Submitted:
26 August 2023
Posted:
28 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Research methods
2.1. Search of literature
2.2. Data extraction and synthesis
2.3. Results of the literature search
3. Traditional uses
4. Phytochemistry of Irvingia spp.
5. Pharmacological activity of Irvingia plants
5.1. Antiprotozoal activity
5.2. Antimicrobial activity
5.3. Antioxidant activity
5.4. Antidiabetic activity
5.5. Other biological activities
6. Toxicity profile of Irvingia spp.
7. Critical assessment and discussion
8. Conclusions and perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tobe, H.; Raven, P.H. Embryology of the Irvingiaceae, a family with uncertain relationships among the Malpighiales. J. Plant Res. 2011, 124(5), 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Flora Online (WFO), 2023. https://www.worldfloraonline.org/, Accessed on 17th August 2023.
- Mahunu, G.K.; Quansah, L.; Tahir, H.E.; Mariod, A.A. Irvingia gabonensis: Phytochemical constituents, bioactive compounds, traditional and medicinal uses. Wild fruits: Composition, Nutritional value and Products. 2019, pp 253-270.
- Gbadegesin, M.A.; degoke, A.M.; Ewere, E.G.; Odunola, O.A. Hepatoprotective and anticlastogenic effects of ethanol extract of Irvingia gabonensis (IG) leaves in sodium arsenite-induced toxicity in male Wistar rats. Niger. J. Physiol. Sci. 2014, 29(1), 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Ewere, E.G.; Oyebadejo, S.A.; Peter, V.C. Ethanolic leaf extract of Irvingia gabonensis (O’Rorke) Baill protects against nephrotoxicity and hepatotoxocity in cadmium-induced Wistar albino rats. Int. J. Pharm. Tox. 2016, 4, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emejulu, A.; Alisi, C.; Asiwe, E.; Igwe, C.; Nwogu, L.; Onwuliri, V. Renal and hepato-protective effects of Irvingia gabonensis juice on sodium fluoride-induced toxicity in Wistar rats. J. Clin. Toxicol. 2016, 6, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyen, L.P.A. Irvingia grandifolia (Engl.) Engl. In: van der Vossen, H.A.M., Mkamilo, G.S. (Editors). PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa / Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen, Netherlands, 2007. Accessed on 16th July 2023.
- Dickel, M.L., Rates, S.M.K., Ritter, M.R. Plants popularly used for loosing weight purposes in Porto Alegre, South Brazil. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109, 60–71. [CrossRef]
- Chassagne, F., Hul, S., Deharo, E., Bourdy, G. Natural remedies used by Bunong people in Mondulkiri province (Northeast Cambodia) with special reference to the treatment of 11 most common ailments. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 191, 41–70. [CrossRef]
- Olowo, S.F., Omotayo, A.O., Lawal, I.O., Ndhlovu, P.T., Aremu, A.O. Ethnobotanical use-pattern for indigenous fruits and vegetables among selected communities in Ondo State, Nigeria South African Journal of Botany Ethnobotanical use-pattern for indigenous fruits and vegetables among selected communities in Ondo State, Nigeria. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 145, 501–511. [CrossRef]
- Abdulrahman, F.; Inyang, I.S.; Abbah, J.; Binda, L.; Amos. S.; Gamaniel, K. Effect of aqueous leaf extract of Irvingia gabonensis on gastrointestinal tract in rodents. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 42(8), 787–791. [Google Scholar]
- Fadare, D.A.; Ajaiyeoba, E.O. Phytochemical and antimicrobial activities of the wild mango-Irvingia gabonensis extracts and fractions. Afr. J. Med. Med. Sci. 2008, 37(2), 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Olanrewaju, I.O,. Mordi, R.C,. Echeme, J.O.; Owoeye, T.F.; Ejilude, O.; Aruwajoye, O.A. 2019. Anti-mycobacterial and GC-MS studies of Irvingia gabonensis Baill Ex. Lanen stem extracts. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1378, 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Ibemologi, A.; Iope, A.T. Antimicrobial activities of Irvingia gabonensis leaf and Cyperus esculentus extracts on some selected isolates. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. Res. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olorundare, O.; Adeneye, A.; Akinsolam, A.; Kolo, P.; Agede, O.; Soyemi, S.; Mgbehoma, A.; Okoye, I.; Albrecht, R.; Mukhtar, H. Irvingia gabonensis seed extract: An effective attenuator of doxorubicin-mediated cardiotoxicity in Wistar rats. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2020, 2020, 1602816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atanu, F.O.; Ikeojukwu, A.; Owolabi, P.A.; Avwioroko. O.J. Evaluation of chemical composition, in vitro antioxidant, and antidiabetic activities of solvent extracts of Irvingia gabonensis leaves. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09922. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otitolaiye, C.; Omonkhua, A.; Oriakhi, K.; Okello, E.; Onoagbe, I.; Okonofua. Phytochemical analysis and in vitro antioxidant potential of aqueous and ethanol extracts of Irvingia gabonensis stem bark. Pharmacognosy Res. 2023, 15(2), 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, N.I.; Zhao, Y. Pharmacological activity of 2,3,8-tri-O-methyl ellagic acid isolated from the stem bark of Irvingia gabonensis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 6(16), 1910–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateus-Reguengo, L.; Barbosa-Pereira, L.; Rembangouet, W.; Bertolino, M.; Giordano, M.; Rojo-Poveda, O.; Zeppa, G. Food applications of Irvingia gabonensis (Aubry-Lecomte ex. O’Rorke) Baill., the ‘bush mango’: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 2446–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chung, M.; Fu, Z.; Choi, J.; Lee, H.J. The Effects of Irvingia gabonensis seed extract supplementation on anthropometric and cardiovascular outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020, 39(5), 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewere, E.G., Okolie, N.P., Ndem, J.I., Eze, G.I., Oyebadejo, S.A. Irvingia gabonensis leaf extract scavenges nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide in vitro and modulates arsenic-induced hepatic oxidative stress in Wistar rats. Clin. PhytoScience. 2022, 8, 15, 1–12. [CrossRef]
- Ndah, N.; Egbe, A.; Bechem, E.; Asaha, S.; Yengo, T.; Chia, E.; Ngaiwi, M. Ethnobotanical study of commonly used medicinal plants of the Takamanda Rainforest South West, Cameroon. Afr. J. Plant Sci. 2013, 7, 21–34. [Google Scholar]
- Akendengué, B. , Louis, A.M. Medicinal plants used by the Masango people in Gabon. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1994, 41(3), 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allabi, A.C., Busia, K., Ekanmian, V., Bakiono, F. The use of medicinal plants in self-care in the Agonlin region of Benin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 133, 234–243. [CrossRef]
- Elkington, B.G.; Sydara, K.; Newsome, A.; Hwang, C.H.; Lankin, D.C.; Simmler, C.; Napolitano, J.G.; Ree, R.; Graham. J.G.; Gyllenhaal, C.; Bouamanivong, S.; Souliya, O.; Pauli, G.F.; Franzblau, S.G.; Soejarto, D.D. New finding of an anti-TB compound in the genus Marsypopetalum (Annonaceae) from a traditional herbal remedy of Laos. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 151, 903–911. [CrossRef]
- Mgbemena, N.M.; Ilechukwu, I.; Okwunodolu, F.U.; Chukwurah, J.-V.O.; Lucky, I.B. Chemical composition, proximate and phytochemical analysis of Irvingia gabonensis and Irvingia wombolu peels, seed coat, leaves and seeds. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2019, 30, 65–69. [CrossRef]
- Kuete, V.; Wabo, G.F.; Ngameni, B.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Metuno, R.; Etoam, F.X.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Beng, V.P.; Meyer, J.J.; Lall, N. Antimicrobial activity of the methanolic extract, fractions and compounds from the stem bark of Irvingia gabonensis (Ixonanthaceae). J Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 114, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donfack, J.H.; Fotso, W.G.; Ngameni, B.; Tsofack, F.N.; Tchoukoua, A.; Ambassa, P.; Abia, W.; Tchana, A.N.; Giardina, S.; Buonocore, D.; Finzi, P.V.; Vidari, G.; Marzatico, F.; Ngadjui, B.T.; Moundipa, P.F. 2010. In vitro hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities of the crude extract and isolated compounds from Irvingia gabonensis. Asian J. Tradit. Med. 2010, 5(3), 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papers, O. Anti-Angiogenic and cytotoxicity studies of some Medicinal Plants. Planta Med. 2010, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atawodi, S.E. Polyphenol content and in vitro antioxidant activity of methanol extract of seeds of Irvingia gabonensis Baill of Nigerian origin. Elec. J. Env. Agricult. Food Chem. 2011, 10, 2314–2321. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, J.; Chen, P. Ultra high-performance liquid chromatography with high-resolution mass spectrometry analysis of African mango (Irvingia gabonensis) seeds, extract, and related dietary supplements. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60(35), 8703–8709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li J, Pan L, Naman CB, Deng Y, Chai H, Keller WJ, Kinghorn AD. Pyrrole alkaloids with potential cancer chemopreventive activity isolated from a goji berry-contaminated commercial sample of African mango. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5054–5060. [CrossRef]
- Ojo, O.A.; Ojo, A.B.; Ajiboye, B.O.; Oyinloye, B.E.; Akinyemi, A.J., Okesola, M.A.; Boligon, A.A.; de Campos, M.M.A. Chromatographic fingerprint analysis, antioxidant properties, and inhibition of cholinergic enzymes (acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase) of phenolic extracts from Irvingia gabonensis (Aubry-Lecomte ex O'Rorke) Baill bark. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 29, 217–224. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee. B.S.; Baek, S.C.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, K.H. Terminalin from African Mango (Irvingia gabonensis) stimulates glucose uptake through inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Atindehou, K.K.; Schmid, C.; Brun, R.; Koné, M.W.; Traore, D. Antitrypanosomal and antiplasmodial activity of medicinal plants from Côte d'Ivoire. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2004, 90, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Pouplin, J.; Tran, H.; Tran, H.; Phan, T.A.; Dolecek, C.; Farrar, J.; Tran, T.H.; Caron, P.; Bodo, B.; Grellier, P. Antimalarial and cytotoxic activities of ethnopharmacologically selected medicinal plants from South Vietnam. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 109(3), 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agubata, C.O.; Nzekwe, I.T.; Attama, A.A.; Mueller-Goymann, C.C.; Onunkwo, G.C. 2015. Formulation, characterization and anti-malarial activity of homolipid-based artemether microparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 478, 202–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamidi, M.; DiGiorgio, C.; Delmas, F.; Favel, A.; Eyele Mve-Mba, C.; Rondi, M.L.; Ollivier, E.; Nze-Ekekang, L.; Balansard, G. In vitro cytotoxic, antileishmanial and antifungal activities of ethnopharmacologically selected Gabonese plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 102(2), 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obianime, A.W.; Uche, F.I. The phytoconstituents and the comparative effects of aqueous extract of Irvingia gabonensis seeds and proviron on the biochemical parameters of male guinea pigs. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2010, 3(2), 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasdemir, D.; Kaiser, M.; Brun, R.; Yardley, V.; Schmidt, T.J.; Tosun, F.; Rüedi, P. Antitrypanosomal and antileishmanial activities of flavonoids and their analogues: in vitro, in vivo, structure-activity relationship, and quantitative structure-activity relationship studies. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50(4), 1352–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, U. , Daniel, H. Early and late apoptosis events in human transformed and non-transformed colonocytes are independent on intracellular acidification. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2004, 14, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamani-Matsuda, M.; Rambert, J.; Malvy, D.; Lejoly-Boisseau, H.; Daulouede, S.; Thiolat, D.; Coves, S.; Courtois, P.; Vincendeau, P.; Mossalayi, M.D. Quercetin induces apoptosis of Trypanosoma brucei gambiense and decreases the proinflammatory response of human macrophages. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, J.R.; McNair, N. Antiparasitic activity of flavonoids and isoflavones against Cryptosporidium parvum and Encephalitozoon intestinalis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 259, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osadebe, P.O.; Abba, C.C.; Agbo, M.O. Antimotility effects of extracts and fractions of Eastern Nigeria mistletoe (Loranthus micranthus Linn). Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2012, 5, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nworie, O.; Orji, J.O.; Ekuma, U.O.; Agah, M.V.; Okoli, C.S.; Nweke, M.C. Antibacterial activity of the leaf and stem bark of Irvingia gabonensis (Bush Mango) against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. Glob J. Pharmacol. 2016, 10(1), 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Unaeze, B.C.; Ilo, C.E.; Egwuatu, C.; Orabueze, I.; Obi, E. Anti-diarrhoeal effects of three Nigerian medicinal plant extracts on E. coli-induced diarrhea. Int. J. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2017, 11, 414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamba, B.E.N.; Mbaveng, A.T.; Nayim, P.; Dzotam, J.K.; Ngalani, O.J.T.; Kuete, V. Antistaphylococcal and antibiotic resistance modulatory activities of thirteen Cameroonian edible plants against resistant phenotypes. Int. J. Microbiol 2018, 2018, 1920198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandji, F.N.B.; Achidi, A.U.; Ngemenya, M.N.; Nyongbela, K.D., Tiencheu, B. 2019. In vitro antifungal, antibacterial activities and nutritional value of nine Cameroonian edible vegetables. Acta Sci. Pol. Technol. Aliment. 2019, 18, 333–341. [CrossRef]
- Wrońska, N.; Szlaur, M.; Zawadzka, K.; Lisowska, K. The synergistic effect of triterpenoids and flavonoids-New approaches for treating bacterial infections? Molecules. 2022, 27, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zore, G.B.; Thakre, A.D.; Jadhav, S.; Karuppayil, S.M. Terpenoids inhibit Candida albicans growth by affecting membrane integrity and arrest of cell cycle. Phytomedicine 2011, 18(13), 1181–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Lin, K.W.; Huang, A.M.; Tu, H.Y.; Wei, B.L.; Hour, T.C.; Yen, M.H.; Pu, Y.S.; Lin, C.N. Terpenoids induce cell cycle arrest and apoptosis from the stems of Celastrus kusanoi associated with reactive oxygen species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58(6), 3808–3812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miklasińska-Majdanik, M.; Kępa, M.; Wojtyczka, R.D.; Idzik, D.; Wąsik, T.J. Phenolic compounds diminish antibiotic resistance of Staphylococcus aureus clinical strains. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018, 15(10), 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbor, G.A.; Oben, J.E.; Ngogang, J.Y.; Xinxing, C.; Vinson, J.A. Antioxidant capacity of some herbs/spices from Cameroon: a comparative study of two methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53(17), 6819–6824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arogba, S.S.; Omede, A. Comparative antioxidant activity of processed Mango (Mangifera indica) and Bush Mango (Irvingia gabonensis) Kernels. Niger. Food J. 2012, 30(2), 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.L.; Akanbi, T.O.; Tawiah, N.A.; Aryee, A.N.A. Valorization of seed and kernel marcs and evaluation of their antioxidant potential. Food Chem. 2022, 390, 133168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijveldt, R.J.; van Nood, E.; van Hoorn, D.E.; Boelens, P.G.; van Norren, K.; van Leeuwen, P.A. Flavonoids: a review of probable mechanisms of action and potential applications. Am J Clin Nutr 2001, 74, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speisk, H.; Shahidi, n9., de Camargo, A.C.; Fuentes, J. Revisiting the oxidation of flavonoids: loss, conservation or enhancement of their antioxidant propertie. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 133. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestro, S.; Mazzon, E. Nrf2 Activation: Involvement in central nervous system traumatic injuries. A promising therapeutic target of natural compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24(1), 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A. Concept, mechanism, and applications of phenolic antioxidants in foods. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassmann, J. Terpenoids as plant antioxidants. Vitam. Horm. 2005 72, 505–535. [CrossRef]
- Chung, L.Y. , Goh, S.fH., Imiyabir, Z. Central nervous system receptor activities of some Malaysian plant species. Pharm. Biol. 2005, 43(3), 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.Y.; Ling, S.K.; Ali, R.M.; Chee, C.F.; Samah, Z.A., Ho, A.S.; Teo, S..; Lee, H.B. 2009. Systematic analysis of in vitro photo-cytotoxic activity in extracts from terrestrial plants in Peninsula Malaysia for photodynamic therapy. J. Photochem. Photobiol B 2009, 96, 216–222. [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.W.; Salhimi, S.M.; Majid, A.M.; Chan, K.L. Anti-angiogenic and cytotoxicity studies of some medicinal plants. Planta Med. 2010, 76(9), 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Del Villar, M.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Pérez-Rubio, K.G.; Cortez-Navarrete, M. Effect of Irvingia gabonensis on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. J. Med. Food. 2018, 21(6), 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nweze, N.E.; Ogidi, A.; Ngongeh. L;A. Anthelmintic potential of three plants used in Nigerian ethnoveterinary medicine. Pharm Biol. 2013, 51(3), 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ugwu, C.E.; Oraeluno, J.N.; Eze, K.C.; Ezenma, C.O.; Nwankwo, A.O. PEGylated aceclofenac solid lipid microparticles homolipid-based solidified reverse micellar solutions for drug delivery. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolo, C.O.; Johnson, P.B.; Abdurahman, E.M.; Abdu-Aguye, I.; Hussaini, I.M. Analgesic effect of Irvingia gabonensis stem bark extract. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 45(2), 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, S.C.; Shivarudraiah, P.; Venkataramaiah, S.B.; Gavara, S.; Soni, M.G. Subchronic toxicity and mutagenicity/genotoxicity studies of Irvingia gabonensis extract (IGOB131). Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50(5), 1468–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezeasor, C.K., Chukwuma, C., Ekere, S.O., Abah, P. Subchronic toxicity studies of aqueous leaf and stem bark extract of Irvingia gabonensis in male albino wistar rats. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 26, 553–559. [CrossRef]
- Tsao R. Chemistry and biochemistry of dietary polyphenols. Nutrients. 2010, 2, 1231–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrapal, M.; Khairnar, S.J.; Khan, J.; Dukhyil, A.B.; Ansari, M.A.; Alomary, M.N.; Alshabrmi, F.M.; Palai, S.; Deb, P.K.; Devi, R. Dietary polyphenols and their role in oxidative stress-induced human diseases: Insights into protective effects, antioxidant potentials and mechanism (s) of action. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country of use | Plant organs used / Route of administration |
Traditional uses | Species | Common names | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Benin | Leaves | Used to treat icterus | Irvingia gabonensis (Aubry-Lecomte exO’Rorke) Baill | Aslotin | [24] |
| Cameroon | Seed/oral administration | The seeds are used as condiments and the decoction is administered (a bowlful 2 times a day until recovery) to reduce the body weight |
-Irvingia gabonensis (Aubry-Lecomte ex O’Rorke) Baill -Irvingia wombolu Vermoesen (Syn: Irvingia tenuinucleata Tiegh.) |
bojep | [8, 22] |
| Gabon | Bark / leaves | The bark decoction is used in a bath to treat asthenia. For children the leaves are pounded and mixed with food. |
Irvingia grandtfolia (Engl.) Engl | Mulenda | [23] |
| Laos | Bark / Wood | The bark or wood is grilled on fire and boiled with salt in water and administered orally to overcome tuberculosis related symptoms. | Irvingia malayana Oliver ex Bennett | Bohk; Yarr/ Niharr | [9, 25] |
| Nigeria | -Fruit, bark, seeds and roots -Fruit and bark |
-These organs are used as food and to get relief from dysentery, diarrhea toothache and diabetes; -These organs are used to relieve dysentery, diarrhea toothache and diabetes. |
-Irvingia gabonensis (Aubry-Lecomteex O'Rorke) Baill. -Irvingia tenuinucleata Tiegh. Irvingiaceae |
-Bush mango, Oro, dika nut tree, Ugiri, Goron, Biri and Apon -Bush mango, Oro |
[10] |
| Serial number | Phytochemical classification | Compound name | Plant species | Plant organs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
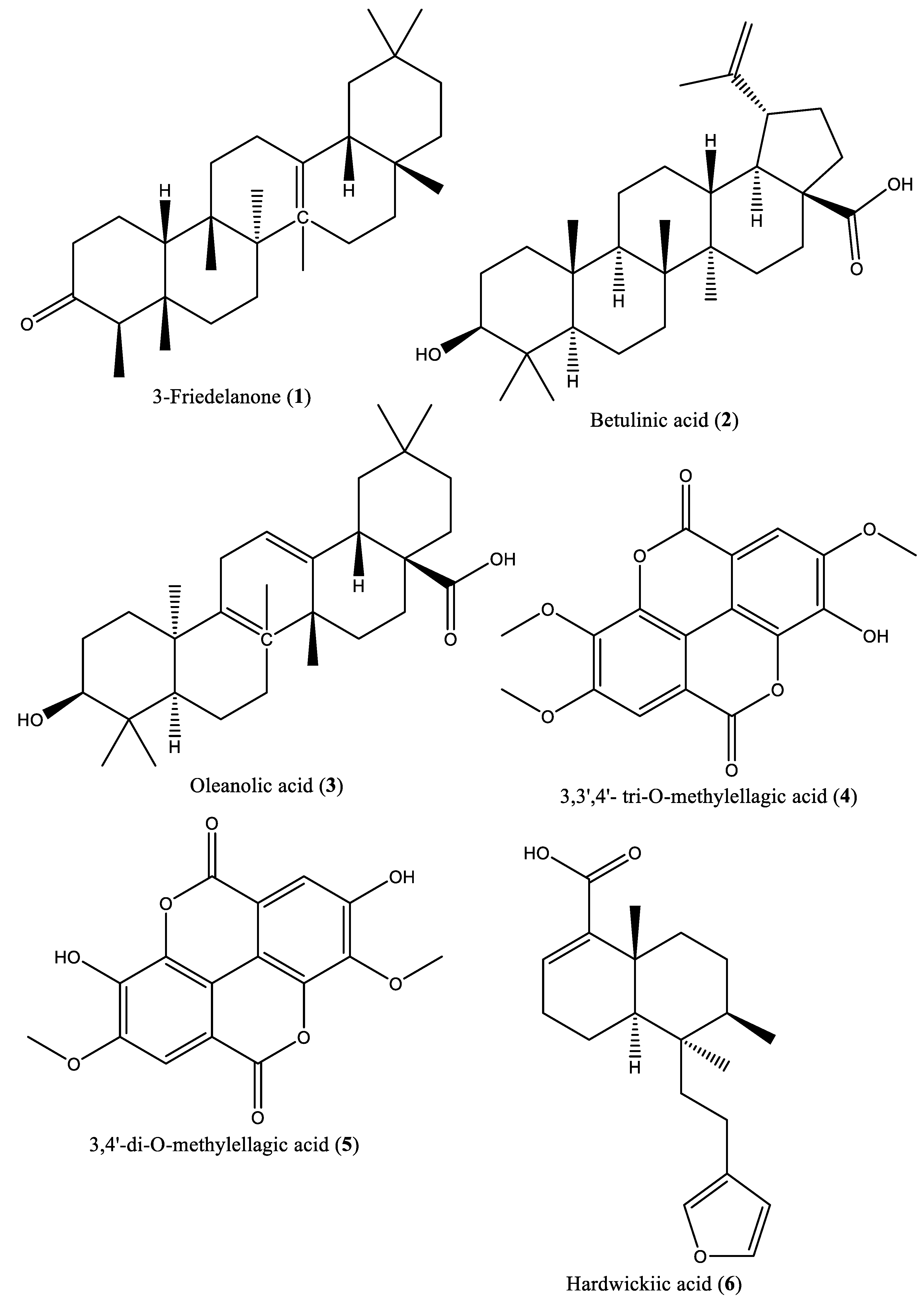
| 1 | Triterpenoid | 3-Friedelanone (1) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [27, 28] |
| 2 | Triterpenoid | Betulinic acid (2) | Irvingia gabonensis; Irvingia malayana | Stem bark | [27, 28, 29] |
| 3 | Triterpenoid | Oleanolic acid (3) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [27, 28] |
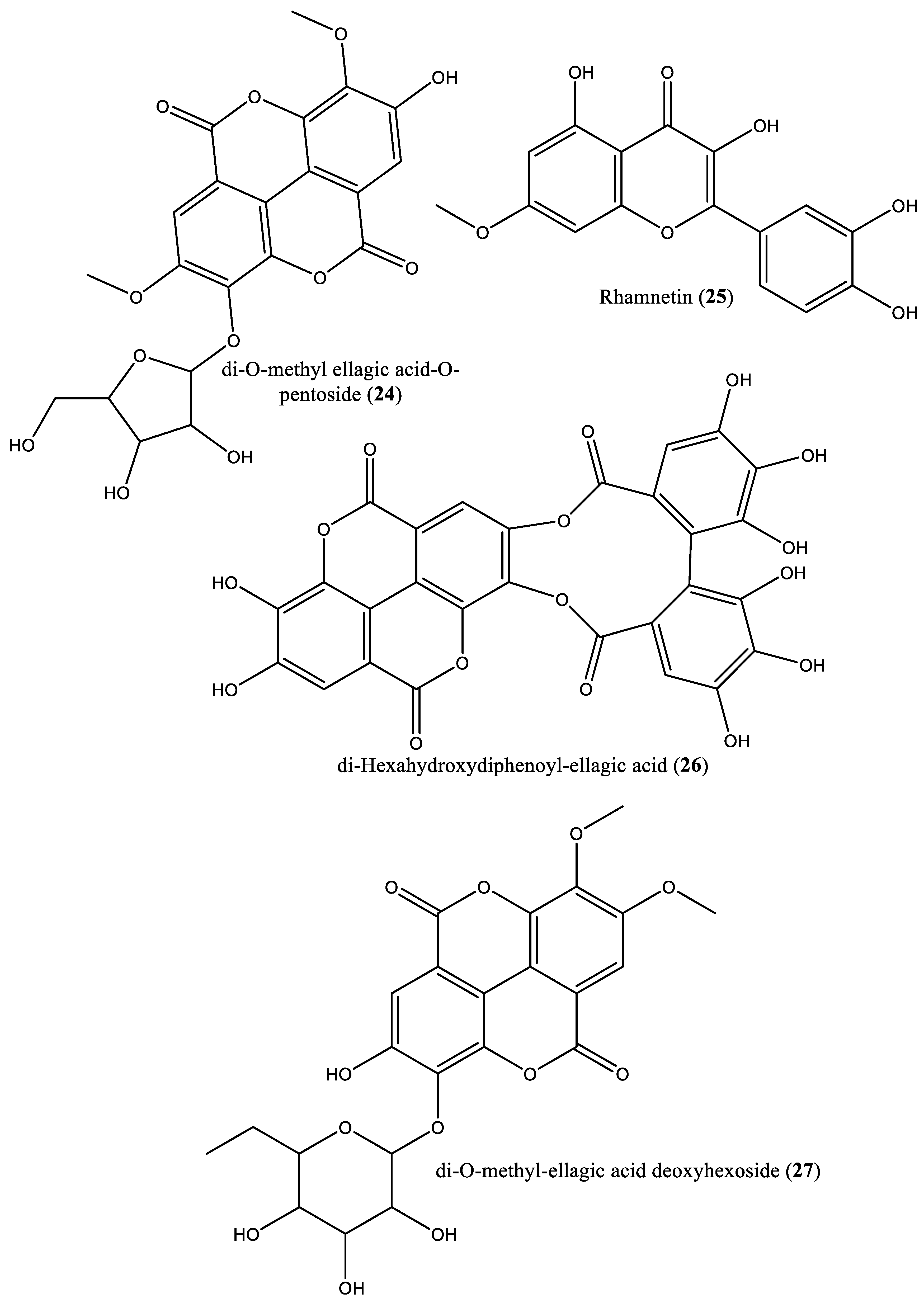
| 4 | Phenolic | 3,3′,4′-tri-O-methylellagic acid (4) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark, seeds, | [27, 28, 31] |
| 5 | Phenolic | 3,4-di-O-methylellagic acid (5) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [27, 28] |
| 6 | Diterpenoid | Hardwickiic acid (6) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [27, 28] |
| 7 | Phenolic acid | Methyl gallate (7) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds, | [28, 30] |
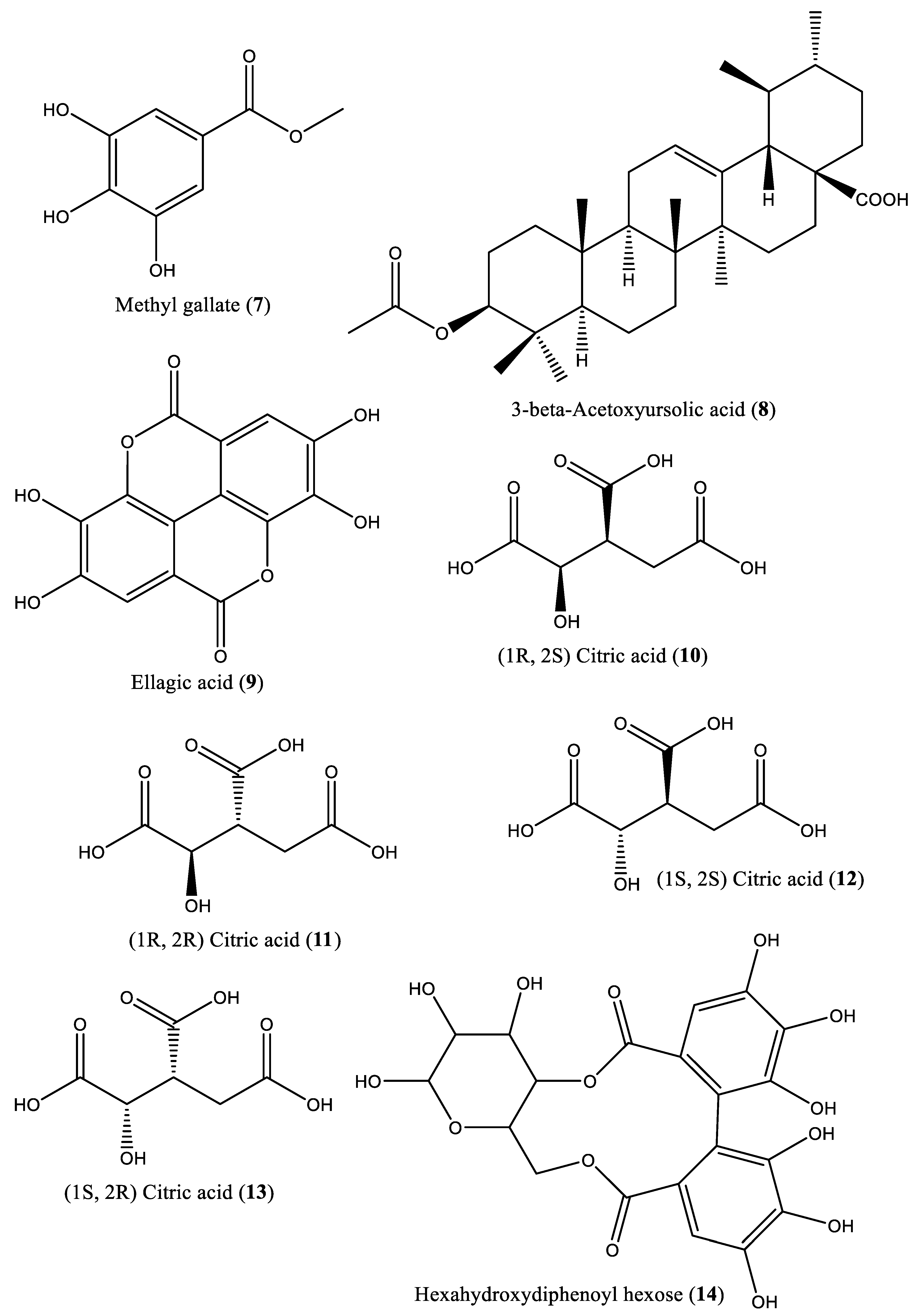
| 8 | Pentacyclic triterpenoid | 3-β-Acetoxyursolic acid (8) | Irvingia gabonensis | [28] | |
| 9 | Phenolic compound | Ellagic acid (9) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds, stem bark | [31, 33] |
| 10 | Organic acid | Citric acid (1R, 2S) (10) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 11 | Organic acid | Citric acid (1R, 2R) (11) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 12 | Organic acid | Citric acid (1S, 2S) (12) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 13 | Organic acid | Citric acid (1S, 2R) (13) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 14 | Ose | Hexahydroxydiphenoyl(HHDP)-hexose (14) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 15 | Ose | di-Hexahydroxydiphenoyl-hexose (15) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
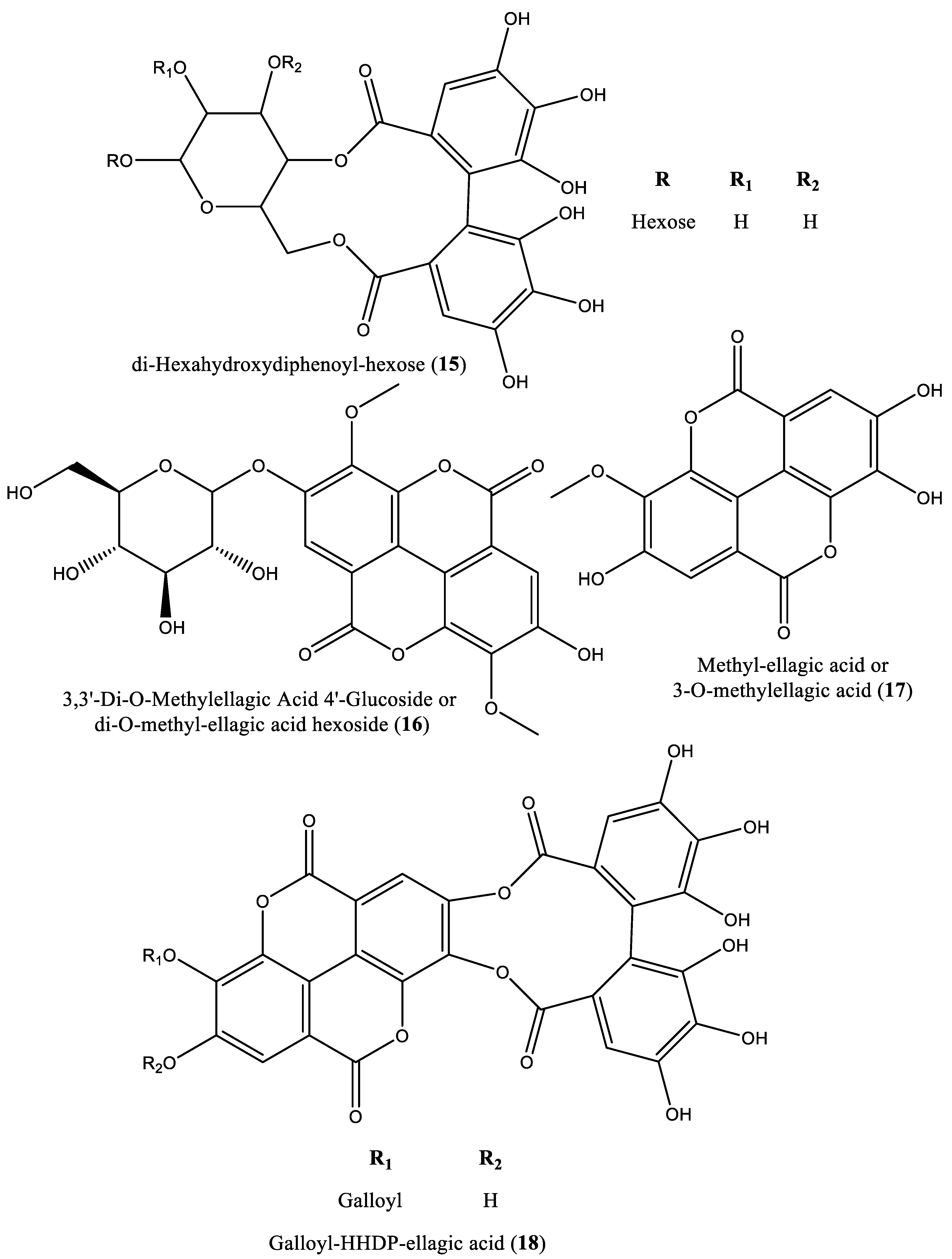
| 16 | Ellagitannin | di-O-Methyl-ellagic acid hexoside (16) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 17 | Phenolic | Methyl-ellagic acid (17) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 18 | Ellagitannin | Galloyl-HHDP-ellagic acid (18) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
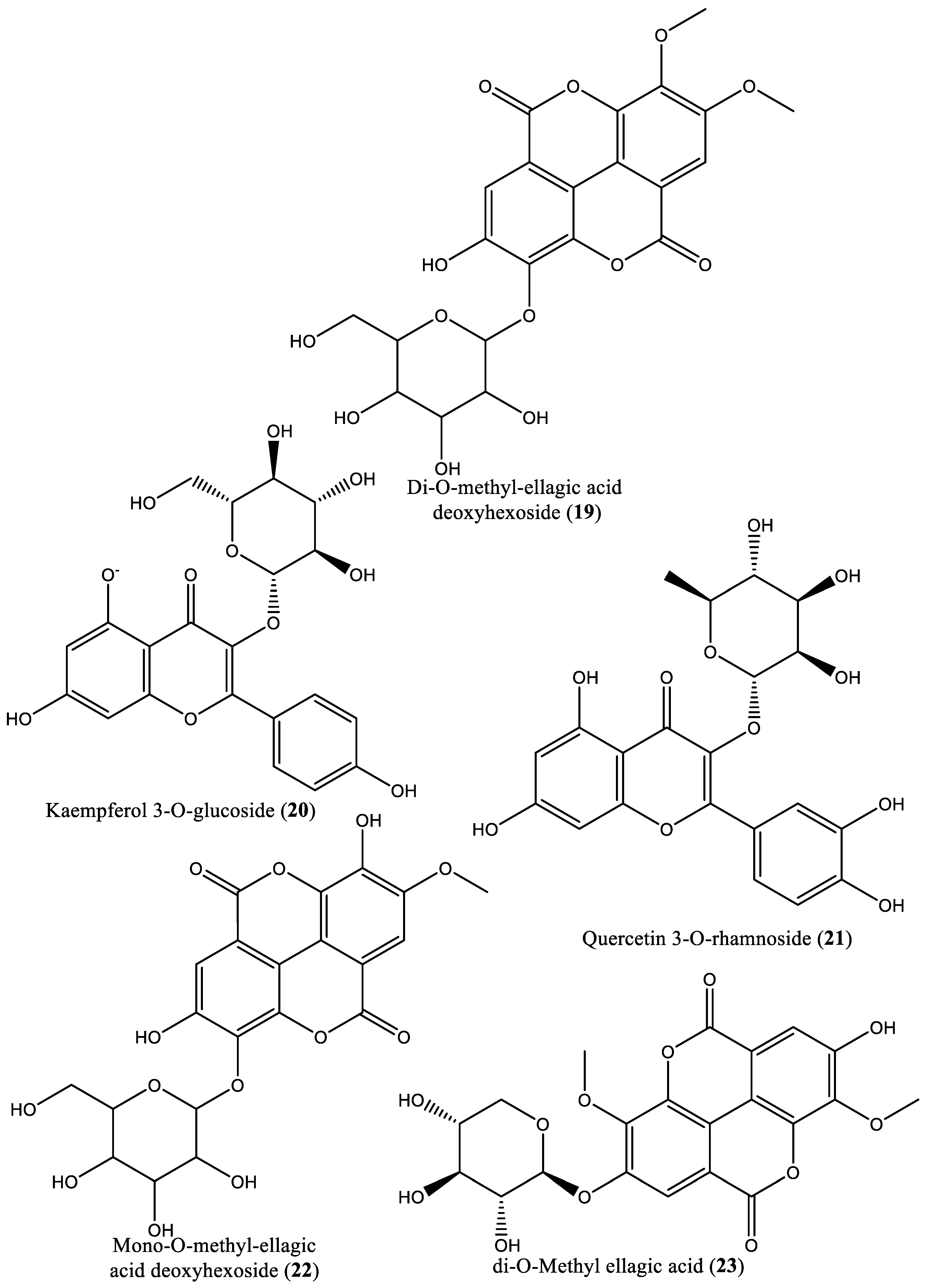
| 19 | Ellagitannin | Di-O-methyl-ellagic acid deoxyhexoside (19) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 20 | Flavonoid | Kaempferol 3-O-glucoside (20) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 21 | Flavonoid | Quercetin 3-O-rhamnoside (21) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 22 | Phenolic | Mono-O-methyl ellagic acid deoxyhexoside (22) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 23 | Phenolic | Di-O-methyl ellagic acid (23) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 24 | Phenolic | Di-O-methyl ellagic acid-O-pentoside (24) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 25 | Flavonoid | Rhamnetin (25) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 26 | Phenolic | Di-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-ellagic acid (26) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 27 | Phenolic | di-O-Methyl-ellagic acid deoxyhexoside (27) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 28 | Phenolic | Galloyl-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-methyl-ellagic acid (28) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
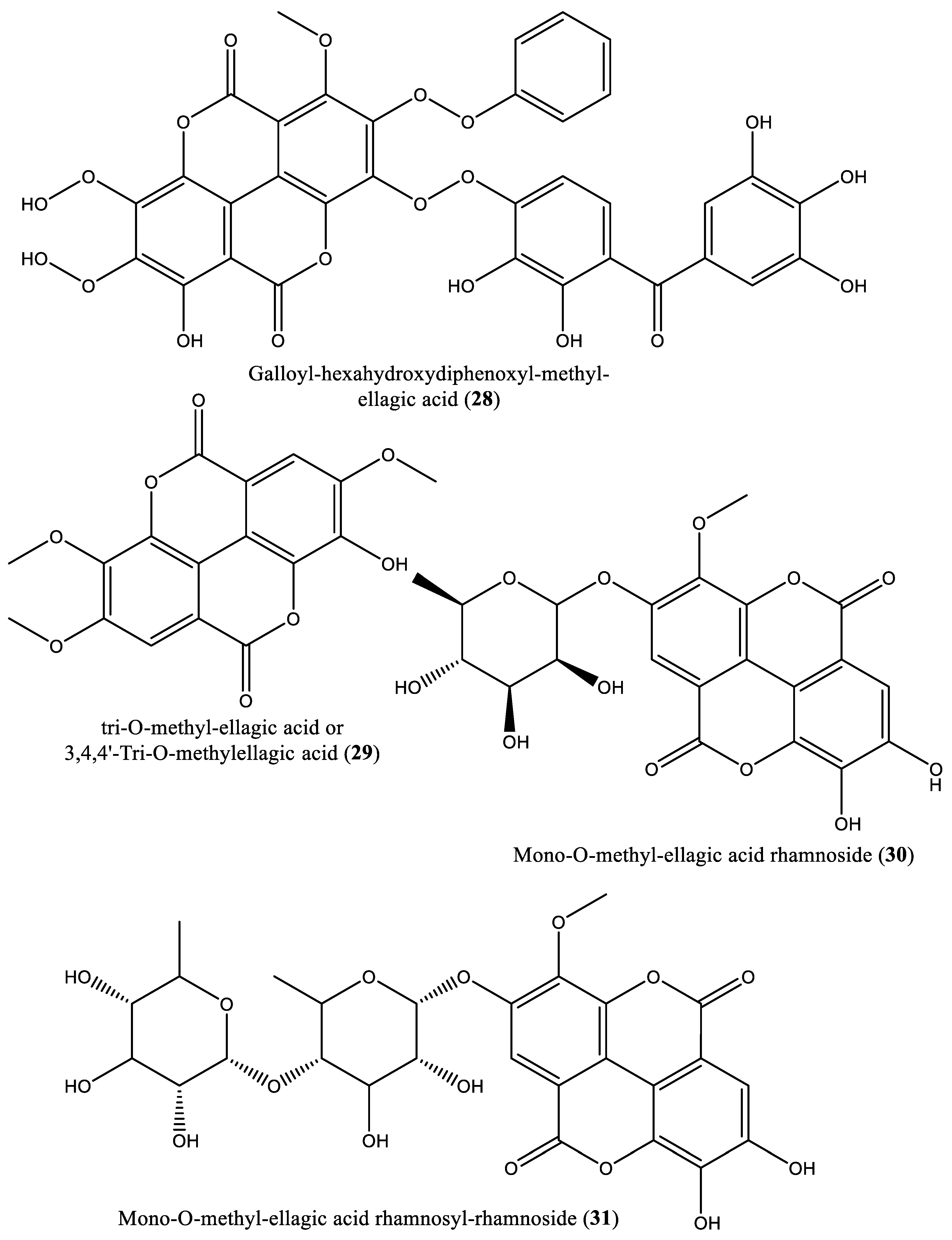
| 29 | Phenolic | tri-O-Methyl-ellagic acid (29) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| Serial number | Phytochemical classification | Compound name | Plant species | Plant organs | Reference |
| 30 | Phenolic | Mono-O-methyl-ellagic acid rhamnoside (30) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 31 | Phenolic | Mono-O-methyl-ellagic acid rhamnosyl-rhamnoside (31) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
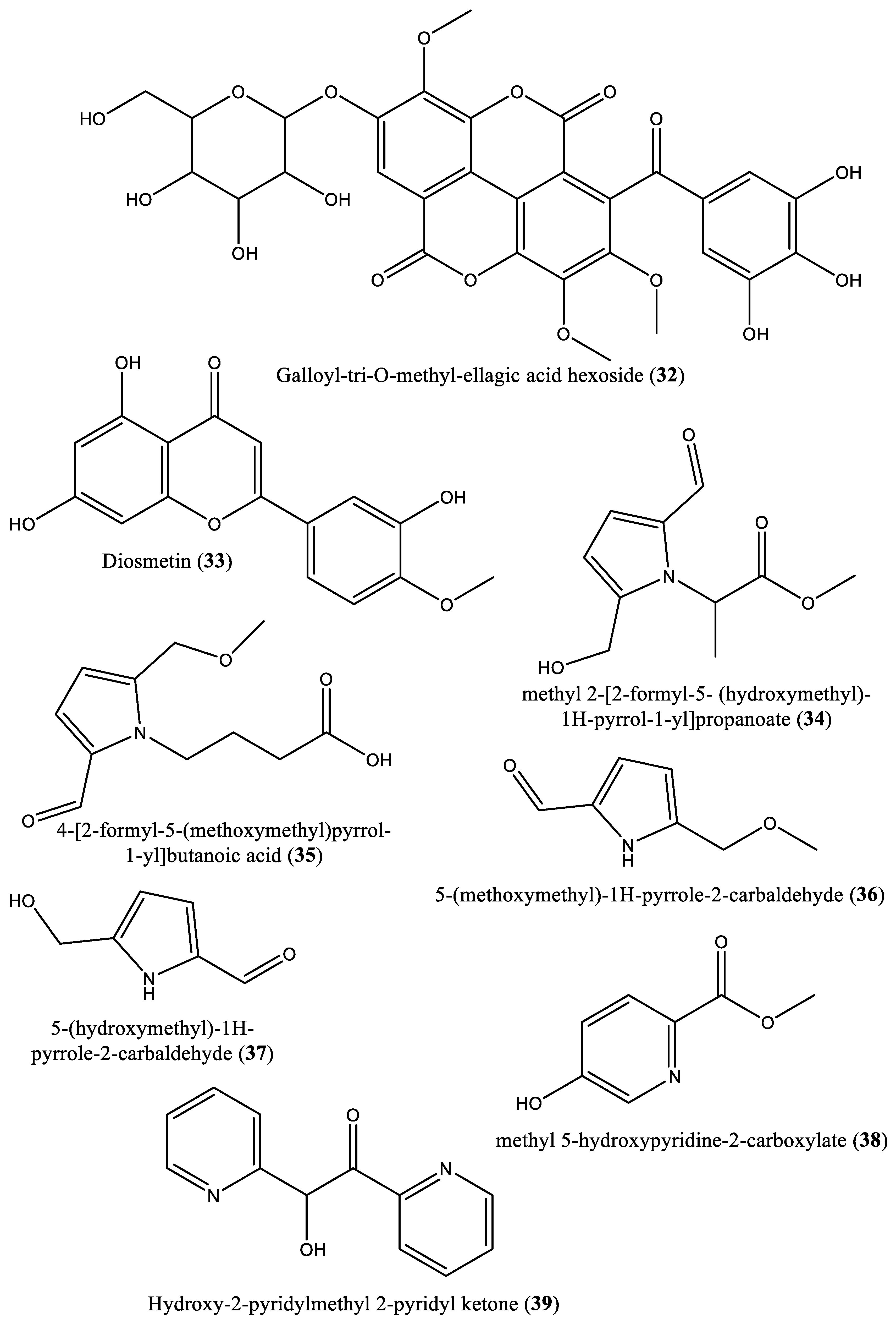
| 32 | Phenolic | Galloyl-tri-O-methyl-ellagic acid hexoside (32) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 33 | Flavonoid | Diosmetin (33) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [31] |
| 34 | Carboxylate | Methyl 2-[2-formyl-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-propanoate (34) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 35 | Carboxylic acid | 4-[formyl-5-(methoxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]butanoic acid (35) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 36 | Carbaldehyde | 5-(Methoxymethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde (36) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 37 | Carbaldehyde | 5-(Hydroxymethyl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carbaldehyde (37) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 38 | Carbaldehyde | Methyl-5-hydroxy-2-pyridinecarboxylate (38) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 39 | Ketone | 5-Hydroxy-2-pyridyl methyl ketone (39) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
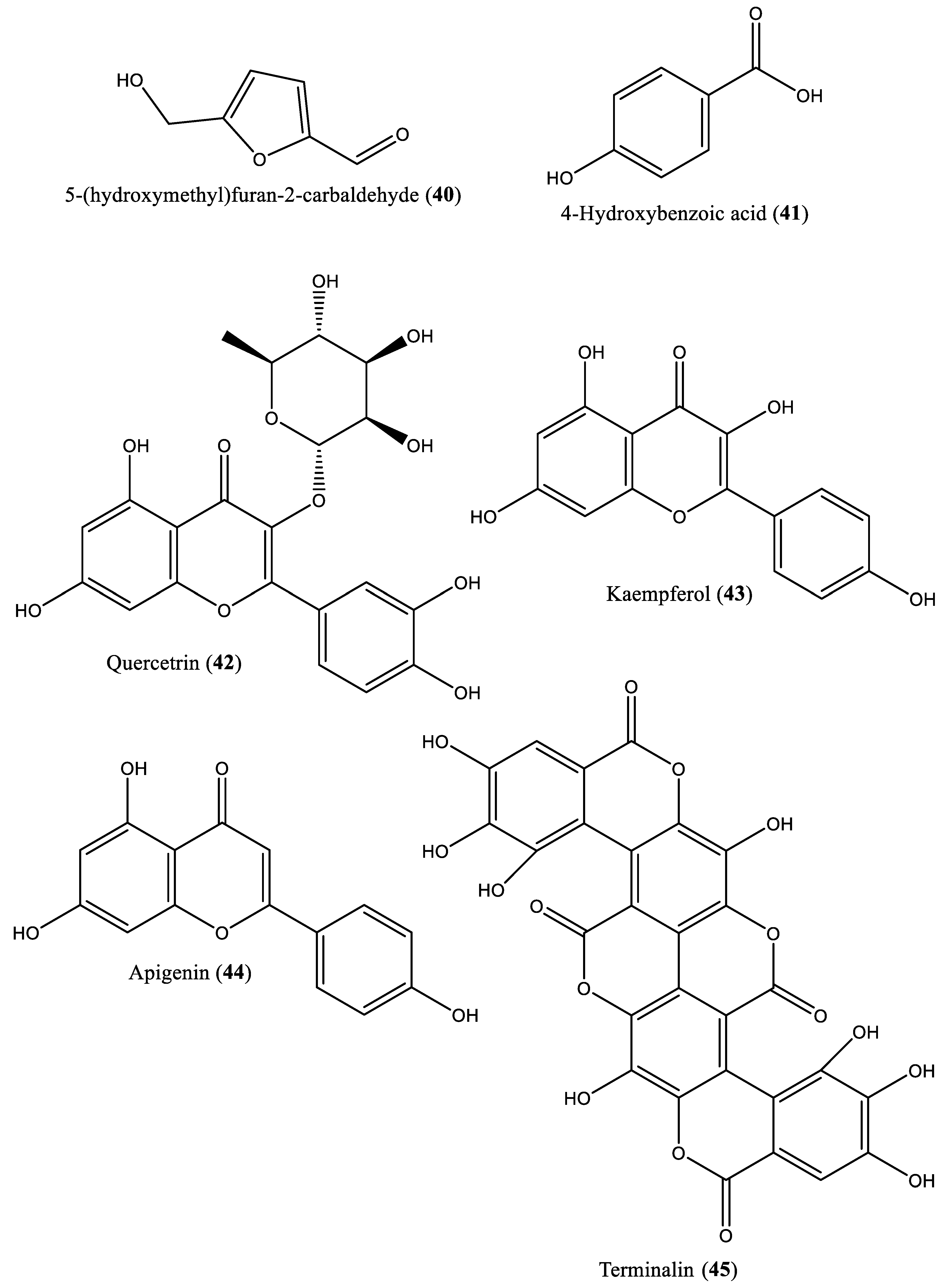
| 40 | Furan | 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furancarbaldehyde (40) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 41 | Phenolic | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (41) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [32] |
| 42 | Flavonoid | Quercetrin (42) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [33] |
| 43 | Flavonoid | Kaempferol (43) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [33] |
| 44 | Flavonoid | Apigenin (44) | Irvingia gabonensis | Stem bark | [33] |
| 45 | Tannin | Terminalin (45) | Irvingia gabonensis | Seeds | [34] |
| Irvingia spp. | Extracts/ Compounds |
Model of the study | Significant results | Toxicity/ Cytotoxicity |
Type of screening | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Irvingia gabonensis |
Crude ethanol extract of the stem bark | -Plasmodium falciparum strain K1 -Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense |
-IC50: >5 µg/ml, vs chloroquine (IC50: 0.064 µg/ml); -IC50: 8 µg/ml, vs suramin (IC50: 0.010 µg/ml). |
NS | Alamar Blue assay | [35] |
| Irvingia malayana Oliv. ex Benn. | Methanol and ethanol (80%) extract from the leaves | -Chloroquine-resistant FcB1/Colombia strain of Plasmodium falciparum -Cytotoxicity: The human cervix carcinoma cells (HeLa), and the human diploid embryonic lung cells (MRC5). |
IC50: 5.0 and 10.5 µg/ml for methanol and ethanol extracts, respectively vs chloroquine (IC50: 0.1 µM) on |
Cytotoxicity *Methanol extract -HeLa cells; IC50: 14.8 µg/ml and SI: 2.9; -MRC5 cells: IC50: 50.5 µg/ml and SI: 10.0. *Ethanol extract -HeLa cells; IC50: 11.7 µg/ml and SI: NT; -MRC5 cells: IC50: 1.1 µg/ml and SI: NT. |
Antiplasmodial test: [3H]Hypoxanthine Uptake Assay; -Cytotoxicity: methyl thiazole tetrazolium (MTT) assay |
[36] |
| Irvingia gabonensis var. excelsa (Irvingia wombolu) | Microparticles prepared from fatty acids from the nuts of Irvingia gabonensis, extracted using petroleum ether (microparticles composed of artemether (4 mg/kg), lipid matrices (LM) and phospholipon1 90G (P90G) [ADP3 (3:1), ADP4 (4:1) and ADP9 (9:1)]) | Plasmodium berghei-infected mice | Percentage of inhibition of Plasmodium berghei: 83.84, 83.68, 82.63 and 87.37% for ADP3 (3:1), ADP4 (4:1) and ADP9 (9:1), respectively vs artemether treatment alone (percent inhibition: 56.32%) inhibition: 56.32%) | NS | Four day suppressive test | [37] |
| Irvingia grandifolia | Methanol, methanol/water (50:50), and dichloromethane extracts prepared from stem barks and leaves | Promastigote form of Leishmania Infantum; Cytotoxicity on Human cell line (Vero cells) |
IC50: >100 µg/ml for the extracts assayed. |
Cytotoxicity *Stem bark: IC50 :7.7, 8.4 and 8.3 µg/ml respectively for the extracts, respectively; *Leaves: IC50: >100, 6.2, and 5.4 µg/ml for the extracts, respectively. |
Cell viability test | [38] |
| Irvingia spp. | Extracts/ Compounds |
Model of the study | Significant results | Toxicity/ Cytotoxicity |
Type of screening | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irvingia gabonensis | Methanol extract, fractions (A, B and C), and compounds [3-friedelanone (1), betulinic acid (2), oleanolic acid (3), 3,3′,4′-tri-O-methylellagic acid (4), 3,4-di-O-methylellagic acid (5) and hardwickiic acid (6)] from the stem bark. | 22 species of microorganisms | MIC values: *Fungi: Candida albicans (MIC values: 39.06-> 312.50 µg/ml); Candida gabrata (MIC values: 19.53-> 312.50 µg/ml); Candida krusei (MIC values: 9.76-> 312.50 µg/ml), vs nystatin (2.44-9.76 µg/ml); *Bacteria: Citrobacter freundii (MIC range: 19.53-> 312.50 µg/ml); Enterobacter aerogens (MICs: 19.53-312.50 µg/ml); Enterobacter cloacae (MICs: 9.76-312.50 µg/ml); Escherichia coli (MIC range: 4.88-156.25 µg/ml); Klebsiella pnemoniae (MICs: 9.76-156.25 µg/ml); Morganella morganii (MICs: 4.88-312.50 µg/ml); Neisseria gonorrhea (MICs: 1.22 - > 312.50 µg/ml); Proteus mirabilis (MICs: 19.53-> 312.50 µg/ml); Proteus vulgaris (MICs: 4.88-> 312.50 µg/ml) ; Proteus aeruginosa (MIC values: 4.88-> 312.50 µg/ml); Shigella dysenteriae (MIC values: 9.76-312.50 µg/ml); Shigella flexneri (MICs: 4.88-312.50 µg/ml) Salmonella typhi (MICs: 4.88-> 312.50 µg/ml) Streptococcus faecalis (MICs: 39.06-> 312.50 µg/ml); Staphylococcus aureus (MICs: 19.53-> 312.50 µg/ml); Bacillus cereus (MICs: 4.88-> 312.50 µg/ml); Bacillus megaterium (MIC range: 4.88-> 312.50 µg/ml); Bacillus stearotherm (MICs: 4.88- > 312.50 µg/ml); Bacillus subtilis (MICs: 4.88-> 312.50 µg/ml) vs gentamicin (MIC range: 0.61 µg/ml-9.76 µg/ml). |
NS | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) assays | [27] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Leaves/ Petroleum ether extract | Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Salmonella typhi. | MIC values: 4.31, 3.53, 5.53 and 5.55 µg/ml, for the strains, respectively | NS | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) assays | [44] |
| Irvingia malayana Oliver ex Bennett | Ethanol extract | -Strains Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans -Cytotoxicity: Vero cells |
Percentage of inhibition at the concentration of 11.4 µg/ml: 19%, 31%, 38%, and 98% against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Candida albicans, respectively. |
Ethanol extract: IC50: 100 µg/ml on Vero cells; SI: > 8.77. |
Alamar Blue, assay |
[25] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Hot water, cold water and ethanol extracts prepared from the leaves and stem bark. | Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli | -Diameter of inhibition: ranging between 8-23 mm, 8-14 mm, and 8-20 mm for the extract, respectively; -MIC range: 6.25-50 mg/ml. |
NS | Agar-well diffusion and agar dilution methods | [45] |
| I. gabonensis | Methanol extract of the seeds | Staphylococcus aureus and Fusarium oxysporum | MIC values: 2 and 6.5 mg/ml against the tested strains, respectively | NS | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) assays | [48] |
| Irvingia spp. | Extracts/ Compounds |
Model of the study | Significant results | Toxicity/ Cytotoxicity |
Type of screening | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irvingia gabonensis | Hexane extract of the seeds | In vitro free radical scavenging tests (ORAC, and TEAC). | -FRAP: 283.91 mg/g; -Total Antioxidant Capacity: 431.58 mg/g. |
NS | Oxygen radical antioxidant capacity (ORAC) test/ Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) test | [53] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Methanol extract of the seeds | In vitro DPPH free radical inhibition | IC50: 177.22 µg/ml | NS | Colorimetric method | [54] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Methyl 2-[2-formyl-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-propanoate (34); 4-[formyl-5-(methoxymethyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]butanoic acid (35); and 5-hydroxy-2-pyridyl methyl ketone (39) | In vitro test | ED50: 16.7, 11.9, >20 µM for compounds 34, 35 and 39, respectively vs quercetin (1.3 µM) |
NS | Hydroxyl Radical-Scavenging assay | [32] |
| Irvingia gabonensis Baill | Methanol extract of the seeds | Hypoxanthine/xanthine oxidase and 2-deoxyguanosine assays as models | IC50: 28 and 281 µl in hypoxanthine/xanthine oxidase assay and 2-deoxyguanosnine tests, respectively. | NS | Hypoxanthine/xanthine oxidase assay and 2-deoxyguanosine assay models | [30] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Ethanol extract of the leaves | -In vitro (nitric oxide and hydrogen peroxide scavenging properties) -In vivo; modulation of the arsenic-induced hepatic oxidative stress in albinos Wistar rats |
-Nitric oxide test: IC50: 258.47 μg/ml vs ascorbic acid (91.95 μg/ml) -Hydrogen peroxide scavenging: IC50: 640.05 μg/ml vs ascorbic acid (109.72 μg/ml); -In vivo assay: decrease in serum ALT, ALP and GGT activities, CAT and MDA concentrations; increase in SOD and GPx concentrations |
NS | *Colorimetric methods and Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent assays; *TECO diagnostic assay kits (Anahaema, USA) |
[21] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Phenolic-rich extract from the stem bark | In vitro: anti-oxidant activity (FRAP, DPPH, ABTS tests) | IC50 (µg/ml): 113.10, 18.98, and 18.25 in FRAP, DPPH, and ABTS assays, respectively. | NS | Colorimetric methods | [33] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Methanol and ethanol extracts and phenol-rich extract from the seeds | In vitro antioxidant assays; |
-FRAP: 0.18, 0.18, and 0.09 mM Fe2+/g, for the extracts, respectively; -TEAC: 3597.11, 3046.60, and 21.38 mM Trolox/g), for the extracts, respectively; -DPPH: EC50: 2.81, 2.81 mg/ml, for methanol and ethanol extracts, respectively. |
NS | FRAP, TEAC, and DPPH assays. | [55] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Aqueous, ethanol, chloroform, and n-hexane extracts from the leaves |
In vitro antioxidant tests (DPPH, FRAP, OH-) |
-DPPH: IC50: 30.74, 21.42, 36.62, and 31.41 μg/ml for the extracts, respectively vs butylated hydroxytoluene (21.73 μg/ml); -FRAP: 23.91, 22.25, 22.43, and 11.57 mM Fe2+ equivalent for the extracts, respectively vs gallic acid: 28.08 mM Fe2+ equivalent; -Percentage of inhibition of OH- radicals: 23.02, 81.43, 69.66, and 23.77% for the extracts, respectively vs gallic acid (100%). |
NS | Colorimetric methods for DPPH, FRAP and OH- radical scavenging tests, respectively | [16] |
| Irvingia spp. | Extracts/ Compounds |
Model of the study | Significant results | Toxicity/ Cytotoxicity |
Type of screening | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irvingia gabonensis | Water and ethanol extract prepared from the stem bark | Male mice | -Reduction of the locomotion in mice treated with water extract (250-750 mg/kg); -Production of time- and dose-related analgesia by both extracts (250-750 mg/kg). |
NS | Hot plate test | [ 67] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Aqueous extract of leaves | -Gastrointestinal motility test in mice, and; -Castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice. |
*Decrease in the gastrointestinal motility: 40.12, 39.45 and 37.45 % at the doses of 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg, respectively; *Protection of mice by 71.43, 81.63, 83.27% at 100, 200 and 400 mg/kg of extract, respectively. |
NS | -Gastrointestinal motility test in mice, and; -Castor oil-induced diarrhea in mice. |
[11] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Ethanol (80%) extract prepared from the leaves. | Model: The worm Heligmosomoides bakeri |
Percentage of larvae death: 71.43, 57.14 and 42.9% of larval deaths at the concentrations of 500, 250, and 125 mg/ml, respectively. | NS |
Cell viability | [65] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Ethanol (50%) extract from the leaves. | Sodium arsenite-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar albino rats | Decrease in the activity of serum biochemical parameters: -ALT: 52.71, 57.24, 40.72 and 39.65 U/l; respectively; -AST : 9, 9.46, 9.23 and 8.92 U/l; respectively; -γGT: 5.21, 3.47, 6.94 and 4.63 U/l, respectively when compared with the group treated with sodium arsenite alone [ALT (78.61 U/l), AST (22.99 U/l), and γGT (10.42 U/l)]. |
NS | Sodium arsenite-induced hepatotoxicity in male Wistar albino rats | [4] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Aqueous, methanol and hexane extracts from the leaves. | In vivo anti-diarrheal activity in rat models | Percentage of protection: -Aqueous extract: 80% at 100 and 200 mg/kg, vs loperamide (80% at 2 mg/kg) -Methanol extract: 80% protection at 200 mg/kg, vs loperamide (80% at 2 mg/kg); -Hexane extract: 40 and 60% protection at 100 and 200 mg/kg, respectively. |
NS | NS | [46] |
| Irvingia wombolu | Solid lipid microparticles prepared from unPEGylated lipid matrices of Irvingia fat matrix (Irvingia-loaded microparticles) | Rat paw edema model | Reduction of the volume of edema in rats in percentages: 38, 40, 87, 65 and 67% after 0.5, 1, 2, 3 and 4h, respectively | NS | Carrageenan rat paw edema test | [66] |
| Irvingia gabonensis | Aqueous, ethanol, chloroform, and n-hexane extracts from the leaves | In vitro antidiabetic test using α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition tests | *α-amylase test: IC50: 30, 45, 130 and 75 µg/ml, respectively, vs acarbose (IC50: 55 µg/ml); * α-glucosidase inhibition test: IC50: 10, 15, 18, and 60 µg/ml, respectively (vs acarbose: 35 µg/ml) |
NS | α-amylase and α-glucosidase inhibition tests | [16] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





