Submitted:
01 September 2023
Posted:
01 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Objects detection
1.2. Relevant datasets
1.3. Current study
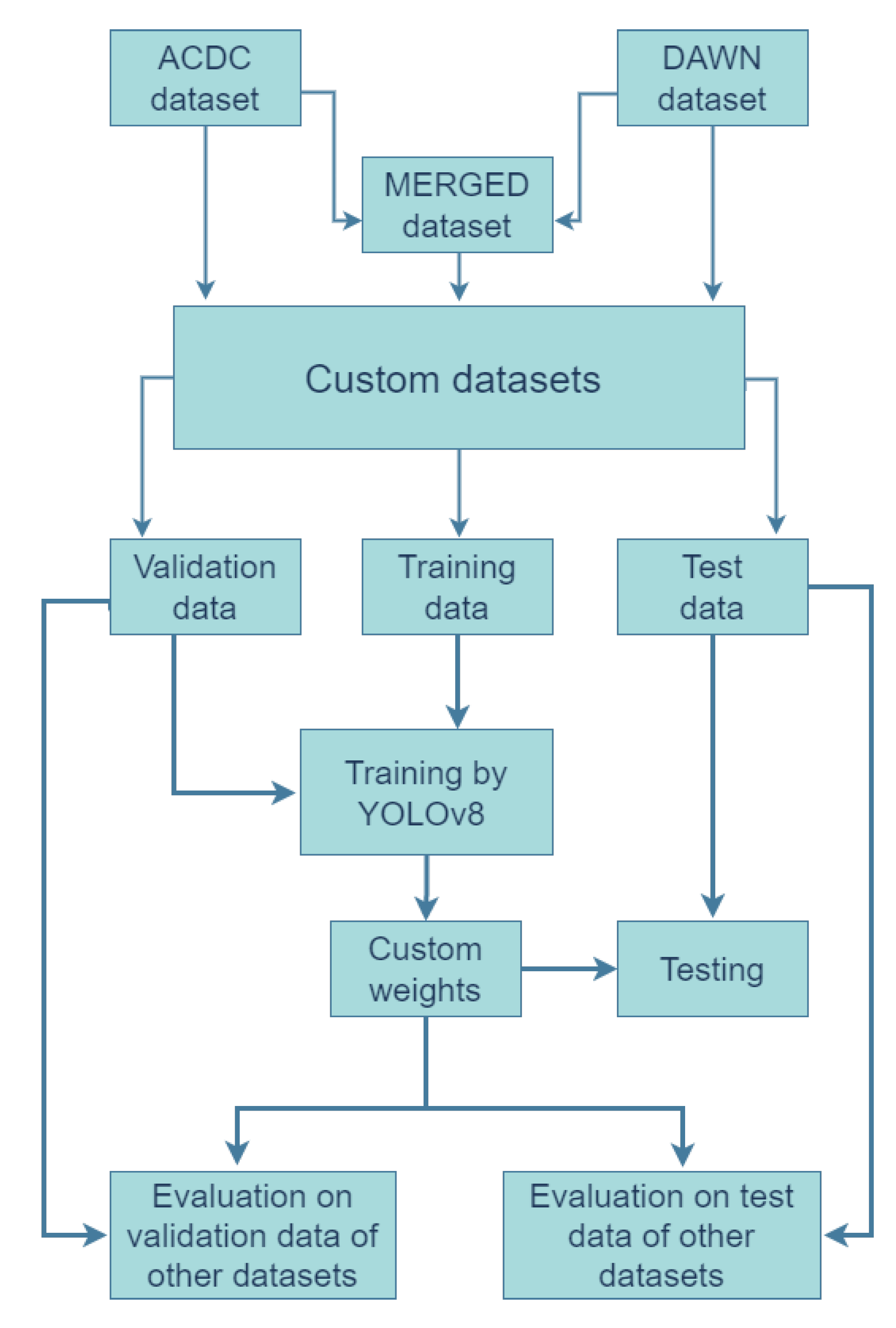
2. Methodology
2.1. Data collection and annotation
2.2. Data processing and merging
2.3. Training and evaluation
3. Experiments and Results Discussion
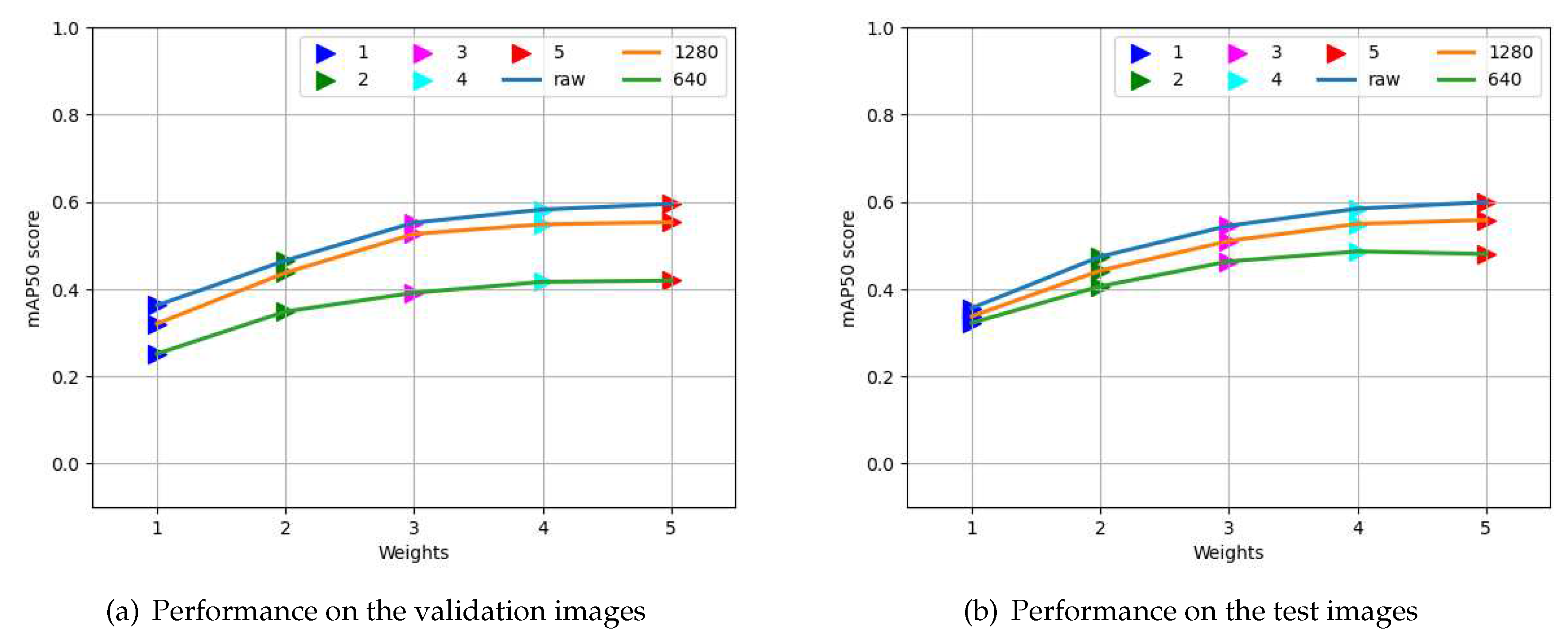
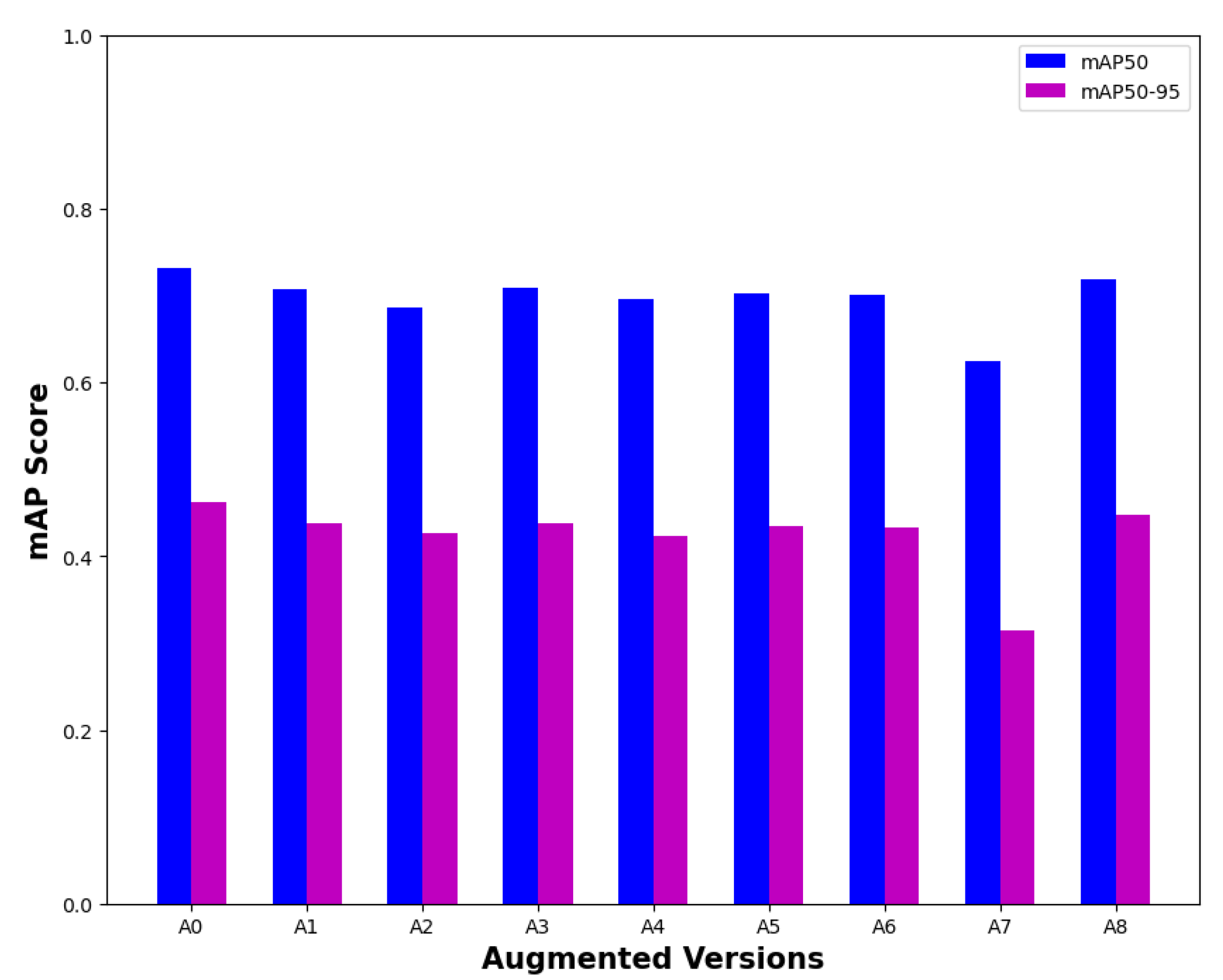
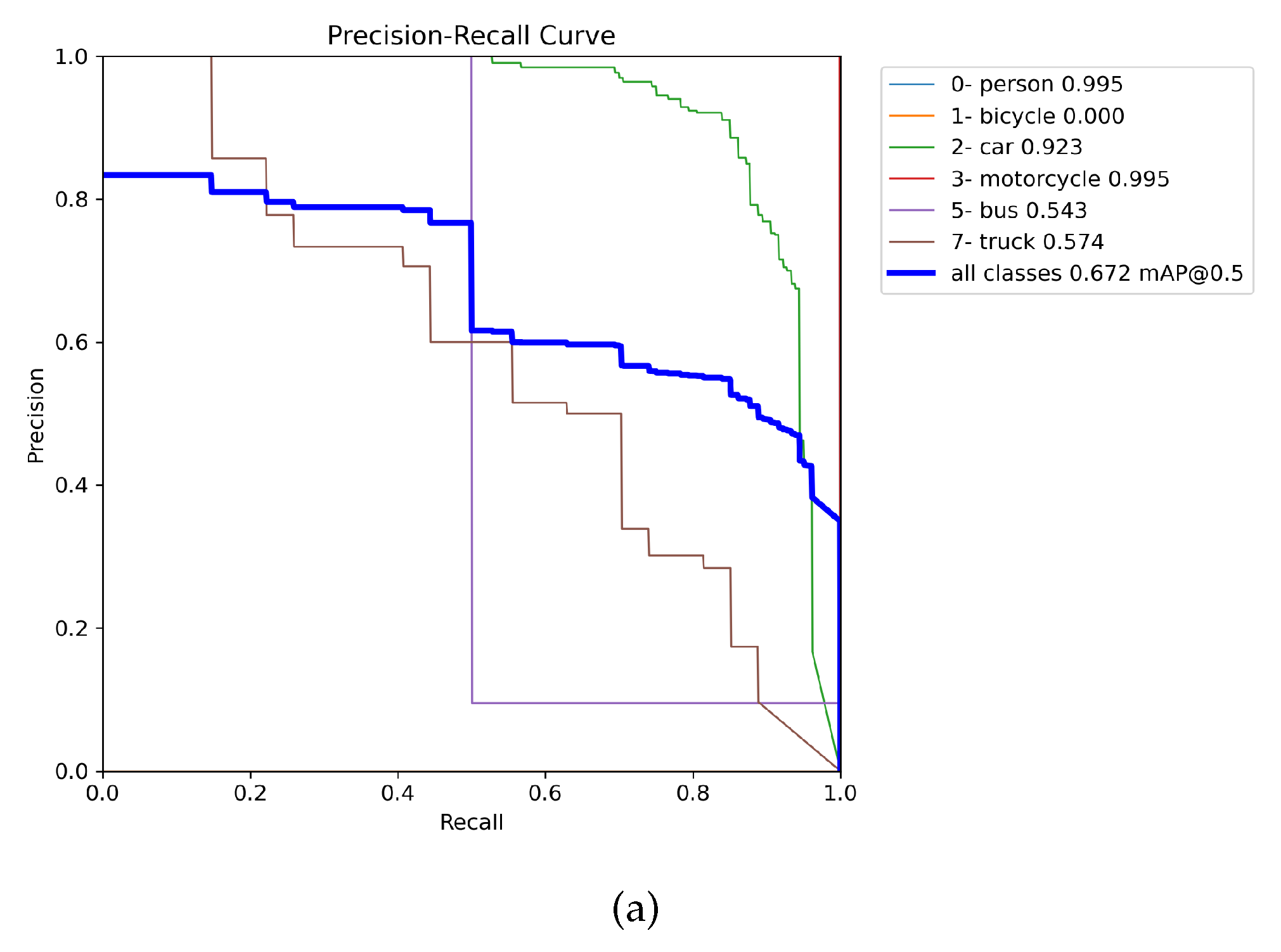
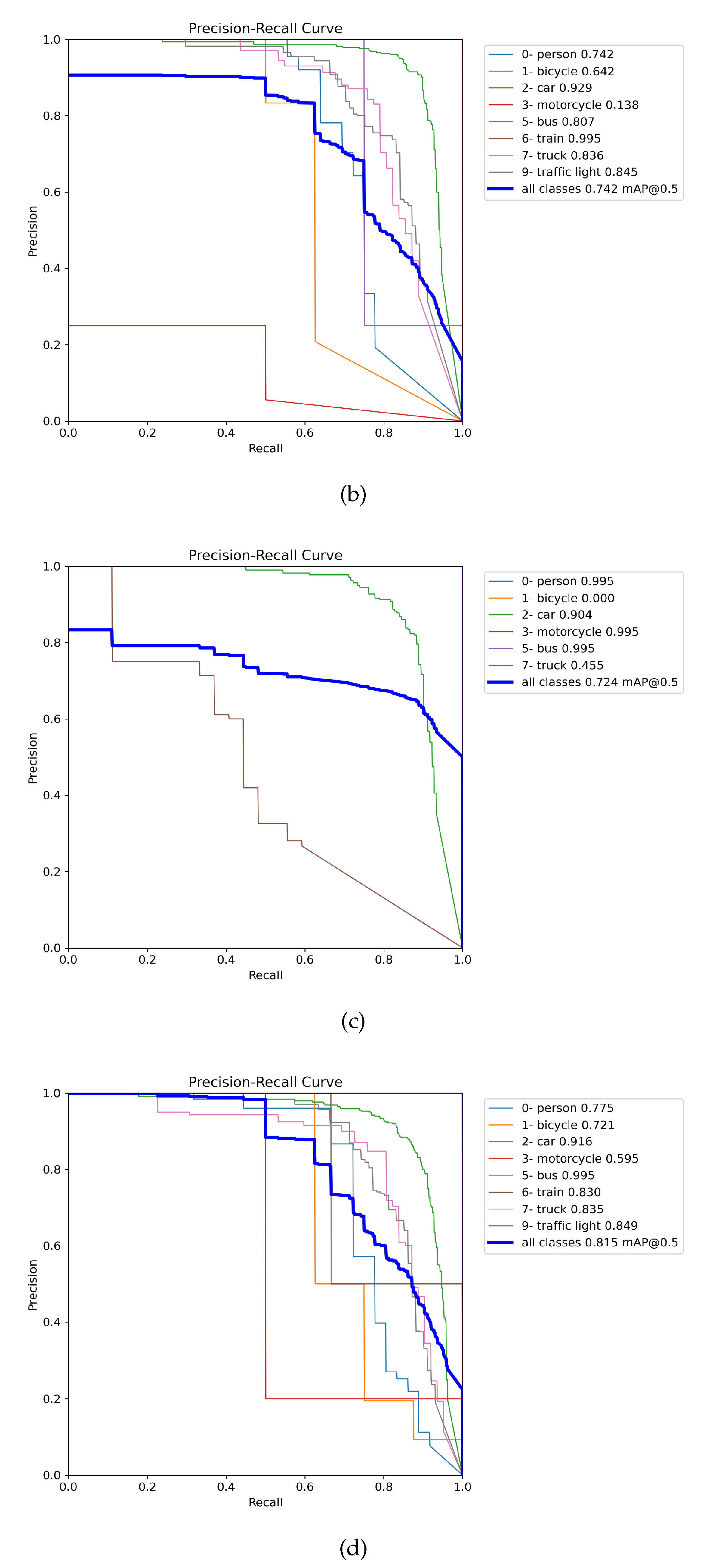
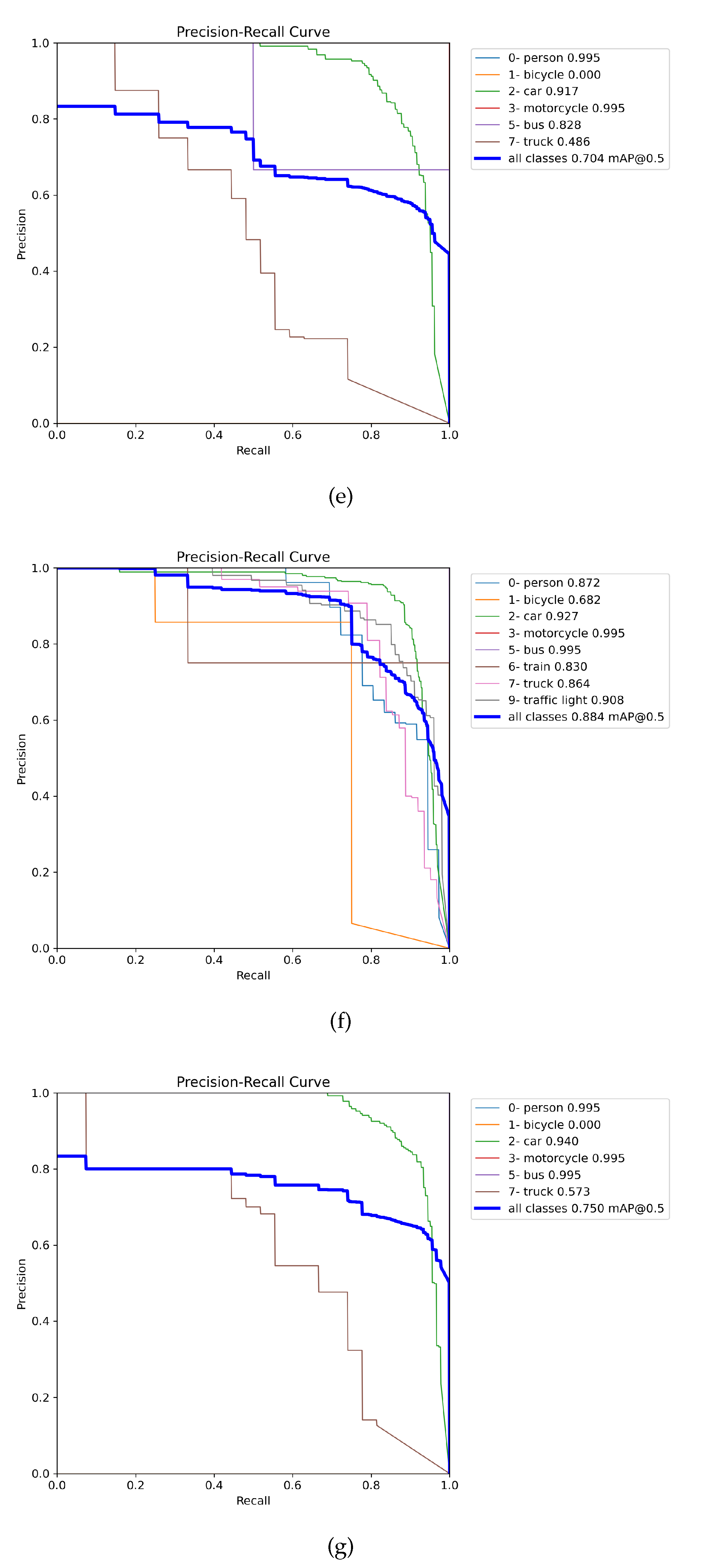
3.1. Choosing the best weights and augmentation
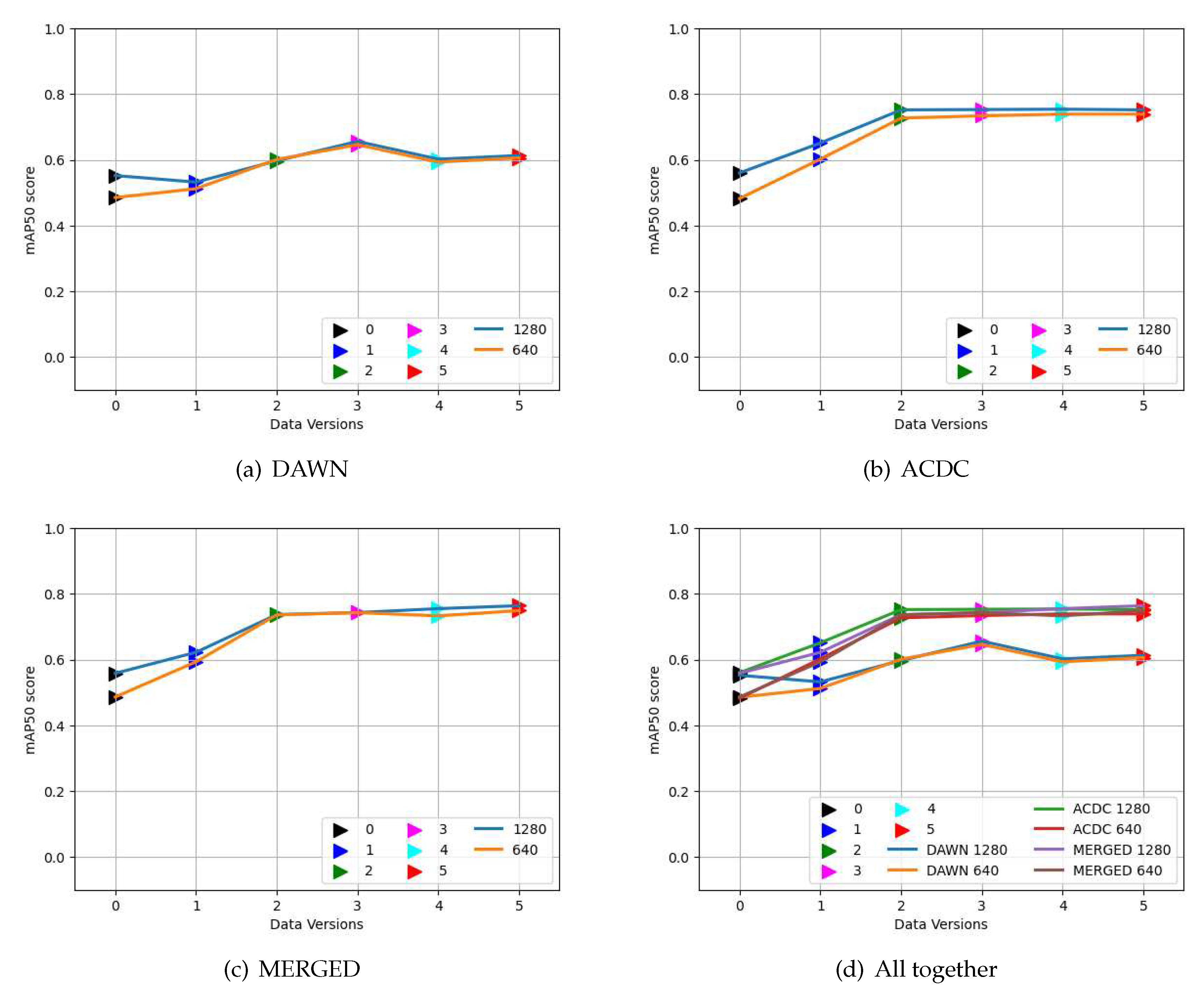
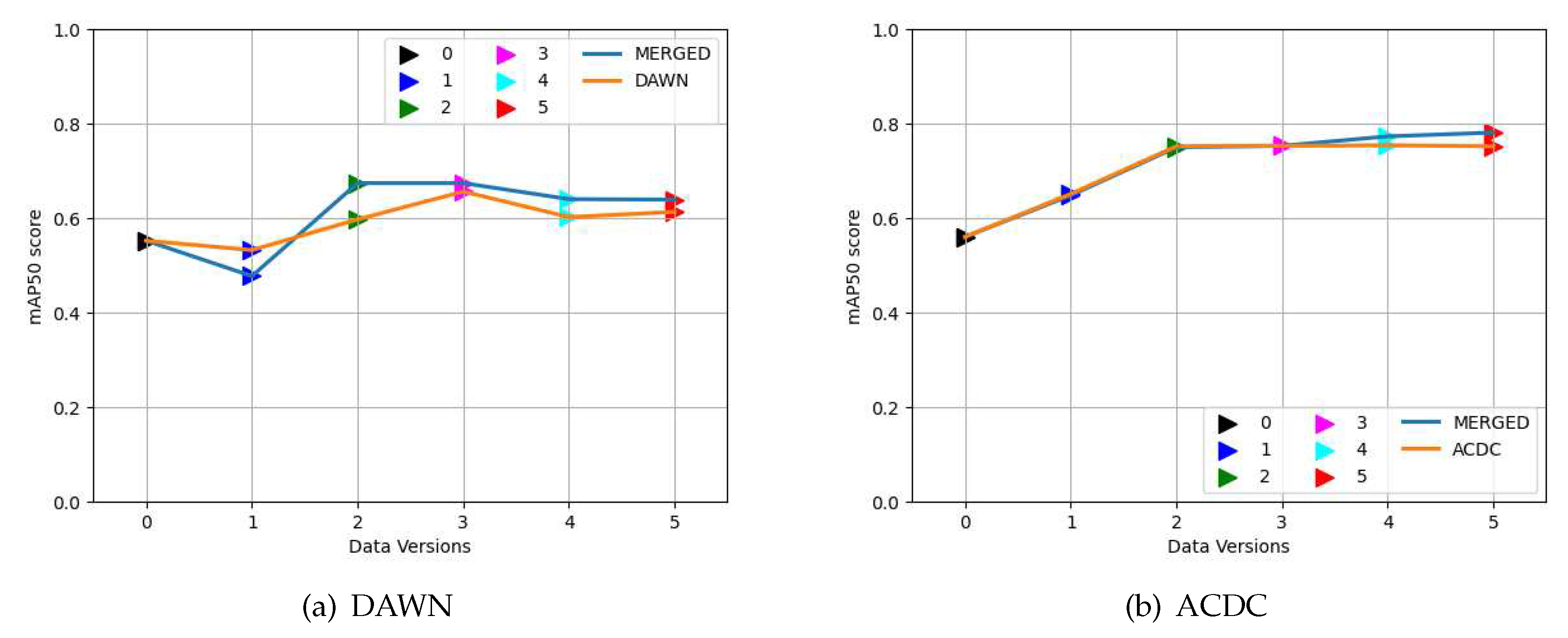
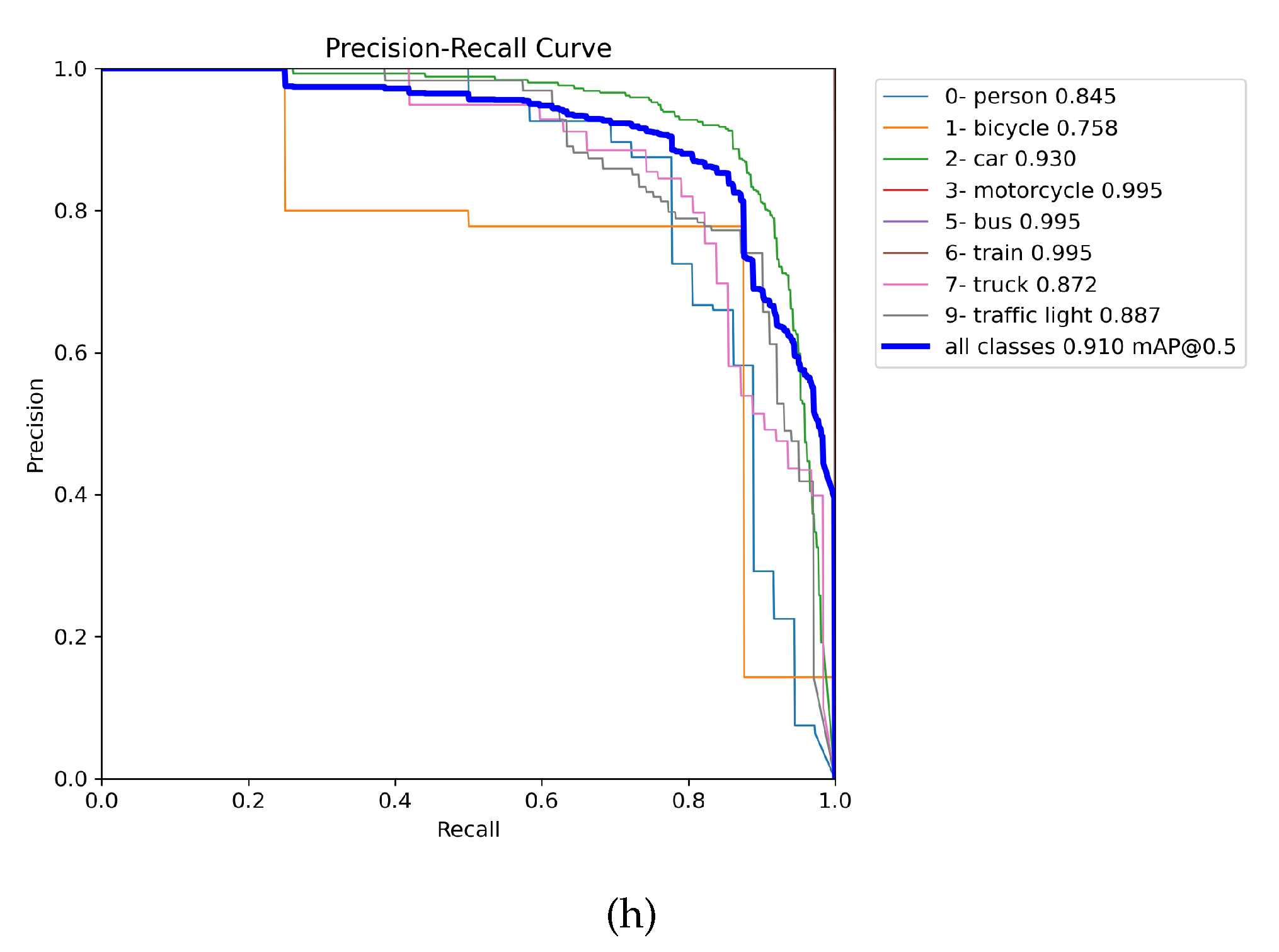
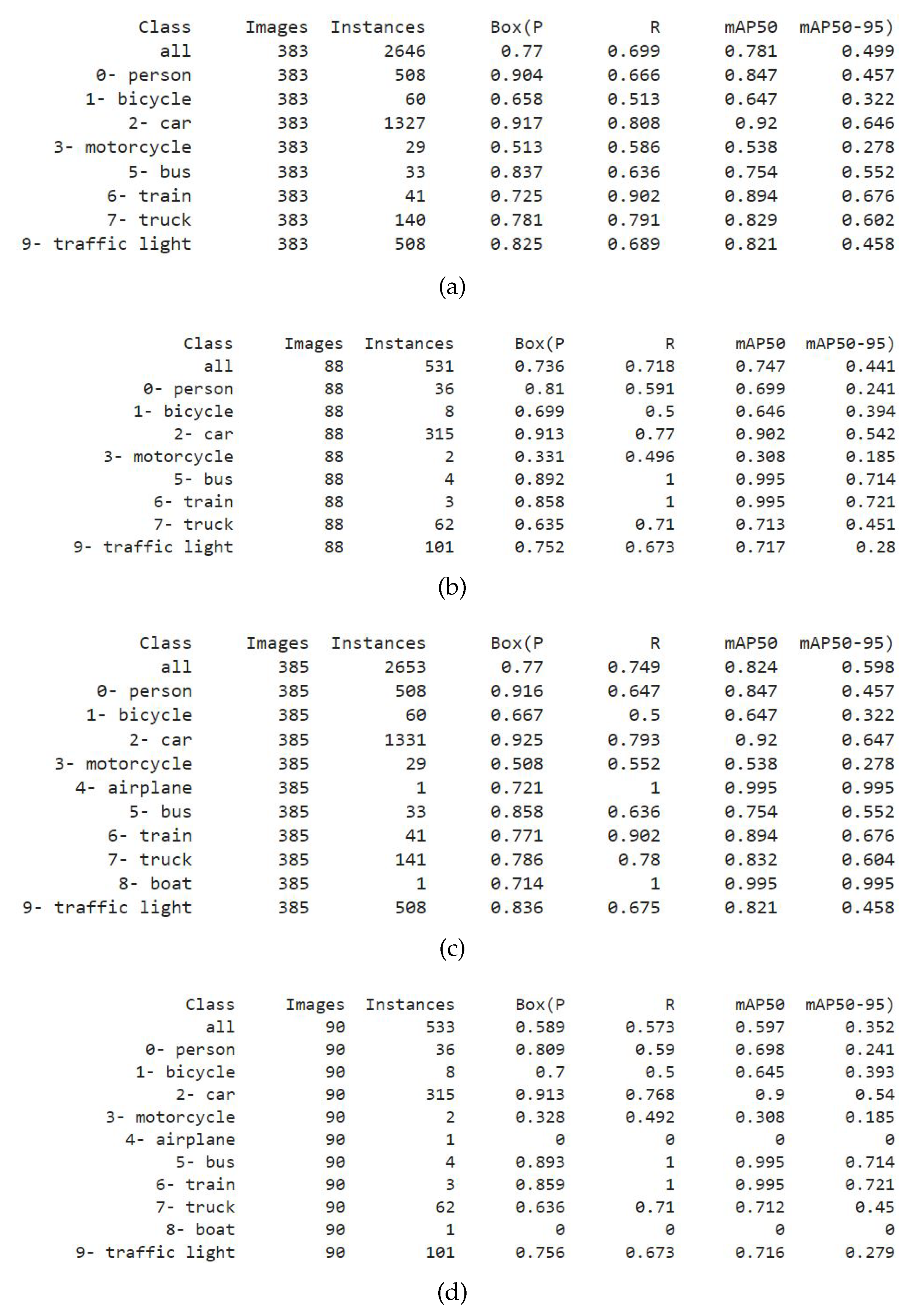
3.2. Evaluation of weights training on the DAWN, ACDC, and MERGED dataset
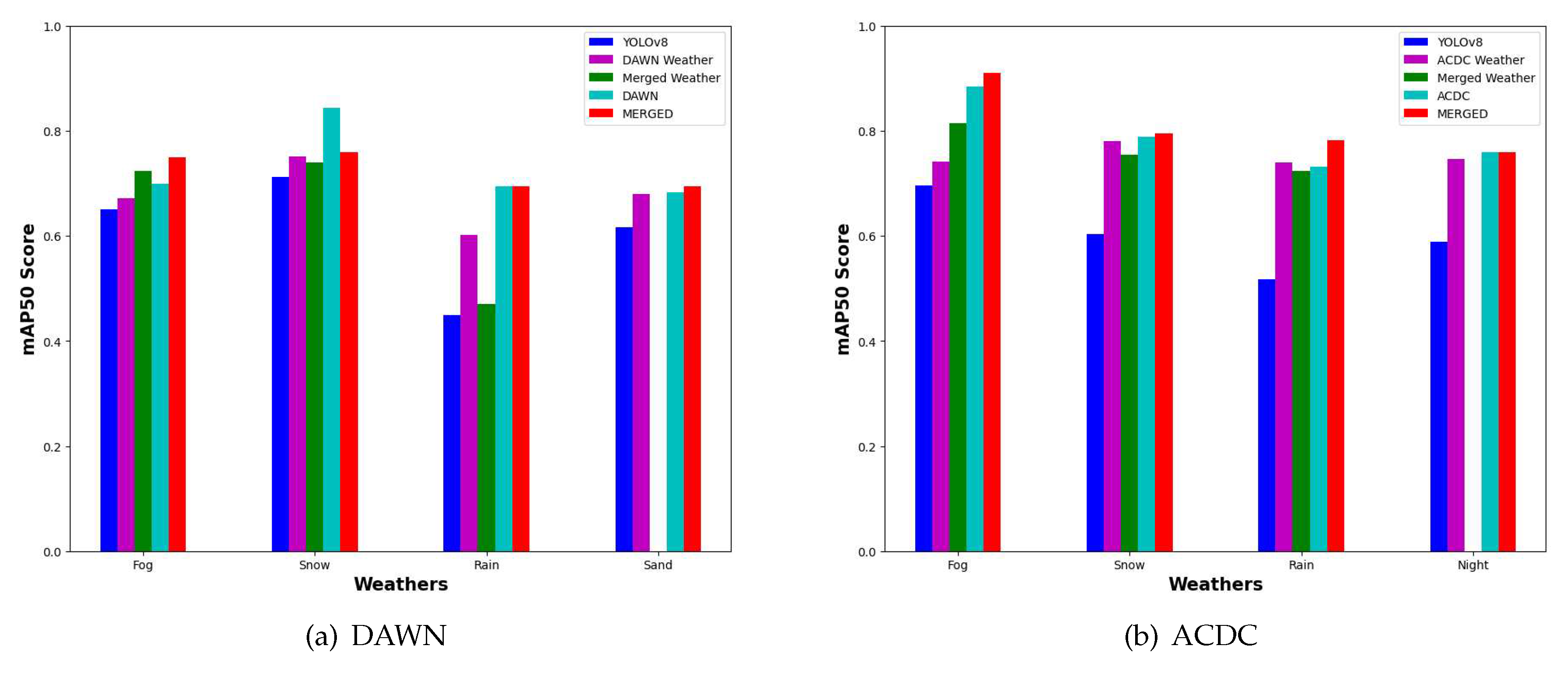
3.3. Effects of the MERGED dataset on the DAWN and ACDC dataset
4. Limitations and future works
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
References
- Taxonomy and Definitions for Terms Related to Driving Automation Systems for On-Road Motor Vehicles (J3016B), 2018, [online] Available: https://www.sae.org/standards/content/j3016_201806/.
- Y. Zhang, A. Carballo, H. Yang, and K. Takeda, “Autonomous driving in adverse weather conditions: A survey,” arXiv [cs.RO], 2021.
- M. Bijelic et al., “Seeing through fog without seeing fog: Deep multimodal sensor fusion in unseen adverse weather,” in 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020. [CrossRef]
- U. Lee et al., “EureCar turbo: A self-driving car that can handle adverse weather conditions,” in 2016 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Qian, S. Zhu, X. Zhang, and L. E. Li, “Robust multimodal vehicle detection in foggy weather using complementary lidar and radar signals,” in 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. S. Mohammed, A. Amamou, F. K. Ayevide, S. Kelouwani, K. Agbossou, and N. Zioui, “The perception system of intelligent ground vehicles in all weather conditions: A systematic literature review,” Sensors (Basel), vol. 20, no. 22, p. 6532, 2020. [CrossRef]
- B. Yang, R. Guo, M. Liang, S. Casas, and R. Urtasun, “RadarNet: Exploiting radar for robust perception of dynamic objects,” in Computer Vision - ECCV 2020, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2020, pp. 496-512. [CrossRef]
- G. Melotti, C. Premebida, N. M. M. da S. Goncalves, U. J. C. Nunes, and D. R. Faria, “Multimodal CNN pedestrian classification: A study on combining LIDAR and camera data,” in 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), 2018. [CrossRef]
- P. Radecki, M. Campbell, and K. Matzen, “All weather perception: Joint data association, tracking, and classification for autonomous ground vehicles,” arXiv [cs.SY], 2016.
- M. Hassaballah, M. A. Kenk, K. Muhammad, and S. Minaee, “Vehicle detection and tracking in adverse weather using a deep learning framework,” IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 4230-4242, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. Tao, J. Xiangkun, D. Xiaodong, S. Jinmiao, and L. Ranran, “Vehicle detection method with low-carbon technology in haze weather based on deep neural network,” Int. J. Low-Carbon Technol., vol. 17, pp. 1151-1157, 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Tumas, A. Nowosielski, and A. Serackis, “Pedestrian detection in severe weather conditions,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 62775-62784, 2020. [CrossRef]
- J. Redmon and A. Farhadi, “YOLOv3:An incremental improvement,” arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. arXiv:1804.02767, 2018.
- G. Li, Y. Yang, and X. Qu, “Deep learning approaches on pedestrian detection in hazy weather,” IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron., vol. 67, no. 10, pp. 8889-8899, 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. Lan, J. Dang, Y. Wang, and S. Wang, “Pedestrian detection based on YOLO network model,” in 2018 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), 2018. [CrossRef]
- S. C. Huang, T. H. Le, and D. W. Jaw, “DSNet: Joint semantic learning for object detection in inclement weather conditions,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., pp. 1-1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Qin, Qingpao, Kan Chang, Mengyuan Huang, and Guiqing Li. “DENet: Detection-driven Enhancement Network for Object Detection under Adverse Weather Conditions.” In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 2813-2829. 2022.
- R. Song, J. Wetherall, S. Maskell, and J. Ralph, “Weather effects on obstacle detection for autonomous car,” in Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Vehicle Technology and Intelligent Transport Systems, 2020.
- N. A. Rawashdeh, J. P. Bos, and N. J. Abu-Alrub, “Drivable path detection using CNN sensor fusion for autonomous driving in the snow,” in Autonomous Systems: Sensors, Processing, and Security for Vehicles and Infrastructure 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. H. Pham, D. N. N. Tran, and J. W. Jeon, “Low-light image enhancement for autonomous driving systems using DriveRetinex-net,” in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Asia (ICCE-Asia), 2020. [CrossRef]
- W. Liu, G. Ren, R. Yu, S. Guo, J. Zhu, and L. Zhang, “Image-Adaptive YOLO for object detection in adverse weather conditions,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Choi, D. Chun, H. Kim, and H. J. Lee, “Gaussian YOLOv3: An accurate and fast object detector using localization uncertainty for autonomous driving,” in 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019. [CrossRef]
- A. Mehra, M. Mandal, P. Narang, and V. Chamola, “ReViewNet: A fast and resource optimized network for enabling safe autonomous driving in hazy weather conditions,” IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 4256-4266, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Li et al., “Detection-friendly dehazing: Object detection in real-world hazy scenes,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. PP, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S., Ren, W., Wang, T., and Cao, X. (2022). Rethinking Image Restoration for Object Detection. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 35, 4461-4474.
- J. Van Brummelen, M. O’Brien, D. Gruyer, and H. Najjaran, “Autonomous vehicle perception: The technology of today and tomorrow,” Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol., vol. 89, pp. 384-406, 2018. [CrossRef]
- V. Musat, I. Fursa, P. Newman, F. Cuzzolin, and A. Bradley, “Multi-weather city: Adverse weather stacking for autonomous driving,” in 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (ICCVW), 2021. [CrossRef]
- I. Fursa et al., “Worsening perception: Real-time degradation of autonomous vehicle perception performance for simulation of adverse weather conditions,” SAE Int. J. Connect. Autom. Veh., vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 87-100, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Deng, W. Dong, R. Socher, L. J. Li, K. Li, and L. Fei-Fei, “ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2009, pp. 248-255. [CrossRef]
- A. Geiger, P. Lenz, and R. Urtasun, “Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite,” in 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2012. [CrossRef]
- T. Y. Lin, M. Maire, S. Belongie, J. Hays, P. Perona, D. Ramanan, P. Dollar, and C. L. Zitnick, “Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context,” in Proc. Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis., 2014, pp. 740-755. [CrossRef]
- M. Cordts, M. Omran, S. Ramos, T. Rehfeld, M. Enzweiler, R. Benenson, U. Franke, S. Roth, and B. Schiele, “The cityscapes dataset for semantic urban scene understanding,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2016, pp. 3213-3223. [CrossRef]
- G. J. Brostow, J. Shotton, J. Fauqueur, and R. Cipolla, “Segmentation and recognition using structure from motion point clouds,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2008, pp. 44-57.
- P. Dollar, C.Wojek, B. Schiele, and P. Perona, “Pedestrian detection: An evaluation of the state of the art,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 743-761, Apr. 2012. [CrossRef]
- S.Munder and D.M. Gavrila, “An experimental study on pedestrian classification,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 28, no. 11, pp. 1863-1868,Nov. 2006. [CrossRef]
- D. Geronimo, A. Sappa, A. Lopez, and D. Ponsa, “Adaptive image sampling and windows classification for on-board pedestrian detection,” in Proc. 5th Int. Conf. Comput. Vis. Syst., 2007, vol. 39. [CrossRef]
- G. Overett, L. Petersson, N. Brewer, L. Andersson, and N. Pettersson, “A new pedestrian dataset for supervised learning,” in Proc. IEEE Intell. Veh. Symp., 2008, pp. 373-378. [CrossRef]
- M. Enzweiler and D. M. Gavrila, “Monocular pedestrian detection: Survey and experiments,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 31, no. 12, pp. 2179-2195, Dec. 2009. [CrossRef]
- N. Dalal and B. Triggs, “Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2005, vol. 1, pp. 886-893. [CrossRef]
- A. Ess, B. Leibe, and L. Van Gool, “Depth and appearance for mobile scene analysis,” in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Comput. Vis., 2007, pp. 1-8. [CrossRef]
- C. Wojek, S. Walk, and B. Schiele, “Multi-cue onboard pedestrian detection,” in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit., 2009, pp. 794-801. [CrossRef]
- B. Leibe, N. Cornelis, K. Cornelis, and L. Van Gool. Dynamic 3D scene anlysis from a moving vehicle. In (CVPR), 2007. [CrossRef]
- T. Scharwächter, M. Enzweiler, U. Franke, and S. Roth. Efficient multi-cue scene segmentation. In (GCPR), 2013.
- M. Sheeny, E. De Pellegrin, S. Mukherjee, A. Ahrabian, S. Wang, and A. Wallace, “RADIATE: A radar dataset for automotive perception in bad weather,” in 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021. [CrossRef]
- Z. Yan, L. Sun, T. Krajnik, and Y. Ruichek, “EU long-term dataset with multiple sensors for autonomous driving,” in 2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), 2020. [CrossRef]
- Y. Choi et al., “KAIST multi-spectral day/night data set for autonomous and assisted driving,” IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 19, no. 3, pp. 934-948, 2018. [CrossRef]
- O. Zendel, K. Honauer, M. Murschitz, D. Steininger, and G. F. Domínguez, “WildDash - creating hazard-aware benchmarks,” in Computer Vision - ECCV 2018, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018, pp. 407-421.
- F. Tung, J. Chen, L. Meng, and J. J. Little, “The raincouver scene parsing benchmark for self-driving in adverse weather and at night,” IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett., vol. 2, no. 4, pp. 2188-2193, 2017. [CrossRef]
- P. Wenzel et al., “4Seasons: A cross-season dataset for multi-weather SLAM in autonomous driving,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021, pp. 404-417. [CrossRef]
- Y. Lei, T. Emaru, A. A. Ravankar, Y. Kobayashi, and S. Wang, “Semantic image segmentation on snow driving scenarios,” in 2020 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. Sun et al., “Scalability in Perception for Autonomous Driving: Waymo Open Dataset,” in 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. F. Chang et al., “Argoverse: 3D tracking and forecasting with rich maps,” in 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Binas, D. Neil, S. C. Liu, and T. Delbruck, “DDD17: End-to-end DAVIS driving dataset,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2017.
- Z. Che et al., “D2-City: A large-scale dashcam video dataset of diverse traffic scenarios,” arXiv [cs.LG], 2019. [CrossRef]
- H. Caesar et al., “nuScenes: A Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving,” in 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Pitropov et al., “Canadian Adverse Driving Conditions dataset,” Int. J. Rob. Res., vol. 40, no. 4-5, pp. 681-690, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Carballo et al., “LIBRE: The Multiple 3D LiDAR Dataset,” arXiv [cs.RO], 2020.
- C. Sakaridis, D. Dai, and L. Van Gool, “Semantic foggy scene understanding with synthetic data,” Int. J. Comput. Vis., vol. 126, no. 9, pp. 973-992, 2018.
- G. Ros, L. Sellart, J. Materzynska, D. Vazquez, and A. M. Lopez, “The SYNTHIA dataset: A large collection of synthetic images for semantic segmentation of urban scenes,” in 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. Liu, Y. Cui, Z. Cao, and Y. Chen, “A large-scale simulation dataset: Boost the detection accuracy for special weather conditions,” in 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), 2020. [CrossRef]
- F. Yu et al., “BDD100K: A diverse driving dataset for heterogeneous multitask learning,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2018.
- M. Braun, S. Krebs, F. Flohr, and D. Gavrila, “EuroCity Persons: A novel benchmark for person detection in traffic scenes,” IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., vol. 41, no. 8, pp. 1844-1861, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Sakaridis, D. Dai, and L. Van Gool, “ACDC: The Adverse Conditions Dataset with Correspondences for semantic driving scene understanding,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2021. [CrossRef]
- G. Neuhold, T. Ollmann, S. R. Bulo, and P. Kontschieder, “The mapillary vistas dataset for semantic understanding of street scenes,” in 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. R. Richter, Z. Hayder, and V. Koltun, “Playing for Benchmarks,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2017. [CrossRef]
- X. Huang, P. Wang, X. Cheng, D. Zhou, Q. Geng, and R. Yang, “The ApolloScape open dataset for autonomous driving and its application,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Gray et al., “GLARE: A dataset for Traffic Sign detection in sun glare,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Kenk and M. Hassaballah, “DAWN: Vehicle detection in adverse weather nature dataset,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2020.
- P. Jiang, D. Ergu, F. Liu, Y. Cai, and B. Ma, “A review of Yolo algorithm developments,” Procedia Comput. Sci., vol. 199, pp. 1066-1073, 2022. [CrossRef]
- T. Diwan, G. Anirudh, and J. V. Tembhurne, “Object detection using YOLO: challenges, architectural successors, datasets and applications,” Multimed. Tools Appl., vol. 82, no. 6, pp. 9243-9275, 2023. [CrossRef]
- J. Terven and D. Cordova-Esparza, “A comprehensive review of YOLO: From YOLOv1 to YOLOv8 and beyond,” arXiv [cs.CV], 2023. [CrossRef]
- G. Jocher, A. Chaurasia, and J. Qiu, “YOLO by Ultralytics.” https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics, 202.
- T. Sharma, B. Debaque, N. Duclos, A. Chehri, B. Kinder, and P. Fortier, “Deep learning-based object detection and scene perception under bad weather conditions,” Electronics (Basel), vol. 11, no. 4, p. 563, 2022. [CrossRef]
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 |

| Weights trained on | Weights evaluated on | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weight trained on Version no. | Input images | Base weights | Size of images during training | Approximate Training time for the MERGED dataset (32 epochs) | Size of validation images | Size of test images |
| V1 | Raw images | yolov8x.pt | 640*640 | 4 hours | Raw images | Raw images |
| V2 | 640*640 (augmented) | yolov8l.pt | 640*640 | 5 hours | 640*640 | 640*640 |
| V3 | 640*640 | yolov8l.pt | 640*640 | 2 hours | 640*640 | 640*640 |
| V4 | 1280*1280 | yolov8x.pt | 640*640 | 3.5 hours | 1280*1280 | 1280*1280 |
| V5 | 1280*1280 (augmented) | yolov8x.pt | 640*640 | 4.5 hours for 16 epochs | 1280*1280 | 1280*1280 |
| DAWN | ACDC | MERGED | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Weather | Train | Valid | Test | Total | Train | Valid | Test | Total | Train | Valid | Test | Total |
| Sand | 223 | 63 | 33 | 319 | * | * | * | * | 223 | 63 | 33 | 319 |
| Fog | 193 | 59 | 27 | 279 | 638 | 179 | 88 | 905 | 831 | 238 | 115 | 1184 |
| Rain | 142 | 40 | 19 | 201 | 698 | 198 | 98 | 994 | 840 | 238 | 117 | 1195 |
| Snow | 142 | 41 | 21 | 204 | 700 | 200 | 100 | 1000 | 842 | 241 | 121 | 1204 |
| Night | * | * | * | * | 679 | 193 | 97 | 969 | 679 | 193 | 97 | 969 |
| Total | 700 | 203 | 100 | 1003 | 2715 | 770 | 383 | 3868 | 3415 | 973 | 483 | 4871 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




