Submitted:
29 August 2023
Posted:
31 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Study
2.2. Power Analysis
2.3. Analyses of Furosemide and Furosemide-Glucuronide in Plasma, Urine, and Plasma Ultrafiltrate
2.4. Quantification of Plasma Cytokine Concentrations
2.5. Pharmacokinetic Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Morgan, E.T. Impact of Infectious and Inflammatory Disease on Cytochrome P450-Mediated Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2009, 85, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardel, O.; Le Vée, M. Regulation of Human Hepatic Drug Transporter Expression by Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 2009, 5, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klöditz, K.; Tewolde, E.; Nordling, Å.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Mechanistic, Functional and Clinical Aspects of pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Mediated Regulation of ADME Gene Expression in 3D Human Liver Spheroids. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, C.; Rollason, V.; Desmeules, J.A.; Samer, C.F. Influence of Inflammation on Cytochromes P450 Activity in Adults: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caris, J.A.; Benzi, J.R. de L.; de Souza, F.F.L.; de Oliveira, R.D.R.; Donadi, E.A.; Lanchote, V.L. Rheumatoid Arthritis Downregulates the Drug Transporter OATP1B1: Fluvastatin as a Probe. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 146, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pippa, L.F.; Vieira, C.P.; Caris, J.A.; Rocha, A.; Marques, M.P.; Garcia, C.P.; Rezende, R.E.F.; Lanchote, V.L. Effect of Chronic Hepatitis C on the Activity of the Membrane Transporters P-gp and OATP1B1/BCRP on Patients With Different Stages of Hepatic Fibrosis. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2023, 114, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cestari, R.N.; de Oliveira, R.D.R.; de Souza, F.F.L.; Pippa, L.F.; Nardotto, G.H.B.; Rocha, A.; Donadi, E.A.; Lanchote, V.L. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Activity Affects the Sinusoidal Uptake Transporter OATP1B1 Evaluated by the Pharmacokinetics of Atorvastatin. Clin Transl Sci 2020, 13, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, S.; Stenqvist, K.; Lidin-Janson, G.; Martinell, J.; Sandberg, T.; Svanborg, C. Comparison of Urine and Serum Concentrations of Interleukin-6 in Women with Acute Pyelonephritis or Asymtomatic Bacteriuria. J Infect Dis 1992, 166, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.H.; Hylander, B.; Wretlind, B.; Brauner, A. Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-8 in Serum and Urine in Patients with Acute Pyelonephritis in Relation to Bacterial-Virulence-Associated Traits and Renal Function. Nephron 1994, 67, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horcajada, J.P.; Velasco, M.; Filella, X.; Alvarez, L.; De Làzzari, E.; Marín, J.L.; Collvinent, B.; Smithson, A.; Martínez, J.A.; Noguero, M.; et al. Evaluation of Inflammatory and Renal-Injury Markers in Women Treated with Antibiotics for Acute Pyelonephritis Caused by Escherichia Coli. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 2004, 11, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, P.; Noshad, H.; Mallah, F.; Ramouz, A. Acute Pyelonephritis in Pregnancy and the Outcomes in Pregnant Patients. Arch Clin Infect Dis 2015, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammarlund-Udenaes, M.; Benet, L.Z. Furosemide Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Health and Disease-An Update. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1989, 17, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerdpin, O.; Knights, K.M.; Elliot, D.J.; Miners, J.O. In Vitro Characterisation of Human Renal and Hepatic Frusemide Glucuronidation and Identification of the UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase Enzymes Involved in This Pathway. Biochem Pharmacol 2008, 76, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, P.V.B.; Moreira, F. de L.; Benzi, J.R. de L.; Duarte, G.; Lanchote, V.L. A Pilot Study of the Maternal-Fetal Pharmacokinetics of Furosemide in Plasma, Urine, and Amniotic Fluid of Hypertensive Parturient Women Under Cesarean Section. J Clin Pharmacol 2020, 60, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuma, T.; McDonagh, A.F.; Lin, E.T.; Benet, L.Z. Photoinduced Covalent Binding of Frusemide and Frusemide Glucuronide to Human Serum Albumin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1999, 48, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Holenarsipur, V.K.; Mariappan, T.T.; Drexler, D.M.; Cantone, J.L.; Rajanna, P.; Gautam, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Gan, J.; Shipkova, P.A.; et al. Evidence for the Validity of Pyridoxic Acid (PDA) as a Plasma-Based Endogenous Probe for OAT1 and OAT3 Function in Healthy Subjects. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2019, 368, 136–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzi, J.R. de L.; Rocha, A.; Colombari, J.C.; Pego, A.M.G.; dos Santos Melli, P.P.; Duarte, G.; Lanchote, V.L. Determination of Furosemide and Its Glucuronide Metabolite in Plasma, Plasma Ultrafiltrate and Urine by HPLC-MS/MS with Application to Secretion and Metabolite Formation Clearances in Non-Pregnant and Pregnant Women. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2023, 235, 115635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinkmann, G.; Klammt, S.; Jäschke, M.; Henschel, J.; Gloger, M.; Reuter, D.A.; Mitzner, S. Impact of Albumin Binding Function on Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Furosemide. Medicina (Lithuania) 2022, 58, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaghloul, D.E.; Ryu, R.; Kestenbaum, B.; Smith, C.; Fay, E.; Hebert, M.F. Renal Function Estimating Equations Performance during Pregnancy and Postpartum. Pharmacotherapy 2023, 43, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistical Guide for Clinical Pharmacology Therapeutics. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2010, 88, 150–152. [CrossRef]
- Abbassi-Ghanavati, M.; Greer, L.G.; Cunningham, F.G. Pregnancy and Laboratory Studies A Reference Table for Clinicians. Obstet Gynecol 2009, 114, 1326–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.O.; Kim, H.S.; Youn, J.C.; Shin, E.C.; Park, S. Serum Cytokine Profiles in Healthy Young and Elderly Population Assessed Using Multiplexed Bead-Based Immunoassays. J Transl Med 2011, 9, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kusuhara, H.; Adachi, M.; Schuetz, J.D.; Takeuchi, K.; Sugiyama, Y. Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 4 Is Involved in the Urinary Excretion of Hydrochlorothiazide and Furosemide. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 2007, 18, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapa, R.; Li, C.Y.; Basit, A.; Thakur, A.; Ladumor, M.K.; Sharma, S.; Singh, S.; Selen, A.; Prasad, B. Contribution of Uptake and Efflux Transporters to Oral Pharmacokinetics of Furosemide. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 32939–32950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prandota, J.; Witkowska, M.; Man, I. Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Furosemide in Man. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 1976, 4, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathialagan, S.; Feng, B.; Rodrigues, A.D.; Varma, M.V.S. Drug-Drug Interactions Involving Renal OCT2/MATE Transporters: Clinical Risk Assessment May Require Endogenous Biomarker-Informed Approach. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2021, 110, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasannejad, H.; Takeda, M.; Taki, K.; Shin, H.J.; Babu, E.; Jutabha, P.; Khamdang, S.; Aleboyeh, M.; Onozato, M.L.; Tojo, A.; et al. Interactions of Human Organic Anion Transporters with Diuretics. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 308, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepist, E.I.; Zhang, X.; Hao, J.; Huang, J.; Kosaka, A.; Birkus, G.; Murray, B.P.; Bannister, R.; Cihlar, T.; Huang, Y.; et al. Contribution of the Organic Anion Transporter OAT2 to the Renal Active Tubular Secretion of Creatinine and Mechanism for Serum Creatinine Elevations Caused by Cobicistat. Kidney Int 2014, 86, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanke-Labesque, F.; Gautier-Veyret, E.; Chhun, S.; Guilhaumou, R. Inflammation Is a Major Regulator of Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Transporters: Consequences for the Personalization of Drug Treatment. Pharmacol Ther 2020, 215, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, R.; Piquette-Miller, M.; Polli, J.W.; Russel, F.G.M.; Sprowl, J.A.; Tohyama, K.; Ware, J.A.; de Wildt, S.N.; Xie, W.; Brouwer, K.L.R. Disease-Associated Changes in Drug Transporters May Impact the Pharmacokinetics and/or Toxicity of Drugs: A White Paper From the International Transporter Consortium. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2018, 104, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cressman, A.M.; Petrovic, V.; Piquette-Miller, M. Inflammation-Mediated Changes in Drug Transporter Expression/Activity: Implications for Therapeutic Drug Response. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol 2012, 5, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibayama, T.; Sugiyama, D.; Kamiyama, E.; Tokui, T.; Hirota, T.; Ikeda, T. Characterization of CS-023 (RO4908463), a Novel Parenteral Carbapenem Antibiotic, and Meropenem as Substrates of Human Renal Transporters. 41 Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet 2007, 22, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akanuma, S.I.; Uchida, Y.; Ohtsuki, S.; Kamiie, J.I.; Tachikawa, M.; Terasaki, T.; Hosoya, K.I. Molecular-Weight-Dependent, Anionic-Substrate-Preferential Transport of β-Lactam Antibiotics via Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 4. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2011, 26, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Wakabayashi, Y.; Higuchi, A.; Kadotani, Y.; Ogino, S.; Ushigome, H.; Akioka, K.; Kaihara, S.; Yoshimura, N. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Mycophenolic Acid in Renal Transplant Recipients. Transplant Proc 2005, 37, 859–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommerer, C.; Müller-Krebs, S.; Schaier, M.; Glander, P.; Budde, K.; Schwenger, V.; Mikus, G.; Zeier, M. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Analysis of Enteric-Coated Mycophenolate Sodium: Limited Sampling Strategies and Clinical Outcome in Renal Transplant Patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2010, 69, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Torre, A.; Bueno-García, E.; López-Martínez, R.; Rioseras, B.; Díaz-Molina, B.; Lambert, J.L.; Quirós, C.; Alonso-Álvarez, S.; Alonso-Arias, R.; Moro-García, M.A. CMV Infection Is Directly Related to the Inflammatory Status in Chronic Heart Failure Patients. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pour, N.K.; McColl, E.R.; Piquette-Miller, M. Impact of Viral Inflammation on the Expression of Renal Drug Transporters in Pregnant Rats. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höcherl, K.; Schmidt, C.; Bucher, M. COX-2 Inhibition Attenuates Endotoxin-Induced Downregulation of Organic Anion Transporters in the Rat Renal Cortex. Kidney Int 2009, 75, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1): An Overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res 2009, 29, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanchote, V.L.; Almeida, R.; Barral, A.; Barral-Netto, M.; Marques, M.P.; Moraes, N. V.; Da Silva, A.M.; Souza, T.M.V.; Suarez-Kurtz, G. Impact of Visceral Leishmaniasis and Curative Chemotherapy on Cytochrome P450 Activity in Brazilian Patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2015, 80, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenoir, C.; Terrier, J.; Gloor, Y.; Curtin, F.; Rollason, V.; Desmeules, J.A.; Daali, Y.; Reny, J.L.; Samer, C.F. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection (COVID-19) on Cytochromes P450 Activity Assessed by the Geneva Cocktail. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2021, 110, 1358–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Vee, M.; Lecureur, V.; Stieger, B.; Fardel, O. Regulation of Drug Transporter Expression in Human Hepatocytes Exposed to the Proinflammatory Cytokines Tumor Necrosis Factor-α or Interleukin-6. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2009, 37, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Vee, M.; Jouan, E.; Stieger, B.; Lecureur, V.; Fardel, O. Regulation of Drug Transporter Expression by Oncostatin M in Human Hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 2011, 82, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, P.; Kerwash, E.; Cole, S. The Use of Pregnancy Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling for Renally Cleared Drugs. J Clin Pharmacol 2022, 62, S129–S139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Olaleye, O.E.; Yu, X.; Jia, W.; Yang, J.; Lu, C.; Liu, S.; Yu, J.; Duan, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Supporting Information for High Degree of Pharmacokinetic Compatibility Exists between the Five-Herb Medicine XueBiJing and Antibiotics Comedicated in Sepsis Care. Acta Pharm Sin B 2019, 9, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhagen, C.A.; Mattie, H.; Van Strijen, E. The Renal Clearance of Cefuroxime and Ceftazidime and the Effect of Probenecid on Their Tubular Excretion. Br J clin Pharmac 1994, 37, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kågedal, M.; Nilsson, D.; Huledal, G.; Reinholdsson, I.; Cheng, Y.F.; Åsenblad, N.; Pekar, D.; Borgå, O. A Study of Organic Acid Transporter-Mediated Pharmacokinetic Interaction between NXY-059 and Cefuroxime. J Clin Pharmacol 2007, 47, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Reference range# | Phase 1 (n = 7) | Phase 2 (n = 7) | |
| Age (years) | - | 24.3 (16.1) | 24.3 (17.4) |
| Gestational age (weeks) | - | 26.7 (19.2) | 29.6 (17.3) |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | - | 28.7 (17.0) | 29.3 (17.2) |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.6 – 1.1 | 0.63 (25.1) | 0.5 (23.0) |
| Estimated creatinine clearance* (mL/min) | > 90.0 | 161.1 (21.3) | 189.2 (14.1) |
| AST (U/L) | 3.0 – 32.0 | 22.0 (42.1) | 22.7 (162.0) |
| ALT (U/L) | 3.0 – 33.0 | 16.0 (66.1) | 24.0 (187.4) |
| GGT (U/L) | 7.0 – 32.0 | 17.5 (66.5) | 27.9 (42.8) |
| Total plasma proteins (g/dL) | 6.1 – 7.90 | 5.9 (6.72) | 6.2 (4.70) |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.4 – 4.8 | 3.5 (9.31) | 3.6 (8.10) |
| α1-Acid glycoprotein | 50.0 – 120.0 | 86.9 (35.1) | 65.0 (23.4) |
| Alkaline phosphatase (U/L) | 65.0 – 300.0 | 157.1 (23.6) | 169.5 (22.7) |
| Fasting glycemia (mg/dL) | 70.0 – 100.0 | 79.8 (12.1) | 76.7 (11.2) |
| Medications in use | cefuroxime; oseltamivir; ferrous sulfate; metamizole; tramadol; folic acid; scopolamine; tinidazole (topical); terbutaline; betamethasone; levothyroxine; ondansetron; progesterone; heparin; sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim | ferrous sulfate; metamizole; folic acid; miconazole (topic); levothyroxine; heparin |
|
Cytokines (pg/mL) and CRP (mg/dL) |
Phase 1 (n = 7) | Phase 2 (n = 7) | p-value |
| IFN-γ | 5.80 (5.50 – 9.41) | 0.92 (0.73 – 1.91) | 0.0313 |
| IL-10 | 32.30 (19.79 – 113.80) | 3.12 (1.53 – 49.7) | 0.3125 |
| IL-12p40 | 3.28 (1.17 – 35.32) | 1.34 (1.07 – 17.4) | >0.999 |
| IL-12p70 | 1.85 (1.04 – 2.37) | 1.04 (1.04 – 1.32) | 0.1563 |
| IL-1β | 1.00 (0.59 – 4.18) | 1.10 (0.60 – 2.40) | >0.999 |
| IL-2 | 0.76 (0.62 – 1.21) | 0.68 (0.61 – 1.16) | 0.6875 |
| IL-6 | 34.04 (1.97 – 126.60) | 0.21 (0.11 – 23.7) | 0.0469 |
| IL-8 | 4.70 (0.22 – 100.83) | 0.28 (0.15 – 31.4) | 0.8438 |
| MCP-1 | 807.34 (418.20 – 1232.50) | 373.32 (277.00 – 403.45) | 0.0313 |
| TNF-α | 41.63 (17.28 – 54.15) | 17.01 (13.30 – 21.42) | 0.0313 |
| CRP | 21.54 (13.46 – 58.84) | 2.34 (1.10 – 3.54) | 0.0313 |
| Geometric mean (CV%) | Geometric mean ratios (90% CI) | p-value | ||
| Phase 1 (n = 7) | Phase 2 (n = 7) | Phase 2/Phase 1 | ||
| AUC0-24 (ng×h/mL) | 1303.0 (38.3) | 1065.0 (7.1) | 0.67 (0.45 – 1.01) | 0.2386 |
| AUC0-∞ (ng×h/mL) | 1373.0 (38.3) | 1196.0 (14.1) | 0.72 (0.48 – 1.08) | 0.4465 |
| CL/F (L/h) | 29.1 (38.8) | 37.6 (7.20) | 1.61 (1.10 – 2.35) | 0.2300 |
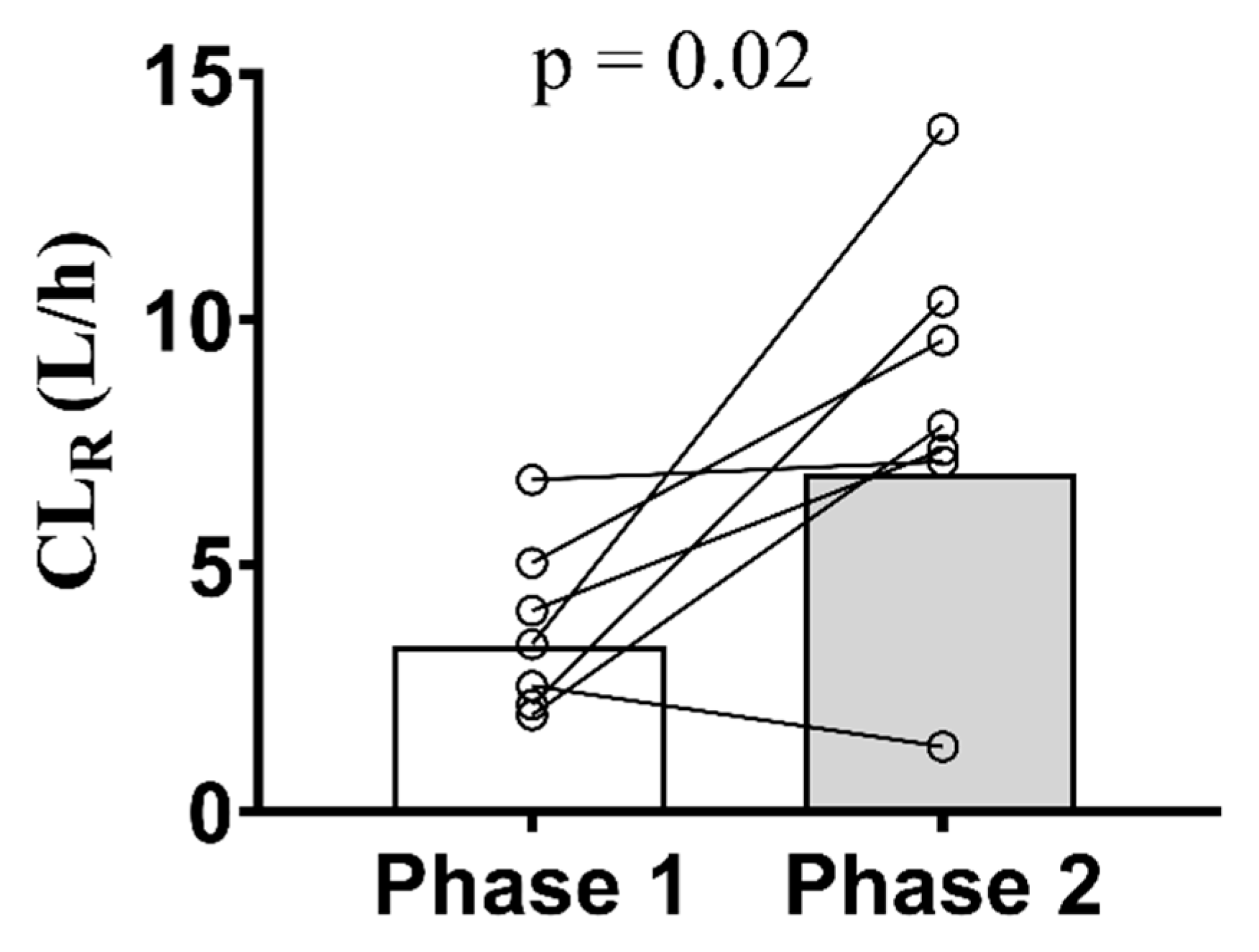
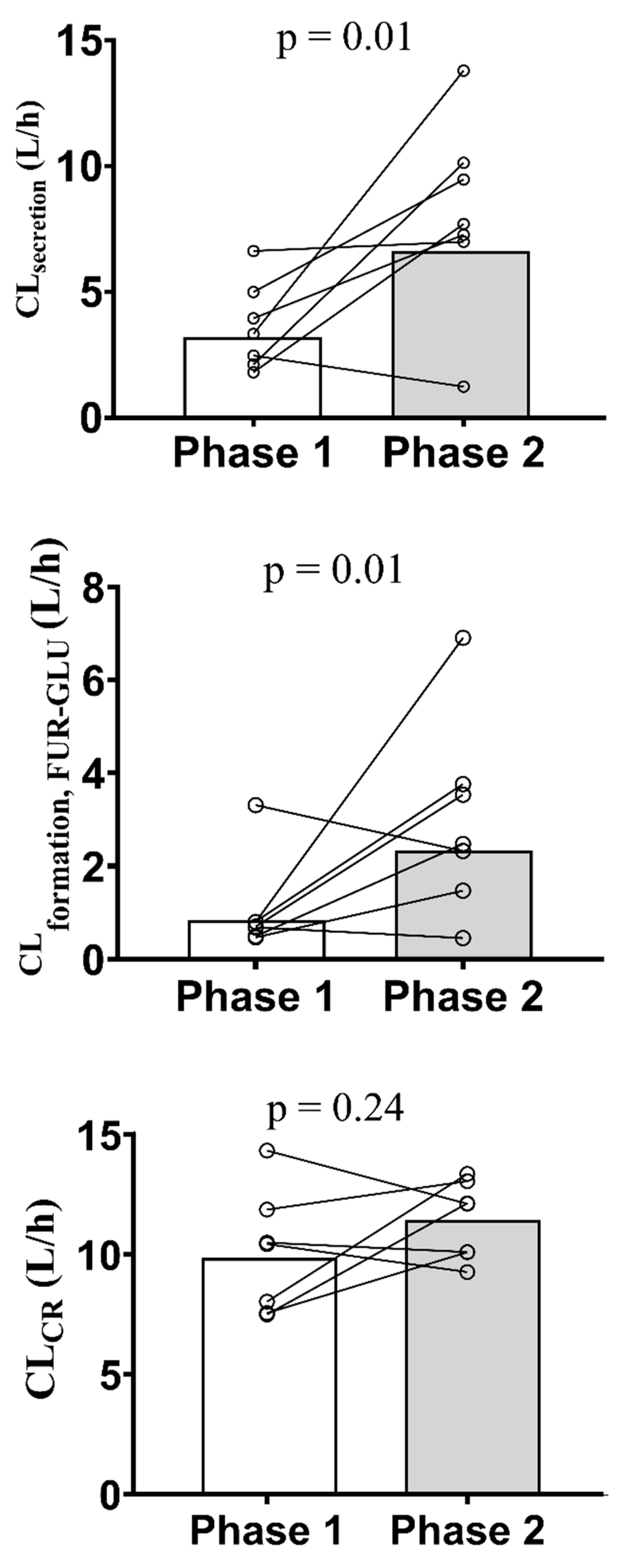
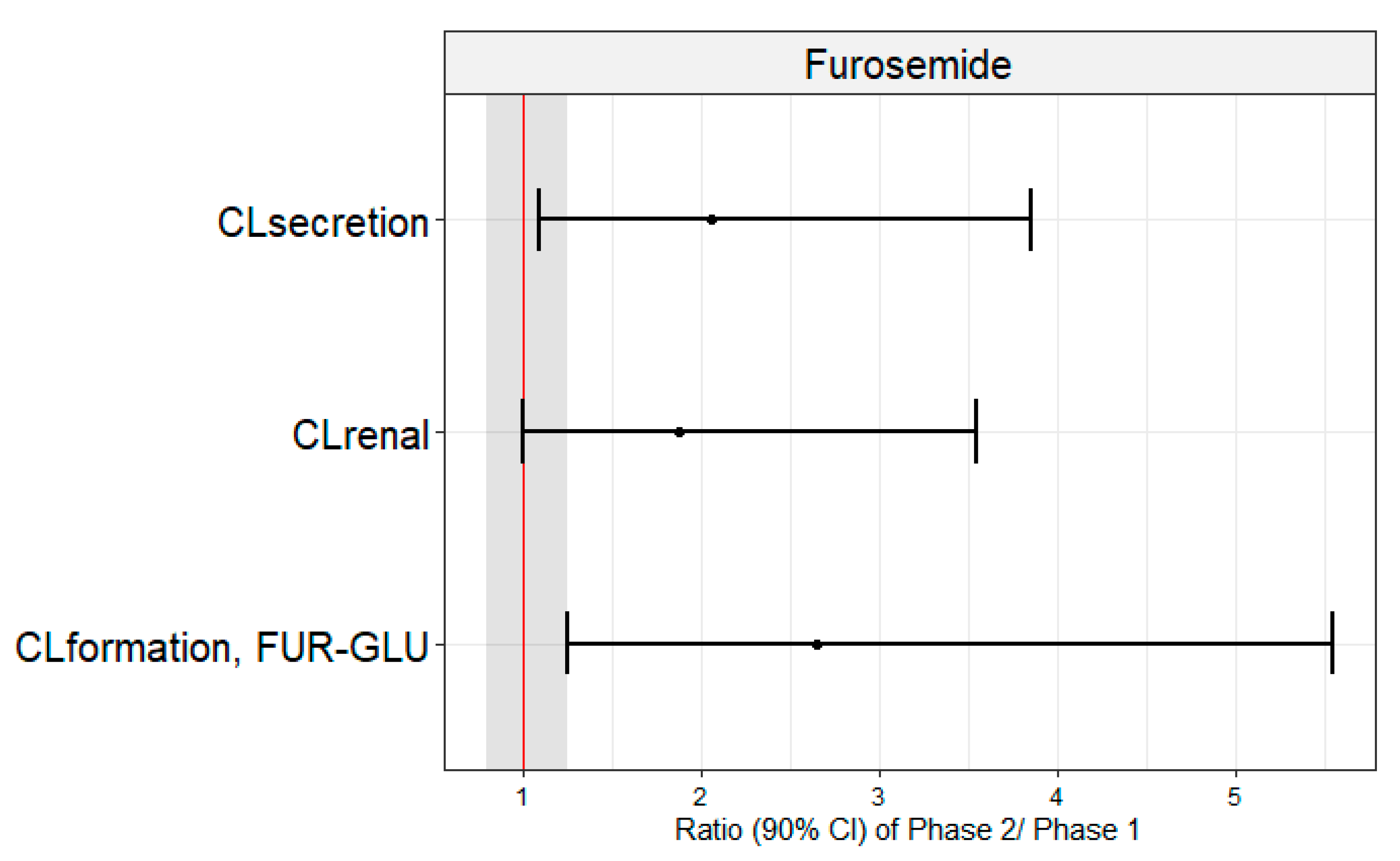
| CLrenal (L/h) | 4.2 (45.5) | 6.9 (43.3) | 1.89 (1.01 – 3.54) | 0.0262 |
| CLsecretion (L/h) | 3.9 (43.4) | 6.7 (43.8) | 2.06 (1.12 – 3.80) | 0.0126 |
| CLformation, FUR-GLU (L/h) | 1.1 (85.9) | 2.3 (64.1) | 2.65 (1.28 – 5.49) | 0.0161 |
| Ae (mg) | 5.5 (20.8) | 7.3 (46.3) | 1.29 (0.73 – 2.28) | 0.3006 |
| CL/Fnon-renal (L/h) | 21.5 (62.4) | 29.1 (14.6) | 1.65 (0.92 – 2.96) | 0.6999 |
| Cmax (ng/mL) | 337.2 (48.5) | 377.4 (39.8) | 0.95 (0.51 – 1.77) | 0.3525 |
| Tmax (h) | 1.5 (1.0 – 4.0)* | 1.0 (1.0 – 2.0)* | 0.7 (0.5 – 1.0) | 0.0938 |
| fu | 0.010 (32.0) | 0.011 (40.3) | 1.04 (0.77 – 1.42) | 0.6499 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





