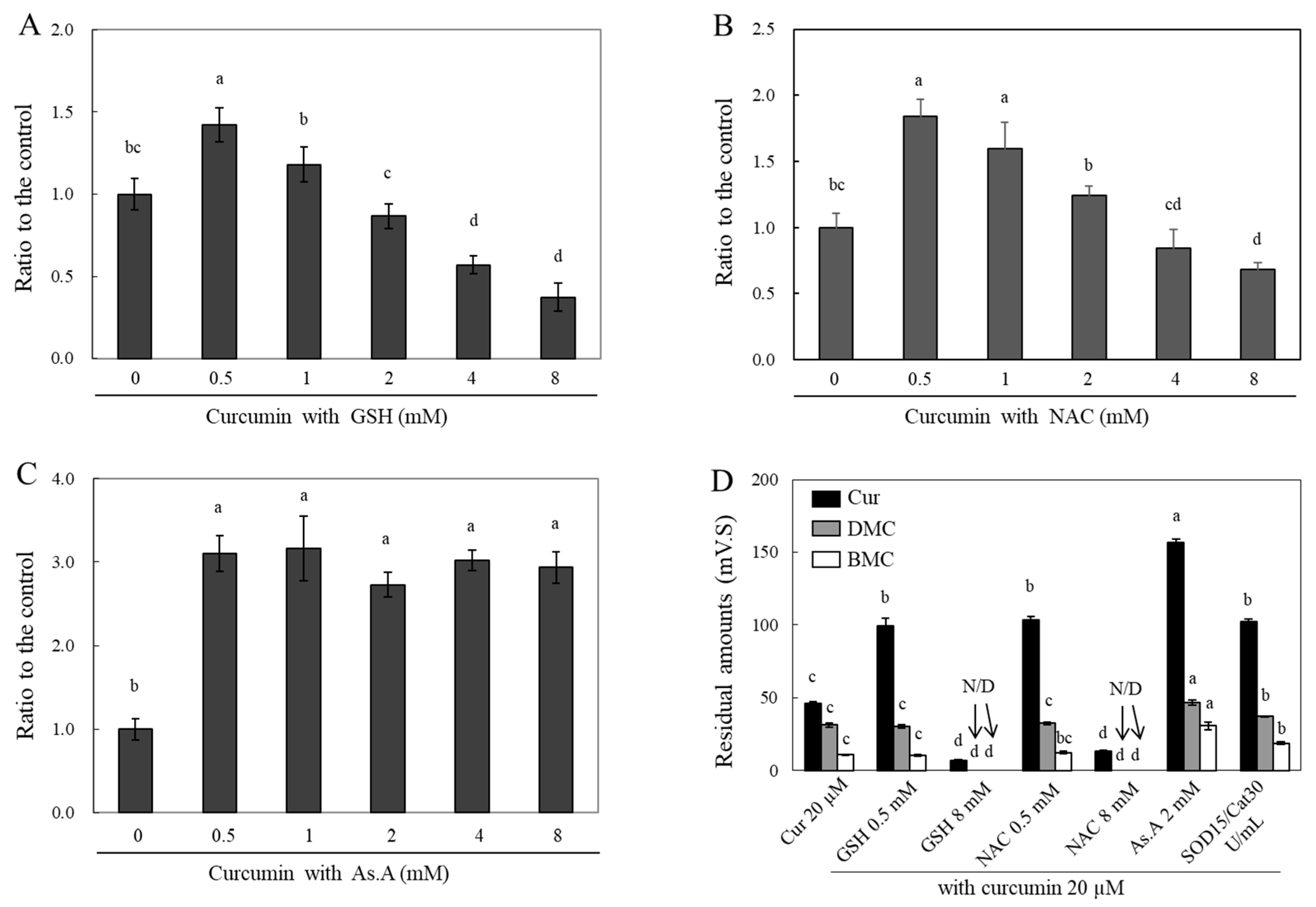
2.4. Changes in cellular levels of curcumin by antioxidants
Curcumin is highly hydrophobic and soluble in lipids. This property allows curcumin to penetrate the plasma membrane [
42]. Accordingly, co-treated antioxidants with curcumin were expected to affect the intracellular curcumin level through modulating its stability in media. To answer this question, HeLa cells were treated with varying concentrations of different antioxidants in the presence of curcumin, and then cell lysates were collected to measure peak absorbance of curcumin at 405 nm (
Figure 4A-C) or to conduct HPLC analysis (
Figure 4D).
Curcumin treatment with different concentrations of GSH (
Figure 4A), NAC (
Figure 4B), and As.A (Fig.4C) for 4 hr was applied to HeLa cells. The cells were subsequently lysed using 70% MeOH, and the absorbance of the cell lysates containing curcumin was measured at 405 nm. The incubation of 0.5 mM GSH with curcumin resulted in significant increase of an absorbance value at 405 nm by 1.42 fold in comparison to curcumin alone (
Figure 4A). Increasing concentrations of GSH up to 2 mM incubated with curcumin led to similar intracellular curcumin levels when compared to the condition of incubation with curcumin alone. Cell incubation with curcumin with 4 and 8 mM GSH caused a significant decrease in absorbance values by 0.57 ± 0.05 and 0.37 ± 0.08 times respectively, in comparison to curcumin alone. In the case of NAC (
Figure 4B), changes in absorbance at 405 nm were similarly modulated as with GSH incubation. Incubation of both 0.5 and 1 mM NAC with curcumin significantly increased the absorbance values to 1.84 and 1.60 fold, respectively, compared to curcumin alone. However, 8 mM NAC incubation with curcumin resulted in a significantly decreased absorbance to 0.68 ± 0.06 fold. After incubating the HeLa cells with 0.5 mM As.A, the cellular curcumin level increased to 3.10 fold (
Figure 4C). Unlike the results of GSH and NAC, concentrations of As.A up to 8 mM did not alter the absorbance values at 405 nm. No significant change in intracellular curcumin level was observed with different concentrations of As.A. This also confirmed that antioxidants lacking thiol group do not interact directly with curcumin and only increased its stability.
The samples for the HPLC analysis were collected by preparing cell lysates according to the methods detailed in the materials and methods section. The intracellular curcumin levels were significantly lower after 2 hr of incubation in the presence of 8 mM GSH and NAC, compared to those in cells treated solely with curcumin (
Figure 4D). The intracellular levels of DMC and BMC decreased to almost basal levels in the presence of 8 mM GSH and NAC. However, intracellular levels of curcumin increased with the addition of low concentrations of GSH and NAC (0.5 mM each), 2 mM As.A and 15/30 units/mL of SOD/catalase by 2.15 and 2.24, 3.39 and 2.21 fold, respectively. Cellular levels of DMC and BMC were significantly increased by 1.50 and 2.86 fold, respectively, in the presence of 2 mM As.A. They were also increased by 1.18 and 1.75 fold, respectively, in the presence of SOD/catalase, compared to the control. Intracellular levels of DMC and BMC did not exhibit noticeable changes at low concentrations (0.5 mM) of GSH and NAC. This could be due to the fact that the 0.5 mM of GSH and NAC was less effective for stabilizing BMC and DMC than curcumin as shown in
Figure 1C and D. These results also suggest that high concentrations of thiol antioxidants reduce intracellular curcumin levels through destabilizing the structure, whereas non-thiol antioxidants and low concentrations of thiol-antioxidants can enhance its stability and cellular uptake. Accordingly, the stability of intracellular curcumin was similarly affected by different antioxidants as the stability of extracellular curcumin stability. After the interaction between curcumin and antioxidants that occurred extracellularly in the medium, the remaining curcumin was presumed to enter the cell. Therefore, increasing the stability of curcumin outside of the cell results in more curcumin passing through the membrane and consequently higher levels in cell lysates.
2.5. Changes in intracellular levels of thiols
If curcumin specifically react with thiol groups in media, intracellular curcumin is also capable of reacting with thiol compounds in cells. To examine the changes in intracellular thiol levels due to the treatment of curcumin with cells, an assay using monobromobimane (mBBr), a thiol-specific fluorescence probe, was conducted [
43]. The intracellular thiol levels were reduced for 2 and 6 hr after exposure to curcumin at a concentration of 20 µM (
Figure 5A), and its effects seem to be dependent on concentration (
Figure 5B). Curcumin might react directly with intracellular thiol-containing biomolecules, such as GSH, or induce oxidative stress that leads to GSH consumption in cells. GSH is considered one of the most abundant endogenous antioxidants. In human, GSH is present in a high concentration between 1 and 10 mM, which allows it to scavenge ROS [
44,
45].
Treatment of various concentrations of curcumin in the presence of As.A (2 mM) resulted in a greater decrease in cellular levels of thiols (
Figure 5C). A low concentration of GSH (0.5 mM) also lowered intracellular thiol levels (
Figure 5D). The levels of thiols inside cells after treatment with curcumin in the presence of 8 mM GSH did not decrease and were even higher than the control levels (
Figure 5D). These results suggest that 0.5 mM GSH or 2 mM As.A can enhance the stability of curcumin in an extracellular medium, resulting in a higher transfer of curcumin into the cells and more thiols being consumed after direct interaction inside of cells. On the other hand, the stability of curcumin is significantly lower in the presence of 8 mM GSH in a culture medium, and the level of curcumin transferred into cells is insufficient to impact intracellular levels of thiols.
2.6. Changes in curcumin-induced HO-1 levels by antioxidants
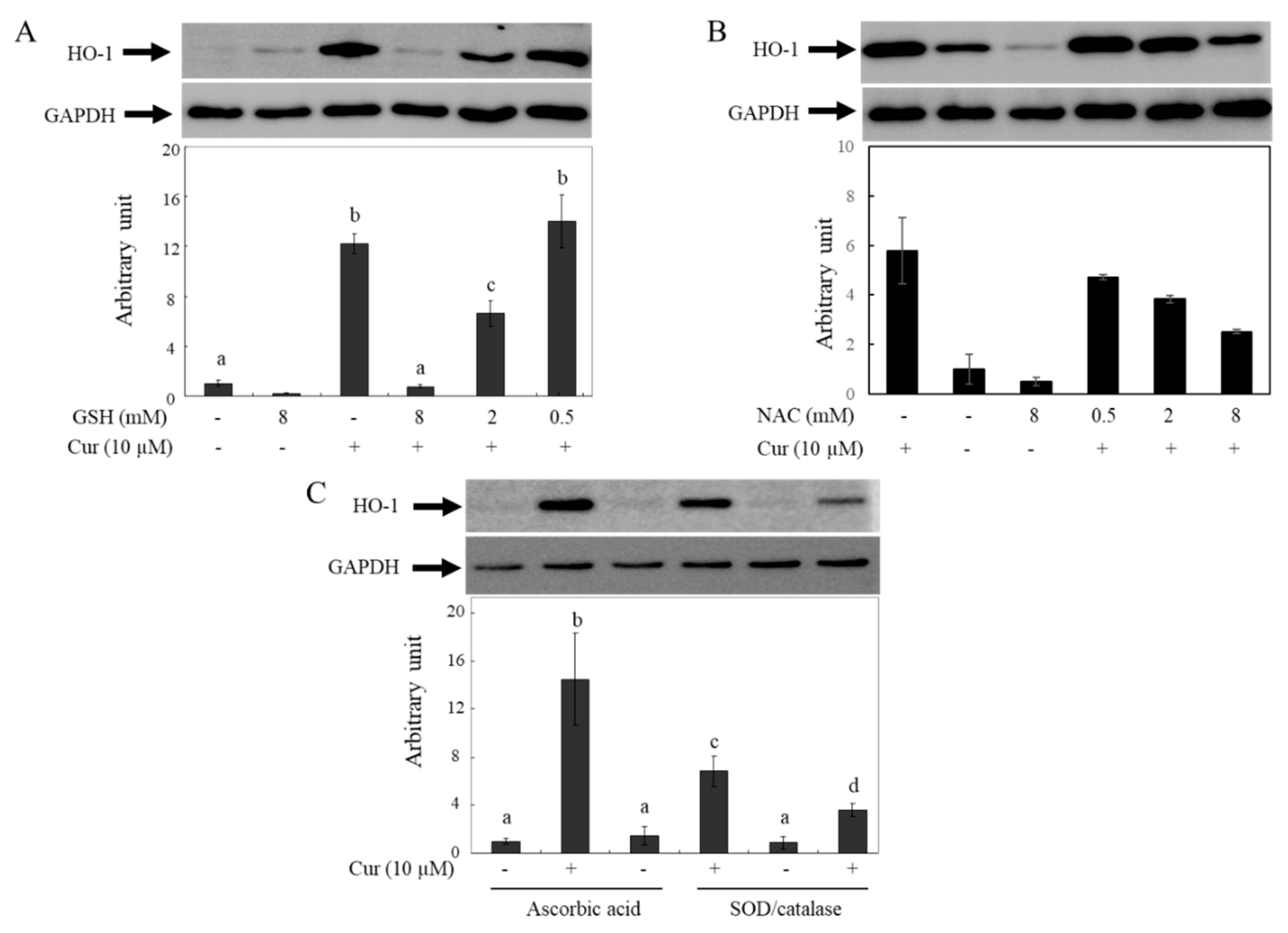
Previous reports have shown that curcumin induces HO-1 expression and that the effects are caused by ROS generated from curcumin. These reports indicate that HO-1 induction by curcumin is hindered in the presence of GSH or NAC [
46]. To confirm whether the decreased bioactivity of curcumin in the presence of GSH or NAC is caused by the removal of ROS or the degradation of curcumin, the effects of different types of antioxidants on HO-1 expression by curcumin were investigated using the Western blot analysis (
Figure 6). The HO-1 protein levels in HeLa cells increased after incubation with 10 µM curcumin for 12 hr, but the effects of curcumin were reduced in a concentration-dependent manner by GSH (
Figure 6A) or NAC (
Figure 6B). Based on our current results, it is hypothesized that the observed phenomenon may be due to curcumin degradation in media by antioxidants containing thiol groups. The induction levels of HO-1 by curcumin increased when co-incubated with non-thiol antioxidants such as As.A and SOD/catalase (
Figure 6C). Hence, the lowered induction level of HO-1 by curcumin in the presence of thiol antioxidants such as GSH and NAC cannot be attributed to their ROS-quenching effects; this phenomenon is related to the stability of curcumin. Non-thiol antioxidants may stabilize curcumin, leading to the transfer of more curcumin into cells and stronger physiological responses, including HO-1 induction. Conversely, antioxidants with a thiol group can reduce the bioactivity of curcumin by decreasing its stability in a cell culture system.
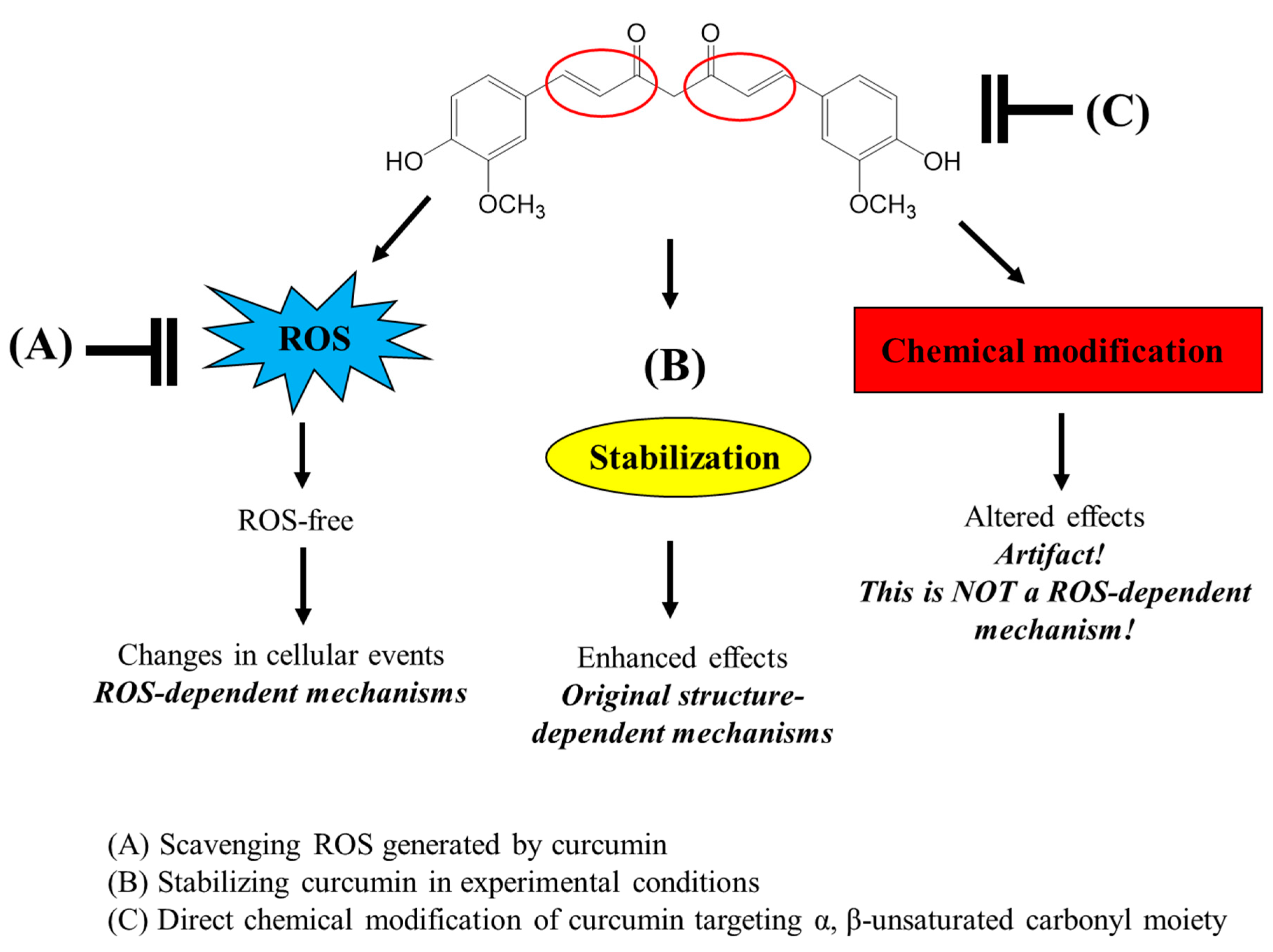
Our current results show that thiol groups can directly modify the chemical structure of curcuminoids by targeting the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety. Although low concentrations of thiol compounds stabilize the structure of curcumin through their general antioxidant action, high levels of thiol groups can attack the α,β-unsaturated ketone structure, leading to rapid decomposition of curcumin and its structurally-related compounds. Many studies have used GSH and NAC to scavenge ROS in experimental systems particularly using cultured cells and have attempted to elucidate ROS-dependent mechanisms of various bioactive compounds. However, the use of these thiol antioxidants should be considered carefully, as they can directly modify the structure of the test compounds rather than scavenge ROS. The possible roles of thiol antioxidants in the interaction of curcumin and various bioactive compounds with α,β-unsaturated carbonyl groups in experimental system with cultured cells are presented in
Figure 7. Furthermore, the direct chemical interaction of thiol groups with various compounds containing α,β-unsaturated carbonyl moiety needs to be carefully considered not only in experimental systems but also in industrial applications such as food and pharmaceuticals.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and cell lines
Curcumin (a mixture of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin; DMC, and bisdemethoxycurcumin; BMC, 79.4, 16.8, and 3.8 % (w/w/w), respectively) was purchased from Acros Organics (Morris Plains, NJ, USA). DMC, BMC, dibenzoylmethane (DBM), N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC), L-glutathione reduced (GSH), L-glutathione oxidized (GSSG), and β-mercaptoethanol (BME) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). HO-1 (Hsp32) polyclonal antibody and GAPDH monoclonal antibody (1D4) were obtained from Assay Designs (Ann Arbor, MI, USA). 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) was from Amresco Inc. (Solon, OH, USA). All other chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. HeLa human cervical carcinoma cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). Cells were maintained in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 unit/mL penicillin, and 0.1 mg/mL streptomycin at 37℃ in 95% humidity and 5% CO₂.
3.2. Determination of curcumin stability with different types of antioxidants
For analyzing changes in chemical stability, curcumin, DMC, or BMC in 1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) with 0.5% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) as vehicle was incubated at room temperature (RT) with or without different antioxidants. At different time point, changes in the absorbance at 405 nm was detected using a microplate reader (Triad LT, Dynex Technologies Inc., Chantilly, VA, USA).
3.3. Analysis of residual levels of curcumin in media and cells
HeLa cells were seeded in a 24-well plate and incubated for 24 hr. The cells then were treated with curcumin, with or without the addition of GSH, NAC, and As.A for durations of 2, 6, and 12 hr. At each time point, 500 µL media was collected, and to this, 5 µL of 10 N HCl was added to stabilize curcumin. An additional 500 µL of ethyl acetate was added to this mixture, followed by an intense 30 sec vortex mixing. The mixtures were then centrifuged at 10,000 g for 5 min, then the organic solvent layer was collected. The extraction step was repeated twice. The resultant organic phases were dried using a vacuum centrifuge (NB-503CIR, N-Biotec, Inc., Seoul, Korea), and the dried extracts were dissolved in the HPLC mobile phase solvent for the HPLC analysis. To analyze cellular uptake of curcumin, HeLa cells were seeded in a 12-well plate. When the cells reached ~80% confluency, the cells were treated with 20 µM of curcumin in serum free DMEM media. After 2 or 4 hr incubation, cells were washed 3 times with ice cold phosphate-buffered saline. Intracellular curcumin was then extracted using 70% MeOH for 30 min and the cell lysates were centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 min at 4°C. The supernatant was analyzed at 405 nm using a microplate reader and used for the HPLC analysis.
3.4. HPLC analysis
Amounts of curcumin and curcuminoids in media and inside of the cells were analyzed with a HPLC equipped with a L-6200 intelligent pump (Hitachi, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) and an UV-975 UV/vis detector (Jasco Co., Tokyo, Japan). A Shiseido C18 packed column (150 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm particle size) was used. The mobile phase consisted of 60% water containing 1% citric acid and 40% THF adjusted to pH 3.0, with concentrated KOH solution (v/v) (40). The solvent was run isocratically at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Peak was achieved at 420 nm, and injection volumes were 20 μL. The operating condition was described as in
Table 1.
3.5. Evaluation of cell cytotoxic properties
Cytotoxic effects of curcumin on HeLa cells were determined using the MTT assay. The cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a density of 104 cells per well and treated the next day with curcumin or DBM in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants. After 24 h, compound-containing medium was removed, and 100 mL of fresh medium containing 0.5 mg/mL MTT was added to each well. The cells were further incubated at 37℃ for 1-2 h. The medium was then replaced with 100 mL of DMSO, and absorbance was measured at 550 nm using a microplate reader (Triad LT).
3.6. Measurement of intracellular thiol levels
The levels of intracellular thiols were measured using a cell-permeable thiol-staining reagent called monobromobimane (mBBr), as described by Kong et al. with slight modifications [
43]. HeLa cells were seeded in 96-well plates with a density of 10
4 cells per well. After 24 hr, the cells were treated with curcumin in the absence or presence of various types of antioxidants. Following different incubation times, the medium was removed and washed with PBS. The cells were incubated with 100 μL of a 40 μM solution of mBBr for 30 min at 37℃. After that, the mBBr solution was removed, and 0.2 N NaOH was added to lyse the cells. The fluorescence intensity from thiols reacting with mBBr was measured using a fluorescent microplate reader (Triad LT). The excitation and emission wavelengths were 365 nm and 465 nm, respectively.
3.7. Western blot
HeLa cells were plated into a 6-well plate. After 24 h, the cells were treated with curcumin in the absence or presence of antioxidants for 12 h. The cells were washed with ice cold PBS twice and lysed with cell lysis buffer (1 mM PMSF, 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM Na2EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1% Triton, 2.5 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 1 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mg/mL leupeptin, in 20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5). The cell lysate was centrifuged at 10,000 g for 10 min at 4℃. The supernatant containing 10 or 20 mg of protein was loaded onto 8% SDS polyacrylamide gel. After electrophoresis, the proteins were transferred onto PVDF membrane. After blocking, blots probed with human heme oxygenase-1 (Hsp32) polyclonal antibody in 5% non-fat milk and 0.05% tween-20 in PBS. After incubation overnight at 4℃, the primary antibody was probed with peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG for 3 hr. After washing with 0.05% TBST four times, the western blotting luminol reagent (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA) was added to blotted proteins and chemiluminescence was detected by a luminescent image analyzer (LAS-4000 mini, Fujifilm, Tokyo, Japan). Protein concentration in the cell lysates were determined using BCA protein assay kit (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA).
3.8. Data analysis
All values represent the mean ± standard deviation (SD). Each experiment was repeated at least 3 times with triplicates with some exceptions. Statistical differences were evaluated using the Student’s t-test or One-way ANOVA in SPSS program (IBM SPSS Statistics 24, SPSS Inc. Chicago, IL, USA) and the Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test (p < 0.05) were used for comparing multiple results.
Author Contributions
J.H. developed the concept and designed the study; B.H.L. performed the experiments and statistical analysis; E.S. provided technical support; B.H.L. and J.H. prepared and edited the manuscript. A part of this study was from B.H.L’s MS thesis at Seoul Women’s University. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants (2021R1F1A1051466) funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (to J.H.) and by the grant from Institute of Health Sciences of Gyeongsang National University (IHS GNU-2022-04) and the research grant of the Gyeongsang National University in 2022 (to B.H.L.).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Sample Availability
Not available.
References
- Ammon, H.P.; Wahl, M.A. Pharmacology of Curcuma longa. Planta Med. 1991, 57, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eigner, D.; Scholz, D. Ferula asa-foetida and Curcuma longa in traditional medical treatment and diet in Nepal. J Ethnopharmacol. 1999, 67, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, V.P.; Sudheer, A.R. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of curcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007, 595, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Luo Y Fau - Qiao, Y.; Qiao Y Fau - Zhang, Z.; Zhang Z Fau - Yin, D.; Yin D Fau - Yao, J.; Yao J Fau - You, J.; You J Fau - He, M.; He, M. Curcumin attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity via suppressing oxidative stress and preventing mitochondrial dysfunction mediated by 14-3-3γ. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 4044–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, A.; Rostamirad, A.; Seyyedebrahimi, S.; Meshkani, R.A.-O. Curcumin ameliorates palmitate-induced inflammation in skeletal muscle cells by regulating JNK/NF-kB pathway and ROS production. Inflammopharmacology. 2018, 26, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang Zs Fau - Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang Yl Fau - Zhou, D.Y.; Zhou, D.Y. Curcumin inhibits cell proliferation by interfering with the cell cycle and inducing apoptosis in colon carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 1999, 19, 3675–3680. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Zhang Z Fau - Hill, D.L.; Hill Dl Fau - Wang, H.; Wang H Fau - Zhang, R.; Zhang, R. Curcumin, a dietary component, has anticancer, chemosensitization, and radiosensitization effects by down-regulating the MDM2 oncogene through the PI3K/mTOR/ETS2 pathway. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troselj Kg Fau - Kujundzic, R.N.; Kujundzic, R.N. Curcumin in combined cancer therapy. Curr Pharm Des. 2014, 20, 6682–6696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Bose M Fau - Ju, J.; Ju J Fau - Ryu, J.-H.; Ryu Jh Fau - Chen, X.; Chen X Fau - Sang, S.; Sang S Fau - Lee, M.-J.; Lee Mj Fau - Yang, C.S.; Yang, C.S. Modulation of arachidonic acid metabolism by curcumin and related beta-diketone derivatives: effects on cytosolic phospholipase A(2), cyclooxygenases and 5-lipoxygenase. Carcinogenesis. 2004, 25, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Tumin, D.; Cismowski, M.; Tobias, J.D.; Gomez, D.; McConnell, P.; Naguib, A.; Yates, A.R.; Winch, P. Effects of Preoperative Curcumin on the Inflammatory Response During Mechanical Circulatory Support: A Porcine Model. Cardiol Res. 2018, 9, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, L.A.; Elias, G.; Rao, M.N. Oxygen radical scavenging activity of phenylbutenones and their correlation with antiinflammatory activity. Arzneimittelforschung 1990, 40, 89–91. [Google Scholar]
- Priyadarsini, K.I.; Maity, D.K.; Naik, G.H.; Kumar, M.S.; Unnikrishnan, M.K.; Satav, J.G.; Mohan, H. Role of phenolic O-H and methylene hydrogen on the free radical reactions and antioxidant activity of curcumin. Free Radic Biol Med 2003, 35, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Álvarez-Diduk, R.; Ramírez-Silva, M.T.; Alarcón-Ángeles, G.; Rojas-Hernández, A. Role of the reacting free radicals on the antioxidant mechanism of curcumin. Chemical Physics 2009, 363, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.W.; Huang, H.C. Effect of curcumin on cell cycle progression and apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1998, 124, 1029–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.J.; Mukhtar, H. Curcumin for chemoprevention of colon cancer. Cancer Letters 2007, 255, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayyullathil, F.; Chathoth, S.; Hago, A.; Patel, M.; Galadari, S. Rapid reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation induced by curcumin leads to caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis in L929 cells. Free radical biology & medicine 2008, 45, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plummer, S.M.; Holloway, K.A.; Manson, M.M.; Munks, R.J.L.; Kaptein, A.; Farrow, S.; Howells, L. Inhibition of cyclo-oxygenase 2 expression in colon cells by the chemopreventive agent curcumin involves inhibition of NF-κB activation via the NIK/IKK signalling complex. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6013–6020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Activation of Transcription Factor NF-κB Is Suppressed by Curcumin (Diferuloylmethane) (∗). Journal of Biological Chemistry 1995, 270, 24995–25000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farombi, E.O.; Shrotriya S Fau - Na, H.-K.; Na Hk Fau - Kim, S.-H.; Kim Sh Fau - Surh, Y.-J.; Surh, Y.J. Curcumin attenuates dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver injury in rats through Nrf2-mediated induction of heme oxygenase-1. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008, 46, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motterlini, R.; Foresti, R.; Bassi, R.; Green, C.J. Curcumin, an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent, induces heme oxygenase-1 and protects endothelial cells against oxidative stress. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2000, 28, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, E.; Foresti, R.; Green, C.J.; Motterlini, R. Changes in temperature modulate heme oxygenase-1 induction by curcumin in renal epithelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 2003, 308, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; Loo, G. Curcumin-induced GADD153 gene up-regulation in human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 2155–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; Loo, G. Curcumin-induced GADD153 upregulation: modulation by glutathione. J Cell Biochem. 2007, 101, 307–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.A.; Gescher Aj Fau - Steward, W.P.; Steward, W.P. Curcumin: the story so far. Eur J Cancer. 2005, 41, 1955–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandur, S.K.; Pandey Mk Fau - Sung, B.; Sung B Fau - Ahn, K.S.; Ahn Ks Fau - Murakami, A.; Murakami A Fau - Sethi, G.; Sethi G Fau - Limtrakul, P.; Limtrakul P Fau - Badmaev, V.; Badmaev V Fau - Aggarwal, B.B.; Aggarwal, B.B. Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, bisdemethoxycurcumin, tetrahydrocurcumin and turmerones differentially regulate anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative responses through a ROS-independent mechanism. Carcinogenesis. 2007, 28, 1765–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, N.; Umar S Fau - Ashafaq, M.; Ashafaq M Fau - Akhtar, M.; Akhtar M Fau - Iqbal, Z.; Iqbal Z Fau - Samim, M.; Samim M Fau - Ahmad, F.J.; Ahmad, F.J. A comparative study of PNIPAM nanoparticles of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin and their effects on oxidative stress markers in experimental stroke. Protoplasma. 2013, 250, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somparn, P.; Phisalaphong C Fau - Nakornchai, S.; Nakornchai S Fau - Unchern, S.; Unchern S Fau - Morales, N.P.; Morales, N.P. Comparative antioxidant activities of curcumin and its demethoxy and hydrogenated derivatives. Biol Pharm Bull. 2007, 30, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Jaganmohan Rao, L.; Sakariah, K.K. Antioxidant activities of curcumin, demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin. Food Chemistry 2006, 98, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankun, J.; Wyganowska-Świątkowska, M.; Dettlaff, K.; Jelińska, A.; Surdacka, A.; Wątróbska-Świetlikowska, D.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E. Determining whether curcumin degradation/condensation is actually bioactivation (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2016, 37, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Kang, S.; Hong, J. Changes in chemical properties, antioxidant activities, and cytotoxicity of turmeric pigments by thermal process. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 50, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, Y.N.; Hong, J. Changes in chemical properties and bioactivities of turmeric pigments by photo-degradation. AIMS Agriculture and Food 2021, 6, 754–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.K.; Pan Mh Fau - Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Recent studies on the biofunctions and biotransformations of curcumin. Biofactors. 2000, 13, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, B.H.; Kim, D.-R.; Kang, S.; Kim, M.-R.; Hong, J. Changes in the Chemical Stability and Antioxidant Activities of Curcuminoids under Various Processing Conditions. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology 2010, 42, 97–102. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.-S.; Huang, H.-P.; Yang, J.-S.; Wu, J.-Y.; Hsia, T.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Lin, C.-W.; Kuo, C.-L.; Gibson Wood, W.; Chung, J.-G. DNA damage and endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated curcumin-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung carcinoma A-549 cells through the activation caspases cascade- and mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Cancer letters 2008, 272, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanyam, M.; Koteswari, A.A.; Kumar, R.S.; Monickaraj, S.F.; Maheswari, J.U.; Mohan, V. Curcumin-induced inhibition of cellular reactive oxygen species generation: Novel therapeutic implications. Journal of Biosciences 2003, 28, 715–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Kang, H.-J.; Moon, A. Inhibition of Invasion and Induction of apoptosis by curcumin in H-ras-Transformed MCF10A human breast epithelial cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research 2001, 24, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, D.-G.; Lee, K.-S.; Bae, J.H.; Min, D.S.; Chang, J.-S.; Jeong, Y.-J.; Lee, Y.H.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of curcumin-induced cytotoxicity: induction of apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species, down-regulation of Bcl-X L and IAP, the release of cytochrome c and inhibition of Akt. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhy, S.U.; Kim, K.; Larsen, L.; Rosengren, R.J.; Safe, S. Curcumin and synthetic analogs induce reactive oxygen species and decreases specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors by targeting microRNAs. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.H.; Choi, H.A.; Kim, M.-R.; Hong, J. Changes in chemical stability and bioactivities of curcumin by ultraviolet radiation. Food Science and Biotechnology 2013, 22, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.N.; Kang, S.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J. Changes in the chemical properties and anti-oxidant activities of curcumin by microwave radiation. Food Science and Biotechnology 2016, 25, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R. Neuron–Glia Coupling in Glutathione Metabolism. In Encyclopedia of Neuroscience, Squire, L.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2009; pp. 733–737. [Google Scholar]
- Sala de Oyanguren, F.J.; Rainey, N.E.; Moustapha, A.; Saric, A.; Sureau, F.; O’Connor, J.-E.; Petit, P.X. Highlighting Curcumin-Induced Crosstalk between Autophagy and Apoptosis as Supported by Its Specific Subcellular Localization. Cells 2020, 9, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, C.S.; Kim Ja Fau - Qian, Z.-J.; Qian Zj Fau - Kim, Y.A.; Kim Ya Fau - Lee, J.I.; Lee Ji Fau - Kim, S.-K.; Kim Sk Fau - Nam, T.J.; Nam Tj Fau - Seo, Y.; Seo, Y. Protective effect of isorhamnetin 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside from Salicornia herbacea against oxidation-induced cell damage. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009, 47, 1914–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Diez, C.; Miguel, V.; Mennerich, D.; Kietzmann, T.; Sánchez-Pérez, P.; Cadenas, S.; Lamas, S. Antioxidant responses and cellular adjustments to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015, 6, 183–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.; Sinskey Aj Fau - Lodish, H.F.; Lodish, H.F. Oxidized redox state of glutathione in the endoplasmic reticulum. Science 1992, 257, 1496–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNally, S.J.; Harrison Em Fau - Ross, J.A.; Ross Ja Fau - Garden, O.J.; Garden Oj Fau - Wigmore, S.J.; Wigmore, S.J. Curcumin induces heme oxygenase 1 through generation of reactive oxygen species, p38 activation and phosphatase inhibition. Int J Mol Med. 2007, 19, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Changes in stability of curcumin by different types of antioxidants. Curcumin (40 μM) was incubated with different concentrations of thiol (A) or non-thiol antioxidants (B) in 1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) at RT. DMC (C) and BMC (D) (each 40 μM) were also incubated with different thiol compounds. At different time points, the absorbance values at 405 nm were measured, and half-life (a period required for 50% color degradation of each curcuminoid) were calculated based on time points of the linear color degradation. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 3 – 4). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 1.
Changes in stability of curcumin by different types of antioxidants. Curcumin (40 μM) was incubated with different concentrations of thiol (A) or non-thiol antioxidants (B) in 1 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) at RT. DMC (C) and BMC (D) (each 40 μM) were also incubated with different thiol compounds. At different time points, the absorbance values at 405 nm were measured, and half-life (a period required for 50% color degradation of each curcuminoid) were calculated based on time points of the linear color degradation. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 3 – 4). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 2.
Changes in curcumin levels by different types of antioxidants in a cell culture condition. Chromatograms of the curcumin agent used in the current HPLC system (A) were shown. The curcumin reagent (40 μM) containing 79.4, 16.8 and 3.8% of curcumin, DMC and BMC, respectively, was incubated in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants under the culture condition with HeLa cells, and the residual levels of curcumin (B), DMC (C), and BMC (D) in the culture medium were analyzed during 12 hr incubation. At each time point, the culture medium was collected, and the amounts of curcuminoids were analyzed by HPLC. Each data point represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 3).
Figure 2.
Changes in curcumin levels by different types of antioxidants in a cell culture condition. Chromatograms of the curcumin agent used in the current HPLC system (A) were shown. The curcumin reagent (40 μM) containing 79.4, 16.8 and 3.8% of curcumin, DMC and BMC, respectively, was incubated in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants under the culture condition with HeLa cells, and the residual levels of curcumin (B), DMC (C), and BMC (D) in the culture medium were analyzed during 12 hr incubation. At each time point, the culture medium was collected, and the amounts of curcuminoids were analyzed by HPLC. Each data point represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 3).
Figure 3.
Changes in cytotoxicity of curcumin and DBM by different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin (20 μM) in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants for 24 hr, and cell viability was analyzed using the MTT assay (A). HeLa cells were also incubated with curcumin in the presence of different concentrations of GSH for 24 hr (B), and IC50 values (concentration induced for 50% inhibition of cell growth) were calculated (C). Cytotoxic effects of DBM on HeLa cells were also evaluated in the presence of SOD/catalase (15/30 U/mL) or NAC (8 mM). Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n=8). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 3.
Changes in cytotoxicity of curcumin and DBM by different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin (20 μM) in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants for 24 hr, and cell viability was analyzed using the MTT assay (A). HeLa cells were also incubated with curcumin in the presence of different concentrations of GSH for 24 hr (B), and IC50 values (concentration induced for 50% inhibition of cell growth) were calculated (C). Cytotoxic effects of DBM on HeLa cells were also evaluated in the presence of SOD/catalase (15/30 U/mL) or NAC (8 mM). Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n=8). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 4.
Changes in intracellular levels of curcumin by different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin (20 μM) in the presence of different concentrations of GSH (A), NAC (B), and As.A (C) for 4 hr. The cells were then lysed using 70% MeOH and absorbance of the cell lysates were measured at 405 nm. HeLa cells were also incubated with curcumin (20 μM) in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants for 2 hr. After harvesting cells as described in materials and methods, individual curcuminoid levels inside of cells were analyzed by HPLC (D). Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 3 – 4). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 4.
Changes in intracellular levels of curcumin by different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin (20 μM) in the presence of different concentrations of GSH (A), NAC (B), and As.A (C) for 4 hr. The cells were then lysed using 70% MeOH and absorbance of the cell lysates were measured at 405 nm. HeLa cells were also incubated with curcumin (20 μM) in the absence or presence of different types of antioxidants for 2 hr. After harvesting cells as described in materials and methods, individual curcuminoid levels inside of cells were analyzed by HPLC (D). Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 3 – 4). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 5.
Changes in intracellular thiol levels by curcumin co-incubated with different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin only (A and B) or with As.A (C) and GSH (D). After 3 hr incubation (B, C and D), cells were treated with mBBr (40 μM) and then further incubated for 30 min at 37℃. Changes in fluorescence intensity were detected with an excitation at 365 nm and an emission at 465 nm. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 8). *, ** significantly different from its corresponding control according to Student’s t-test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). #, ## significantly different in the same concentration group according to Student’s t-test (#, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01).
Figure 5.
Changes in intracellular thiol levels by curcumin co-incubated with different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin only (A and B) or with As.A (C) and GSH (D). After 3 hr incubation (B, C and D), cells were treated with mBBr (40 μM) and then further incubated for 30 min at 37℃. Changes in fluorescence intensity were detected with an excitation at 365 nm and an emission at 465 nm. Each value represents the mean ± S.D. (n = 8). *, ** significantly different from its corresponding control according to Student’s t-test (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01). #, ## significantly different in the same concentration group according to Student’s t-test (#, p < 0.05; ##, p < 0.01).
Figure 6.
Changes in curcumin-induced HO-1 level by different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin in the absence or presence of GSH (A), NAC (B) and As.A or SOD/catalase (C) for 12 hr. Western blot analysis was performed on cell lysates containing 20 μg (A and B) or 10 μg (C) protein with an antibody against HO-1 (Hsp32). The chemiluminescence was detected and quantified by a luminescent image analyzer. The results are mean ± S.D. (n=3 in case of A and C) or mean of duplicates with error bar (B). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 6.
Changes in curcumin-induced HO-1 level by different types of antioxidants. HeLa cells were treated with curcumin in the absence or presence of GSH (A), NAC (B) and As.A or SOD/catalase (C) for 12 hr. Western blot analysis was performed on cell lysates containing 20 μg (A and B) or 10 μg (C) protein with an antibody against HO-1 (Hsp32). The chemiluminescence was detected and quantified by a luminescent image analyzer. The results are mean ± S.D. (n=3 in case of A and C) or mean of duplicates with error bar (B). Different letters indicate a significant difference (p < 0.05) based on one-way ANOVA and the Tukey’s HSD test.
Figure 7.
Different roles of thiol antioxidants in modulating bioactivities of curcumin in experimental conditions.
Figure 7.
Different roles of thiol antioxidants in modulating bioactivities of curcumin in experimental conditions.
Table 1.
Operating condition of HPLC for curcuminoid analysis.
Table 1.
Operating condition of HPLC for curcuminoid analysis.
| Instrument |
L-6200 (Hitachi, Ltd. Tokyo, Japan) |
| Column |
packed column C18 (Shiseido, 4.6 mm ID × 150 mm × 5 µm) |
| Detector |
UV detector (UV-975, Jasco, Tokyo, Japan) |
| Flow rate |
1 mL/min |
| Injection volume |
20 µL |
| Mobile phase |
40% THF : 60% water : 1% citric acid |
| (v/v/v, adjust concentrated KOH, pH 3) |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).