2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
All experimental procedures were ethically approved by the Animal Care Committee of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, under approval number 23 177-07/G 13-1-034, and conducted following the guidelines outlined in the EU Directive 2010/63/EU for animal experiments. Mice deficient in the gene encoding apolipoprotein E (ApoE-/-) and wild-type controls (C57BL/6J) were acquired from The Jackson Laboratory, Bar Harbor, ME, USA. Male mice were fed a standard rodent chow (Altromin, Lage, Germany) and utilized for the experiments at 12 months of age. The mice were housed in a controlled environment with a 12-hour light/dark cycle, a temperature of 22±2 °C, humidity maintained at 55±10%, and provided with ad libitum access to food and tap water.
2.2. Measurement of Blood Pressure and Total Serum Cholesterol
Blood pressure measurements were conducted in conscious restrained mice using a computerized tail-cuff system (CODA® Monitor, Kent Scientific). To familiarize the mice with the procedure, they underwent a two-day training period. During measurements, mice were placed in restraint tubes to minimize movement and positioned on a warming platform (maintained at 32-35°C) to ensure comfort. Before starting the actual experiment, the tails of the mice were gently cuffed, and an acclimatization period of 5 minutes was allowed to let the mice adjust to the setup. Each measurement session comprised 20 cycles, with the initial 5 cycles designated for acclimatization and excluded from the analysis. The average of the subsequent 15 cycles was recorded as the blood pressure reading for each mouse. Following the experiment, mice were euthanized by CO2 exposure. Blood samples were collected from the heart, and the serum total cholesterol levels were determined using the scil Reflovet® Plus analyzer (scil animal care company GmbH, Viernheim, Germany).
2.3. Pharmacological Studies
Pharmacological studies were performed in the aorta, which is known for developing endothelial dysfunction and morphologic changes in ApoE-/- mice and therefore served as a positive control, and in the ophthalmic artery [
13,
14,
15]. Mice were euthanized by inhalation of CO
2. Subsequently, the abdominal aorta and the ophthalmic artery were carefully dissected and placed in cold Krebs-Henseleit buffer with the following ionic composition (in mM): 118.3 NaCl, 25.0 NaHCO3, 11.0 glucose, 4.7 KCl, 2.5 CaCl2, 1.2 MgSO4, and 1.2 KH2PO4 (Carl Roth GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany). After cleaning the segments of the abdominal aorta and the ophthalmic artery from surrounding tissue, they were transferred into a perfusion chamber and cannulated and sutured onto micropipettes as previously described [
15,
16,
17]. The segments were pressurized using the pipettes to 80 mm Hg for the aorta and 50 mm Hg for the ophthalmic artery by utilizing two reservoirs filled with Krebs-Henseleit buffer. The vessels were then visualized using a video camera attached to an inverted microscope. The perfusion chamber was continuously supplied with carbonated and oxygenated Krebs-Henseleit buffer at 37°C and maintained at pH 7.4. An equilibration period of 45 minutes preceded the commencement of functional studies. The suitability of the blood vessels for experiments was ensured by confirming a minimum of 20% constriction from the resting luminal vessel diameter after perfusion with high KCl solution (100 mM) for the aorta or 50% constriction for the ophthalmic artery.
Next, concentration-response curves were gained for phenylephrine (10-8-10-3 M, Sigma-Aldrich Chemie GmbH, Munich, Germany), an α1-adrenoceptor agonist. In vessel segments preconstricted with phenylephrine to 70-50% of their initial diameter, concentration-response curves for the endothelium-independent vasodilator, nitroprusside (10-9-10-4 M, Sigma-Aldrich), and for the endothelium-dependent vasodilator, acetylcholine (10-9-10-4 M, Sigma-Aldrich), were obtained.
In a second series of experiments, various inhibitors were applied to investigate endothelium-dependent vasodilation pathways in the ophthalmic artery. After obtaining a concentration-response curve for acetylcholine (10-9-10-4 M) in arteries preconstricted with phenylephrine, the vessels were washed for 10 minutes and then incubated for 30 minutes with the respective blocker. Subsequently, the vessel was preconstricted again to a similar level as before, and a concentration-response curve for acetylcholine (10-9-10-4 M) was obtained.
To examine the contribution of NOS isoforms to endothelium-dependent vasodilation responses, vessels were incubated with either the arginine analog, Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 10-4 M, Sigma-Aldrich), a non-isoform-selective NOS inhibitor, 1-[2-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]imidazole (TRIM, 10-4 M, Sigma-Aldrich), a selective inhibitor of neuronal NOS (nNOS), or aminoguanidine (3 x 10-4 M, Sigma-Aldrich), a selective inhibitor of inducible NOS (iNOS). Since there are no highly selective inhibitors for eNOS available at present, the contribution of eNOS to vasodilation responses had to be derived from experiments using nNOS, iNOS and nonspecific NOS inhibition. To assess the contribution of cyclooxygenase (COX) metabolites to endothelium-dependent vasodilation, reactivity to acetylcholine before and after incubation with indomethacin (10-5 M, Sigma-Aldrich), a non-isoform-selective inhibitor of COX-1 and COX-2, was tested. Moreover, the effects of combined blockade of COX and NOS by simultaneously incubating with L-NAME (10-4 M) and indomethacin (10-5 M) were tested, to exclude the possibility that both signaling pathways compensate for each other. To assess the contribution of endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factors (EDHFs) to acetylcholine-induced vasodilation, responsiveness of the ophthalmic artery to acetylcholine was tested in presence of L-NAME and indomethacin before and after incubation with KCl (30 mM), which prevents hyperpolarization, and thus blocks the EDHF-dependent portion of vasodilation responses.
To test for possible EDHF pathways involved, reactivity of the ophthalmic artery to acetylcholine was tested in the presence of L-NAME and indomethacin before and after incubation with 17-octadecynoic acid (17-ODYA, 10
-4 M, Tocris Bioscience, Bristol, UK), a suicide substrate inhibitor of both ω- hydroxylation and epoxygenation of arachidonic acid via the cytochrome P450 monoxygenase (CYP450) pathway, baicalein (10
-5 M, Sigma-Aldrich), a specific inhibitor of 12/15-lipoxygenase, and 18α-glycyrrhetinic acid (18α-GA, 3×10
−5 M, Sigma-Aldrich), a gap junction blocker. The pathways were previously shown to be involved in EDFH-dependent ophthalmic artery responses of wild-type mice of the C57Bl/6 J background [
18].
2.4. Vascular Mechanics
Chronic hypertension and hypercholesteremia have been reported as triggers of a remodeling in the blood vessel walls [
19,
20]. These conditions can drive to an alteration of the vascular mechanics, more specifically of the stress-strain relation, as previously described in mouse arteries [
21]. For studies of vascular mechanics, the ophthalmic artery smooth muscle was deactivated by incubation with Krebs buffer containing 67 mmol/L etheylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) for 20 minutes, which produces complete deactivation of smooth muscle [
22]. Then, pressure–diameter relationships were obtained in deactivated ophthalmic arteries between luminal pressures of 80 and 0 mmHg in steps of 10 mmHg, similar to previous reports [
23]. At each pressure level, the artery segment was allowed to equilibrate for 1 min before internal and external diameter were measured. Circumferential stress (σ) was calculated from intravascular pressure (P), internal diameter (Di), and wall thickness (WT): σ = (P ∙ Di)/(2 ∙ WT). Circumferential strain (ε) was calculated by the following formula: ε = (ΔD/D₀)/D
0. D
0 represents the original diameter, defined as the internal diameter at a pressure of 0 mmHg.
2.5. Oil Red O Staining
Oil Red O (ORO) staining was used to assess lipid content in cross sections of the aorta and the ophthalmic artery from ApoE-/- and wild-type mice. Cryosections (10 µm) were air-dried, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 5 min, rinsed with running tap water for 1 min and dehydrated with 60% isopropanol. Next, the tissue sections were stained with freshly prepared ORO solution (Carl Roth GmbH, Karlsruhe, Germany; 0.5 g in 100 ml isopropanol and diluted with distilled water at a ratio of 3:2) for 15 min and then rinsed with 60% isopropanol, stained with hematoxylin (5 dips), rinsed with distilled water and finally mounted with glycerin jelly and cover-slipped. For measurements of staining intensity, the hematoxylin step was omitted. Staining was measured by a blinded evaluator using ImageJ software (NIH,
http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/).
2.5. Quantification of ROS
Superoxide formation was assessed in cryosections of the aorta and the ophthalmic artery by the oxidative fluorescent dye dihydroethidium (DHE)
in situ as described previously [
24]. After mice had been sacrificed and the aorta and the ophthalmic artery isolated, frozen cross-sections of 10 µm thickness were prepared. After thawing, the tissue sections were immediately incubated with 10 µmol/l DHE for 30 min. Photographs of the vascular cross-sections were taken using a fluorescent microscope at an excitation wavelength of 520 nm and an emission wavelength of 610 nm. The intensity of the staining was measured by a blinded evaluator using ImageJ software (NIH,
http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/).
2.6. Quantification of Redox Genes by Real-time PCR
Messenger RNA for the prooxidative redox enzymes, NOX1, NOX2, NOX4, and xanthine dehydrogenase (XDH) was quantified in the aorta and the ophthalmic artery from both mouse genotypes using real-time PCR. Under physiological conditions, XDH is active primarily as a dehydrogenase. However, various stimuli, including hypoxia and inflammation, promote the conversion of XDH to the superoxide-producing xanthine oxidase (XO), which promotes endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Immediately after animals’ death, blood vessels were rapidly excised and placed in cold phosphate buffered solution (PBS, Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany). Under a stereo microscope, vessels were cleaned from surrounding tissue and blood, and then cut into small pieces. Next, the tissue samples were transferred into a 1.5-ml tube and rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen. Subsequently, the samples were homogenized (FastPrep; MP Biomedicals, Illkirch, France), and total RNA was isolated with the RNeasy Kit (QIAGEN, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Next, mRNA was reverse transcribed with M-MLV reverse transcriptase and random hexamers (Promega, Mannheim, Germany). Quantitative PCR was conducted with the ViiA 7 system (Applied Biosystems, Darmstadt, Germany). SYBR green was used for DNA detection. Relative mRNA levels of target genes were quantified using comparative threshold (CT) normalized to β-actin
(ACTB). Messenger RNA expression is presented as the fold-change in ApoE-/- mice versus wild-type mice. The PCR primer sequences are presented in
Table 1.
2.7. Immunostainings
To localize and to assess the level of expression of the prooxidative enzymes, NOX1, NOX2, NOX4 and XDH/XO, and of LOX-1, aortas and ophthalmic arteries from wild-type and ApoE-/- mice were dissected, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde overnight and embedded into paraffin blocks. Vascular cross-sections (7 µm thickness) were incubated with a rabbit antibody directed either against NOX1, NOX2, NOX4, XDH/XO, or LOX-1 (for specifications see
Table 2). As a secondary antibody, a Rhodamine Red-X-coupled, goat anti-rabbit polyclonal antibody (Dianova GmbH, Hamburg, Germany; catalog number: 111-295-003; dilution 1:200, incubation time: 1 h at RT) was used. Negative control sections were incubated with blocking media and the secondary antibody. Finally, slides were mounted using VECTASHIELD® Mounting Medium with DAPI (BIOZOL Diagnostica Vertrieb GmbH, Eching, Germany) and cover-slipped.
2.8. Statistics
Responses to the vasoconstrictor, phenylephrine, are shown as relative change in luminal vessel diameter from resting diameter, while responses to the vasodilators, acetylcholine and nitroprusside, are expressed as relative change in luminal diameter from preconstricted diameter. Two-way ANOVA for repeated measurements was used to compare concentration-response curves. Blood pressure levels, total serum cholesterol, staining intensity and mRNA expression levels were compared using the unpaired t test. The significance level was 0.05, and n represents the number of mice.
4. Discussion
There are several new findings in this study. First, aortas from 12-month-old ApoE-/- mice displayed impaired vasodilation responses to acetylcholine and were characterized by excessive lipid storage in the vascular wall, especially the endothelium. Additionally, aortas displayed elevated ROS, NOX1, NOX2 and NOX4 expression levels, and increased LOX-1 immunoreactivity in the endothelium and smooth muscle, indicative of oxidative stress-mediated vascular damage. In contrast, ophthalmic arteries from ApoE-/- mice had preserved vasoconstriction and vasodilation responses, normal vascular mechanics, no signs of histological changes due to chronic hypercholesterolemia, normal ROS and prooxidative enzyme levels, and no signs of LOX-1 upregulation in the vascular wall. Likewise, the contribution of signaling pathways to acetylcholine-induced vasodilation did not differ between the ophthalmic artery of ApoE-/- and wild-type mice, suggesting that no compensatory pathways have been activated in ApoE-/- mice to retain endothelium-dependent vasodilation.
During hypercholesterolemia, oxidized low-density lipoproteins (Ox-LDLs) may trigger the expression of prooxidative enzymes in the vascular wall that contribute to generation of ROS, which at high concentrations, elicit endothelial dysfunction in part by affecting eNOS function and by inactivation of nitric oxide [
27,
28,
29,
30]. Impaired responses to endothelium-dependent vasodilators have been reported in both large and small arteries of hypercholesterolemic patients [
31,
32,
33,
34,
35]. Of note, in the human retina, vascular hyperemic responses to flicker light stimulation were reduced with increasing serum cholesterol levels even within the physiological range [
8,
9]. Likewise, ApoE-/- mice were reported to develop endothelial dysfunction in both large and small blood vessels, including retinal arterioles [
36,
37,
38,
39].
However, there were also reports on experiments in small arteries of hypercholesterolemic animal models and humans that did not develop impairment of endothelial function. For example, in isolated mesenteric arteries from ApoE-/- mice, endothelium-dependent relaxations to acetylcholine remained intact or were even enhanced [
26]. In another model of dyslipidemia, EDHF-mediated reactivity of gracilis muscle arteries in response to acetylcholine was also shown to be enhanced [
40]. Similarly, in cremaster muscle arterioles of ApoE-/- and LDL receptor-deficient mice, endothelium-dependent vasodilation was retained [
41]. In human gastroepiploic arteries, hypercholesterolemia significantly reduced responses in large, but not in small vessels [
42].
However, why endothelium-dependent vasodilation of some small arteries is barely affected by hypercholesterolemia is unknown at present. Possible explanations are reduced uptake of Ox-LDLs by endothelial cells, resistance of intracellular prooxidative signaling pathways to activation by Ox-LDLs, increased intracellular antioxidant enzyme activity or alternative signaling pathways that are less susceptible to the effects of hypercholesterolemia. For example, large conductance, Ca
2+-activated K
+ channels (BK
Ca) have been proposed to rescue EDHF-dependent vasodilation responses in mesenteric arteries of ApoE-/- mice [
26]. In another study on gracilis muscle arteries from dyslipidemic mice, a compensatory role for a CYP450 metabolite of arachidonic acid was proposed to preserve endothelial function [
40]. Specifically, the activity of the CYP450 generates epoxyecosatrienoic acids (EETs), facilitating vasodilation through gap junction communication [
18]. In this context, the 12/15 lipoxygenase (12/15 LOX) enzyme also plays a pivotal role in physiological vasorelaxation by producing 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (12-HETE) [
43]. These arachidonic acid metabolites trigger an increase in intracellular potassium (K⁺) concentration within the vascular smooth muscle layer via gap junctions, ultimately enabling normal vasodilation [
18].
Previous studies from our laboratory revealed that in the mouse ophthalmic artery, vasodilation responses to acetylcholine are mediated by M
3 receptors and several endothelium-dependent mechanisms involving eNOS, lipoxygenase- and CYP450-derived metabolites, inwardly rectifying potassium (Kir) channels and gap junctions [
16,
18,
44,
45]. In contrast, during chronic genetic eNOS deficiency or angiotensin II exposure, which induces oxidative stress and eNOS dysfunction, endothelium-dependent vasodilation was predominantly mediated by EDHF-dependent signaling pathways, suggesting that the mouse ophthalmic artery is equipped with signaling mechanisms that may help to retain endothelium-dependent vasodilation when one signaling pathway is not available [
25,
43]. In the present study, eNOS contributed to a similar extent to cholinergic, endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the ophthalmic artery of both mouse genotypes indicating that eNOS was not dysfunctional in the ophthalmic artery of ApoE-/- mice. Specifically, the activity of eNOS leads to the release of nitric oxide, which in turn activates the soluble enzyme guanylate cyclase (sGC). This enzyme facilitates the production of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), subsequently activating protein kinase G (PKG). This cascade ultimately induces relaxation in of vascular smooth muscle cells by reducing intracellular calcium ion concentration [
18]. Moreover, there was no hint that alternative signaling pathways had been activated in ophthalmic arteries from ApoE-/- mice, because blockade of nNOS, iNOS, COX, lipoxygenase, CYP450 and gap junctions had similar effects on endothelium-dependent vasodilation as in wild-type mice. All together, these findings suggest that hypercholesterolemia did not exert marked effects on endothelial function in the ophthalmic artery, which contrasts with our previously published findings in retinal arterioles, where pronounced endothelial dysfunction was observed in ApoE-/- mice [
46].
We used ApoE-/- mice for our studies, because this is an established mouse model that develops spontaneous severe hypercholesterolemia, elevated vascular ROS and cytokine levels, endothelial dysfunction, and atherosclerotic lesions similar to those seen in humans in various arteries [
13,
36,
39]. In the present study, ApoE-/- mice had markedly elevated ROS levels and a reduced endothelial function in the aorta, which is in line with previous studies [
15,
47]. Interestingly, in contrast to the findings in the aorta, no elevation of ROS levels was found in the ophthalmic artery.
The prooxidant enzymes NOX and XDH/XO were previously shown to contribute to vascular damage during hypercholesterolemia in ApoE-/- mice [
48,
49,
50]. However, the role of individual NOX isoforms in atherosclerosis is heavily debated. While NOX1 and NOX2 were mostly shown to contribute to atherosclerotic lesions, the role of NOX4 is controversial [
49,
51]. Whereas some studies support the concept that NOX4 is a mediator of atherosclerosis during hypercholesterolemia, other groups have reported opposing findings [
52,
53,
54,
55,
56,
57].
In the present study, we found that NOX4 mRNA expression was 15-fold higher in the abdominal aorta of ApoE-/- mice compared to wild-type controls, whereas NOX1, NOX2 and XO mRNA levels did not differ. Interestingly, NOX4 protein expression was upregulated in the media, but not in the endothelium of the ApoE-/- mouse aorta, suggesting that NOX4 did not contribute to endothelial dysfunction. Previous studies suggested a role of NOX4 in cell growth, apoptosis, senescence and autophagy of aortic smooth muscle cells during hypercholesterolemia [
53,
58].
Conversely, the expression of NOX1 and NOX2 proteins exhibited upregulation specifically within the endothelium of the ApoE-/- mouse aorta, implying their involvement in the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and subsequent endothelial dysfunction. This increase in NOX1 and NOX2 expression was confined to the aortic endothelium, constituting a minor fraction of the overall cellular volume within the aorta. This observation lends credence to the idea that the absence of elevated mRNA levels for these enzyme isoforms is reasonable, given the localized nature of their upregulation.
Notably, none of the tested prooxidant enzymes displayed elevated mRNA and protein expression levels in the ophthalmic artery from ApoE-/- mice, which is in line with the normal ROS levels and the retained endothelial signaling pathways. Since functional and morphological changes could not be found in the ophthalmic artery of ApoE-/- mice despite marked changes in the aorta, we assume that LOX-1 receptor signaling may be responsible for the difference between these two vascular beds. Previous findings suggested that LOX-1 expression and its translocation into the cell membrane can be triggered by oxLDL itself in some tissues/blood vessels [
27]. In line with these findings, we found that expression of LOX-1 is indeed upregulated in the aorta of ApoE-/- mice. However, in the ophthalmic artery, no such evidence for LOX-1 upregulation in ApoE-/- mice could be found, which may be a possible reason for the resistance of this vessel to chronic hypercholesterolemia. Based on the findings of the present study we propose the following scheme (
Figure 9).
Our findings support a previous study in humans that did not reveal any differences in retrobulbar blood flow velocities between hypercholesterolemic and control subjects although differences in finger nailfold capillary blood flow velocities have been found [
59]. Both studies indicate that retrobulbar vessel function may be more resistant to increased levels of atherogenic lipoproteins than in other vascular beds.
Interestingly, human retinal blood vessels showed reduced vasodilation responses at high cholesterol levels [
8,
9]. However, various anatomical and functional differences exist between retrobulbar and retinal blood vessels, e.g., innervation by autonomic nerve fibers, autoregulation as well as endothelium-dependent vasodilation and compensation mechanisms [
18,
25,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]. Hence, differences regarding the susceptibility of the endothelial cells to high cholesterol levels between retrobulbar blood vessels and retinal arterioles are possible.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.G. and H.L.; methodology, F.B., N.X., C.Y., S.J. and J.K.Z.; software, N.X. and A.G.; validation, A.G., J.K.Z. and A.M.; formal analysis, A.P., A.G. and A.M.; investigation, F.B., C.Y., E.E., N.X., J.K.Z., A.M., S.J. and A.G.; resources, N.P., A.P., H.L. and A.G.; data curation, A.G.; writing—original draft preparation, F.B. and A.G.; writing—review and editing, A.M.; visualization, F.B. and A.G.; supervision, C.M. and A.G.; project administration, A.G.; funding acquisition, N.P. and A.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
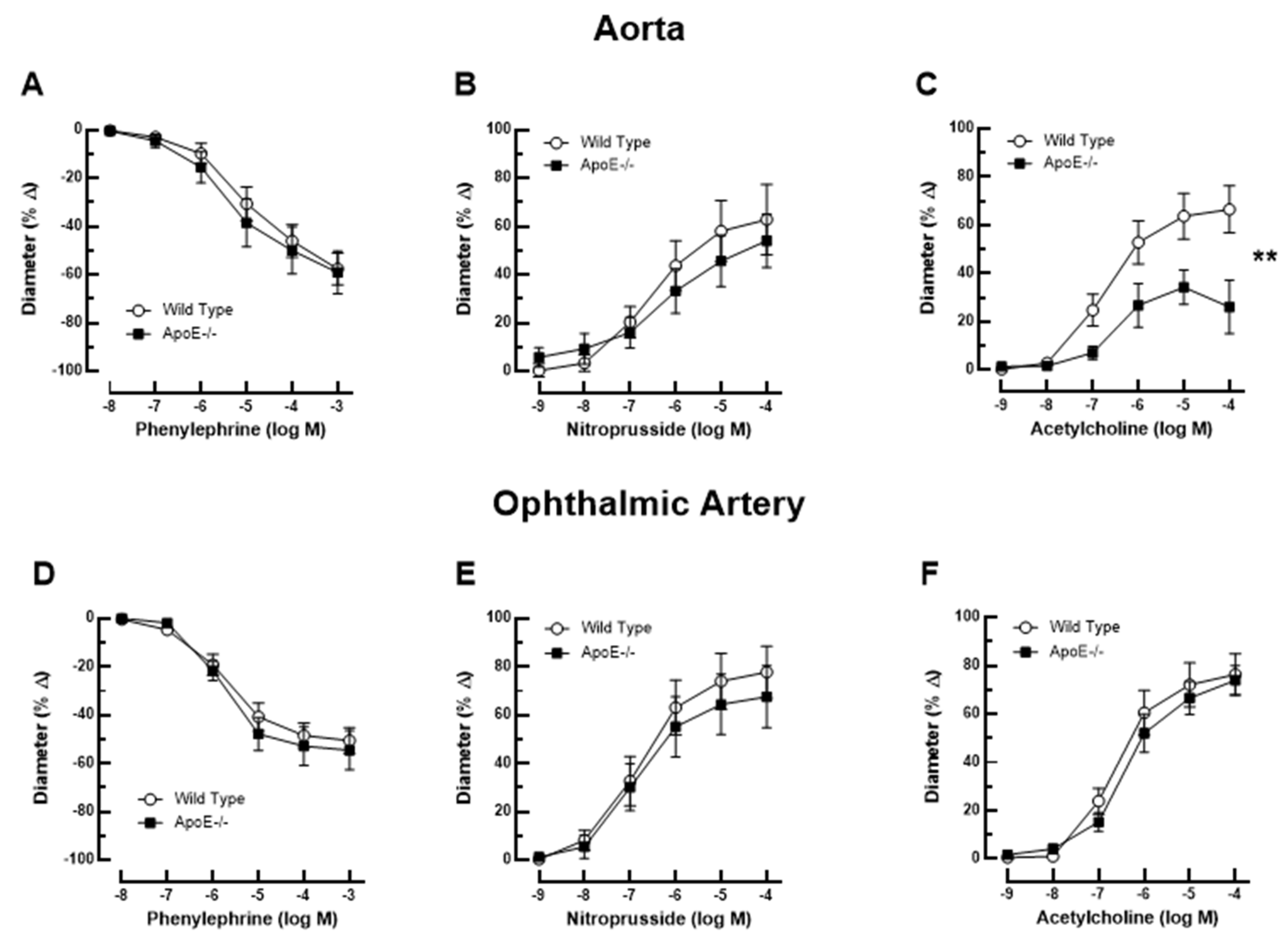
Figure 1.
Responses of the aorta from ApoE-/- and wild-type mice to phenylephrine (A), to nitroprusside (B), and to acetylcholine (C). Of note, reactivity of the aorta to acetylcholine was impaired in ApoE-/- mice. Ophthalmic artery reactivity to phenylephrine (D), to nitroprusside (E) and to acetylcholine (F) did not differ between both mouse genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n=8 per concentration and genotype; **P < 0.01).
Figure 1.
Responses of the aorta from ApoE-/- and wild-type mice to phenylephrine (A), to nitroprusside (B), and to acetylcholine (C). Of note, reactivity of the aorta to acetylcholine was impaired in ApoE-/- mice. Ophthalmic artery reactivity to phenylephrine (D), to nitroprusside (E) and to acetylcholine (F) did not differ between both mouse genotypes. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n=8 per concentration and genotype; **P < 0.01).
Figure 2.
Ophthalmic artery responses of ApoE-/- and wild-type mice to acetylcholine before and after incubation with the non-isoform-selective NOS inhibitor, L-NAME (A), the selective nNOS blocker, TRIM (B), and the selective iNOS inhibitor, aminoguanidine (C). Among these three NOS blockers, only L-NAME markedly blocked responses in ApoE-/- and wild-type mice, indicative of eNOS involvement. The non-isoform-selective COX inhibitor, indomethacin (D), had no effect on cholinergic vasodilation, while combined blockade with L-NAME and indomethacin (E) blocked vasodilation responses to a similar extent as L-NAME alone. The residual portion of the vasodilation response in ophthalmic arteries incubated with L-NAME and indomethacin was almost completely abolished after adding 30 mM of KCl (F), indicative of EDHF involvement. Blockade of the CYP450 and 12/15-lipoxygenase pathways with 17-ODYA (G) and baicalein (H), respectively, as well as of gap junctions with 18α-GA (I) reduced vasodilation responses to a similar extent in L-NAME and indomethacin-incubated ophthalmic arteries of both mouse genotypes, suggesting the contribution of these pathways to vasodilation. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n=8 per concentration and genotype; ### P<0.001, ApoE-/- mice treated versus non-treated; *** P<0.001, wild-type mice treated versus non-treated).
Figure 2.
Ophthalmic artery responses of ApoE-/- and wild-type mice to acetylcholine before and after incubation with the non-isoform-selective NOS inhibitor, L-NAME (A), the selective nNOS blocker, TRIM (B), and the selective iNOS inhibitor, aminoguanidine (C). Among these three NOS blockers, only L-NAME markedly blocked responses in ApoE-/- and wild-type mice, indicative of eNOS involvement. The non-isoform-selective COX inhibitor, indomethacin (D), had no effect on cholinergic vasodilation, while combined blockade with L-NAME and indomethacin (E) blocked vasodilation responses to a similar extent as L-NAME alone. The residual portion of the vasodilation response in ophthalmic arteries incubated with L-NAME and indomethacin was almost completely abolished after adding 30 mM of KCl (F), indicative of EDHF involvement. Blockade of the CYP450 and 12/15-lipoxygenase pathways with 17-ODYA (G) and baicalein (H), respectively, as well as of gap junctions with 18α-GA (I) reduced vasodilation responses to a similar extent in L-NAME and indomethacin-incubated ophthalmic arteries of both mouse genotypes, suggesting the contribution of these pathways to vasodilation. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n=8 per concentration and genotype; ### P<0.001, ApoE-/- mice treated versus non-treated; *** P<0.001, wild-type mice treated versus non-treated).
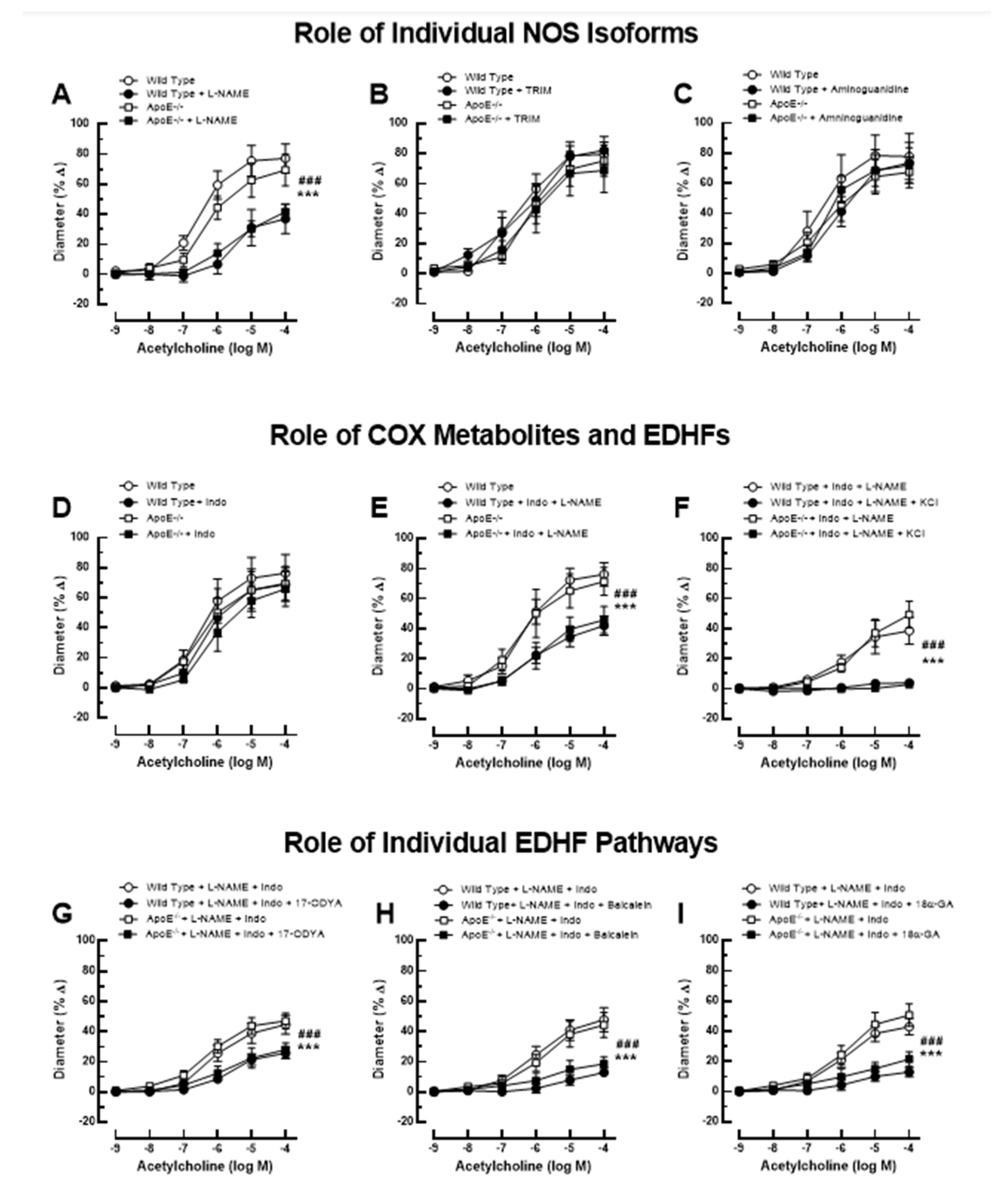
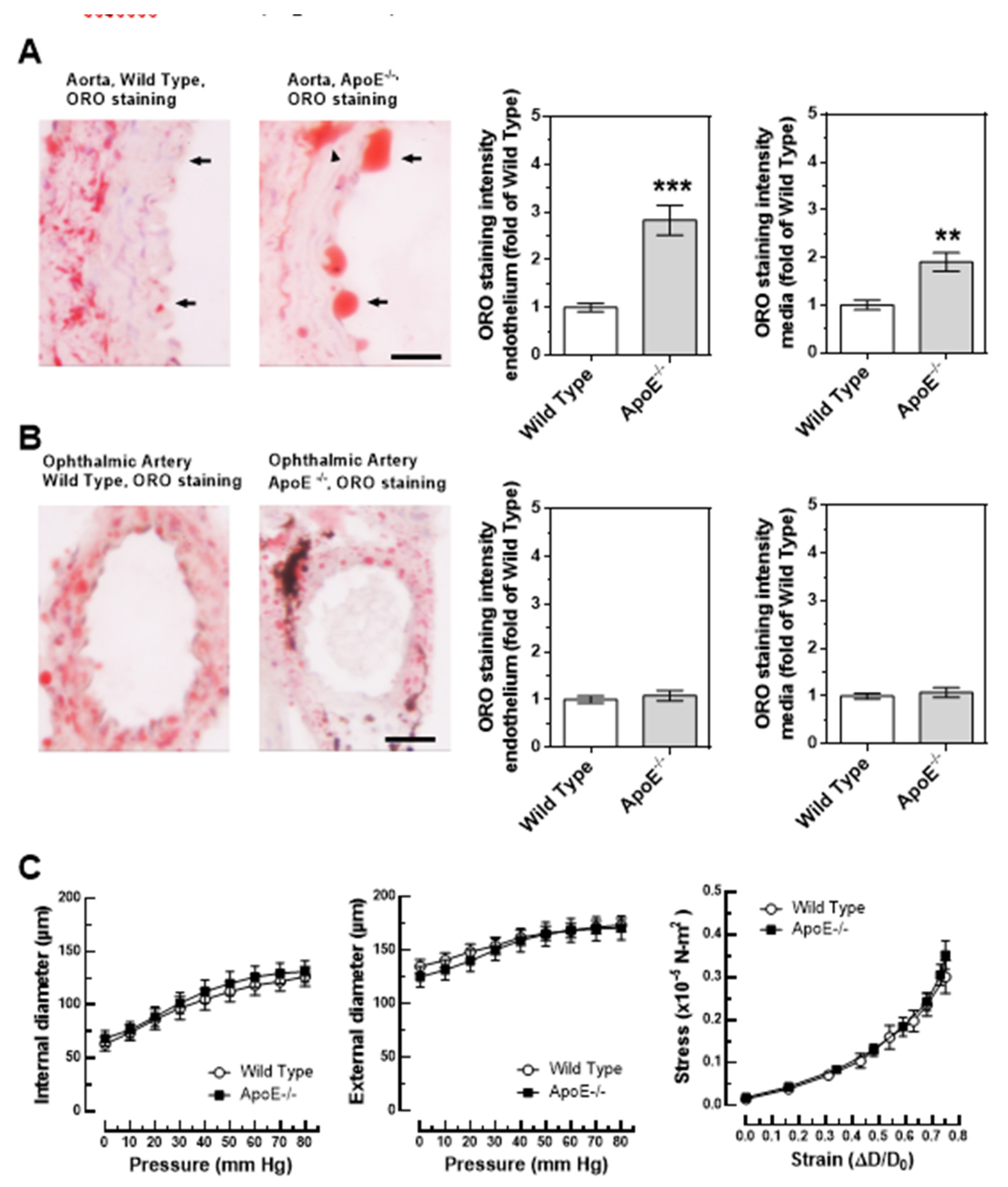
Figure 3.
Lipid content, visualized by Oil Red O (ORO, red color) was markedly increased in the aorta of ApoE-/- mice and was especially pronounced in the endothelium (A). In contrast, lipid content was similar in the ophthalmic artery from wild-type and ApoE-/- mice (B). Relation between vascular internal and external diameter (µm) to the luminal pressure (mmHg), as well as the stress (in ×10−5 N-m²) - strain (in ΔD-D₀) – relation did not differ between ophthalmic arteries of wild type and ApoE-/- mice (C). Data are presented as mean ± SE; *** p < 0.0001; **p < 0.001; the arrows point to the endothelium, the arrowhead points to a lipid-rich lesion in the media; scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 3.
Lipid content, visualized by Oil Red O (ORO, red color) was markedly increased in the aorta of ApoE-/- mice and was especially pronounced in the endothelium (A). In contrast, lipid content was similar in the ophthalmic artery from wild-type and ApoE-/- mice (B). Relation between vascular internal and external diameter (µm) to the luminal pressure (mmHg), as well as the stress (in ×10−5 N-m²) - strain (in ΔD-D₀) – relation did not differ between ophthalmic arteries of wild type and ApoE-/- mice (C). Data are presented as mean ± SE; *** p < 0.0001; **p < 0.001; the arrows point to the endothelium, the arrowhead points to a lipid-rich lesion in the media; scale bar = 20 µm.
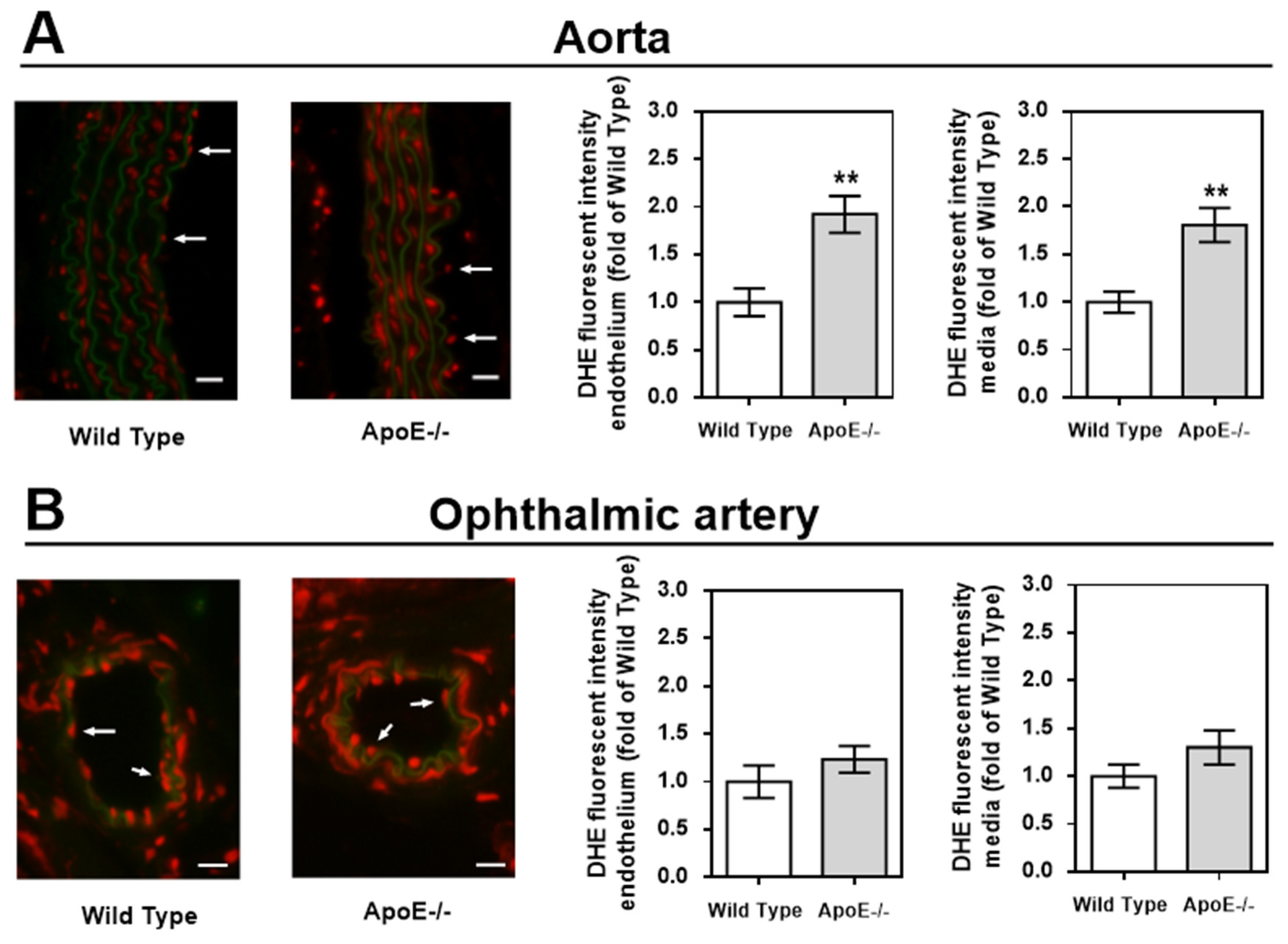
Figure 4.
DHE staining intensity (red color) was markedly increased in the vascular wall of the aorta (A) but not of the ophthalmic artery (B). For each vascular bed and mouse genotype, a representative photograph is presented as a merged picture of the DHE staining and the autofluorescence of the elastic lamina (green) to visualize the localization of cells within the vascular wall. Data are presented as mean ± SE normalized to wild-type controls (n=8 per genotype; **p < 0.01, ApoE-/- versus wild-type mice). Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 4.
DHE staining intensity (red color) was markedly increased in the vascular wall of the aorta (A) but not of the ophthalmic artery (B). For each vascular bed and mouse genotype, a representative photograph is presented as a merged picture of the DHE staining and the autofluorescence of the elastic lamina (green) to visualize the localization of cells within the vascular wall. Data are presented as mean ± SE normalized to wild-type controls (n=8 per genotype; **p < 0.01, ApoE-/- versus wild-type mice). Scale bar = 20 µm.
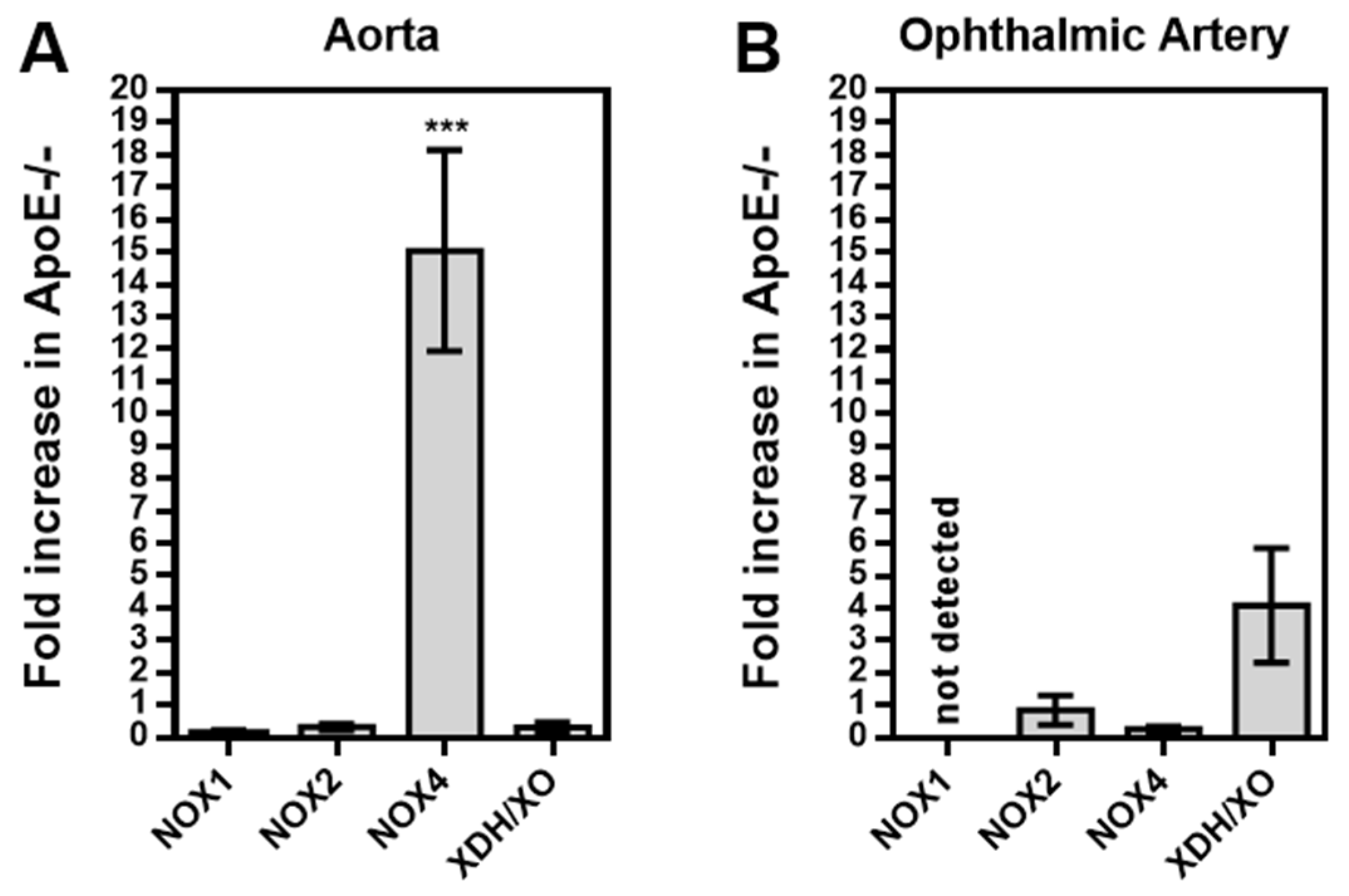
Figure 5.
Messenger RNA expression for the prooxidative redox enzymes NOX1, NOX2, NOX4 and XDH/XO in the aorta (A) and the ophthalmic artery (B) presented as the fold-change (mean ± SE) in ApoE-/- mice versus wild-type controls (aorta: n=8, ophthalmic artery: n=6; ***p < 0.001, ApoE-/- versus wild-type mice).
Figure 5.
Messenger RNA expression for the prooxidative redox enzymes NOX1, NOX2, NOX4 and XDH/XO in the aorta (A) and the ophthalmic artery (B) presented as the fold-change (mean ± SE) in ApoE-/- mice versus wild-type controls (aorta: n=8, ophthalmic artery: n=6; ***p < 0.001, ApoE-/- versus wild-type mice).
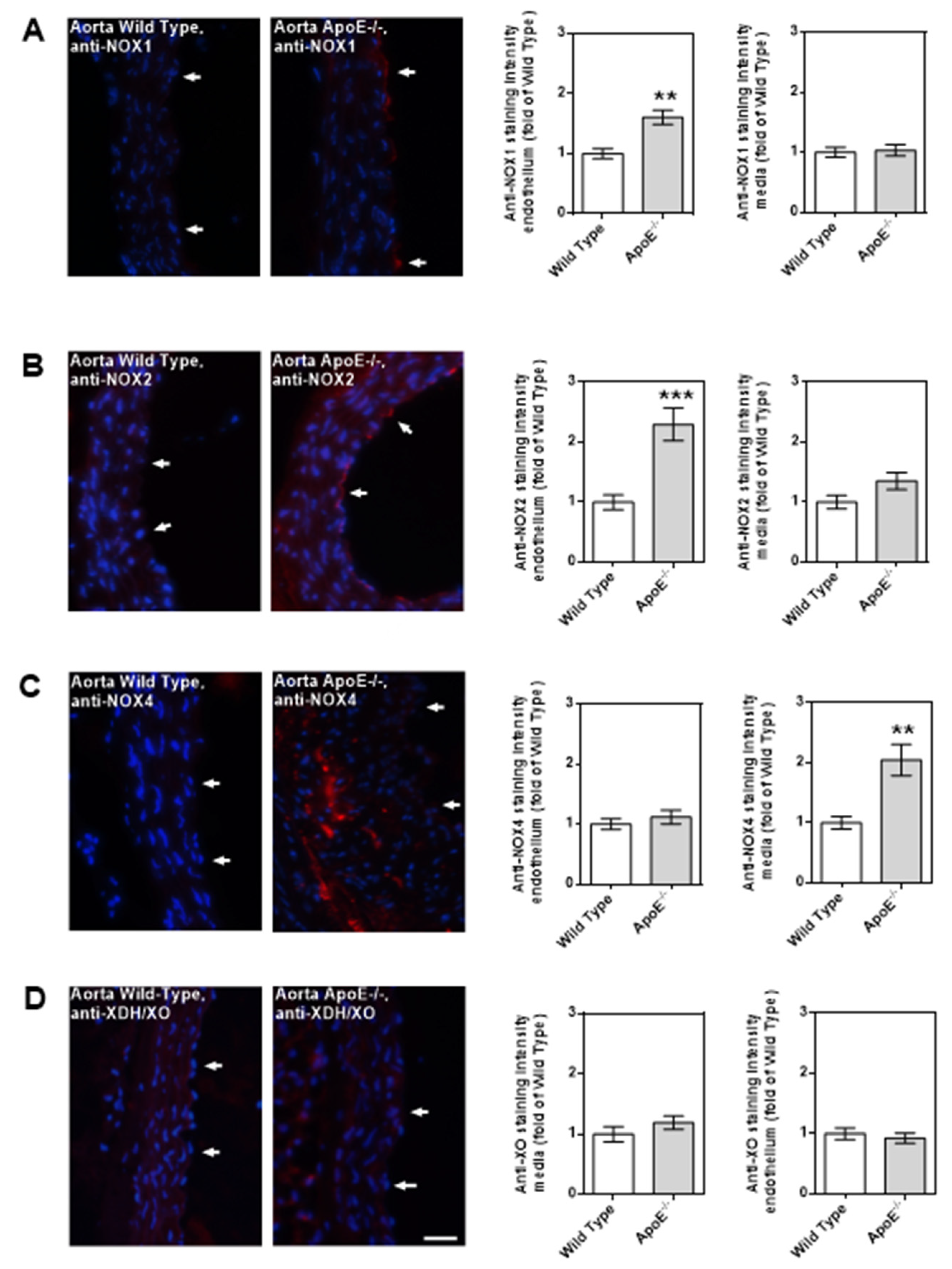
Figure 6.
Immunofluorescence stainings for prooxidative redox enzymes in aortic tissue sections. Immunoreactivity to NOX1 was markedly elevated in the endothelium of ApoE-/- mice (A). Likewise, NOX2 immunoreactivity was pronounced in the ApoE-/- mouse endothelium (B). Interestingly, NOX immunoreactivity was not elevated in the endothelium, but in the media of ApoE-/- mice (C). Immunoreactivity to XDH/XO was negligible in bot wild-type and ApoE-/- mice (D). Data are presented as mean ± SE normalized to wild-type controls (n=8 per genotype; *** < 0.001; **p < 0.01, ApoE-/- versus wild-type mice). The white arrows point to the endothelial layer. Blue: DAPI; Red: Rhodamine Red-X-coupled. Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 6.
Immunofluorescence stainings for prooxidative redox enzymes in aortic tissue sections. Immunoreactivity to NOX1 was markedly elevated in the endothelium of ApoE-/- mice (A). Likewise, NOX2 immunoreactivity was pronounced in the ApoE-/- mouse endothelium (B). Interestingly, NOX immunoreactivity was not elevated in the endothelium, but in the media of ApoE-/- mice (C). Immunoreactivity to XDH/XO was negligible in bot wild-type and ApoE-/- mice (D). Data are presented as mean ± SE normalized to wild-type controls (n=8 per genotype; *** < 0.001; **p < 0.01, ApoE-/- versus wild-type mice). The white arrows point to the endothelial layer. Blue: DAPI; Red: Rhodamine Red-X-coupled. Scale bar = 20 µm.
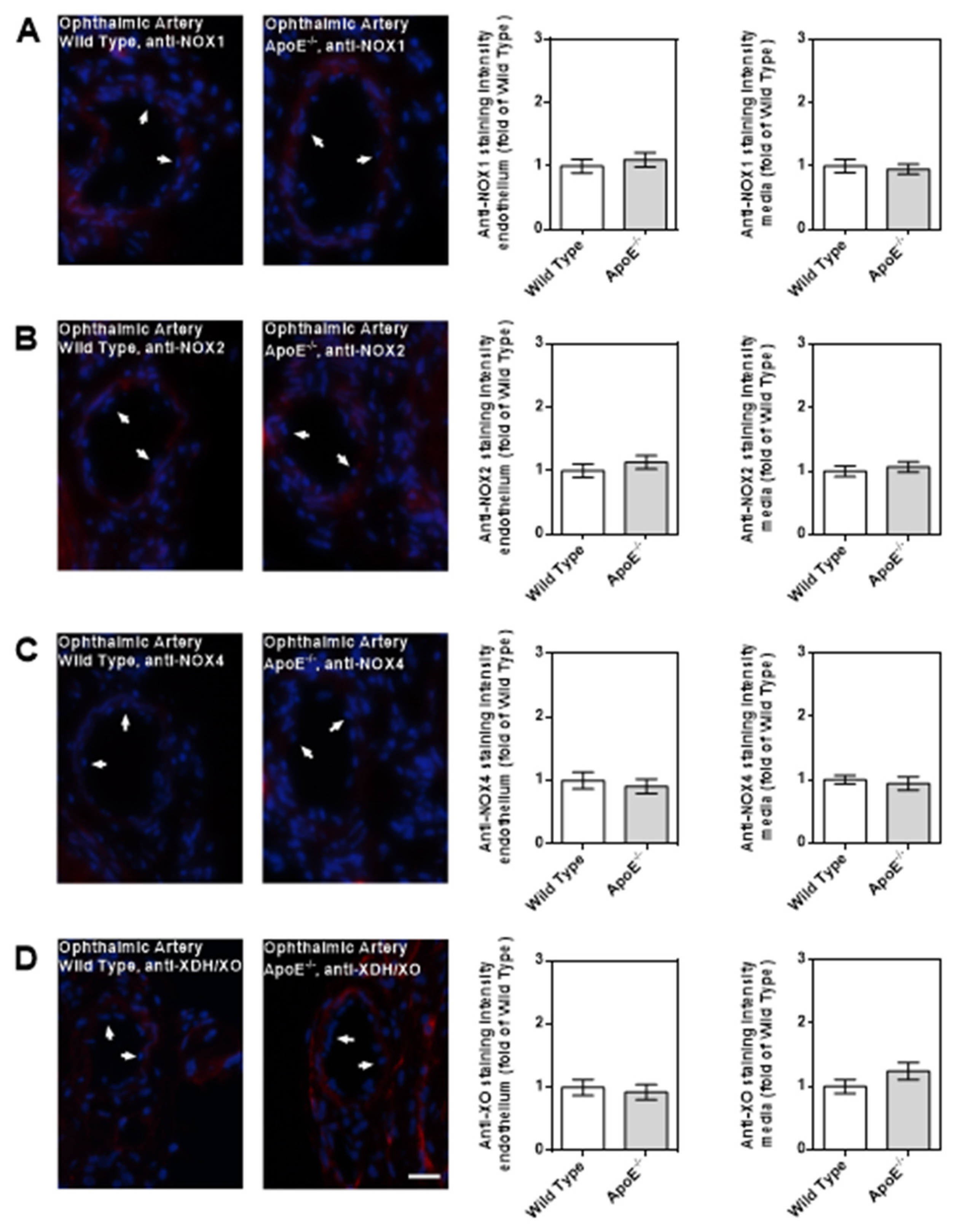
Figure 7.
Immunofluorescence stainings for prooxidative redox enzymes in ophthalmic artery cross-sections. Immunoreactivity to NOX1 (A), NOX2 (B) and to NOX4 (C) was negligible in both wild-type and ApoE-/- mice. Only faint immunoreactivity to XDH/XO was visible in the media and adventitia of the ophthalmic artery but was similar in wild-type and ApoE-/- mice (D). Data are presented as mean ± SE normalized to wild-type controls (n=8 per genotype). The white arrows point to the endothelial layer. Blue: DAPI ; Red: Rhodamine Red-X-coupled. Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 7.
Immunofluorescence stainings for prooxidative redox enzymes in ophthalmic artery cross-sections. Immunoreactivity to NOX1 (A), NOX2 (B) and to NOX4 (C) was negligible in both wild-type and ApoE-/- mice. Only faint immunoreactivity to XDH/XO was visible in the media and adventitia of the ophthalmic artery but was similar in wild-type and ApoE-/- mice (D). Data are presented as mean ± SE normalized to wild-type controls (n=8 per genotype). The white arrows point to the endothelial layer. Blue: DAPI ; Red: Rhodamine Red-X-coupled. Scale bar = 20 µm.
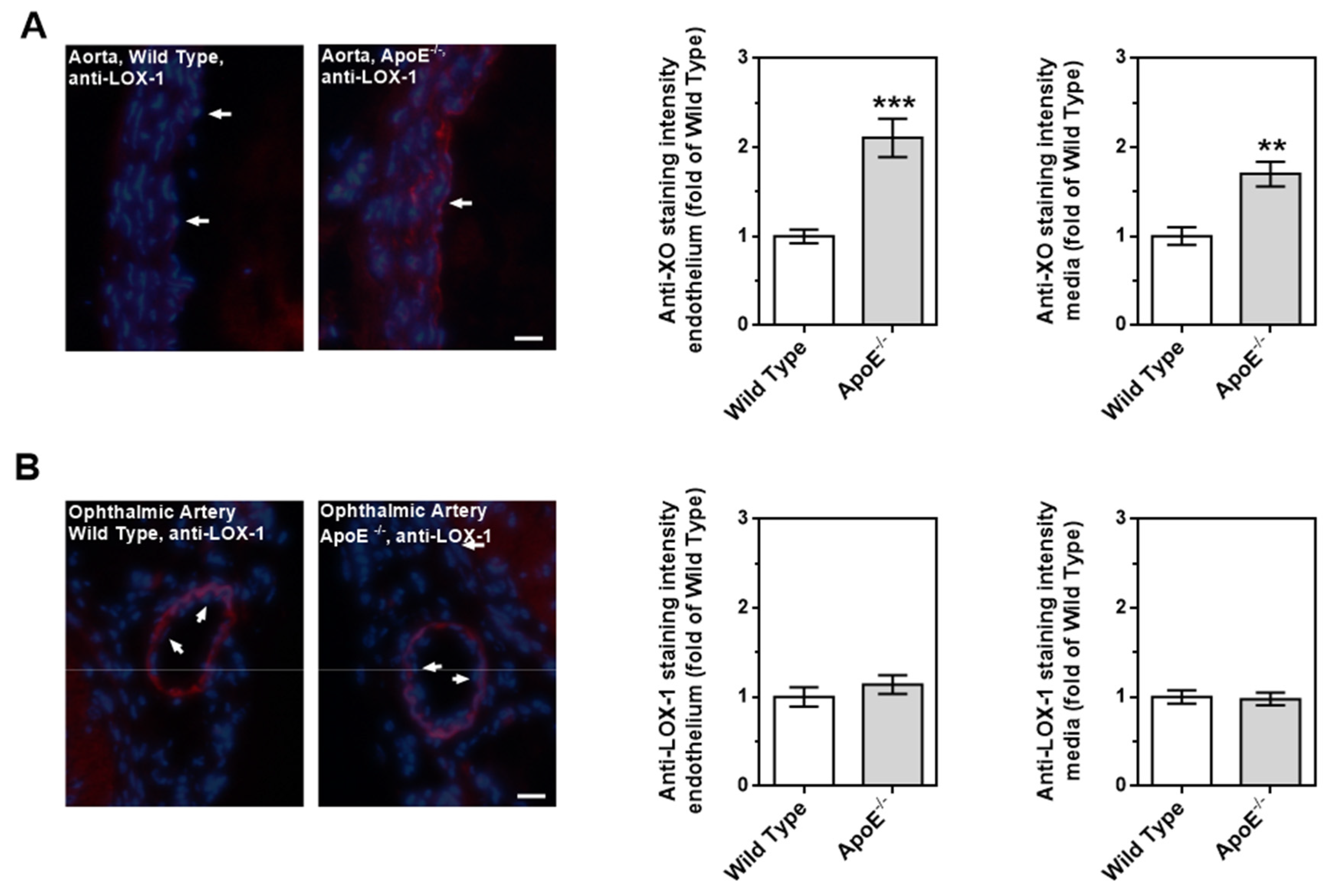
Figure 8.
Expression of LOX-1 detected via immunoreactivity in the aorta and in the ophthalmic artery of ApoE-/- mice. The white arrows indicate the endothelial layer. In the aorta (A), the expression of LOX-1 receptor was particularly increased in the vascular endothelium and in the smooth muscle, whereas in the ophthalmic artery (B) its expression was very low in both endothelium and smooth muscle. Blue: DAPI ; Red: Rhodamine Red-X-coupled. Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 8.
Expression of LOX-1 detected via immunoreactivity in the aorta and in the ophthalmic artery of ApoE-/- mice. The white arrows indicate the endothelial layer. In the aorta (A), the expression of LOX-1 receptor was particularly increased in the vascular endothelium and in the smooth muscle, whereas in the ophthalmic artery (B) its expression was very low in both endothelium and smooth muscle. Blue: DAPI ; Red: Rhodamine Red-X-coupled. Scale bar = 20 µm.
Figure 9.
Intracellular pathways in the vascular endothelium and in the smooth muscle of the Aorta (A) and the ophthalmic artery (B) in ApoE-/- mice. Of note, in the aorta the expression of NOX1 and NOX2, responsible for the ROS-production and for the endothelial dysfunction, was increased in the endothelium, however not in the smooth muscle, where an increased expression and activity of NOX4 could be shown. This suggests that NOX4 plays a role in modification of atherosclerotic plaques in the vascular smooth muscle layer. Unlike in the aorta, in the ophthalmic artery, no LOX-1 upregulation and no increase in ROS production was observed. Moreover, endothelium-dependent vasodilatory mechanisms were not altered in the ophthalmic artery. OxLDL: oxidative low density lipoprotein; LOX-1: lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor; NOX: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase; ROS: reactive oxygen species; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Kir: inwardly rectifying potassium channels; 12/15 LOX: 12/15 lipoxygenase; CYP450: cytochrome p450 monoxygenase; NO: nitric oxide; sGC: soluble guanylate cyclase; cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PKG: protein kinase G.; GJ: gap junctions; EET: epoxyecosatrienoic acid; 12-HETE: 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid.
Figure 9.
Intracellular pathways in the vascular endothelium and in the smooth muscle of the Aorta (A) and the ophthalmic artery (B) in ApoE-/- mice. Of note, in the aorta the expression of NOX1 and NOX2, responsible for the ROS-production and for the endothelial dysfunction, was increased in the endothelium, however not in the smooth muscle, where an increased expression and activity of NOX4 could be shown. This suggests that NOX4 plays a role in modification of atherosclerotic plaques in the vascular smooth muscle layer. Unlike in the aorta, in the ophthalmic artery, no LOX-1 upregulation and no increase in ROS production was observed. Moreover, endothelium-dependent vasodilatory mechanisms were not altered in the ophthalmic artery. OxLDL: oxidative low density lipoprotein; LOX-1: lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor; NOX: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase; ROS: reactive oxygen species; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; Kir: inwardly rectifying potassium channels; 12/15 LOX: 12/15 lipoxygenase; CYP450: cytochrome p450 monoxygenase; NO: nitric oxide; sGC: soluble guanylate cyclase; cGMP: cyclic guanosine monophosphate; PKG: protein kinase G.; GJ: gap junctions; EET: epoxyecosatrienoic acid; 12-HETE: 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid.
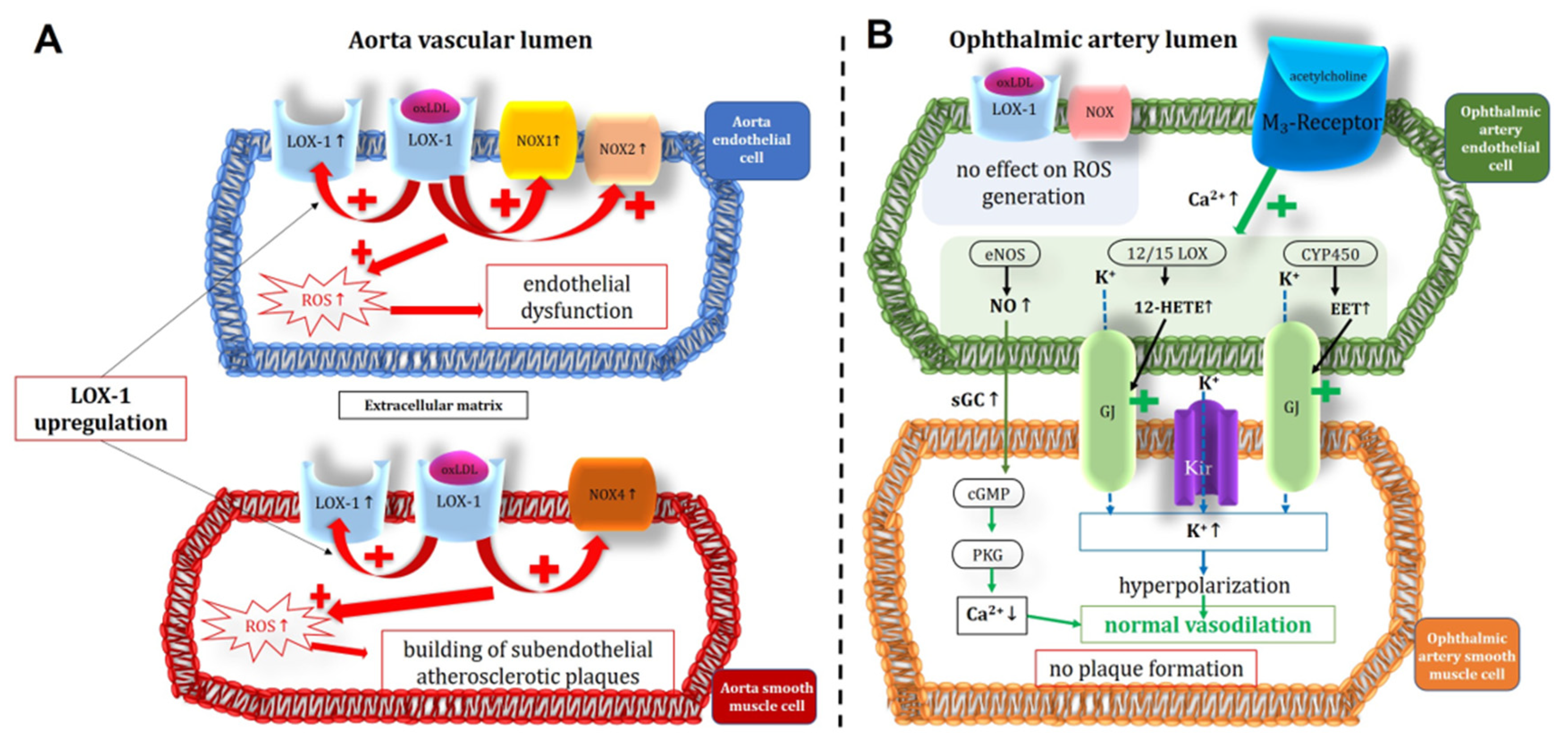
Table 1.
Primer sequences used for quantitative PCR analysis.
Table 1.
Primer sequences used for quantitative PCR analysis.
| Gene |
Accession Number |
Forward |
Reverse |
| NOX1 |
NM_172203.2 |
GGTTGGGGCTGAACATTTTTC |
TCGACACACAGGAATCAGGAT |
| NOX2 |
NM_007807.5 |
GCACCTGCAGCCTGCCTGAATT |
TTGTGTGGATGGCGGTGTGCA |
| NOX4 |
NM_015760.5 |
GGCTGGCCAACGAAGGGGTTAA |
GAGGCTGCAGTTGAGGTTCAGGACA |
| XDH |
NM_011723.3 |
CGATGACGAGGACAACGGTA
CACCCGCGAGCACAGCTTCTTT |
TGAAGGCGGTCATACTTGGAG
AATACAGCCCGGGGAGCATC |
| ACTB |
NM_007393.5 |
Table 2.
Specifications of primary antibodies used for immunofluorescence studies.
Table 2.
Specifications of primary antibodies used for immunofluorescence studies.
| Target antigen |
Catalog number, company |
Species, clonality |
Dilution |
| NOX1 |
ab131088, Abcam, Waltham, MA, USA |
Rabbit, polyclonal |
1:200 |
| NOX2 |
ab129068, Abcam, Waltham, MA, USA |
Rabbit, monoclonal |
1:200 |
| NOX4 |
ab109225, Abcam, Waltham, MA, USA |
Rabbit, monoclonal |
1:200 |
| XDH/XO |
NBP2-75717, Bio-Techne GmbH, Wiesbaden, Germany |
Rabbit, monoclonal |
1:50 |
| LOX-1 |
bs-2044R, BIOZOL Diagnostica Vertrieb GmbH, Eching, Germany |
Rabbit, polyclonal |
1:100 |
Table 3.
Blood pressure and total serum cholesterol in wild-type and ApoE-/- mice. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 8 per genotype).
Table 3.
Blood pressure and total serum cholesterol in wild-type and ApoE-/- mice. Data are presented as mean ± SE (n = 8 per genotype).
| Systemic parameters |
Wild Type |
ApoE-/- |
P value |
| Systolic blood pressure (in mmHg) |
103 ± 4.50 |
112 ± 4.85 |
0.1678 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (in mmHg) |
73.2 ± 3.90 |
65.0 ± 5.61 |
0.2521 |
| Mean blood pressure (in mmHg) |
82.6 ± 3.89 |
80.5 ± 4.78 |
0.7354 |
| Total serum cholesterol (mg/dL) |
149 ± 5.79 |
501 ± 14.9 |
<0.0001 |