1. Introduction
Rice is one of the world’s major staple crops, as it constitutes the primary diet for over half of the global population [
1,
2]. Crop protection operations in rice cultivation are a crucial aspect of rice management due to the occurrence of pests and diseases throughout the rice plant’s lifecycle. During pesticide application, rice canopy parameters significantly influence the dispersion and retention of droplets[
3,
4]. The deposition of spray droplets in dense canopies is 40% lower than in canopies with moderate and low densities [
5]. Consequently, the effective detection of rice canopy density can offer valuable insights for calculating spray quantities during variable-rate application processes.
The primary metrics for assessing rice canopy density include Leaf Area Index (LAI) [
6] and plant height. LAI represents the total area of plant leaves per unit ground surface area [
7,
8]. A higher LAI value indicates a denser canopy with greater leaf area density, signifying higher canopy density. Field surveys have revealed that rice canopy density undergoes significant changes from tillering to jointing stages, with LAI increasing rapidly during this period. After jointing, the trend of LAI variation becomes more stable, and canopy density changes are less pronounced [
9].
Plant height is a key trait affecting the yield potential of rice [
10]. It refers to the vertical distance from the ground to the top of the plant. Crop height can directly reflect the growth status of the crop and be used for estimating crop biomass [
11]. For measuring crop LAI, traditional destructive sampling to assess LAI is both labor-intensive and time-consuming, making it unsuitable for measuring a large number of crop samples. Various non-destructive methods for estimating LAI inevitably introduce measurement errors associated with operators. Currently, there is no established method for non-destructively estimating crop LAI throughout the entire growing season [
12], and a similar issue exists for measuring plant height.
Various sensing technologies such as RGB cameras [
13], ultrasonic sensors [
14], multispectral and hyperspectral sensors [
15], as well as laser scanners [
16], have been utilized for characterizing crop canopies [
17]. Stereo vision technology is employed to describe intricate geometric features and extends traditional 2D imaging methods to characterize three-dimensional (3D) plant structures using multi-view images [
18]. However, these techniques have certain drawbacks, including stereo matching errors caused by lighting and shadows, incomplete reconstructed data due to occlusion between plant components, and a trade-off between accuracy and efficiency [
19].
Ultrasonic sensors are relatively inexpensive and easy to use, but they often have lower measurement accuracy and are susceptible to interference from the surroundings and measurement distances. Spectral images provide rich spectral and texture information but lack structural information that aids in understanding plant functionality. Optical images can effectively extract specific 3D phenotypic features (such as leaf area, canopy size, and plant height) in controlled environments. However, accurately and comprehensively characterizing 3D plant structures in outdoor environments often presents limitations.
The emergence of optical detection and LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology has provided a powerful tool for acquiring three-dimensional structural data of crops. LiDAR technology actively emits laser pulses and measures the distance to a target using time-of-flight principles. LiDAR has found wide applications in forest resource surveys [
20] and ecosystem monitoring [
21]. The laser beam emitted by LiDAR sensors has advantages such as high energy density, small divergence angle, and long linear propagation distance. It can partially penetrate vegetation canopies and overcome challenges associated with image-based phenotyping, such as illumination and saturation effects. Recently, LiDAR has gained increasing attention in plant phenotyping research [
22]. LiDAR systems installed on unmanned aerial vehicles or ground platforms can provide accurate measurements of phenotypic traits of crops such as peanuts, maize, and fruit trees at the regional level [
23,
24,
25].
However, these crops are more inclined to grow in the early stages, with clear row spacing and less leaf overlap, thus possessing distinct crop features. In contrast, the rice canopy becomes dense in the mid to late growth stages, making it difficult to distinguish planting rows. Rice is cultivated in paddies, making it challenging for conventional ground platforms to access the fields. Moreover, there are water-filled channels and depressions in the paddy fields, making it difficult for ground platforms and LiDAR systems to maintain smooth movement. The airflow generated by drones can disturb the rice canopy. These factors collectively increase the difficulty of using LiDAR technology for measuring the dense canopy height and Leaf Area Index (LAI) of rice in the later growth stages.Therefore, the primary objective of this research is to utilize LiDAR technology in paddy fields to estimate the dense canopy height and LAI of rice. This aims to provide support for the sustainable development of rice variable-rate spraying and agricultural production.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The experiment was conducted in a rice field located in the Runguo Agricultural Base in Zhenjiang City, Jiangsu Province, China, in the year 2022. The geographical coordinates are approximately 32°54’19" N latitude and 116°23’28" E longitude. The rice was in the heading stage of growth during the experiment, with a planting configuration of 18 centimeters between rows and 10 centimeters between individual plants within a row.
Figure 1.
Rice sampling field.
Figure 1.
Rice sampling field.
2.2. System Architecture
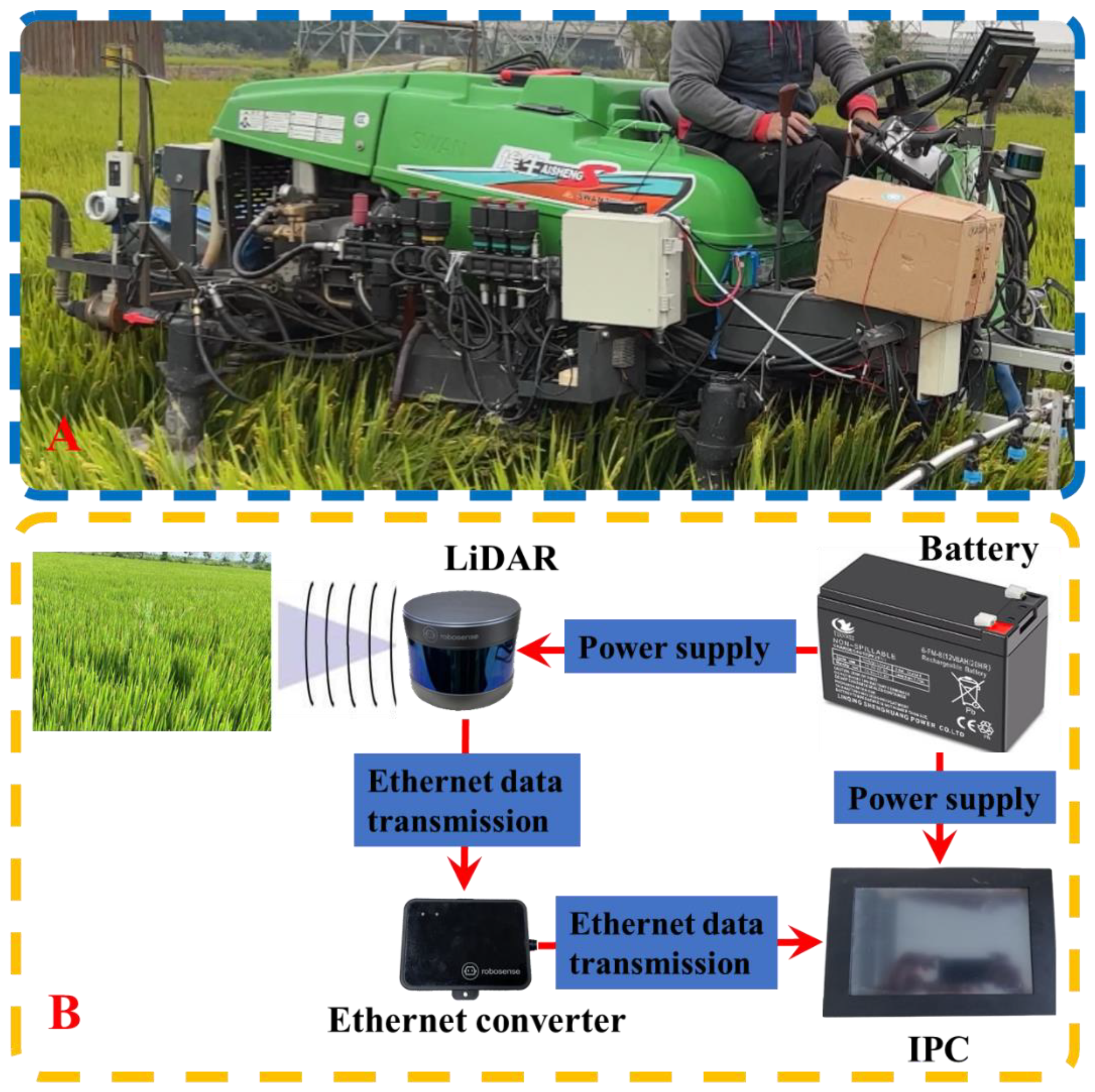
The radar data collection platform (
Figure 2A) consists of a spray boom sprayer (Swan Group Essen SWAN3WP-500) and a framework equipped with a ground-based LiDAR sensor (RS-Lidar-16, SICK AG, Waldkirch, Germany). The setup also includes an industrial control unit, a battery unit (24 V, 18.0 Amp.Hr.), and other necessary cables. The specifications of the LiDAR are presented in
Table 1.
Table 1.
The LiDAR specifications.
Table 1.
The LiDAR specifications.
| Indicator |
Value |
| Laser beams |
16 |
| Range |
20cm~150m |
| Range resolution |
+/- 2cm |
| Scan FOV |
30°x360° |
| Vertical angle resolution |
2° |
| Rotation rate |
300/600/1200 (r/min) |
| Laser wavelength |
905nm |
| Size |
109mm(diameter)*82.7mm(height) |
| Working temperature |
-10°C ~ + 60°C |
| Weight |
0.84kg |
Table 2.
The LiDAR specifications.
Table 2.
The LiDAR specifications.
| Indicator |
Value |
| Size (mm) |
3430 (length) * 1750 (width) * 2360 (height) |
| Track width (mm) |
1540 |
| Minimum ground clearance (mm) |
1055 |
| Quality (kg) |
880 |
| Engine power rating (KW/rpm) |
17.1/3600 |
| Travel speed (km/h) |
0-11 |
| Battery |
12V45Ah |
The LiDAR is mounted on a high clearance sprayer platform situated 1.5 meters above the ground, angled downward at 30 degrees (
Figure 2A). To obtain a comprehensive view of the entire rice canopy, the LiDAR is configured to operate in continuous line scanning mode, covering a 360-degree field of view with a resolution of 0.09 degrees. For each line scan, the LiDAR outputs 320,000 points per second. To ensure high-speed data collection, the LiDAR is connected to an industrial control unit (
Figure 2B) via a serial-to-Ethernet converter. The LiDAR scan data, including distance, angle, and reflectivity information, are encapsulated into packets using the Main Stream Output Protocol (MSOP) and sent to the industrial control unit. RSVIEW 1.4.3 is employed for point cloud data collection and storage, as well as for communication with the LiDAR. It correctly receives data packets, extracts point cloud data, converts polar coordinates into Cartesian coordinates, and eventually saves the data in a Pcap file. All line scan data are timestamped with distance and time information.
Figure 2.
Point cloud data acquisition platform and point cloud data acquisition system.
Figure 2.
Point cloud data acquisition platform and point cloud data acquisition system.
2.3. Field Setup and Data Acquisition
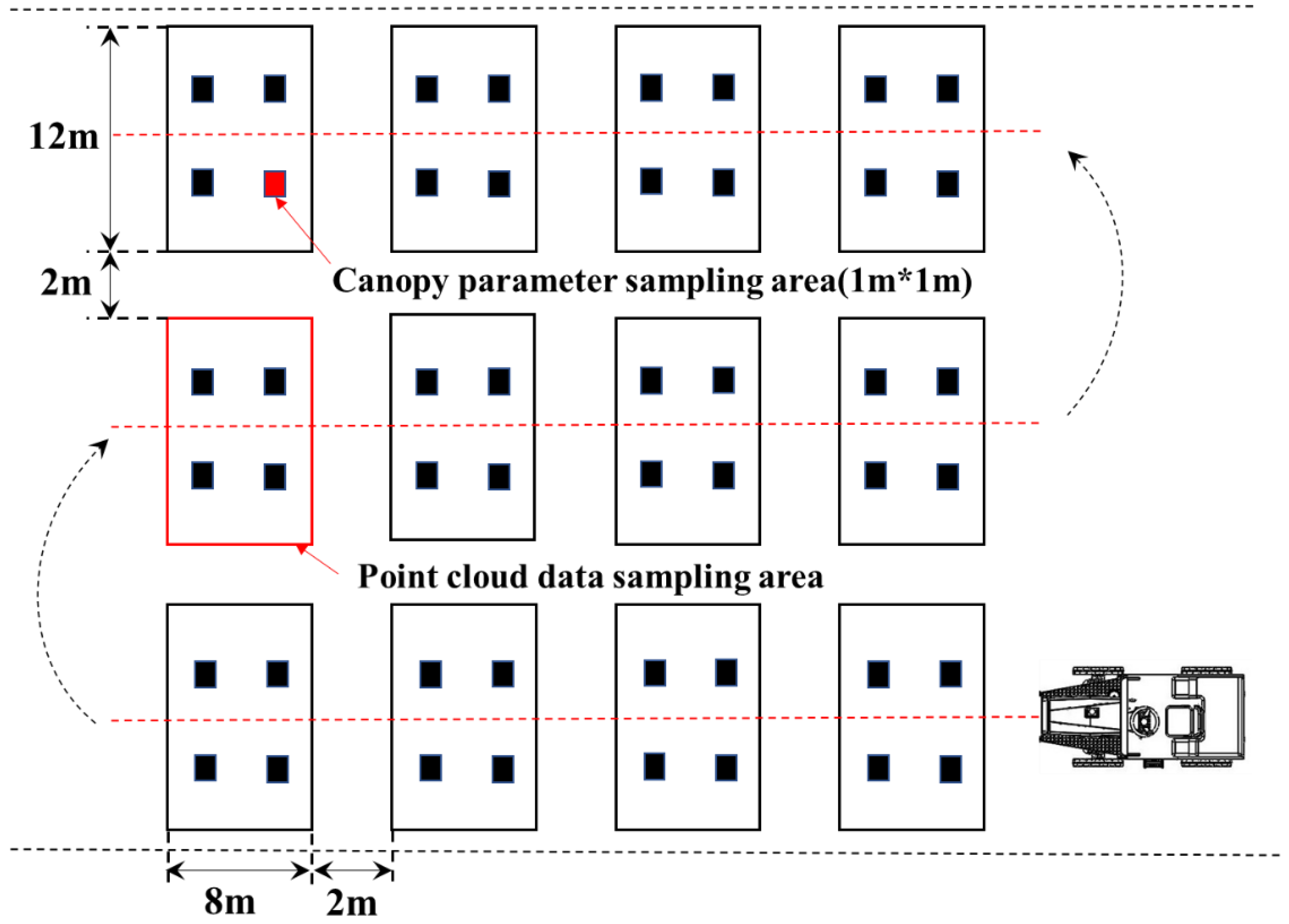
The point cloud data collection platform is utilized to gather information about the rice canopy in the designated field. The sprayer machine travels along the rice planting rows, minimizing damage to rice plants and ensuring that the LiDAR’s detection of rice canopy information remains unaffected. Each field plot is 12 m wide and 8 m long. The 12 plots are arranged in three rows in the field, separated by 2 m of border space (
Figure 3). The point cloud data collection system scans the entire field, covering all 12 plots. The scan data for each individual plot is stored in separate files on the industrial control unit.
Figure 3.
The distribution of rice canopy point cloud data collection plots.
Figure 3.
The distribution of rice canopy point cloud data collection plots.
2.4. Ground-Truth Data Collection
To validate the estimated values obtained from the LiDAR, four 1m x 1m rice canopy parameter sampling areas were established within each of the 12 rice fields. These areas were designated for measuring the ground truth of actual rice canopy height and Leaf Area Index (LAI). The sampling areas were uniformly distributed across each field plot. Within each sampling area, the heights (excluding awns) and leaf areas of all rice plants were measured. Rice plant heights were measured manually, while rice leaf area was collected using a CI-203 Leaf Area Meter produced by CID, USA. This portable leaf area meter has a maximum measurement width of 102mm, accuracy of <1%, and a resolution of 0.05mm². The Leaf Area Index for each field plot was calculated using Formula (1).
Figure 4.
The leaf area meter is used to measure the leaf area of rice plants.
Figure 4.
The leaf area meter is used to measure the leaf area of rice plants.
In the formula, LAI represents the Leaf Area Index of the field plot, LA stands for the total leaf area of the plants within the sampling area, and ni denotes the identification number of the sampling area.
2.5. Raw Data
The raw data primarily consists of distance information, angle information, timestamp information, and reflectivity information. The LiDAR is configured with its center as the origin, using horizontal rotation angles and distance parameters. The resolution of the horizontal rotation angle values is 0.01 degrees. The angle and distance information in polar coordinates is transformed into Cartesian coordinates (xyz) in the LiDAR’s coordinate system. The defined timestamps are used to record the system’s time with a resolution of 1 ms.
The data also includes reflectivity information of the measured objects. Reflectivity is a measure of an object’s ability to reflect light and is greatly influenced by the material properties of the object. During the collection of rice canopy point cloud data, the LiDAR moves along the rice canopy data collection system, continuously capturing data at a sampling interval of 0.1s.
2.6. Data Preprocessing
Each LiDAR dataset from the 12 plots is collected based on the predefined experimental setup and requires preprocessing. The process involves defining the region of interest and using the point cloud data collection system to scan with a horizontal width of 12 meters while moving uniformly along the rows for 8 meters within the plot. This scanning process captures the rice canopy point cloud data within each field plot. The point cloud data is then converted from polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates and integrated into a common reference coordinate system. Subsequently, the point cloud data is registered, overlapping points are trimmed, and redundant points are removed.
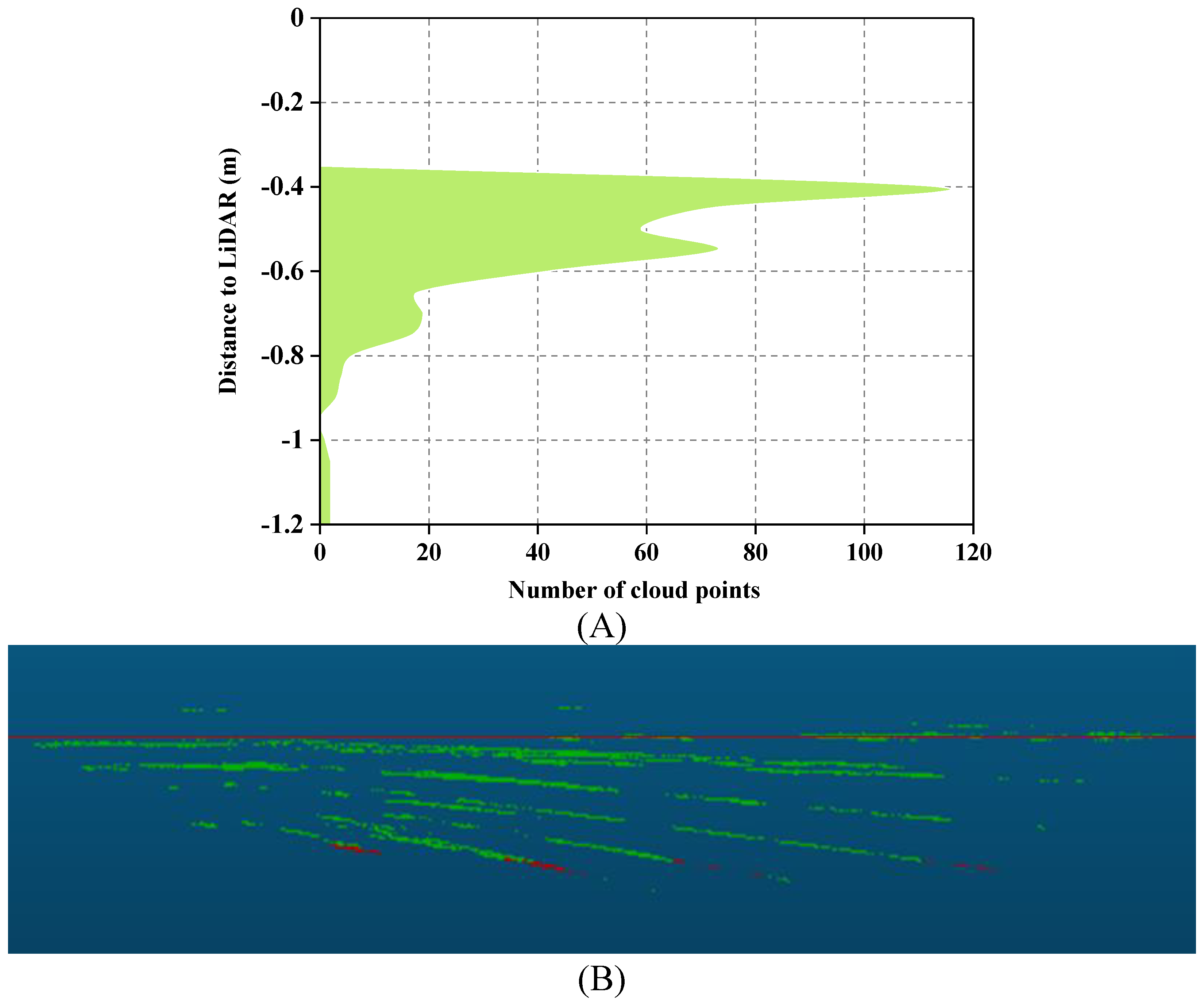
Once integrated, the point cloud data of the region of interest appears as shown in
Figure 5, where all the datasets are combined and processed to depict the rice canopy information accurately.
Figure 5.
Illustrates the determination of canopy height using LiDAR. (A) Displays the distance-area accumulation plot relative to LiDAR. (B) Presents a side view of the point clouds from the same column as (A). Non-ground points are represented by green point clouds, ground points are represented by red point clouds, and the red line corresponds to the height at the 0.975 percentile.
Figure 5.
Illustrates the determination of canopy height using LiDAR. (A) Displays the distance-area accumulation plot relative to LiDAR. (B) Presents a side view of the point clouds from the same column as (A). Non-ground points are represented by green point clouds, ground points are represented by red point clouds, and the red line corresponds to the height at the 0.975 percentile.
2.6.1. Rice Canopy Height Calculation
To determine rice canopy height using LiDAR, it’s necessary to estimate the ground elevation and subtract it from the absolute height of the points. In this study, the nominal distance from the LiDAR to the ground is relatively fixed, and the LiDAR’s position is above the rice canopy. The method used involves selecting the top point cloud of the canopy detected by LiDAR using a percentile-based approach and calculating a surface model for the rice canopy [
23]. The estimated canopy height is the difference between the ground elevation on the Z-axis and the percentile value.
To determine the optimal percentile value that defines the top of the rice canopy, a range of percentile values from 0.8 to 1 was tested with an increment of 0.005. Manual measurements of canopy height were performed using a ruler [
26]. The Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) was calculated between the canopy height estimated by LiDAR detection and the canopy height measured manually. This provides an assessment of the accuracy of the LiDAR-based estimation of canopy height compared to manual measurements.
2.6.2. LAI Estimation of Rice Canopy
The LAI estimation model is primarily determined through its correlation with the gap fraction derived from LiDAR data [
27]. The underlying theory is based on the transformed equation of the Beer-Lambert law (Eq.2).
In Eq.2, LAI stands for Leaf Area Index, I represents the light intensity below the canopy, I0 represents the light intensity above the canopy, and k is the extinction coefficient.
Various laser penetration metrics (LPM) are used as proxies for I/I0 to estimate LAI. For point cloud data, LPM can be calculated as the ratio of ground echoes to total echoes or the ratio of ground echo intensity to total echo intensity (based on intensity) [
28,
29].
To establish an LAI estimation model for rice canopies, following the Beer-Lambert law, a linear model is used to compare LiDAR-derived LPM
1 and LPM
2. Regression analysis is performed between these LPM values and LAI measurements obtained in the field. This regression analysis helps establish a relationship between the laser penetration metrics and the actual Leaf Area Index of the rice canopy.
In Eq.3 and Eq.4, LPM1 and LPM2 refer to laser penetration metrics. Specifically, LPM1 is the ratio of the number of ground echoes (Nground) to the total number of echoes (Ntotal). LPM2 is calculated based on echo intensity and is the ratio of the intensity of ground echoes (Sground) to the total intensity of echoes (Stotal).
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rice Canopy Height Estimation and Accuracy Assessment
LiDAR detection of rice canopy height is illustrated in
Figure 5. The analysis involves examining the Z-axis coordinates of all point clouds within the region of interest detected by LiDAR. A histogram (
Figure 5A) is constructed with the data accumulation of the maximum Z-axis values from the point clouds.
Figure 5B provides a side view of the point clouds in the region of interest. In this representation, the blue line represents the ground obtained from the peak of the histogram, while the red line corresponds to the height at the 0.975 percentile.
From the point cloud side view in
Figure 5B, it’s evident that points closer to the ground are fewer in number. This is attributed to the dense canopy formed in the middle and later stages of rice growth, which reduces the likelihood of laser penetration into the canopy interior. Consequently, the majority of the point cloud concentrates on the upper part of the canopy. The results of rice canopy height verification are shown in
Figure 6. An analysis of the Z-axis coordinates of all point clouds within the region of interest detected by LiDAR was conducted. Percentiles were calculated with a 0.5% increment, ranging from 80% to 100%. The optimal percentile was determined by minimizing the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between manually measured canopy heights and canopy heights obtained from various percentiles of LiDAR detection. The optimal percentile was found to be 0.975 (
Figure 6A). Linear regression analysis was performed between manually measured canopy heights and LiDAR-detected heights. The coefficient of determination (R
2) was 0.941, RMSE was 0.019 meters, and the slope was 1.266 (
Figure 6B).
Figure 6.
depicts the validation of rice canopy height. (A) Illustrates the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between manually measured canopy heights from different plots and the LIDAR-derived canopy heights at different percentile values. (B) Displays a scatter plot and a fitted plot comparing the average manually measured canopy height from various plots with the canopy height obtained from LiDAR detection at the 0.975 percentile. Error lines represent the positive and negative standard deviations for each plot.
Figure 6.
depicts the validation of rice canopy height. (A) Illustrates the Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) between manually measured canopy heights from different plots and the LIDAR-derived canopy heights at different percentile values. (B) Displays a scatter plot and a fitted plot comparing the average manually measured canopy height from various plots with the canopy height obtained from LiDAR detection at the 0.975 percentile. Error lines represent the positive and negative standard deviations for each plot.
The comparison between the manually measured average canopy heights of rice from different plots and the detected average canopy heights using LiDAR is provided.
Table 3 not only presents the detection errors between the two methods but also includes the standard deviation of manually measured canopy heights. The minimum and maximum errors in detected canopy heights are 0.24% and 12.98%, respectively.
Table 3.
Detection and estimation results of average height of rice canopy.
Table 3.
Detection and estimation results of average height of rice canopy.
| Plot |
Average height of rice canopy (cm) |
| Manual measured |
Std |
LiDAR measured |
Error (%) |
| 1 |
0.72 |
0.13 |
0.67242 |
7.08 |
| 2 |
0.74 |
0.06 |
0.66734 |
10.89 |
| 3 |
0.83 |
0.09 |
0.78127 |
6.24 |
| 4 |
0.76 |
0.06 |
0.67266 |
12.98 |
| 5 |
0.85 |
0.04 |
0.79745 |
6.59 |
| 6 |
0.77 |
0.11 |
0.7214 |
6.74 |
| 7 |
0.84 |
0.09 |
0.8204 |
2.39 |
| 8 |
0.85 |
0.08 |
0.79758 |
6.57 |
| 9 |
0.86 |
0.04 |
0.85796 |
0.24 |
| 10 |
0.82 |
0.08 |
0.78918 |
3.91 |
| 11 |
0.87 |
0.13 |
0.85257 |
2.04 |
| 12 |
0.71 |
0.16 |
0.65143 |
8.99 |
The experiment demonstrates that estimating rice canopy height through LiDAR is feasible, yet accurate ground elevation data is still crucial. As observed from
Figure 6, during the later growth stages of rice when the canopy becomes denser, only a limited amount of laser beams can penetrate through the canopy to reach the ground, with the majority of LiDAR points originating from the canopy top. Despite reducing the area of interest to a smaller region (12*6m), there still remains a canopy height detection error ranging from 0.24% to 12.98%.
3.2. LAI Estimation Using LiDAR Data
The rice canopy point cloud data collected by LiDAR was used to assess and compare two methods for estimating rice Leaf Area Index (LAI). The impact of key parameters, namely two Laser Penetration Metrics (LPM), on LiDAR-detected LAI was evaluated. Regression analysis was conducted between LiDAR-derived LAI using the two LPMs and field-measured LAI. The coefficient of determination (R
2) and Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) were calculated to evaluate the fitness of the constructed models.
Table 4 provides the data for the two penetration metrics, as well as manually measured Leaf Area Index and measurement standard deviation.
Table 4.
Measurement and estimation results of rice LAI.
Table 4.
Measurement and estimation results of rice LAI.
| Plot |
LAI of rice (m2·m-2) |
| Measurement |
Std |
LPM1 |
LPM2 |
| 1 |
8.03 |
0.85 |
0.315385 |
0.278176 |
| 2 |
7.87 |
0.69 |
0.357357 |
0.286521 |
| 3 |
8.76 |
0.97 |
0.109817 |
0.078993 |
| 4 |
8.24 |
0.39 |
0.410256 |
0.364966 |
| 5 |
8.55 |
1.06 |
0.168514 |
0.123336 |
| 6 |
8.33 |
0.81 |
0.194831 |
0.165871 |
| 7 |
8.57 |
0.45 |
0.117978 |
0.0979711 |
| 8 |
8.55 |
0.93 |
0.0438413 |
0.0323046 |
| 9 |
8.79 |
1.04 |
0.121986 |
0.0874539 |
| 10 |
8.42 |
0.65 |
0.0533563 |
0.0388916 |
| 11 |
8.51 |
0.58 |
0.208683 |
0.0341212 |
| 12 |
7.92 |
0.46 |
0.107438 |
0.0856531 |
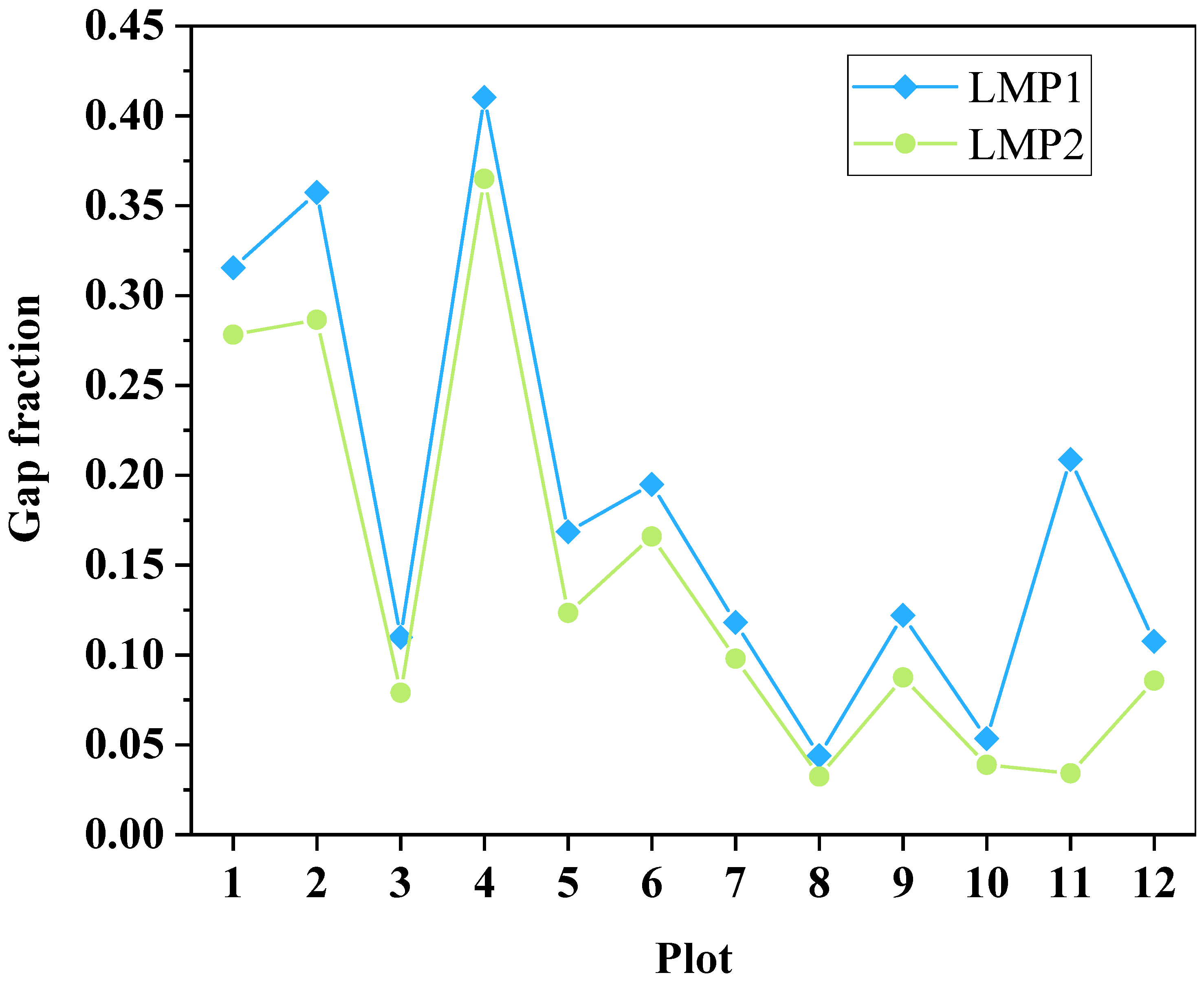
A factorial analysis of variance was conducted on the two different gap fractions for various plots to assess the correlation between the two distinct gap fractions. The results indicate a strong positive correlation between the two different gap fractions (F=12.866, P<0.05).
Figure 7 presents a comparative illustration of the gap fractions from different plots.
Figure 7.
Comparison of gap fractions among different plots.
Figure 7.
Comparison of gap fractions among different plots.
Different inter-row gap scores (LPM1 and LPM2) were subjected to a factorial analysis of variance across different field plots to assess the correlation between these gap scores and the average rice LAI measured manually. The results indicated varying degrees of correlation between different gap scores and the average rice LAI. Specifically, there was weak correlation between LPM1 and rice canopy LAI (F=4.599, P=0.058>0.05), while LPM2 showed a stronger correlation with manually detected rice canopy LAI (F=3.499, P=0.043<0.05).
A simple linear regression analysis was performed between the different inter-row gap scores (LPM
1 and LPM
2) and the manually measured average rice canopy LAI across various field plots. Different LPM analyses yielded varying R
2 and RMSE values: for LPM
1, R
2 was 0.24 and RMSE was 0.1; for LPM
2, R
2 was 0.28 and RMSE was 0.09. Previous LAI estimation models based on LPM achieved variances of 69-94% for most studies, which were primarily focused on estimating forest canopy LAI. Even for low-statured wetland vegetation (<2m), variances of 55-60% in LAI estimation were attainable [
29]. In this study, the rice canopy height was less than 1m. LiDAR’s capability to produce ground echoes in densely vegetated and low-statured canopy regions was limited due to its poorer penetration ability in such environments[
30]. In comparison to forest and relatively low-statured vegetation, rice is much shorter, and its dense canopy reduces the probability of laser pulses penetrating the canopy to reach the ground. This is a critical factor affecting the accuracy of LAI estimation using LPM.
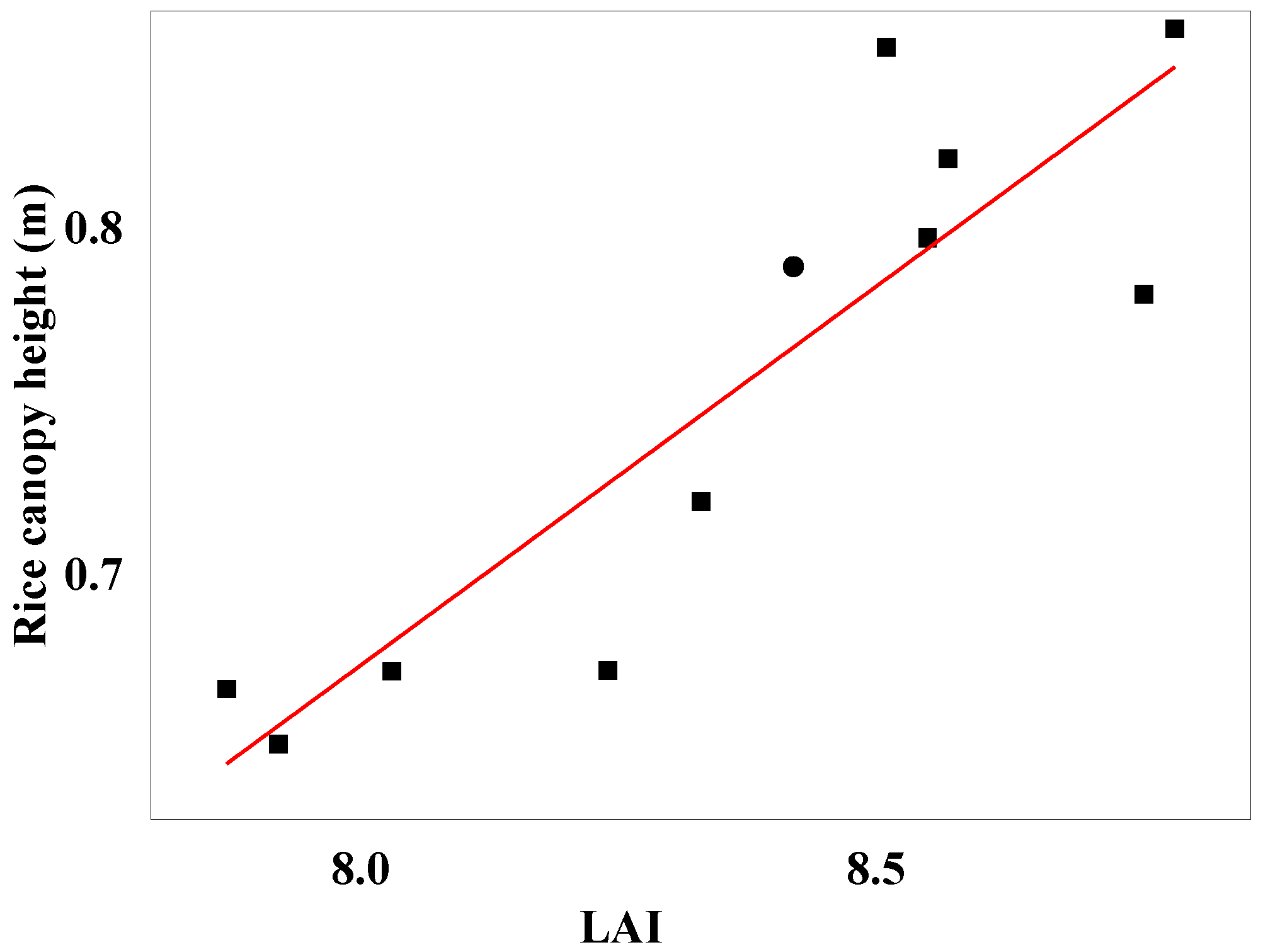
In this study, a simple linear regression analysis was conducted between the manually measured LAI from different field plots and the rice canopy height detected by LiDAR. The obtained R
2 value was 0.77, and the RMSE was 0.03. These results strongly indicate a significant correlation between rice canopy height and rice canopy LAI. The scatter plot of rice canopy LAI against LiDAR-detected rice canopy height is depicted in
Figure 8.
Figure 8.
Relationship between ricecanopy height and LAI.
Figure 8.
Relationship between ricecanopy height and LAI.
4. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the feasibility of using LiDAR for detecting rice canopy height and density. Through the analysis of LiDAR point clouds, accurate estimation of canopy height can be achieved. The use of gap fraction estimation for rice LAI based on ground returns and return intensity showed a strong correlation between different methods of gap fraction calculation. However, during the later stages of rice growth, the dense canopy reduces the likelihood of laser penetration to the ground, making it challenging to estimate LAI using gap fraction, even though a correlation exists between LAI and gap fraction based on return intensity. Regression analysis between LiDAR-predicted canopy height and LAI revealed the potential for estimating LAI through canopy height. In summary, LiDAR point clouds hold significant potential for assessing morphological parameters and distribution in crops, yet challenges persist in applications involving low-stature and dense crops like rice. This research contributes to improving the accuracy of estimating rice canopy height and LAI. Further studies are needed to enhance filtering algorithms for accurate classification of low-stature and dense crops.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Xinhua Wei; Validation, Fei Wang; Formal analysis, QI Song; Writing – original draft, Linlong Jing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Technological Innovation 2030—Major Projects Topics (2022DZ0115804).
References
- Mohanty, S., Wassmann, R., Nelson, A., Moya, P., & Jagadish, S. V. K. (2013). Rice and climate change: significance for food security and vulnerability. International Rice Research Institute, 14, 1-14.
- Elert, E. (2014). Rice by the numbers: A good grain. Nature, 514(7524), S50-S50. [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A., Sinfort, C., Tinet, C., Pierrat, D., & Huberson, S. (2006). A Lagrangian model for spray behaviour within vine canopies. Journal of Aerosol Science, 37(5), 658–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaerosci.2005.05.016. [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M., & Salyani, M. (2004). Modeling of spray penetration and deposition on citrus tree canopies. Transactions of the ASAE, 47(3), 619-627. https://doi.org/10.13031/2013.16091. [CrossRef]
- Gaskin, R. E., Manktelow, D. W., Cook, S., May, W. A., & Van_Leeuwen, R. M. (2013). Effects of canopy density on spray deposition in kiwifruit. New Zealand Plant Protection, 66, 194–198. https://doi.org/10.30843/nzpp.2013.66.5607. [CrossRef]
- Yang X. H., Wang F. M., Huang J. F., Wang J. W., Wang R. C., Shen Z. Q., Wang X. Z. (2009). Comparison between radial basis function neural network and regression model for estimation of rice biophysical parameters using remote sensing. Pedosphere, 19(2), 176-188. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G., & Moskal, L. M. (2009). Retrieving leaf area index (LAI) using remote sensing: theories, methods and sensors. Sensors, 9(4), 2719-2745. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X., He, L., Salas, W., Li, C., Moore Iii, B., Zhao, R., ... & Boles, S. (2002). Quantitative relationships between field-measured leaf area index and vegetation index derived from VEGETATION images for paddy rice fields. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(18), 3595-3604. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y. J., & Tian, Q. J. (2015, October). Using hyperspectral data for rice LAI estimation at different phenological periods. In AOPC 2015: Advanced Display Technology; and Micro/Nano Optical Imaging Technologies and Applications (Vol. 9672, pp. 132-139). SPIE.
- Zhang, Y., Yu, C., Lin, J., Liu, J., Liu, B., Wang, J., ... & Zhao, T. (2017). OsMPH1 regulates plant height and improves grain yield in rice. PloS one, 12(7), e0180825. [CrossRef]
- Confalonieri, R., Bregaglio, S., Rosenmund, A. S., Acutis, M., & Savin, I. (2011). A model for simulating the height of rice plants. European journal of agronomy, 34(1), 20-25. [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S., Koba, K., Okamura, M., Watanabe, Y., Hosoi, J., Nakagomi, K., ... & Sugiura, D. (2021). Novel technique for non-destructive LAI estimation by continuous measurement of NIR and PAR in rice canopy. Field Crops Research, 263, 108070. [CrossRef]
- Raj, R., Walker, J. P., Pingale, R., Nandan, R., Naik, B., & Jagarlapudi, A. (2021). Leaf area index estimation using top-of-canopy airborne RGB images. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 96, 102282. [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, H., Minaei, S., Ghobadian, B., & Masoudi, H. (2015). Ultrasonic sensing of pistachio canopy for low-volume precision spraying. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 112, 149-160. [CrossRef]
- Zaman-Allah, M., Vergara, O., Araus, J. L., Tarekegne, A., Magorokosho, C., Zarco-Tejada, P. J., ... & Cairns, J. (2015). Unmanned aerial platform-based multi-spectral imaging for field phenotyping of maize. Plant methods, 11(1), 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S., & Li, C. (2017). In-field high throughput phenotyping and phenotype data analysis for cotton plant growth using LiDAR. In 2017 ASABE Annual International Meeting (p. 1). American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers. [CrossRef]
- Jin, X., Zarco-Tejada, P. J., Schmidhalter, U., Reynolds, M. P., Hawkesford, M. J., Varshney, R. K., ... & Li, S. (2020). High-throughput estimation of crop traits: A review of ground and aerial phenotyping platforms. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Magazine, 9(1), 200-231. [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y., Tang, L., Srinivasan, S., & Schnable, P. S. (2019). Field-based architectural traits characterisation of maize plant using time-of-flight 3D imaging. Biosystems Engineering, 178, 86-101. [CrossRef]
- Li, L., Zhang, Q., & Huang, D. (2014). A review of imaging techniques for plant phenotyping. Sensors, 14(11), 20078-20111. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y., Guo, Q., Collins, B. M., Fry, D. L., Hu, T., & Kelly, M. (2016). Forest fuel treatment detection using multi-temporal airborne lidar data and high-resolution aerial imagery: a case study in the Sierra Nevada Mountains, California. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 37(14), 3322-3345. [CrossRef]
- Toda, L. L., Yokingco, J. C. E., Paringit, E. C., & Lasco, R. D. (2017). A LiDAR-based flood modelling approach for mapping rice cultivation areas in Apalit, Pampanga. Applied Geography, 80, 34-47. [CrossRef]
- Sun, S., Li, C., Paterson, A. H., Jiang, Y., Xu, R., Robertson, J. S., ... & Chee, P. W. (2018). In-field high throughput phenotyping and cotton plant growth analysis using LiDAR. Frontiers in Plant Science, 9, 16. [CrossRef]
- Friedli, M., Kirchgessner, N., Grieder, C., Liebisch, F., Mannale, M., & Walter, A. (2016). Terrestrial 3D laser scanning to track the increase in canopy height of both monocot and dicot crop species under field conditions. Plant methods, 12, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y., Wu, F., Ao, Z., Jin, S., Qin, F., Liu, B., ... & Guo, Q. (2019). Evaluating maize phenotype dynamics under drought stress using terrestrial lidar. Plant methods, 15, 1-16. [CrossRef]
- Estornell, J., Hadas, E., Martí, J., & López-Cortés, I. (2021). Tree extraction and estimation of walnut structure parameters using airborne LiDAR data. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 96, 102273. [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Berni, J. A., Deery, D. M., Rozas-Larraondo, P., Condon, A. T. G., Rebetzke, G. J., James, R. A., ... & Sirault, X. R. (2018). High throughput determination of plant height, ground cover, and above-ground biomass in wheat with LiDAR. Frontiers in plant science, 9, 237. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y., & Fang, H. (2020). Estimation of LAI with the LiDAR technology: A review. Remote Sensing, 12(20), 3457. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K., & Popescu, S. (2009). Lidar-based mapping of leaf area index and its use for validating GLOBCARBON satellite LAI product in a temperate forest of the southern USA. Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(8), 1628-1645. [CrossRef]
- Luo, S., Chen, J. M., Wang, C., Gonsamo, A., Xi, X., Lin, Y., ... & Qin, H. (2017). Comparative performances of airborne LiDAR height and intensity data for leaf area index estimation. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 11(1), 300-310. [CrossRef]
- Sadro S, Gastil-Buhl M, Melack J. Characterizing patterns of plant distribution in a southern California salt marsh using remotely sensed topographic and hyperspectral data and local tidal fluctuations. Remote Sensing of Environment. 2007 Sep 28;110(2):226-39. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).