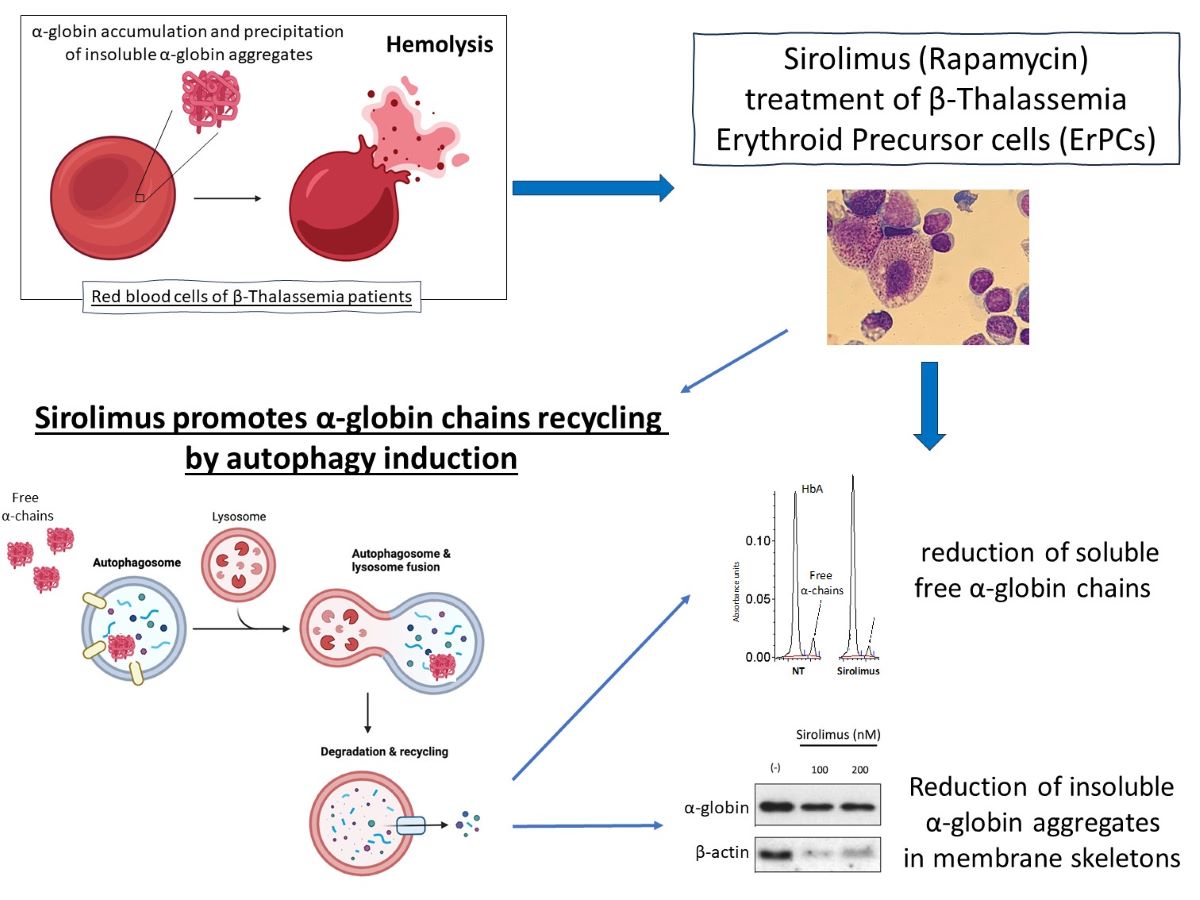
1. Introduction
The β-thalassemias are among the most common inherited monogenic hemoglobinopathies worldwide. The genetic alterations leading to the phenotype of β-thalassemias are a variety of autosomal mutations of the gene encoding the β-globin. This causes the absence or the low-level of β-globin in and adult hemoglobin (HbA) in erythropoietic cells [
1,
2,
3]. The most severe phenotypes display clinically relevant anemia and require regular transfusion (transfusion-dependent β-thalassemia, TDT, including thalassemia major). Worldwide, more than 300 mutations affecting the expression of the β-globin gene and causing β-thalassemia have now been reported [
4]. The low production of β-globin and HbA leads to an excess content of free α-globin, that precipitates and is highly toxic to the erythroid cells [
5]. In fact, it is widely accepted that one of the major complications in β-thalassemia is the excess of free α-globin chains [
6,
7,
8]. In this respect, rapamycin (sirolimus) [
9] is a repositioned drug of great interest.
Two major effects of sirolimus might occur in isolated erythroid precursor cells (ErPCs) from β-thalassemia patients, (a) the increased production of γ-globin mRNA and HbF [
10] and (b) the decrease of free α-globin chains [
11]. Concerning the decrease of free α-globin chains, this might be linked to activation of the γ-globin genes and production of γ-globin to generate the α
2γ
2 HbF tetramer [
10]. In addition, the decrease of free α-globin chains found in sirolimus-treated erythroid cultures might be due to activation of ULK1 (Unc-51–like kinase 1) dependent increase of autophagy [
12], as proposed by Lechauve et al. Since in vivo treatment of patients affected with hemoglobinopathies [
13,
14] and the first clinical trials on β-thalassemia patients [
15,
16,
17,
18] have been designed with low sirolimus amounts (in principle not affecting the immune system) [
19,
20,
21,
22], we tested whether low sirolimus concentrations (100-200 nM) were able to stimulate ULK-1 dependent autophagy [
12,
23,
24] with an associated decrease of the excess of free α-globin chains.
2. Results
A possible strategy to verify whether the autophagy process is implicated in α-globin clearance is to compare autophagy status in erythroid precursor cells (ErPCs) of healthy donors (cells lacking free α-globin accumulation), versus ErPCs of β-Thalassemia patients.
Therefore, the first point of the study was to verify whether autophagy is operating in erythroid cells from β-Thalassemia patients, where the excess of free α-globin chains is a clear pathophysiologic parameter. The second point was to confirm the excess of free α-globin chains in β-Thalassemia patients. The third point was to determine the effects of an inducer of fetal hemoglobin (sirolimus) on erythroid cells, both in vitro (using ErPCs isolated from β-Thalassemia patients, and in vivo (studying ErPCs isolated from sirolimus-treated β-Thalassemia patients participating to the NCT03877809 clinical trial [
16].
2.1. The autophagy program is activated in erythroid precursor cells from β-thalassemia patients
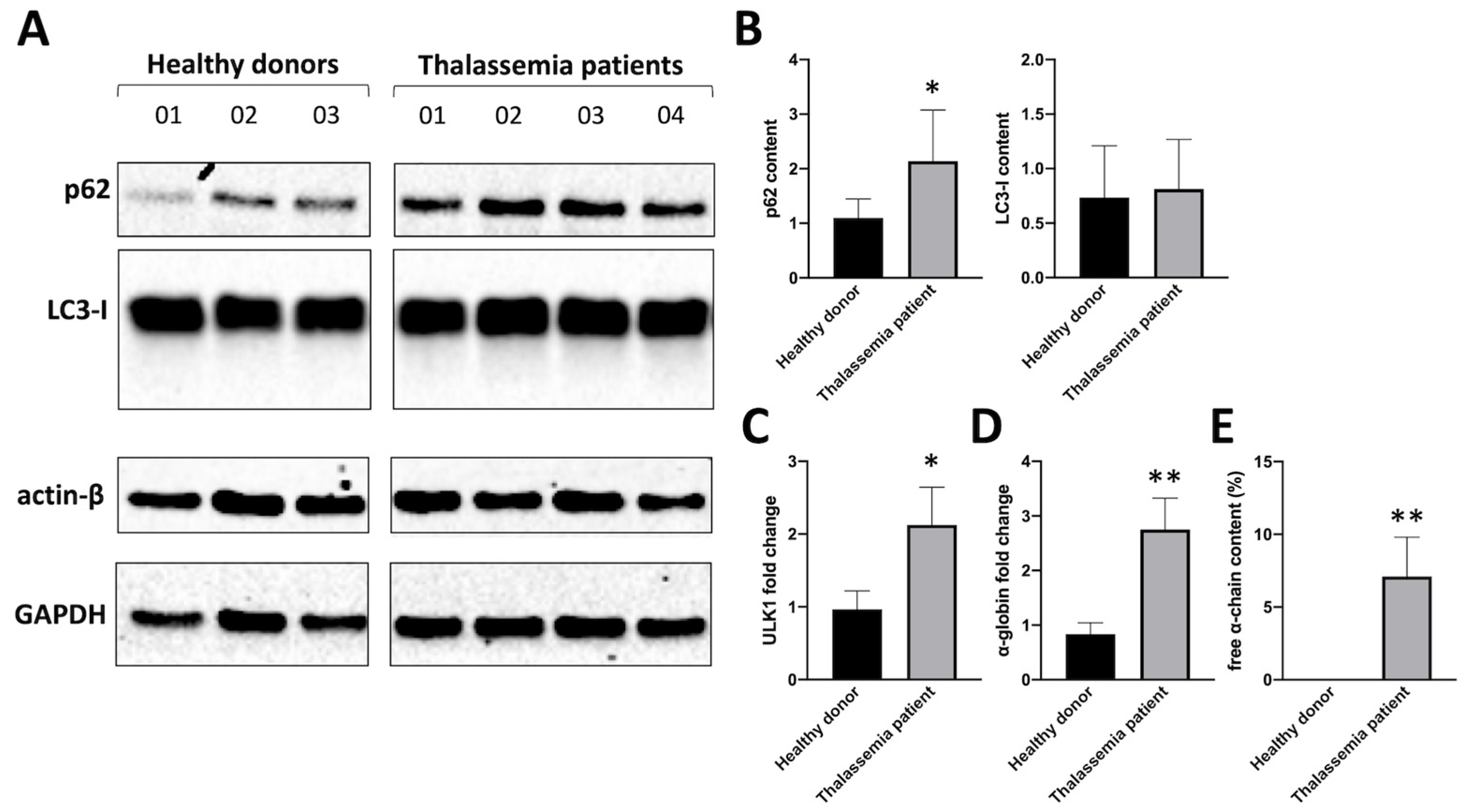
Figure 1A shows western blotting analyses suggesting that biochemical markers associated with autophagy are activated in β-thalassemia patients. Erythoid precursor cells (ErPCs) from three healthy donors and four β-thalassemia patients (carrying a β
0/β
0 genotype) were isolated and proteins analyzed by Western blotting.
Figure 1B shows the quantitative analysis of p62 and LC3-I content, confirming that the major differences were found when analysis of p62 conent was performed. Notably, p62 content in β-Thalassemia ErPCs was found to be much higher respect to healthy donor and this information is relevant, because p62 may be upregulated for the great quantity of free α-globin protein accumulated in these cells, that must be transported into autophagosomes (presumably by p62 itself).
As ULK-1 is deeply involved in autophagy (especially in the case of excess α-globin chain production by erythroid cells, as demonstrated by Lechauve et al. [
12]), the expression of ULK-1 mRNA and α-globin mRNA was analyzed by RT-qPCR.
Figure 1 (C and D) shows the changes of ULK-1 mRNA (
Figure 1C) and α-globin mRNA (
Figure 1D) in the β-thalassemia ErPCs, compared with ErPCs from healthy donors. HPLC analysis of hemoglobin was also performed on cell lysates to verify free α-globin excess in β-thalassemia cultured cells, confirming the expected accumulation of free α-globin chains in ErPCs of β-Thalassemia patients, while healthy donor does not present any peak in the HPLC chromatogram corresponding to free α-globin chains (
Figure 1E).
2.2. Sirolimus potentiates autophagy in erythroid precursor cells from β-thalassemia patients
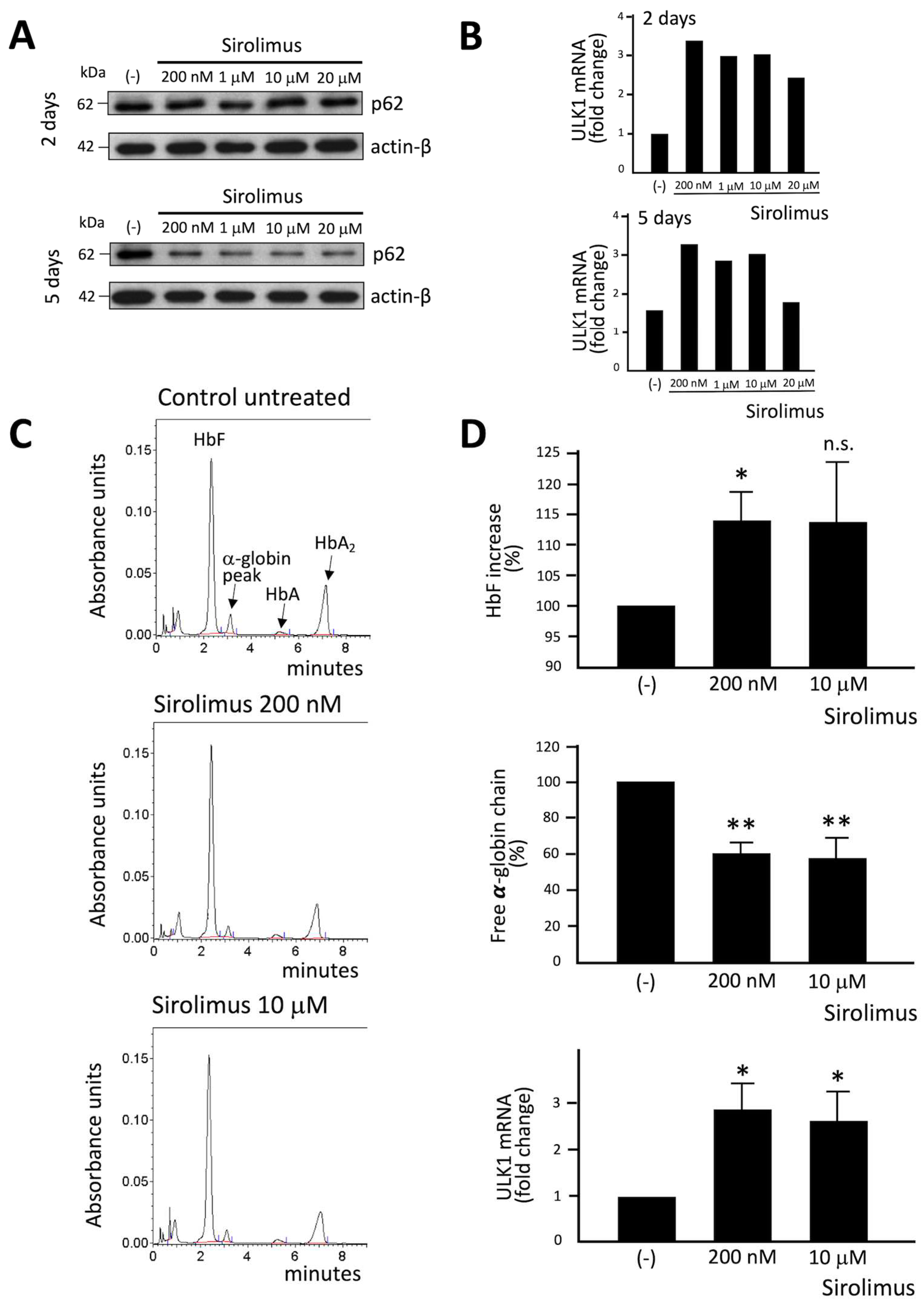
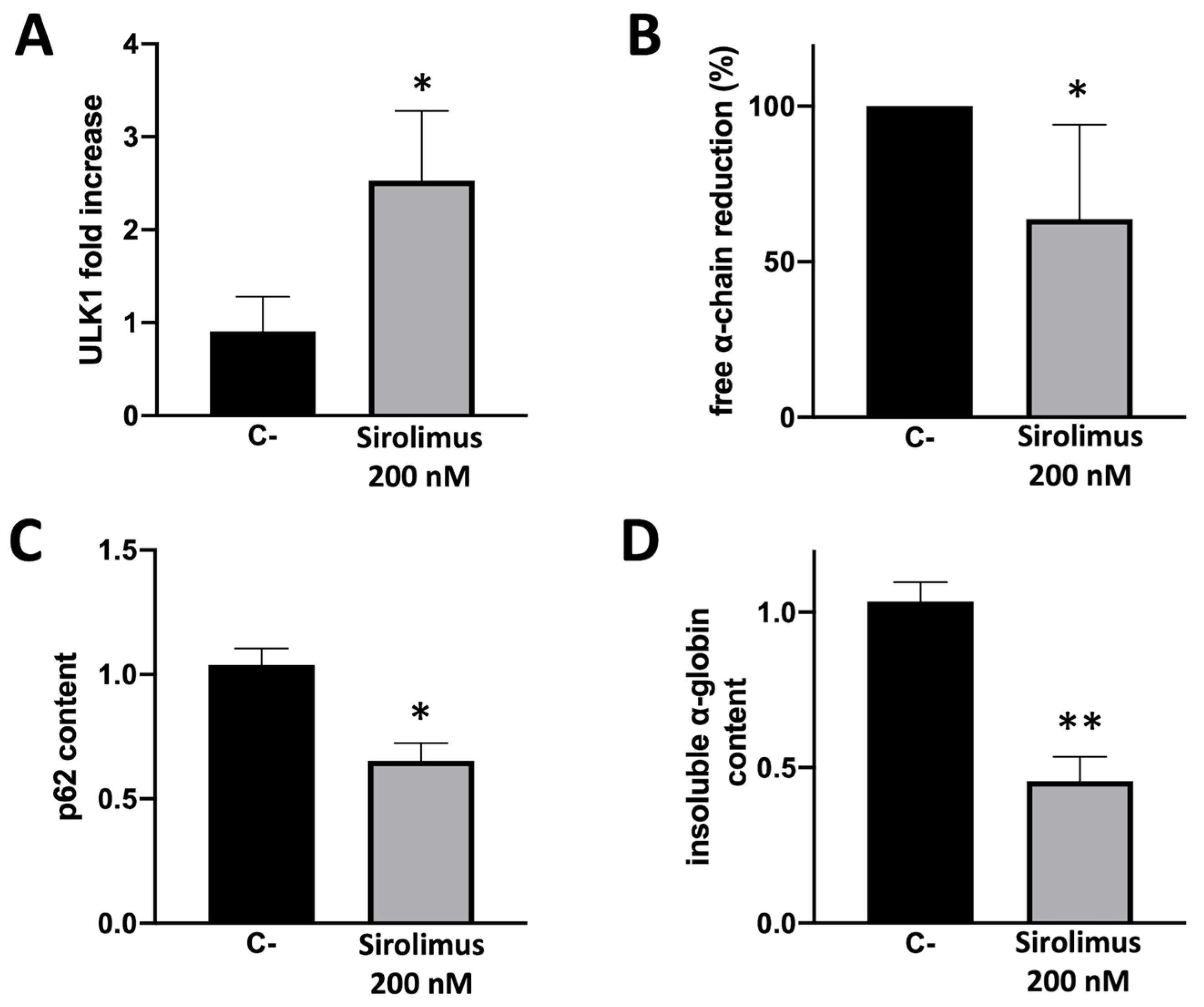
We tested several concentrations of Sirolimus (ranging from 200 nM and 20 μM respectively), in order to know the working concentration necessary to obtain a biological effect. We have also further investigated ULK1 gene expression (ULK1 complex drives formation of the phagophore and thereby autophagy initiation) by RT-qPCR and p62 levels by Western Blot technique. Western blot analysis showed that p62 content decreased in sirolimus treated ErPCs (
Figure 2A), especially after 5 days treatment. ULK1 mRNA content was found increased following Sirolimus treatment (
Figure 2B). 200 nM sirolimus and 2 days treatment were sufficient to induce ULK-1 gene expression.
The data on p62 were of interest, as the p62 protein is responsible for misfolded protein capturing and addressing to autophagosomes for subsequent degradation. The decrease of cellular content of p62 under treatment with autophagy inducers is considered to be evidence of activation of autophagy process. In this regard, is particularly intriguing the correlation with data obtained by HPLC analysis (
Figure 2C), showing a correlation between the decrease of p62 levels and free α-globin chain decrease after 2 and 5 days of treatment with Sirolimus. In fact, after 5 days of treatment, each tested concentration of Sirolimus produced a marked decrease in p62 and free α-globin chains levels (
Figure 2A–C).
Increased expression of γ-globin was verified following Sirolimus treatment and, as expected, HbF percentage is significatively higher in treated ErPCs (despite the great variability among patients) (
Figure 2D, upper side of the panel).
In conclusion, the reduction of free α-chain reduction values due to Sirolimus treatment of β-Thalassemia ErPCs in vitro (
Figure 2C,D, middle side of the panel) might be caused by two concurrent molecular events, i.e. the induction of HbF (
Figure 2D, upper side of the panel) and the increase of autophagy-associated ULK-1 gene expression (
Figure 2D, lower side of the panel).
2.3. Sirolimus-induced autophagy reduces accumulation of insoluble α-chains in membrane skeletons of cultured ErPCs
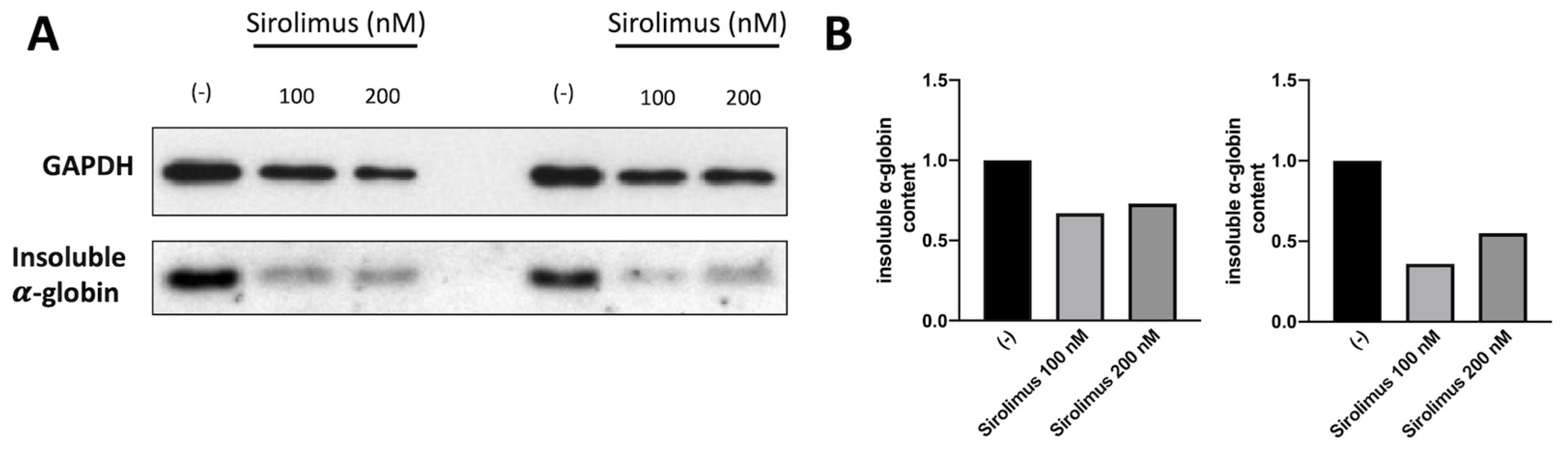
A key experiment in understanding whether Sirolimus-mediated induction of autophagy (see
Figure 1 and
Figure 2) affects α-globin clearance has been performed by analyzing the content of insoluble α-globin in lysed membranes of β-Thalassemia ErPCs. In fact, it is well known that α-globin excess produces insoluble α-globin aggregates that are toxic for cells and cause the premature cell death of ErPCs (the major cause of ineffective erythropoiesis). For this reason, the α-globin aggregates are stocked in “inclusion bodies” that are usually linked to the cytoplasmatic membrane. Accordingly, if Sirolimus is able to reduce the content of free α-globin by γ-globin pairing and/or autophagy induction, the content of insoluble α-globin in inclusion bodies should be lower. To verify this, we have lysed treated β-Thalassemia ErPCs in order to remove all soluble α-globin content (analyzed by HPLC), and we washed several time the membrane skeletons before proceeding with insoluble protein extraction as explained in the methods section. By following this protocol, we can check the content of accumulated α-globin protein in membrane skeletons of cultured ErPCs (
Figure 3).
Representative data shown in
Figure 3 indicate that even low concentrations of Sirolimus can induce α-globin clearance and lower accumulation of insoluble α-globin aggregates. These data suggest that autophagy induction may play a key role in the biological effect of Sirolimus on α-globin clearance in β-Thalassemia, in addition to γ-globin mRNA induction and HbF production.
We have analyzed five different patients treated with sirolimus 200 nM in vitro and we have found a significative increase in ULK1 gene expression, with a concomitant decrease of p62 adaptor protein together with a decrease in soluble and insoluble α-chain accumulation in erythroid cells (
Figure 4).
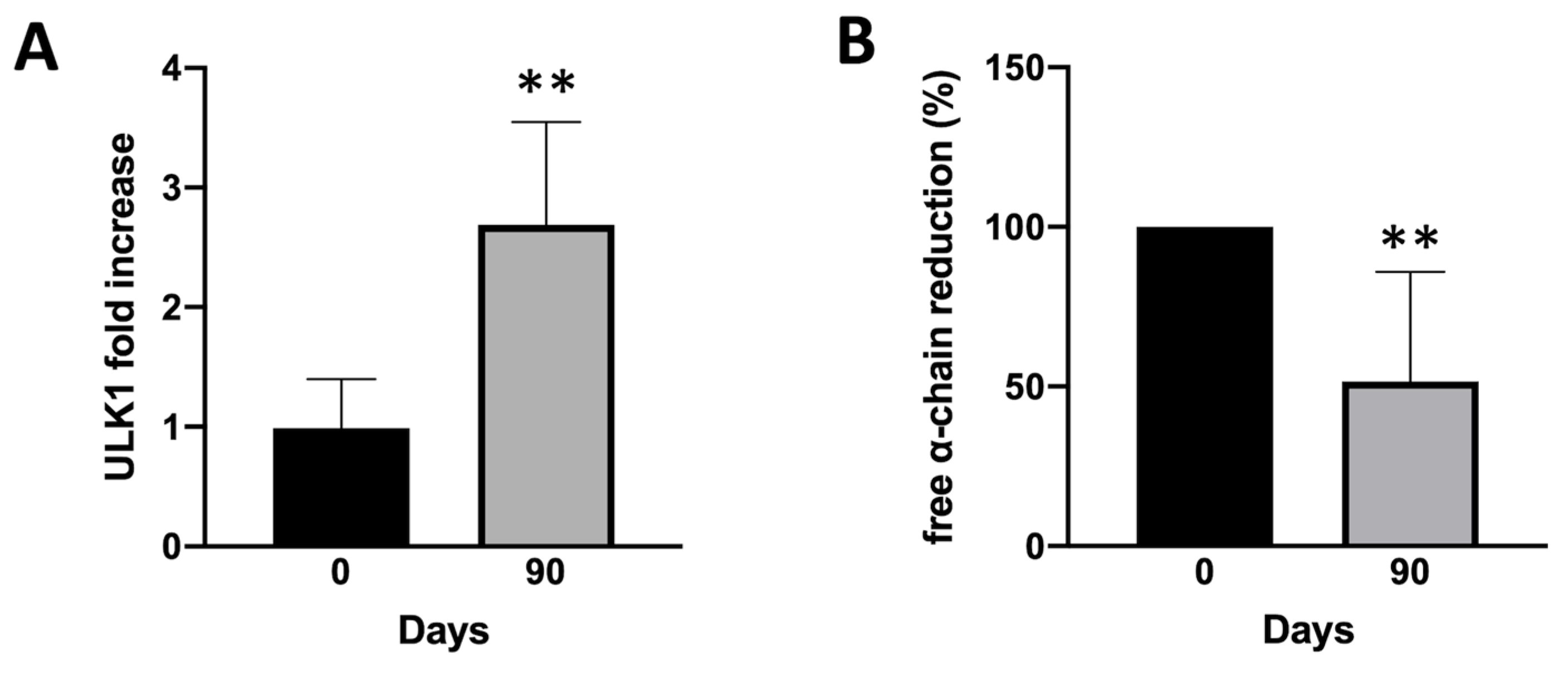
2.4. Sirolimus treatment in vivo leads to a lower accumulation of free α-chains
To sustain the hypothesis derived from experiments conducted in vitro, we wanted to retrospectively test the bio-banked RNA samples derived from SIRTHALACLIN clinical trial (NCT03877809) for ULK1 mRNA content (
Figure 5).
RT-qPCR analysis confirmed a clear increase in ULK-1 gene expression in ErPCs isolated from β-Thalassemia patients enrolled in SIRTHALACLIN clinical study after 3 months of daily Sirolimus administration. Once again, ULK-1 mRNA content seems to be higher when ErPCs are exposed to Sirolimus (this time in vivo) and, if this is correlated with autophagy induction as showed above, could be an important part of Sirolimus biological effects.
3. Discussion
The employment of mTOR inhibitors for the treatment of β-thalassemia and sickle-cell disease is supported by several laboratory investigations, pre-clinical studies and clinical data [
13,
25,
26,
27]. In agreement with this conclusion, the in vivo effects of mTOR inhibition were reported in a pre-clinical study by Wang et al. [
28], who found that sirolimus improved anemia and reduced organ damages in a murine model of sickle cell disease. Accordingly, Khaibullina et al. reported that sirolimus increases HbF in another model of sickle cell mice [
29].
Concerning clinical data, Al-Khatti and Alkhunaizi, reported a study on two patients with SCD who were treated with sirolimus as part of their post-kidney transplantation immunosuppressive regimen. During this study, they observed an increase in HbF levels in the treated patients. In addition, there was a further increase in HbF level when sirolimus and hydroxycarbamide were combined [
14]. The conclusion of this study was in line with the paper by Gaudre et al. [
13] reporting improved HbF production with everolimus, another mTOR inhibitor. This study was also conducted on a kidney transplant recipient patient with SCD. These studies supported the recent Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) of sirolimus by the European Medicinal Agency (EMA) for the treatment of β-thalassemia (code EU/3/15/1585) and of SCD (code EU/3/17/1970). ODD of sirolimus as HbF inducer in β-thalassemia and SCD was also obtained by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Clinical data of the possible use of sirolimus in β-thalassemia will be obtained by two clinical trials, NCT03877809 and NCT04247750, focusing on the in vivo effects of sirolimus in treated β-thalassemia patients [
16,
17]. A first report concerning the NCT03877809 trial (Sirthalaclin) was recently published by Zuccato et al. [
18], who demonstrated increased content of γ-globin mRNA and increased production of HbF in ErPCs isolated from sirolimus-treated β-thalassemia patients.
In addition of the effects of rapamycin on HbF, this drug might be of great interest in protocols for β-thalassemia, because it reduced the α-globin/β-globin unbalance by activating autophagy. This was proposed by Lechauve et al. (2019) who reported the ULK1 (Unc-51–like kinase 1) dependent increase of autophagy in a mouse thalassemia model system, leading to a sharp decrease of free α-globin chains [
12].
Our research group has recently obtained K562 cellular clones that are able to hyper-express α-globin protein [
30], in this work we have demonstrated that accumulation of toxic α-globin is able to induce apoptosis proportionally to its production/accumulation rate. Interestingly, we have founded that autophagy is spontaneously triggered by accumulation of α-globin protein and cellular clones that produce higher levels of the protein seems to have higher levels of p62 adaptor protein, probably in order to manage α-globin clearance. In the present work we have obtained similar evidence analyzing p62 content in healthy donor cells compared to β-thalassemia erythroid cells, confirming that accumulation of α-globin protein requires higher levels of p62.
Moreover, we demonstrated that sirolimus treatment of cultured β-thalassemia ErPCs in vitro can trigger/potentiate autophagy process by reducing p62 levels and concurrently reduce free α-globin chains presence in the cytoplasm and insoluble α-globin aggregates content in membrane skeletons. This data obtained on human β-thalassemia ErPCs, confirm and strengthen the data obtained by Lechauve et al. [
12] in a β-thalassemia mouse model. In addition, we have obtained the same results using a much lower concentration of sirolimus on cells, comparable to therapeutic dosages employed in clinical trials as NCT03877809 and NCT04247750.
The most important result of our study is the demonstration that low concentrations of sirolimus (100 and 200 nM) were able to induce ULK1 and to reduce p62, strongly suggesting activation of autophagy in erythroid precursor cells (ErPCs) from β-thalassemia patients (
Figure 4). This was confirmed in our study using ErPCs from sirolimus treated β-thalassemia patients participating to the NCT03877809 trial (Sirthalaclin) clinical trial. In these ErPCs ULK1 was found upregulated (
Figure 5A) and the excess of free α-globin chains strongly reduced (
Figure 5B).
In conclusion, presented data support the hypothesis that, in addition to induction of fetal hemoglobin, Sirolimus reduces the excess of free α-globin chains by activating autophagy via ULK-1 gene expression, both in vitro and in vivo. Autophagy, reduction of the excess of insoluble free α-globin chains and expression of autophagy-related genes (including ULK-1) should be considered, in addition of γ-globin and HbF production, as endpoints in sirolimus based clinical trials for β-thalassemia, such as the NCT03877809 (2019) and NCT04247750 (2020) clinical trials.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Culture and treatment of Human Erythroid Precursor Cells
The two-phase liquid culture procedure was employed as previously described [
18,
31,
32,
33]. Mononuclear cells were isolated from peripheral blood samples of β-thalassemia patients by centrifugation using Lympholyte® (Cederlane, Burlington, ON, Canada). After isolation, the mononuclear cells were washed three times in PBS solution and seeded in α-minimal essential medium (α-MEM, Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) supplemented with 10% FBS (Celbio, Milano, Italy), 1 µg/ml cyclosporine A (Sandoz, Basel, Switzerland), and 10% conditioned medium from CM5637 bladder carcinoma cell line culture. The cultures were incubated in standard atmosphere of 5% CO2 at 37°C. After 7 days in this phase I culture, non-adherent cells were harvested from the flask, washed with PBS, and then cultured in phase II medium, composed of α-MEM medium, 30% FBS, 1% deionized bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), 10
-5 M β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), 2 mM L-glutamine (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA), 10
-6 M dexamethasone (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) and 1 U/ml human recombinant erythropoietin (EPO) (Tebu-bio, Magenta, Milano, Italy) and stem cell factor (SCF, BioSource International, Camarillo, CA, USA) at the final concentration of 10 ng/ml. After five days of expansion in phase II medium, cells were plated at 2 mln cells/mL concentration and treated with Sirolimus (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) resuspended in EtOH for additional 5 days.
4.2. RNA extraction and RT-qPCR analysis
The total cellular RNA was extracted from ErPCs by using TRI Reagent® (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, Missouri, USA) and following the manufacturer’s instructions. The isolated RNA was washed once with cold 75% ethanol, dried and dissolved in 10 μl nuclease free water before use.
For gene expression analysis 500 ng of total RNA was reverse transcribed by using the TaqMan® Reverse Transcription Reagents and random hexamers (Applied Biosystems, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Quantitative real time PCR assay, to quantify the expression of the globin genes, was carried out using two different reaction mixtures, the first one containing α, β, γ-globin probe and primers, the second one containing GAPDH, RPL13A, β-actin probes and primers. In parallel, ULK1 gene expression was quantified and normalized with the same reference sequences employed for globin gene expression normalization. The primers and probes used are listed in
Table 1.
Each reaction mixture contained 1x TaKaRa Ex Taq® DNA Polymerase (Takara Bio Inc., Shiga, Japan), 300 nM forward and reverse primers and the 200 nM probes (Integrated DNA Technologies, Castenaso, Italy). The assays were carried out using CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA). After an initial denaturation at 95°C for 1 min, the reactions were performed for 50 cycles (95°C for 15 sec, 60°C for 60 sec). Data were analyzed by employing the CFX manager software (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA). To compare gene expression of each template amplified, the ΔΔCt method was used [
34].
4.3. HPLC analyses of hemoglobin
To evaluate free α-globin variation, HPLC analysis was carried using fresh lysates of ErPCs. The ErPCs were centrifuged at 1500 rpm for 5 minutes and washed with PBS. The pellets were then lysed in a predefined volume of water for HPLC (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Missouri, USA) in order to obtain protein extracts suitable for HPLC analysis. Lysed pellets in water for HPLC were incubated 20 minutes in ice and then pelleted at 16000 rpm for 15 minutes at 4°C, finally protein extracts were recovered in a pre-chilled 1,5 mL tube and injected in HPLC system. Hemoglobin analysis was performed by loading the protein extracts into a PolyCAT-A cation exchange column and then eluted in a sodium-chloride-BisTris-KCN aqueous mobile phase using HPLC Beckman Coulter instrument System Gold 126 Solvent Module-166 Detector [
31]. The reading is performed at a wavelength of 415nm, and a commercial solution of purified human HbF (Sigma-Aldrich, Saint Louis, Missouri, USA) extracts has been used as standard.
4.4. Western Blotting of soluble fractions
To analyze soluble fractions of ErPCs, we employed the same protein extracts prepared for HPLC analysis as above explained. Protein concentration was determined using PierceTM BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) before to run the gels. Twenty μg of cytoplasmic extracts were denatured for 5 min at 98°C in SDS sample buffer (Cell Signalling Technology, Danverss, MA, USA) and loaded on hand casted SDS-PAGE 15% gel (10 cm × 8 cm) in Tris-glycine Buffer (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA). Spectra prestained multicolour protein ladder (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) was always used as standards to determine molecular weight (size range 10–260 kDa). The electrotransfer to 0.2 μm pore size nitrocellulose membrane (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA) was performed over-night at 360 mA and 4°C in standard Tris-Glycine-MeOH transfer buffer. The membranes were prestained with Ponceau S Solution (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO, USA) to verify the efficiency of the transfer, washed with TBS-T (Cell Signalling Technology, Danversss, MA, USA) and then blocked with standard blocking buffer (5% milk in TBST) for 1 h at room temperature. The membranes were washed three times with TBS-T and incubated with the primary antibody in 10 ml of 5% BSA in TBS-T with gentle shaking overnight at 4 °C. The next day, the membranes were washed three times with TBST and incubated in 10 ml of blocking buffer, with gentle shaking for 2 h at room temperature, with an appropriate HRP-conjugated secondary antibody. Finally, after three washes with TBS-T, each membrane was incubated with 5 ml LumiGLO® detection working solution (Cell Signalling Technology, Danverss, MA, USA) and exposed to x-ray film (Pierce, Euroclone S.p.A., Pero, MI, Italy). In order to re-probe the membranes, they were stripped using the RestoreTM Western Blot Stripping Buffer (Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA), incubating the membranes for 30 minutes at 37-42°C with moderate agitation. Blots image were acquired and analyzed using Bio-Rad Image Lab Software (Bio-Rad, Hercules, California, USA). A list of employed primary and secondary antibody is reported in
Table 2.
4.5. Western Blotting of insoluble fractions
The protocol followed for detection of insoluble α-chains starts with standard cytoplasmatic extracts obtained from cultured ErPCs (as described for HPLC samples). Once the cytoplasmatic extracts are separated from lysed membranes, several wash steps in hypotonic water are needed to clean membrane skeletons pellet from residual hemoglobin (at least five wash step in PBS). At the end of washing steps, membranes are extracted from the pellet with addition of Sodium Borate extraction buffer (Sodium Borate 68mM-pH 8,2 and 0,1% Tween-20) for 20 minutes, keeping the samples in ice and vortexing every 5 minutes. Finally, the samples are centrifuged at 4°C for 30 minutes at 16000g, extracted insoluble proteins pellets are resuspended in adequate volume of 1x SDS sample buffer, boiled 5 minutes and well vortexed and stocked at -80°C [
35]. As reported in
Table 3, in this case data were normalized with GAPDH, as it was more present inside membranes protein extracts in respect to standard cytoplasmatic extracts. After sample preparation, the western blot procedure was the same described above in western blotting of soluble fractions.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
All the data were normally distributed and presented as mean ± S.D. Statistical differences between groups were compared using Prism Software v9.02 and employing two-tail paired t-test. Statistical differences were considered significant when p< 0.05 (*), highly significant when p< 0.01 (**).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.Z., A.F., M.R.G. and R.G.; methodology, validation, M.Z., C.Z.; J.G., L.C.C.; formal analysis, M.Z., C.Z., J.G., A.S. and M.F.; investigation, M.Z. and A.F.; lab resources, R.G. and A.F.; data curation, M.Z., A.S., M.F., M.R.G. and A.F.; statistical analysis, M.Z., J.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.Z., R.G. and A.F.; writing—review and editing, M.Z., R.G. and A.F.; supervision, R.G. and A.F.; project administration, A.F. and M.P.; funding acquisition, R.G., M.P. and A.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was sponsored by the Wellcome Trust (innovator award 208872/Z/17/Z) and AIFA (AIFA-2016-02364887). The research leading to these results has received funding also from the UE THALAMOSS Project (Thalassemia Modular Stratification System for Personalized Therapy of Βeta-Thalassemia; no. 306201-FP7-HEALTH-2012-INNOVATION-1), FIR and FAR funds from the University of Ferrara. This research was also supported by the Interuniversity Consortium for the Biotechnology (CIB), Italy.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and the use of human material was approved by the Ethics Committee of Ferrara’s District, protocol name: THAL-THER, document number 533/2018/Sper/AOUFe, approved on 14 November 2018. All samples of peripheral blood were obtained after receiving written informed consent from donor patients or their legal representatives. Recruitment of the SIRTHALACLIN pilot clinical trial and data collection (EudraCT n° 2018-001942-33, NCT 03877809) was at the Thalassemia Centre of Azienda Ospedaliera-Universitaria S.Anna (Ferrara, Italy). The β-thalassemia patients have been recruited among patients with β+/β+ and β+/β0 genotypes. The study was approved by Ethical Committee in charge of human studies at Arcispedale S.Anna, Ferrara (release of the approval: November 14, 2018). Informed written consent from all participants was obtained before recruiting them into the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all β-thalassemia patients involved in the study before the blood was drawn. No details have been included in the manuscript that allows patient identification.
Data Availability Statement
Materials and further information on the data will be freely available upon request to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
We thank Associazione Tutti per Chiara Onlus for supporting M.Z. with a post-doc fellowship. This study is dedicated to the memory of Chiara Gemmo and Elio Zago.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Weatherall, D.J. Phenotype-genotype relationships in monogenic disease: lessons from the thalassaemias. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanello, R. , Origa, R. β-thalassemia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2010, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Origa, R. β-Thalassemia. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thein, S.L. (2013). The molecular basis of β-thalassemia. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2013, 3, a011700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieder, R.F. , James, G.W. 3rd. Imbalance in alpha and beta globin synthesis associated with a hemoglobinopathy. J. Clin. Invest. 1974, 54, 948–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Villalobos, M. , Blanquer, M., Moraleda, J.M., Salido, E.J., Perez-Oliva, A.B. New Insights Into Patho-physiology of β-Thalassemia. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 880752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.Y. , Ren, Z.R., Zhang, J.Z., Guo, X.B., Wang, Q.X., Wang, S., Lin, D., Gong, X.L., Li, W., Huang, S.Z., et al. Restoration of the balanced alpha/beta-globin gene expression in beta654-thalassemia mice using combined RNAi and antisense RNA approach. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 2616–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettananda, S. , Gibbons, R.J., Higgs, D.R. α-Globin as a molecular target in the treatment of β-thalassemia. Blood 2015, 125, 3694–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B. , Zhang, Q., Ma, L., Zhao, D.S., Zhao, P., Yan, P. Overview of Research into mTOR Inhibitors. Molecules 2022, 27, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibach, E. , Bianchi, N., Borgatti, M., Zuccato, C., Finotti, A., Lampronti, I., Prus, E., Mischiati, C., Gambari, R. Effects of rapamycin on accumulation of alpha-, β- and gamma-globin mRNAs in erythroid precursor cells from β-thalassaemia patients. Eur. J. Haematol. 2006, 77, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, L.C. , Breda, L., Breveglieri, G., Zuccato, C., Finotti, A., Lampronti, I., Borgatti, M., Chiavilli, F., Gamberini, M.R., Satta, S., Manunza, L., De Martis, F.R., Moi, P., Rivella, S., Gambari, R., Bianchi, N. A validated cellular biobank for β-thalassemia. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechauve, C. , Keith, J., Khandros, E., Fowler, S., Mayberry, K., Freiwan, A., Thom, C.S., Delbini, P., Romero, E.B., Zhang, J., Motta, I., Tillman, H., Cappellini, M.D., Kundu, M., Weiss, M.J. The autophagy-activating kinase ULK1 mediates clearance of free α-globin in β-thalassemia. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaav4881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gaudre, N. , Cougoul, P., Bartolucci, P., Dörr, G., Bura-Riviere, A., Kamar, N., Del Bello, A. Improved Fetal Hemoglobin With mTOR Inhibitor-Based Immunosuppression in a Kidney Transplant Recipient With Sickle Cell Disease. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 2212–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khatti, A.A. , Alkhunaizi, A.M. Additive effect of sirolimus and hydroxycarbamide on fetal haemoglobin level in kidney transplant patients with sickle cell disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 959–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamberini, M.R. , Prosdocimi, M., Gambari, R. Sirolimus for Treatment of β-Thalassemia: From Pre-Clinical Studies to the Design of Clinical Trials. Health Educ. Public Health 2021, 4, 425–435. [Google Scholar]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT03877809, A Personalized Medicine Approach for Beta-thalassemia Transfusion Dependent Patients: Testing SIROLIMUS in a First Pilot Clinical Trial (SIRTHALACLIN), March 18, 2019. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03877809 (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- ClinicalTrials.gov. NCT04247750, Treatment of Beta-thalassemia Patients With Rapamycin (Sirolimus): From Pre-clinical Research to a Clinical Trial (THALA-RAP), January 30, 2020. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04247750 (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Zuccato, C. , Cosenza, L.C., Zurlo, M., Gasparello, J., Papi, C., D’Aversa, E., Breveglieri, G., Lampronti, I., Finotti, A., Borgatti, M., Scapoli, C., Stievano, A., Fortini, M., Ramazzotti, E., Marchetti, N., Prosdocimi, M., Gamberini, M.R., Gambari, R. Expression of γ-globin genes in β-thalassemia patients treated with sirolimus: results from a pilot clinical trial (Sirthalaclin). Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2022, 13, 20406207221100648. [Google Scholar]
- Zurlo, M. , Nicoli, F., Proietto, D., Dallan, B., Zuccato, C., Cosenza, L.C., Gasparello, J., Papi, C., d’Aversa, E., Borgatti, M., Scapoli, C., Finotti, A., Gambari, R. Effects of Sirolimus treatment on patients with β-Thalassemia: Lymphocyte immunophenotype and biological activity of memory CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 353–364. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, S. , Lee, E., Lee, K.W. Therapeutic Implications of Autophagy Inducers in Immunological Disorders, Infection, and Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallet, N. , Fernández-Ramos, A.A., Loriot, M.A. Impact of Immunosuppressive Drugs on the Metabolism of T Cells. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 341, 169–200. [Google Scholar]
- Rostamzadeh, D. , Yousefi, M., Haghshenas, M.R., Ahmadi, M., Dolati, S., Babaloo, Z. mTOR Signaling pathway as a master regulator of memory CD8+ T-cells, Th17, and NK cells development and their functional properties. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 12353–12368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.G. , Hurley, J.H. Structure and function of the ULK1 complex in autophagy. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 39, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zachari, M. , Ganley, I.G. The mammalian ULK1 complex and autophagy initiation. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mischiati, C. , Sereni, A., Lampronti, I., Bianchi, N., Borgatti, M., Prus, E., Fibach, E., Gambari, R. Rapamycin-mediated induction of gamma-globin mRNA accumulation in human erythroid cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2004, 126, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecoraro, A. , Troia, A., Calzolari, R., Scazzone, C., Rigano, P., Martorana, A., Sacco, M., Maggio, A., Di Marzo, R. Efficacy of Rapamycin as Inducer of Hb F in Primary Erythroid Cultures from Sickle Cell Disease and β-Thalassemia Patients. Hemoglobin 2015, 39, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acar, M. , Jupelli, M., MacBeth, K., Schwickart, M. Rapamycin (Sirolimus) and Rap-536 Increase Red Blood Cell Parameters through Distinct Mechanisms in Wild-Type and Thalassemic Mice. Blood 2020, 136, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. , Tran, J., Wang, H., Guo, C., Harro, D., Campbell, A.D., Eitzman, D.T. mTOR Inhibition improves anaemia and reduces organ damage in a murine model of sickle cell disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaibullina, A. , Almeida, L.E., Wang, L., Kamimura, S., Wong, E.C., Nouraie, M., Maric, I., Albani, S., Finkel, J., Quezado, Z.M. Rapamycin increases fetal hemoglobin and ameliorates the nociception phenotype in sickle cell mice. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2015, 55, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurlo, M. , Gasparello, J., Cosenza, L.C., Breveglieri, G., Papi, C., Zuccato, C., Gambari, R., Finotti, A. Production and Characterization of K562 Cellular Clones Hyper-Expressing the Gene Encoding α-Globin: Preliminary Analysis of Biomarkers Associated with Autophagy. Genes 2023, 14, 556. [Google Scholar]
- Zuccato, C. , Cosenza, L.C., Zurlo, M., Lampronti, I., Borgatti, M., Scapoli, C., Gambari, R., Finotti, A. Treatment of Erythroid Precursor Cells from β-Thalassemia Patients with Cinchona Alkaloids: Induction of Fetal Hemoglobin Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 13433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, L.C. , Gasparello, J., Romanini, N., Zurlo, M., Zuccato, C., Gambari, R., Finotti, A. Efficient CRISPR-Cas9-based genome editing of β-globin gene on erythroid cells from homozygous β039-thalassemia patients. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 21, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, L.C. , Zuccato, C., Zurlo, M., Gambari, R., Finotti, A. Co-Treatment of Erythroid Cells from β-Thalassemia Patients with CRISPR-Cas9-Based β039-Globin Gene Editing and Induction of Fetal Hemoglobin. Genes 2022, 13, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuccato, C. , Cosenza, L.C., Zurlo, M., Breveglieri, G., Bianchi, N., Lampronti, I., Gasparello, J., Scapoli, C., Borgatti, M., Finotti, A., Gambari, R. The rs368698783 (G>A) Polymorphism Affecting LYAR Binding to the Aγ-Globin Gene Is Associated with High Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF) in β-Thalassemia Erythroid Precursor Cells Treated with HbF Inducers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 776. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khandros, E. , Thom, C.S., D’Souza, J., Weiss, M.J. Integrated protein quality-control pathways regulate free α-globin in murine β-thalassemia. Blood 2012, 119, 5265–5275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).