1. Introduction
Andrographis paniculata is a medicinal plant that has been used for centuries in traditional Ayurvedic and Chinese medicine. The leaves of
Andrographis paniculata are particularly valued for their health benefits and therapeutic properties.
Andrographis paniculata shows
anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-microbial, immunomodulatory and so on health beneficiary effects [
1].
Andrographis paniculata contains several bioactive compounds that contribute to its medicinal properties. Such as andrographolide, neoandrographolide, apigenin, luteolin, apigenin, gallic acid, xanthones, and many more. which have been reported for their immense health-beneficial effects against many disorders and diseases [2-5].
Andrographis paniculata leaves
have shown potential in skin protection and skincare due to their various bioactive compounds and properties. While research in this area is limited, we have investigated the
Andrographis paniculata leaves extracts (ALE) on skin barrier functions.
Abiotic antioxidant activities could be a significant indication of the potential role in mitigating the detrimental effects of oxidative stress on overall health and skin tissue. Excessive oxidative stress takes place when there is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the endogenous antioxidant defense mechanisms [6-8]. Oxidative stress has been implicated in various chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, diabetes, and cancer. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) can cause damage to cellular components, such as DNA, proteins, and lipids, leading to inflammation, tissue damage, and chronic diseases [9]. Skin is constantly exposed to environmental factors, such as UV radiation, pollution, and toxins, which generate ROS and contribute to oxidative stress. This oxidative stress can result in premature aging, skin damage, and various skin disorders. Abiotic antioxidants, both systemically ingested and topically applied, can help counteract the harmful effects of oxidative stress on the skin. They scavenging of ROS reduces inflammation, protect against DNA damage, and enhance the skin's natural defense mechanisms, thereby promoting healthier and more youthful-looking skin [10].
Hyaluronan synthase 1 (HAS-1), aquaporin 3 (AQP3), and loricrin play important roles in UV-induced keratinocyte responses. HAS-1 synthesizes hyaluronic acid (HA), contributing to skin hydration, wound healing, and antioxidant defense against UV-induced oxidative damage. UV radiation upregulates HAS-1, increasing HA production. AQP3 is a water and glycerol transporter, maintains skin hydration [11,12]. UV radiation downregulates AQP3, impairing water transport and barrier function, leading to dryness and susceptibility to UV damage. Loricrin is found in the outermost skin layer and maintains the skin barrier. UV radiation reduces loricrin expression that compromising barrier function and hydration. UVB radiation activates and phosphorylates MAPKs (ERK, JNK, p38), triggering inflammation. Phosphorylated MAPKs activate transcription factors like AP-1, which induces inflammatory molecules. Persistent MAPK activation contributes to sunburn, photodermatitis, photodamage, and photo-carcinogenesis by promoting abnormal cell growth. Inhibiting MAPK phosphorylation can reduce UVB-induced inflammation, cytokine production, and abnormal cell growth and making MAPKs putative therapeutic targets for UVB-related skin conditions. MAPK activation plays crucial role in inflammation via triggering NF-κB and apoptosis via caspase cascades [13,14]. Thus, secretes inflammatory cytokines and suppresses growth factors and anti-apoptotic mediators. Thereby, suppression of MAPKs overactivation, inflammation and modulating PPAR-α, HAS-1 AQP3, loricrin in UVB-induced keratinocytes could be a potent manifestation of skin protective agent.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2-yl)-2,5 diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) were purchased from Sigma Aldrich. DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium), DPBS, Penicillin Streptomycin (P.S), and Trypsin EDTA were purchased from WELGENE Inc. (Seoul, Korea). Western blot primary and secondary antibodies were collected from Cell Signaling Technology. All other chemicals were analytical-grade and used without any further purification.
2.2. Sample Preparation
Andrographis paniculata leaves (200 g) were extracted using two solvents; distilled water (DW) and 70% ethanol respectively.100g of leaves were dissolved in one liter of DW or 70% ethanol and kept for 24 hours. The extracts collected by filtration and the process had been repeated three times. Then, the extracts were concentrated by a vacuum rotary evaporator and lyophilized using a freeze dryer. Finally, the Andrographis paniculata leaves extracts (ALE) were collected and put at -20°C before use.
2.3. Sample Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Assay
The total phenolic and flavonoid content of ALE were determined by Folin-Ciocalteu and Aluminum colorimetric method. Gallic acid was used for the standard curve for phenolic content and catechin for flavonoid content. Total phenol content was expressed as mg of gallic acid equivalent (GAE) per gram extract and total flavonoid content was expressed as mg of catechin equivalent (CE) per gram extract.
2.4. DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Assay
Abiotic antioxidant activities of ALE were investigated by DPPH, ABTS and H2O2 radical scavenging assays. The scavenging activities of water and ethanol extracts against the Diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) free radical were determined using a previously described method. Different concentrations of the sample and ascorbic acid (AA) were prepared in water and ethanol. Then, 80 µL of each sample or standard solution was mixed with 80 µL of DPPH solution (0.2 mM in methanol). The mixture was shaken in the dark for 30 minutes at 70 rpm, and the absorbance was measured at 517 nm.
2.5. ABTS Free Radical Scavenging Assay
ABTS powder was dissolved in water and adjusted to a concentration of 7 mM. ABTS+ was produced by reacting ABTS with potassium persulfate solution at a final concentration of 2.45 mM. The resulting ABTS radical solution was diluted with 0.01 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.4) to achieve an absorbance of 0.70 ± 0.02 at 734 nm. Different concentrations of the sample and a single concentration of AA were mixed with the ABTS+ solution in cuvettes. The absorbance at 734 nm was measured after 5 minutes of reaction at room temperature. The controls consisted of the solvent [3].
2.6. Hydrogen Peroxide Free Radical Scavenging Assay
For H2O2 radical scavenging assay, a 0.1 mL aliquot of the sample was transferred to eppendorf tubes, and the volume was adjusted to 0.4 mL with 50 mM phosphate buffer (pH 7.4). Then, 0.6 mL of a 2 mM H2O2 solution was added. The reaction mixture was vortexed, and after 10 minutes, the absorbance was measured at 230 nm. AA was used as the positive control[15].
2.7. Cell culture
Human keratinocyte HaCaT cells were maintained in DMEM supplemented with 10%FBS and 1% P.S. The cells were incubated in a humidified incubator at 37°C and 5% CO2.
2.8. MTT Assay
The cell viability of ALE on HaCaT cells was evaluated by MTT assay [12]. Human keratinocyte HaCaT cells were seeded as 5×104 cells in each well in a 96-wallplate and incubated for 24 hours. Then, cells were treated with various concentrations of ALE for another 24 hours and MTT (final concentration 0.5mg/mL) was added and incubated for 2 hours. Afterward, the formazan blue was dissolved in DMSO and the absorbance was taken at 570nm in VersaMax microplate reader (Molecular Device).
2.9. Reverse Transcriptase Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) Analysis
Total RNA from UVB-induced HaCaT cells with or without treatment of ALE DW/EtOH extract were extracted by TRIzol (Invitrogen Life Technologies). The RNA was transcribed using cDNA synthesis kits (superscript II) [6,16]. Then, amplified by targeted primers and mRNA probes were stained by EtBr in agarose gel, and band intensities had been analyzed by ImageJ.
Table 1.
Sequences of primers used for RT-PCR in this study.
Table 1.
Sequences of primers used for RT-PCR in this study.
| Name |
Forward |
Reverse |
| HAS-1 |
5′ CCACCCAGTACAGCGTCAAC 3′
|
5′ CATGGTGCTTCTGTCGCTCT 3′
|
| AQP3 |
5’ CCTTTGGCTTTGCTGTCACTCT 3′
|
5′ CGGGGTTGTTGTAGGGGTCA 3′ |
| Loricrin |
5′ AGTGGACTGCGTGAAGAC 3′ |
5′ AGTGGACTGCGTGAAGAC 3′ |
| GAPDH |
5’ GGTCACCAGGGCTGCTTTTA 3’ |
5’ GATGGCATGGACTGTGGTCA 3’ |
2.10. Western Blot Analysis
The whole protein from HaCaT cells were extracted by PRO-PREP buffer (iNITRON) and quantified by Bradford assay. An equal amount of protein was subjected to 10% SDS-PAGE gel and separated by electrophoresis. Then, the proteins were transferred into PVDF membrane and blocked by 5% BSA. After blocking, the membranes were cut according to corresponding primary antibodies kDa and incubated with primary antibodies overnight at 4°C. Afterward, the membranes were incubated with secondary antibody and the band images were detected in ChemiDoc XRS+(Bio-Rad) using ECL kit [6,8].
2.11. HPLC Analysis
The analysis of bioactive compounds present in ALE was carried out using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), and the results are presented in Table 2. The table provides detailed information about the detected bioactive compounds, including their retention times, concentrations, and possibly other relevant data.
Table 2.
HPLC Condition.
| Instrument |
Agilent HPLC 1260 |
| Parameter |
Condition |
| Column |
Agilent Eclipse XDB-C18 (5µm, 4.6 × 150mm) |
| Column Temp. |
25ºC |
| Injection Volume |
20 µL |
| Flow rate |
1mL/min |
| Wavelength |
254nm |
| Mobile Phase A |
0.1% Formic acid in Water |
| Mobile Phase B |
0.1% Formic acid in Acetonitrile |
Gradient
|
Time (min) |
A(%) |
B(%) |
| 0 |
90 |
10 |
| 30 |
70 |
30 |
| 55 |
85 |
15 |
| 60 |
85 |
15 |
| 61 |
90 |
10 |
| 65 |
90 |
10 |
2.12. Statistical Analysis
The data were analyzed using MS Excel and GraphPad Prism. All data replicated at least three times using ANOVA and nonparametric Tukey’s multiple comparison T-test. and the results are presented as the means ± SD for all experimental data.
3. Results
3.1. Total Phenolic and Flavonoid Content of ALE
ALE has high content of bioactive compounds like phenolics and flavonoids. ALE DW phenolic and flavonoid contents are 51.87±2.33 mg and 17.97±0.14 mg per gram extract respectively (
Table 3). On the other hand, 70% ethanolic extraction showed higher content of total phenolic content (TPC) and total flavonoid content (TFC). ALE EtOH phenolic and flavonoid contents are 45.36±0.72 and 16.02±0.47mg per gram extract.
Table 3.
Total phenolic, Flavonoid assay and yield.
Table 3.
Total phenolic, Flavonoid assay and yield.
| Extract |
Total Phenolic
(mg GAE†/g of extract) |
Total flavonoid
(mg CE†† /g of extract) |
Yield
(%) |
| ALE DW |
51.87±2.33 |
17.97±0.14 |
8.36 |
| ALE EtOH |
45.36±0.72 |
16.02±0.47 |
7.75 |
3.2. Free Radical Scavenging Activities of ALE
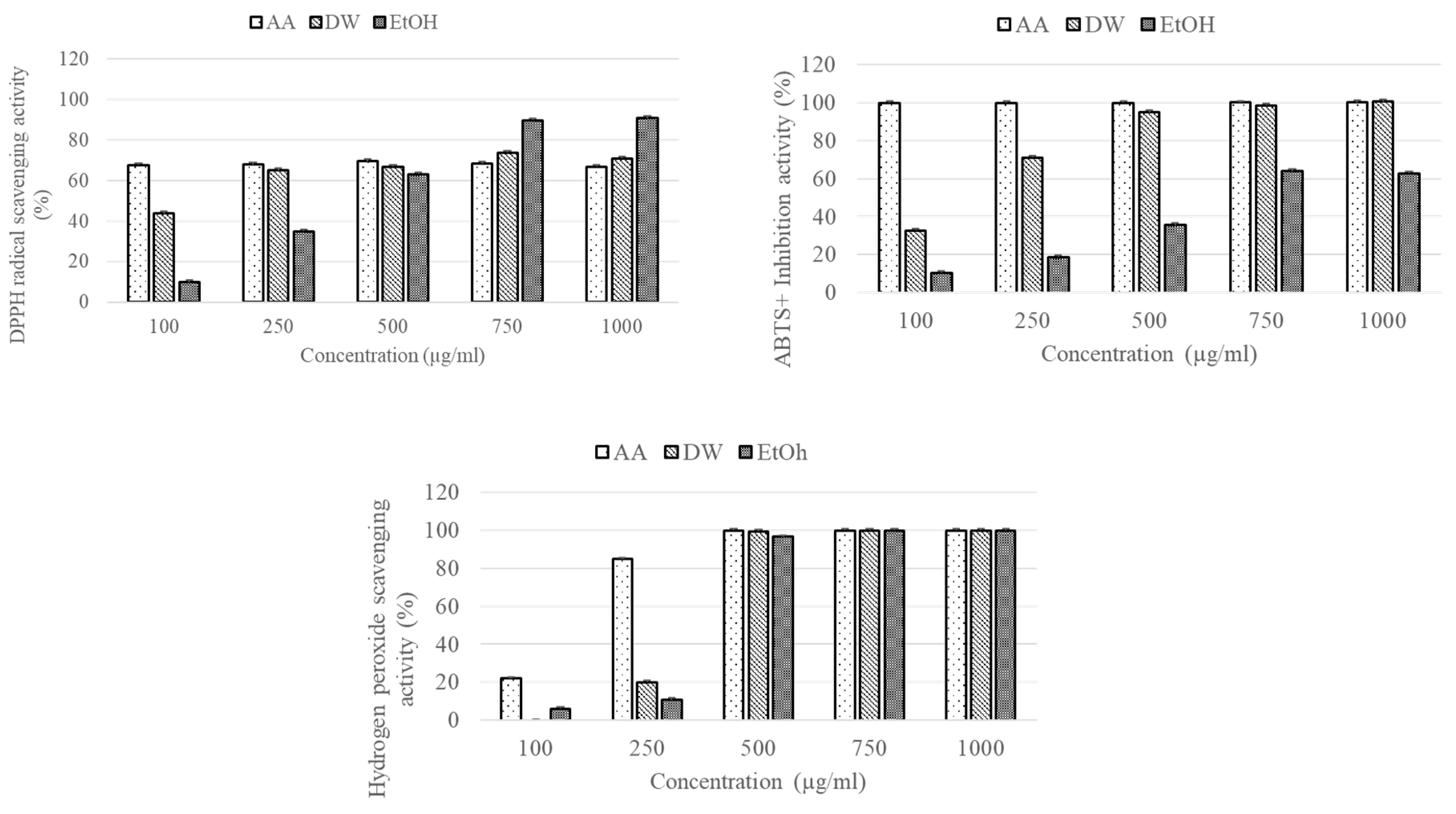
ALE exerted DPPH, ABTS, and hydrogen peroxide radical scavenging activities in a dose-dependent manner (
Figure 1). However, the water extract demonstrated higher antioxidant effects by more effectively scavenging the free radical than the ethanol extract of
ALE.
Figure 1.
The DPPH, ABTS, hydrogen peroxide free radical scavenging activities of ALE. Histograms were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3.
Figure 1.
The DPPH, ABTS, hydrogen peroxide free radical scavenging activities of ALE. Histograms were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3.
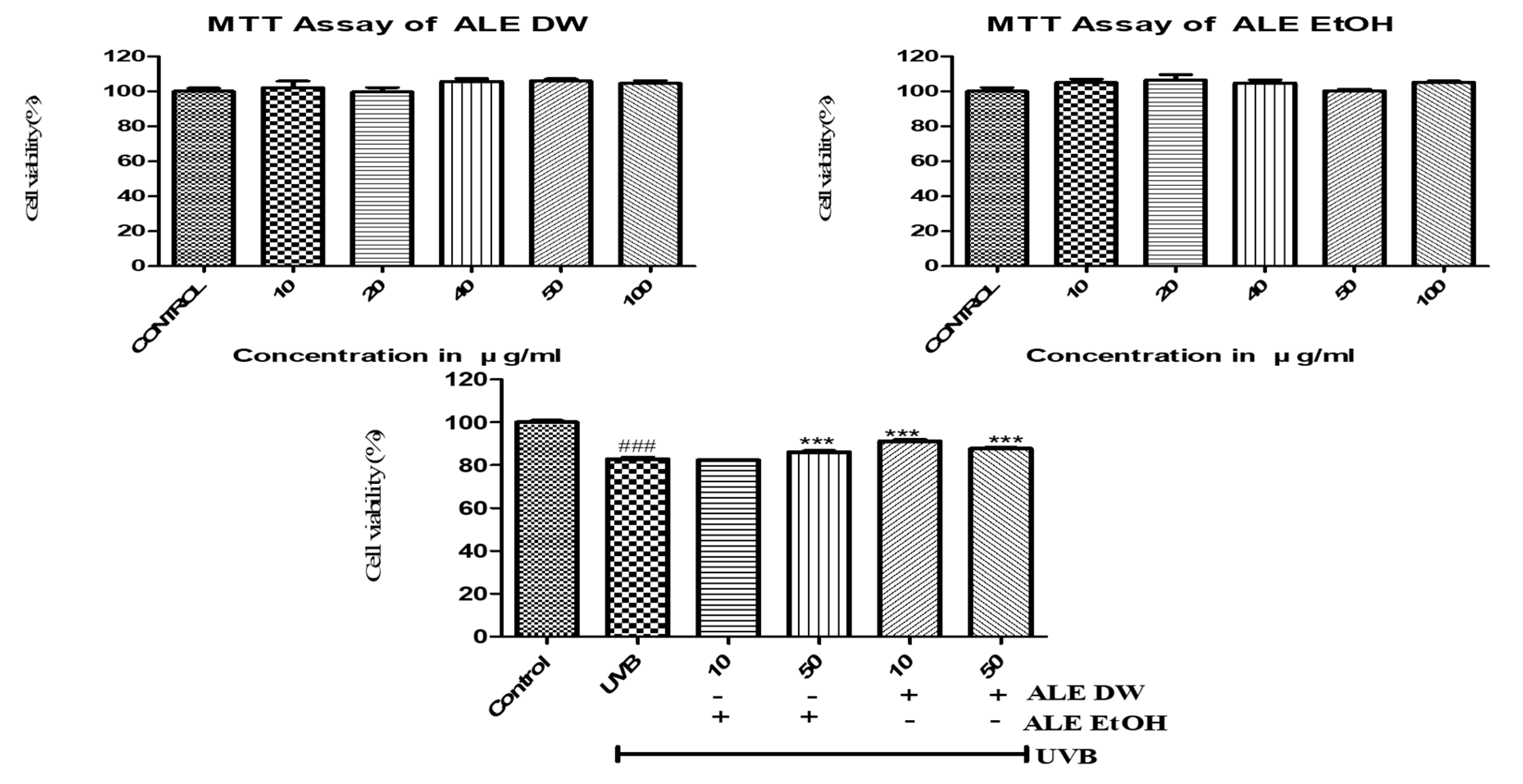
3.3. Effects of ALE on Cell Viability
ALE DW and EtOH extracts cell viability was evaluated on HaCaT cells. ALE showed no toxic effects up to 100 μg/mL, whereas less than 80% cell viability is considered cytotoxic. We used up to 50 μg/mL of ALE for further experiments (
Figure 2). ALE both extracts water and ethanol alleviated cell death in UVB-induced HaCaT cells.
Figure 2.
The effects of ALE on cell viability in HaCaT cells and UV-induced HaCaT Cells. Histograms were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the only UVB-treated group.
Figure 2.
The effects of ALE on cell viability in HaCaT cells and UV-induced HaCaT Cells. Histograms were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the only UVB-treated group.
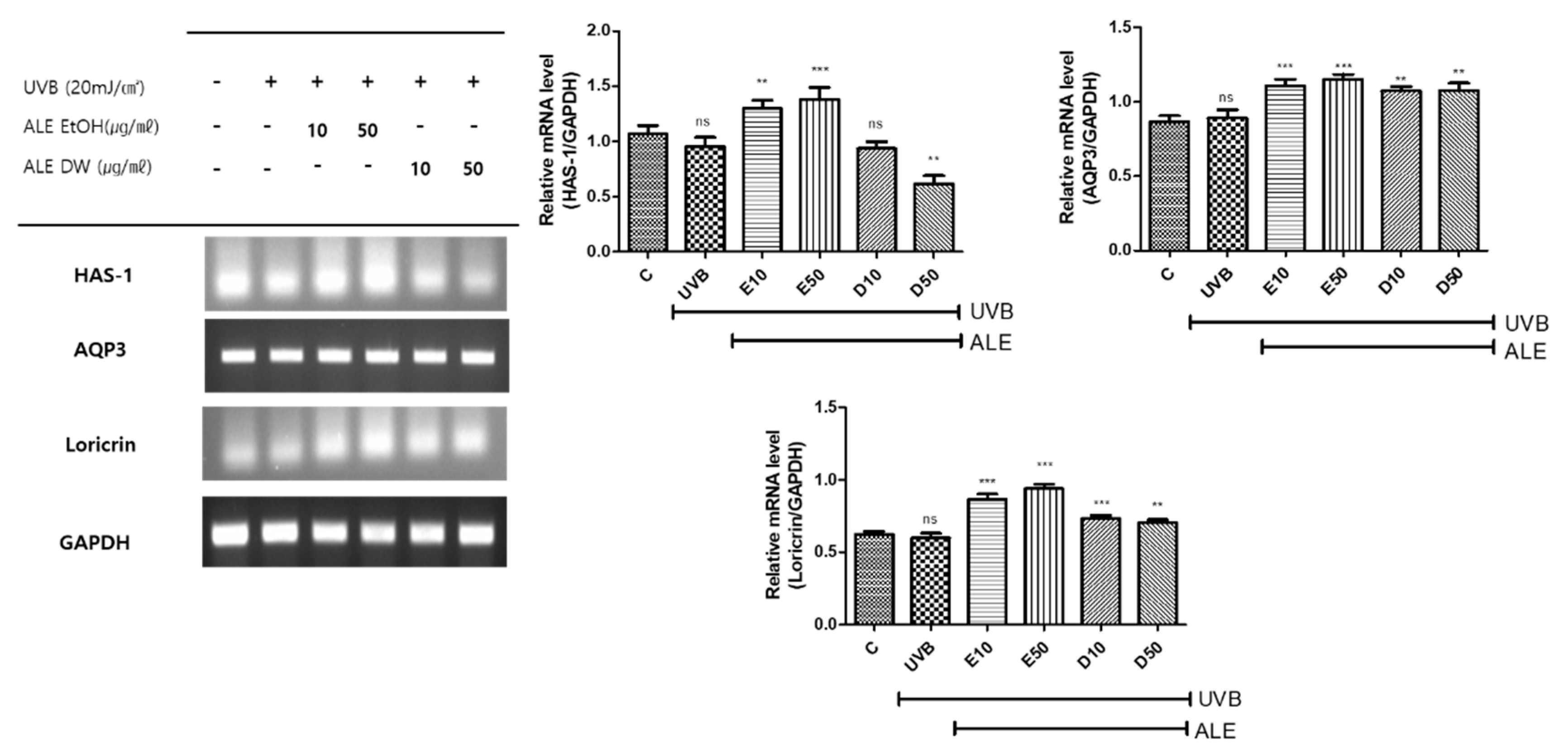
3.4. Effects of ALE on HAS-1, AQP3 and Loricrin Expressions in UVB-induced HaCaT Cells
The keratinocytes of the skin play an essential role in barrier and protective functions. However, UV affects skin barrier functions through aberrations of molecular signaling pathways. UVB decreased the mRNA expression of HAS-1, AQP3, and loricrin, and ALE both DW and EtOH significantly up-regulated HAS-1, AQP3, and loricrin (
Figure 3). HAS-1 is important for maintaining skin structure and function. HAS-1 and AQP3 both play a central role in skin hydration. AQP3 is a water channel protein expressed in keratinocytes, the main cell type found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Loricrin is a protein expressed in the epidermis and it is a component of the corneal cell sheath, which is a layer of protein that surrounds and protects the cells of the stratum corneum. HAS-1, AQP3, and loricrin are important for maintaining the skin barrier and preventing skin disorders.
Figure 3.
The effects of ALE on mRNA expression of HAS-1, AQP3 and Loricrin in UV-induced HaCaT Cells. Histograms were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the only UVB-treated group.
Figure 3.
The effects of ALE on mRNA expression of HAS-1, AQP3 and Loricrin in UV-induced HaCaT Cells. Histograms were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the only UVB-treated group.
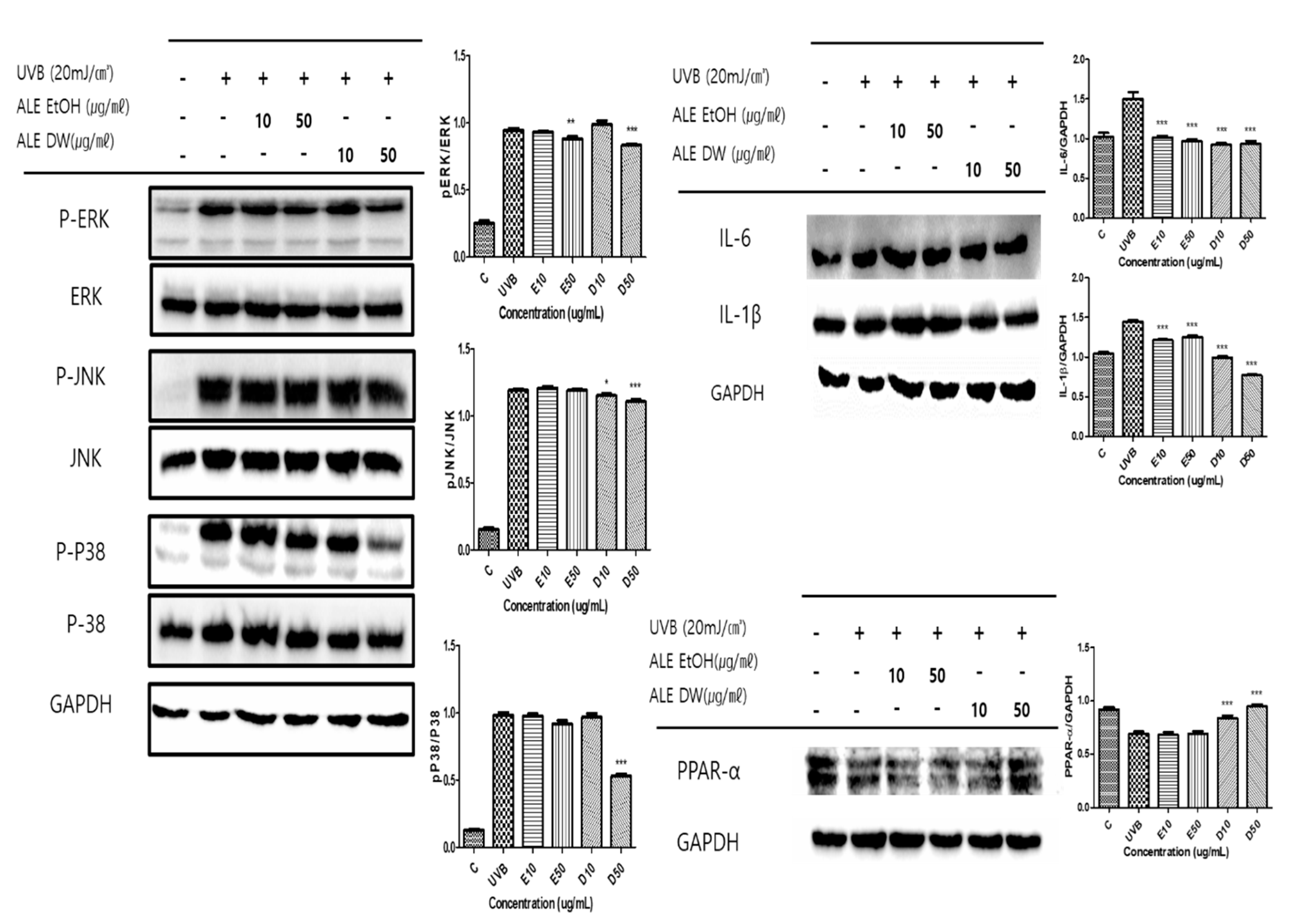
3.5. Effects of ALE on MAPKs Phosphorylation, Inflammation and PPAR-α Expression in UVB-induced HaCaT Cells
In response to a range of stimuli including UV exposure, oxidative stress, and inflammatory mediators, phosphorylation of MAPKs can occur within keratinocytes. Activation of downstream signaling pathways as a consequence of this heightened phosphorylation can lead to alterations in both gene expression and cellular activity. The MAPK family consists of ERK, JNK, and P-38 proteins. Upon exposure to UVB stimulation, a marked increase in the levels of phosphorylated ERK, JNK, and P-38 expressions were observed. The EtOH extract demonstrated a more enhancement in skin barrier functions compared to the DW extract of ALE. Consequently, the DW extract exhibited greater efficacy in reversing MAPK activity then ethanolic extract of ALE (
Figure 4)
. The maintenance of skin homeostasis and the defense against infections are heavily reliant on controlling keratinocyte inflammation. Excessive inflammation can act as a trigger for various skin conditions, encompassing psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, and skin cancer. Notably, PPAR-α in keratinocytes plays a multifaceted role, including the regulation of inflammation, lipid metabolism, and epidermal development. Moreover, PPAR-α has been shown positively regulates the expression of key genes involved in forming the skin barrier, such as filaggrin and loricrin, thereby fostering keratinocyte differentiation. Additionally, the presence of PPAR-α has demonstrated anti-inflammatory properties in UVB-induced keratinocytes.
Figure 4.
The effects of ALE on MAPKs activation, IL-6, IL-1β and PPAR-α expressions in UV-induced HaCaT Cells. Histogram were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the only UVB-treated group.
Figure 4.
The effects of ALE on MAPKs activation, IL-6, IL-1β and PPAR-α expressions in UV-induced HaCaT Cells. Histogram were presented as mean ± SD, where n = 3. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the only UVB-treated group.
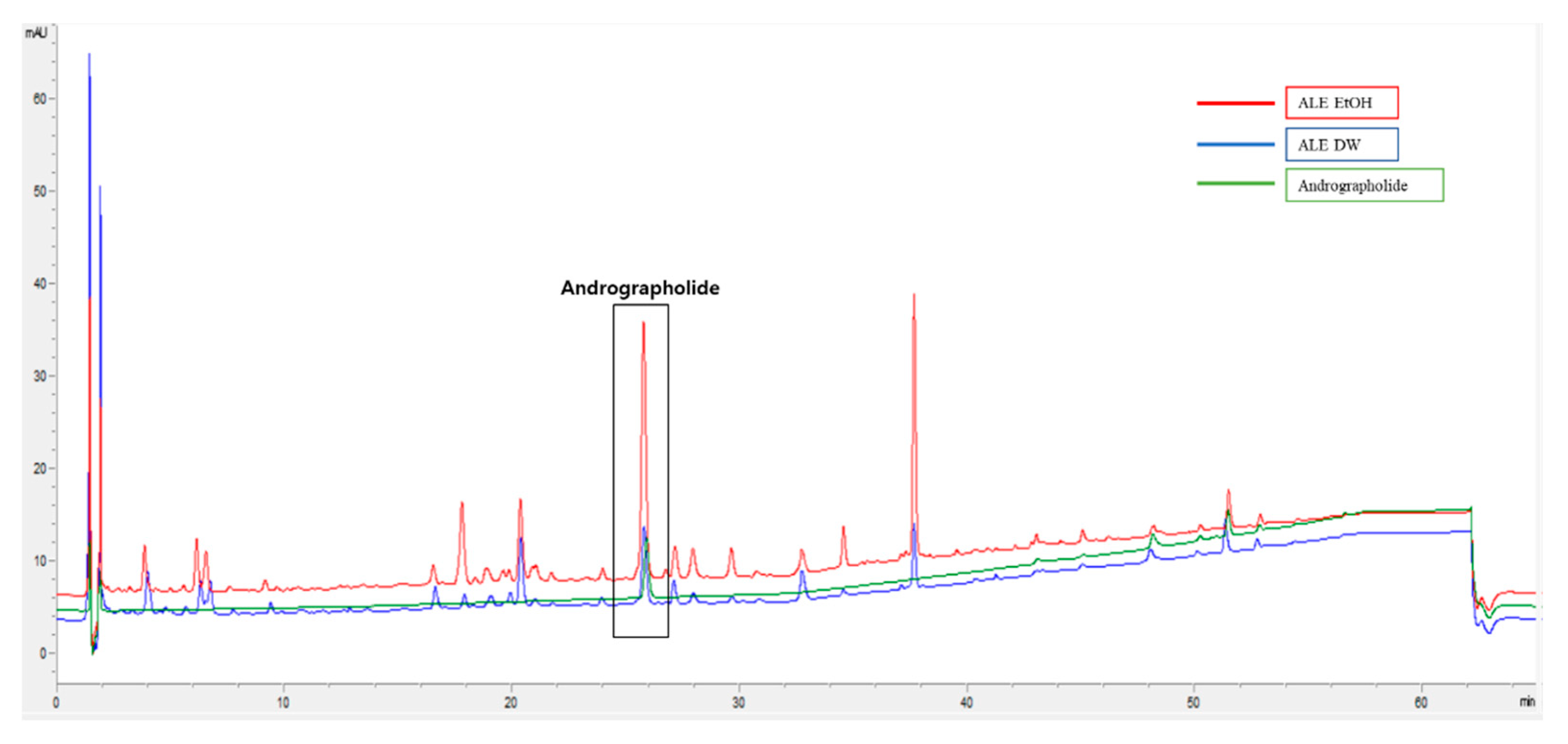
3.6. Bioactive Compounds in ALE
We conducted a comprehensive analysis of the bioactive compounds present in both the ALE water and ethanolic extracts, employing advanced HPLC techniques. Our findings distinctly reveal the presence of the prominent bioactive compound, andrographolide, within both extracts (
Figure 5). Building upon our earlier research, we effectively demonstrated the impact of these extracts on fortifying skin protection and enhancing barrier functions [12]. Furthermore, utilizing LC QTOF/MS, we delved deeply into the composition of ALE and successfully identified a range of established health-promoting phytochemicals, including Vitetrifolin C, 4,8,12-Trimethyl tridecanoic acid, Karacoline, Shikonofuran A, and so on (
supplementary figures).
Figure 5.
HPLC chromatograms of th ALE EtOh and DW extract.
Figure 5.
HPLC chromatograms of th ALE EtOh and DW extract.
4. Discussion
We investigated the potential advantages of extracts from Andrographis paniculata leaves (ALE) concerning diverse facets of skin well-being. The outcomes unveiled a wealth of bioactive compounds housed within ALE, particularly phenolics and flavonoids, thus attesting to its nutritive richness. Alongside this, we embarked on a comprehensive exploration, encompassing antioxidant capabilities, cellular viability, and the ramifications on pivotal molecular expressions within UVB-induced HaCaT cells. ALE emerged as a reservoir teeming with phenolics and flavonoids, renowned for their prowess as antioxidants [2]. Evidently, the aqueous extract and the ethanolic extract of ALE exhibited augmented levels of total phenolic and flavonoid content. These compounds notably contributed to the neutralization of free radicals, as corroborated by the demonstrated activities in quenching DPPH, ABTS, and hydrogen peroxide radicals. Notably, the aqueous extract demonstrated heightened antioxidant efficacy in comparison to the ethanol extract, thus underlining the latent potential of ALE as an inherent antioxidant nurturing skin vitality.
In our study, both aqueous and ethanol extracts revealed an absence of any detrimental effects up to a concentration of 100 μg/mL, thereby affirming their safety profile for practical usage. Furthermore, the ALE extracts exhibited a noteworthy capacity to mitigate cell demise within UVB-induced HaCaT cells, thereby hinting at a potential safeguarding mechanism against the deleterious impact of UVB-induced harm. Moreover, ALE emerged as a regulator of PPAR-α expression within UVB-stimulated keratinocytes, as underscored by previous research [17]. PPAR-α, an orchestrator of inflammation modulation, lipid metabolism, and epidermal maturation, garnered attention. Notably, ALE treatment exhibited the capability to enhance PPAR-α expression, subsequently stimulating the synthesis of critical genes responsible for forming the skin's protective barrier, including filaggrin and loricrin [9,18]. This augmentation firmly underscores ALE's promise in nurturing skin health and preserving equilibrium. Delving deeper, the study delved into ALE's impact on genes integral to bolstering the skin's barrier function. Upon UVB exposure, a discernible reduction in the mRNA expression of HAS-1, AQP3, and loricrin, genes pivotal for upholding skin architecture, hydration, and barrier integrity, was detected. The revelation, however, took an encouraging turn as both aqueous and ethanol ALE extracts demonstrated a remarkable propensity for upregulating the expression of these genes. Such findings underscore ALE's latent capacity to rejuvenate and elevate the skin's protective barrier as a critical defense against skin-related ailments, epitomizing the overarching well-being of the skin.
Intriguing insights were gained by exploring the impact of ALE on the expression of pivotal genes linked to skin barrier function. Upon UVB exposure, a notable reduction in mRNA expression levels of HAS-1, AQP3, and loricrin was observed, genes vital for upholding the structural integrity, hydration, and barrier function of the skin. However, in a remarkable turn of events, both the aqueous and ethanol extracts of ALE exhibited a significant capacity to elevate the expression of these genes. This compelling evidence strongly suggests that ALE holds the promise of revitalizing and fortifying the skin barrier—a pivotal defense against skin disorders and the maintenance of holistic skin well-being.
5. Conclusion
ALE, abundant in natural bioactive compounds, has exhibited a plethora of health-enhancing benefits throughout its extensive use as a traditional medicinal remedy. Notably, it has demonstrated impressive abiotic antioxidant prowess through its effective neutralization of DPPH, ABTS, and H2O2 radicals. In the realm of skincare, ALE has proven its ability to bolster essential defensive elements like HAS-1, AQP3, loricrin, and the growth factor PPAR-α within UVB-challenged HaCaT cells. Remarkably, this botanical extract has exhibited the remarkable capacity to counteract the hyperphosphorylation of MAPKs and the upregulation of IL-6 and IL-1β expression in UVB-induced HaCaT cells. With its abundant reserves of renowned natural bio-actives, ALE emerges as a compelling candidate. In light of these findings, it is conceivable that ALE could evolve into a promising therapeutic intervention for skin-related afflictions.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Konkuk University 2023.
References
- Akbar, S. Andrographis paniculata: a review of pharmacological activities and clinical effects. Altern. Med. Rev. 2011, 16. [Google Scholar]
- Salleh, L.M.; Hartati, H.; Jamaludin, R.; Yunus, M.A.C.; Yakub, H.; Aziz, A.A. Antioxidant Activity and Total Phenolic Contents in Methanol Extracts from Swietenia Mahagoni and Andrographis Paniculata. J. Teknol. 2014, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazid, A.B. , et al. , Green chicory leaf extract exerts anti-inflammatory effects through suppressing LPS-induced MAPK/NF-κB activation and hepatoprotective activity in vitro. Food Agricultural Immunology, 2020, 31, 513–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Liu, L.; Lai, T.; Zhang, R.; Wei, Z.; Xiao, J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, M. Phenolic profile, free amino acids composition and antioxidant potential of dried longan fermented by lactic acid bacteria. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 4782–4791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Mei, F.; Sun, Y.; Pan, G.; Liu, B.; Liu, K. Quercetin, Luteolin, and Epigallocatechin Gallate Promote Glucose Disposal in Adipocytes with Regulation of AMP-Activated Kinase and/or Sirtuin 1 Activity. Planta Medica 2014, 80, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazid, A.B., et al., Sodium Butyrate Alleviates Potential Alzheimer’s Disease In Vitro by Suppressing Aβ and Tau Activation and Ameliorates Aβ-induced Toxicity Food and Agricultural Immunology, 2023. 34. [CrossRef]
- Mojica, L., et al., Bean cultivars (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) have similar high antioxidant capacity, in vitro inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase while diverse phenolic composition and concentration. Food Research International, 2015. 69: p. 38-48. [CrossRef]
- Jaradat, N., et al., Chromatography analysis, in light of vitro antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiobesity, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, anticancer, and three-dimensional cancer spheroids’ formation blocking activities of Laurus nobilis aromatic oil from Palestine. Chemical and Biological Technologies in Agriculture, 2023. 10(1): p. 25.
- Kaczmarek, A.; Vandenabeele, P.; Krysko, D.V. Necroptosis: The Release of Damage-Associated Molecular Patterns and Its Physiological Relevance. Immunity 2013, 38, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 613–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T., et al., Fargesin inhibits melanin synthesis in murine malignant and immortalized melanocytes by regulating PKA/CREB and P38/MAPK signaling pathways. Journal of Dermatological Science, 2019. 94(1): p. 213-219. [CrossRef]
- Bayazid, A.B.; Jang, Y.A. The Role of Andrographolide on Skin Inflammations and Modulation of Skin Barrier Functions in Human Keratinocyte. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2021, 26, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Bae, J.-K.; Chae, H.-S.; Nhoek, P.; Choi, J.-S.; Chin, Y.-W. Isoliquiritigenin ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis through the inhibition of MAPK pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 31, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Kou, J.; Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Yang, Z. Alpinetin attenuates inflammatory responses by suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling pathways in DSS-induced acute colitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatti, M.Z.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, A.; Saeed, A.; Malik, S.A. Antioxidant and phytochemical analysis of Ranunculus arvensis L. extracts. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayazid, A.B.; Kim, J.G.; Azam, S.; Jeong, S.A.; Kim, D.H.; Park, C.W.; Lim, B.O. Sodium butyrate ameliorates neurotoxicity and exerts anti-inflammatory effects in high fat diet-fed mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2022, 159, 112743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, N.; Macarulla, M.T.; Aguirre, L.; Martínez-Castaño, M.G.; Portillo, M.P. Quercetin can reduce insulin resistance without decreasing adipose tissue and skeletal muscle fat accumulation. Genes Nutr. 2013, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Kim, J.G.; Jang, Y.A.; Bayazid, A.B.; Lim, B.O. Fermented black rice and blueberry with Lactobacillus plantarum MG4221 improve UVB-induced skin injury. Food Agric. Immunol. 2021, 32, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).