1. Introduction
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is defined as idiopathic (IAP) when the aetiology is unclear after a full clinical assessment and comprehensive diagnostic investigation, which includes imaging exams such as transabdominal ultrasound (US) and computed tomography (CT), and a comprehensive panel of laboratory tests comprising calcium and triglycerides levels [
1].
The most common causes of AP are gallstones, alcohol, chronic pancreatitis and other pancreatic parenchymal, ductal and ampullary disorders, followed by pancreatic neoplasms along with hypertriglyceridemia, hypercalcemia and drug-related pancreatitis. The aetiology of AP remains unclear in approximately 10-30% of patients, and these cases are defined as IAP [
2,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Determining the aetiology of AP can be challenging especially in those patients who do not have a significant history of alcohol use and in those who do not exhibit evidence of gallstone disease. During the initial workup, several causes for pancreatitis may be missed despite a timely diagnostic approach with conventional imaging techniques and routine laboratory tests. Therefore, in clinical settings of unexplained, A.P.; advanced imaging techniques and endoscopic procedures are often considered.
Although not always used primarily for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in biliary disorders, EUS remains the cornerstone of the diagnostic and staging algorithm for various lesions of the gastrointestinal tract and has evolved as one of the most accurate imaging options in the evaluation of several pancreatic diseases [
6,
7,
8,
9], In prospective studies, EUS has been shown to reliably identify the cause in up to 79% of patients after a single episode of, A.P. Commonly detected aetiologies include choledocholithiasis, biliary sludge, chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatic tumour undiscovered on cross-sectional imaging, and for this reason, EUS is usually recommended in individuals of 40 years of age or older with AP and no identifiable aetiology [
1,
10]. There is no definitive data on risks and benefits of immediate endoscopic examination in the evaluation of AP when no causative aetiology may be directly identified. In accordance with current guidelines, patients with possible IAP should be referred to centres of expertise for pancreatic diseases to enable a more accurate aetiological investigation [
10,
11].
In the present study, we aimed to review the role of EUS in the diagnosis of IAP, discussing the accuracy, timing and safety of EUS in different clinical settings and the possible future perspectives derived from the recent technological advances and improved endoscopic devices.
2. Materials and Methods
This review was performed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines. A systematic literature search was conducted to identify relevant studies for this review. An online search was conducted using PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library. Articles were comprehensively searched using appropriate keywords and MeSH terms related to the use of EUS for identifying the actual cause of IAP; search terms included the following: “idiopathic acute pancreatitis” AND “endoscopic ultrasound” OR “endoscopic ultrasonography” OR “EUS” OR “endosonography” OR “echoendoscopy”. The search was limited to articles published in English from the initial reports of the diagnostic application of EUS in the clinical setting in 1995 through April 2023.
All prospective and retrospective studies and systematic reviews that involved patients diagnosed with IAP and utilized EUS as a diagnostic modality were considered for inclusion. Letters, editorials, short reviews, and conference abstracts were excluded. Data extraction was independently performed by four authors (CF, RL, PA, AA) using a standardized data extraction form. Any discrepancies or disagreements in data extraction were resolved through discussion and consensus among the four authors who performed the search.
3. Results
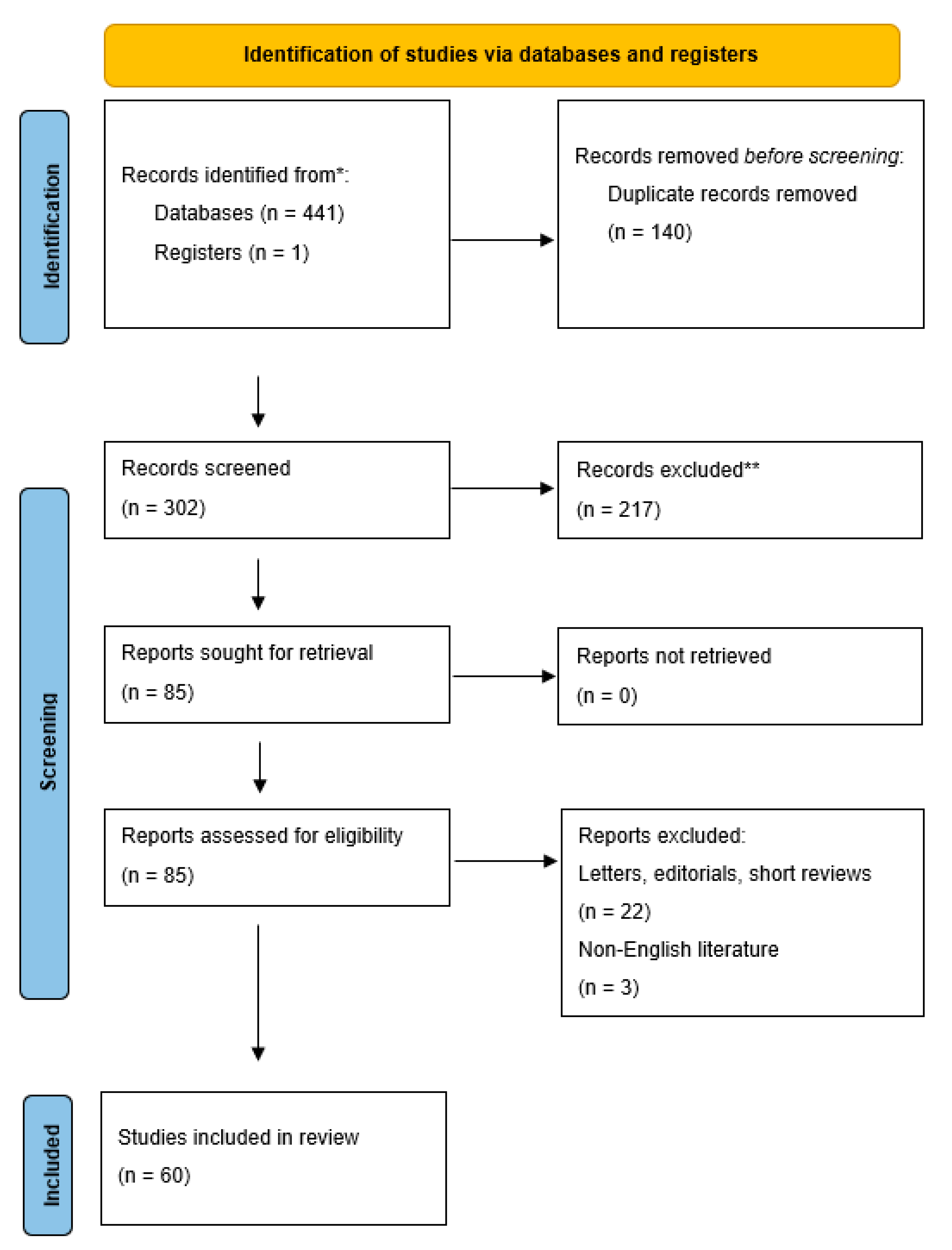
From a total of 302 studies, 60 clinical reports were finally included in this review (
Figure 1).
3.1. Role of EUS in IAP
EUS is a minimally invasive procedure that combines endoscopy and high-frequency ultrasound to provide direct visualization of the pancreas and the surrounding anatomical structures, including the biliary system, the Vater papilla, the pancreatic duct, and the duodenal wall. EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration and biopsy (EUS-FNA and FNB) further enable sampling of pancreatic tissue and fluid, aiding in diagnosis of pancreatic diseases. EUS can also be performed in conjunction with Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) to treat the conditions diagnosed with the EUS. EUS is a specialized procedure that requires skilled endoscopists with experience in pancreatic imaging and interventions. It is essential to have access to a well-equipped endoscopy unit and experienced medical professionals for the procedure[
9,
10,
11],
Several important causes of AP initially diagnosed as idiopathic can be identified through EUS. These include microlithiasis in almost 30-40% of patients; other aetiologies potentially detectable by EUS are small common bile duct stones,
pancreas divisum, small pancreatic tumours, pancreatic duct strictures, and sphincter of Oddi dysfunction [
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. EUS has also been useful in identifying subtle structural abnormalities, such as choledochal cysts, cystic dystrophy of the duodenal wall, and ampullary stenosis, which may contribute to pancreatitis development, and pancreatic parasites [
21,
22]. Additionally, EUS-FNA can be used to support the diagnosis of autoimmune pancreatitis, ruling out malignancy and guiding appropriate management [
23,
24].
EUS was confirmed in all studies included in this review as a valuable tool for evaluating patients with IAP, where the exact cause cannot be determined after a comprehensive clinical, laboratory, and imaging workup. While MRI and CT can identify most of the pancreatic parenchyma and duct abnormalities, they usually do not accurately detect microlithiasis. Current IAP/APA (International Association of Pancreatology and American Pancreatic Association) guidelines suggest that EUS should be performed in IAP even after the first episode, as it can identify the aetiology and potential complications of AP [
10]. EUS and MRCP should both be used in the diagnostic workup of IAP. EUS has a higher diagnostic accuracy in the aetiological diagnosis of IAP, whereas MRCP or secretin enhanced MRCP (S-MRCP) are superior to EUS in diagnosing a possible anatomic alteration in the biliopancreatic duct system [
25,
36,
37,
38,
39,
40].
3.2. Optimal timing for EUS in IAP
In all studies EUS is never recommended as a first-line investigation but rather as a second-line screening procedure or as a follow-up procedure when the initial workup is inconclusive. In particular, EUS is indicated when conventional imaging studies, such as abdominal ultrasound and CT fail to identify the cause of AP [
10,
25].
There is no specific optimal timing for performing EUS after the onset of, A.P. However, it is generally recommended to perform EUS within the first few weeks when the acute phase of pancreatitis has resolved; this is done to avoid potential complications of the procedure. However, in severe AP cases it is possible to anticipate EUS, particularly in those patients with recurrent AP and in those with a high likelihood of having structural abnormalities not identified by standard imaging [
26,
27,
28].
3.3. Role of EUS in biliary pancreatitis
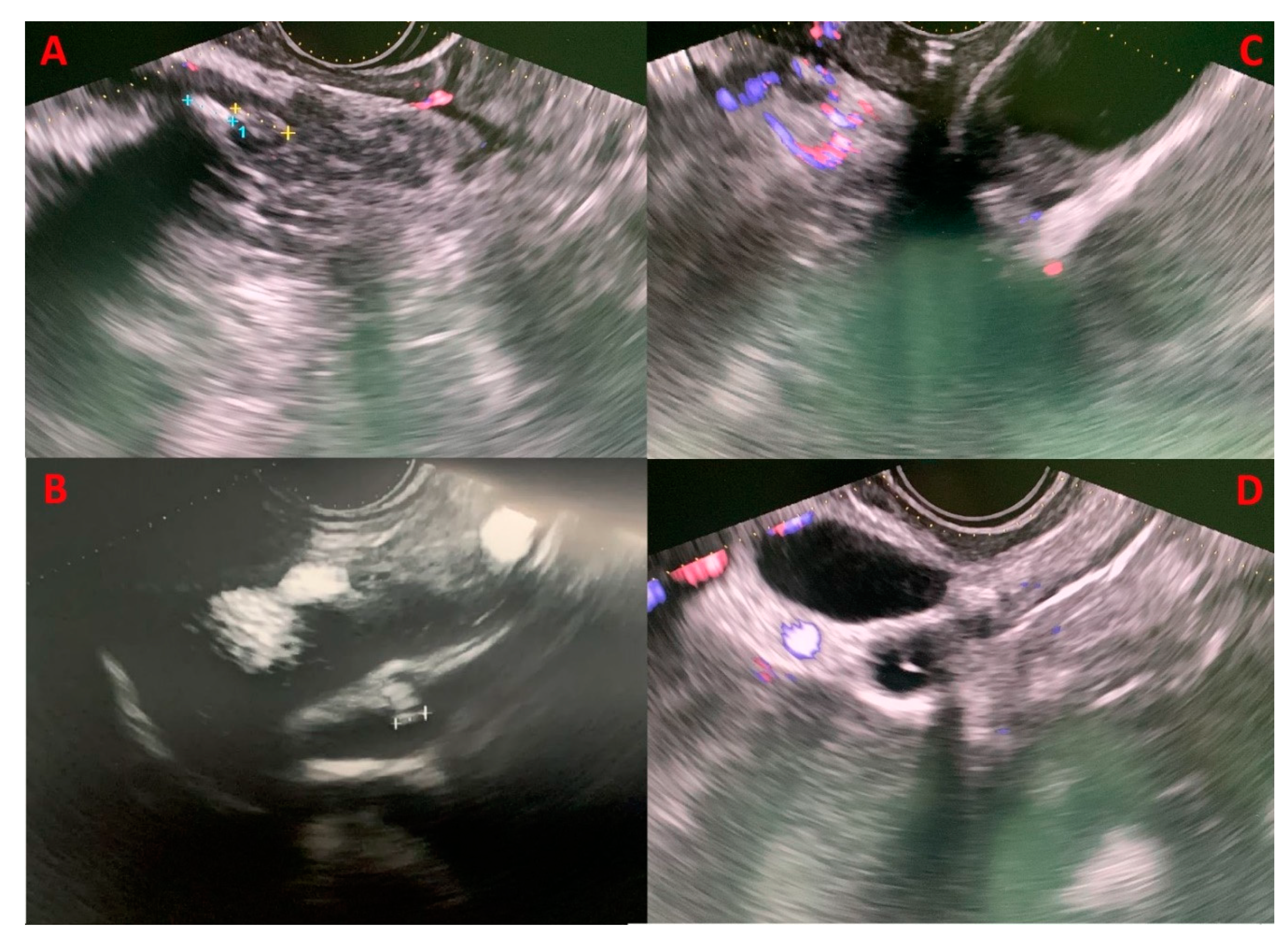
Recent data suggested that with EUS, a biliary aetiology could be established in 37% of IAP patients [
23,
25,
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46,
47] (
Figure 2). When a biliary cause is found, it should be treated with ERCP, laparoscopic cholecystectomy (LC) or both. Some centres even recommend empiric LC in patients after single or recurrent attacks of IAP due to possible occult biliary disease [
29,
30]. There is an association between elevated ALT levels and acute biliary pancreatitis, with a positive predictive value of 85% for ALT>150 U/L within 48 hours after the onset of symptoms. Therefore, elevated ALT levels in IAP are strongly suggestive of a biliary aetiology [
31,
32,
33]. Even if LC could be beneficial in such cases where the cause was microlithiasis or biliary sludge that was not identified, EUS can rule out other rare causes of, A.P. A thorough investigation of the patient’s biliary anatomy with MRI and EUS could identify rare conditions that could cause a pancreatitis recurrence or some conditions that if left untreated would give the patients higher morbidity and mortality, such as chronic pancreatitis,
pancreas divisum, pancreatic neoplasm, cystic neoplasm, IPMN, pancreatic duct stones, pancreatic duct strictures, and other anatomic abnormalities [
25]. IAP has indeed a relatively high recurrence rate, up to 25% during the 3 years after the first episode [
34]. Chronic pancreatitis seems to be more frequent in patients with recurrent IAP, and it could be the manifestation of progressive organ damage from recurrent episodes of IAP [
35].
3.4. Role of EUS in idiopathic acute recurrent pancreatitis, Pancreas Divisum, and Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction
Idiopathic acute recurrent pancreatitis (IARP) is the occurrence of two or more episodes of IAP, without concurrent clinical or imaging evidence suggestive of chronic pancreatitis or other diseases. If left untreated, the underlying cause of IARP could lead to chronic pancreatitis. As LC is often performed in patients with IAP, many patients with IARP have a history of a cholecystectomy. Although there is lower rate of diagnosis of biliary disease in patients without gallbladder, lithiasis is still the second most common EUS finding in IARP after chronic pancreatitis. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and
pancreas divisum have been associated with high recurrence rates in other studies of IARP [
48,
49,
50,
51,
52].
Pancreas divisum is a congenital anomaly resulting from the failure of fusion of the ventral and dorsal pancreatic ducts; it is sometimes identified as a potential cause of IAP. EUS offers direct visualization of the pancreatic duct system with a high sensitivity, similarly to MRCP [
36]. In cases where
pancreas divisum is associated with pancreatitis, the literature suggests that ERCP with minor papilla sphincterotomy and dorsal duct (Santorini) stent placement can effectively serve as preventive measures against future episodes and maybe provide relief from symptoms [
34,
53,
54,
55,
56]. As a treatment tailored according to the aetiology is associated with a reduction of recurrences, an EUS-based management strategy is suggested in patients with IARP [
54].
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD) encompasses clinical syndromes with biliary and pancreatic manifestations. Biliary SOD commonly follows cholecystectomy, while pancreatic SOD relates to IARP [
57,
58]. The revised Milwaukee Biliary Group classification can assist in diagnosing and categorizing SOD into three types. Type I exhibits biliary-type pain, abnormal liver function tests, and a dilated bile duct. Type II involves biliary-type pain with one laboratory or imaging abnormality, while Type III involves recurrent biliary-type pain alone [
59]. Manometric evidence of SOD varies among patients. Treatment of Type I SOD involves ERCP with biliary sphincterotomy. Type II SOD, with less objective evidence, may require ERCP with sphincterotomy guided by sphincter of Oddi manometry (SOM) or empiric biliary sphincterotomy. The relationship between manometric findings, disease aetiology, and response to therapy remains unclear, and empiric sphincterotomy is considered as an alternative. Recent trials suggest limited benefits of ERCP and sphincterotomy for Type III SOD. Pancreatic SOD predisposes to recurrent acute pancreatitis, and sphincterotomy can reduce its frequency, though recurrence rates remain significant. Temporary pancreatic stenting during sphincterotomy reduces procedure-induced pancreatitis risk [
57,
58]. In conclusion, SOD is a complex condition with different subtypes and management strategies. The role of SOD and medical therapy efficacy remain uncertain [
59].
3.5. Role of EUS in Pancreatic Tumours and Autoimmune Pancreatitis
IAP can be associated with pancreatic tumours, although they account for a small percentage of cases. Whether benign or malignant, pancreatic tumours can contribute to AP through various mechanisms. When a tumour is in the head of the pancreas, it can obstruct the pancreatic duct or the common bile duct, impairing the drainage of pancreatic enzymes and triggering inflammation. Sometimes, tumours can directly induce local inflammation and disrupt normal pancreatic tissue, leading to pancreatitis development. It is important to note that pancreatic tumours associated with IAP are relatively uncommon, only between 2 and 5% of cases. However, given the implications for patient management and prognosis, pancreatic tumour should be excluded in patients with IAP, especially older individuals, or those with risk factors for malignancy [
60,
61,
62]. The same diagnostic imaging techniques used to evaluate pancreatitis, such as, C.T.; MRCP and EUS, are used to detect the presence of pancreatic tumours [
41,
63]. Pancreatitis secondary to obstruction of the pancreatic duct from tumours is more likely to be mild and recurrent, as ductal obstruction is usually partial [
64].
It should not be forgotten that autoimmune pancreatitis, which is a rare form of chronic pancreatitis that can sometimes present acutely, can form tumour-like masses or duct strictures, especially in pancreatic involvement of IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD). As IgG4-RD generally presents with other clinical features such as retroperitoneal fibrosis, nephritis, thyroiditis, sclerosing cholangitis, sialadenitis and interstitial pneumonia, testing for IgG4 serum concentration is suggested when IAP is associated with any of these signs [
65]. Autoimmune pancreatitis is more common in the elderly, and up to 50% of these patients are diagnosed with a distant malignancy within 1 year of the pancreatitis episode, especially gastric, lung, or prostate carcinoma. This association could suggest that autoimmune pancreatitis may represent a paraneoplastic syndrome [
66].
To summarize, while tumours and autoimmune disease are not a frequent cause of IAP, they should be considered in the diagnostic evaluation, particularly in older individuals or those with additional risk factors. Pancreatic tumours can cause pancreatitis because of their location or for some local physiological effects; timely recognition and appropriate management of pancreatic tumours associated with pancreatitis are essential for optimizing patient outcomes. Autoimmune pancreatitis and IgG4-RD can sometimes mimic tumours by creating masses or may possibly associated with the presence of a distant tumour. Lastly, it is important to remember that certain tumours can result in secondary pancreatitis due to hypercalcemia. These tumours include multiple myeloma, parathyroid tumours, leukaemia, and small cell lung cancer [
11,
16].
3.6. Safety of EUS
EUS generally has a low complication rate. Serious complications such as oesophageal or duodenal perforation are extremely rare but higher than those observed with conventional endoscopy due to the rigid linear US transducer mounted on the tip of the echo-endoscope. Besides, when EUS is used to guide therapeutic interventions, or to obtain fine-needle aspiration biopsies to examine suspicious pancreatic lesions, some post-procedural bleeding episodes have been described. All reports dealing with safety are in accord with the fact that the experience of the endoscopist performing the procedure can impact its safety and diagnostic accuracy. Performance of EUS by experiences specialists can minimize potential complications and increase the likelihood to obtain an accurate diagnostic information. EUS is considered a valuable and safe diagnostic tool even in children [49.67].
3.7. Recent advances in technology and improved endoscopic devices
Incorporation of advanced imaging modalities, such as contrast-enhanced EUS, intraductal EUS and elastography, may provide additional information about tissue characteristics and vascularity, aiding in the differentiation of benign and malignant lesions.68,69 This could help to identify the specific cause of IAP in some cases.
EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) and fine-needle biopsy (EUS-FNB) have proven valuable in obtaining tissue samples for pathological analysis. Future advancements in interventional EUS techniques could potentially allow for real-time on-site evaluation of obtained tissue samples, enabling a more rapid and accurate diagnosis of the underlying cause of pancreatitis.
With ongoing advancements in molecular and genetic testing, EUS-guided acquisition of tissue samples could facilitate targeted analysis of specific genes and molecular markers associated with pancreatitis. This personalized approach may lead to a better understanding of the underlying mechanisms of IAP and potentially aid in tailoring treatment strategies.
The integration of AI and machine learning algorithms into EUS imaging analysis in the future could help endoscopists to detect subtle abnormalities and patterns that might be missed by the human eye [
70]. AI-driven diagnostic support may lead to earlier and more accurate identification of the cause of, A.P.; especially in cases where the aetiology is challenging to determine.
4. Discussion
AP is a common gastrointestinal disease characterized by acute inflammation of the pancreatic gland. Its incidence varies between 4.9 and 73.4 cases per 100000.
1 The diagnosis of AP requires the presence of at least two criteria: typical abdominal pain, high serum lipase or amylase levels and radiological imaging (US, CT or MRI) consistent with AP [
10,
71]. The majority of patients with AP show a mild-to-moderate disease course, but up to 20% of them will develop acute severe necrotizing pancreatitis, which has a mortality ranging from 10 to 20% of cases [
72,
73,
74]. In the present review, we aimed to report available data concerning the indication, role, accuracy, timing and safety of an early EUS in patients initially diagnosed with IAP.
EUS has shown significant promise in the diagnosis and management of various gastrointestinal disorders, including IAP, and some recently improved endoscopic devices can also increase the diagnostic yield of EUS in IAP. Enhanced Resolution and Imaging Capabilities with better image resolution and visualization of the pancreas and surrounding structures allow for more accurate identification of abnormalities, such as pancreatic duct strictures, stones, and tumours, which could be potential causes of, A.P.
The identification of the underlying cause of IAP has significant clinical implications. It enables targeted therapeutic interventions tailored to the specific aetiology, potentially preventing recurrent episodes and disease progression. EUS allows to decide on the appropriate treatment, such as sphincterotomy, stone extraction, or stent placement, and allows to address biliary pathologies [50.75–78]. Additionally, EUS facilitates early detection of neoplastic lesions, leading to timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, ultimately improving patient outcomes. While EUS has proven valuable in uncovering the cause of IAP, it has some limitations. The procedure requires specialized expertise and may not be readily available in all healthcare settings. Furthermore, rare or less common causes may still remain undetected even with EUS evaluation. Future research should focus on optimizing EUS techniques, exploring the role of advanced imaging modalities, and conducting prospective studies to establish the cost-effectiveness and long-term benefits of EUS-guided management strategies.
Apart from its diagnostic role, EUS has also shown potential as a therapeutic tool [
79]. For instance, EUS-guided drainage of pseudocysts or biliary duct strictures could offer a less invasive approach to managing certain causes of pancreatitis [
75,
80]. As therapeutic EUS techniques evolve, they may complement the diagnostic process and improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, EUS has revolutionized the evaluation of IAP by revealing previously undetectable underlying causes. Through its ability to provide detailed imaging of the pancreas and adjacent structures, coupled with EUS-guided sampling techniques, it has improved diagnostic accuracy and therapeutic decision-making. Incorporating EUS into the diagnostic workup of IAP allows for targeted interventions, optimizing patient management and improving outcomes.
The limitations of this review include the potential for publication bias, as only studies published in English were included. The reliance on existing literature and the subjective nature of narrative synthesis may introduce inherent biases. Additionally, the inclusion of studies with varying quality levels and the possibility of selective reporting of outcomes may impact the overall findings.
Author Contributions
F.C., L.R. contributed equally to this study. Conceptualization, P.A., L.R., and, F.C.; methodology, P.G., P.F. and, A.A.; validation, P.A., and, P.G.; formal analysis, P.A., L.R, .and, F.C;. resources, and data extraction, L.R., F.C., A.A. and, P.F.; writing, L.R., F.C. and, P.A.; writing—review and editing, P.A.; supervision, P.A. P.G. and, P.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
As this review involved the analysis of existing published data, ethical approval was not required.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Gloria Innocenti (Centro di Documentazione Biomedica, ASST Grande Ospedale Metropolitano Niguarda, Milan, Italy) for his valuable support and excellent technical assistance.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
EUS: Endoscopic Ultrasound, AP: Acute Pancreatitis: IAP: idiopathic acute pancreatitis; US: Ultrasound, CT: Computerized Tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance Imaging; MRCP: Magnetic Resonance Cholangio Pancreatography; EUS-FNA: EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration; EUS-FNB EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy; IARP: Idiopathic acute recurrent pancreatitis; IAP/APA International Association of Pancreatology and American Pancreatic Association; LC: laparoscopic cholecystectomy, SOD: Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction; of IgG4-RD: IgG4-related disease.
References
- Tenner, S.; Baillie, J.; DeWitt, J.; Vege, S.S. American College of Gastroenterology Guideline: Management of Acute Pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013, 108, 1400–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.P.; Nicholls, J.F.; Park, H.Z. Biliary Sludge as a Cause of Acute Pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 1992, 326, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canlas, K.R. Role of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography in acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007, 13(47), 6314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio Blanco, G.; Gesuale, C.; Varanese, M.; Monteleone, G.; Paoluzi, O.A. Idiopathic acute pancreatitis: a review on etiology and diagnostic work-up. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2019, 12, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmary, P.; Grammatikopoulos, T.; Cai, W.; et al. Acute Pancreatitis: Diagnosis and Treatment. Drugs. 2022, 82, 1251–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinney, T.P.; Lai, R.; Freeman, M.L. Endoscopic approach to acute pancreatitis. Rev Gastroenterol Disord. 2006, 6, 119–135. [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez, L.V.; Catalano, M.F. Endoscopic techniques (ERCP, EUS) for the evaluation of unexplained acute pancreatitis. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2004, 6, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusoff, I.F.; Raymond, G.; Sahai, A.V. A prospective comparison of the yield of EUS in primary vs. recurrent idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2004, 60, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.J.; Vicuña, M.; Irisarri, R.; et al. Diagnostic yield and reliability of endoscopic ultrasonography in patients with idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 375–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. IAP/APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2013, 13, e1–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongprasobchai, S.; Thamcharoen, R.; Manatsathit, S. Changing of the etiology of acute pancreatitis after using a systematic search. J Med Assoc Thai. 2009, 92 (Suppl. 2), S38–S42. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, C.V.; Pereira-Lima, J.; Hartmann, A.A. The role of linear endosonography for the diagnosis of acute pancreatitis when other methods failed. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019, 43, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornett, D.D.; Spier, B.J.; Eggert, A.A.; Pfau, P.R. The Causes and Outcome of Acute Pancreatitis Associated with Serum Lipase >10,000 U/L. Dig Dis Sci. 2011, 56, 3376–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ardengh, J.C.; Malheiros, C.A.; Rahal, F.; Pereira, V.; Ganc, A.J. Microlithiasis of the gallbladder: role of endoscopic ultrasonography in patients with idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 2010, 56, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris-Stiff, G.; Al-Allak, A.; Frost, B.; Lewis, W.G.; Puntis, M.C.A.; Roberts, A. Does endoscopic ultrasound have anything to offer in the diagnosis of idiopathic acute pancreatitis? JOP. 2009, 10, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, C.M.; Kilgore, M. Cost Minimization Analysis Comparing Diagnostic Strategies in Unexplained Pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2009, 38, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, M.; Wallace, M.B. Diagnostic approach to patients with acute idiopathic and recurrent pancreatitis, what should be done? World J Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, M.; Topazian, M. Endoscopic ultrasound in idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, S.A.; Alderson, D. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the evaluation of idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 2002, 87, 1650–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.-L.; Lo, C.-M.; Chan, J.K.F.; Poon, R.T.P.; Fan, S.-T. EUS for detection of occult cholelithiasis in patients with idiopathic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000, 51, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Somani, P. EUS of pancreatic ascariasis. Arab J Gastroenterol. 2018, 19, 47–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbu, S.T.; Valeanu, D.; Muresan, A.; Munteanu, D.; Casoinic, F. Cystic Dystrophy of the Duodenal Wall in Heterotopic Pancreas with Groove Pancreatitis: A Diagnostic and Therapeutic Challenge. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2018, 113, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, R.; Eslick, G.; Cox, M. Endoscopic Ultrasound for Routine Assessment in Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2019, 23, 1694–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umans, D.S.; Rangkuti, C.K.; Sperna Weiland, C.J.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasonography can detect a cause in the majority of patients with idiopathic acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 2020, 52, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, T.; Dixit, V.K.; Yadav, D.P.; et al. Idiopathic acute pancreatitis—A myth or reality? Role of endoscopic ultrasonography and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography in its diagnosis. Indian J Gastroenterol. 2021, 40, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, P.; Kumbhari, V.; Antwi, S.O.; et al. Simple risk score to predict the likelihood of a positive EUS in idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022, 96, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoury, T.; Shahin, A.; Sbeit, W. Exploring the Optimal Timing of Endoscopic Ultrasound Performance Post-Acute Idiopathic Pancreatitis. Diagnostics. 2022, 12, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.S.; Bhasin, D.K.; Sharma, V.; Sharma, R.; Chaudhary, V.; Chhabra, P. Can early endoscopic ultrasound predict pancreatic necrosis in acute pancreatitis? Ann Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 404–408. [Google Scholar]
- Räty, S.; Pulkkinen, J.; Nordback, I.; et al. Can Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Prevent Recurrent Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis? Ann Surg. 2015, 262, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.L.; Abbas, S.M.; Watters, D.A.K. How Does Cholecystectomy Influence Recurrence of Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis? J Gastrointest Surg. 2016, 20, 1997–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Fan, S.T.; Lo, C.M.; et al. Clinico-biochemical prediction of biliary cause of acute pancreatitis in the era of endoscopic ultrasonography. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005, 22, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moolla, Z.; Anderson, F.; Thomson, S.R. Use of Amylase and Alanine Transaminase to Predict Acute Gallstone Pancreatitis in a Population with High HIV Prevalence. World J Surg. 2013, 37, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammori, B.J.; Boreham, B.; Lewis, P.; Roberts, S.A. The Biochemical Detection of Biliary Etiology of Acute Pancreatitis on Admission: A Revisit in the Modern Era of Biliary Imaging. Pancreas. 2003, 26, e32–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, M.C.; Seay, T.; Kim, H.; Varadarajulu, S. Prospective Endoscopic Ultrasound-Based Approach to the Evaluation of Idiopathic Pancreatitis: Causes, Response to Therapy, and Long-term Outcome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2016, 111, 1339–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsmark, C.E. Management of Chronic Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 2013, 144, 1282–1291.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, X.; Xia, L.; Lu, N. Comparison of EUS with MRCP in idiopathic acute pancreatitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018, 87, 1180–1188.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila, J.J.; Mendioroz, F.J.J.; Yeaton, P.; et al. EUS is superior to secretin-enhanced cholangio-MRI to establish the etiology of idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Endosc Int Open. 2020, 08, E1441–E1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repiso Ortega, A.; Gómez-Rodríguez, R.; Romero, M.; Fernández-Zapardiel, S.; del Mar Céspedes, M.; Carrobles, J.-M. Prospective Comparison of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in the Etiological Diagnosis of “Idiopathic” Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreas. 2011, 40, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, A.; Arcidiacono, P.G.; Curioni, S.; Giussani, A.; Testoni, P.A. Diagnostic yield of ERCP and secretin-enhanced MRCP and EUS in patients with acute recurrent pancreatitis of unknown aetiology. Dig Liver Dis. 2009, 41, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testoni, P.A.; Mariani, A.; Curioni, S.; Zanello, A.; Masci, E. MRCP-secretin test–guided management of idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis: long-term outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008, 67, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.B.; Paik, C.-N.; Song, D.S.; et al. The Role of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in Patients With Acute Pancreatitis After Negative Computed Tomography Findings of the Etiology. Pancreas. 2018, 47, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umans, D.S.; Timmerhuis, H.C.; Hallensleben, N.D.; et al. Role of endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnostic work-up of idiopathic acute pancreatitis (PICUS): study protocol for a nationwide prospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2020, 10, e035504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.S. Evaluating the role of endoscopic ultrasound in pancreatitis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022; 16, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, A.; Bournet, B.; Otal, P.; Canevet, G.; Moreau, J.; Buscail, L. Endoscopic Ultrasound and Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography in Patients with Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 2013, 58, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.S.; Bhasin, D.K.; Rao, C.; Singh, K. Role of endoscopic ultrasound in idiopathic acute pancreatitis with negative ultrasound, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography. Ann Gastroenterol. 2012, 25, 133–137. [Google Scholar]
- Sotoudehmanesh, R.; Hooshyar, A.; Kolahdoozan, S.; Zeinali, F.; Shahraeeni, S.; Keshtkar, A.-A. Prognostic Value of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Acute Pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 2011, 10, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poves, E.; del Pozo, D.; Tabernero, S.; Bardina, A.; Martínez, P.; Castillo, M.C. Clinical impact of High-Definition Endoscopic Ultrasonography (EUS) in a district hospital. Rev Española Enfermedades Dig. 2010, 102, 698–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde-López, F. Endoscopic ultrasound as a diagnostic and predictive tool in idiopathic acute pancreatitis. Ann Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadyada, S.P.; Thapa, B.R.; Dhaka, N.; Bhatia, A.; Menon, J. Role of Diagnostic Endoscopic Ultrasound in Idiopathic Acute Pancreatitis and Acute Recurrent Pancreatitis in Children. Pancreas. 2019, 48, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-I.; Yang, J.; Friedland, S.; et al. Lumen apposing metal stents are superior to plastic stents in pancreatic walled-off necrosis: a large international multicenter study. Endosc Int Open. 2019, 7, E347–E354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajith, K.G.; Chacko, A.; Dutta, A.K. Recurrent Acute Pancreatitis: Clinical Profile and an Approach to Diagnosis. Dig Dis Sci. 2010, 55, 3610–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, W.J.; Pineau, B.C.; Tarnasky, P.R.; et al. Evaluation of Unexplained Acute and Acute Recurrent Pancreatitis Using Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography, Sphincter of Oddi Manometry and Endoscopic Ultrasound. Endoscopy. 2002, 34, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMagno, M.J.; Wamsteker, E.-J. Pancreas Divisum. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011, 13, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tepox-Padrón, A.; Bernal-Mendez, R.A.; Duarte-Medrano, G.; et al. Utility of endoscopic ultrasound in idiopathic acute recurrent pancreatitis. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021, 8, e000538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyries, L.; Barthet, M.; Delvasto, C.; Zamora, C.; Bernard, J.-P.; Sahel, J. Long-term results of endoscopic management of pancreas divisum with recurrent acute pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002, 55, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahakian, A.B.; Aslanian, H.R. Diagnosis of Pancreas Divisum Using Linear-Array Endosonography. Video J Encycl GI Endosc. 2014, 2, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riff, B.P.; Chandrasekhara, V. The Role of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in Management of Pancreatic Diseases. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2016, 45, 45–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elta, G.H. Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction and bile duct microlithiasis in acute idiopathic pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandstätter, G.; Schinzel, S.; Wurzer, H. Influence of spasmolytic analgesics on motility of sphincter of oddi. Dig Dis Sci. 1996, 41, 1814–1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallensleben, N.D.; Umans, D.S.; Bouwense, S.A.; et al. The diagnostic work-up and outcomes of ‘presumed’ idiopathic acute pancreatitis: A post-hoc analysis of a multicentre observational cohort. United Eur Gastroenterol, J. 2020, 8, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartell, N.; Bittner, K.; Vetter, M.S.; Kothari, T.; Kaul, V.; Kothari, S. Role of Endoscopic Ultrasound in Detecting Pancreatic Cancer Missed on Cross-Sectional Imaging in Patients Presenting with Pancreatitis: A Retrospective Review. Dig Dis Sci. 2019, 64, 3623–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulla Rocha, J.L.; Alvarez Sanchez, M.V.; Paz Esquete, J.; et al. Evaluation of the bilio-pancreatic region using endoscopic ultrasonography in patients referred with and without abdominal pain and CA 19-9 serum level elevation. JOP. 2007, 8, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, T.B. Acute Pancreatitis. Ann Intern Med. 2021, 174 :ITC17-ITC32. I. [CrossRef]
- Minato, Y.; Kamisawa, T.; Tabata, T.; et al. Pancreatic cancer causing acute pancreatitis: a comparative study with cancer patients without pancreatitis and pancreatitis patients without cancer. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2013, 20, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugino, C.A.; Stone, J.H. IgG4-related disease: an update on pathophysiology and implications for clinical care. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 702–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, A.; Watanabe, T.; Kamata, K.; Minaga, K.; Kudo, M. Recent Updates on the Relationship between Cancer and Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Intern Med. 2019, 58, 1533–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varadarajulu, S.; Wilcox, C.M.; Eloubeidi, M.A. Impact of EUS in the evaluation of pancreaticobiliary disorders in children. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005, 62, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; et al. The role of intraductal US in the management of idiopathic recurrent pancreatitis without a definite cause on ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011, 73, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tringali, A.; Lemmers, A.; Meves, V.; et al. Intraductal biliopancreatic imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) technology review. Endoscopy. 2015, 47, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorris, M.; Hoogenboom, S.A.; Wallace, M.B.; van Hooft, J.E. Artificial intelligence for the management of pancreatic diseases. Dig Endosc. 2021 Jan;33(2):231-241. [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; et al. Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagenholz, P.J.; Ferna´ndez-del Castillo, C.; Harris, N.S.; Pelletier, A.J.; Camargo, C.A. Direct Medical Costs of Acute Pancreatitis Hospitalizations in the United States. Pancreas. 2007, 35, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peery, A.F.; Crockett, S.D.; Murphy, C.C.; et al. Burden and Cost of Gastrointestinal, Liver, and Pancreatic Diseases in the United States: Update 2018. Gastroenterology. 2019, 156, 254–272.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, S.E.; Morrison-Rees, S.; John, A.; Williams, J.G.; Brown, T.H.; Samuel, D.G. The incidence and aetiology of acute pancreatitis across Europe. Pancreatology. 2017, 17, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharaiha, R.Z.; DeFilippis, E.M.; Kedia, P.; et al. Metal versus plastic for pancreatic pseudocyst drainage: clinical outcomes and success. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015, 82, 822–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.S.; Bhasin, D.K.; Reddy, Y.R.; et al. Morphological features of fluid collections on endoscopic ultrasound in acute necrotizing pancreatitis: do they change over time? Ann Gastroenterol. 2014, 27, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.S.; Bhasin, D.K.; Rao, C.; Gupta, R.; Singh, K. Non-fluoroscopic endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural drainage of symptomatic non-bulging walled-off pancreatic necrosis. Dig Endosc. 2013;25: 47-52. [CrossRef]
- Testoni, P.A. Endoscopic stenting in benign pancreatic diseases. JOP. 2007, 8 (Suppl. 1), 141–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.S.; Kumar, A.; Lal, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of angioembolisation followed by endoscopic ultrasound guided transmural drainage for pancreatic fluid collections associated with arterial pseudoaneurysm. Pancreatology. 2017, 17, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, P.Y.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Vilmann, P.; et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: Medium-term assessment of outcomes and complications. Endosc Ultrasound. 2013, 2, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).