1. Introduction
Spinal cord injury is relatively common and can have life-altering effects. In Canada, there are approximately 86,000 people with spinal cord injuries, and 4,300 new cases each year [
1,
2]. The number of Canadians with incomplete spinal cord injuries is increasing [
3]. As Canada’s population ages, in 10 years the number of people living with spinal cord injury will likely rise to more than 120,000 [
2]. In Canada, 52% of people have incomplete tetraplegia, 18% have incomplete paraplegia and the remainder (30%) have complete paraplegia or tetraplegia [
4]. Depending on the extent of their injury, people with incomplete spinal cord injury frequently regain some form of functional ambulation thanks to improvements in acute rehabilitation [
1,
5,
6]. For example, people with an American Spinal Cord Injury Association Impairment Scale score of C or D are likely to ambulate [
7].
Empirical evidence suggests that people with an incomplete spinal cord injury who can ambulate struggle with physical and psychological issues differently from those with complete injuries. Although many people want to walk after spinal cord injury, a cross-sectional cohort study found that long-term ambulation post spinal cord injury was related to undesirable outcomes such as fatigue, pain, and depressive symptoms in 56% of the study participants [
8]. Several studies have suggested that the relationship between the ability to walk and life satisfaction may be mediated by both physical factors (pain, fatigue) and psychological factors (depression, frustration) [
9,
10,
11]. A survey study identified having an incomplete injury and poor mental well-being were the main factors associated with depression [
12]. Another survey found that people with an American Spinal Cord Injury Association Impairment Scale score of D had lower social participation compared to those with scores of A, B, or C [
13].
Various demographic factors have been associated with a positive quality of life (defined as how people perceive their emotional and physical well-being and it encompasses a wide range of areas, including corporal, emotional, economical, devotional, and social prosperity [
14]) in combined samples (i.e., those with complete and incomplete injuries). Two systematic reviews [
15,
16,
17], a cross-sectional study [
18], a case-control study [
19], and an empirical research study [
20], identified a range of factors that positively influenced life satisfaction, including getting injured at a younger age, having a lower level of spinal cord injury, being employed, being married, not living in poverty, living in urban areas, getting more leisure-time physical activity, keeping a positive attitude, enjoying accessible transportation, time since injury and having recovered from any previous health issues.
Our review of the literature identified few studies exploring the quality of life among people with spinal cord injury who can ambulate. A cross-sectional survey study conducted in Norway suggested that people with incomplete spinal cord injury who participated in physical activities (e.g., walking, biking, strength training) had higher life satisfaction [
21]. People with an American Spinal Cord Injury Association Impairment Scale of D were substantially less happy with their mental health compared to people with an American Spinal Cord Injury Impairment Scale of A/B/C as reported by a Sweden cross-sectional cohort study [
22]. A cross-sectional study from the United States reported that veterans with an American Spinal Cord Injury Association Impairment Scale score of D reported more pain, depressive symptoms, and general poor health compared to other American Spinal Cord Injury Association Impairment Scale scores [
23]. A qualitative study conducted in Australia suggested this may be due to a variety of potential causes such as being annoyed with the speed of completing daily activities, being exhausted from walking, feeling misunderstood owing to invisible impairment leading to less support from the community, and having symptoms being overlooked [
11].
Given the limited understanding of the quality of life of people with incomplete spinal cord injury who can ambulate, especially from a Canadian perspective, we conducted a study with two main objectives: 1) to examine associations between subjective quality of life and other socio-demographic variables in this population and 2) to explore differences in experiences of people with different levels of quality of life (low, moderate, and high) using a novel mixed-methods approach.
2. Methods
This study used an explanatory design in which qualitative data were used to explain the quantitative findings; i.e., the qualitative findings were built upon the quantitative findings [
24,
25]. Specifically, we used the quantitative data to identify participants with three levels of quality of life (low, moderate, and high) and to compare sociodemographic characteristics in those three groups. We explored the experiences of participants in each of these groups qualitatively.
Qualitative description was the method used to analyze the qualitative data set and the qualitative findings were reported using the consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research guidelines [
26,
27] (
Table S1). The overall study has been reported using the Good Reporting of a Mixed Methods Study Framework [
28] as reported in (
Table S2).
2.1. Study Participants
Participants were eligible if they were: (1) diagnosed with incomplete spinal cord injury, (2) able to walk 15 meters with or without aids short distances, (3) resided in British Columbia, (4) 19 years or older, (5) able to understand and to read English and (6) able to provide their own consent.
2.2. Recruitment
We recruited a convenience sample of 24 participants and there were no dropouts. The study was advertised on the International Collaboration on Repair Discoveries website, on the Mortenson Lab Social media channels, at the GF Strong Rehabilitation Centre, and in the Spin Magazine that was distributed by Spinal Cord Injury – British Columbia quarterly. Previous study participants who indicated an interest in being notified about future studies were also contacted.
2.3. Data Collection
Participants were recruited over a period of five months and provided informed written consent to participate in the study. Due to the COVID pandemic, data were collected virtually (i.e., via zoom or telephone). Before the interview, participants completed the standardized measures and demographic survey on an online survey program (Qualtrics). All audio was digitally recorded on the interviewer’s computer using the University of British Columbia Zoom account and was transcribed verbatim. All transcripts were password protected. Prior to the interviews, participants were emailed detailed information about how to install and use Zoom (a direct link to download zoom was provided). In case of any difficulties during the Zoom meeting (e.g., loss of internet connection) participants were contacted on their phones to continue with the interview. Participants were reminded to be alone in the room during the interview. If the participant was unable to use Zoom because of lack of internet and or difficulty with hand function, the three student authors administered the interview orally over the phone. The study was an unblinded qualitative study.
2.4. Measures
Participants completed one demographic survey and four standardized measures as described below.
2.4.1. Demographic survey
A demographic form was used to gather descriptive information. This survey collected data about participants’ age, sex at birth, type of spinal cord injury, number of years living with injury, employment status, living situation, education level, and marital status.
2.4.2. Functional Ambulation Measure
Participants reported their ambulatory ability according to the Functional Ambulation Categories [
29]. The six levels are; non-functional ambulator (level 0), ambulatory dependent on physical assistance (level 1), ambulator dependent on physical assistance (level 2), ambulator dependent on supervision (level 3), ambulator independent on flat surface only (level 4) and independent ambulator (level 5). A score of 0 indicates one cannot walk and a score of 5 indicates one can walk freely.
2.4.3. Life Satisfaction Questionnaire – 11
Quality of life was assessed using the life satisfaction questionnaire [
30] consisting of 11 questions on specific domains. The 11 items in the questionnaire are life as a whole, work, finance, leisure, contact with friends, sexual life, daily activities, family life, partner relationship, somatic health, and psychological health. Each item gets a score of 1 to 6 depending on how satisfied the person feels. A score of 1 is very dissatisfied and a score of 6 is very satisfied [
31].
2.4.4. Spinal Cord Independence Measure – III
Function, was assessed using the self-report version of the Spinal cord independence measure [
32] of 19 items divided into three categories: respiration and sphincter management, self-care, and mobility. Each item gets a score of 0-100, where a score of 0 indicates total dependence and 100 indicates complete independence.
2.4.5. 12- Item Short-Form Survey
Health-related quality of life was measured using the 12 - item short-form health survey [
33] consisting of 12 questions covering eight specific domains. This is a shorter version of the 36 – item short-form health survey. The eight domains are mental health, physical role, bodily pain, social functioning, vitality, general health perspective, physical functioning, and emotional health. Each item gets a score of 0 to 100, with 0 indicating poor health and 100 indicating very good health. There are two summary scores used to calculate the overall score of the 12 – item short-form health survey namely the physical component score and the mental component score.
2.4.6. Semi-Structured Interviews
Semi-structured interviews were conducted after participants had completed the online survey. Interviews were conducted only once by three graduate students (The student who was the lead author was a female Master’s student with training in occupational therapy; and the two other students who were co-authors, were female Occupational Therapy Master’s students) who were trained in qualitative research. They were guided by the student supervisor and senior authors who have extensive experience with mixed-methods research. Interviews lasted between 45 to 90 minutes and were done one-on-one (interview + interviewee). Participants were informed to be alone in the room during the interview. No relationship was developed prior to the interviews with the participants and none of them were familiar with any of the interviewers. The interview guide (Document S1) was developed and piloted collaboratively with the research team and three co-authors who were working for a non - profit organization that provides assistance to people with spinal cord injury.
2.5. Data analysis
2.5.1. Quantitative
To address the first research question, the lead author divided participants into three levels of quality of life with the following cut points: low (≤ 28), moderate (29-47), and high (≥ 48). These cut points were used so that we had a relatively equal number of people in each group. Descriptive statistics data including mean, standard deviation, number, and percentage for categorical and continuous variables were used to characterize participants in each group.
To test for the normality of data, we conducted Kolmogorov – Smirnov tests. Three scores were abnormally distributed, the physical component score of the 12- item short-form health survey (p = 0.05), the spinal cord independence measure (p= 0.02), and the functional ambulatory measure (p=≤0.01).
We looked at the relationship between quality of life and other sociodemographic variables on a bivariate level rather than comparing the three levels of quality of life. A Spearman correlation was used for continuous variables and Mann Whitney U tests or Kruskal Wallis tests were used for categorical data. A significance level of p≤ 0.05 was used for all tests; however, it is important to consider the strength of associations [
34]. In terms of effect sizes for Spearman’s rho, a negligible relationship is r
s = 0.00- 0.20; a weak relationship is r
s = 0.21 – 0.40; a moderate relationship is r
s = 0.41 – 0.60; a strong relationship is r
s = 0.61 – 0.80 and a very strong relationship is r
s = 0.81 – 1.00 [
35]. For Cohen’ D a small effect size is d =0.20, a medium-size effect is d= 0.50 and a large-size effect is d= 0.80 [
36]. For Cohen’s F, a small effect is f = 0.10, a medium effect is f = 0.25 and a large effect is f= 0.40 [
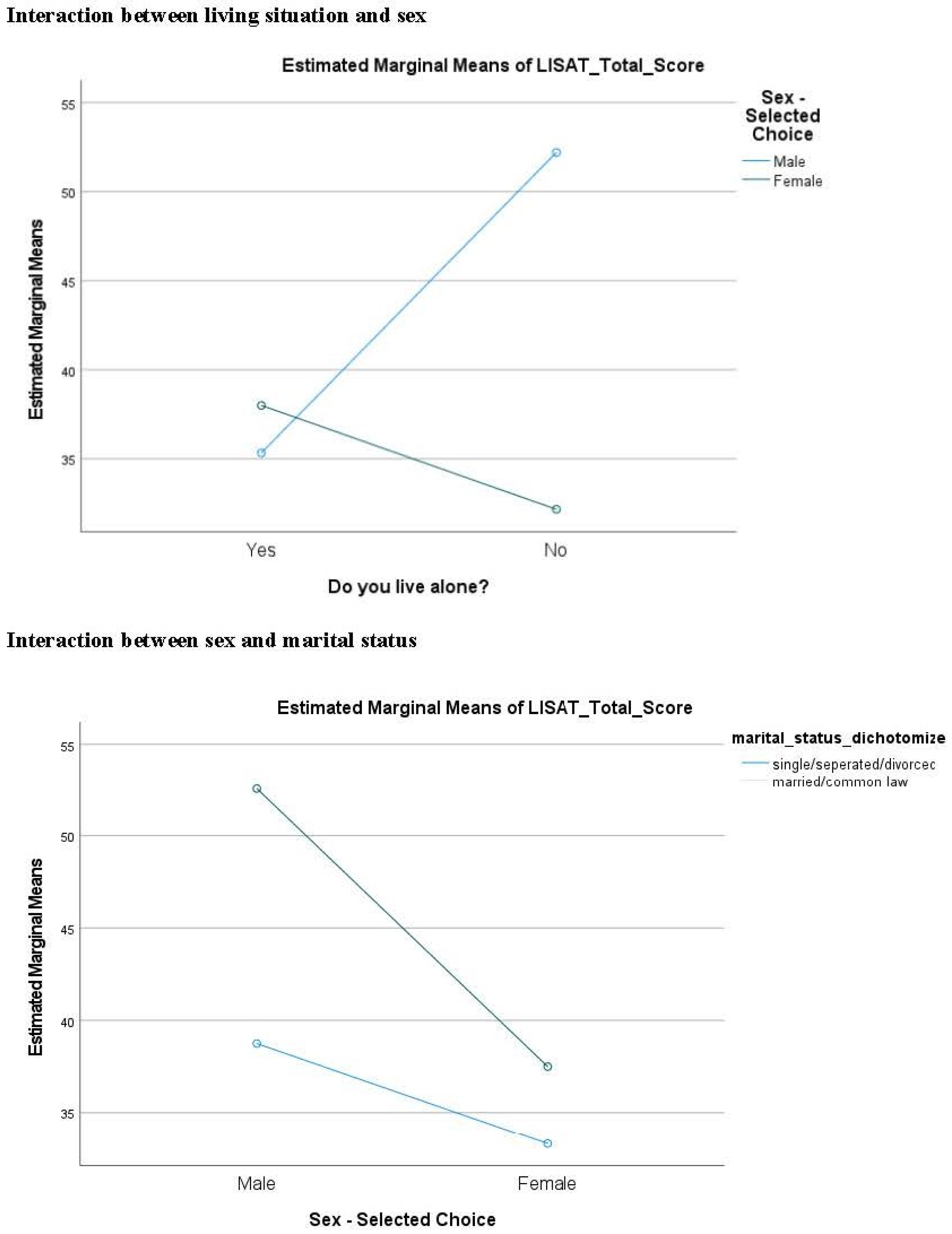
36]. To understand better the relationship between sex, marital status, and living situation we plotted the interactions between sex and living situation, sex and marital status, and living situation and marital status (We were not able to produce a plot for the interaction between living situation and marital status because the sample size was too small.) (Figure A1). Data were analyzed using the IBM SPSS software.
2.5.2. Qualitative
To analyze the data, the transcripts for each participant were reviewed by the lead author to identify potential barriers and facilitators to their quality of life. The data was managed in Nvivo, then a table documenting potential barriers and facilitators to quality of life in each group (i.e., low, moderate, and high) was made.
To promote the rigor of the study we used the four transcendent trustworthiness criteria identified by Morrow [
37]: 1) social validity, 2) reflexivity and subjectivity, 3) adequacy of data, and 4) adequacy of interpretation. In terms of social validity, the study was suggested by people working at a non-profit organization for people with spinal cord injury. They were part of the team as co-authors and have lived experience of spinal cord injury. Reflexivity and subjectivity require researchers to consider their positioning when collecting and interpreting data [
37]. For reflexivity and subjectivity, the three student authors conducting the interviews maintained reflexive journals that documented their reflections and personal positioning. For example, they recorded how they anticipated participants would respond to each interview question. They probed for negative cases if participants were telling them things they expected to hear.
Adequacy of data is concerned with the quantity and quality of data, as having a greater number of participants would guarantee the validity of the findings. Some argue that the collection of data should be done until the point of redundancy when there is no more new information to be acquired from the ongoing data collection. Redundancy also known as saturation happens when no new information emerges but questions have been raised about how this idea is operationalized [
38]. Others have recommended sufficiency rather than saturation with qualitative research [
39,
40,
41].
Adequacy of interpretation is to involve multiple researchers in the data collection and analysis so that their complementary perspectives would enrich the findings. To promote adequacy of interpretation we addressed these criteria by doing the following: involvement of multiple researchers in data collection and analysis; creation of a casual and trusting relationship to try and make participants feel comfortable (by being friendly as opposed to being just an interviewer, when the interview finished, we let the participant continue talking about anything they wanted to add/share). Previous research has suggested that some participants are more relaxed and confident to talk because they were in their safe space (in their house) [
42]. We shared the summary of the results with the participants and we requested feedback to which five of them responded and all agreed to our key conclusion.
3. Results
3.1. Quantitative
Considering the sample as a whole (n=24), it was noted in
Table 1 that there were slightly more men than women (column 3). On average, most of the participants had a traumatic spinal cord injury (column 3) and most of them attended rehabilitation (column3) after injury. Only 4 participants were employed after injury (column 3) and a majority lived with somebody (column 3). According to the three different levels of quality of life (low n=5, moderate n= 9, high n=10), the majority of participants in the low quality of life group (column 4) were females whereas the majority of participants in the high quality of life group (column 6) were males.
The two columns (column 7 and column 8) reported the correlation and effect size. A strong correlation was found between the life satisfaction questionnaire and the 12-item short-form health survey (physical component scores and mental component scores). Men, people who attended rehabilitation, and people who were married appeared to have a higher quality of life (large effect sizes).
Not shown in
Table 1, based on (Figure A1) there appeared to be an interaction between sex and living situation. Men and women who lived alone had similar low quality of life. Men living with someone else had the highest quality of life, whereas women living with others had the lowest quality of life. Comparing sex and marital status, men who were married had the highest quality of life whereas women who were married seemed to have similar quality of life as single men. Unmarried women had a lower quality of life. Due to a small sample size, we were unable to generate a plot to explore the relationship between marital status and living situation.
3.2. Qualitative
Table 2, described qualitative barriers and facilitators to quality of life by reviewing participants’ lived experiences. People in the low quality of life group experienced more barriers compared to those in the high quality of life group who had more facilitators and very few barriers. A balance between facilitators and barriers to quality of life was identified in the moderate quality of life group. Some issues were facilitators in one group and barriers in another group, e.g., social support is a facilitator in the high quality of life group but is a barrier in the low quality of life group. Other issues seemed to overlap many times in between groups, e.g., learning to adapt to life after the injury is a facilitator for both groups in moderate and high quality of life, and feeling judged is a barrier for both groups in low and moderate quality of life.
3.2.1. Low Quality of Life (N= 5)
Participants in this group described six factors that they perceived negatively affected their quality of life: feeling socially isolated, having financial concerns, feeling judged, feeling left out due to city layout and infrastructure not being wheelchair or walker-friendly, expressing that spinal cord injury was caused due to medical negligence and describing their deteriorating mobility. In this group, only one participant described one factor (ability to adapt to injury) that positively impacted their quality of life.
Three participants described their friends ended their friendship following their injuries. As noted in
Table 3, P11 attributed this to problems she had with pain and not getting equipment in a timely manner. With the start of the COVID restrictions, all the participants in the low quality of life group felt extremely isolated for a variety of reasons. For example, three participants lived alone or were restricted to limited social interactions due to travel restrictions, quarantine measures, and the fear of contracting the disease. Despite the possibility of virtual communication, these participants preferred in-person interactions as expressed by participant P14 in
Table 3. Participant P06, a 31-year-old male injured in the lumbar region described how the pandemic restrictions made him feel more socially isolated. He had a small group of friends and they had stopped seeing each other because of COVID restrictions. As the pandemic progressed his group of friends grew smaller, which made him spend more time playing games on his computer.
Four participants indicated that their limited income led to unmet medical needs, and the inability to acquire important assistive devices such as a foot orthosis or a powered wheelchair. Most of them were unemployed (n=4) and depended only on their disability pension, so they explained how expensive medical equipment was, as noted by Participant P06 in
Table 3.
All participants in the low quality of life expressed concerns about very expensive medical equipment. Participant P14 suggested removing taxes on medical equipment, to increase the affordability of equipment that people need in terms of daily living to be able to have a better quality of life.
Participants reported three types of social-environmental barriers to quality of life as a result of being judged by abled-bodied people: being invisible, being hyper-visible, and being treated inhumanely. All participants in the low quality of life group reported feeling ignored often by able-bodied people. P14 expressed how they made her feel invisible as described in
Table 3. All five participants described being stigmatized which they attributed to the use of their mobility device or having an impairment that was visible to others (e.g., limping). P14 reported how she experienced prejudice in
Table 3. Two participants related some events where they felt they were being treated inhumanely. Participant 13 a female 68 years old who is injured at L3-L5, had to stop going to pottery workshops because she felt excluded by others who attended. Participant P06 described that other people perceived him as a “half-person” because he uses a wheelchair which could cause some people to look down on him figuratively and literally.
More than half of the participants in this group experienced the loss of independence because of the city’s unsupportive infrastructure such as having no curb cuts, narrow sidewalks, the presence of cobblestone/ stairs, hilly topography, and a broken elevator. Participant P11 reported how accessibility challenges made it difficult to get around as described in
Table 3. Participants explained that some places that were supposedly accessible turned out to be inaccessible in practice. Participant P14 indicated that a lot of buildings are not completely accessible for people with a disability, because they do not have an accessible washroom or have multi-levels with no functioning elevators. Four out of five participants indicated they did not have any formal rehabilitation after their injury, which they felt could have improved their lives considerably. Participant P01 was refused multiple times to get rehabilitation and was very vocal that if she had not been denied care, her health would not have deteriorated as noted in
Table 3.
All participants in this group indicated how ongoing secondary health conditions (e.g., ongoing pain, spasticity, and tiredness) made daily life challenging (e.g., simple activities required a lot of planning, extra energy, and necessitated rest) and caused degradation in mobility. Participant P13 reported she felt like she was prematurely aging as depicted in
Table 3. Three participants reported how their walking fluctuated and ultimately deteriorated after their injury. Participant P06 indicated his gait had worsened over time post-injury. He started from walking with a cane, progressed to no cane, then regressed to a walker, and now uses a wheelchair for outdoor activities instead of his walker.
3.2.2. Moderate Quality of Life (N= 9)
Participants in this group described two factors that appeared to affect their quality of life negatively: feeling judged and decreasing mobility. Similar to the low quality of life group, all participants in the moderate quality of life group reported feeling judged or discriminated against. Furthermore, all nine participants stated that they have been challenged by abled-bodied people, and some of them reported being stared at or they would be whispering among them.
Participant P16 described her experience in
Table 4. In contrast, one participant P09 in this group described having a positive interaction with abled-bodied people as described in
Table 4. Two participants mentioned that they understood the curiosity and the avoidance of some people towards people with a disability. Participant P20, 60 years old female living injured at L3-L4 indicated she is no longer surprised and does not feel it is a problem when people avoid her because she believes that abled–bodied people might not know how to approach people with disability.
Like those in the low quality of life group, more than half of these participants reported mobility challenges. For example, P18 related how his gait deteriorated following surgery in
Table 4. Participants (N= 5) in the moderate quality of life group described leg weakness. P07, a 62 years old male, had a motor vehicle accident 45 years ago and was injured at the C6-C7 level. He related that before he could climb a couple of stairs but now after so many years with the spinal cord injury, he has trouble climbing stairs and would fall too many times. Sometimes he can usually tell if he is about to fall over, but other times his legs would just give out and he would fall over and lie flat on the ground for minutes or hours until he felt his legs again.
Participants in this group described three factors that appeared to positively affect their quality of life: learning to adapt to life after injury, appreciating their support system (family and social support), and having financial stability. Seven participants indicated how they used devices and adapted to their environments. Participant P09 explained in
Table 4, how she navigated through challenges. After their injury, seven participants explained how they got used to and accepted things that they could not do. Participant 10, a female of 46 years old injured at C5-C6 for eight years described how she learned to overcome chronic pain as noted in
Table 4. It was still difficult for four participants to adapt especially when pain is always lingering. They said that with pain, any simple task would take twice the time to complete, others related having to lie down for one hour to calm down the pain which can be related to what participant 10 said in
Table 4. Participant P10 described that her days were always planned, there was no spontaneity in what she did because planning helped her to perform better during the day and have her routine going. She indicated that everything needed to be planned to avoid wasting energy, experiencing muscle spasms, or increasing pain.
Most of the participants in this group (n=7) indicated family support was important for recovery. They appreciated their social support which included their family and others. P04 a 36 years old female with a congenital spinal birth defect (C5 – C6 is fused) described in
Table 4 how much she felt blessed to be well surrounded. Four participants considered themselves lucky to have social support because this gave them the courage to keep moving in life, overcome obstacles, and maintain good mental health as expressed by Participant P07 in
Table 4. One participant felt fortunate to be part of a supportive community. When the wife of participant P20 (60 years old male injured at L3-L4) was away at work, he reported he could rely on his neighbors for help. More than half of the participants (N=5) did not describe having major financial barriers. Participant P10 expressed gratitude for financial stability as stated in
Table 4. Five participants were grateful they were able to maintain financial stability during COVID restrictions as described by Participant P09 in
Table 4.
3.2.3. High Quality of Life (N=10)
Participants in this group described a variety of factors that appeared to positively affect their quality of life: demonstrating resilience, learning to adapt to life after injury, appreciating their support system (family and social support, feeling included in spinal cord injury programs and community), experiencing little difference with day-to-day life during COVID restrictions and having financial stability.
Many of the participants (N=7) demonstrated resilience by emphasizing the determination they exhibited to recover after their injuries as Participant P03 described in
Table 5. Among the 10 participants, seven of them experienced ongoing physical improvements. P22 who now can walk 50 meters without any walking support reported this in
Table 5. Participant P17 a 28-year-old female, injured at the thoracic level explained that seeing progression since her injury kept her determined to do more, and also not letting herself worry about the things she cannot do and just focusing more on what she can do instead also helped.
Similarly to the moderate quality of life, participants (N=8) in the high quality of life group described how they successfully adapted their lives after injury. Participant P08 related how he reinterpreted things to adapt his life according to his injury as described in
Table 5. Participant P02 is a 27 years male, who has a C4 – C6 spinal cord injury for 4 years and has a lot of determination to live his life to the fullest. He explained that if he wanted to get out into places that he used to go to, before his accident, then he will do it, and even if he must take his power- assisted wheelchair instead of the walking poles he would do it. The power-assisted wheelchair would allow him to go up and down some trails which he loved doing before his injury.
More than half of the participants in the high quality of life group, like those in the moderate quality of life group, valued their support system. Seven participants emphasized the importance of having family or social support to enhance mental well-being as participant P24 explained in
Table 5. Six participants felt part of a community with shared beliefs, common interests, and common experiences. The spinal cord injury groups were very powerful as expressed by participant 24 in
Table 5. P19, a 60 years old male injured at the thoracic level for 13 years, related how the peer support group gave him the courage to accomplish his goals.
Half of the participants from the high quality of life group experienced little difference in their daily life during COVID restrictions. Participant P23 a 67 years old male, injured at L4-L5 explained that COVID had no impact on his routine because he and his wife were retired and spent most of their time at home. Two participants (P03, P21 (66 years old female, T11-T12)) reported that they were already isolated before the COVID pandemic because of their immunocompromised system. Participants (N= 5) in the high quality of life group were financially stable, as were those in the moderate quality of life group. P12 who is a 69 years old male with a C2-C3 spinal cord injury 17 years ago, expressed that he has been financially stable through the settlement money he got from his lawsuit and the money he got from a program known as self-managed care option for home support services.
4. Discussion
This study explored the quality of life experiences of people with incomplete spinal cord injury who can ambulate with a special focus on North Americans. This is the only study that we are aware of that has identified factors associated with different levels of quality of life in this population. Also, this study is novel because we were able to outline and discover specific perceptions of participants based on their quality of life indicators. Another novelty is that it is one of the first studies in this area since the start of the pandemic. The findings emphasize the detrimental effects of COVID on the quality of life of people with incomplete spinal cord injury who can ambulate, especially among those with lower levels of quality of life. We have organized our discussion as follows: contributors to low quality of life, barriers to quality of life among those with low and moderate quality of life, facilitators to quality of life among those with moderate and high quality of life, and facilitators to a high quality of life.
4.1. Contributors to Low Quality of Life
Our findings emphasize five main potential contributors to lower quality of life: social isolation, unemployment, secondary complications, not attending rehabilitation, and the number of years living with injury. Qualitatively, social isolation appeared to be an important contributor to low quality of life; quantitatively, living alone versus with others demonstrated a moderate effect size, which may have been exacerbated by pandemic-related lockdowns. Similar findings were reported in a cross-sectional study [
13]. Potential reasons for social isolation that have been identified include challenges to participate in meaningful community activities because of problems with the built (e.g., accessibility) and social (e.g., discrimination) environment [
43,
44,
45]. Low quality of life may be related to stigmatization in terms of how people with incomplete spinal cord injury are treated by others, but also in terms of how they may have internalized negative attitudes towards people with disabilities (i.e., self-stigma) [
46].
Unemployment, which is a common issue among people with either complete or incomplete spinal cord injury, appeared to be associated with a lower level of quality of life qualitatively and quantitatively (i.e., medium effect size). The finding that more than half of the participants were unemployed and depended on pensions or compensation for their day-to-day life was congruent with Canadian data that reported, 72 % of people with spinal cord injury who are of working age get some type of financial compensation and 59% are unemployed [
4]. Work-related travel has become inextricably linked to economic activity, making employment and the ability to move inseparable [
47]. From the results, 80% of participants identified the environment or the infrastructure as a barrier to community mobility. This corresponds with a Sweden study that reported people with spinal cord injury felt that environmental factors including infrastructure and transportation among others are key determinants of good quality of life [
48]. Lack of employment may negatively affect people’s sense of self-worth, may reflect problems managing secondary health conditions, and may have financial implications [
49,
50].
Our findings emphasize how secondary complications such as pain, fatigue, depression, and frustration are common in people with spinal cord injury [
9,
10,
11] and have adverse effects on the quality of life. This is similar to the previous cross-sectional and qualitative exploration studies that reported secondary complications such as pain and spasticity may exacerbate fatigue, and in turn have an adverse effect on emotional and physical well-being [
8,
22,
23]. A lack of rehabilitation, which was identified as a contributor to lower quality of life in our sample, has previously been found to be associated with increased secondary complications and lower functional status, which negatively impacted the quality of life [
3,
51,
52,
53]. Our study findings emphasize the potential long-term benefits of rehabilitation, which demonstrated a large effect size.
There are mixed findings about the relationship between the number of years post-injury and quality of life. Some studies showed a positive relationship [
54,
55,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64]and some demonstrated stability [
65,
66,
67,
68,
69]. Others, similar to ours, show a negative relationship [
65,
66,
67,
68,
69,
70]. A few caveats with the previous studies are that they are quite dated (i.e., most were published over 20 years ago and they drew on longitudinal data that was sometimes collected over a 30-year time frame). Most of the participants in these studies had complete injuries, so it may be that our findings are more reflective of people with incomplete injuries. This idea was reinforced by several participants in the lower quality of life group who described perceiving they were aging prematurely.
4.2. Barriers to Quality of Life among Those with Low and Moderate Quality of Life
Our findings point to two other major potential barriers to quality of life: feeling judged and mobility deterioration. Participants in the low and moderate quality of life groups reported feeling judged because of challenges with their gait and ambiguity of the nature of their impairments. This negative experience is unique to this population of people with incomplete injuries who can walk compared to people with complete injuries who rely on wheelchairs. This finding is consistent with a qualitative study conducted in Australia which noted that people with incomplete spinal cord injury who can walk felt misunderstood owing to the uncertain nature of their disabilities (because wheelchairs are clear disability signifiers), and reported receiving less support from the community, and described having symptoms being overlooked [
11]. The prejudice they experience likely reflects the stigma associated with things like mobility assistive technology and gait abnormalities [
71]. It may also be reinforced by self-stigma if people with incomplete spinal cord injury have internalized these negative public attitudes [
72]. To avoid social stigma, some people with disabilities will attempt to “pass” as someone without a disability [
71] which is known as passing up, and sometimes the person accentuates his disability which is known as passing down. Passing can reflect internalized oppression if it is intended to promote assimilation. It may also be an act of resistance if someone passes strategically to avoid social oppression [
73].
Many participants in both the low and moderate quality of life groups experienced mobility deterioration. The ability to ambulate, which was evaluated by the functional ambulatory category revealed a small effect size quantitatively but qualitatively mobility was an important factor. Several previous studies have reported that deterioration in the ability to walk may lead to increases in fatigue, dependence on others, and time required to complete daily activities, which contribute to reduced quality of life [
9,
11,
15,
62].
4.3. Facilitators to Quality of Life among Those with Moderate and High Quality of Life
Our findings emphasize three main potential facilitators of moderate and high quality of life: adapting to life after injury, social and family support, and financial stability. More than half of the participants from each group (moderate and high quality of life) adapted their lives to their injury in various ways and this, in turn, had a positive effect on their quality of life. This result is congruent with three studies on social-ecological resilience; that found that when people are faced with a lot of challenges, they have the ability to adjust to different situations in the occurrence of a change in the environment, especially unanticipated changes, in ways that continue to support the well-being of a person [
74,
75,
76,
77].
The finding that most participants in the high quality of life group were married or living with someone and this variable had a large effect size resonates with previous studies showing similar findings [
19,
78,
79,
80,
81]. These studies suggested this may be attributed to the social support couples give each other; so, the relationship might have been stronger if we had measured marital quality [
82].
Peer group support and a strong community are very important for this isolated population because there is a lot of shared experience that is not seen in the general population. More than half of the participants in this group emphasized the importance of peer support, which is congruent with findings from three studies that reported in-person peer support meetings to be a highly effective way of sharing knowledge, developing skills, and decreasing secondary complications in people with spinal cord injury [
81,
82,
83,
84,
85]. Recognizing other people with spinal cord injury as peers may promote a positive social identity. This shared identity may be a source of pride for people with disabilities [
86], which may also promote quality of life.
More than 50% of participants in both groups of moderate and high quality of life described being financially stable. Although a positive relationship between income and quality of life was not found quantitatively, this may be due to the large proportion of missing data. Not surprising, other studies among people with spinal cord injury and other disabilities have found that not living in poverty has a positive influence on the quality of life [
20,
78,
87].
4.4. Facilitators to High Quality of Life
Two possible facilitators of high quality of life are highlighted in our research: resilience and being male. Our findings suggested that resilient people led a better quality of life. Seven out of 10 participants who had a high quality of life appeared to demonstrate resilience (e.g., had a positive attitude, did not give up on challenges, and were happier). This aligns with the results of two studies that concluded resilient people are less distressed emotionally, have positive thinking, have less anxiety, and are happier [
88,
89]. According to research done on resilience, the protective mechanism that is responsible for survival is not just individual but is just as likely to be a social and ecological feature of a person's existence [
90,
91,
92]. Around 70% of participants in this group adapted their routine and life to their injury which is congruent with two studies that found that people with spinal cord injury are known for their positive adjustment and tenacity, with research suggesting that over 60% of persons with spinal cord injury adjust/adapt effectively following injury [
93,
94].
Being male was associated with a higher quality of life and demonstrated a large effect size. In this group, 80% of participants were male which is congruent with a study that found that being male had a positive impact on quality of life [
20]. This contrasted with two previous studies that found men had poorer long-term quality of life after a spinal cord injury [
62,
64] which may be because people with incomplete spinal cord injury may not have the same health complications as people with complete spinal cord injury. Our current finding may reflect trends in the general population, which have found that older men reported a higher quality of life than older women which has been attributed to gender inequities [
95].
5. Limitations and Future Directions
The study had three main limitations. For qualitative analysis the sample was large, but for quantitative analysis, it was relatively small and multiple comparisons were made, which increased the potential for Type I and Type II errors. The use of non-parametric tests also likely decreased the power to detect significant differences. The cross-sectional nature of the study precludes making causal attributions.
Findings from this study could inform a variety of future studies. Although we measured many relevant variables, there are other potential confounding variables, such as resiliency, which could be collected and analyzed in a study with a larger sample size. A thorough intersectional analysis could help understand how disability intersects with other identities in a way that contributes to experiences of privilege or oppression.
6. Conclusions
People with incomplete spinal cord injury who can ambulate share many of the same challenges as other people with complete spinal cord injuries such as secondary complications, socially isolated, and financial constraints. Those who can ambulate have some unique experiences regarding unsupportive infrastructure, unsupportive physical environment, lack of programs designed specifically for people with incomplete spinal cord injury who can ambulate, degradation in mobility, and the stigma associated with those who can potentially pass as someone without a spinal cord injury. Service providers should evaluate their programs to ensure it is inclusive of people with spinal cord injury who can ambulate and may consider offering some specific programs targeting this group. For example, this could involve sensitivity training for the general population, which would help to reduce negative attitudes and misperceptions of invisible impairments and promote inclusion. Findings from this study also suggest the need to improve the built and social environment for people with incomplete spinal cord injury. To reduce healthcare inequalities, changes are needed to the way the equipment and support services are provided to this population. These changes may help to address inequalities which will ultimately improve the quality of life of people with this type of spinal cord injury.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Table S1: Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research checklist1. Table S2: Good reporting of a mixed methods study checklist 1. Document S1 :Interview guide.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.J., B.H., S.M., J.E., A.B., H.C., J.M., R.C., J.W., and B.M.; methodology, M.J. and B.M.; formal analysis, M.J., B.H., S.M.; investigation, M.J., B.H., S.M.; resources, J.M., R.C., J.W.; data curation, M.J., B.H., S.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.J.; writing—review and editing, M.J., B.H., S.M., J.E., A.B., H.C., J.M., R.C., J.W., and B.M.; visualization, M.J., B.H., S.M., B.M.; supervision, J.E., A.B., H.C., J.M., B.M.; project administration, M.J., B.M.; funding acquisition, M.J., B.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by ICORD Seed Grant and the Canadian Institute of Health Research New Investigator Grant Award MSH – 147809.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the University of British Columbia's Behavioral Research Ethics Board and local health authorities (certificate no. H20-01478).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are not available due to participant privacy.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge our study participants for sharing their experiences and taking the time to contribute to this research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A
Figure A1.
Relationship Among Sex, Marital Status, and Living Situation.
Figure A1.
Relationship Among Sex, Marital Status, and Living Situation.
References
- Noonan, V.K.; Fingas, M.; Farry, A.; Baxter, D.; Singh, A.; Fehlings, M.G. , et al. Incidence and prevalence of spinal cord injury in Canada: a national perspective. Neuroepidemiology. 2012, 38, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick Hansen SCI Registry Community Report [Internet]. Vancouver: Praxis Spinal Cord Institute. c2017 - [Cited 2023 Feb 27]. Available from: https://praxisinstitute.org/wpcontent/uploads/2019/10/RHSCIR_CommunityReport_2017.pdf/RHSCIR_CommunityReport_2017.
- Noreau, L.; Noonan, V.K.; Cobb, J.; Leblond, J.; Dumont, F.S. Spinal cord injury community survey: a national, comprehensive study to portray the lives of Canadians with spinal cord injury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2014, 20, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rick Hansen Spinal Cord Injury Registry - A look at traumatic spinal cord injury in Canada in 2019. [Internet]. Vancouver : Praxis Spinal Cord Institute. c2021 [cited 2023 Feb 27]. Available from: https://praxisinstitute.org/wpcontent/uploads/2021/02/RHSCIR-2019-Report_WEB.pdf.
- Brotherton, S.S.; Krause, J.S.; Nietert, P.J. Falls in individuals with incomplete spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2007, 45, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijendijk JHB, Post MWM, Asbeck van FWA. Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injuries in the Netherlands in 2010. Spinal Cord. 2014, 52, 258–263. [CrossRef]
- Scivoletto, G.; Tamburella, F.; Laurenza, L.; Torre, M.; Molinari, M. Who is going to walk? A review of the factors influencing walking recovery after spinal cord injury. Front Hum Neurosci. 2014, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiPiro, N.D.; Saunders, L.L.; Brotherton, S.; Kraft, S.; Krause, J.S. Pain and fatigue as mediators of the relationship between mobility aid usage and depressive symptomatology in ambulatory individuals with SCI. Spinal Cord. 2014, 52, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freixes, O.; Rivas, M.E.; Agrati PEBochkezanian, V.; Waldman, S.V.; Olmos, L.E. Fatigue level in spinal cord injury AIS D community ambulatory subjects. Spinal Cord. 2012, 50, 422–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginis KAM, Papathomas A, Perrier MJ, Smith B; SHAPE-SCI Research Group. Psychosocial factors associated with physical activity in ambulatory and manual wheelchair users with spinal cord injury: a mixed-methods study. Disabil Rehabil. 2017, 39(2), 187–192. [CrossRef]
- Jannings, W.; Pryor, J. The experiences and needs of persons with spinal cord injury who can walk. Disabil Rehabil. 2012, 34, 1820–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, C.J.; Vogel, L.C.; Chlan, K.M.; Betz, R.R.; McDonald, C.M. Depression in adults who sustained spinal cord injuries as children or adolescents. J Spinal Cord Med. 2007, 30(Suppl 1), S76–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riordan, A.; Kelly, E.H.; Klaas, S.J.; Vogel, L.C. Psychosocial outcomes among youth with spinal cord injury by neurological impairment. J Spinal Cord Med. 2015, 38, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteneck, G.G. The 44th annual John Stanley Coulter Lecture. Measuring what matters: key rehabilitation outcomes. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1994, 75, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ginis KAM, Latimer AE, Arbour-Nicitopoulos KP, Buchholz AC, Bray SR, Craven BC, et al. Leisure time physical activity in a population-based sample of people with spinal cord injury part I: demographic and injury-related correlates. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2010, 91, 722–728. [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara BM, Hitzig SL, Miller WC, Eng JJ; SCIRE Research Team. An evidence-based review on the influence of aging with a spinal cord injury on subjective quality of life. Spinal Cord. 2012, 50, 570–578. [CrossRef]
- Tomasone, J.R.; Wesch, N.N.; Ginis, K.A.M.; Noreau, L. Spinal cord injury, physical activity, and quality of life: a systematic review. Kinesiol Rev. 2013, 2, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leduc, B.E.; Lepage, Y. Health-related quality of life after spinal cord injury. Disabil Rehabil. 2002, 24, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putzke, J.D.; Elliott, T.R.; Richards, J.S. Marital status and adjustment one year post spinal cord injury. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2001, 8, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulik A, Neyaskina Y, Frizen M, Shiryaeva O; Surikova Y. Unique nature of the quality of life in the context of extreme climatic, geographical and specific socio-cultural living conditions. Int J Environ Sci Educ. 2016, 11, 6581–6591.
- Lannem, A.M.; Sorensen, M.; Froslie, K.F.; Hjeltnes, N. Incomplete spinal cord injury, exercise and life satisfaction. Spinal Cord. 2009, 47, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, S.; Hedgren, L.; Sundelin, A.; Lexell, J. Global and domain-specific life satisfaction among older adults with long-term spinal cord injury. J Spinal Cord Med. 2021, 44, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ames H, Wilson C, Barnett SD, Njoh E, Ottomanelli L. Does functional motor incomplete (AIS D) spinal cord injury confer unanticipated challenges? Rehabil Psychol. 2017, 62, 401–406. [CrossRef]
- Creswell, J.W.; Plano Clark, V.L.; Gutmann, M.; Hanson, W.E. Advanced mixed methods research designs. In: Tashakkori A, Teddlie C, editors. Handbook of Mixed Methods in Social and Behavioral Research. California: Sage; 2003. pp. 209–240.
- Creswell, J.W.; Plano Clark, V.L. Designing and Conducting Mixed Methods Research. 2nd ed. California: Sage, 2011.
- Sandelowski, M. Whatever happened to qualitative description? . Res Nurs Health. 2000, 23, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Cathain, A.; Murphy, E.; Nicholl, J. The quality of mixed methods studies in health services research. J Health Serv Res Policy. 2008, 13, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, A.; Sainsbury, P.; Craig, J. Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups. Int J Qual Health Care. 2007, 19, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrholz, J.; Wagner, K.; Rutte, K.; Meissner, D.; Pohl, M. Predictive validity and responsiveness of the Functional Ambulation Category in hemiparetic patients after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1314–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fugl-Meyer, A.R.; Bränholm, I.B.; Fugl-Meyer, K.S. Happiness and domain-specific life satisfaction in adult Northern Swedes. Clin Rehabil. 1991, 5, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melin, R.; Fugl-Meyer, K.S.; Fugl-Meyer, A.R. Life satisfaction in 18-64 years old Swedes in relation to education, employment situation, health and physical activity. J Rehabil Med. 2003, 35, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catz A, Itzkovich M, Agranov E, Ring H, Tamir A. spinal cord independence measure: a new disability scale for patients with spinal cord lesions. Spinal Cord. 1997, 35, 850–856. [CrossRef]
- Ware, J.J.; Sherbourne, C. The MOS 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36)-I. conceptual framework and item selection. Med Care. 1992, 30, 473–483. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using effect size—Or why the P value is not enough. J Grad Med Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prion, S.; Haerling, K.A. Making sense of methods and measurement: Spearman-Rho ranked-ordered coefficient. Clin. Simul. Nurs. 2014, 10, 535–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. New York: Routledge Academic; 1988.
- Morrow, S.L. Quality and trustworthiness in qualitative research in counseling psychology. J Couns Psychol. 2005, 52, 250–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, S.L.; Trotter, S.P. Data Saturation. The International Encyclopedia of Communication Research Methods. New Jersey: Wiley Blackwell; 2017.
- Fusch, P.I.; Ness, L.R. Are we there yet? Data saturation in qualitative research. Qual. Rep. 2015, 20, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Guest, G.; Bunce, A.; Johnson, L. How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods. 2006;18, 59–82. [CrossRef]
- Dey, I. Grounding Grounded Theory: Guidelines for Qualitative Inquiry. San Diego: Academic Press; 1999.
- Archibald, M.M.; Ambagtsheer, R.C.; Casey, M.G.; Lawless, M. Using Zoom Videoconferencing for Qualitative Data Collection: Perceptions and Experiences of Researchers and Participants. Int J Qual Meth. 2019, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, L.; Callaway, L.; McDonald, R.; Farnworth, L.; Brown, G.; Broom, L. Time Use following Spinal Cord Injury: An Examination of the Literature. Brit Occup Ther. 2011, 74, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, M.; Gordon, W.; Spielman, L.; Haddad, L. Participation by Individuals with Spinal Cord Injury in Social and Recreational Activity Outside the Home. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2002, 7, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiteneck, G.; Meade, M.A.; Dijkers, M.; Tate, D.G.; Bushnik, T.; Forchheimer, M.B. Environmental factors and their role in participation and life satisfaction after spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004, 85, 1793–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.C.; Larson, J.E. Personal Responses to Disability Stigma: From Self-Stigma to Empowerment. Rehabilitation Education. 2007, 20, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cresswell, T.; Dorow, S.; Roseman, S. Putting mobility theory to work: Conceptualizing employment-related geographical mobility. Environ Plann A. 2016, 48, 1787–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstin W, Gabriele B, Richard L. What promotes physical activity after spinal cord injury? An interview study from a patient perspective. Disabil Rehabil. 2006, 28, 481–488. [CrossRef]
- Conti A, Clari M, Nolan M, Wallace E, Tommasini M, Mozzone S, et al. The Relationship Between Psychological and Physical Secondary Conditions and Family Caregiver Burden in Spinal Cord Injury: A Correlational Study. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2019, 25, 271–280. [CrossRef]
- Craig, A.; Nicholson, K.P.; Guest, R.; Tran, Y.; Middleton, J. Adjustment following chronic spinal cord injury: Determining factors that contribute to social participation. BR J Health Psychol. 2015, 20, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivers CS, Fallah N, Noonan VK, Whitehurst DG, Schwartz CE, Finkelstein JA, et al. Health conditions: effect on function, health related quality of life, and life satisfaction after traumatic spinal cord injury. A prospective observational Registry Cohort Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2018, 99, 443–451. [CrossRef]
- Stillman, M.D.; Barber, J.; Burns, S.; Williams, S.; Hoffman, J.M. Complications of spinal cord injury over the first year after discharge from inpatient rehabilitation. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2017, 98, 1800–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Koppenhagen CF, Post MW, van der Woude LH, de Groot S, de Witte LP, van Asbeck FW, et al. Recovery of life satisfaction in persons with spinal cord injury during inpatient rehabilitation. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 2009, 88, 887–895. [CrossRef]
- Bushnik, T. Access to equipment, participation, and quality of life in aging individuals with high tetraplegia (C1-C4). Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2002, 7, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bushnik, T.; Charlifue, S. Longitudinal study of individuals with high tetraplegia (C1-C4) 14 to 24 years postinjury. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2005, 10, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeVivo, M.J.; Chen, Y. Trends in new injuries, prevalent cases, and aging with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011, 92, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalpakjian CZ, Houlihan B, Meade MA, Karana-Zebari D, Heinemann AW, Dijkers MP, et al. Marital status, marital transitions, well-being, and spinal cord injury: an examination of the effects of sex and time. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011, 92, 433–440. [CrossRef]
- Kemp, B.J.; Krause, J.S. Depression and life satisfaction among people ageing with post-polio and spinal cord injury. Disabil Rehabil. 1999, 21, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.S. Longitudinal changes in adjustment after spinal cord injury: a 15-year study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1992, 73, 564–568. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.S.; Coker, J.L. Aging after spinal cord injury: A 30-year longitudinal study. J Spinal Cord Med 2006, 29, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.W.; Reinhardt, J.D. Participation and Life Satisfaction in Aged People with Spinal Cord Injury: Does Age at Onset Make a Difference? . Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2015, 21, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putzke, J.D.; Richards, J.S.; Hicken, B.L.; DeVivo, M.J. Predictors of life satisfaction: a spinal cord injury cohort study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002, 83, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensman, R. Adjustment to traumatic spinal cord injury. A longitudinal study of self-reported quality of life. Paraplegia. 1994, 32, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen CM, Post MW, Hoekstra T, van der Woude LH, de Groot S, Snoek GJ et al. Trajectories in the course of life satisfaction after spinal cord injury: identification and predictors. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011, 92, 207–213. [CrossRef]
- Charlifue, S.W.; Gerhart, K.; Whiteneck, G.G. Conceptualizing and quantifying functional change: An examination of aging with spinal cord injury. Top Geriatr Rehabil. 1998, 13, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlifue, S.W.; Weitzenkamp, D.A.; Whiteneck, G.G. Longitudinal outcomes in spinal cord injury: aging, secondary conditions, and well-being. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999, 80, 1429–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlifue, S.; Gerhart, K. Community integration in spinal cord injury of long duration. NeuroRehabilitation. 2004, 19, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pershouse KJ, Barker RN, Kendall MB, Buettner PG, Kuipers P, Schuurs SB et al. Investigating changes in quality of life and function along the lifespan for people with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012, 93, 413–419. [CrossRef]
- Savic, G.; Charlifue, S.; Glass, C.; Soni, B.M.; Gerhart, K.A.; Jamous, M. British Ageing with SCI study: Changes in physical and psychological outcomes over time. Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 2010, 15, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, J.S. Adjustment after spinal cord injury: a 9-year longitudinal study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1997, 78, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffman, E. Stigma Notes on the Management of Spoiled Identity. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall; 1963.
- Vogel, D.L.; Bitman, R.L.; Hammer, J.H.; Wade, N.G. Is stigma internalized? The longitudinal impact of public stigma on self-stigma. J Couns Psychol. 2013, 60, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanuha, V.K. “The Social Process of "Passing" to Manage Stigma: Acts of Internalized Oppression or Acts of Resistance? ”. J Sociol Soc Welfare. 1999, 26, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, D.M.; Park, Y.S.; Stehling-Ariza, T.; Redlener, I. Children as bellwethers of recovery: dysfunctional systems and the effects of parents, households, and neighborhoods on serious emotional disturbance in children after Hurricane Katrina. Disaster Med Public Health Prep. 2010, 4, S17–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cicchetti, D. A developmental psychopathology perspective on bipolar disorder. In: Miklowitz D, Cicchetti D, editors. Understanding bipolar disorder: A developmental psychopathology perspective. New York : Guilford press; 2010. pp. 1–34.
- Kassis, W.; Artz, S.; Moldenhauer, S. Laying Down the Family Burden: A Cross-Cultural Analysis of Resilience in the Midst of Family Violence. Child and Youth Services. 2013, 34, 37–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tol WA, Barbui C, Galappatti A, Silove D, Betancourt TS, Souza R et al. Mental health and psychosocial support in humanitarian settings: linking practice and research. Lancet. 2011, 378, 1581–1591. [CrossRef]
- Dijkers, M.P. Quality of life of individuals with spinal cord injury: a review of conceptualization, measurement, and research findings. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2005, 42 (Suppl. 1), 87–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowler, R.; Richards, J.S.; Putzke, J.D.; Gordon, W.; Tate, D. Impact of demographic and medical factors on satisfaction with life after spinal cord injury: a normative study. J Spinal Cord Med. 2001, 24, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jörgensen, S.; Iwarsson, S.; Lexell, J. Secondary Health Conditions, Activity Limitations, and Life Satisfaction in Older Adults With Long-Term Spinal Cord Injury. PM R. 2017, 9, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagawa-Singer, M.; Padilla, G.V.; Ashing-Giwa, K. Health-related quality of life and culture. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2010, 26, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, D.; Freedman, V.A.; Cornman, J.C.; Schwarz, N. Happy Marriage, Happy Life? Marital Quality and Subjective Well-Being in Later Life. J Marriage Fam. 2014, 76, 930–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.M.; Price, L.; Freeman, J.A. Qualitative evaluation of a community peer support service for people with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord. 2013, 51, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljungberg, I.; Kroll, T.; Libin, A.; Gordon, S. Using peer mentoring for people with spinal cord injury to enhance self-efficacy beliefs and prevent medical complications. J Clin Nurs. 2011, 20, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veith, E.M.; Sherman, J.E.; Pellino, T.A.; Tasui, N.Y. Qualitative analysis of the peer-mentoring relationship among individuals with spinal cord injury. Rehabil Psychol. 2006, 51, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebers, T.A. Disability Theory. United States: University of Michigan Press; 2009.
- Martz, E.; Livneh, H. Psychosocial adaptation to disability within the context of positive psychology: findings from the literature. J Occup Rehabil. 2016, 26, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujikawa M, Lee E, Chan F, Catalano D, Hunter C, Bengtson K et al. The Connor - Davidson resilience scale as a positive psychology measure for people with spinal cord injuries. Rehabil Res Policy Educ. 2013, 27, 213–22.
- White, B.; Driver, S.; Warren, A.M. Resilience and indicators of adjustment during rehabilitation from a spinal cord injury. Rehabil Psychol. 2010, 55, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masten, A.S. Resilience in children threatened by extreme adversity: frameworks for research, practice, and translational synergy. Dev Psychopathol. 2011, 23, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, M. Social ecological complexity and resilience processes. Behav Brain Sci.2015; 38: e124. [CrossRef]
- Theron, L.C.; Liebenberg, L.; Ungar, M. Youth resilience and culture: Commonalities and complexities. Netherlands: Springer; 2015.
- Bonanno, G.A.; Kennedy, P.; Galatzer-Levy, I.R.; Lude, P.; Elfström, M.L. Trajectories of resilience, depression, and anxiety following spinal cord injury. Rehabil Psychol. 2012, 57, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- deRoon-Cassini TA, Mancini AD, Rusch MD, Bonanno GA. Psychopathology and resilience following traumatic injury: a latent growth mixture model analysis. Rehabil Psychol. 2010, 55, 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Xu, H.; Wu, B. Gender differences in quality of life among community-dwelling older adults in low- and middle-income countries: results from the Study on global AGEing and adult health (SAGE). BMC Public Health. 2020, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Table 1.
Mann - Whitney U, Kruskal - Wallis, Spearman correlation, Cohen’s d, Cohen’s F with demographic factors, standardized measures, and 3 levels of quality of life.
Table 1.
Mann - Whitney U, Kruskal - Wallis, Spearman correlation, Cohen’s d, Cohen’s F with demographic factors, standardized measures, and 3 levels of quality of life.
| Variable |
Label (Potential range) |
[Mean ± SD] / N (%) |
Low
Quality of Life (N=5) N (%)/ Mean ± SD |
Moderate Quality of life (N=9) N (%)/
[Mean ± SD] |
High
Quality of Life (N=10) N (%)/
[Mean ± SD] |
Statistic
1U/ 2(H) / 3[rs] |
Cohen’s
d / (f) |
P |
| Gender |
Male |
13 (54.16) [48.31±10.68] |
1 (20.00) |
4 (44.44) |
8 (80.00) |
30.001
|
1.12 |
0.02 |
| Female |
11 (45.83) [34.82± 13.28] |
4 (80.00) |
5 (55.56) |
2 (20.00) |
| Type of injury4 |
Traumatic |
14 (58.30)
[45.79±13.05] |
2 (40.00) |
4(44.44) |
8 (80.00) |
32.001
|
0.29 |
0.41 |
| Non Traumatic |
6 (25.00)
[40.67± 14.62] |
1 (20.00) |
3(33.33) |
2 (20.00) |
| Level of spinal cord injury |
Cervical |
9 (37.50) |
- |
4 (44.44) |
4 (40.00) |
(0.58)2
|
(0.03) |
0.75 |
| Thoracic |
6 (25.00) |
2 (40.00) |
2 (22.22) |
3 (30.00) |
| Lumbar |
9 (37.50) |
3 (60.00) |
3 (33.33) |
3 (30.00) |
| Attended rehabilitation |
Yes |
16 (66.67)
[46.38±10.36] |
1 (20.00) |
7 (77.78) |
8 (80.00) |
29.001
|
0.957 |
0.032 |
| No |
8 (33.33)
[33.62±15.76] |
4 (80.00) |
2 (22.22) |
2 (20.00) |
| Employed |
Yes |
4 (16.67) [43.75±16.86] |
1 (20.00) |
1 (11.11) |
2 (20.00) |
34.501
|
0.13 |
0.67 |
| No |
20 (83.33) [41.80±13.28] |
4 (80.00) |
8 (88.89) |
8(80.00) |
| Marital Status |
Never married/Separate/
Divorce |
11 (45.83)
[35.27±14.16] |
5 (100.00) |
3 (33.33) |
3 (30.00) |
37.001
|
1.02 |
0.04 |
| Married/ Common Law |
13 (54.17) [47.92± 10.24] |
- |
6 (66.67) |
7 (70.00) |
| Location of residence |
City |
13 (54.16) |
3 (60.00) |
3 (33.33) |
7 (70.00) |
(1.49)2
|
(0.06) |
0.48 |
| Suburban |
7 (29.17) |
- |
5 (55.56) |
2 (20.00) |
| Rural |
4 (16.67) |
2 (40.00) |
1 (11.11) |
1 (10.00) |
| Living situation |
Live alone |
8 (33.33)
[37.00±14.21] |
3 (60.00)
|
3 (33.33)
|
2 (20.00)
|
44.501
|
0.57 |
0.23 |
Live with
somebody |
16 (66.67) [44.69± 12.88] |
2 (40.00) |
6 (66.67) |
8 (80.00) |
| Level of education |
2=High school |
7 (29.17) |
[3.60 ± 1.14] |
[3.56±1.51] |
[3.70±1.57] |
[0.07]3
|
- |
0.72
|
| 3=College/Trade School |
5 (20.83) |
| 4=University degree |
5 (20.83) |
| 5=Graduate studies |
4 (16.67) |
| 6=Postgraduate |
3 (12.50) |
| Number of Years Living with an injury |
(2 – 52) |
[21.88 ± 16.30] |
[26.20±16.92] |
[27.67±18.53] |
[14.50±12.01] |
[-0.40] 3
|
- |
0.05 |
| Gross annual income 5 |
(1-7)6
|
[1.83 ± 2.88] |
[2.20 ± 2.39] |
[0.78±2.39] |
[2.60±3.44] |
[0.15] 3
|
- |
0.48 |
| Age (Years) |
(27 – 72) |
[54.60 ± 14.60] |
[50.60±15.44] |
[54.22±12.17] |
[57.30±16.95] |
[0.19]3
|
- |
0.37 |
| 12 – Item Short-form health survey: Mental component scores |
(22 -60) |
[39.95 ± 11.11] |
[29.77±5.29] |
[36.04±7.34] |
[48.56±9.99] |
[0.74]3
|
- |
<0.01 |
| 12 – Item Short-form health survey:Physical component scores |
(20 -57) |
[35.10 ± 9.86] |
[28.99±10.36] |
[29.95±4.63] |
[42.80±8.27] |
[0.68]3
|
- |
<0.01 |
| Spinal cord independence measure - III |
(38 -100) |
[79.04 ±13.90] |
[70.20±18.19] |
[75.44±13.72] |
[86.70±7.62] |
[0.34]3
|
- |
0.11 |
| Functional ambulatory category |
4=Ambulate independently level surface only |
12 (50.00)
[38.50±12.52] |
3(60.00) |
6(66.67) |
3(30.00) |
46.501
|
0.54 |
0.14 |
| 5=Ambulate independently |
12 (50.00)
[45.75±14.08] |
2(40.00) |
3(33.33) |
7(70.00) |
| Life satisfaction questionnaire – 11 |
(20- 64) |
[42.13 ± 13.54] |
[22±2.35] |
[39±4.44] |
[55±5.46] |
- |
- |
- |
Table 2.
Potential reason for quality of life ratings.
Table 2.
Potential reason for quality of life ratings.
| |
Low Quality of life (P1, P6, P11, P13, P14) |
Moderate Quality of life (P4, P5, P7, P9, P10, P15, P16, P18, P20) |
High Quality of life (P3, P2, P8, P17, P12, P19, P21, P22, P23, P24) |
| Potential Barriers to Quality of Life |
Feeling socially isolated Having financial concerns Feeling judged by abled-bodied people Feeling left out due to City layout and buildings not wheelchair friendly Expressing that spinal cord injury was due to medical negligence Describing their deteriorating mobility Feeling left out due to lack of resources for people with disabilities |
Feeling judged Describing their deteriorating mobility -
Feeling socially isolated
Having financial concerns -
Feeling left because of
- o
Lack of resources for people with disabilities - o
City layout and buildings are not wheelchair friendly - o
Spinal cord injury programs are designed for people with complete spinal cord injury
|
|
| Potential Facilitators to Quality of Life |
|
-
Learning to adapt to life after injury
- o
Appreciating their support system
Having social support Having financial stability Feeling included in spinal cord injury programs -
Benefiting from COVID restrictions such as
- o
Improved the financial situation - o
Improved access to medical care
-
Benefiting from
- o
Adapted/ modified house - o
City layout and buildings wheelchair friendly
Expressing gratitude to still be able to walk |
-
Learning to adapt to life after injury
- o
Demonstrating resilience
-
Appreciating their support system
- o
Feeling included in spinal cord injury programs and community - o
Having family support - o
Having Social support
Experiencing little difference with day to day life during COVID restrictions Having financial stability -
Benefiting from
- o
Adapted/ modified house - o
City layout and buildings wheelchair friendly
-
Benefiting from COVID restrictions such as
- o
Improved social life - o
Improved access to medical care
Being able to ambulate without an assistive device Describing a sense of gratitude |
Table 3.
Low life satisfaction quotes organised by factor.
Table 3.
Low life satisfaction quotes organised by factor.
| Topic |
Quotation |
Participant information |
| Feeling socially isolated |
| Losing friends because of pain intolerance |
‘I have ongoing and significant pain, difficulty sitting, and difficulty walking. I can't sit in an upright position for very long without pain, I can sit in my wheelchair for about two hours but I couldn't sit in a regular kitchen chair on a couch. I wasn't able to go to see friends anymore for lunch or coffee because I couldn't sit. I went a long time without a wheelchair before I was finally approved for one.’ |
P11, female, 63 years old, T6 |
| Losing human contact and preferred in person interaction |
‘I miss some of the important people in my life because we are not able to connect in the same way. Phone calls are not the same as actually going out and meeting people, person to person, and doing something fun together or going out for a meal or hanging out at a social event, it’s not the same connection.’ |
P14, female, 51 years old, thoracic |
| Having financial concerns |
| Identifying financial need as barrier for participation |
‘That’s been a barrier because of the low income that I get from my pension. If I wanted to get an electric assistive device this is kind of expensive, I do need home adaptations right now, but those cost a high price so I have to adapt myself to my house set up for the time being which is tiring and consumes most of my energy.’ |
P06, a 31-year-old male, injured in the lumbar region |
| Being judged |
| Feeling invisible |
‘That’s pretty much an everyday occurrence. People treat me like this because I’m physically disabled and think I’m mentally disabled and they’ll ask the person I’m with the question, instead of asking me, which is very infuriating because I’m an adult and you know, highly competent, I can talk for myself.’ |
P14, female, 51 years old, thoracic |
| Experiencing prejudice |
‘Discrimination happens all the time because people have attitudinal barriers. They’re straight-up rude and basically kind of treat you like you’re a non-human. And that pretty much is all the time because I look physically disabled when I’m out and about, I get stares, I get looks, it’s pretty much constant.’ |
P14, female, 51 years old, thoracic |
| Feeling left out due to city layout and infrastructure |
| Experiencing accessibility challenges in the built environment |
‘The area where I live is a bit hilly. So it's difficult either using my walker/ my cane /my wheelchair; there are some streets I can't go on. I find that some of those curb cuts on the sidewalk are steep and sometimes I have to get out of my wheelchair and push it up the curb cuts, then I can get back in. Some of the stores in the area I live have a couple of steps up or down, to get into the stores, so of course, I don't go there. If a place is not wheelchair accessible I don't go there.’ |
P11, female, 63 years old, T6 |
| Expressing that spinal cord injury was due to medical negligence |
| Expressing deterioration in health due to medical negligence |
‘If I would've had the machine to help me breathe, my health, my walking, and everything else would never have deteriorated. I never had to end up in the hospital and now I have to go to the hospital to see a cardiologist, All because I didn't get the right rehabilitation for my deteriorating leg, hip, and back muscles with the machine to help me breathe.’ |
P01, female, 40 years old, T6-T7 |
| Expressing a degradation in mobility |
| Feeling like prematurely aging |
‘It's like living with a 121-year-old woman, that's what I'm like. I bring in the groceries from the car using the walker, I'll be paralyzed in bed for 8 - 14 hours. So right after I - I lie in bed for 13 hours, sometimes slept all day, like I was just paralyzed, just couldn't do a thing. in six months I'll get paralyzed 130 times and could not move.’ |
P13, female, 68-year-old, L3-L5 |
Table 4.
Moderate life satisfaction quotes organized by factor.
Table 4.
Moderate life satisfaction quotes organized by factor.
| Topic |
Quotation |
Participant information |
|
| Feeling judged |
|
| Feeling hyper visible |
‘They don’t realize maybe how disabled I am, why I’m disabled, or why I’m using a cane. So, even when I’m in a wheelchair, I always have my canes with me (move or go somewhere, where I can’t go with my wheelchair), so if I stand up and use the canes, I kind of get this look, oh why are you using your canes? Why are you using a chair then? I might get a strange look.’ |
P16, female, 67 years old, C3-C4 |
|
| Expressing a positive experience with abled bodied people |
‘I've been lucky because, in pickleball and ping pong and all the other sport-type activities I wanted to join, I never had to join through a disability-specific organization because I've always been accepted by able-bodied people to join as a guy in a wheelchair.’ |
P09, male, 67 years old, C6- C7 |
|
| Experiencing a decrease in mobility |
| Acknowledging a decrease in mobility after surgery |
‘Before I could walk with 2 poles, but now I cannot walk with them instead I have to use a walker, without the walker it's just that I look like I’m a little drunk because my coordination is not there all the time. My equilibrium is not what it used to be, if I unexpectedly come on a change in the terrain I'm walking on, it's a big problem for me because I can't react normally and could end up falling. I look like I'm drunk really and that saddens me.’ |
P18, male, 54 years old, lumbar |
|
| Learning to adapt to life after injury |
| Navigating through challenges |
‘I have turned my wheelchair into a tricycle, so Vancouver is full of hills, … now perfectly able to go up and down hills anywhere I want. The apartment that I have has been completely modified for accessibility, the cabinets come down to my level, I have a cooktop and a kitchen sink that can come down to my level, and the entire washroom is accessible for me in my wheelchair. So my apartment does not have barriers for me.’ |
P09, male, 67 years old, C6- C7 |
|
| Making peace with things I cannot do |
‘I would be getting up most of the mornings with back pain, but I had been living with back pain the majority of the time, and I've just gotten used to it. And I functioned with it.’ |
P10, female, 46 years old, C5-C6 |
|
| Adjusting to their routine |
‘My day is very limited in what I did in my day. A lot of tasks would take me twice as long to do. I have to make sure I'm not sitting too long because then the pain kicks in, but at the same time, I can't do movement for long periods. If I do go on the treadmill I need to sleep that day for 20 minutes to an hour.’ |
P10, female, 46 years old, C5-C6 |
|
| Appreciating their support system |
| Feeling blessed to have support |
‘I'll have meetings with my pastor who's also a good friend, so mentally, I do alright. With my boyfriend's family and abled-bodied friends I feel [I am] in an inclusive environment and it just I feel supported.’ |
P04, female, 36 years old, C5 – C6 |
|
| Expressing a support system gives courage to keep moving forward in life |
‘I have friends and they are always looking for places for me to rest, which is nice. We’ll just sit here for a while. Because they know I have limits and I do get tired. They don’t want me to fall over because then they have to pick me up - which has happened a few times.’ |
P07, male, 62 years old male, C6-C7 |
|
| Having financial stability |
| Showing gratitude that partner still has a job |
‘At the moment I'm very fortunate with my husband that he has a good job and he's working. At the moment we're okay financially.’ |
P10, female, 46 years old, C5-C6 |
|
| Feeling fortunate for financial stability |
‘I'm very fortunate that I did not lose my job [because of the pandemic]. I worked for 5 years after my accident, then I retired. I have a good federal pension, so COVID has had no impact and my accident has had minimal impact. I was well insured when I had my accident so that helped me very well. I have no financial issues that arise after my accident. I don't have to wait for approval for spending money, to go somewhere, whatever it is.’ |
P09, male, 67 years old, C6- C7 |
|
Table 5.
High life satisfaction quotes organized by factor.
Table 5.
High life satisfaction quotes organized by factor.
| Topic |
Quotation |
Participant information |
| Demonstrating resilience |
| Expressing determination to recover from injury |
‘It took me three months to make it out to the end of the driveway after I got out of the hospital. I must've fallen at least twice a day. My problem was my feet, I'd be walking along and all of a sudden one leg would go out. It took a long time to learn to keep the feet going where I wanted to, even after I managed to learn to get the feet to go where I wanted to, I had to watch it. I could go for a walk but I wouldn't see anything besides the concrete (laugh).’ |
P03, male, 67 years old, C5-C6 |
| Seeing progress over time |
‘Recently because I'm still seeing progressing like I'm still seeing improvement in my recovery, so that's why I'm still attacking this uh as aggressively, now I can walk 50 meters without needing a walking device, and I feel fortunate that I can walk.’ |
P22, male, 49 years old, C6 |
| Learning to adapt to life after injury |
| Facing challenges |
‘I don't look at barriers, I look at them more like challenges, I usually come up with a way of um modifying something so I can still do it. I'll give you an example I started deer hunting, and my wife said, "Why don't you go and get some venison," because I grew up on that when we were young with our families. So I got my bow and go out and did that, but I couldn't carry the deer on my shoulders as I could before, so I made a kind of a sled and a harness and ski poles.’ |
P08, male, 72 years old, lumbar |
| Appreciating their support system |
| Being thankful for having support |
‘If my wife, wasn’t there, I would be struggling at this point. I really would. And so, she has been, she’s been my rock type of thing. She’s really helped. And I couldn’t like I said I don’t think I would be here if it wasn’t for that because there’s thoughts, you know right after, and I didn’t see a future, I didn’t see anything. And that was really difficult.’ |
P24, male, 68 years old, L3-L5 |
| Feeling a sense of belongingness to a group |
‘I feel included and welcomed [at the spinal cord injury organization]. Well, I have the same problems, in terms of bowels and bladder, if you went to a family physician, they may see one or two cases in their whole time, in their practice. Whereas, the people who specialize in this, so, or the people in the ambulatory group, you’re talking to people who do it 24/7, and have these problems. So, they have much better answers than, the doctors. So, it’s quite good and powerful to have this cohort. Just talking to each other about the problems we face.’ |
P24, male, 68 years old, L3-L5 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).