1. Introduction
Currently, back pain presents a high lifetime prevalence from 77% to 85% and a great point prevalence from 30% to 43% (1,2). Back pain, encompassing discomfort in the neck, thoracic, and lumbar regions, is a prevalent condition frequently encountered in physiotherapy practice(3). In Spain, one of the countries that together with Switzerland has the largest number of prevalence studies for low back and neck pain, non-specific neck and back pain showed a 1-year prevalence of 19.5 and 19.9%, respectively, and the cost of neck pain in primary care is quite high (4,5). Low back pain is the second most frequent reason to visit a physician for pain in primary care (6). Both chronic non-specific back and cervical pain conditions were more prevalent among women (26.4% for neck pain and 24.5% for back pain) than men (12.3% for neck pain and 15.1% for back pain)(7). However, there is also evidence that there may be no association between sex and low back pain, and that the sex differences found are due more to differences between populations at the cultural level or the characteristics of the health system(8). Adults with an age range from 31 to 50 years was 1.5 times more likely to present non-specific low back pain than adults with an age range from 16 to 30 years(9). In addition, a strong association was reported between non-specific neck and low back pain conditions (10,11)
Non-specific back pain may produce subsequent disability regarding daily living activities among patients who suffer from this musculoskeletal condition (12). It seems that low back pain with a recognized etiology (related to a particular pathology, such as infections, tumors, osteoporosis, fractures, structural deformities, inflammatory conditions, inflammatory conditions, radicular syndrome, or cauda equina) occurs in only 10-15% of cases(13). Conversely, low back pain with an unidentified cause account for 85-90% of all instances of low back pain(13,14). Indeed, some potential risk factors were described for disabling back pain, such as older age, female sex, existence of back pain family history or prior own history of back pain(15). In addition, environmental agents such as low socioeconomic status and depression are present in the pathophysiology of low back pain and could be mediated in part by long-term reprogramming through epigenetic mechanisms(16). Nevertheless, some factors such as spinal posture, illness factors and muscle endurance did not seem to be risk factors in order to develop disabling back pain (17). However, a recent study found that age, sex, BMI, educational level, marital status, exercise frequency, history of low back pain, work intensity, work posture, exposure to sources of vibration and psychological state were significantly associated with the occurrence of non-specific low back pain(18).
Evidence guidelines recommend that in low back pain patients should be active and given good prognostic advice (19). Physical inactivity is also recognized as a possible cause related to low back pain(20). Regarding interventions for non-specific back pain, low to moderate quality evidence for pain intensity and disability clinical improvements was reported detailing that some complementary health approaches (such as mindfulness, yoga, manual therapy or acupuncture), percutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, exercise, education or pharmacological interventions(21–24). However, in a recent systematic review, manual therapy (Craniosacral Therapy) appears to be more effective than the other approaches he compared (yoga, Ayurvedic Massage, Pilates, Meditation, Meditation + Yoga, Qigong, Tai Chi, and Dance)(25) . The available evidence supporting alternative treatments for neck pain, such as massage, acupuncture, manipulation, soft cervical collar, electrotherapy, trigger point injections, botulinum injections, and yoga, as superior to sham or other conventional treatments, is not robust(26). Thus, further interventional studies are necessary in order to find better interventions to generate clinical improvements in pain intensity and disability of patients who suffer from non-specific back pain (27). Indeed, exercise interventions, including some different physical activity modalities such as core stability and mobility exercises, may be considered as moderate-quality treatments to provide improvement in back pain disability for mid-term and long-term in patients with chronic non-specific back pain(28,29). Nevertheless, future research is needed to get beneficial guidance for a more rigorous study in this field (30,31).
According to these recommendations, we hypothesized that an exercise protocol would show positive effects on disability and pain intensity of patients who suffered from chronic non-specific back pain. Thus, the main aim of this study was to determine the effects of an exercise protocol on disability and pain intensity of patients with chronic non-specific spinal pain in a hospital physical therapy unit. The secondary aim was to divide the sample according to median pain intensity and disability to assess post-intervention outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
Study design
Single-group retrospective-descriptive study with before-after design (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational studies in Epidemiology guidelines, STROBE) (32). The study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda Hospital (act nº 24-04-20, dated 24 April 2020). All the procedures were applied in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration.
Participants
The study included patients treated at the Physiotherapy Outpatient Service of the Guadarrama Hospital between March 2015 and March 2017, as part of the program for the prevention of vertebral pain focused on health education through the promotion of physical activity and the learning of therapeutic exercise guidelines carried out on patients referred from Guadarrama Primary Health Center (Guadarrama), San Carlos Primary Health Center (San Lorenzo del Escorial) and El Escorial Primary Health Center (El Escorial) all belong to the Public Northwest Health Area of the Community of Madrid (Spain). The inclusion criteria established in the program were: a) patients of both genders aged 20-80 years belonging to the primary care area, b) presenting chronic cervicalgia or nonspecific low back pain (more than 3 months of evolution). Patients with a) an initial score of less than 15 on the Cervical Disability Index (NDI), b) an initial score equal to or less than 20 on the Oswestry Lumbar Disability Scale (OS), or c) acute spinal pathology or other associated musculoskeletal processes requiring individualized treatment were excluded.
Measurement outcomes
Patients with low back pain were evaluated at the beginning and end of treatment using the Oswestry Lumbar Incapacity Scale (OS)(33) and the 10-point Analog Visual Scale (VAS). Patients with non-specific neck pain were evaluated at the beginning and end of the protocol using the Cervical Disability Index (NDI) (34) and 10 points Numerical pain rating scale (NPRS 10) (35).
The NDI is a self-administered scale consisting of 10 Likert type items that assess the impact of cervical pain in activities of daily living (ADLs) on the domains of pain intensity, self-care, load bearing, reading, headache, concentration, work, driving, sleep and play activities. Each question is scored from 0 (no disability) to 5 (complete disability) with a maximum score of 50. Depending on this score, the scale presents the no disability (<5), mild (5-14), moderate (15-24), severe (25-34) and complete disability (>34) levels. This is a scale with a standard error of measurement (SEM) of 4.3 (36) with excellent test-retest reliability (Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC)=0.96) (37) and consistency (Cronbach alpha=0.92).(38) Has a minimal clinically important change for patients with non-specific neck pain of described of 10 points (39).
The OS is also an administered scale of 10 Likert type items that evaluate functionality in relation to low back pain in the dimensions pain intensity, personal care, load support, gait, seating, standing, sleep, sexual activity, social life and repercussion when traveling. Each question is scored from 0 (no disability) to 5 (complete disability) with a score expressed as a percentage, the maximum being 100%. Depending on this percentage, the scale presents the minimum (<20%), moderate (20% -40%), intense (40% -60%), disability (60% -80%) and maximum (>80%) levels. It has a SEM of 3.54 with excellent test-retest reliability (ICC=0.97) and internal consistency (Cronbach alpha=0.90)(40) Has a minimal clinically important change for patients with mechanically induced low back pain described of 12.8 points (41).
The NPRS 10 is a 10-point interval numeric scale that assesses perceived pain from 0 (no pain) to 10 (maximum pain imaginable). Depending on the score, chronic musculoskeletal pain can be categorized as mild (<6), moderate (6-7) and severe (>7) (42). It has excellent test-retest reliability (Cronbach alpha=0.98) (43) and a significant minimal clinical change for patients with described chronic pain of 1.7 points or a reduction of 28% (44).
Protocol
All patients were evaluated in the physiotherapy consultation at the beginning and at the end of treatment by an external evaluator who was blind to the treatments received by patients. The patients included in the program were assigned to one of the two groups, either the morning shift or the afternoon shift of the Physiotherapy Service of the Guadarrama Hospital. Each group, of 8-10 patients, was directed by one of the physiotherapists of the corresponding shift. Before the beginning of the protocol, the physiotherapists were trained in the administration of the exercise program.
The patients carried out 10 sessions of about 30 minutes duration, during 2 weeks, with a protocol of exercises of automobilization of the cervical and lumbar regions based on the Mckenzie concept(45), as well as therapeutic exercise of the deep pre-vertebral musculature and activation of transverse and multifidus (46–48). All the more detailed description of the protocol is in the
Supplementary Material.
Statistical analysis
For statistical analysis it was used with program R Ver. 3.3.3. (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Institute for Statistics and Mathematics, Welthandelsplatz 1, 1020 Vienna, Austria). The level of significance was established at p<0.05. The Kolmogorov-Smirnoff test with Lillieford correction was used to determine the non-normal distribution of baseline and outcome variables. Qualitative variables were described in absolute values and frequencies and quantitative variables with mean and standard deviation (SD) or with median and interquartile range (IQR) depending on whether or not there was a normal distribution.
The Wilcoxon test was used on the initial and final scores of the Oswestry, NDI and NPRS 10 lumbar and cervical scales. Among the categorized outcome variables, the McNemar-Bowker test was applied with post hoc tests with Bonferroni correction. The Mann-Whitney or Kruskal-Wallis U test was applied between the result and basal variables. On the other hand, the exact Fisher test was applied between the categorized result variables and the categorical basals.
The effect size between the quantitative variables (r) was defined as < .20 (not relevant), ≥0.20 and <0.50 (small), ≥0.50 and <0.80 (moderate) and ≥0.80 (large); in the qualitative variables the effect size (Cohen g) was defined as ≥0.05 and <0.15 (small), ≥0.15 and <0.25 (moderate) and ≥0.25 (large) and (Cramer V) as <0.212 (small), ≥0.212 and <0.354 (medium) and ≥0.354 (large).
3. Results
149 patients were treated, 32 men and 117 women with a mean age of 60 [50, 69] years, the median age of majority (56.4%). Almost half (46.3%) had low back pain and did not report back pain (84.6%) (
Table 1).
Low back pain patients
The Mann-Whitney U test (Kruskal-Wallis in the case of categorized age) does not indicate significant differences of the initial and final outcome variables as a function of the basal variables except for the uncategorized age (p>0.001) although the presence of basal differences does not allow conclusions to be drawn.
Fisher's exact test of the initial and final categorized outcome variables, as a function of the categorized baseline variables, does not indicate significant differences (p>0.05) except in the case of NPRS 10, although the presence of baseline differences does not allow conclusions to be drawn.
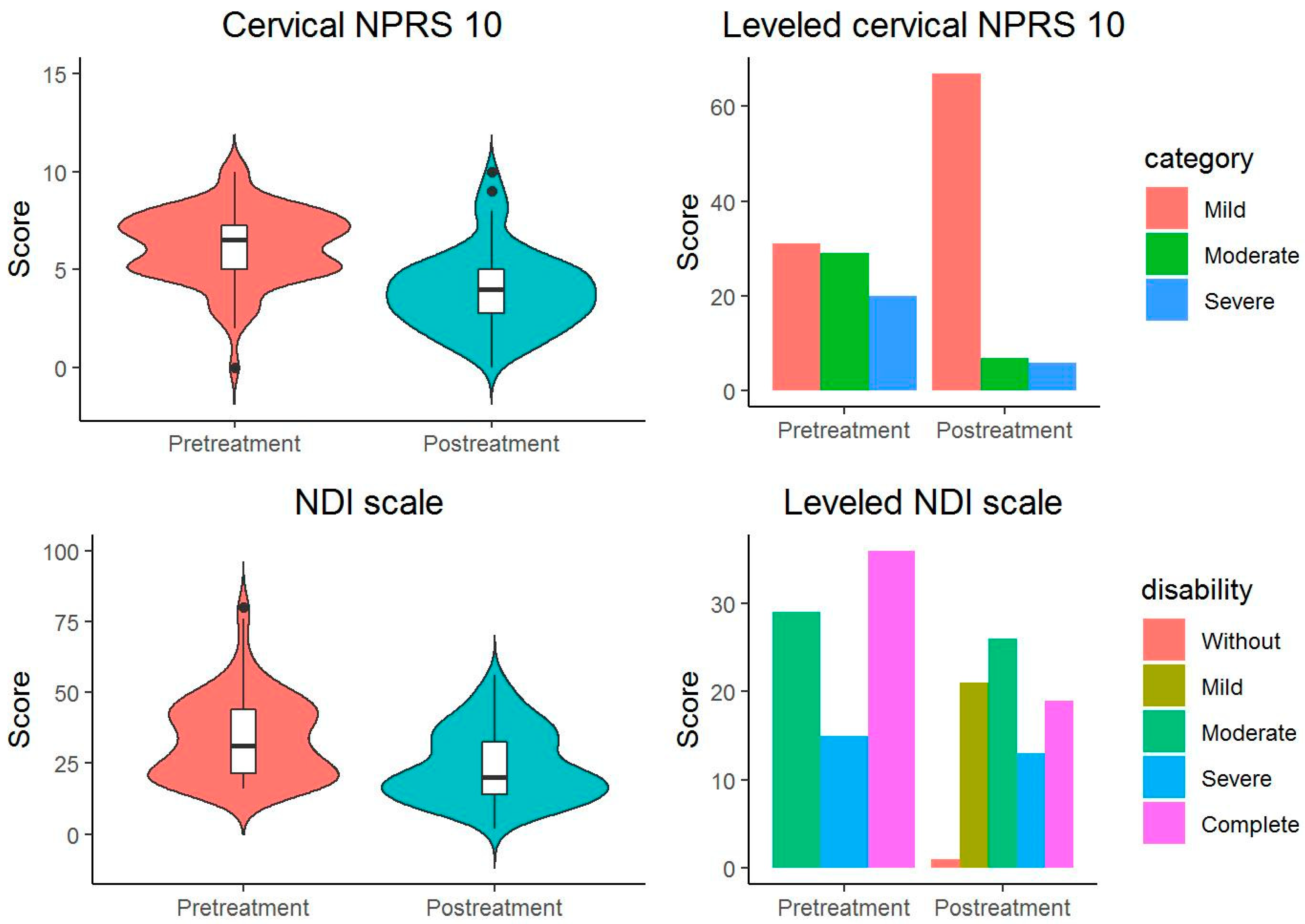
The sign test of the Wilcoxon ranges of uncategorized initial versus final outcome variables indicates significant differences: a) initial vs final OS scale (Z=8.348, p<0.001) with a difference of 8 [12 (median) 95% CI (9, 13)] points and a moderate and significant effect size (r=0.759, 95% CI [0.651, 0.837]), b) NPRS 10 initial lumbar vs. final (Z=8.046, p<0.001) with a median difference of 2 [95% CI (2, 3)] points and a moderate and significant effect size (r=0.731, 95% CI [0.622, 0.812]).
The McNemar-Bowker test between the initial and final categorized outcome variables shows significant differences: a) in the proportion of the OS scale categories (X
2(3)=9.333, p=0.025) with a large overall effect size (Cohen's g=0.375 95% CI [0.167, 0.5]), specifically, between the Intense and Moderate categories (p=0.038) with a large effect size (Cohen's g=0.333 95% CI [0.1, 0.5]), b) in the proportion of the NPRS 10 scale categories categorized (X
2(3)=38.23, p<0.001) with a large overall effect size (Cohen's g=0.411 95% CI [0.336, 0.481]), among the categories a) Slight-Moderate (p<0.001) with a large effect size (Cohen's g=0.423 95%. CI [0.3, 0.5]), and b) Slight-Severe (p<0.001) with a large effect size (Cohen's g=0.423 95% CI [0.3, 0.5]) (
Figure 1 and
Table 2).
Patients with cervicalgia
The Mann-Whitney U test (Kruskal-Wallis in the case of categorized age) does not indicate significant differences in the initial and final outcome variables as a function of the basal variables except for uncategorized age (p>0.001) although the presence of basal differences does not allow conclusions to be drawn.
Fisher's exact test of the initial and final categorized outcome variables as a function of the categorized baseline variables does not indicate significant differences (p>0.05) except in the case of the final score in NPRS 10 as a function of the presence of dorsalgia (p=0.028) with a medium effect size (Cramer's V=0.29, IC95% [0, 1]); the post-hoc test fails to detect between which levels significant changes occur, however, it is evident that more than half of the patients (89.1%) presented at the end of treatment a mild level of cervical pain without being associated with the presence of dorsalgia.
Signal testing of the Wilcoxon ranges of uncategorized initial versus final outcome variables indicates significant differences (
Table 3): a) initial vs. final NDI (Z=5.887, p<0.001) with a difference of 11 [8 (median) 95%. CI (6, 11)] points and a large and significant effect size (r=0.658, 95% CI [0.52, 0.779]), b) NPRS 10 cervical initial vs. final (Z=6.803, p<0.001) with a difference of 3 [95% CI (2, 3)] points and a moderate and significant effect size (r=0.761, 95% CI [0.641, 0.842]).
The McNemar-Bowker test between the initial and final categorized outcome variables shows significant differences: a) in the proportion of categories on the NDI scale (X
2 (3)=11,807, p=0.008) with a large overall effect size (Cohen's g=0.293 95% CI [0.18, 0.433]), specifically between the categories Moderate Disability and Complete Disability (p=0.01) with a large and significant effect size (Cohen's g=0.423 95% CI [0.25, 0.5]), b) in the proportion of the categories of the categorized NPRS 10 scale (X
2(3)=39, p<0.001) with a large overall effect size (Cohen's g=0.5), between the categories a) Mild-Moderate (p<0.001) with a large effect size (Cohen's g=0.5), and b) Mild-Severe (p<0.001) with a large effect size (Cohen's g=0.5) (
Figure 2 and
Table 3).
Between-group comparison
The chronic low back pain and chronic neck pain populations were split according to median (Me) pain intensity to see the post-intervention behavior of the self-reported disability variable and vice versa.
Patients with low back pain
The pre-intervention mean of NPRS for patients with upper pain intensity was 8.68±5.30 while the pre-intervention mean of NPRS for patients with lower pain intensity was 4.48±1.28. When comparing the mean values of the OS variable between these groups at post-intervention, statistically significant between-groups differences were found with a small effect size (mean differences [MD]=-10.785 (-15.761, -5.81); p<0.001, d=0.37). In addition, the pre-intervention mean of OS for patients with upper disability was 42.24±13.37 while the pre-intervention mean of OS for patients with lower disability was 22.48±1.88. When comparing the mean values of the NPRS variable between these groups at post-intervention, statistically significant between-groups differences were found with a small effect size (MD=-0.997 (-1.823, -0.171); p=0.008, d=0.242).
Patients with cervicalgia
The pre-intervention mean of NPRS for patients with upper pain intensity was 7.67±0.86 while the pre-intervention mean of NPRS for patients with lower pain intensity was 4.72±1.26. When comparing the mean values of the NDI variable between these groups post-intervention, statistically significant between-groups differences were found with a small effect size (MD=-8.1 (-14.048, -2.152); p=0.01, d=0.285). However, when comparing the mean values of the NPRS variable between groups with upper (45.45±10.40) and lower (21.50±4.65) NDI, no statistically significant differences were found between the groups (MD=-0.675 (-1.606, 0.256); p=0.2).
4. Discussion
This study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of a therapeutic exercise program for spinal pain. After our program the pain intensity reduced significantly. Our results also showed that this exercise program was acceptable, and participants were improved their back health status (49).
In a recent systematic review (50) concluded that none type of exercise is the best treatment for patients with low back pain, but this study showed that actives therapies, like Pilates, aerobic exercise, stabilization/motor control exercise and resistance exercise are the more effectives for improve pain and disability. In this network meta-analysis concluded that the three likely best exercise obtained better outcomes for improve pain than Mckenzie in 16 points on pain outcomes. Moreover Pilates, yoga, aerobic and stabilization/motor control exercise and water-based exercise showed a improve of 11 points in the Oswestry disability index that is considered clinically relevant (51), but not for McKenzie exercise that which only scored 3 points but in contrast in our study we founded 8 points of difference, although 11 points are considered clinically relevant and in our study we only reached 8 points, the range established for minimally detectable changes in Oswestry disability index is between 4-16 points, thus achieving an acceptable range of improvement (52).
However, there is low quality evidence in the literature that McKenzie was not effective for pain and function in patients with chronic low back pain and low quality of evidence that Pilates, stabilization/motor control, resistance and aerobic exercise were able to improve pain, and function(53).
In several studies where they applied Mckenzie exercise have founded an improved between 50% to 68,76% in pain intensity but short-term and no for long term(54–56), that outcomes although are superior to the results obtained in our study where the percentage of change of improvement has reached 33.33%.
The percentage of change of improvement of disability in our study has reached 30,7%, that outcomes are lower than previous studies where they reached between 50% to 77,77% from immediately to 3 months after(57–59), but in a recent study no differences for disability was found for McKenzie exercise (60). Two previous observational studies without a control group have shown that the McKenzie method allows for the classification of patients with neck pain and provides improvements in patients in terms of neck disability(61,62). In a recent published systematic review with meta-analysis, they concluded that McKenzie provides very small but statistically significant improvements in neck pain of all severity compared to control interventions(63). However, in a recent Cochrane review of the McKenzie method for treating non-specific (sub)acute low back pain found by testing with low to very low certainty that the treatment effects observed with respect to pain and disability were not clinically significant(64).
Other therapeutic exercises activities, such as Pilates, neuromuscular balls or yoga, are often recommended for general back pain. However, some high-quality trials could offer evidence about the effectiveness of this clinical intervention. Researchers have made some trials to improve the scientific evidence. A meta-analysis probed that core stability exercise is highly recommend in improving physical function and reduce pain in patients with chronic LBP in the short term (65–67).
Therapeutic exercise is the most effective intervention for the management of back pain (68). Physical activity and therapeutic exercise lead an activation of endogenous pain inhibitory mechanisms and lead to a reduction in sensitivity to noxious stimuli related to the modality of physical activity (69,70) [
74,
75,
76].
Hayden et al. (71) shows how resistance exercises, which improves the abdominal-wall and back muscles are effective in treatment of low back pain. Also, this finding is consistent with other researches who reported that psychotherapy (relaxation techniques) is effective in the treatment of employees with low back pain (72).
Another research offers inconclusive evidence for the effectiveness of non-invasive management of cervicobrachial pain. Manual therapy intervention combined with exercise showed a better health status in patients than manual therapy (73). Also a treatment intervention for neck pain adding core stability exercise provided more reliable evidence for future studies (74). But in contrast in Cochrane’s systematic reviews of the effectiveness of exercise on neck pain they report that strengthening and resistance/stabilization exercises have a small to large impact on neck pain (75,76). It has even been found that the effect of combining exercise with other therapies such as manual therapy increases positive results in pain and disability(77,78).
In a recent clinical trial involving 45 patients experiencing neck pain(79), the participants were divided into three groups: Group 1 received conventional treatment, Group 2 received conventional treatment along with deep cervical flexor training, and Group 3 received conventional treatment combined with neck and core stabilization exercises. The study revealed that, in addition to conventional treatment, implementing trunk stabilization exercises or deep cervical flexor training for patients with neck pain may yield greater effectiveness in reducing pain and disability while increasing the range of motion compared to conventional treatment alone.
This study shows that after a two-week intervention therapeutic exercise improved pain intensity, functional disability, and patient satisfaction, as well as activation of transversus of abdominis and superficial fibers of multifidus muscles in subjects with low back pain (80)
Some studies offer a low-moderate quality evidence that control-stabilization exercises interventions improve the pain intensity referred and disability in subjects with chronic low-back pain compared to passive control group or compared to other exercises (81).
Our study shows a pain status improvement in patients with back pain that had completed a therapeutic exercise program. Exercise therapy by itself related with relaxation is a therapeutic option commonly prescribed in the treatment of patients with back pain. It is considered as an interesting intervention for increasing range of movement(82). Improvement in range of movement is related to increased blood-flow to muscles and reduced stiffed-joints (83). Our results are in line with the conclusions of a recent systematic review have found that non-pharmacological treatments present strong evidence for conic musculoskeletal pain in primary care (84).
Limitations
The main limitation of the present study lies in the absence of a comparator group, due to its character as a habitual clinical practice, so the results have to be interpreted with caution.
In addition, patients' expectations were not evaluated. In this context, Ballestra et al. (85) demonstrated that specific patient expectations, such as anticipating a personalized treatment with regular follow-ups, hoping for optimal outcomes, having realistic or accepting attitudes towards alleviating health issues, fostering effective dialogue and communication, seeking individual recognition, and desiring comprehensive explanations of their condition, may be associated with improved recovery outcomes.
A recent systematic review found evidence of increased levels of the proinflammatory biomarkers CRP, IL-6 and TNF-α and decreased levels of the anti-inflammatory biomarker IL-10 in patients with acute and chronic non-specific low back pain(86). Therefore, we believe that it would have been valuable to consider incorporating a laboratory blood study into the analysis.
5. Conclusions
A therapeutic multimodal exercise protocol may provide beneficial effects on disability and pain intensity in patients with chronic non-specific spinal pain, including neck and low back pain conditions. Could be considered for inclusion as spinal pain prevention program in primary healthcare. Further studies are necessary including a control group in order to compare this therapeutic exercise protocol in patients who suffer from spinal pain.
Supplementary Materials
detailed description of the therapeutic exercise protocol.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The APC was funded by Fundación de Investigation Biomedica del Hospital Puerta deHierro de Majadahonda, C/Joaquín Rodrigo 2, Edif Laboratorios, Planta 0, 28222, Madrid.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Puerta de Hierro Majadahonda Hospital (act nº 24-04-20, dated 24 April 2020) and is registered in ClinicalTrials.org as NCT03462693.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study. Written informed consent has been obtained from the patient(s) to publish this paper.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions.
Acknowledgments
To physiotherapists and patients for their participation.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fett, D.; Trompeter, K.; Platen, P. Prevalence of back pain in a group of elite athletes exposed to repetitive overhead activity. PLoS One. 2019, 14, e0210429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwertner, D.S.; Oliveira, R.A.N.S.; Koerich, M.H.A.L.; Motta, A.F.; Pimenta, A.L.; Gioda, F.R. Prevalence of low back pain in young Brazilians and associated factors: Sex, physical activity, sedentary behavior, sleep and body mass index. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2019, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Carnero, J.; Beltrán-Alacreu, H.; Arribas-Romano, A.; Cerezo-Téllez, E.; Cuenca-Zaldivar, J.N.; Sánchez-Romero, E.A.; et al. Prediction of Patient Satisfaction after Treatment of Chronic Neck Pain with Mulligan’s Mobilization. Life. 2022, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, B.I.; Deyo, R.A.; Mirza, S.K.; Turner, J.A.; Comstock, B.A.; Hollingworth, W.; et al. Expenditures and health status among adults with back and neck problems. JAMA - Journal of the American Medical Association. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz Laguna, J.; Puhan, M.A.; Rodríguez Artalejo, F.; De Pauw, R.; Wyper, G.M.A.; Devleesschauwer, B.; et al. Certainty of the Global Burden of Disease 2019 Modelled Prevalence Estimates for Musculoskeletal Conditions: A Meta-Epidemiological Study. Int J Public Health. 2023, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deyo, R.A.; Weinstein, J.N. Low back pain. N Engl J Med. 2001, 344, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Palacios-Ceña, D.; Carrasco-Garrido, P.; Jiménez-Sánchez, S.; et al. Prevalence of Neck and Low Back Pain in Community-Dwelling Adults in Spain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011, 36, E213–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calais-Ferreira, L.; Pozzobon, D.; Pinheiro, M.B.; Blyth, F.M.; Ordoñana, J.R.; Duncan, G.E.; et al. Sex differences in lifetime prevalence of low back pain: A multinational study of opposite-sex twin pairs. European Journal of Pain. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Meucci, R.D.; Fassa, A.G.; Faria, N.M.X. Prevalence of chronic low back pain: systematic review. Rev Saude Publica. 2015, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacios-Ceña, D.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Hernández-Barrera, V.; Carrasco-Garrido, P.; Jiménez-García, R.; Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C. Prevalence of neck and low back pain in community-dwelling adults in Spain: an updated population-based national study (2009/10? 2011/12). European Spine Journal. 2015, 24, 482–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øverås, C.K.; Nilsen, T.I.L.; Søgaard, K.; Mork, P.J.; Hartvigsen, J. Temporal stability in the prevalence and pattern of co-occurring musculoskeletal pain among people with persistent low back pain: population-based data from the Norwegian HUNT Study, 1995 to 2019. Pain 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makris, U.E.; Weinreich, M.A.; Fraenkel, L.; Han, L.; Leo-Summers, L.; Gill, T.M. Restricting Back Pain and Subsequent Disability in Activities of Daily Living Among Community-Living Older Adults. J Aging Health. 2018, 30, 1482–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagué, F.; Mannion, A.F.; Pellisé, F.; Cedraschi, C. Non-specific low back pain. The Lancet. 2012, 379, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Romero, E.A.; Alonso Pérez, J.L.; Muñoz Fernández, A.C.; Battaglino, A.; Castaldo, M.; Cleland, J.A.; et al. Reliability of Sonography Measures of the Lumbar Multifidus and Transversus Abdominis during Static and Dynamic Activities in Subjects with Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Diagnostics. 2021, 11, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, L.; Vasanthan, L.; Standen, M.; Kuisma, R.; Paungmali, A.; Pirunsan, U.; et al. Causal Relationship Between the Risk Factors and Work-Related Musculoskeletal Disorders Among Professional Drivers: A Systematic Review. Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society. 2023, 65, 62–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffilli, A.; Neri, S.; Manzetti, M.; Barile, F.; Viroli, G.; Traversari, M.; et al. Epigenetic Factors Related to Low Back Pain: A Systematic Review of the Current Literature. Int J Mol Sci. 2023, 24, 1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beynon, A.M.; Hebert, J.J.; Lebouef-Yde, C.; Walker, B.F. Potential risk factors and triggers for back pain in children and young adults. A scoping review, part II: Unclear or mixed types of back pain. Vol. 27, Chiropractic and Manual Therapies. BioMed Central Ltd.; 2019. p. 61.
- Lu, W.; Shen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Hu, X.; Ruan, C.; Ma, W.; et al. Risk factors analysis and risk prediction model construction of non-specific low back pain: an ambidirectional cohort study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023, 18, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaseem, A.; Wilt, T.J.; McLean, R.M.; Forciea, M.A. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: A clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Wanjau, M.N.; Möller, H.; Haigh, F.; Milat, A.; Hayek, R.; Lucas, P.; et al. The Potential Impact of Physical Activity on the Burden of Osteoarthritis and Low Back Pain in Australia: A Systematic Review of Reviews and Life Table Analysis. J Phys Act Health. 2023, 20, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Furlan, A.D.; Lam, W.Y.; Hsu, M.Y.; Ning, Z.; Lao, L. Acupuncture for chronic nonspecific low back pain. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zaina, F.; Côté, P.; Cancelliere, C.; Di Felice, F.; Donzelli, S.; Rauch, A.; et al. A Systematic Review of Clinical Practice Guidelines for Persons With Non-specific Low Back Pain With and Without Radiculopathy: Identification of Best Evidence for Rehabilitation to Develop the WHO’s Package of Interventions for Rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Do Nascimento, P.R.C.; Costa, L.O.P.; Araujo, A.C.; Poitras, S.; Bilodeau, M. Effectiveness of interventions for non-specific low back pain in older adults. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Physiotherapy. 2019, 105, 147–162. [Google Scholar]
- Huntoon, M.A.S.K.H.J.C.N.B.J.W. A Retrospective Review of Real-world Outcomes Following 60-day Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Pain. Pain Physician. 2023, 23, 273–281. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Ding, Y.; et al. Effect of mindfulness-based mind-body therapies in patients with non-specific low back pain—A network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childress, M.A.S.S.J. Neck Pain: Initial Evaluation and Management. Am Fam Physician. 2020, 102, 150–156. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, P.R.C.; Costa, L.O.P.; Araujo, A.C.; Poitras, S.; Bilodeau, M. Effectiveness of interventions for non-specific low back pain in older adults. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vol. 105, Physiotherapy (United Kingdom). Elsevier Ltd; 2019. p. 147–62.
- Pedersen, B.K.; Saltin, B. Exercise as medicine - evidence for prescribing exercise as therapy in 26 different chronic diseases. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2015, 25, 1–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinacker, J.M.; van Mechelen, W.; Bloch, W.; Börjesson, M.; Casasco, M.; Wolfarth, B.; et al. Global Alliance for the Promotion of Physical Activity: the Hamburg Declaration. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med. 2023, 9, e001626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, H.; Mackey, M.; Stamatakis, E.; Pinheiro, M.B.; Wicks, M.; Shirley, D. The effectiveness of incidental physical activity interventions compared to other interventions in the management of people with low back pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Physical Therapy in Sport. 2019, 36, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhao, X.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, L. Effects of core stability exercise for patients with neck pain: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2019, 98, e17240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P. Declaración de la iniciativa STROBE (Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology): Directrices para la comunicación de estudios observacionales. Rev Esp Salud Publica. 2008, 82, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcántara-Bumbiedro, S.; Flórez-García, M.T.; Echávarri-Pérez, C.; García-Pérez, F. Escala de incapacidad por dolor lumbar de Oswestry. Rehabilitacion (Madr). 2006, 40, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso Andrade Ortega, J.; Damián Delgado Martínez, A.; Almécija Ruiz, R. Validación de una versión española del Índice de Discapacidad Cervical. Med Clin (Barc). 2008, 130, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero Ibáñez, R.; Briega, A.M. Escalas de valoración del dolor. Jano 2012, LXVIII, 41–4. [Google Scholar]
- Young, B.A.; Walker, M.J.; Strunce, J.B.; Boyles, R.E.; Whitman, J.M.; Childs, J.D. Responsiveness of the Neck Disability Index in patients with mechanical neck disorders. Spine Journal. 2009, 9, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, A.A.M.; Omar, M.T.A.; Vernon, H. Cross-cultural adaptation, reliability, and validity of the arabic version of neck disability index in patients with neck pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013, 38, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hains, F.; Waalen, J.; Mior, S. Psychometric properties of the neck disability index. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1998, 21, 75–80. [Google Scholar]
- Young, B.A.; Walker, M.J.; Strunce, J.B.; Boyles, R.E.; Whitman, J.M.; Childs, J.D. Responsiveness of the Neck Disability Index in patients with mechanical neck disorders. Spine Journal. 2009, 9, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso Andrade Ortega, J.; Damián Delgado Martínez, A.; Almécija Ruiz, R. Validación de una versión española del Índice de Discapacidad Cervical. Med Clin (Barc). 2008, 130, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnsen, L.G.; Hellum, C.; Nygaard, Ø.P.; Storheim, K.; Brox, J.I.; Rossvoll, I.; et al. Comparison of the SF6D, the EQ5D, and the oswestry disability index in patients with chronic low back pain and degenerative disc disease. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013, 14, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, A.M.; Schiphorst Preuper, H.R.; Balk, G.A.; Stewart, R.E. Cut-off points for mild, moderate, and severe pain on the visual analogue scale for pain in patients with chronic musculoskeletal pain. Pain. 2014, 155, 2545–2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, M.P.; McFarland, C.A. Increasing the reliability and validity of pain intensity measurement in chronic pain patients. Pain. 1993, 55, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrar, J.T.; Young, J.P.; LaMoreaux, L.; Werth, J.L.; Poole, R.M. Clinical importance of changes in chronic pain intensity measured on an 11-point numerical pain rating scale. Pain. 2001. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, S.J.L.J.S.P. McKenzie Back Exercises. StatPearls, editor. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023.
- Jonhnson, J. The multifidus. Back Pain Solution. Oakland, USA: New Harbinger Publications Inc; 2002.
- McKenzie, R. Treat your own back. 9th ed. Waikanae, New Zealand: Orthopedic Physical Therapy Products; 2011.
- McKenzie, R. Treat your own neck. 5th ed. Raumati Beach, New Zealand: Orthopedic Physical Therapy Products; 2011.
- Li, Y.; Tse, M.Y.M. An Online Pain Education Program for Working Adults: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial. J Med Internet Res. 2020, 22, e15071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, P.J.; Miller, C.T.; Mundell, N.L.; Verswijveren, S.J.; Tagliaferri, S.D.; Brisby, H.; et al. Which specific modes of exercise training are most effective for treating low back pain? Network meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, H.H.; Hartvigsen, J.; Manniche, C.; Korsholm, L.; Grunnet-Nilsson, N. Responsiveness and minimal clinically important difference for pain and disability instruments in low back pain patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2006, 25, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauridsen, H.H.; Hartvigsen, J.; Manniche, C.; Korsholm, L.; Grunnet-Nilsson, N. Responsiveness and minimal clinically important difference for pain and disability instruments in low back pain patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2006, 25, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owen, P.J.; Miller, C.T.; Mundell, N.L.; Verswijveren, S.J.; Tagliaferri, S.D.; Brisby, H.; et al. Which specific modes of exercise training are most effective for treating low back pain? Network meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, T.; Larsen, K.; Nordsteen, J.; Olsen, S.; Fournier, G.; Jacobsen, S. The McKenzie method compared with manipulation when used adjunctive to information and advice in low back pain patients presenting with centralization or peripheralization: A randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011, 36, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.N.; Costa, L.D.C.M.; Hancock, M.J.; De Souza, F.S.; Gomes, G.V.F.D.O.; De Almeida, M.O.; et al. McKenzie Method of Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy was slightly more effective than placebo for pain, but not for disability, in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomised placebo controlled trial with short and longer term follow-up. Br J Sports Med. 2018, 52, 594–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paatelma, M.; Kilpikoski, S.; Simonen, R.; Heinonen, A.; Alen, M.; Videman, T. Orthopaedic manual therapy, Mckenzie method or advice only for low back pain in working adults: A randomized controlled trial with one year follow-up. J Rehabil Med. 2008, 40, 858–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.N.; Costa, L.D.C.M.; da Silva, T.M.; Gondo, F.L.B.; Cyrillo, F.N.; Costa, R.A.; et al. Effectiveness of back school versus McKenzie exercises in patients with chronic nonspecific low back pain: a randomized controlled trial. Phys Ther. 2013, 93, 729–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.; Larsen, K.; Nordsteen, J.; Olsen, S.; Fournier, G.; Jacobsen, S. The McKenzie method compared with manipulation when used adjunctive to information and advice in low back pain patients presenting with centralization or peripheralization: A randomized controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011, 36, 1999–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paatelma, M.; Kilpikoski, S.; Simonen, R.; Heinonen, A.; Alen, M.; Videman, T. Orthopaedic manual therapy, Mckenzie method or advice only for low back pain in working adults: A randomized controlled trial with one year follow-up. J Rehabil Med. 2008, 40, 858–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.N.; Costa, L.D.C.M.; Hancock, M.J.; De Souza, F.S.; Gomes, G.V.F.D.O.; De Almeida, M.O.; et al. McKenzie Method of Mechanical Diagnosis and Therapy was slightly more effective than placebo for pain, but not for disability, in patients with chronic non-specific low back pain: A randomised placebo controlled trial with short and longer term follow-up. Br J Sports Med. 2018, 52, 594–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luetchford, S.; Declich, M.; Tavella, R.; Zaninelli, D.; May, S. Diagnosis of cervical and thoracic musculoskeletal spinal pain receptive to mechanical movement strategies: a multicenter observational study. Journal of Manual and Manipulative Therapy. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Yarznbowicz, R.; Tao, M.; Wlodarski, M.; Dolutan, J. Pain pattern classification and directional preference for patients with neck pain. Journal of Manual and Manipulative Therapy. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Baumann, A.N.; Orellana, K.; Landis, L.; Crawford, M.; Oleson, C.J.; Rogers, H.; et al. The McKenzie Method Is an Effective Rehabilitation Paradigm for Treating Adults With Moderate-to-Severe Neck Pain: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Cureus. 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, M.O.; Narciso Garcia, A.; Menezes Costa, L.C.; van Tulder, M.W.; Lin, C.W.C.; Machado, L.A. The McKenzie method for (sub)acute non-specific low back pain. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2023, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Q.; Zheng, J.J.; Yu, Z.W.; Bi, X.; Lou, S.J.; Liu, J.; et al. A Meta-Analysis of Core Stability Exercise versus General Exercise for Chronic Low Back Pain. Eldabe S, editor. PLoS One. 2012, 7, e52082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulombe, B.J.; Games, K.E.; Neil, E.R.; Eberman, L.E. Core Stability Exercise Versus General Exercise for Chronic Low Back Pain. J Athl Train. 2017, 52, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhao, X.; Ma, M.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, L. Effects of core stability exercise for patients with neck pain: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. 2019, 98, e17240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falla, D.; Hodges, P.W. Individualized Exercise Interventions for Spinal Pain. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2017, 45, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naugle, K.M.; Naugle, K.E.; Fillingim, R.B.; Samuels, B.; Riley, J.L. Intensity thresholds for aerobic exercise-induced hypoalgesia. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, C.D.; Huber, J.K.; Ellingson, L.D.; Ade, C.J.; Taylor, E.L.; Griffeth, E.M.; et al. Exercise-Induced Hypoalgesia Is Not Influenced by Physical Activity Type and Amount. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2017, 49, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayden, J.A.; Van Tulder, M.W.; Tomlinson, G. Systematic review: Strategies for using exercise therapy to improve outcomes in chronic low back pain. American College of Physicians 2005, 142, 776–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, M. A comparison of the effects of jaw relaxation and music on postoperative pain. Nurs Res. 1995, 44, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salt, E.; Wright, C.; Kelly, S.; Dean, A. A systematic literature review on the effectiveness of non-invasive therapy for cervicobrachial pain. Man Ther. 2011, 16, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, B.; Hall, T.; Bossert, J.; Dugeny, A.; Cagnie, B.; Pitance, L. The efficacy of manual therapy and exercise for treating non-specific neck pain: A systematic review. Vol. 30, Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation. IOS Press; 2017. p. 1149–69.
- Gross, A.R.; Paquin, J.P.; Dupont, G.; Blanchette, S.; Lalonde, P.; Cristie, T.; et al. Exercises for mechanical neck disorders: A Cochrane review update. Man Ther. 2016, 24, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, A.; Kay, T.M.; Paquin, J.P.; Blanchette, S.; Lalonde, P.; Christie, T.; et al. Exercises for mechanical neck disorders. Vol. 2017, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. John Wiley and Sons Ltd; 2015.
- Leaver, A.M.; Refshauge, K.M.; Maher, C.G.; McAuley, J.H. Conservative interventions provide short-term relief for non-specific neck pain: A systematic review. J Physiother. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.; Miller, J.; D’Sylva, J.; Burnie, S.J.; Goldsmith, C.H.; Graham, N.; et al. Manipulation or mobilisation for neck pain: a Cochrane Review. Man Ther. 2010, 15, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumuscu, B.H.; Kisa, E.P.; Kara Kaya, B.; Muammer, R. Comparison of three different exercise trainings in patients with chronic neck pain: a randomized controlled study. Korean J Pain. 2023, 36, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Areeudomwong, P.; Buttagat, V. Comparison of Core Stabilisation Exercise and Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation Training on Pain-related and Neuromuscular Response Outcomes for Chronic Low Back Pain: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Malays J Med Sci. 2019, 26, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niederer, D.; Mueller, J. Sustainability effects of motor control stabilisation exercises on pain and function in chronic nonspecific low back pain patients: A systematic review with meta-analysis and meta-regression. PLoS One. 2020, 15, e0227423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloxham, S.R.; Layden, J.; Jane, B.; Peers, C.; Scragg, S. The longitudinal effects of a physical activity programme on the physical fitness and disability of back pain patients: Service evaluation. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2020, 33, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, R.; Bloxham, S. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Exercise and Physical Activity on Non-Specific Chronic Low Back Pain. Healthcare. 2016, 4, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babatunde, O.O.; Jordan, J.L.; Van Der Windt, D.A.; Hill, J.C.; Foster, N.E.; Protheroe, J. Effective treatment options for musculoskeletal pain in primary care: A systematic overview of current evidence. Vol. 12, PLoS ONE. Public Library of Science; 2017.
- Ballestra, E.; Battaglino, A.; Cotella, D.; Rossettini, G.; Sanchez-Romero, E.A.; Villafane, J.H. Do patients’ expectations influence conservative treatment in Chronic Low Back Pain? A Narrative Review. Retos 2022, 46, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, E.M.; Neves, J.R.; Laranjeira, M.; Reis, J. The importance of inflammatory biomarkers in non-specific acute and chronic low back pain: a systematic review. European Spine Journal. 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).