Submitted:
25 August 2023
Posted:
29 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Problem at hand
2.1. Dimension of problem
2.2. Mastectomy vs. Breast-conserving surgery
2.3. Lymphadenectomy and sentinel-lymph node biopsy
2.4. Impact of radiotherapy in surgical options and results
2.5. Quality of life following surgery for breast cancer
2.6. Oncologic follow-up and results after reconstructive surgery
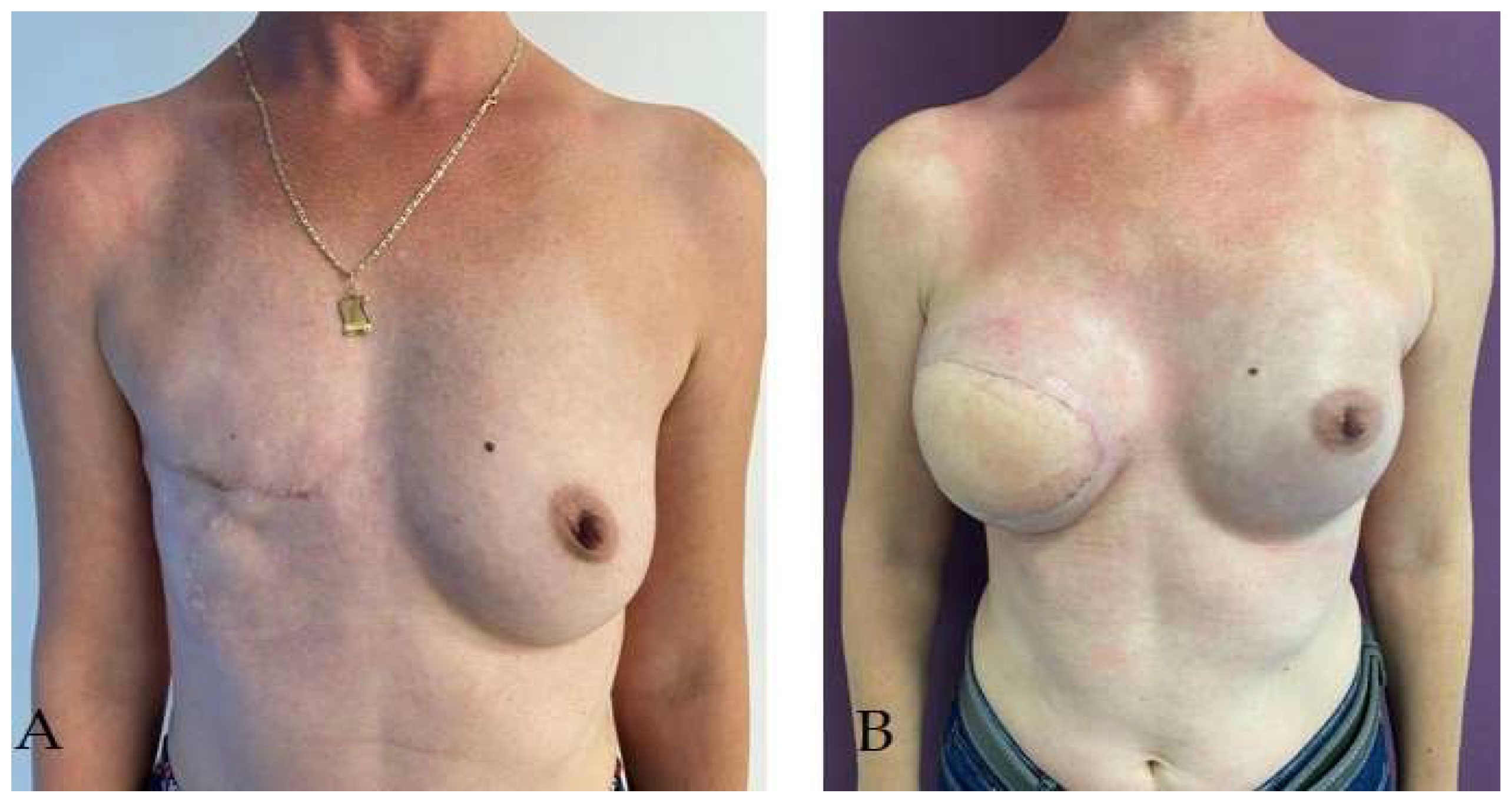
3. Breast reconstruction
3.1. Timing of breast reconstruction – immediate or delayed
3.2. Two-stage breast reconstruction
3.3. Breast reconstruction with implant
3.4. Autologous breast reconstruction techniques
- The advantages of flap reconstruction
- b. Types of transferred free flaps
- c) Latissimus dorsi pediculated flap
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Statistics on Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/breast-cancer (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Kummerow, K.L.; Du, L.; Penson, D.F.; Shyr, Y.; Hooks, M.A. Nationwide Trends in Mastectomy for Early-Stage Breast Cancer. JAMA Surg 2015, 150, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttle, T.M.; Habermann, E.B.; Grund, E.H.; Morris, T.J.; Virnig, B.A. Increasing Use of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy for Breast Cancer Patients: A Trend toward More Aggressive Surgical Treatment. J Clin Oncol. 2007, 25, 5203–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soran, A.; Kamali Polat, A.; Johnson, R.; McGuire, K.P. Increasing Trend of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy: What Are the Factors behind This Phenomenon? Surgeon. 2014, 12, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Samaha, Y.; Ives, G.; Lee, T.-Y.; Cui, X.; Ray, E. Chest Feminization in Male-to-Female Transgender Patients: A Review of Options. [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Steliarova-Foucher, E.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Rosso, S.; Coebergh, J.W.W.; Comber, H.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer Incidence and Mortality Patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 Countries in 2012. Eur J Cancer 2013, 49, 1374–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Garnier, H.; Colonna, M. Epidémiologie Des Cancers Du Sein Breast Cancer Epidemiology. 2019.
- Overview of Breast Reconstruction – UpToDate. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/overview-of-breast-reconstruction?search=Overview%20of%20breast%20reconstruction&source=search_result&selectedTitle=1~150&usage_type=default&display_rank=1 (accessed on 21 July 2023).
- Angelos, P.; Kohler, L.; Professor, A.; Bedrosian, I.; Euhus, D.M.; Herrmann, V.M.; Katz, S.J.; Pusic, A.; Surg, A.; Author, O. Prophylactic Mastectomy: Challenging Considerations for the Surgeon HHS Public Access Author Manuscript. Ann Surg Oncol 2015, 22, 3208–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragun, A.E.; Pan, J.; Riley, E.C.; Kruse, B.; Wilson, M.R.; Rai, S.; Jain, D. Increasing Use of Elective Mastectomy and Contralateral Prophylactic Surgery among Breast Conservation Candidates: A 14-Year Report from a Comprehensive Cancer Center. Am J Clin Oncol. 2013, 36, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, K.A.; Eisen, A.; Poll, A.; Candib, A.; McCready, D.; Cil, T.; Wright, F.; Demsky, R.; Mancuso, T.; Sun, P.; et al. Frequency of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy in Breast Cancer Patients with a Negative BRCA1 and BRCA2 Rapid Genetic Test Result. Ann Surg Oncol 2021, 28, 4967–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, T.J.; Wilson, S.C.; Massie, J.P.; Morrison, S.D.; Satterwhite, T. Breast Augmentation in Male-to-Female Transgender Patients: Technical Considerations and Outcomes. JPRAS Open 2019, 21, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeny, J.C.; Zolper, E.G.; Fan, K.L.; Del Corral, G. Breast Augmentation for Transfeminine Patients: Methods, Complications, and Outcomes. Gland Surg 2020, 9, 788–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeny, J.C.; Zolper, E.G.; Manrique, O.J.; Fan, K.L.; Corral, G. Del Breast Augmentation in the Transgender Patient: Narrative Review of Current Techniques and Complications. Ann Transl Med 2021, 9, 611–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.D. Preoperative Planning and Breast Implant Selection for Volume Difference Management in Asymmetrical Breasts. Plast Aesthet Res 2017, 4, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patlazhan, G.; Shkolnaya, O.; Torubarov, I.; Gomes, M. Our 10 Years’ Experience in Breast Asymmetry Correction. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2020, 44, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, B.; Alajmi, H.; Ladak, A.; Samargandi, O.A. Breast Equalization Augmentation: The Use of Ultrasonic Assisted Liposuction for Correction of Primary Breast Asymmetry with Bilateral Augmentation. Aesthetic Plast Surg 2022, 46, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benedict, S.; Cole, D.J.; Baron, L.; Baron, P. Factors Influencing Choice Between Mastectomy and Lumpectomy for Women in the Carolinas; 2001; Vol. 76;
- Nold, R.J.; Beamer, R.L.; Helmer, S.D.; McBoyle, M.F. Factors Influencing a Woman’s Choice to Undergo Breast-Conserving Surgery versus Modified Radical Mastectomy. Am J Surg 2000, 180, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Peled, A.W.; Chin, R.; Fowble, B.; Alvarado, M.; Ewing, C.; Esserman, L.; Foster, R.; Sbitany, H. The Impact of Radiation Therapy, Lymph Node Dissection, and Hormonal Therapy on Outcomes of Tissue Expander-Implant Exchange in Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2016, 137, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, R.; Klein, G.; Dagum, A.; Khan, S.; Bui, D.T. The Effect of Axillary Lymph Node Sampling during Mastectomy on Immediate Alloplastic Breast Reconstruction Complications. In Proceedings of the Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery - Global Open; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, May 1 2019; Vol. 7; p. 2224. [Google Scholar]
- Morrow, M.; Li, Y.; Alderman, A.K.; Jagsi, R.; Hamilton, A.S.; Graff, J.J.; Hawley, S.T.; Katz, S.J. Access to Breast Reconstruction After Mastectomy and Patient Perspectives on Reconstruction Decision Making. JAMA Surg 2014, 149, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffen, L.E.; Johnson, A.; Levine, B.J.; Mayer, D.K.; Avis, N.E. Met and Unmet Expectations for Breast Reconstruction in Early Posttreatment Breast Cancer Survivors. Plastic Surgical Nursing 2017, 37, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, E.G.; Cederna, P.S.; Lowery, J.C.; Davis, J.A.; Myra Kim, H.; Roth, R.S.; Goldfarb, S.; Izenberg, P.H.; Houin, H.P.; Shaheen, K.W.; et al. Prospective Analysis of Psychosocial Outcomes in Breast Reconstruction: One-Year Postoperative Results from the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcome Study; 2000; Vol. 106;
- Rubino, C.; Figus, A.; Lorettu, L.; Sechi, G. Post-Mastectomy Reconstruction: A Comparative Analysis on Psychosocial and Psychopathological Outcomes. Journal of Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery 2007, 60, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helms, R.L.; O’Hea, E.L.; Corso, M. Helms, R.L.; O’Hea, E.L.; Corso, M. Body Image Issues in Women with Breast Cancer. 2008, 13, 313–325. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.G.; Strassle, P.D.; McGuire, K.P. Role of Age, Tumor Grade, and Radiation Therapy on Immediate Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. Clin Breast Cancer 2018, 18, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.U.; Day, S.J.; Pencek, M.; Roussel, L.O.; Christiano, J.G.; Punekar, I.R.; Koltz, P.F.; Langstein, H.N. Functional Return after Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Study of Objective and Patient-Reported Outcomes. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2020, 73, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myung, Y.; Choi, B.; Kwon, H.; Heo, C.Y.; Kim, E.K.; Kang, E.; Jeong, J.H.; Yang, E.J. Quantitative Analysis of Shoulder Function and Strength after Breast Reconstruction: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Medicine 2018, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotaru, V.; Chitoran, E.; Cirimbei, C.; Cirimbei, S.; Simion, L. Preservation of Sensory Nerves During Axillary Lymphadenectomy, Proceedings of the 35th Balkan Medical Week, Athens, Greece, 25-27 September 2018 Available online:. Available online: https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/full-record/WOS:000471903700045 (accessed on 20 July 2023).
- Doherty, C.; Mcclure, J.A.; Baxter, N.N.; Brackstone, M. Complications From Postmastectomy Radiation Therapy in Patients Undergoing Immediate Breast Reconstruction: A Population-Based Study-NC-ND License (Http://Creativecommons.Org/Licenses/by-Nc-Nd/4.0/). 2023. [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, L.; Loreti, A.; Cortese, G.; Spallone, D.; Toto, V.; Cavaliere, F.; Farina, M.; La Pinta, M.; Manna, E.; Detto, L.; et al. Regret and Quality of Life After Mastectomy With or Without Reconstruction. Clin Breast Cancer 2021, 21, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuliński, W.; Kosno, M. QUALITY OF LIFE IN WOMEN AFTER MASTECTOMY. CLINICAL AND SOCIAL STUDY. Wiad Lek 2021, 74, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.N.H.; Pignone, M.P.; Deal, A.M.; Blizard, L.; Hunt, C.; Huh, R.; Liu, Y.J.; Ubel, P.A. Accuracy of Predictions of Patients with Breast Cancer of Future Well-Being after Immediate Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg 2018, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Q.; Tan, Q.; Lian, B.; Mo, Q.; Huang, Z.; Wei, C. Postoperative Outcomes of Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy A Retrospective Study. 2018. [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz, L.; Moody, A.M.; Tappy, E.E.; Blankenship, S.A.; Hecht, E.M. Overall Survival, Disease-Free Survival, Local Recurrence, and Nipple–Areolar Recurrence in the Setting of Nipple-Sparing Mastectomy: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. Ann Surg Oncol 2015, 22, 3241–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, J.Y.; Gentilini, O.; Rotmensz, N.; Rey, P.; Rietjens, M.; Garusi, C.; Botteri, E.; De Lorenzi, F.; Martella, S.; Bosco, R.; et al. Oncological Results of Immediate Breast Reconstruction: Long Term Follow-up of a Large Series at a Single Institution. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008, 112, 545–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.H.; Hong, K.Y.; Lee, H.B.; Moon, H.G.; Han, W.; Noh, D.Y.; Lim, J.; Yoon, S.; Chang, H.; Jin, U.S. Oncologic Outcomes after Immediate Breast Reconstruction Following Mastectomy: Comparison of Implant and Flap Using Propensity Score Matching. BMC Cancer 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujihara, M.; Yamasaki, R.; Ito, M.; Shien, T.; Maeda, R.; Kin, T.; Ueno, A.; Kajiwara, Y.; Kawasaki, K.; Ichimura, K.; et al. Risk Factors of Local Recurrence Following Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction in Breast Cancer Patients. BMC Women’s Health 2021, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mammography in the Evaluation of Masses in Breasts Reconstruction : Annals of Plastic Surgery. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/annalsplasticsurgery/Abstract/1998/09000/Mammography_in_the_Evaluation_of_Masses_in_Breasts.1.aspx (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Hsu, W.; Sheen-Chen, S.M.; Eng, H.L.; Ko, S.F. Mammographic Microcalcification in an Autogenously Reconstructed Breast Simulating Recurrent Carcinoma. 2018, 94, 574–576. [CrossRef]
- Juanpere, S.; Perez, E.; Huc, O.; Motos, N.; Pont, J.; Pedraza, S. Imaging of Breast Implants—a Pictorial Review. Insights into Imaging 2011, 2, 653–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathelin, C.; Bruant-Rodier, C. Indications for Breast Reconstruction after Mastectomy According to the Oncological Situation. Annales de Chirurgie Plastique Esthetique 2018, 63, 580–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atisha, D.; Alderman, A.K.; Lowery, J.C.; Kuhn, L.E.; Davis, J.; Wilkins, E.G. Prospective Analysis of Long-Term Psychosocial Outcomes in Breast Reconstruction: Two-Year Postoperative Results from the Michigan Breast Reconstruction Outcomes Study. Ann Surg 2008, 247, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, J.; Zhong, T. Patient-Centered Breast Reconstruction Based on Health-Related Quality-of-Life Evidence. Clin Plast Surg 2018, 45, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; McCarthy, C.; Min, S.; Zhang, J.; Beber, B.; Pusic, A.L.; Hofer, S.O.P. Patient Satisfaction and Health-Related Quality of Life after Autologous Tissue Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Analysis of Early Postoperative Outcomes. Cancer 2012, 118, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, T.; Hu, J.; Bagher, S.; Vo, A.; O’Neill, A.C.; Butler, K.; Novak, C.B.; Hofer, S.O.P.; Metcalfe, K.A. A Comparison of Psychological Response, Body Image, Sexuality, and Quality of Life between Immediate and Delayed Autologous Tissue Breast Reconstruction: A Prospective Long-Term Outcome Study. In Proceedings of the Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, October 1 2016; Vol. 138; pp. 772–780. [Google Scholar]
- Simmons, R.M.; Fish, S.K.; Gayle, L.; La Trenta, G.S.; Swistel, A.; Christos, P.; Osborne, M.P. Local and Distant Recurrence Rates in Skin-Sparing Mastectomies Compared With Non-Skin-Sparing Mastectomies; 1999.
- Toth, B.A.; Lappert, P. Modified Skin Incisions for Mastectomy: The Need for Plastic Surgical Input in Preoperative Planning. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991, 87, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, S.; Khoo, A.; Singletary, E.; Ames, F.; Wang, B.G.; Reece, G.; Miller, M.; Evans, G.; Robb, G. Local Recurrence Risk after Skin-Sparing and Conventional Mastectomy: A 6-Year Follow-Up. Plast Reconstr Surg 1999, 104, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, V.; Vicini, E.; Corso, G.; Morigi, C.; Fontana, S.; Sacchini, V.; Veronesi, P. Nipple-Sparing and Skin-Sparing Mastectomy: Review of Aims, Oncological Safety and Contraindications. Breast 2017, 34, S82–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, M.; Bordea, C.; Noditi, A.; Blidaru, A. Assessment of Mastectomy Skin Flaps for Immediate Implant-Based Breast Reconstruction. J Med Life 2018, 11, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.J.; Hou, M.F.; Lin, S.D.; Chuang, H.Y.; Huang, M.Y.; Fu, O.Y.; Lian, S.L. Comparison of Local Recurrence and Distant Metastases between Breast Cancer Patients after Postmastectomy Radiotherapy with and without Immediate TRAM Flap Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2006, 118, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieni, M.; Avram, R.; Dickson, L.; Farrokhyar, F.; Lovrics, P.; Faidi, S.; Sne, N. Local Breast Cancer Recurrence after Mastectomy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction for Invasive Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. The Breast 2012, 21, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strålman, K.; Mollerup, C.L.; Kristoffersen, U.S.; Elberg, J.J. Long-Term Outcome after Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction. Acta Oncol (Madr) 2008, 47, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronowitz, S.J. Delayed-Immediate Breast Reconstruction: Technical and Timing Considerations. Plast Reconstr Surg 2010, 125, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradishar, W.J.; Lurie, R.H.; Blair, S.L.; San Diego Moores Cancer Center Harold Burstein, U.J.; Center Amy Cyr, C.; Elias, A.D.; Forero, A.; Hermes Giordano, S.; Goldstein, L.J.; Isakoff, S.J.; et al. Invasive Breast Cancer NCCN Guidelines ® NCCN Breast Cancer Panel Members; 2016; Vol. 14;
- Harris, E.E.R.; Freilich, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Chuong, M.; Acs, G. The Impact of the Size of Nodal Metastases on Recurrence Risk in Breast Cancer Patients with 1-3 Positive Axillary Nodes after Mastectomy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2013, 85, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McBride, A.; Allen, P.; Woodward, W.; Kim, M.; Kuerer, H.M.; Drinka, E.K.; Sahin, A.; Strom, E.A.; Buzdar, A.; Valero, V.; et al. Locoregional Recurrence Risk for Patients with T1,2 Breast Cancer with 1-3 Positive Lymph Nodes Treated with Mastectomy and Systemic Treatment. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2014, 89, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronowitz, S.J.; Hunt, K.K.; Kuerer, H.M.; Babiera, G.; McNeese, M.D.; Buchholz, T.A.; Strom, E.A.; Robb, G.L. Delayed-Immediate Breast Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2004, 113, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- See, M.S.F.; Farhadi, J. Radiation Therapy and Immediate Breast Reconstruction: Novel Approaches and Evidence Base for Radiation Effects on the Reconstructed Breast. Clin Plast Surg 2018, 45, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, E.; Pesce, M.; Santi, P.L.; Raposio, E. Two-Stage Tissue-Expander Breast Reconstruction: A Focus on the Surgical Technique. Biomed Res Int 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cemal, Y.; Albornoz, C.R.; Disa, J.J.; Mccarthy, C.M.; Mehrara, B.J.; Pusic, A.L.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Matros, E. A Paradigm Shift in U.S. Breast Reconstruction: Part 2. the Influence of Changing Mastectomy Patterns on Reconstructive Rate and Method. Plast Reconstr Surg 2013, 131, 320e–326e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherine, E.G.; Woods, J.E.; O’Fallon, M.; Beard, M.; Kurland, L.T.; Melton, J.L. Complications Leading to Surgery after Breast Implantation. New England Journal of Medicine 1997, 336, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percec, I.; Bucky, L.P. Successful Prosthetic Breast Reconstruction after Radiation Therapy. Ann Plast Surg 2008, 60, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thamm, O.C.; Andree, C. Immediate Versus Delayed Breast Reconstruction: Evolving Concepts and Evidence Base. Clin Plast Surg 2018, 45, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahabedian, M.Y. Acellular Dermal Matrices in Primary Breast Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2012, 130, 44S–53S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uitto, J.; Olsen, D.R.; Fazio, M.J. Extracellular Matrix of the Skin: 50 Years of Progress. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 1989, 92, S61–S77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.Y.; Hu, Z.I.; Mehrara, B.J.; Wilkins, E.G. Radiotherapy in the Setting of Breast Reconstruction: Types, Techniques, and Timing. Lancet Oncol 2017, 18, e742–e753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.W.; Lin, A.; Hoang, D.; Carey, J. Trends in Breast Reconstruction Techniques at a Large Safety Net Hospital: A 10-Year Institutional Review. Annals of Breast Surgery 2018, 2, 14–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshima, I.; Soeda, S. Inferior Epigastric Artery Skin Flaps without Rectus Abdominis Muscle. Journal of Plastic Surgery 1989, 42, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, C.; Allen, R.J. The Evolution of Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction: Twenty Years after the First DIEP Flap. J Reconstr Microsurg 2014, 30, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, P. Iginio Tansini and the Origin of the Latissimus Dorsi Musculocutaneous Flap. Plast Reconstr Surg 1989, 65, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champaneria, M.C.; Wong, W.W.; Hill, M.E.; Gupta, S.C. The Evolution of Breast Reconstruction: A Historical Perspective. World J Surg 2012, 36, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostwick, J.; Vasconez, L.O.; Jurkiewicz, M.J. Breast Reconstruction after a Radical Mastectomy. Plast Reconstr Surg 1978, 61, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, W.J.; Hill, H.L.; Brown, R.G. LATISSIMUS DORSI MYOCUTANEOUS FLAP FOR BREAST RECONSTRUCTION. Br J Plast Surg 1977, 30, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papp, C.; McCraw, J.B. Autogenous Latissimus Breast Reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg 1998, 25, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLong, M.R.; Tandon, V.J.; Rudkin, G.H.; Da Lio, A.L. Latissimus Dorsi Flap Breast Reconstruction-A Nationwide Inpatient Sample Review. Ann Plast Surg 2017, 78, S185–S188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spear, S.L.; Clemens, M.W. Latissimus Dorsi Flap Breast Reconstruction. Plastic Surgery. 3rd ed. 2012, 370–392. [Google Scholar]
- Hardwicke, J.T.; Prinsloo, D.J. An Analysis of 277 Consecutive Latissimus Dorsi Breast Reconstructions: A Focus on Capsular Contracture. Plast Reconstr Surg 2011, 128, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, A.G.; Morris, D.J.; Houlihan, M.J.; Slavin, S.A. Breast Reconstruction in a Changing Breast Cancer Treatment Paradigm. Plast Reconstr Surg 2008, 121, 1116–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, U.; Cascinelli, N.; Mariani, L.; Greco, M.; Saccozzi, R.; Luini, A.; Aguilar, M.; Marubini, E. Twenty-Year Follow-up of a Randomized Study Comparing Breast-Conserving Surgery with Radical Mastectomy for Early Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2002, 347, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, M.; Jagsi, R.; Alderman, A.K.; Griggs, J.J.; Hawley, S.T.; Hamilton, A.S.; Graff, J.J.; Katz, S.J. Surgeon Recommendations and Receipt of Mastectomy for Treatment of Breast Cancer. JAMA : the journal of the American Medical Association 2009, 302, 1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughey, J.C.; Attai, D.J.; Chen, S.L.; Cody, H.S.; Dietz, J.R.; Feldman, S.M.; Greenberg, C.C.; Kass, R.B.; Landercasper, J.; Lemaine, V.; et al. Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy (CPM) Consensus Statement from the American Society of Breast Surgeons: Data on CPM Outcomes and Risks. Ann Surg Oncol 2016, 23, 3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchal, H.; Matros, E. Current Trends in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg 2017, 140, 7S–13S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughey, J.C.; Hoskin, T.L.; Degnim, A.C.; Sellers, T.A.; Johnson, J.L.; Kasner, M.J.; Hartmann, L.C.; Frost, M.H. Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy Is Associated with a Survival Advantage in High-Risk Women with a Personal History of Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2010, 17, 2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boughey, J.C.; Schilz, S.R.; Van Houten, H.K.; Zhu, L.; Habermann, E.B.; Lemaine, V. Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy with Immediate Breast Reconstruction Increases Healthcare Utilization and Cost. Ann Surg Oncol 2017, 24, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskin, T.L.; Hieken, T.J.; Degnim, A.C.; Jakub, J.W.; Jacobson, S.R.; Boughey, J.C. Use of Immediate Breast Reconstruction and Choice for Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy. Surgery 2016, 159, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdahl, L.; Shah, A.R.; Boughey, J.C.; Hieken, T.J.; Hoskin, T.L.; Degnim, A.C. Comparison of Side-Specific Complications After Contra lateral Prophylactic Mastectomy vs. Treatment Mastectomy for Unilateral Breast Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2014, 37, 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Osman, F.; Saleh, F.; Jackson, T.D.; Corrigan, M.A.; Cil, T. Increased Postoperative Complications in Bilateral Mastectomy Patients Compared to Unilateral Mastectomy: An Analysis of the NSQIP Database. Ann Surg Oncol 2013, 20, 3212–3217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Lancaster, R. Evolution of Operative Technique for Mastectomy. Surg Clin North Am 2018, 98, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blidaru, A.; Bordea, C.I.; Ichim, E.; El Houcheimi, B.; Matei Purge, I.; Noditi, A.; Sterie, I.; Gherghe, M.; Radu, M. Breast Cancer Surgery in Images. Chirurgia (Bucur) 2017, 112, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, J.; Gohari, S.S.; Rizki, H.; Faheem, I.; Langridge, B.; Kümmel, S.; Johnson, L.; Schmid, P. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on the Effect of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy on Complications Following Immediate Breast Reconstruction. Breast 2021, 55, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, B.; Li, J.; Huang, X.; Shen, Z.; Shao, Z.; Yu, P.; et al. Adjuvant Chemotherapy Increases the Prevalence of Fat Necrosis in Immediate Free Abdominal Flap Breast Reconstruction. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg 2014, 67, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sabawi, B.; Sosin, M.; Carey, J.N.; Nahabedian, M.Y.; Patel, K.M. Breast Reconstruction and Adjuvant Therapy: A Systematic Review of Surgical Outcomes. J Surg Oncol 2015, 112, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.C.; Pribaz, J.; Zook, E.G.; Leighton, W.D.; Eriksson, E.; Smith, C.J. Functional Evaluation of Latissimus Dorsi Donor Site. Plast Reconstr Surg 1986, 78, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Huh, J.S.; Min, Y.S.; Kim, H.J.; Park, H.Y.; Jung, T. Du Physical and Functional Ability Recovery Patterns and Quality of Life after Immediate Autologous Latissimus Dorsi Breast Reconstruction: A 1-Year Prospective Observational Study. Plast Reconstr Surg 2015, 136, 1146–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindegren, A.; Halle, M.; Docherty Skogh, A.C.; Edsander-Nord, A. Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction in the Irradiated Breast: A Comparative Study of DIEP and Latissimus Dorsi Flap Outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg 2012, 130, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yueh, J.H.; Slavin, S.A.; Adesiyun, T.; Nyame, T.T.; Gautam, S.; Morris, D.J.; Tobias, A.M.; Lee, B.T. Patient Satisfaction in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction: A Comparative Evaluation of DIEP, TRAM, Latissimus Flap, and Implant Techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg 2010, 125, 1585–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Mohan, A.T.; Vijayasekaran, A.; Hou, C.; Sur, Y.J.; Morsy, M.; Saint-Cyr, M. Maximizing the Volume of Latissimus Dorsi Flap in Autologous Breast Reconstruction with Simultaneous Multisite Fat Grafting. Aesthet Surg J 2016, 36, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
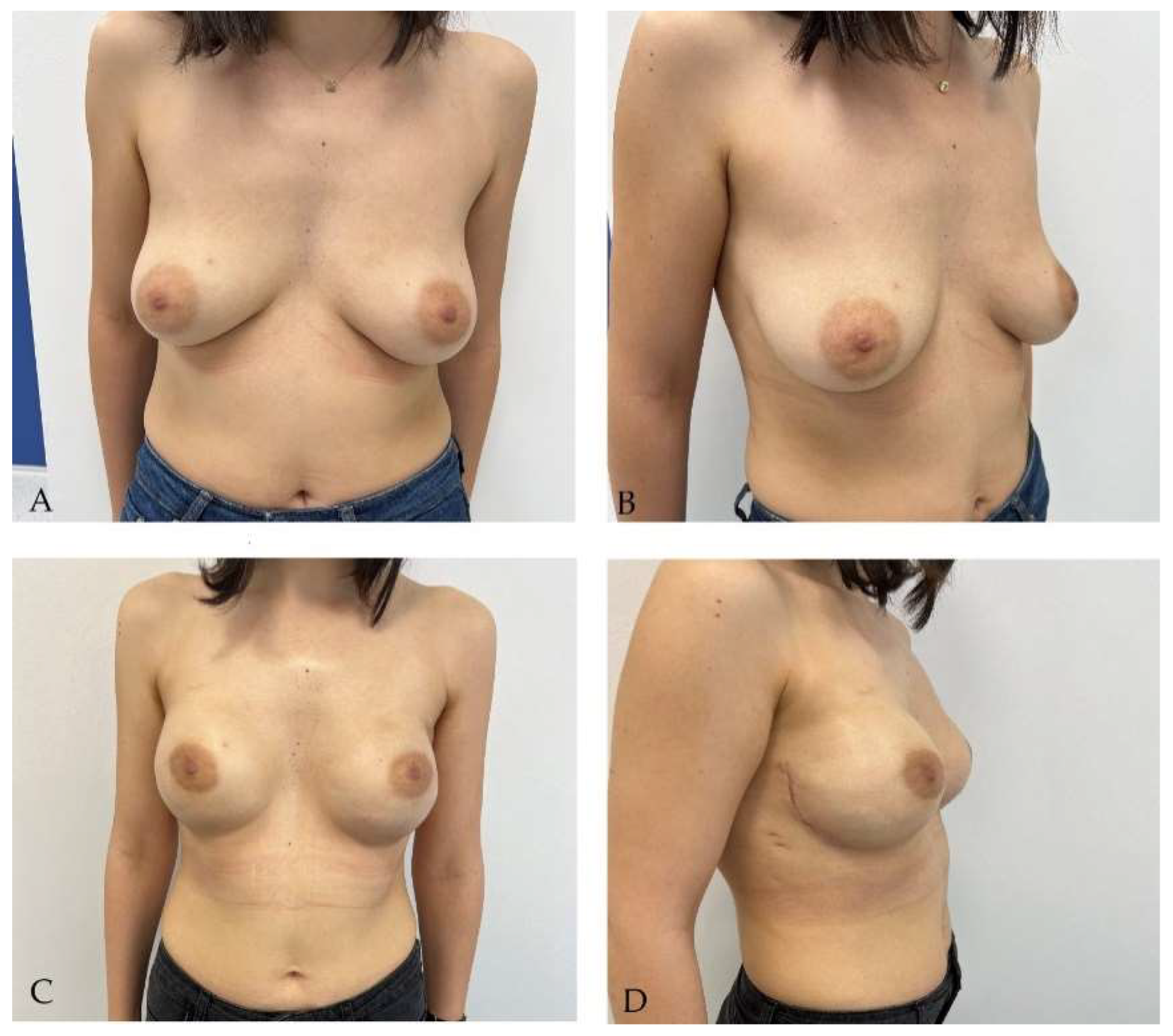
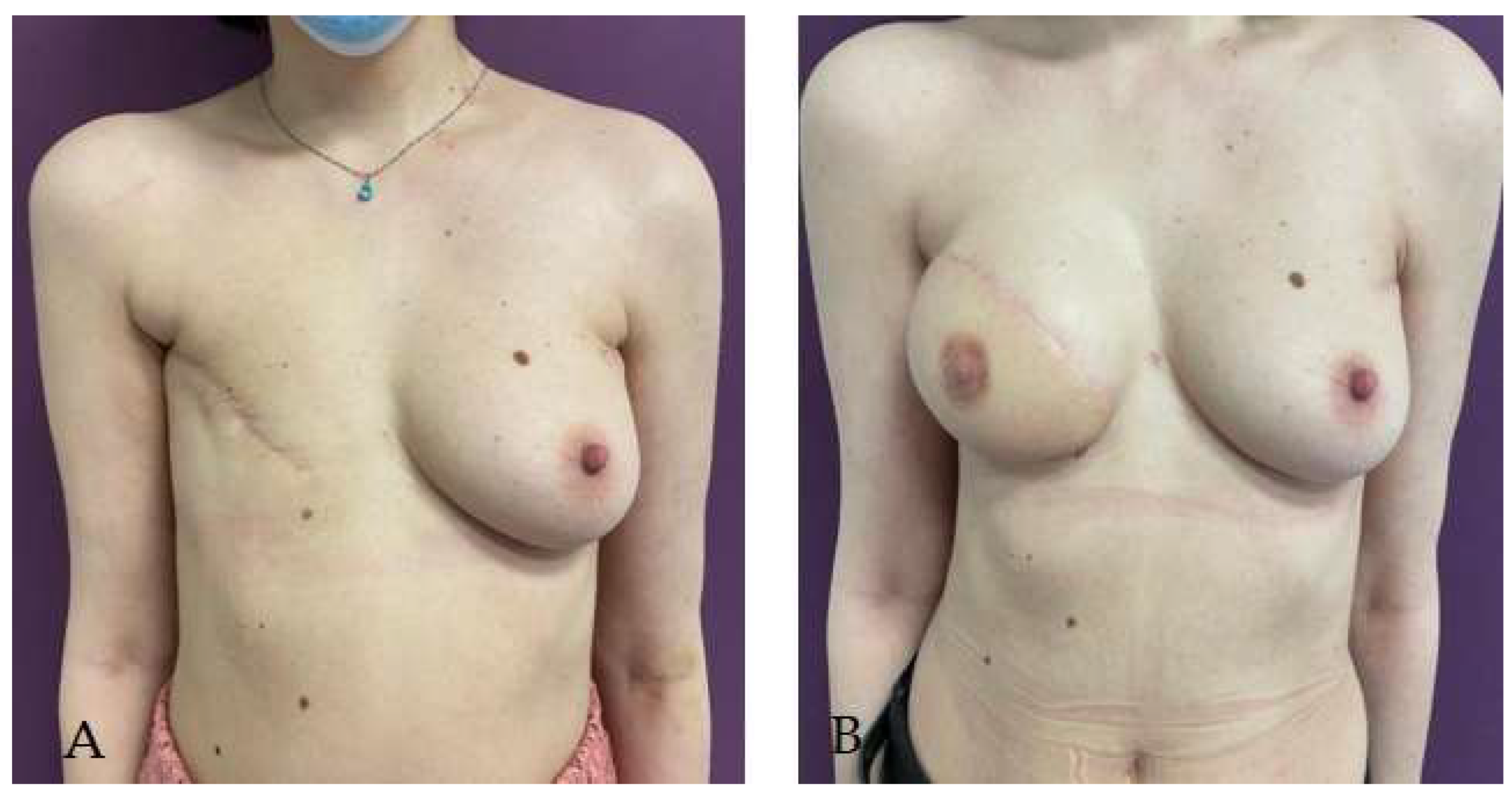
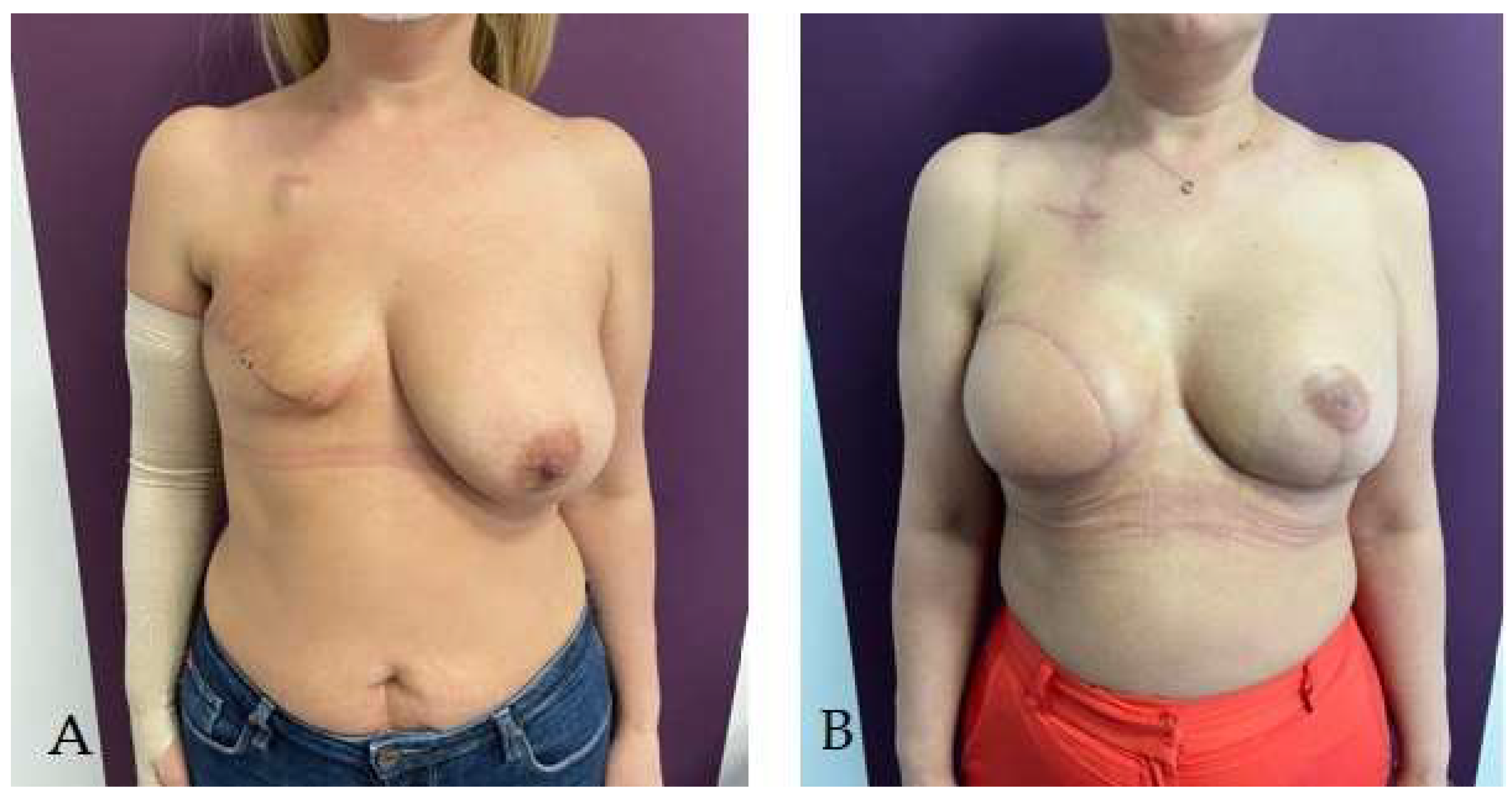
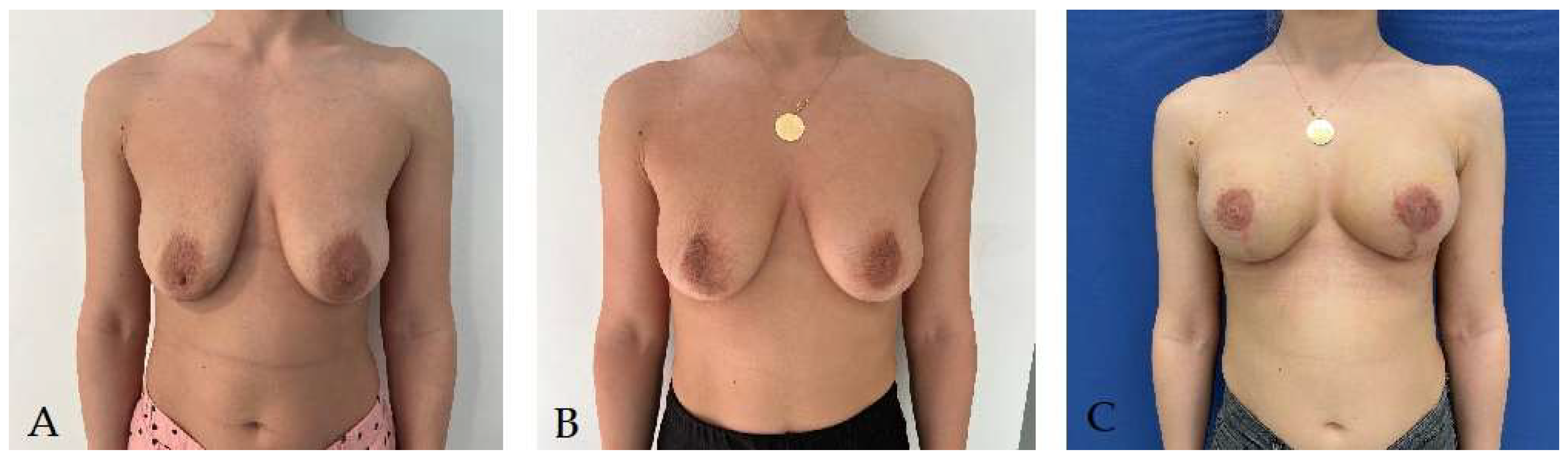
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




