Submitted:
22 August 2023
Posted:
22 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Open Circuit Potential (OCP) Monitoring.
2.2. Electrodes Surface Characterization.
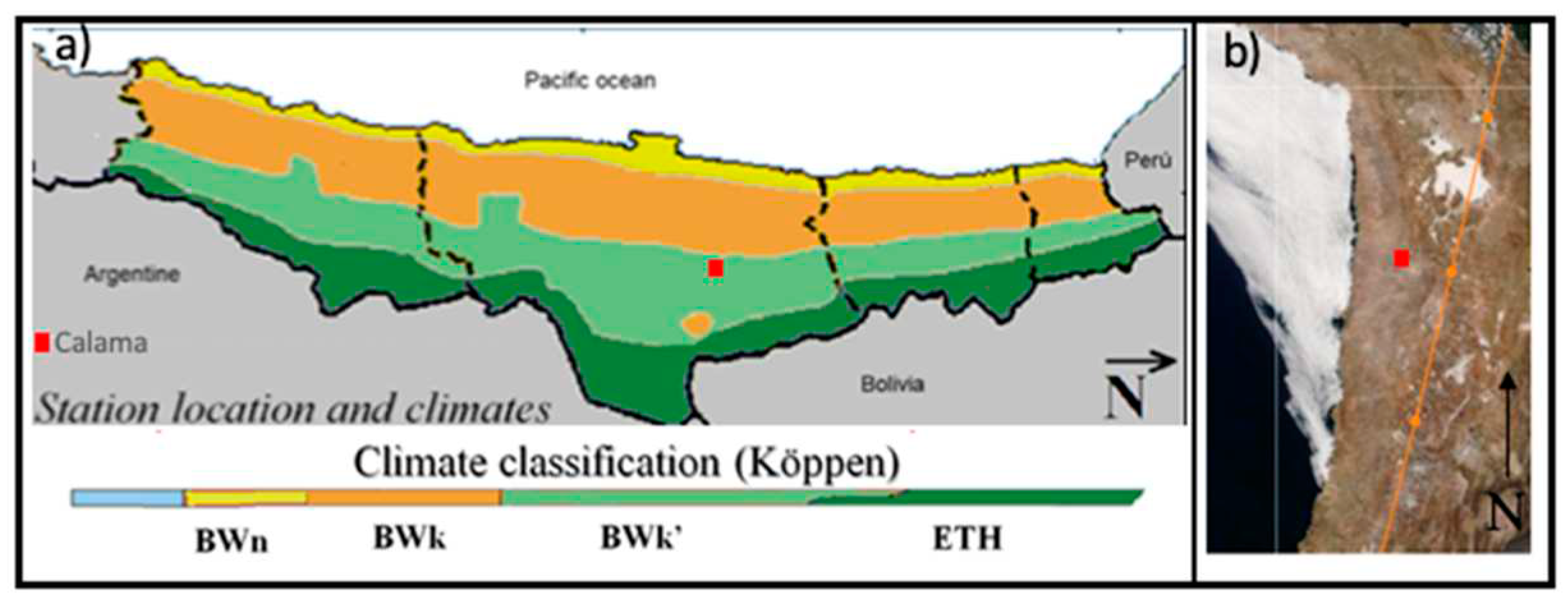
2.3. Meteorology Monitoring.
2.4. Experimental Data Analysis.
2.5. CAM Species Plants as PMFC.
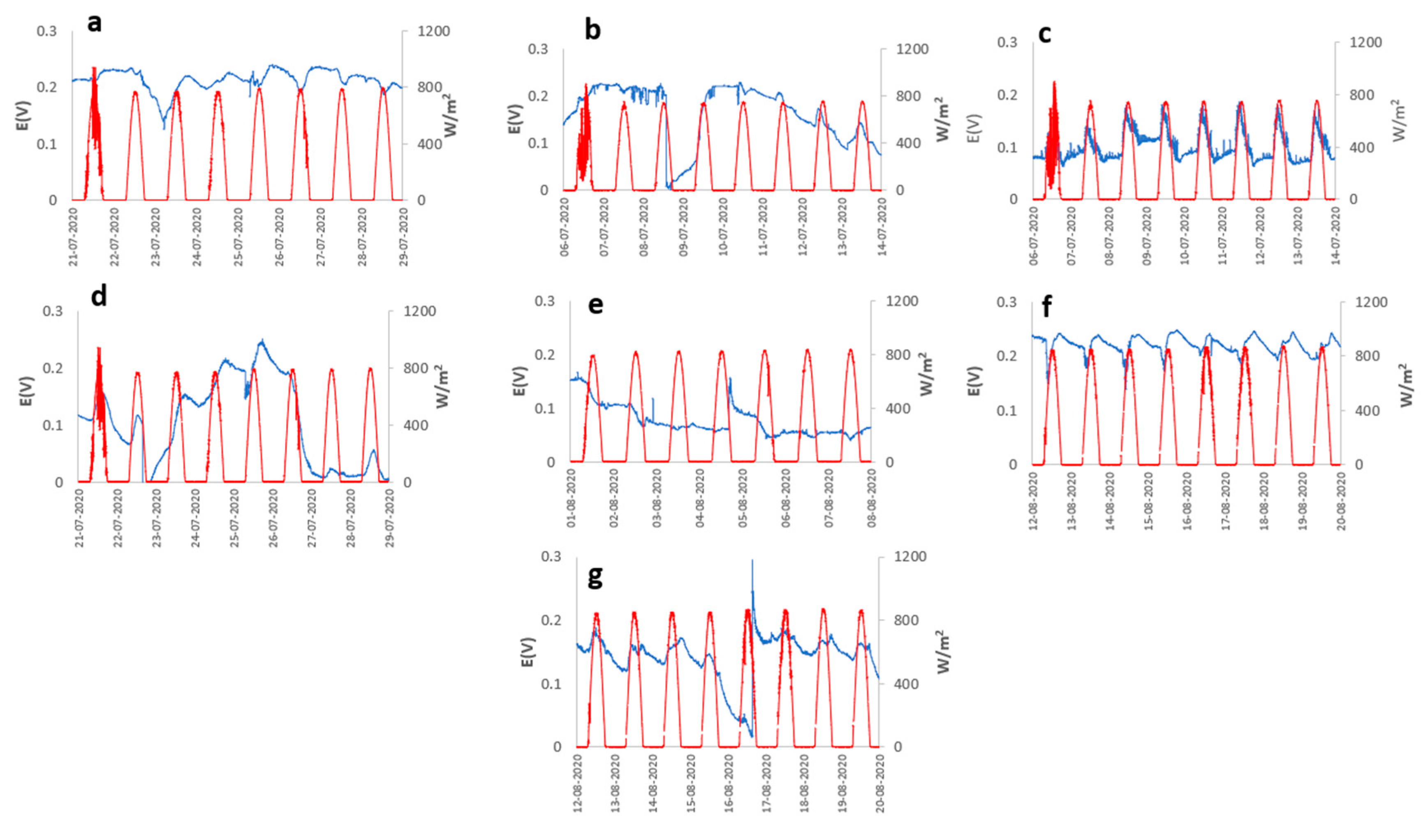
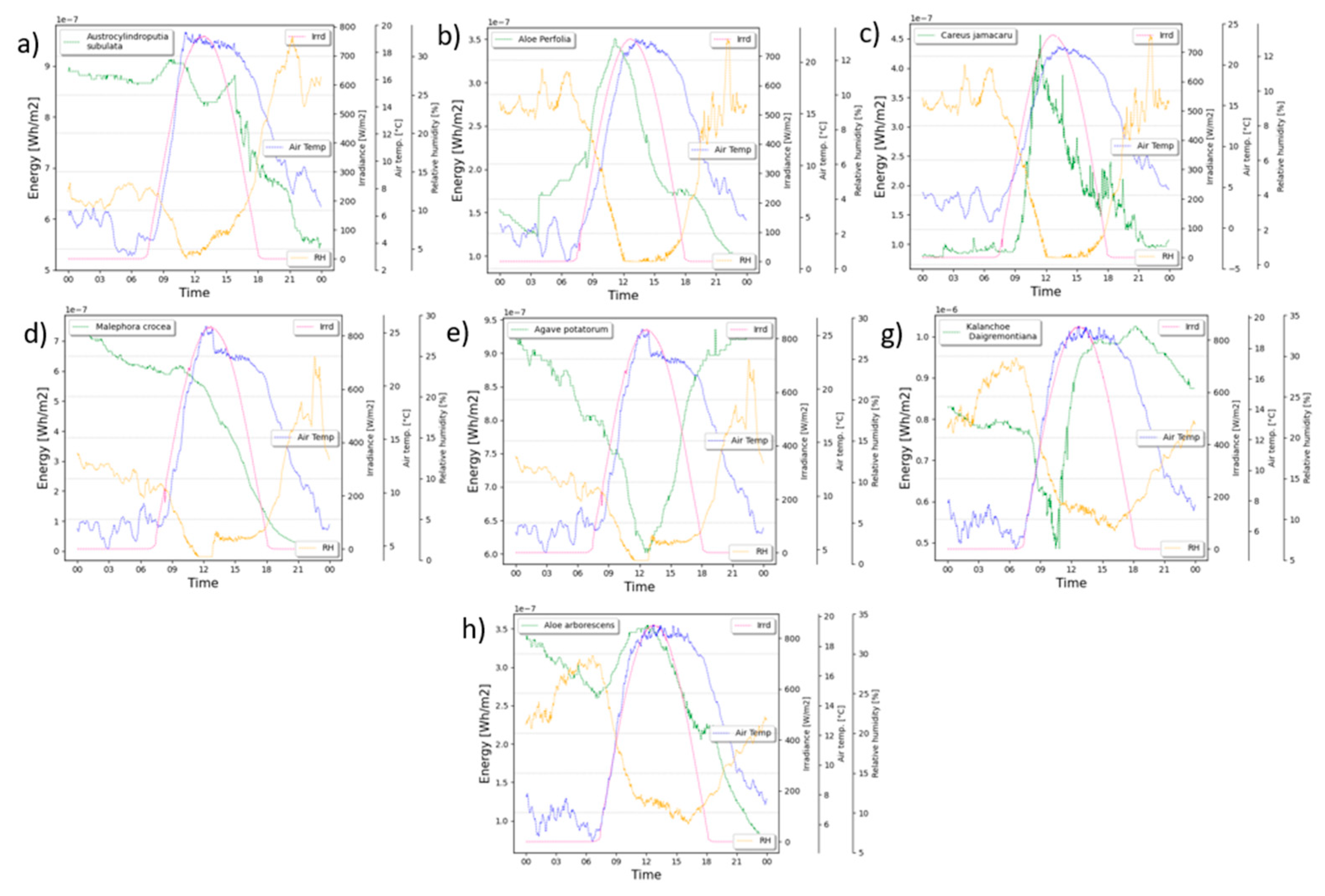
3. Results and Discussion
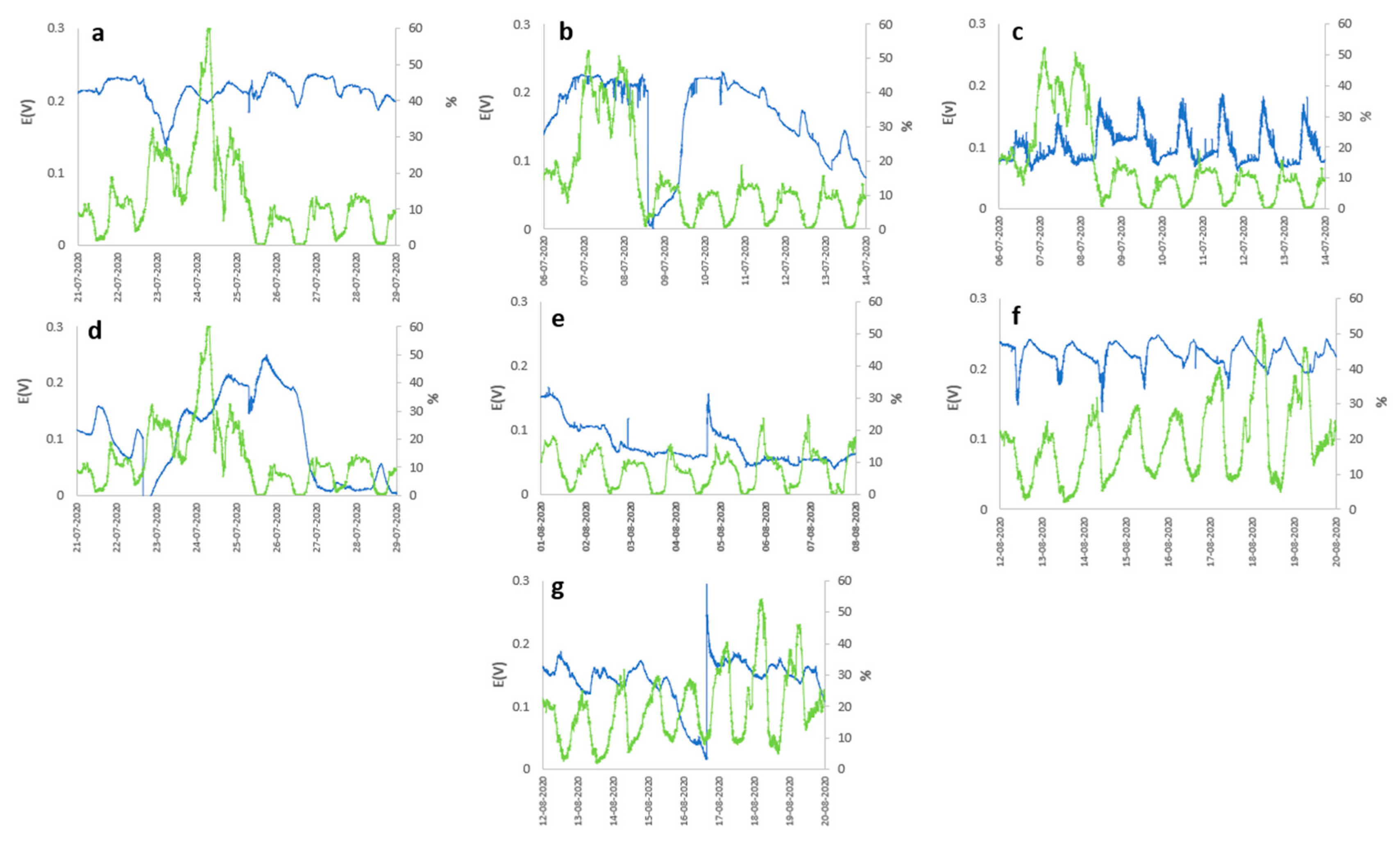
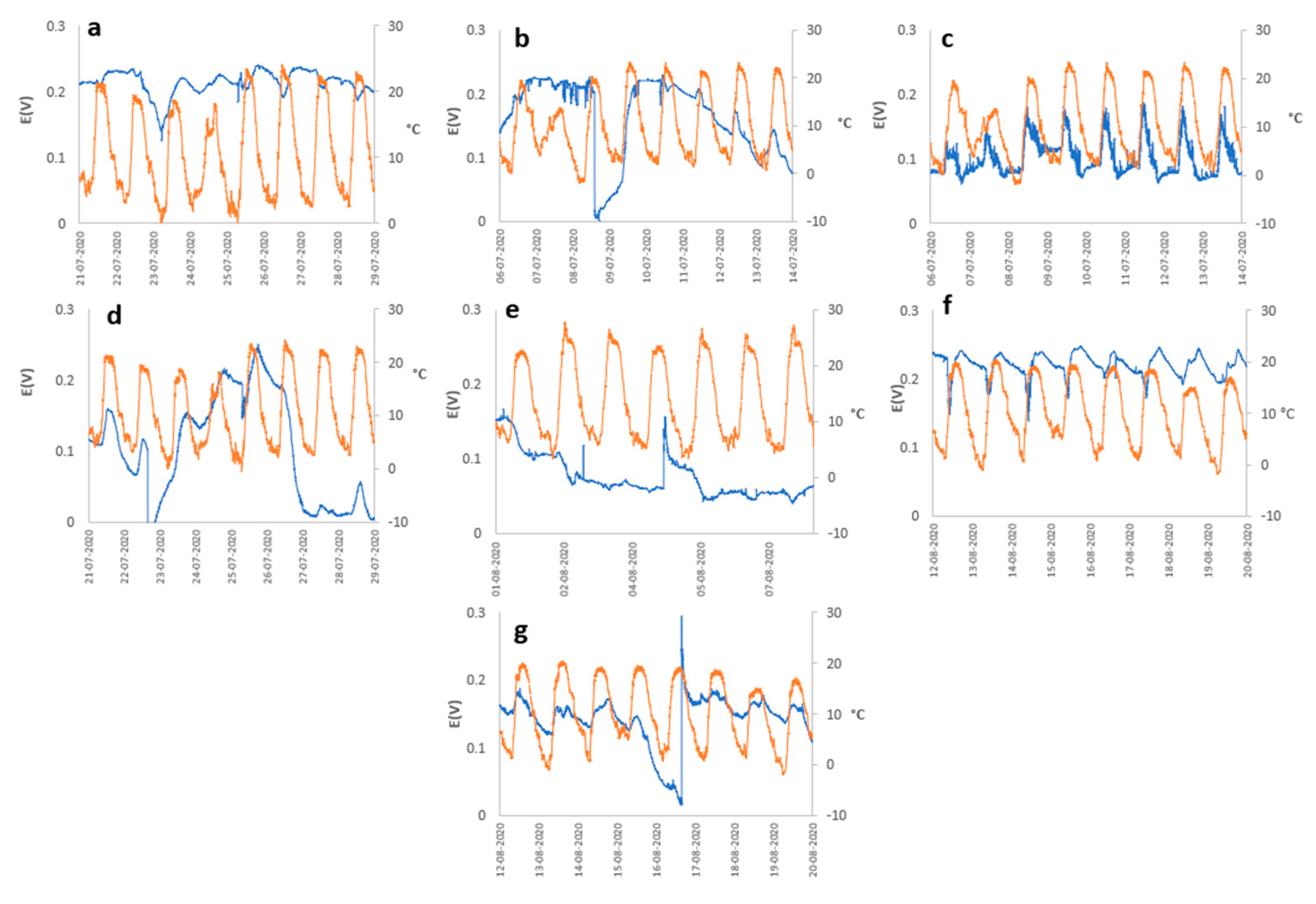
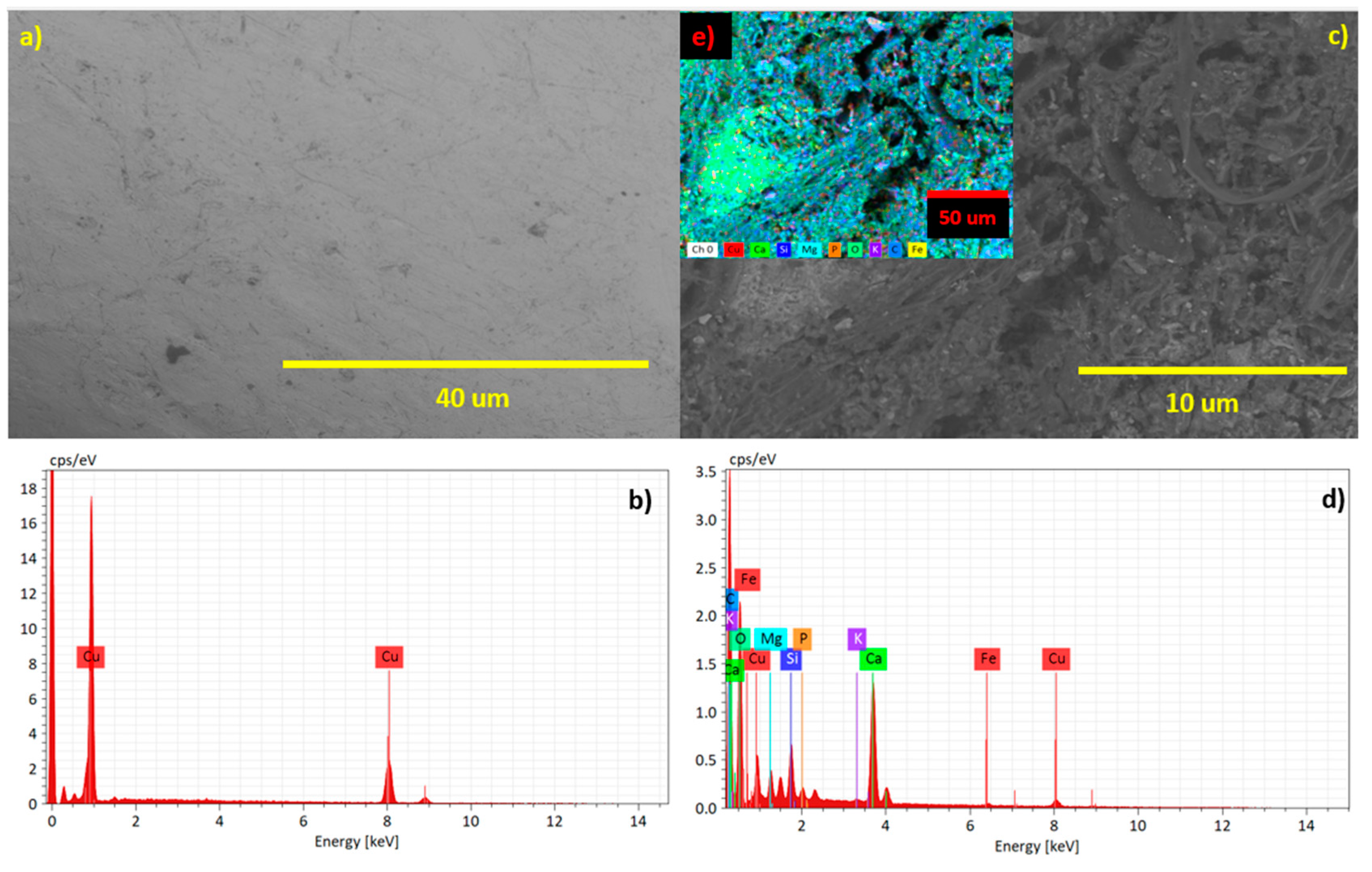
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- C. Parrado, A. Girard, F. Simon, and E. Fuentealba, “2050 LCOE (Levelized Cost of Energy) projection for a hybrid PV (photovoltaic)-CSP (concentrated solar power) plant in the Atacama Desert, Chile,” Energy, vol. 94, pp. 422–430, 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. T. Kiehl and K. E. Trenberth, “Earth’s Annual Global Mean Energy Budget.”.
- D. Kim and V. Ramanathan, “Solar radiation budget and radiative forcing due to aerosols and clouds,” Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, vol. 113, no. 2, Jan. 2008. [CrossRef]
- R. Nitisoravut and R. Regmi, “Plant microbial fuel cells: A promising biosystems engineering,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 76, no. September 2016, pp. 81–89, 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. De Schamphelaire et al., “Microbial fuel cells generating electricity from rhizodeposits of rice plants,” Environ Sci Technol, vol. 42, no. 8, pp. 3053–3058, 2008. [CrossRef]
- K. Raman and J. C. W. Lan, “Performance and kinetic study of photo microbial fuel cells (PMFCs) with different electrode distances,” Appl Energy, vol. 100, pp. 100–105, 2012. [CrossRef]
- K. Wetser, E. Sudirjo, C. J. N. Buisman, and D. P. B. T. B. Strik, “Electricity generation by a plant microbial fuel cell with an integrated oxygen reducing biocathode,” Appl Energy, vol. 137, pp. 151–157, 2015. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Timmers et al., “Microbial community structure elucidates performance of glyceria maxima plant microbial fuel cell,” Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, vol. 94, no. 2, pp. 537–548, 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. Shaikh et al., “Bioelectricity production using plant-microbial fuel cell: Present state of art,” South African Journal of Botany, vol. 140, pp. 393–408, 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Kouzuma, N. Kaku, and K. Watanabe, “Microbial electricity generation in rice paddy fields : recent advances and perspectives in rhizosphere microbial fuel cells,” pp. 9521–9526, 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Moqsud, M. A. Hannan, and K. Omine, “Assessment of factors influencing bioelectricity generation in paddy plant microbial fuel cells,” vol. 4, no. 12, pp. 840–850, 2015.
- D. P. B. T. B. Strik, R. A. Timmers, M. Helder, K. J. J. Steinbusch, H. V. M. Hamelers, and C. J. N. Buisman, “Microbial solar cells: Applying photosynthetic and electrochemically active organisms,” Trends in Biotechnology, vol. 29, no. 1. pp. 41–49, Jan. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Helder, D. P. Strik, H. V. M. Hamelers, and C. J. N. Buisman, “The flat-plate plant-microbial fuel cell : the effect of a new design on internal resistances The flat-plate plant-microbial fuel cell : the effect of a new design on internal resistances,” 2012.
- M. Helder, D. P. B. T. B. Strik, R. A. Timmers, S. M. T. Raes, H. V. M. Hamelers, and C. J. N. Buisman, “Resilience of roof-top Plant-Microbial Fuel Cells during Dutch winter,” Biomass Bioenergy, vol. 51, no. 0, pp. 1–7, 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. Helder, D. PBTB Strik, H. V. Hamelers, and C. J. Buisman, “The flat-plate plant-microbial fuel cell: the effect of a new design on internal resistances,” 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. Shaikh et al., “Bioelectricity production using plant-microbial fuel cell: Present state of art,” South African Journal of Botany, vol. 140, pp. 393–408, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Brunelli, P. Tosato, and M. Rossi, “Flora Health Wireless Monitoring with Plant-Microbial Fuel Cell,” Procedia Eng, vol. 168, pp. 1646–1650, 2016. [CrossRef]
- D. Brunelli, P. Tosato, and M. Rossi, “Flora monitoring with a plant-microbial fuel cell,” in Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Springer Verlag, 2017, pp. 41–48. [CrossRef]
- D. Brunelli, P. Tosato, and M. Rossi, “Microbial Fuel Cell as a Biosensor and a Power Source for Flora Health Monitoring.”.
- M. Helder, D. P. B. T. B. Strik, H. V. M. Hamelers, R. C. P. Kuijken, and C. J. N. Buisman, “Bioresource Technology New plant-growth medium for increased power output of the Plant-Microbial Fuel Cell,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 104, pp. 417–423, 2012. [CrossRef]
- C. Wang, L. Guo, Y. Li, and Z. Wang, “Systematic Comparison of C3 and C4 Plants Based on Metabolic Network Analysis,” BMC Syst Biol, vol. 6, no. SUPPL.2, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Maddalwar, K. Kumar Nayak, M. Kumar, and L. Singh, “Plant microbial fuel cell: Opportunities, challenges, and prospects,” Bioresource Technology, vol. 341. Elsevier Ltd, Dec. 01, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Helder, D. P. B. T. B. Strik, H. V. M. Hamelers, R. C. P. Kuijken, and C. J. N. Buisman, “New plant-growth medium for increased power output of the Plant-Microbial Fuel Cell,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 104, pp. 417–423, Jan. 2012. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Timmers, D. P. B. T. B. Strik, H. V. M. Hamelers, and C. J. N. Buisman, “Characterization of the internal resistance of a plant microbial fuel cell,” Electrochim Acta, vol. 72, pp. 165–171, Jun. 2012. [CrossRef]
- C. C. Lin, C. H. Wei, C. I. Chen, C. J. Shieh, and Y. C. Liu, “Characteristics of the photosynthesis microbial fuel cell with a Spirulina platensis biofilm,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 135, pp. 640–643, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Srikanth, T. Pavani, P. N. Sarma, and S. Venkata Mohan, “Synergistic interaction of biocatalyst with bio-anode as a function of electrode materials,” Int J Hydrogen Energy, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 2271–2280, Feb. 2011. [CrossRef]
- A. Baudler, M. Langner, C. Rohr, A. Greiner, and U. Schröder, “Metal–Polymer Hybrid Architectures as Novel Anode Platform for Microbial Electrochemical Technologies,” ChemSusChem, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 253–257, Jan. 2017. [CrossRef]
- X. Qi, P. Liu, P. Liang, W. Hao, M. Li, and X. Huang, “Dual-signal-biosensor based on luminescent bacteria biofilm for real-time online alert of Cu(II) shock,” Biosens Bioelectron, vol. 142, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhang et al., “Electrochemical and microbial community responses of electrochemically active biofilms to copper ions in bioelectrochemical systems,” Chemosphere, vol. 196, pp. 377–385, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- A. Baudler, I. Schmidt, M. Langner, A. Greiner, and U. Schröder, “Does it have to be carbon? Metal anodes in microbial fuel cells and related bioelectrochemical systems,” Energy Environ Sci, vol. 8, no. 7, pp. 2048–2055, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. Asif et al., “Unveiling microbiologically influenced corrosion engineering to transfigure damages into benefits: A textile sensor for H2O2 detection in clinical cancer tissues,” Chemical Engineering Journal, vol. 427, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- X. Zhu and B. E. Logan, “Copper anode corrosion affects power generation in microbial fuel cells,” Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology, vol. 89, no. 3, pp. 471–474, 2014. [CrossRef]
- K. R. S. Pamintuan and K. M. Sanchez, “Power generation in a plant-microbial fuel cell assembly with graphite and stainless steel electrodes growing Vigna Radiata,” in IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, IOP Publishing Ltd, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- P. Bombelli et al., “Comparison of power output by rice (Oryza sativa) and an associated weed (Echinochloa glabrescens) in vascular plant bio-photovoltaic (VP-BPV) systems,” Appl Microbiol Biotechnol, vol. 97, no. 1, pp. 429–438, Jan. 2013. [CrossRef]
- D. R. Lovley, “Microbial fuel cells: novel microbial physiologies and engineering approaches,” Current Opinion in Biotechnology, vol. 17, no. 3. pp. 327–332, Jun. 2006. [CrossRef]
- D. Watts, M. F. Valdés, D. Jara, and A. Watson, “Potential residential PV development in Chile: The effect of Net Metering and Net Billing schemes for grid-connected PV systems,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, vol. 41. Elsevier Ltd, pp. 1037–1051, Jan. 01, 2015. [CrossRef]
- C. Herrera et al., “Recharge and residence times of groundwater in hyper arid areas: The confined aquifer of Calama, Loa River Basin, Atacama Desert, Chile,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 752, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- A. Marzo et al., “Sunbelt spectra comparison with standard ASTM G173: The Chilean case,” in AIP Conference Proceedings, American Institute of Physics Inc., Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Trigo-Gonzalez et al., “Development and comparison of PV production estimation models for mc-Si technologies in Chile and Spain,” J Clean Prod, vol. 281, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Trigo-González et al., “Hourly PV production estimation by means of an exportable multiple linear regression model,” Renew Energy, vol. 135, pp. 303–312, May 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. M. Ezzat, A. M. El Sayed, and M. M. Salama, “Use of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) technique to study the genetic diversity of eight aloe species,” Planta Med, vol. 82, no. 15, pp. 1381–1386, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. J. Pegu and M. A. Sharma, “International Journal of Trend in Scientific Research and Development (IJTSRD) Review on Aloe Vera the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0).” [Online]. Available: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0.
- V. Nessner Kavamura, R. G. Taketani, M. D. Lançoni, F. D. Andreote, R. Mendes, and I. Soares de Melo, “Water Regime Influences Bulk Soil and Rhizosphere of Cereus jamacaru Bacterial Communities in the Brazilian Caatinga Biome,” PLoS One, vol. 8, no. 9, Sep. 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. C. Vencioneck Dutra et al., “Cereus jamacaru D.C. hydroalcoholic extract promotes anti-cytotoxic and antitumor activity,” Pharmaceuticals, vol. 11, no. 4, Dec. 2018. [CrossRef]
- N. Lídia et al., “Seed reserve composition and mobilization during germination and early seedling establishment of Cereus jamacaru D.C. ssp. jamacaru (Cactaceae),” 2012. [Online]. Available: www.scielo.br/aabc.
- M. V. Meiado, L. S. C. De Albuquerque, E. A. Rocha, M. Rojas-Aréchiga, and I. R. Leal, “Seed germination responses of Cereus jamacaru DC. ssp. jamacaru (Cactaceae) to environmental factors,” Plant Species Biol, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 120–128, May 2010. [CrossRef]
- J. D. P. Bezerra et al., “Fungal endophytes from cactus Cereus jamacaru in Brazilian tropical dry forest: A first study,” Symbiosis, vol. 60, no. 2, pp. 53–63, Jun. 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Al-Robai, A. A. Ahmed, H. A. Mohamed, and F. O. Alzahrani, “Austrocylindropuntia subulata (Muehlenpf.) Backeb. (Cactaceae, Opuntioideae): an invasive new cactus record to the flora of Saudi Arabia,” Bioinvasions Rec, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 360–366, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. El Bouaidi et al., “Nature-based coagulants for drinking water treatment: An ecotoxicological overview,” Water Environment Research, vol. 94, no. 8, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- E. Basavand, P. Khodaygan, V. Babaeizad, H. Rahimian, and H. A. Mirhosseini, “Soft rot disease caused by Klebsiella aerogenes on Austrocylindropuntia subulata in Iran,” Indian Phytopathol, vol. 73, no. 2, pp. 371–372, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- P. A. Santiago-García, E. Mellado-Mojica, F. M. León-Martínez, J. G. Dzul-Cauich, M. G. López, and M. I. García-Vieyra, “Fructans (agavins) from Agave angustifolia and Agave potatorum as fat replacement in yogurt: Effects on physicochemical, rheological, and sensory properties,” LWT, vol. 140, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Rangel-Landa, A. Casas, and P. Dávila, “Facilitation of Agave potatorum: An ecological approach for assisted population recovery,” For Ecol Manage, vol. 347, pp. 57–74, Jul. 2015. [CrossRef]
- D. Soto-Castro, A. Pérez-Herrera, E. García-Sánchez, and P. A. Santiago-García, “Identification and Quantification of Bioactive Compounds in Agave potatorum Zucc. Leaves at Different Stages of Development and a Preliminary Biological Assay,” Waste Biomass Valorization, vol. 12, no. 8, pp. 4537–4547, Aug. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Torres, A. Casas, E. Vega, M. Martínez-Ramos, and A. Delgado-Lemus, “Population Dynamics and Sustainable Management of Mescal Agaves in Central Mexico: Agave potatorum in the Tehuacán-Cuicatlán Valley,” Econ Bot, vol. 69, no. 1, pp. 26–41, 2015. [CrossRef]
- X. Aguirre-Dugua and L. E. Eguiarte, “Genetic diversity, conservation and sustainable use of wild Agave cupreata and Agave potatorum extracted for mezcal production in Mexico,” J Arid Environ, vol. 90, pp. 36–44, Mar. 2013. [CrossRef]
- M. Veste and W. B. Herppich, “Comparative ecophysiology of the leaf-succulents Augea capensis (C3) and Malephora purpureo-crocea (CAM) in the Knersvlakte, Succulent Karoo, South Africa,” Flora: Morphology, Distribution, Functional Ecology of Plants, vol. 278, May 2021. [CrossRef]
- Arturo Goldarazena, Hugo Aguilar, Halil Kutuk, and Carl C. Childers, “Biology of three species of Agistemus (Acari: Stigmaeidae): life table parameters using eggs of Panonychus citri or pollen of Malephora crocea as food,” Exp Appl Acarol, vol. 32, pp. 281–291, 2004. [CrossRef]
- G. A. Molina et al., “Green synthesis of Ag nanoflowers using Kalanchoe Daigremontiana extract for enhanced photocatalytic and antibacterial activities,” Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces, vol. 180, pp. 141–149, Aug. 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. van Maarseveen and R. Jetter, “Composition of the epicuticular and intracuticular wax layers on Kalanchoe daigremontiana (Hamet et Perr. de la Bathie) leaves,” Phytochemistry, vol. 70, no. 7, pp. 899–906, May 2009. [CrossRef]
- Kolodziejczyk-Czepas et al., “Antioxidant efficacy of Kalanchoe daigremontiana bufadienolide-rich fraction in blood plasma in vitro,” Pharm Biol, vol. 54, no. 12, pp. 3182–3188, Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. Domenico, “Effective microorganisms for germination and root growth in Kalanchoe daigremontiana,” World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews, no. 03, pp. 2581–9615, 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Von Caemmerer and H. Griffiths, “Stomatal responses to CO2 during a diel Crassulacean acid metabolism cycle in Kalanchoe daigremontiana and Kalanchoe pinnata,” Plant Cell Environ, vol. 32, no. 5, pp. 567–576, May 2009. [CrossRef]
- U. Supratman, T. Fujita, K. Akiyama, and H. Hayashi, “Insecticidal compounds from Kalanchoe daigremontiana x tubiflora,” Phytochemistry, vol. 58, pp. 311–314, 2001. [CrossRef]
- Y. Jia, G. Zhao, and J. Jia, “Preliminary evaluation: The effects of Aloe ferox Miller and Aloe arborescens Miller on wound healing,” J Ethnopharmacol, vol. 120, no. 2, pp. 181–189, Nov. 2008. [CrossRef]
- F. Guillén et al., “Aloe arborescens and Aloe vera gels as coatings in delaying postharvest ripening in peach and plum fruit,” Postharvest Biol Technol, vol. 83, pp. 54–57, Sep. 2013. [CrossRef]
- F. A. Andersen, “Final report on the safety assessment of aloe andongensis extract, aloe andongensis leaf juice, aloe arborescens leaf extract, aloe arborescens leaf juice, aloe arborescens leaf protoplasts, aloe barbadensis flower extract, aloe barbadensis leaf, aloe barbadensis leaf extract, aloe barbadensis leaf juice, aloe barbadensis leaf polysaccharides, aloe barbadensis leaf water, ferox leaf extract,...,” International Journal of Toxicology, vol. 26, no. SUPPL. 2. pp. 1–50, 2007. [CrossRef]
- S. Hartzell, M. S. Bartlett, and A. Porporato, “Unified representation of the C3, C4, and CAM photosynthetic pathways with the Photo3 model,” Ecol Modell, vol. 384, 2018. [CrossRef]
- H. Yuan, Y. Hou, I. M. Abu-Reesh, J. Chen, and Z. He, “Oxygen reduction reaction catalysts used in microbial fuel cells for energy-efficient wastewater treatment: A review,” Materials Horizons, vol. 3, no. 5. Royal Society of Chemistry, pp. 382–401, Sep. 01, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Wang et al., “Bioenergy generation and rhizodegradation as affected by microbial community distribution in a coupled constructed wetland-microbial fuel cell system associated with three macrophytes,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 607–608, no. 2017, pp. 53–62, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. C. Sophia and S. Sreeja, “Green energy generation from plant microbial fuel cells (PMFC) using compost and a novel clay separator,” Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, vol. 21, pp. 59–66, 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. A. Timmers, D. P. B. T. B. Strik, C. Arampatzoglou, C. J. N. Buisman, and H. V. M. Hamelers, “Bioresource Technology Rhizosphere anode model explains high oxygen levels during operation of a Glyceria maxima PMFC,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 108, pp. 60–67, 2012. [CrossRef]
- A. A. Mier et al., “A review of recent advances in electrode materials for emerging bioelectrochemical systems: From biofilm-bearing anodes to specialized cathodes,” Chemosphere, vol. 283, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- D. Akman, K. Cirik, S. Ozdemir, B. Ozkaya, and O. Cinar, “Bioelectricity generation in continuously-fed microbial fuel cell: Effects of anode electrode material and hydraulic retention time,” Bioresour Technol, vol. 149, pp. 459–464, 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. I. Torres, A. K. Marcus, P. Parameswaran, and B. E. Rittmann, “Kinetic experiments for evaluating the nernst-monod model for anode-respiring bacteria (ARB) in a biofilm anode,” Environ Sci Technol, vol. 42, no. 17, 2008. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




