Submitted:
22 August 2023
Posted:
22 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
3. Proposed Framework
| Algorithm 1: Comparative Analysis of Classifier Algorithms |
|
Input: LFW dataset images (X), corresponding labels (y) Output: Best performing classifier with its accuracy |
| 1: Upload images (X) and labels (Y) from the LFW dataset. 2: PCA features are extracted. Determine the number of principal components (n_components). Perform PCA on the images (X) using n_components and whiten=True. Reduce the image dimensions by transforming it to a pixelated representation (X_pca). 3. Divide the data into testing and training sets. 4. Create multiple classifiers and train them: Initialize SVM, Random Forest, K-Nearest Neighbor, and Neural Network classifier objects. 5. Create a dictionary 'results' to store accuracy data. 6. For each of the classifiers in 'classifiers': a. Use X_train and Y_train to train the classifier. b. Apply the trained classifier to predict X_test labels. c. Calculate accuracy by comparing y_test with y_predicted labels (y_pred). d. Keeping accuracy in a data table called 'results' with classifier names as keys. 7. Compare the performance of the classifiers: 8. Display the accuracy of the best classifier. |
3.1. Dimensional reduction
| Algorithm 2: PCA-Based Feature Extraction |
|
Input: X (image data), n_components Output: X_pca (transformed feature matrix) |
|
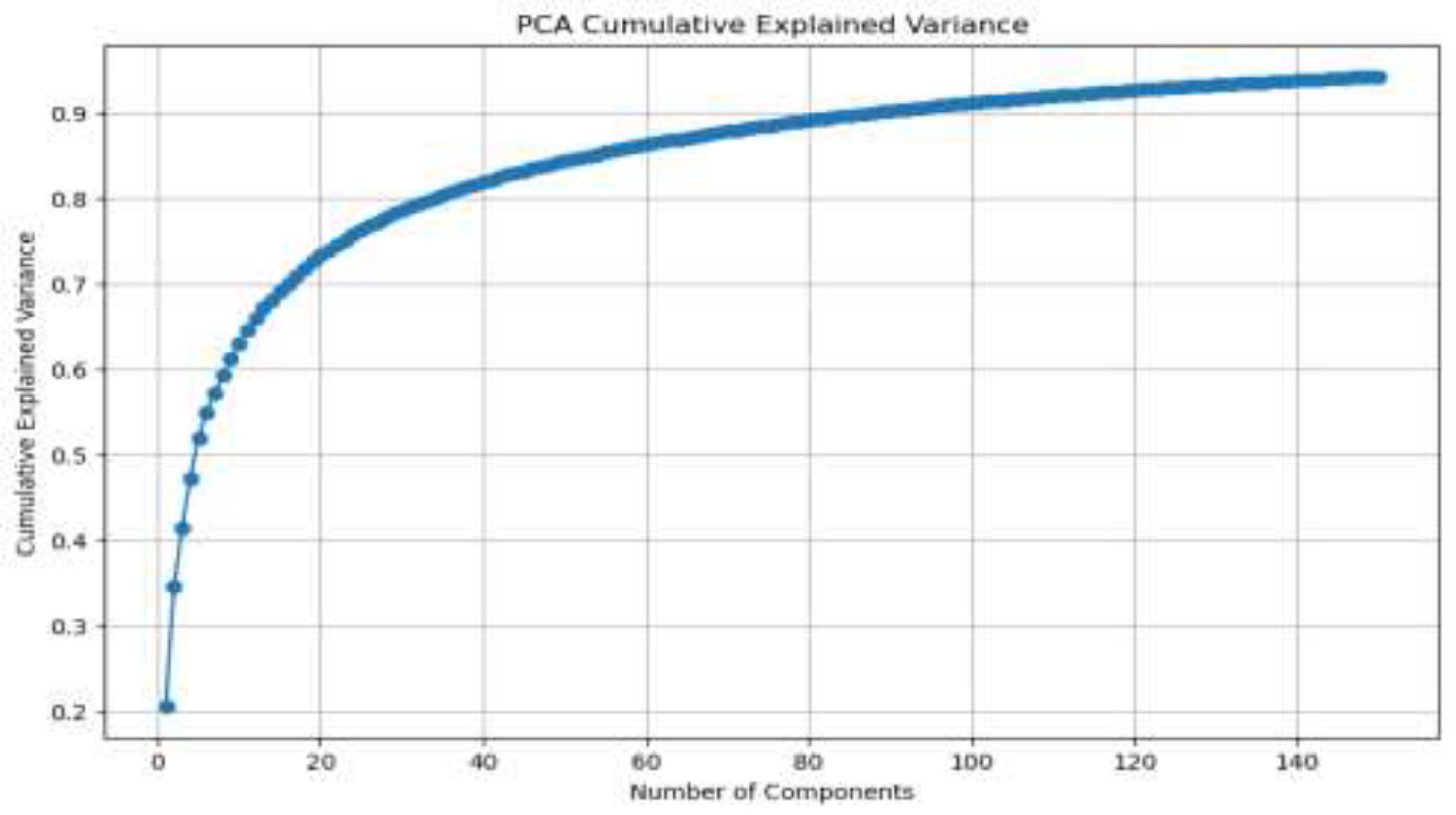
3.2. Algorithms
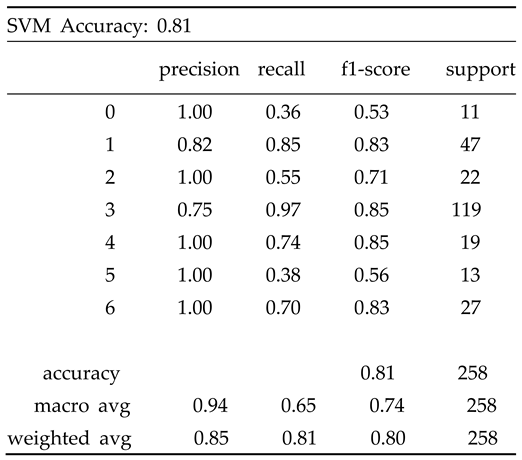
| Algorithm 3: Support Vector Machine (SVM) [22] |
|
Input: X_train_pca, y_train (training labels), X_test_pca Output: y_pred (predicted labels), accuracy |
|
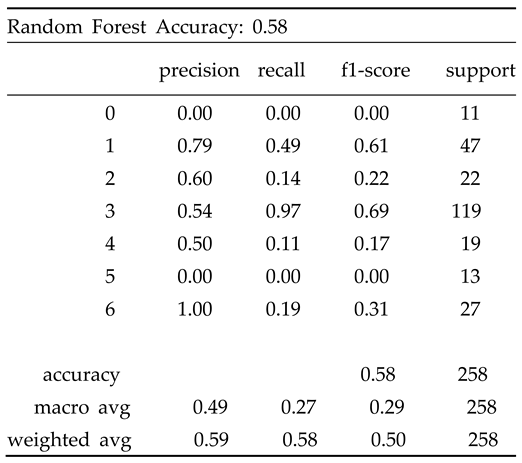
| Algorithm 4: Random Forest Classifier [23] |
|
Input: X_train_pca, y_train (training labels), X_test_pca Output: y_pred (predicted labels), accuracy |
| 1. Set the default parameters for the Random Forest classifier. 2. Use the X_train_pca and Y_train functions to train the Random Forest classi-fier. 3. Utilize the Random Forest classifier to predict labels for X_test_pca. 4. Calculate accuracy using accuracy_score and comparing y_test and y_pred. 5. Create classification report for y_test and y_pred using classifica-tion_report. 4. Get y_pred, accuracy, and classification_report. |
| Algorithm 5: K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) [24] |
|
Input: X_train_pca, y_train (training labels), X_test_pca Output: y_pred (predicted labels), accuracy |
| 1. Set the default parameters for the Random Forest classifier. 2. Use the X_train_pca and Y_train functions to train the Random Forest classi-fier. 3. Utilize the Random Forest classifier to predict labels for X_test_pca. 4. Calculate accuracy using accuracy_score and comparing y_test and y_pred. 5. Create classification report for y_test and y_pred using classifica-tion_report. 4. Get y_pred, accuracy, and classification_report. |
| Algorithm 5: Neural Network [25] |
|
Input: X_train_pca, y_train (training labels), X_test_pca Output: y_pred (predicted labels), accuracy |
|
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. LFW Database
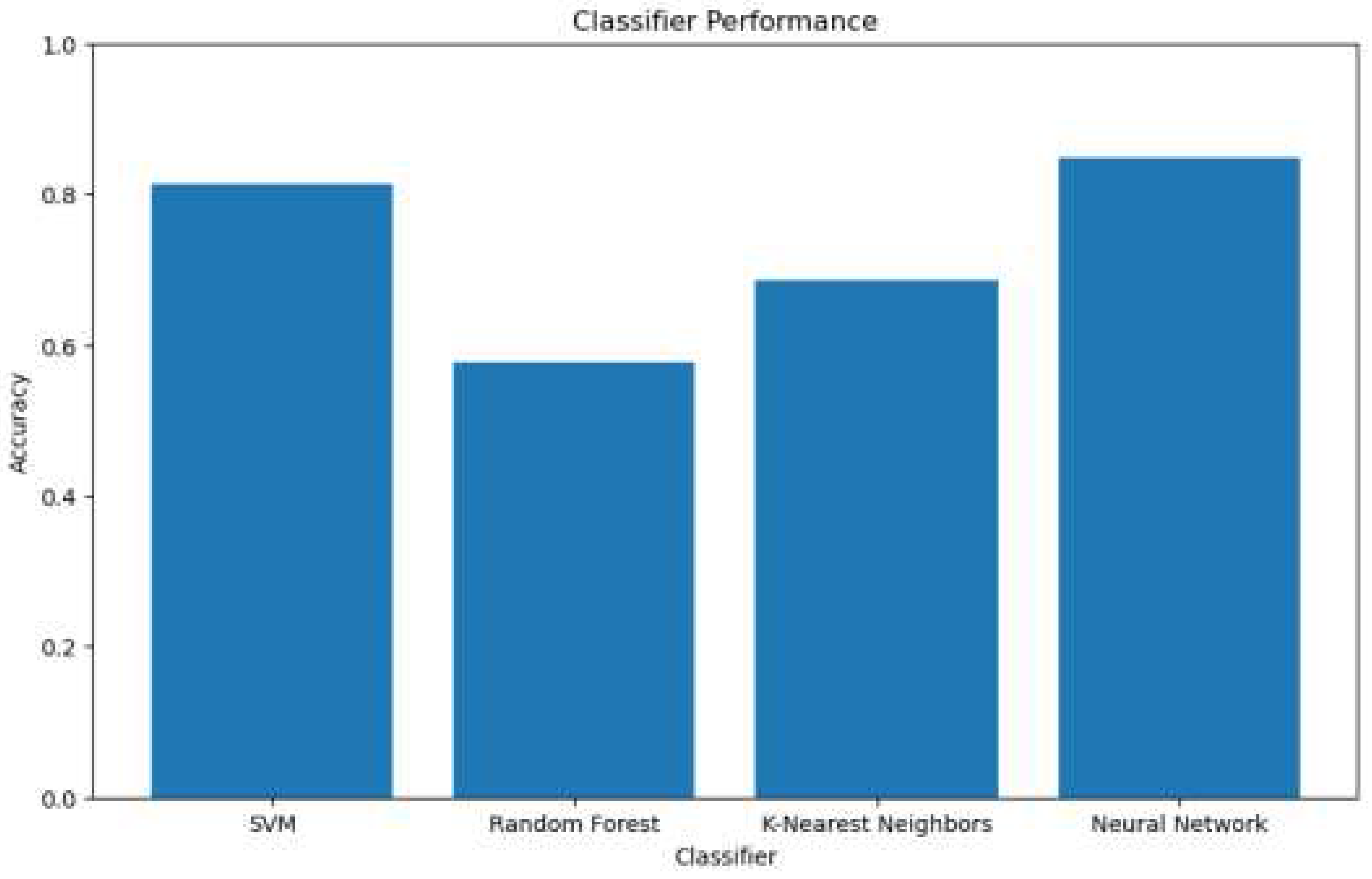
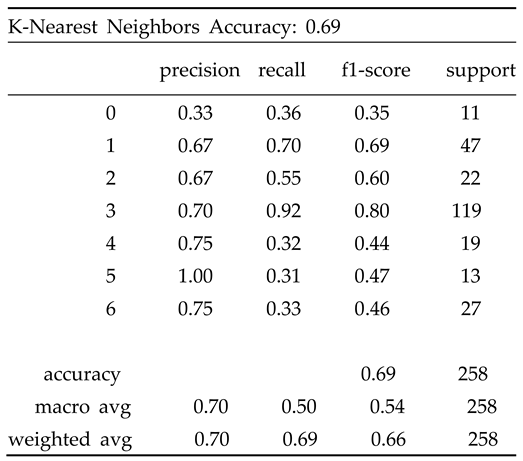
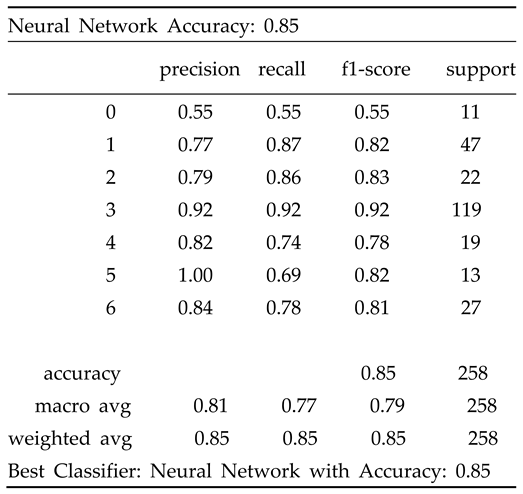
4.2. Result
 |
5. Conclusions
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poon, Bruce, M. Ashraful Amin, and Hong Yan. "Performance evaluation and comparison of PCA Based human face recognition methods for distorted images." International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2011,2, 245-259. [CrossRef]
- Karanwal, S. A comparative study of 14 state of art descriptors for face recognition. Multimedia Tools and Applications. 2021 Mar;80(8):12195-234. [CrossRef]
- Malakar, S., Chiracharit, W., Chamnongthai, K. and Charoenpong, Masked face recognition using principal component analysis and deep learning. In 18th International conference on electrical engineering/electronics, computer, telecommunications and information technology (ECTI-CON),785-788, May, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Sundararajan K, Woodard DL. Deep learning for biometrics: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR). 2018,51(3):1-34. [CrossRef]
- Liu, Bing, Xuchu Yu, Pengqiang Zhang, Anzhu Yu, Qiongying Fu, and Xiangpo Wei. "Supervised deep feature extraction for hyperspectral image classification." IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing 56, 2017, 4, 1909–1921. [CrossRef]
- Sagi O, Rokach L. Ensemble learning: A survey. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. 2018, 8, 4,1249.
- Kim SK, Park YJ, Toh KA, Lee S. SVM-based feature extraction for face recognition. Pattern Recognition. 2010,43(8),2871-81. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Li Y, Song Y, Rong X. Facial expression recognition based on random forest and convolutional neural network. Information. 2019, 10(12), 375. [CrossRef]
- Almabdy S, Elrefaei L. Deep convolutional neural network-based approaches for face recognition. Applied Sciences. 2019 Oct 17;9(20):4397. [CrossRef]
- Akbulut Y, Sengur A, Guo Y, Smarandache F. NS-k-NN: Neutrosophic set-based k-nearest neighbors classifier. Symmetry. 2017,9(9):179. [CrossRef]
- Minaee S, Abdolrashidi A, Su H, Bennamoun M, Zhang D. Biometrics recognition using deep learning: A survey. Artificial Intelligence Review. 2023,1-49. [CrossRef]
- Lei Z, Liao S, Pietikäinen M, Li SZ. Face recognition by exploring information jointly in space, scale and orientation. IEEE transactions on image processing. 2010,20(1),247-56. [CrossRef]
- Song F, Guo Z, Mei D. Feature selection using principal component analysis. In2010 international conference on system science, engineering design and manufacturing informatization 2010 Nov 12,1, 27-30. IEEE. [CrossRef]
- Almabdy SM, Elrefaei LA. An overview of deep learning techniques for biometric systems. Artificial Intelligence for Sustainable Development: Theory, Practice and Future Applications. 2021:127-70. [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta D, Roy A, Nag A. Advances in user authentication. Cham, Switzerland: Springer International Publishing; 2017 Aug 22.
- Phillips PJ, Wechsler H, Huang J, Rauss PJ. The FERET database and evaluation procedure for face-recognition algorithms. Image and vision computing. 1998 Apr 27;16(5):295-306. [CrossRef]
- Ayesha S, Hanif MK, Talib R. Overview and comparative study of dimensionality reduction techniques for high dimensional data. Information Fusion. 2020,1;59:44-58. [CrossRef]
- Singhal N, Ganganwar V, Yadav M, Chauhan A, Jakhar M, Sharma K. Comparative study of machine learning and deep learning algorithm for face recognition. Jordanian Journal of Computers and Information Technology. 2021,1;7(3). [CrossRef]
- Razzak MI, Naz S, Zaib A. Deep learning for medical image processing: Overview, challenges and the future. Classification in BioApps: Automation of Decision Making. 2018,323-50.
- Bailey KO, Okolica JS, Peterson GL. User identification and authentication using multi-modal behavioral biometrics. Computers & Security. 2014 Jun 1;43:77-89. [CrossRef]
- Wang PS, editor. Pattern recognition, machine intelligence and biometrics. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2011 Dec 27.
- Wang L, editor. Support vector machines: theory and applications. Springer Science & Business Media; 2005.
- Belgiu M, Drăguţ L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing. 2016,114:24-31. [CrossRef]
- Peterson LE. K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia. 2009 Feb 21;4(2):1883. Peterson LE. K-nearest neighbor. Scholarpedia. 2009,4(2),1883.
- Pinkus, A. Approximation theory of the MLP model in neural networks. Acta numerica. 1999, 8, 143–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang GB, Mattar M, Berg T, Learned-Miller E. Labeled faces in the wild: A database forstudying face recognition in unconstrained environments. InWorkshop on faces in'Real-Life'Images: detection, alignment, and recognition 2008 Oct.


 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




