1. Introduction
Chronic bone disease that weakens bones and raises the possibility of fractures as people age is called osteoporosis. As predicted in previous study, there is an evident rise to 62 lakhs cases by 2050 from 16 lakhs cases in 1990 [
1]. Osteoporosis, a disease that reduces bone mass and strength, can be treated using a number of different approaches. But there are several restrictions and long-term safety concerns associated with the current therapies [
2]. Therefore, more study is required to determine the best therapy choice. Most therapeutic strategies for reducing bone loss and avoiding fractures can be grouped into two categories i.e., anabolic drugs and anti-resorptive drugs [
3]. Bisphosphonates, calcitonin, estrogen selective receptor modulators and monoclonal antibodies like denosumab are all examples of anti-resorptive medications that work by decreasing the activity of osteoclasts to build bone strength. In contrast, anabolic drugs (recombinant human parathyroid hormone, calcitonin, and estrogen) are able to induce formation of bones and can reverse bone degeneration which is caused by the progression of osteoporosis [
4]. With inhibition of Farnesyl Pyrophosphate Synthase (FPPS), a key enzyme in membrane protein prenylation as well as osteoclast detachment from bone, BPs disrupt osteoclastic activity. In the end, they cause apoptosis in osteoclasts, which decreases bone resorption. Treatment with alendronate and risedronate (RIS) is regarded first-line therapy for controlling and preventing osteoporosis in post-menopausal for both the men and women [
3].
Bone problems including Paget’s disease and osteoporosis are treatable using RIS. It can be swallowed, but taking it that way comes with some precautions to prevent esophageal ulcers, such as taking it while standing up and then washing it down with water[
5,
6]. If taken with food, absorption is even worse. Therefore, it is strongly advised that no meal to be consumed within two hours and thirty minutes before medication. In addition, it belongs to class III of the biopharmaceutics categorization system (high solubility/low permeability) and has a poor oral bioavailability of 1% [
7]. Therefore, there is a need for effective drug delivery systems for RIS that increase bioavailability and decrease the likelihood of esophageal pain.
Given its structural similarity to minerals found in dentin or natural bones and its bioactivity, osteoconductive, non-inflammatory and biocompatibility properties, Hydroxyapatite (HA) was used widely as a biomaterial for bone regeneration [
8,
9]. As BPs attach to HA, binding capacity of bone increases. In addition, BPs have the unique ability to prevent the breakdown of hydroxyapatite (HA) already present in the bone [
10]. As a result of this property, HA is a trusted conveyance for the delivery of BPs. [
11]. Due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability, poly (lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) is used in drug delivery systems. Drug release characteristics could be altered by tailoring PLGA’s copolymer ratio, molecular weight, porosity, particle size, and manufacturing conditions [
12,
13].
Naturally occurring chitosan (CS) has the right properties to serve as a polymeric carrier for nanoparticles (NPs) [
14]. Biocompatibility, biodegradability, nontoxicity, and low cost all fall into this category. Further, it exhibits bio-adhesive properties and the potential to greatly increase the permeability of hydrophilic compounds [
15,
16]. To boost chitosan’s mucoadhesive properties, a wide variety of chitosan derivatives have been developed [
17]. Because they form covalent bonds with the mucus layer, that are theoretically stronger as compared with the non-covalent bonds, thiol-functionalized polymers have an adhesion advantage over other derivatives [
18]. These thiolated polymers (also known as thiomers) interacts with cysteine-rich sub-domains of mucus glycoproteins through Disulphide Exchange Mechanisms. This is because Thiolated Chitosan (TCS) are able to form inter- and intra-molecular disulphide bonds at physiological pH, which gives them their
in-situ gelling capabilities. As a result of the latter process, the carrier matrix is guaranteed to be robust and with integrity [
19].
This study proposes the development of nanoconjugates of RIS attached with HA and further conjugate with mPEG for its delivery to the affected bones for the treatment of osteoporosis. Polymer conjugation offers better encapsulation for such a moiety, making the medication more accessible despite its low penetration. The first-step-prepared nanoconjugate was encapsulated in TCS that had been synthesized from CS. In this research, we describe the development of mucoadhesive conjugated nanoparticles, which combine the advantages of a small particle size with increased penetration and blood circulation time.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Jubilant Life Sciences provide a sample of risedronate sodium (RIS), also known as [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridinyl) ethylidene] bis [phosphonic acid] mono-sodium salt hemi-pentahydrate (350.13g/mol) (Noida, Uttar Pardesh, India). Lipoid is found to be the source of mPEG 2000-DSPE (PE 18:0/18:0-PEG, 2000) (Ludwigshafen, Germany). From S.G. Enterprises 502.31 g/mol hydroxyapatite (HA) and thioglycolic acid (TGA) 92.12 g/mol were purchased. Dialysis bags (MW 12000Da, with 2.5mm flat width, 16mm diameter, and 60mL/ft capacity), chitosan (MWCO: 75,0000Da), sodium tripolyphosphates (TPP), dimethylformamide (DMF) (MWCO: 73.09 g/mol), and DMF were all obtained from Sigma Aldrich, India. Spectro-chem supplied N-hydroxy succinimide (NHS), an Ellman’s reagent, and 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride (EDAC). The other substances and reagents of analytical grade were employed in the study.
2.2. Animals
Wistar rats (225-250g, both sex) were used in the ex vivo gut permeation experiment, and the plan for using animals in experimentation was approved by the Jamia Hamdard University, Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) (Approval no. 1821/CPCSEA). Lab animals were fed pellets (Lipton, Mumbai, India) and always had access to clean water. The procedures for caring and using lab animals were followed as per instructions from “National Institutes of Health” throughout all operations involving animals.
2.3. In-silico molecular docking
2.3.1. Preparation of Ligand
In this experiment, RIS and RIS-HA-TCS as the ligands were used. The three-dimensional structure of RIS was downloaded in sdf format via PubChem (
http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/). The .SDF file was converted into .pdb file utilising the software OpenBabel. The ligands.pdb file was converted to the more portable. pdbqt format with the help of Autodock Tools 1.5.6. ChemDraw Professional version 15 was used to create a 3D model of RIS-HA-TCS.
2.3.2. Preparation of proteins
The RCSB (Research Collaboratory for Structural Bioinformatics) protein databank contains the three-dimensional structures of the various molecule of protein. Human farnesyl diphosphate synthase structures were found in the RCSB’s Protein Data Bank (PDB) ID: 1YV5.The water molecules were detected from the enzyme structure using AutoDock tools 1.5.6. Further Kollman charges and polar hydrogen molecules were added. The final structure was saved in. pdbqt format.
2.3.3. Docking analysis using Autodock tools 1.5.6
The structures of ligand molecule were inserted into protein structures using AutoDock tools 1.5.6. The complete structures of protein were inserted into the grid box and the coordinates of grid box were saved. The flexible ligand molecule was inserted into rigid protein molecule. Lamarckian genetic algorithm was used to determine the flexible anchoring at the receptor (active site). To determine the energy between the receptor and ligand, calculations were done and expressed in Kcal/mol.
2.3.4. Interaction plot of ligand and protein
The ligand protein molecule interactions were analysed using discovery studio 2021 version. Different hydrophilic and hydrophobic bonds were expressed by different colours.
2.4. Experimental design
Several independent factors in the creation of nanoparticles were optimized using Design Expert
® software; V.13.0; Stat-Ease Inc., Minneapolis, USA). Three centered points were investigated in 15 experimental runs based on a Box-Behnken design. This experimental design was used to observe at how different dependent variables were affected by independent variables.
Y1: Particle Size;
Y2: Polydispersity Index (PDI), and
Y3: Percent Entrapment Efficiency were dependent factors, while TPP(A), TCS(B), and Drug-HA(C) were the independent variables, with high (+1), medium (0), and low (-1) values, respectively. All these variables are represented in
Table 1.
2.5. Synthesis of Thiolated Chitosan (TCS)
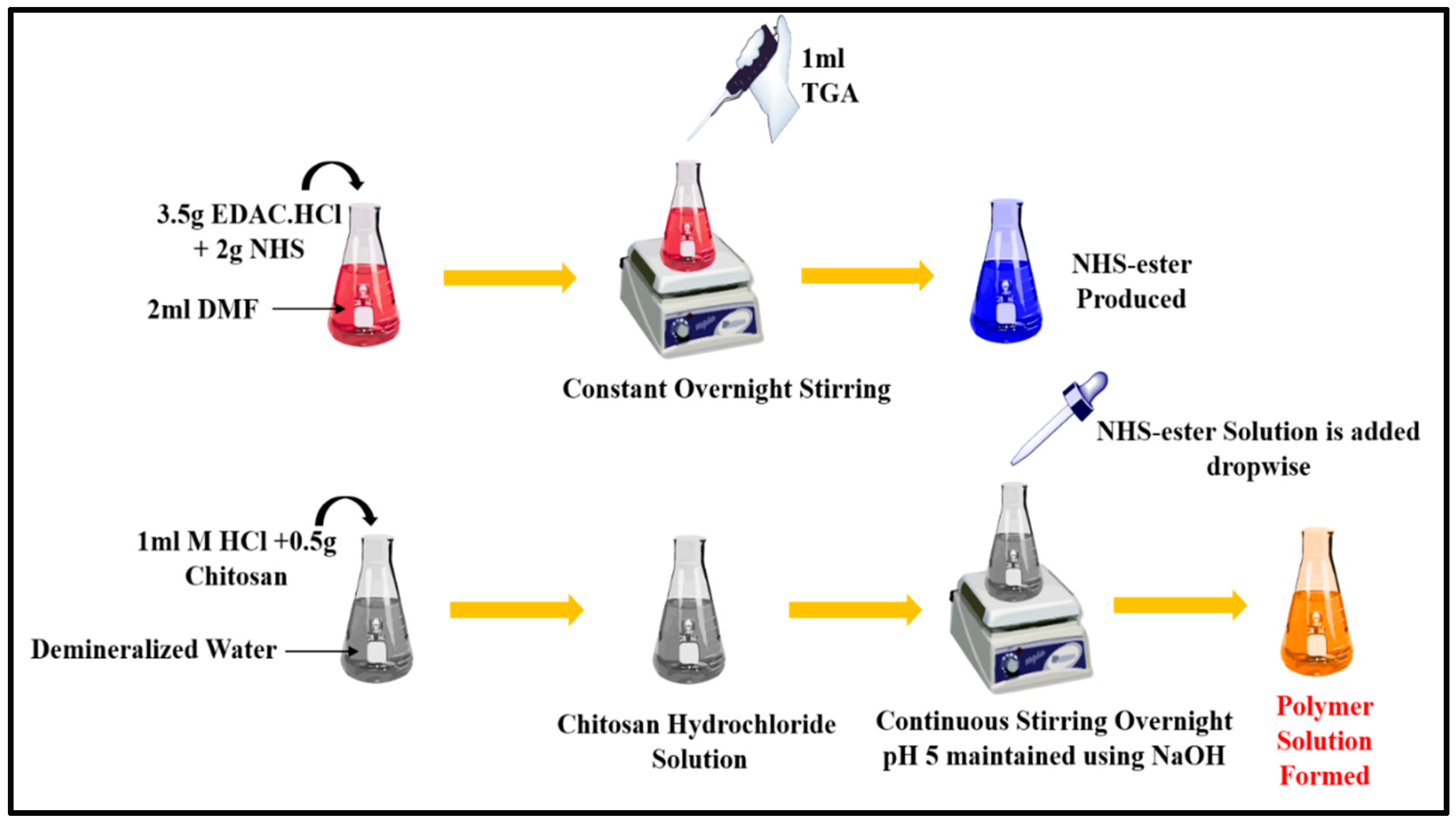
TCS was synthesized from chitosan as depicted in
Figure 1 following the method reported and modified slightly [
20]. Briefly, 2 ml DMF was added to a flask containing NHS (2mg), EDAC·HCl (3.5mg) and TGA (1ml) and this mixture was constantly stirred overnight. After completing the reaction, reactive NHS-ester was generated. Then, the solution of chitosan hydrochloride was prepared by adding demineralized water to 500mg of hydrated chitosan in 1 M HCl in a 4ml flask and shaken to dissolve the content. After that the pH of the chitosan hydrochloride solution was adjusted to 5 with 10M NaOH, then the reactive NHS-ester was added drop by drop. After being stirred constantly, this mixture was left for incubation at room temperature for 24 hours. Extensive dialyzing in tubing (molecular weight cut-off 12000Da; cellulose membrane; dialysis tubing; Sigma Aldrich, India) against HCl (5mM) which was followed by three cycles of dialyzing against HCl (1mM) at 8°C in dark to isolate TCS. Samples and control (chitosan solution) were lyophilized (LABFREEZE, lab scale freeze dryer), then kept at 4 °C; this process involved freezing aqueous polymer solutions. Ellman’s reagent technique, FT-IR, DSC were applied for characterizing TCS polymer and establishing the presence of a thiol group (Perkin-Elmer Spectrum).
2.5.1. Determination of the thiol groups in TCS
The amount of thiol group substitution in the synthesized polymer was measured by spectroscopy using Ellman’s reagent [
20]. The symmetric aryl disulfide Ellman’s reagent is highly reactive with the free thiol in the thiol-disulfide interchange. For the preparation of the 2 mg/ml solution, the conjugate compounds and controls were initially dissolved in 5mm of ultrapure water in 2ml. 250µl of aliquots were each given 0.4mg/ml of DTNB in pH 8 phosphate buffer (0.5mol/l) and phosphate buffer of pH 8 (0.5M) of Ellman’s reagent, respectively. At room temperature, the sample was stored for 3 hours away from light. To remove any remaining particles, this solution was centrifuged at a speed of 8000 rpm for a period of 20 minutes. After that, a UV-VIS spectrophotometer was used to detect absorbance at 450 nm (Shimadzu Corp, Kyoto, Japan). Unaltered chitosan was used as control group.
Perkin-Elmer Spectrum used the KBr (potassium bromide) method to determine FT-IR spectra of TCS and chitosan. The characteristics peaks present in the newly synthesized polymer (amide bonds and thiol peaks) confirmed the presence of TCS [
20].
The thermotropic evaluation of TCS and chitosan were investigated using DSC (Perkin Elmer, Pyris 6, Waltham, MA). In an aluminium crimped pan, about 2 mg of sample was kept with a lid and subjected to heating between 40 and 400 degrees Celsius at a scanning rate of 10 degrees Celsius per minute. As a reference, same empty (blank) pan was used.
2.6. Fabrication of RIS -HA particles
Plain HA particles were mixed with 10 ml of 0.5 mg/ml solution of RIS in distilled water to create RIS-HA particles. For 8 hours, the solution was stirred at 37ºC (
Table 2). After isolating the deposited phase, it was washed thrice using distilled water and then dried. Drug adsorption on HA was measured, and the particles were conjugated with TCS [
4].
Table 2 displays the yields and percent entrapment of RIS with a variety of RIS to HA ratios.
Where, W1 is the amount of drug in the beginning, W2 is the amount of free/un-entrapped drug and W1-W2 is the amount of drug entrapped.
2.7. Preparation of RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles
The cross-linking agent TPP forms a gel by ionic reaction with the positively charged amino group of TCS [
21]. TPP was used to prepare RIS-loaded nanoparticles. All the concentrations of different variables have been mentioned in
Table 1. TCS (25-35 mg/ml) was briefly dissolved in 2% w/w CH
3COOH solution and then allowed to stir overnight at 25
0C. A small amount of NaOH (2M) solution was added, and the pH of the resulting solution was raised from 4 to 5. After that, RIS-HA (10-20 mg/ml) was added in 2:1 ratio and vortexed further. The TPP aqueous solution (1-2 mg/ml) was made with distilled water and kept in the refrigerator at 0-2ºC for 4 hours. At 60ºC, the TCS solution was stirred for 10 minutes. After transferring the TCS solution to the flask containing the finished RIS-HA, the aqueous TPP solution was added while stirring constantly for 10 minutes. Once removed from the ice bath, the RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles were stirred for an additional 15 minutes to achieve an opalescent suspension. The RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles were stored in an airtight container for future use after centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 30 min[
22].
2.8. Optimization of RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles
The ideal formulation was chosen for further studies with the goal of having the optimum particle size, the minimum PDI, and the highest possible drug entrapment. In order to reach the set objective, the effect of variables was analysed on PDI, particle size, and %EE.
2.8.1. Conjugation of RIS-HA-TCS with mPEG
RIS -HA-TCS NPs were further modified with mPEG. Firstly, 100mg of RIS-HA-TCS NPs were suspended in 20mL water, and then, after stirring at room temperature overnight, hydroxyl-mPEG -NHS ester (50mg) was mixed to react with the amino groups on RIS -HA-TCS NPs surface. The required RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG were obtained after centrifugation (5000 rpm) for 10 minutes; these were then stored in a well-closed container until future use [
23].
2.9. Characterization of polymeric nanoparticles
2.9.1. Particle size and Polydispersity index (PDI)
Using Malvern Zetasizer (Malvern Master Sizer 2000, SM, Malvern, UK), laser light scattering was used for determining particle size of both the optimized formulation RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles. After diluting with distilled water, RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles were mixed in the sample unit. The experiments were carried out three times (n=3).
2.9.2. Determination of drug Entrapment Efficiency (%EE)
The entrapment efficiency of RIS in the nanoparticles was determined indirectly by determine the free or un-entrapped RIS present in the optimized formulation after centrifugation. In this process the optimized formulation was centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 30 mins at 4 °C. A UV-Visible spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, Model UV-1601, Kyoto, Japan) was used to measure the concentration of RIS in the supernatant that was taken in the tube after it had been separated and diluted 10 times with distilled water and set to 263 nm. Therefore, the following calculation was used to determine the EE as a percentage. The experiment was conducted three times, and the results were presented as mean value ± standard deviation.
Where, W1 is the amount of drug in the beginning, W2 is the amount of free/un-entrapped drug and W1-W2 is the amount of drug entrapped.
2.9.3. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM)
Transmission electron microscopy (Morgagni 268D-SEI) operated at 100kV with point-to-point resolution was used to examine the morphology of RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles. Negatively dyed with phosphotungstic acid, the RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles were diluted 50-fold in double-distilled water and dried on the carbon-coated grid for examination.
2.9.4. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
The thermotropic properties of RIS, HA, mPEG, a physical mixture of RIS with excipients, and lyophilized optimized RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles were observed using DSC (Pyris 6, Perkin Elmer, Waltham, MA). The samples were placed an aluminium pan and subjected to heating between 40 and 400 degrees Celsius at a scanning rate of 10 degrees Celsius per minute.
2.9.5. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)
Lyophilized optimized RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles, as well as FTIR spectra of RIS, HA, mPEG, surfactant, and physical mixtures of RIS with excipients, were recorded (Bruker Optik GmbH, Ettlingen, Germany). The scanning range was adjusted from 4000 cm-1 to 400 cm-1 with a resolution of 4 cm-1.
2.10. In-vitro release study
The dialysis bag (12000g/mol:MW and16mm: diameter) method was used in the drug release experiment [
24].The dialysis bag was immersed in simulated intestinal fluid, pH 6.8 for pre-treatment and kept for 24 hours before the experiment began. To dissolve the optimal formulation of 5 mg RIS, a dialysis sac was submerged in 500mL of freshly produced SIF at 37ºC in a dissolving flask. Samples of 2mL were taken at regular intervals (15min, 30min, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24h) while the digital magnetic stirrer was running at 100 rpm. To keep the sink state, an equal amount of SIF was refilled. Finally, a UV-VIS spectrophotometer set to 263 nm was used to determine the exact amount of RIS in each sample. The release of RIS from optimized RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles was compared with the RIS suspension and commercially available preparation (RISOSFOS 35mg/Week). The study was performed thrice (n = 3).
2.11. Ex-vivo intestinal permeation study
A modified version of the everted sac model was used to examine the passage of RIS through the intestinal barrier [
25,
26]. Following an overnight fasting, animals were administered diethyl ether anaesthesia before being sacrificed via cervical dislocation. After surgically removing the small intestine, a 5-cm portion was carved out, and the food remnants were washed away in normal saline. After everting the intestine with a glass rod, 2ml of Krebs-Ringer solution was injected. In Kreb’s -Ringer solution (50 ml), the portion of intestine sac was kept containing 2000μg RIS, the entire setup was kept at 37± 0.5ºC, aerated with O
2 (95%) and CO
2 (5%). At 0, 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, and 90 minutes, 2ml aliquots of serosal medium were obtained for quantification of RIS permeated. A UV-VIS spectrophotometer calibrated to a wavelength of 263 nm was used to measure the amount of RIS that passed through the gut. Filtration of sample was done through a syringe filter (0.45 µm pore size) before analysis. For the optimized RIS-HA-TCS, RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles, and commercial formulation, a similar experiment was carried out. The below given formula was used for calculating the Apparent Permeability (Papp) coefficient of RIS suspension, marketed formulation, optimised RIS-HA-TCS, and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles:
Where, F is permeation flux, C
0 is concentration at outset, and A is ileum’s total surface area.
3. Results
3.1. In-silico activity
AutoDock Vina was used for carrying out the docking studies of RIS and conjugated RIS for farnesyl pyrophosphate synthetase enzyme. Binding energies below 5 kcal/mol represents weak binding, whereas higher values, above 10kcal/mol, signify strong binding. Furthermore, the protein ligand interaction structures were obtained using Discovery studio and they are depicted in
Figure 2. The binding affinity for RIS and RIS-TCS-HA were found to be -6.86 and -27.70 kcal/mol respectively. Moreover, number of hydrogen bonds for both RIS and RIS-TCS-HA were found to be 5. These results showed that the formulation that we prepared in our study had four times better binding than RIS alone.
3.2. Synthesis of Thiolated Chitosan (TCS):
The TCS synthesised by the above method was found to be more significant than alternate methods [
27]. We chose DMF as the reaction medium instead of water as compared to the previously published studies. First, the reactive NHS-ester, which was discovered to be more reliable and stable for the subsequent reaction, was synthesised [
28]. Next, the cationic chitosan polymer’s main amino groups were coupled with the reactive NHS-ester. These modifications were made a) for preventing unstable Oacylisourea ester hydrolysing in H
2O and b) It’s possible that the concentration of the target reactant may rise if the reactive NHS-ester was to be produced. As shown in
Figure 3, TCS appeared as white, fibrous in structure and odourless. TCS was also soluble in an aqueous medium.
3.3. Determination of the thiol groups in TCS
3.3.1. Ellman’s method
The thiol group immobilization by the polymer was found to be 2402.23 ± 2.71μmol/g.
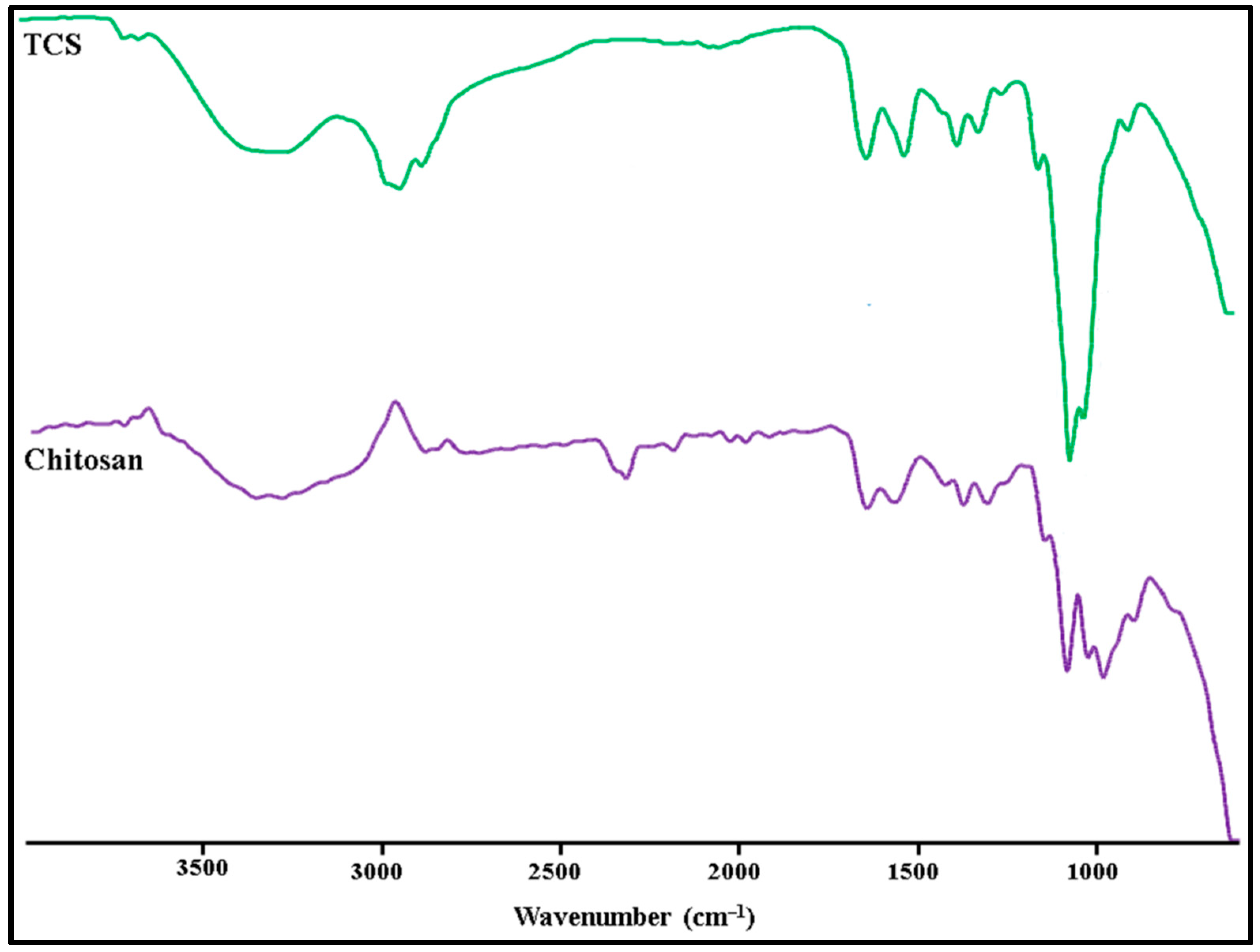
3.3.2. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR)
In
Figure 4 the FT-IR spectra of TCS and chitosan are shown. The following distinctive peaks were observed in the chitosan spectrum, a) 3410cm
−1 due to O-H and N-H, b) 2924cm
−1 due to C-H,1623 cm
−1, c) 1513cm
−1 due to N–H, d) 1088cm
−1 due to C–N, e) 1380cm
−1 (C-H), f) 651 cm
-1 (NH
2) g) 1248cm
−1 (O-H), h) 1153cm
−1 (C-O-C). In TCS, all characteristic peaks were observed except NH
2 peaks.Additional peaks of the newly created -CONH
2 bond were also found: amide band I at 1629 cm
-1,amide band at 1524 cm
-1, and thiol group peaks at 1251 cm
-1 due to NH
2 reaction between chitosan and carboxyl groups of TGA [
29].
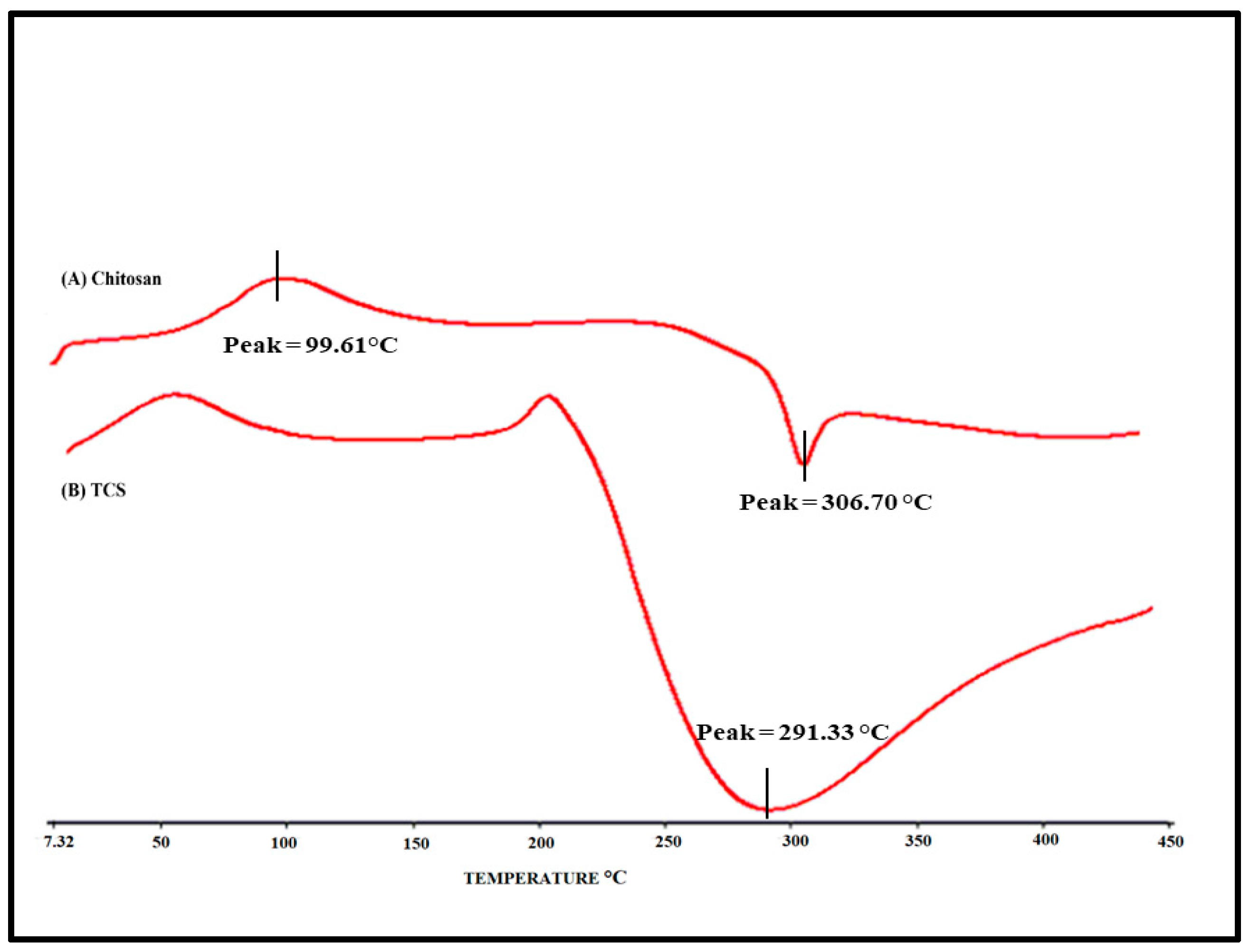
3.3.3. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC)
Figure 5 illustrates the DSC thermogram of chitosan and TCS. As evident from the thermogram, an endothermic peak was observed at 98.95ºC and an exothermic peak was observed at 306.876ºC in a chitosan sample and a peak at 217.2ºC was observed in TCS thermogram. A peak at 217.2ºC was observed due to TCS which was formed when the chitosan was cross-linked with TGA. As evident from the DSC of Chitosan, this peak was absent. The cross-linking of chitosan with TGA [
30] which was not present in chitosan, is indicated by the considerable change in the peak and endothermic enthalpy values.
3.4. Fabrication of RIS -HA particles
The nanoparticles prepared by combining RIS with HA in different ratios showed different entrapment value. Among all the different ratios, the RIS:HA ratio of 2:1 was finally selected for further studies as it had shown higher drug entrapment value (93.97% ±1.56) and sufficient yield value (74.80%±2.61).
3.5. Experimental design optimization
Box- Behnken statistical design (BBD) was used to formulate and optimize the RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles in which the influence of different variables on the responses were observed simultaneously [
24]. Here the impact of independent variables: (A) TPP, (B) TCS, and (C) Drug-HA on the dependent variables (
Y1) Particle size, (
Y2) Polydispersity index (PDI), and (
Y3) Entrapment efficiency (EE) was observed as shown in
Table 3. As depicted in
Table 4, for all the response parameters the “Predicted R
2” values and the “Adjusted R
2” were in a reasonable agreement. To be in a reasonable agreement, the Predicted R
2 and Adjusted R
2 values must be within around 0.20 of one another [
31]. The quadratic model was shown to have a low coefficient of variance across all responses, indicating its viability for use in design space exploration.
Table 4 provides a summary of the polynomial equations for the dependent variables
Y1, Y2, Y3. Positive signs in the polynomial equation signified a direct correlation between the factor and responses (dependent variables), whereas negative signs represented an antagonistic connection between factors and responses.
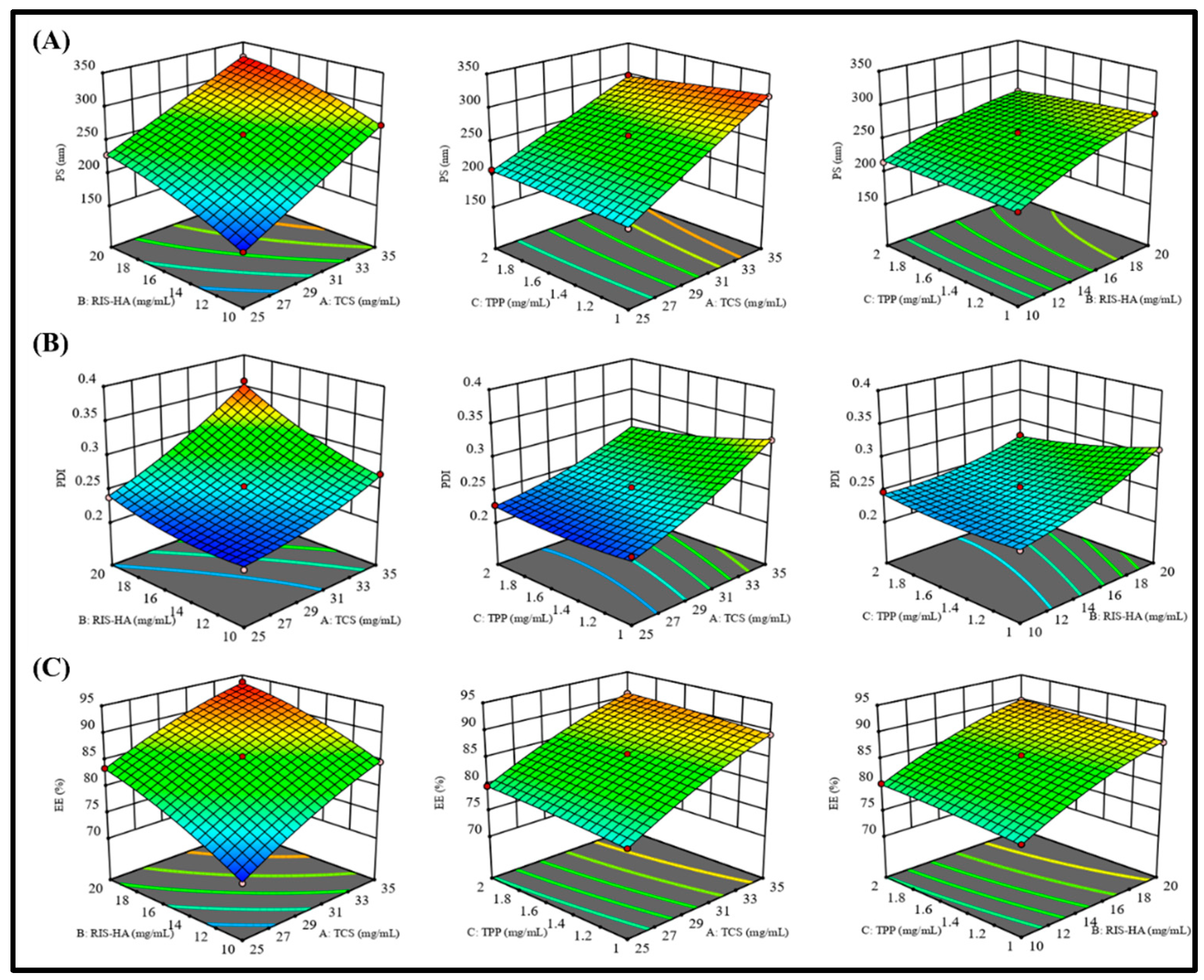
Figure 6 showed response surface graphs.
3.4.1. The effect of independent variables on particle size (Y1)
As polymer (TCS), crosslinking agent (TPP), and Drug-HA complex concentrations were increased, particle size was shown to decrease. One possible explanation for this finding is that the polymeric layer shrank because of increased crosslinking between positively charged amino groups in TCS and the PO
4- ions in TPP [
32].
3.4.2. The effect of independent variables on PDI (Y2)
Table 3 displays that the PDI value for all the produced nanoparticles was less than 0.5, indicating a smaller size distribution [
33].
3.4.3. The effect of independent variables on encapsulation efficiency (Y3)
The effects of independent factors on %EE were explained using response surface plots, like the one in
Figure 6, was used to explain the impact of factors on the encapsulation efficiency. Due to the crosslinking of the TCS polymer and TPP as crosslinking agent, decrease in the amount of drug leakage was observed but it caused nanoparticles to develop a rigid structure [
34]. These findings corroborated with an earlier study reported [
35] where it was found that greater drug entrapment efficiency was associated with the development of higher disulphide bonds between TCS and PO
4- ion crosslinking.
3.5. Selection of optimized RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles
Using the mathematical optimization technique implemented in Design Expert® software, the RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles with the highest % EE and the smallest particle size and PDI were selected. The formulation containing 30 mg/mL of TCS, 15 mg/mL of Drug-HA, and 1.5 mg/mL of TPP was created to fulfill the criterion of optimized formulation after “trading off” distinct responses with statistical desirability function. The optimized RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles (RUN 6) exhibited the particle size of 252.1±2.44nm, 0.11 ±0.01 PDI, and %EE of 85.4± 2.21%.
The optimized formulation was found to be an opalescent solution.
The formulation without mPEG was termed RIS-HA-TCS and the formulation containing mPEG was represented as RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG. mPEG was used to increase the drug half-life and stability. The particle size of RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG formulation was significantly higher than RIS-HA-TCS formulation, but its PDI was lower than RIS-HA-TCS which indicated the mono-dispersity of particles. The entrapment efficiency of RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG was high as compared to RIS-HA-TCS.
3.6. Characterization of RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG
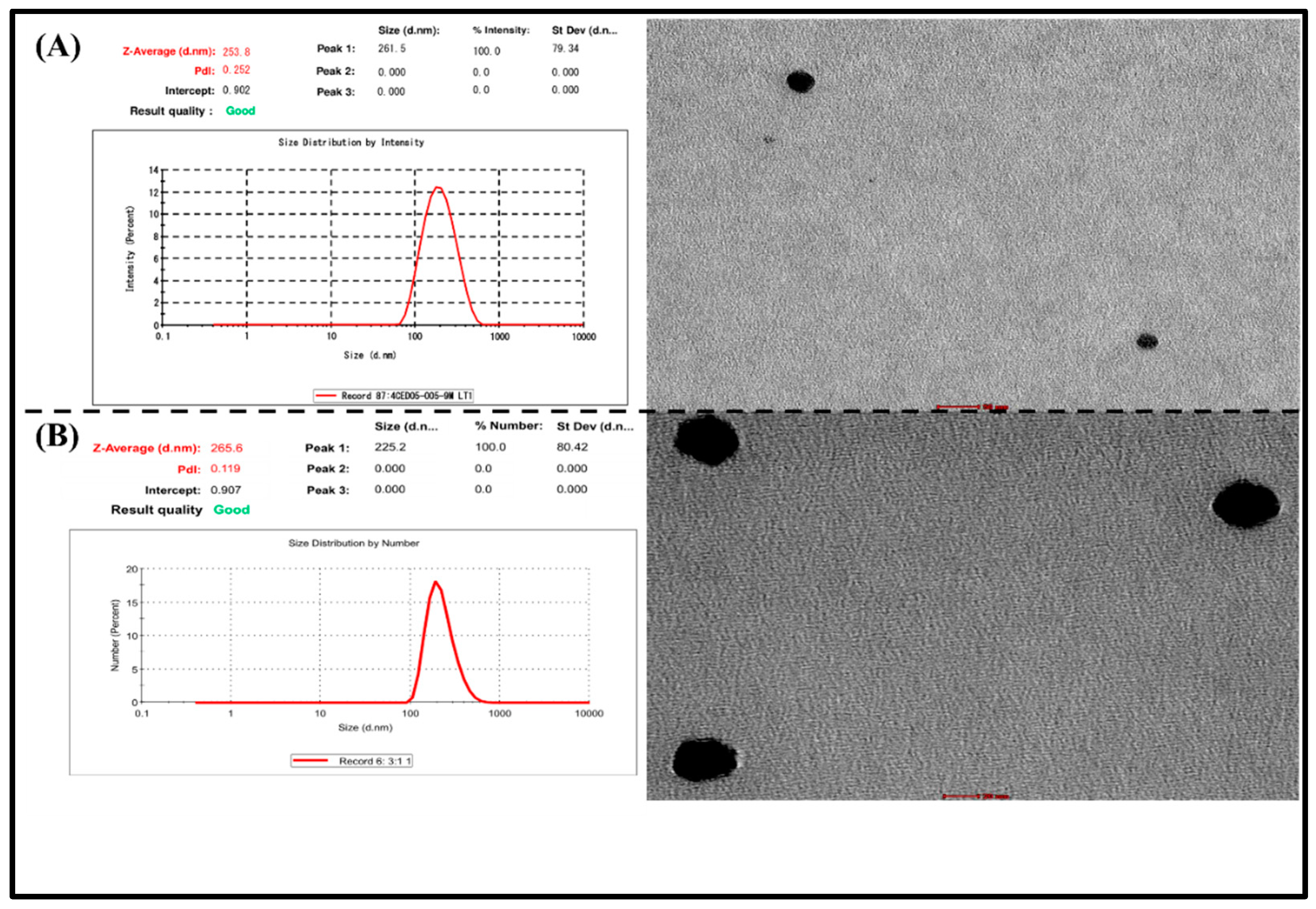
3.6.1. Particle size and polydispersity index
The particle size of RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles was found to be 252.1 ± 2.44 and 264.9± 1.91 nm respectively, whereas PDI of RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG were 0.2 ± 0.01 and 0.120 ±0.01, which indicated a mono-dispersed system i.e., RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles were found to be uniformly dispersed in the entire formulation. Both formulations’ particle sizes were appropriate for oral drug administration. The PDI value closer to zero showed that the RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG formulation was more homogeneous. These results are demonstrated in
Figure 7.
3.6.2. Entrapment efficiency (%EE)
Entrapment efficiency of RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles was found to be 85.4± 2.21%, and 91.1±1.17%, respectively. Increase in TCS, TPP, and drug- HA concentrations was associated with increase in EE percentages. This is because the TCS polymer crosslinked with TPP formed nanoparticles with a hard structure, reducing the drug leakage [
34].
3.6.3. Transmission electron microscopy analysis
Using Transmission electron microscope, shape morphology of RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles were observed. The TEM exhibited spherical shape, uniformly dispersed and non-aggregated NPs. The spherical nanoparticles showed that TCS and TPP were successfully crosslinked. Specifically, the ionic gelation that gave the nanoparticles their structural stability was caused by the crosslinking between negatively charged phosphate ions of TPP and positively charged amine groups of TCS [
36]. These results are demonstrated in
Figure 7.
3.6.4. Differential scanning calorimetry
The DSC thermogram of RIS, HA, mPEG, a physical mixture of excipients with drug, fabricated RIS-HA and optimized RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles are represented in
Figure 8. As evident, the thermogram showed that RIS had two endothermic peaks at 205
0C and 245
0C corresponding to the solvent loss. An exothermic peak at 265
0C corresponded to the melting point of the drug [
37]. As evident from the published literature, pure mPEG showed a distinct phase transition at around 40
0C and its degradation peaks are observed at around 280
0C [
38,
39]. The endothermic peak of the HA DSC thermogram occurred at approximately 60 °C, perhaps as a result of moisture loss, while the endothermic peak occurred at approximately 270 °C, was likely as a result of HA degradation. As the melting point of HA is around 1100 °C, thus it was not captured in DSC [
40]. At the same temperature range, The DSC of drug –excipient showed that the primary peaks of the RIS and excipients were evident and there was no interaction between them. The RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles showed no sharp endothermic peak of RIS because RIS was fully incorporated and molecularly distributed in the solid matrix in amorphous state. An endothermic peak at melting point of 164.5 °C corresponds to the mannitol (cryoprotectant) and was the only peak observed in nanoparticles [
41].
3.6.5. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) spectra
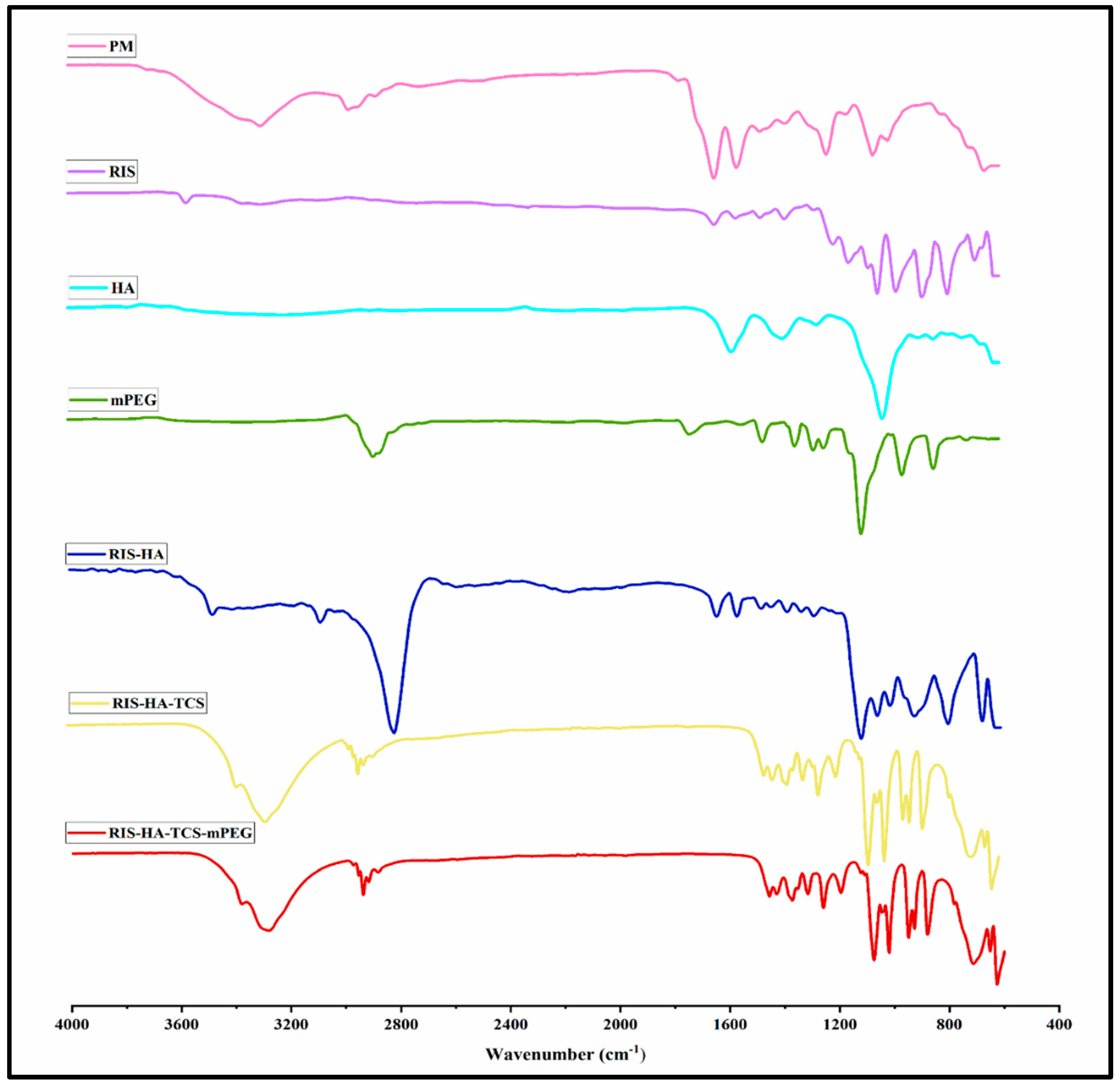
FTIR Spectra overlay of RIS, HA, TCS, and mPEG are shown in
Figure 9. The following peaks for RIS were observed a)1150 cm
-1 due to an aliphatic P-O stretch, b) Aromatic P-O stretch is at 1190 cm
-1, while aromatic C-H stretch is at 3080–3010 cm
-1, c) O-H Stretch at 3609-3329cm
-1, and d) Stretching from C-C, 1601 cm
-1, and from C-N, 1430 cm
-1 [
37]. The spectra of TCS showed the following distinctive peaks, a) 3410cm
−1 due to O–H and N–H, b) 2924cm
−1 due to C–H, c) 1513cm
−1 due to N–H, d) 1088cm
−1 due to C–N, e) 1380cm
−1 due to C–H, f) 1248cm
−1 due to O–H, g) 1153cm
−1 (C-O-C) , and h) 1629 cm
-1 (amide band I), i)1524 cm
-1 (amid band II) and thiol groups represented by 1251 cm
-1 peak [
29]. HA was found to have a peak between 2400-1600 cm
-1(O=P-H stretching) [
42].Alkane (C-H), C=C and C=0 stretch , frequencies of methoxy polyethylene glycol molecule are responsible for the 2885, 1712, 1466, and 1111cm
-1 peaks [
43]. All the respective peaks for RIS, HA, TCS and mPEG were also observed in the formulation.
3.7. In vitro drug release experiment
For the purpose of measuring RIS release
in vitro, the dynamic dialysis approach, which is often used to keep nanoparticles from leaking into the dissolving medium, was implemented [
44].
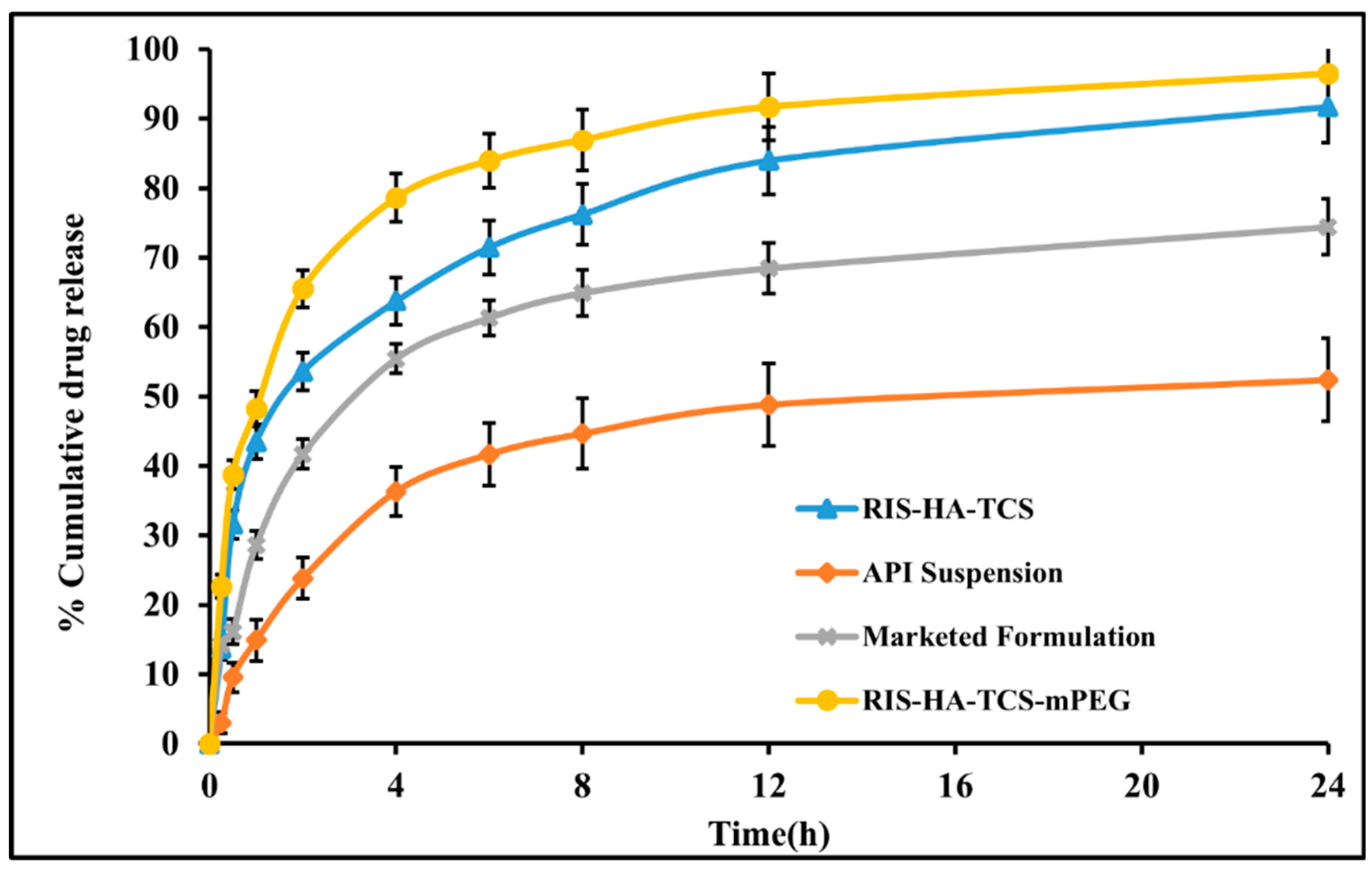
In-vitro experiments were performed in SIF (pH6.8) for the optimized RIS-HA-TCS, RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG, API suspension and marketed formulation
Figure 10. The drug release in the first 2 hours after administering RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG were found to be 52.32 ±2.72% and 66.13±2.52% respectively, followed by a slow drug release for the next 24 hours (91.74 ±5.14% and 95.13±4.64%, respectively). Under the similar experimental condition, pure API suspension and commercialized formulation demonstrated 56.11 ±5.19% and 74.69±3.98% drug release over a period of 24 h when tested for in vitro release. With an increase in polymer content, more nanoparticles were retained by the intestinal tissue, as determined by the in vitro drug release research. These findings may be attributed to the enhanced release of drug from nanoparticles firmly adhered to the mucous layer through covalent linkage, due to presence of increased TCS content [
27]. These results were in good agreement with Zhou [
45], who discovered that the oral administration of an insulin thiolated nanoparticles improved insulin adherence to the mucosal membrane.
3.8. Ex vivo intestinal permeation study
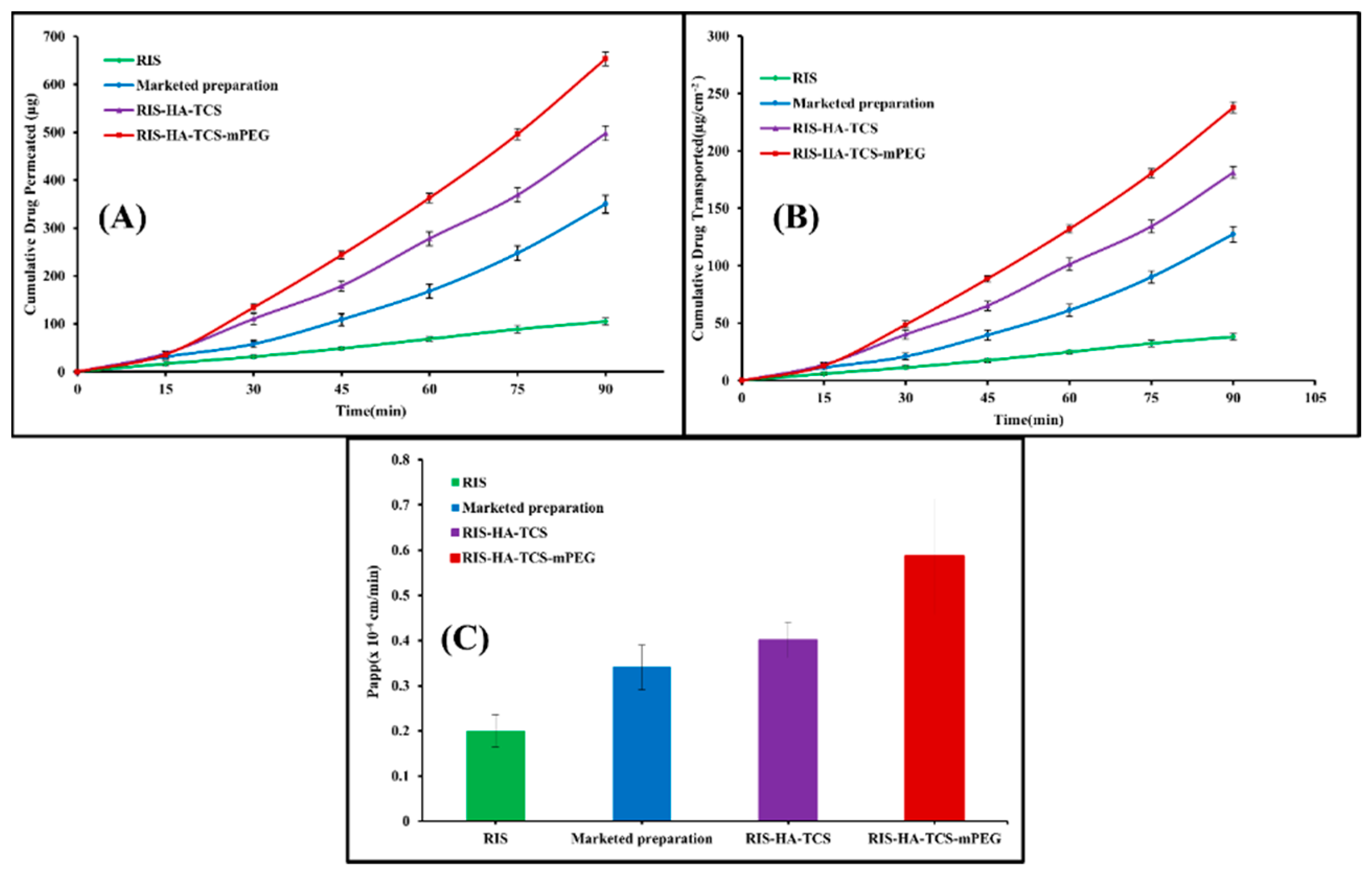
The gut permeability of RIS was determined using a non-everted gut permeation investigation using nanoparticles, a drug suspension, and a commercially available preparation. This research explains how drugs are absorbed by the body once they reach the digestive tract. In
Figure 11, the intestinal penetration profile of RIS from the optimized RIS-HA-TCS, the RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG, RIS suspension and the commercially available preparation is shown. Papp of the RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG nanoparticles was found to be 0.5858±0.1227×10
-4cm/min which was higher in comparison with RIS-HA-TCS formulation 0.4011±0.03938×10
-4cm/min, marketed preparation (0.3401±0.04912×10
-4cm/min) and RIS suspension (0.2005±0.03599×10
-4cm/min). Because nanoparticles diffuse more quickly across the gut membrane [
46] their tiny size and total internalization of RIS into nanoparticles were attributed to the significantly improved release of RIS by RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG and RIS-HA-TCS.
4. Conclusions
The RIS-HA-TCS loaded NPs were prepared and characterized for the treatment of osteoporosis via oral route. Using ionic gelation method, formulation was prepared successfully and optimized with design expert software using Box Behnken design. Optimized RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles showed higher entrapment efficiency, low PDI and optimum particle size. Moreover, RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles were PEGylated to increase the drug half-life and stability. In comparison to RIS-HA-TCS, RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG particle size was better in size and the entrapment effectiveness was higher. PEGylated NPs also showed enhanced in vitro drug release and ex vivo permeability. Actually, thiolated chitosan had a significant impact on the RIS release rate as well. When compared to CS, TCS NPs had significant benefits as a carrier for oral controlled administration of the drug with a wide range of therapeutic applications. However, further exploration of pharmacokinetics, histopathology and pharmacodynamics studies are needed to decide whether RIS-TCS-HA with or without mPEG can be used as a novel approach for the treating osteoporosis through oral route.
Author Contributions
Investigation, Methodology, Data curation, and Writing, Z.S.; Resources, formal analysis, and review editing, T.R.; Methodology, M.R.; formal analysis, M.A.; Project administration, D.V.; Conceptualization and Project administration, S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to Lipoid (Ludwigshafen, Germany) for providing mPEG to us.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
BPs: Bisphosphonates, NPs: Nanoparticles, CS: Chitosan, FPPS: farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase, %EE: Percentage entrapment efficiency, PDI: Polydispersity index HA: Hydroxyapatite, PLGA: Poly (lactide-co-glycolide), RIS: Risedronate, SERM: Selective estrogen receptor modulators, TCS: Thiolated chitosan.
References
- Kendler, D.; Body, J.-J.; Brandi, M.; Broady, R.; Cannata-Andia, J.; Cannata-Ortiz, M.; El Maghraoui, A.; Guglielmi, G.; Hadji, P.; Pierroz, D.J.J.o.B.O. Osteoporosis management in hematologic stem cell transplant recipients: Executive summary. 2021, 28, 100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajuria, D.K.; Razdan, R.; Mahapatra, D.R. Drugs for the management of osteoporosis: a review. Rev Bras Reumatol 2011, 51, 365–371, 379-382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonnick, S.; Saag, K.G.; Kiel, D.P.; McClung, M.; Hochberg, M.; Burnett, S.-A.M.; Sebba, A.; Kagan, R.; Chen, E.; Thompson, D.E.J.T.J.o.C.E.; et al. Comparison of weekly treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis with alendronate versus risedronate over two years. 2006, 91, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Manglani, K.; Gupta, S.; Vohora, D.; Ahmad, F.J.; Talegaonkar, S.J.P.r. Design and development of bioceramic based functionalized PLGA nanoparticles of risedronate for bone targeting: in-vitro characterization and pharmacodynamic evaluation. 2015, 32, 3149–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, D.; Peter, J., St.; Eusebio, R.; Pallone, K.; Kelly, S.; Russell, D.; Nesbitt, J.; Thompson, G.; Powell, J.J.B.j.o.c.p. Effect of renal function on risedronate pharmacokinetics after a single oral dose. 2000, 49, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, A.; Wilson, C.; Frier, M.; Vincent, R.; Blackshaw, P.; Dansereau, R.; Juhlin, K.; Bekker, P.; Spiller, R.J.I.j.o.p. Esophageal transit of risedronate cellulose-coated tablet and gelatin capsule formulations. 1999, 186, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, I.-W.; Han, H.-K.J.I.J.o.N. Effective mucoadhesive liposomal delivery system for risedronate: Preparation and in vitro/in vivo characterization. 2014, 9, 2299. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Wang, Y.; Wei, K.; Ren, L.; Lai, C.J.J.o.M.S.M.i.M. Self-assembly of nanohydroxyapatite in mesoporous silica. 2008, 19, 2933–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balani, K.; Anderson, R.; Laha, T.; Andara, M.; Tercero, J.; Crumpler, E.; Agarwal, A.J.B. Plasma-sprayed carbon nanotube reinforced hydroxyapatite coatings and their interaction with human osteoblasts in vitro. 2007, 28, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, S.C.; Harshita; Mishra, P.K.; Talegaonkar, S. Ceramic Nanoparticles: Fabrication Methods and Applications in Drug Delivery. Current pharmaceutical design 2015, 21, 6165–6188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzo, B.; Iafisco, M.; Laforgia, M.; Margiotta, N.; Natile, G.; Bianchi, C.L.; Walsh, D.; Mann, S.; Roveri, N.J.A.F.M. Biomimetic hydroxyapatite–drug nanocrystals as potential bone substitutes with antitumor drug delivery properties. 2007, 17, 2180–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cenni, E.; Granchi, D.; Avnet, S.; Fotia, C.; Salerno, M.; Micieli, D.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Pignatello, R.; Castelli, F.; Baldini, N. Biocompatibility of poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles conjugated with alendronate. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1400–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talegaonkar, S.; Azeem, A.; Ahmad, F.J.; Khar, R.K.; Pathan, S.A.; Khan, Z.I. Microemulsions: a novel approach to enhanced drug delivery. Recent patents on drug delivery & formulation 2008, 2, 238–257. [Google Scholar]
- Sarmento, B.; Andrade, F.; da Silva, S.B.; Rodrigues, F.; das Neves, J.; Ferreira, D. Cell-based in vitro models for predicting drug permeability. Expert opinion on drug metabolism & toxicology 2012, 8, 607–621. [Google Scholar]
- Hirano, S.; Seino, H.; Akiyama, Y.; Nonaka, I. Chitosan: A Biocompatible Material for Oral and Intravenous Administrations. 1990, 1, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.A.; Patil, K.S.; Yeole, P.G. Intranasal mucoadhesive buspirone formulation: in vitro characterization and nasal clearance studies. Die Pharmazie 2008, 63, 348–351. [Google Scholar]
- Kafedjiiski, K.; Krauland, A.H.; Hoffer, M.H.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.J.B. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of a novel thiolated chitosan. 2005, 26, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkop-Schnürch, A.; Guggi, D.; Pinter, Y. Thiolated chitosans: development and in vitro evaluation of a mucoadhesive, permeation enhancing oral drug delivery system. Journal of controlled release : official journal of the Controlled Release Society 2004, 94, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dünnhaupt, S.; Barthelmes, J.; Thurner, C.C.; Waldner, C.; Sakloetsakun, D.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. S-protected thiolated chitosan: synthesis and in vitro characterization. Carbohydrate polymers 2012, 90, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, C.E.; Frick, W.; Losert, U.M.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A.J.I.j.o.p. Chitosan-thioglycolic acid conjugate: a new scaffold material for tissue engineering? 2003, 256, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquivel, R.; Juárez, J.; Almada, M.; Ibarra, J.; Valdez, M.A.J.I.J.o.P.S. Synthesis and Characterization of New Thiolated Chitosan Nanoparticles Obtained by Ionic Gelation Method. 2015, 2015, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Pinho Neves, A.L.; Milioli, C.C.; Müller, L.; Riella, H.G.; Kuhnen, N.C.; Stulzer, H.K. Factorial design as tool in chitosan nanoparticles development by ionic gelation technique. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects 2014, 445, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jialang, Z.; Jingyuan, Z.; Maosheng, X.; Yen, W.; Yuanqing, Z.; Yubing, L.; Zuanguang, C. PEGylated chitosan nanoparticles with embedded bismuth sulfide for dual-wavelength fluorescent imaging and photothermal therapy. Carbohydrate polymers. 2018, 184, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabahar, K.; Udhumansha, U.; Qushawy, M. Optimization of Thiolated Chitosan Nanoparticles for the Enhancement of in Vivo Hypoglycemic Efficacy of Sitagliptin in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q. Thiolated chitosan-modified PLA-PCL-TPGS nanoparticles for oral chemotherapy of lung cancer. Nanoscale research letters 2013, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soni, K.; Rizwanullah, M.; Kohli, K. Development and optimization of sulforaphane-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers by the Box-Behnken design for improved oral efficacy against cancer: in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo assessments. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology 2018, 46, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kast, C.E.; Bernkop-Schnürch, A. Thiolated polymers--thiomers: development and in vitro evaluation of chitosan-thioglycolic acid conjugates. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2345–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, S.; Rao, S.N.; Fitzmaurice, D. Characterization of Protein Aggregated Gold Nanocrystals. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B 2000, 104, 4765–4776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, A.; Deepa, N.; Chennazhi, K.P.; Nair, S.V.; Tamura, H.; Jayakumar, R. Development of mucoadhesive thiolated chitosan nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Carbohydrate polymers 2011, 83, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Srinivasan, B.; Anbu, J.; Azamthulla, M.; Teja, B.V.; Ramachandra, S.G.; N, K.; Lakkawar, A.W.J.J.o.D.D.S. Technology. Pamidronate functionalized mucoadhesive compact for treatment of osteoporosis-in vitro and in vivo characterization. 2019, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Annadurai, G.; Ling, L.Y.; Lee, J.F. Statistical optimization of medium components and growth conditions by response surface methodology to enhance phenol degradation by Pseudomonas putida. Journal of hazardous materials 2008, 151, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, P.; Udhumansha, U.; Rathnam, G.; Ganesh, M.; Jang, H.T. Capecitabine encapsulated chitosan succinate-sodium alginate macromolecular complex beads for colon cancer targeted delivery: in vitro evaluation. International journal of biological macromolecules 2018, 117, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdizadeh Barzoki, Z.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mortazavian, E.; Rafiee-Tehrani, N.; Behmadi, H.; Rafiee-Tehrani, M.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A. Determination of diffusion coefficient for released nanoparticles from developed gelatin/chitosan bilayered buccal films. International journal of biological macromolecules 2018, 112, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakar, J.; Nayak, A.K. Formulation and statistical optimization of multiple-unit ibuprofen-loaded buoyant system using 23-factorial design. Chemical Engineering Research and Design 2012, 90, 1834–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.Y.; Zeng, S.Y. Preparation and Characterization of Quaternized Chitosan Coated Alginate Microspheres for Blue Dextran Delivery. Polymers 2017, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubaidulla, U.; Khar, R.K.; Ahmad, F.J.; Sultana, Y.; Panda, A.K. Development and characterization of chitosan succinate microspheres for the improved oral bioavailability of insulin. Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 2007, 96, 3010–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, D.; Srinivasan, B.; Anbu, J.; Azamthulla, M.; Banala, V.T.; Ramachandra, S.G. Improvement of bone microarchitecture in methylprednisolone induced rat model of osteoporosis by using thiolated chitosan-based risedronate mucoadhesive film. Drug development and industrial pharmacy 2018, 44, 1845–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, M.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y.J.S.e.m.; cells, s. Cellulose-based solid–solid phase change materials synthesized in ionic liquid. 2009, 93, 1321–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zu, C.; Yu, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Sun, R.; Chaurasiya, B.; Tang, B.; Chen, D.; Tu, J.; Shen, Y.J.D.d. Highly loaded deoxypodophyllotoxin nano-formulation delivered by methoxy polyethylene glycol-block-poly (D, L-lactide) micelles for efficient cancer therapy. 2020, 27, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipton, A.N.J.J.o.P.; Microbiology, A. In-vitro Evaluation of Chitosan-Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite Scaffolds as Bone Substitutes with Antibiofilm Properties. 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Rizwanullah, M.; Amin, S.; Ahmad, J. Improved pharmacokinetics and antihyperlipidemic efficacy of rosuvastatin-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers. Journal of drug targeting 2017, 25, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rawat, P.; Manglani, K.; Gupta, S.; Kalam, A.; Vohora, D.; Ahmad, F.J.; Talegaonkar, S. Design and Development of Bioceramic Based Functionalized PLGA Nanoparticles of Risedronate for Bone Targeting: In-vitro Characterization and Pharmacodynamic Evaluation. Pharm Res 2015, 32, 3149–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Nashar, D.; Khalaf, A.; Naser, A.; Abdel-Wahhab, H.; Ellaban, A.J.E.J.o.C. Study the Effect of a Polymerizable Surfactant on the Physico‒Mechanical Properties of Natural Rubber (NR) and Styrene Butadiene Rubber (SBR). 2018, 61, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Zhou, R.; Liu, L.; Lu, Y.; Qi, J.; Wu, W. Liposomes containing bile salts as novel ocular delivery systems for tacrolimus (FK506): in vitro characterization and improved corneal permeation. International journal of nanomedicine 2013, 8, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.; He, B.; Dai, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Wang, X. Thiolated Nanoparticles Overcome the Mucus Barrier and Epithelial Barrier for Oral Delivery of Insulin. Molecular pharmaceutics 2020, 17, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, S.; Sarwar, H.S.; Sohail, M.F.; Imran, M.; Salman Qureshi, O.; Raza, A.; Ahmad, N.M.; Iqbal, A.; Shahnaz, G. Synthesis and characterization of pre-activated thiolated chitosan nanoparticles for oral delivery of octreotide. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2020, 58, 101807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Synthesis of thiolated chitosan (TCS) from chitosan.
Figure 1.
Synthesis of thiolated chitosan (TCS) from chitosan.
Figure 2.
Docking results: (i) Chitosan, and (ii) Thiolated chitosan.
Figure 2.
Docking results: (i) Chitosan, and (ii) Thiolated chitosan.
Figure 3.
Structure of the prepared TCS.
Figure 3.
Structure of the prepared TCS.
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra: a) TCS and b) Chitosan.
Figure 4.
FTIR spectra: a) TCS and b) Chitosan.
Figure 5.
DSC thermogram: A) Chitosan and B) TCS.
Figure 5.
DSC thermogram: A) Chitosan and B) TCS.
Figure 6.
Response surface curve: showing the effect of factors on dependent variables: (A) Particle size (nm), (B) PDI, and (C) Entrapment efficiency (%) of RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles within Box-Behnken statistical design.
Figure 6.
Response surface curve: showing the effect of factors on dependent variables: (A) Particle size (nm), (B) PDI, and (C) Entrapment efficiency (%) of RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles within Box-Behnken statistical design.
Figure 7.
Image represents: (A) particle size and TEM of RIS-HA-TCS and (B) Particle size and TEM of RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 7.
Image represents: (A) particle size and TEM of RIS-HA-TCS and (B) Particle size and TEM of RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 8.
DSC thermogram :(A) RIS, (B) HA, (C)mPEG, (D) Physical mixture, (E) Fabricated RIS-HA (F) Optimized RIS-HA-TCS and (G) RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 8.
DSC thermogram :(A) RIS, (B) HA, (C)mPEG, (D) Physical mixture, (E) Fabricated RIS-HA (F) Optimized RIS-HA-TCS and (G) RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 9.
FTIR spectra for a) PM, b) RIS, c) HA, d) mPEG, e) RIS-HA, f) RIS-HA-TCS and g) RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 9.
FTIR spectra for a) PM, b) RIS, c) HA, d) mPEG, e) RIS-HA, f) RIS-HA-TCS and g) RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 10.
In-vitro drug release profile of RIS from API suspension, Marketed preparation, RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG in SIF pH 6.8.
Figure 10.
In-vitro drug release profile of RIS from API suspension, Marketed preparation, RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG in SIF pH 6.8.
Figure 11.
Intestinal permeation study result showing: (A) Cumulative amount of drug permeated (µg) vs time (min), (B)cumulative amount of drug transported(µgcm-2) vs time(min), (C) Papp of RIS, marketed formulation, RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Figure 11.
Intestinal permeation study result showing: (A) Cumulative amount of drug permeated (µg) vs time (min), (B)cumulative amount of drug transported(µgcm-2) vs time(min), (C) Papp of RIS, marketed formulation, RIS-HA-TCS and RIS-HA-TCS-mPEG.
Table 1.
Various variables (independent and dependent) used for the preparation and optimization of RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles in the Box-Behnken design (BBD).
Table 1.
Various variables (independent and dependent) used for the preparation and optimization of RIS-HA-TCS nanoparticles in the Box-Behnken design (BBD).
| Variables |
Constraints |
| Independent |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
| A = TPP (mg/ml) |
2 |
1.5 |
1 |
| B = TCS (mg/ml) |
35 |
30 |
25 |
| C = Drug-HA (mg/ml) |
20 |
15 |
10 |
| Dependent |
Objectives |
|
Y1 = particle size(nm)
|
Optimum |
|
Y2 = PDI
|
Minimize |
|
Y3 = EE (%)
|
Maximize |
Table 2.
Yield of product and Entrapment efficiency of RIS-HA particles.
Table 2.
Yield of product and Entrapment efficiency of RIS-HA particles.
| S.NO. |
RIS: HA |
Process yield |
RIS %EE |
| 1. |
1:1 |
73.27+4.37 |
70.30+1.01% |
| 2. |
1:2 |
74.80+2.61 |
73.87+0.72% |
| 3. |
1:3 |
84.57+3.06 |
62.27+1.27% |
| 4. |
1:4 |
70.83+4.93 |
87.23+0.91% |
| 5. |
1:5 |
86.07+3.19 |
84.30+0.70% |
| 6. |
2:1 |
60.87+6.62 |
93.97+1.56% |
| 7. |
3:1 |
75.17+5.33 |
59.00+1.28% |
| 8. |
4:1 |
79.90+7.81 |
76.14+1.15% |
| 9. |
5:1 |
65.33+2.96 |
69.33+1.08% |
Table 3.
The Box-Behnken experimental design of polymeric nanoparticles (RIS-HA-TCS) and evaluated response parameters (n=3).
Table 3.
The Box-Behnken experimental design of polymeric nanoparticles (RIS-HA-TCS) and evaluated response parameters (n=3).
| Run |
A: TCS |
B: RIS-HA |
C: TPP |
Particle size |
PDI |
EE |
| |
(mg/ml) |
(mg/ml) |
(mg/ml) |
(nm) |
|
(%) |
| 1 |
30 |
15 |
1.5 |
259.63 |
0.255 |
85.37 |
| 2 |
30 |
15 |
1.5 |
256.46 |
0.252 |
85.42 |
| 3 |
30 |
20 |
1 |
288.23 |
0.312 |
88.14 |
| 4 |
25 |
15 |
2 |
207.38 |
0.227 |
79.66 |
| 5 |
30 |
10 |
2 |
214.77 |
0.247 |
80.31 |
| 6 |
30 |
15 |
1.5 |
253.82 |
0.252 |
85.73 |
| 7 |
35 |
15 |
2 |
298.16 |
0.283 |
90.67 |
| 8 |
25 |
10 |
1.5 |
163.65 |
0.214 |
71.92 |
| 9 |
25 |
15 |
1 |
198.21 |
0.231 |
77.68 |
| 10 |
25 |
20 |
1.5 |
228.24 |
0.238 |
83.47 |
| 11 |
35 |
20 |
1.5 |
326.38 |
0.359 |
93.65 |
| 12 |
35 |
10 |
1.5 |
273.28 |
0.273 |
84.68 |
| 13 |
30 |
10 |
1 |
217.23 |
0.238 |
78.34 |
| 14 |
35 |
15 |
1 |
317.17 |
0.326 |
89.23 |
| 15 |
30 |
20 |
2 |
267.12 |
0.275 |
89.83 |
Table 4.
Regression analysis parameters for the responses Y1, Y2 and Y3.
Table 4.
Regression analysis parameters for the responses Y1, Y2 and Y3.
| Models |
R2
|
R2 (Adjusted) |
R2 (Predicted) |
S.D. |
C.V. (%) |
| Response, Y1 |
0.9786 |
0.9728 |
0.9577 |
7.61 |
|
| Linear |
‒ |
| 2F1 |
0.9893 |
0.9813 |
0.9574 |
6.31 |
‒ |
| Quadratic |
0.9985 |
0.9958 |
0.9837 |
3.00 |
1.19 |
| Response, Y2 |
0.8829 |
0.8509 |
0.7699 |
0.0155 |
|
| Linear |
‒ |
| 2F1 |
0.9654 |
0.9394 |
0.9026 |
0.0099 |
‒ |
| Quadratic |
0.9928 |
0.9797 |
0.8877 |
0.0057 |
2.16 |
| Response, Y3 |
0.9799 |
0.9744 |
0.9667 |
0.92 |
|
| Linear |
‒ |
| 2F1 |
0.9836 |
0.9713 |
0.9537 |
0.98 |
‒ |
| Quadratic |
0.9994 |
0.9983 |
0.9927 |
0.23 |
0.28 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).