Submitted:
31 August 2023
Posted:
01 September 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
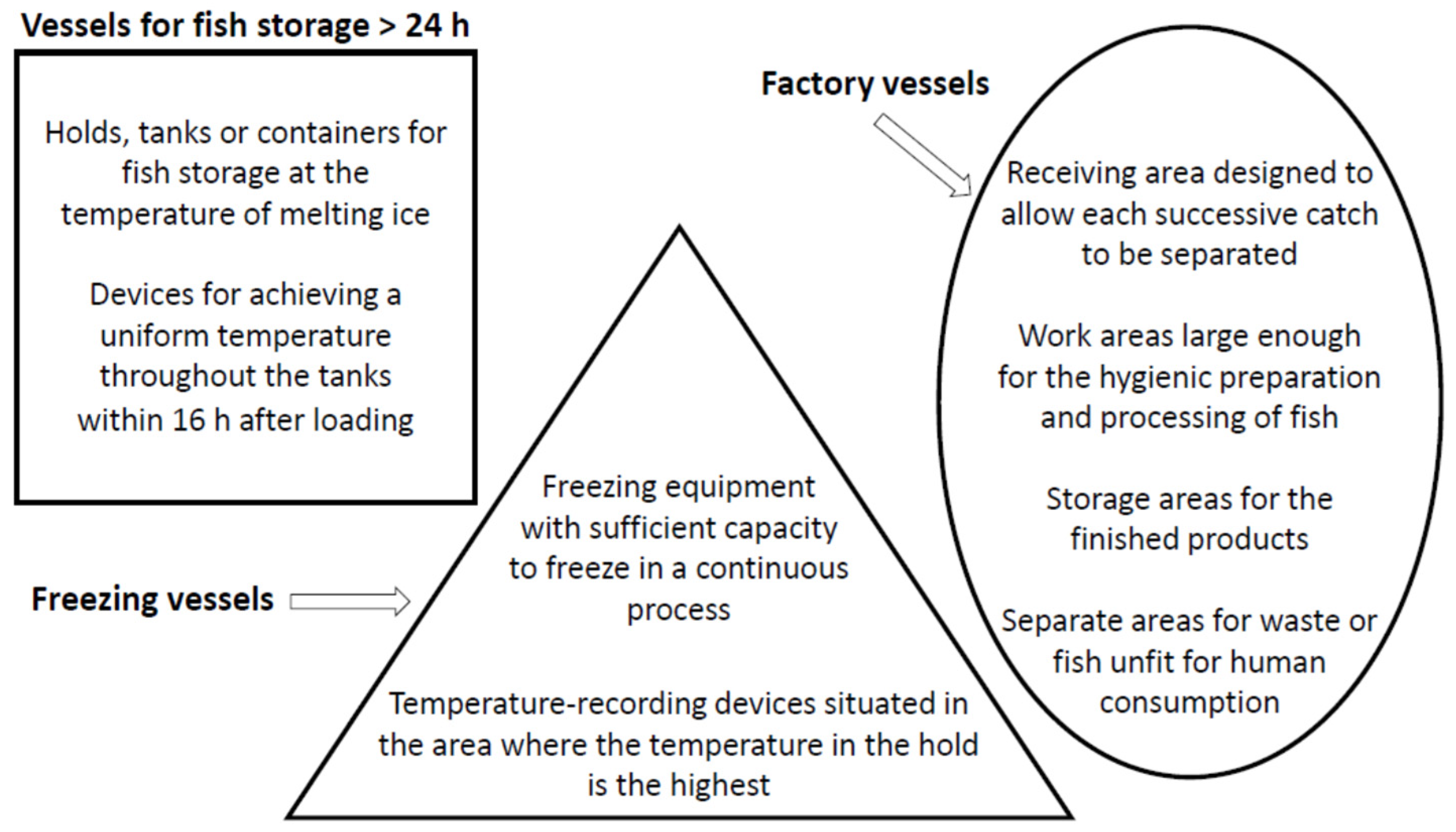
2. Structural Requirements for Vessels and Correct handling And Storage of Fish
3. Influence of Microbial Contamination on Fish Quality
3.1. Natural Microbiota of Fish
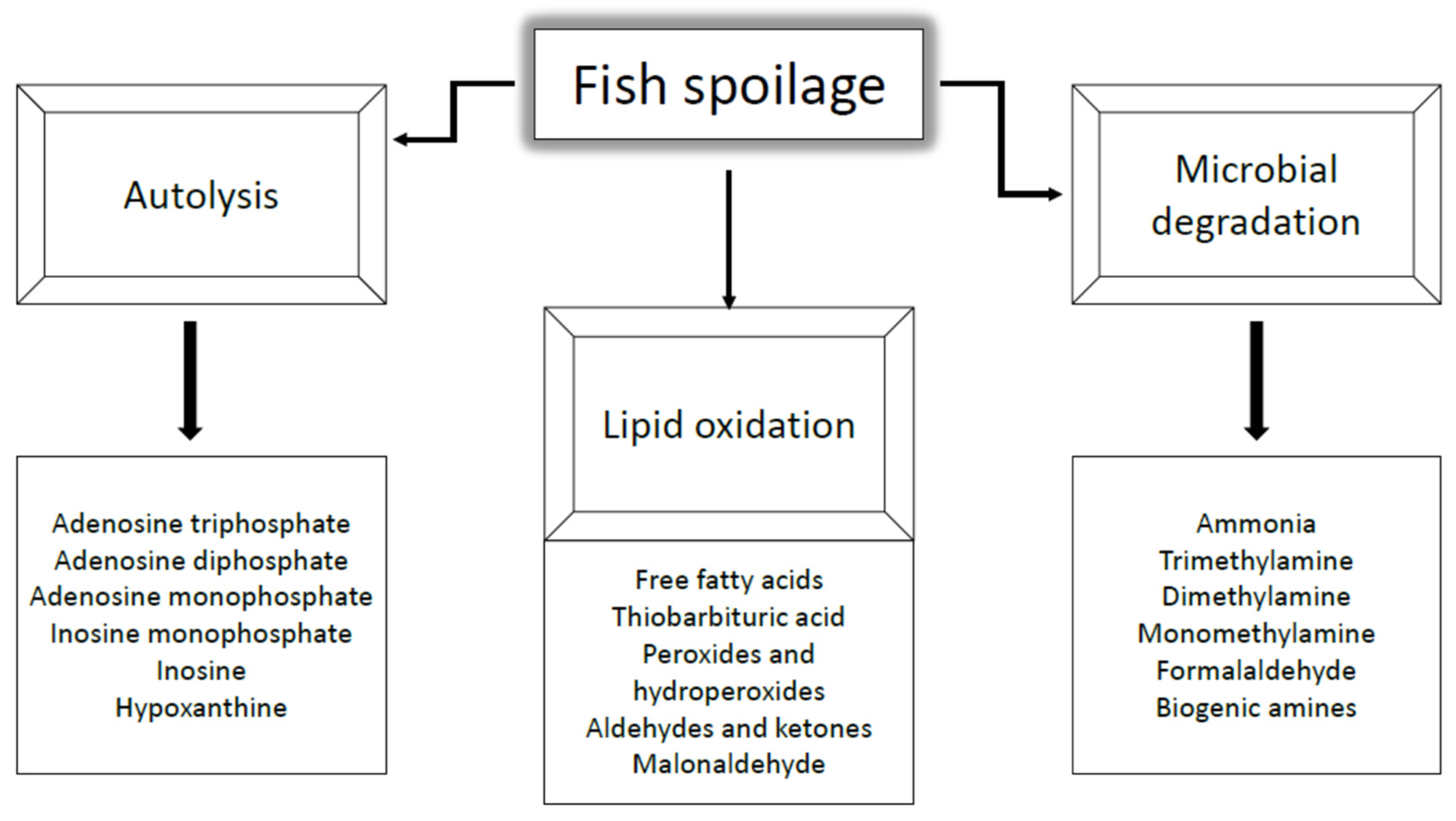
3.2. Spoilage Phenomena
4. Biological Hazards Affecting Fish Safety
4.1. Pathogenic Bacteria
4.2. Viruses
4.3. Parasites
4.4. Histamine Formation
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edirisinghe, S.K.; Wickramasinghe, I.; Wansapala, M.A.J.; Warahena, A.S.K. Adoption of hygienic practices in selected fish markets along the fish supply chain, in Sri Lanka. Food Research 2022, 6, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022. Towards Blue Transformation. Rome, FAO, 2022; pp. 1–266. [CrossRef]
- Visciano, P. Chemicals and Safety of Chemical Contaminants in Seafood. In Food Safety Chemistry. Toxicant Occurrence, Analysis and Mitigation; Liangli, L.Y., Shuo,W., Bao-Guo, S., Eds.; CRC Press; Taylor & Francis Group, Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 215–236.
- Kuley, E.; Yavuzer, M.N.; Yavuzer, E.; Durmuş, M.; Yazgan, H.; Gezginç, Y.; Özogul, F. Inhibitory effects of safflower and bitter melon extracts on biogenic amine formation by fish spoilage bacteria and food borne pathogens. Food Bioscience 2019, 32, 100478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saelens, G.; Houf, K. Systematic review and critical reflection on the isolation and identification methods for spoilage associated bacteria in fresh marine fish. Journal of Microbiological Methods 2022, 203, 106599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Limia, L.; Cutillas, R.; Carballo, J.; Franco, I.; Martínez, S. Free amino acids and biogenic amines in canned European eels: Influence of processing step, filling medium and storage time. Foods 2020, 9, 1377. [Google Scholar]
- Comas-Basté, O.; Latorre-Moratalla, M.L.; Sánchez-Pérez, S.; Veciana-Nogués, M.T.; Vidal-Carou, M.C. Histamine and other biogenic amines in food. From scombroid poisoning to histamine intolerance. In Biogenic Amines; Proestos, C., Ed.; IntechOpen, London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, W.P.; Silva, T.M.; Guidi, L.R.; Tette, P.A.S.; Byrro, R.M.D.; Paula Santiago-Silva, P.; Christian Fernandes, C.; Gloria, M.B.A. Quality assurance of histamine analysis in fresh and canned fish. Food Chemistry 2016, 211, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavisetty, S.C.B.; Vu, H.T.K.; Benjakul, S.; Vongkamjan, K. Rapid pathogen detection tools in seafood safety. Current Opinion in Food Science 2018, 20, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, D.L. Spoilage of Animal product. Seafood. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, Second Edition, Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L. Eds.; 2014, 3, pp. 453–458. [CrossRef]
- Ghaly, A.E.; Dave, D.; Budge, S.; Brooks, M.S. Fish spoilage mechanisms and preservation techniques: Review. American Journal of Applied Sciences 2010, 7, 859–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anagnostopoulos, D.A.; Parlapani, F.; Boziaris, I.S. The evolution of knowledge on seafood spoilage microbiota from the 20th to the 21st century: Have we finished or just begun? Trends in Food Science & Technology 2022, 120, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boziaris, I.S., Parlapani, F.F. Specific Spoilage Organisms (SSO) in Fish. In The Microbiological Quality of Food: Foodborne Spoilers; Bevilacqua, A.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Sykes, R. Eds.; Elsevier, Woodhead Publishing Series in Food Science, Technology and Nutrition 2017, pp. 61–98.
- Freitas, J.; Vaz-Pires, P.; Câmara, J.S. Quality Index Method for fish quality control: Understanding the applications, the appointed limits and the upcoming trends. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 111, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogn-Grundvåg, G.; Zhang, D.; Dreyer, B. Fishing methods for Atlantic cod and haddock: quality and price versus costs. Fisheries Research 2020, 230, 105672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, A.; Abraha, B.; Samuel, M.; Mohammedidris, H.; Abraham, W.; Mahmud, E. Fish preservation: A multi-dimensional approach. MOJ Food Processing & Technology 2018, 6, 303–310. [Google Scholar]
- Beverly, S. Proper fish handling for quality and safety. In Fisheries Newsletter, Number 134, January–April 2011. 20 April.
- Duarte, A.M.; Silva, F.; Pinto, F.R.; Barroso, S.; Gil, M.M. Quality assessment of chilled and frozen fish—Mini review. Foods 2020, 9, 1739. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Benjakul, S. Proteolysis and its control using protease inhibitors in fish and fish products: A review. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 2018, 17, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microbial spoilage of fish and fish products and its preservation, by Sanjogta Thapa Magar. Edited By: Sagar Aryal, September 24, 2021. https://microbenotes.com/microbial-spoilage-of-fish-preservation/ (accessed on 18 August 2023).
- Watts, E. Seafood handling, processing, and packaging. Reference Module in Food Sciences 2022, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Maheswarappa, N.B. Superchilling of muscle foods: Potential alternative for chilling and freezing. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2019, 59, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, J.; Martins, A.; Fidalgo, L.G.; Lima, V.; Amaral, R.A.; Pinto, C.A.; Silva, A.M.; Saraiva, J.A. Fresh fish degradation and advances in preservation using physical emerging technologies. Foods, 2021, 10, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, S.; Arason, S.; Margeirsson, B.; Bergsson, A.B.; Palsson, O.P. The effects of superchilling on shelf-life and quality indicators of whole Atlantic cod and fillets. LWT - Food Science and Technology 2019, 100, 426–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benner, R.A. Organisms of concern but not foodborne or confirmed foodborne. Encyclopedia of Food Safety 2014, 2, 245–250. [Google Scholar]
- FDA. Chapter 4 - Pathogens From the Harvest Area. In Fish and Fish Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed., Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020a; pp. 75–90.
- Parlapani, F.F. Microbial diversity of seafood. Current Opinion in Food Science 2021, 37, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakara, P.K.; Vatsa, S.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. A comprehensive review on freshness of fish and assessment: Analytical methods and recent innovations. Food Research International 2020, 133, 109157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakara, P.K.; Srivastav, P.P.; Pathak, S.S. Kinetics of total volatile basic nitrogen and trimethylamine formation in stored rohu (Labeo rohita) fish. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology 2019, 28, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, S.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Hong, H.; Liu, J.; Luo, Y. Biochemical changes and amino acid deamination & decarboxylation activities of spoilage microbiota in chill-stored grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) fillets. Food Chemistry 2021, 336, 127683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedane, T.D.; Agga, G.E.; Gutema, F.D. Hygienic assessment of fish handling practices along production and supply chain and its public health implications in Central Oromia, Ethiopia. Scientific Reports 2022, 12, 13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Chapter 12 - Pathogenic Bacteria Growth and Toxin Formation (Other Than Clostridium botulinum) as a Result of Time and Temperature Abuse. In Fish and Fish Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed., Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020b; pp. 209–244.
- Toyofuku, H. Safety of Food and Beverages: Seafood. Reference Module in Food Sciences 2023, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Oh, M.; Kim, B.S. Phage biocontrol of zoonotic food-borne pathogen Vibrio parahaemolyticus for seafood safety. Food Control 2023, 144, 109334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z. , Larsen, A.M., Bullard, S.A., Wright, A.C., Arias, C.R. Prevalence and population structure of Vibrio vulnificus on fishes from the northern Gulf of Mexico. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 2012, 78, 7611–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pei, X.; Yan, J.; Liu, D.; Zhang, H.; Yu, B.; Li, N.; Yang, D. Prevalence of foodborne pathogens isolated from retail freshwater fish and shellfish in China. Food Control 2019, 99, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.B.; Schweiger, T.; Lenz, C.A.; Vogel, R.F. Inactivation of non-proteolytic Clostridium botulinum type E in low-acid foods and phosphate buffer by heat and pressure. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Chapter 13 - Clostridium botulinum Toxin Formation. In Fish and Fish Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed., Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020c; pp. 245–292.
- Lenz, C.A.; Reineke, K.; Knorr, D.; Vogel, R.F. High pressure thermal inactivation of Clostridium botulinum type E endospores – kinetic modeling and mechanistic insights. Frontiers in Microbiology 2015, 6, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababouch, L. Food safety assurance systems: Good practices in fisheries and aquaculture. Encyclopedia of Food Safety 2014, 4, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Chhabra, P.; de Graaf, M.; Parra, G.I.; Chan, M.C.W.; Green, K.; Martella, V.; Wang, Q.; White, P.A.; Katayama, K.; Vennema, H.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Vinjé, J. Updated classification of norovirus genogroups and genotypes. Journal of General Virology 2019, 100, 1393–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulondo, G.; Khumela, R.; Kabue, J.P.; Traore, A.N.; Potgieter, N. Molecular characterization of Norovirus strains isolated from older children and adults in impoverished communities of Vhembe District, South Africa. Advances in Virology 2020, 8436951, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thébault, A.; David, J.; Kooh, P.; Cadavez, V.; Gonzales-Barron, U.; Pavio, N. Risk factors for sporadic norovirus infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microbial Risk Analysis 2020, 17, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, Y.; Amarasiri, M.; Kamio, S.; Sakagami, A.; Ito, H.; Uprety, S.; Umam, A.N.; Miura, T.; Nguyen, T.H.; Sano, D. Human norovirus disease burden of consuming Crassostrea gigas oysters: A case study from Japan. Food Control 2021, 121, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fusco, G.; Di Bartolo, I.; Cioffi, B.; Ianiro, G.; Palermo, P.; Monini, M.; Amoroso, M.G. Prevalence of foodborne viruses in mussels in Southern Italy. Food and Environmental Virology 2017, 9, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintó, R.M.; Pérez-Rodríguez, F.J.; Costafreda, M.I.; Chavarria, M.; Guix, S.; Ribes, E.; Bosch, A. Pathogenicity and virulence of hepatitis A virus. Virulence 2021, 12, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Chapter 5 - Parasites. In Fish and Fish Products Hazards and Controls Guidance, 4th ed., Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2020d; pp. 91–98.
- Kopper, G.; Mirecki, S.; Kljujev, I.S.; Raicevic, V.B.; Lalevic, B.T.; Jovicic-Petrovic, J.; Stojanovski, S.; Blazekovic-Dimovska, D. Chapter 27 - Hygiene in Primary Production. In Food Safety Management (Second Edition). A Practical Guide for the Food Industry, 2023, pp. 521–585. [CrossRef]
- Mattiucci, S.; Cipriani, P.; Levsen, A.; Paoletti, M.; Nascetti, G. Molecular epidemiology of Anisakis and anisakiasis: An ecological and evolutionary road map. In Advances in Parasitology, Rollinson, D., Stothard, J.R. (Eds.) 2018, 99, pp. 94–263. [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, P.; Acerra, V.; Bellisario, B.; Sbataglia, G.L.; Cheleschi, R.; Nascetti, G.; Mattiucci, S. Larval migration of the zoonotic parasite Anisakis pegreffii (Nematoda: Anisakidae) in European anchovy, Engraulis encrasicolus: Implications to seafood safety. Food Control 2016, 59, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Strachan, N.J.; Hastie, L.C.; MacKenzie, K.; Seton, H.C.; Pierce, G.J. Employing visual inspection and magnetic resonance imaging to investigate Anisakis simplex s.l. infection in herring viscera. Food Control 2017, 75, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipriani, P.; Sbaraglia, G.; Paoletti, M.; Giulietti, L.; Bellisario, B.; Palomba, L.; Bušelić, I.; Mladineo, I.; Nascetti, G.; Mattiucci, S. The Mediterranean European hake, Merluccius merluccius: detecting drivers influencing the Anisakis spp. larvae distribution. Fisheries Research 2018, 202, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, J.; Murata, R.; Hosaka, M.; Araki, J. Risk factors for human Anisakis infection and association between the geographic origins of Scomber japonicus and anisakid nematodes. International Journal of Food Microbiology 2010, 137, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visciano, P.; Campana, G.; Annunziata, L.; Vergara, A.; Ianieri, A. Effect of storage temperature on histamine formation in Sardina pilchardus and Engraulis encrasicolus after catch. Journal of Food Biochemistry 2007, 31, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visciano, P. Fast and reliable methods for histamine detection in fish. In Book of Abstracts of 4th Edition of Euro-Global Conference on Food Science and Technology, Virtual event, 12-13 September 2022, p. 46.
- Fusek, M.; Michálek, J.; Buñková, L.; Buñka, F. Modelling biogenic amines in fish meat in Central Europe using censored distributions. Chemosphere 2020, 251, 126390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority. Assessment of the incidents of histamine intoxication in some EU countries. EFSA supporting publication 2017:EN-1301. [CrossRef]
- Tsironi, T.N.; Taoukis, P.S. Current practice and innovations in fish packaging. Journal of Aquatic Food Product Technology 2018, 27, 1024–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Whitefish | Bluefish |
|---|---|---|
| Skin | Bright, iridescent pigment or opalescent, no discoloration | Bright, shining iridescent colors, clear distinction between dorsal and central surfaces |
| Skin mucus | Aqueous, transparent | Aqueous, transparent |
| Eye | Convex, black bright pupil, transparent cornea | Convex, blue-black bright pupil, transparent eyelid |
| Gills | Bright color, no mucus | Uniformly dark red to purple, no mucus |
| Gill covers | - | Silvery |
| Peritoneum (gutted fish) | Smooth, bright, difficult to detach from flesh | - |
| Smell | Seaweedy | Fresh seaweed, pungent, iodine |
| Flesh | Firm, elastic, smooth surface | Very firm, rigid |
| Pathogen | pH | Temperature |
|---|---|---|
| Listeria monocytogenes | 4.4 – 9.4 | -0.4 – 45 |
| Vibrio parahaemolyticus | 4.8 – 11 | 5 – 45.3 |
| Vibrio vulnificus | 5 – 10 | 8 – 43 |
| Vibrio cholerae | 5 – 10 | 10 – 43 |
| Escherichia coli | 4 – 10 | 6.5 – 49.4 |
| Salmonella spp. | 3.7 – 9.5 | 5.2 – 46.2 |
| Shigella spp. | 4.8 – 9.3 | 6.1 – 47.1 |
| Staphylococcus aureus | 4 – 10 | 7 – 50 |
| Clostridium botulinum type E | 5 – 9 | 3.3 – 45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





