1. Introduction
Laccase (p-diphenol:dioxygen oxidoreductase) is an oxidoreductase (EC 1.10.3.2) with four copper atoms in the active site that catalyzes the monoelectronic oxidation of four reduced substrates, usually phenols or aromatic amines, coupled with the reduction of molecular oxygen to water. Laccase is one of the oldest enzymes ever studied, first described in 1883. In recent years, when it was discovered that laccase is part of the arsenal of enzymes involved in the degradation of wood by decaying fungi, attention to these enzymes has increased significantly [
1,
2].
Laccases are widespread in the fungi kingdom, but they have also been observed in higher plants, a few insects and in some species of prokaryotes [
1]. All laccases described from fungi are glycoproteins. The most studied and the first discovered is that of
Rhus vernicifera [
3]. Plant laccases are less studied as they are difficult to identify and isolate due to the fact that their activity overlaps with the activity of numerous polyphenoloxidases, peroxidases, catecholases. On the other hand, in the kingdom of fungi, laccase is very widespread; so far more than 100 such laccases have been characterized. Laccases are often found in the cytoplasm, but there are also many cases in which the laccase is isolated from the extracellular environment. While the structure of the active site seems to be conserved across species and regardless of cellular localization, there is a great diversity among the laccases of fungal origin in terms of the secondary and tertiary structure, but also the position and degree of glycosylation [
2,
4,
5,
6].
The main role of laccases in plants is that of lignification; these enzymes are found in the wall of transport vessels in higher plants and are responsible for the formation of lignin through oxidative polymerization of monolignols together with peroxidase. Lignin is the second most widespread biopolymer after cellulose, synthesized from various structural subunits that repeat irregularly, but with three main monomers - p-coumaryl alcohol, synaptic alcohol and conifer alcohol [
7,
8].
Laccase plays a role in the defense of plants because, due to this enzyme that causes oxidative reactions on the surface of an injury, at the level of some tissues, it helps to heal injuries and defend the plant against pathogens by acting as inhibitors [
1].
In fungi, an important role of laccases is that of delignification, in which lignin is depolymerized and transformed into very small lignin units or monolignols [
9].
In the framework of fungal pathogenesis, the effect of laccase has also extended to humans.
Crzptococcus neoformans acts especially in people who are infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. This enzyme is involved in melanin synthesis by oxidizing some catecholamines, after that it is oxidatively coupled with dihydroxy-indole. The polymeric compound works as an antioxidant thus protecting the fungus from cellular effectors that are involved in the immune response. Laccase is not produced by mammalian organisms, but it can thus be the target of drugs to eliminate this fungus from patients. Fungal laccases can also metabolize phytoanticipins, which are antibiotics present in some plant tissues, secreted in order to protect the plant from phytopathogenic fungi and reduce the activity lignification of the host [
10].
In insects, laccase catalyzes the oxidative coupling of some catecholamines with amino groups from proteins, leading to the sclerotinization of the exoskeleton [
11].
Monomeric as well as multimeric (dimeric, tetrameric) laccases have been reported. In all cases, each monomer contains four copper atoms that are located in three active sites called type 1 (T1), type 2 (T2) and type 3 (T3). The T1 and T2 sites each contain one Cu atom, while the T3 site contains a bimetallic Cu center; the T2 and T3 copper atoms together form a trimetallic cluster [
2]. The tertiary structure of laccase contains three distinct domains of β-folded sheets of comparable size and comparable architecture. These three domains are found in many cupredoxin proteins and are denoted by the letters A, B and C (13). The cupredoxin type packing mode is found in a wide range of proteins that have multi-copper centers in their structure, such as ascorbate oxidase, ceruloplasmin, but also proteins with a monometallic copper center and is characterized by the presence of the secondary structure of β-folded sheets. All domains are important for the catalytic activity of laccase: the substrate binding site located between domain B and C, the monometallic copper center T1 located in domain C and the trimetallic cluster located at the interface between A and C [
2].
The T1 copper is trigonally coordinated by two histidines and one cysteine; copper-sulfur bond is strongly covalent and is observed in the UV-vis spectrum around the value of 600 nm as a LMCT type transition (Ligand to metal charge transfer) giving laccases a characteristic blue color (14). Laccases were also discovered that had a T1 monometallic copper center but did not have the blue color and the absorption band in the UV-vis spectrum at 600 nm was missing. These enzymes were called "yellow" or "white" laccases; their reduction potential is higher than that of the other laccases, so they are very important in biotechnological applications [
2,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17,
18]. The copper atom in the T2 site is coordinated by two histidines and a water or a hydroxyl, the copper atoms in the T3 site are coordinated by three histidines and joined at the end by a hydroxyl bridge. Cu2+ atoms T1 and T2 are paramagnetic and those in T3 are antiferromagnetically coupled [
2].
The catalytic mechanism of laccase is initiated when the Cu(II) T1 center is reduced by an electron from the organic substrate. This electron is then passed on to the trimetallic center and the step is repeated with three more substrate molecules, until a four-electron reduction of the trinuclear site is achieved; coupled with this phenomenon, the trinuclear site binds molecular oxygen, so that the four electrons received from T1 are eventually passed on from T2 and T3 to O
2, eventually generating H
2O as a final product. The organic substrate oxidized by one electron at the T1 center is liberated in the form of a free radical; this radical can then initiate chain reaction in the reaction medium, with complex reaction products that often lead to (radicalic) polymerization [
2].
Laccases are used in the food industry, the paper industry, bioremediation, the textile industry, the cosmetic industry, biocatalysis, pesticides and dyes because in the oxidation reactions there is no need for expensive electron acceptors, for example for the main product is oxygen and as a secondary product being the water. In most cases, the substrates of interest cannot be oxidized by laccase directly because they cannot enter the active site of the protein, being too bulky and/or with too high reduction potentials, so chemical mediators are used which are used as intermediate substrates in many instances. The radicals that form as a result of the oxidation of compounds by laccases are able to interact with the substrate even though it is one with a high redox potential. The most used chemical mediators in laccase reactions are, for example: ABTS, violauric acid, syringic acid methyl ester, N-hydroxybenzotriazole, hydroxyanthranilic acid, TEMPO which have the property of oxidizing the laccase substrate of interest.
In the paper processing industry, laccase is useful for its ability to remove the lignin from various wood materials and to obtain a white paper – and can thus replace chemical oxidants that are used in industrial processes such as chlorine-based bleaching agents (ClO
2,ClO
-) or active oxygen-based bleaching agents (H
2O
2,O
3), which have a high risk of pollution and/or yield unwanted secondary reaction products. The most effective method proved to be the one that uses degradative fungi such as
Ceriporiopsis subvermispora [
19]. An important problem both in the paper and in the pulp industry is that lipophilic materials such as fatty acids, resins, triglycerides, sterols that reduce the strength of the paper, affect the life of the industrial equipment and increase energy consumption [
20]; laccase reduces the content of these unwanted materials in the process through a radical-type mechanism [
21].
An important use of laccase is the one in which it is used in the manufacture of laminated plywood, which is based on a reaction between lignin and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzylurea. In lignin there is a urea group that will react with the urea-formaldehyde (UF) type resin, thus replacing expensive adhesives and finally obtaining materials with high density, reducing the necessary resin consumption and showing a high internal strength [
22].
Laccase is used in many processes in the food industry such as those for changing the color and appearance of food and beverages because compounds such as polyphenolic carbohydrates, unsaturated fatty acids are substrates for laccase. This enzyme can prevent certain changes in the composition of food and drinks, such as increasing turbidity, changing the flavor of beer and juices. In order not to affect the quality of food products, laccase can be used to remove molecular oxygen, the enzyme thus used as an oxygen remover reducing the perishability of the product. This enzyme has also been used to remove unpleasant odors or enhance the color of some teas [
23,
24,
25].
Laccase is used as a substitute for some hair dyes that contain hydrogen peroxide (an agent often used in the hair dye industry), which is less irritating and easier to handle than common oxidants. Certain cosmetic and dermatological products have been discovered to contain skin bleaching enzymes and laccase [
24,
25].
Bioremediation processes relying on laccase activity have also been reported. The fungus
F. flavus discolors certain dyes such as Brilliant Green, Crystal Violet, Azure B, Congo Red, Remazol Brilliant R Blue [
26]. It has also been shown that laccase together with certain stabilizers can treat waste water [
27].
Laccases from
Trametes versicolor were useful for the decolorization of humic acids from lignin (brown coal) and the transformation of 4-methyl-hydroxyanthranilic acid into 2-amino-4,6-dimethyl-3-phenoxazinone-1 acid ,9-carboxylic, phenoxazinone pigment found in actinomycetes [
28]. The
Lentinus crinitus laccase was successfully used in the decolorization of Reactiv Blue dye, this enzyme is stable at temperature, pH, ionic strength, which denotes a good advantage for industrial applications [
29].
The
Trametes versicolor laccase was employed to increase the resistance to phenolic compounds improving the production of ethanol for fuel from different lignocellulosic materials, as some phenolic compounds are inhibitors for fermentation and by expressing laccase the ethanol content was significantly increased [
30].
Laccase from the
Trametes hirsuta mushroom helps to increase dough strength and decrease the extensibility of both gluten and flour dough [
31,
32]. This enzyme is important in baking because it has the ability to crosslink various biopolymers.
Many of the industrial/synthetic applications of laccases involve reaction conditions – and especially temperatures – harsher than those typically encountered by the laccases in their native fungal or plant environments. As such, modified laccases with increased thermal stability are a desirable goal for industrial applications. Derivatization with polyethylene glycol is one option widely employed for increasing the stability of proteins. Here, derivatization of a laccase from the fungus Sclerotinia sclerotiorum is reported, using an (methyl-PEG12)3-PEG4) N-succinimide ester in order to improve the thermostability of the enzyme. The PEGylated laccase is characterized using gel electrophoresis, size-exclusion chromatography, catalytic parameters and thermal stability. A 50% increase in residual activity after incubation at 50°C for up to two hours was achieved for the PEGylated laccase compared to the native enzyme.
2. Materials and Methods
The pegylation reagent, (methyl-PEG
12)
3-PEG
4-N-hydroxysuccinimide ester, was purchased from Pierce and stored/employed in DMSO stock solutions.
S. sclerotiorum laccase was purified as previously described [
13,
14].
The purified and the modified laccase was analyzed respectively separated from secondary reaction products using a Superdex 200 5/150 GL steric exclusion column controlled by FPLC AKTA purifier which is connected to a computer. The samples were collected in an automatic fraction collector. UV-VIS spectra of pure and modified laccase were recorded using a Carry 50 spectrophotometer.
Electrophoresis: Gels for electrophoresis were prepared using the following solutions: (1) Separation gel (5ml): ultrapure water (1.1ml), Tris buffer solution 1.5 M, pH=8.8 (1.3ml), acrylamide concentration 30% (2.5ml), SDS 10% (50µl), APS 10% (50µl), TEMED (2µl); (2) Concentration gel (2ml): ultrapure water (1.4ml), Tris buffer solution 1M pH=6.8 (250µl), acrylamide 30% (330µl), SDS 10% (20µl), APS 10% (20µl), TEMED (2µl ). A mixture of Tris 0.25M, Glycine 1.92M, SDS 1% was used for the "running buffer". The following mixture was used for protein denaturation: Tris buffer solution 1M pH=6.8, SDS 4%, glycerol 20%, bromophenol blue 0.1%, 2 mercaptoethanol 10% and ultrapure water. After prior denaturation, the samples were incubated for 5 minutes at 90°C, after which they were placed in the electrophoresis cell (Serva). Markers (Thermo Scientific Pierce Prestained Markers) betagalactosidase (120 kDa), BSA (85 kDa), ovalbumin (50 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (35 kDa), beta-lactoglobulin (25 kDa), and lysozyme (20 kDa). The coloring solution had the following composition: 0.2% CBB ethanol: water: acetic acid in a volume ratio of 45:45:10 and the bleaching solution: ethanol: water: acetic acid in a volume ratio of 25:65:10.
For the PEGylation reaction, 6 reaction mixtures were prepared in buffer solution 10 µM TAPS, 100 µM NaCl pH 7.8 and labeled from 1 to 6 in which the laccase had a constant concentration of 10 µM and the concentration of TMSPEG varied from 10 to 4200 according to
Table 1. The solutions were mixed in Eppendorf tubes that have a volume of 1.5 ml, where the laccase samples subjected to PEGylation were placed together with a magnetic stirrer that helps to stir the reaction mixture, after that the samples are placed on a magnetic plate supported by a stand for 2 hours. After 2 hours, the samples were filtered to remove suspensions and then loaded on the gel filtration column. TAPS buffer solution was used as eluent (10 mM TAPS, 100 mM NaCl, adjusted with NaOH to pH 7.8). Fractions of 200 µL were collected. In addition to the 6 samples, a reference containing 10 µM laccase and 3.36% DMSO (the maximum concentration used in samples 1-6) was also analyzed, in order to check the influence of the solvent on these activities. The UV-VIS spectrum of the collected fractions was recorded to confirm the presence or absence of the protein and to determine its concentration. Fractions containing only PEGylated laccase at maximum concentration were mixed and collected for further analysis.
Samples 3, 6 and the reference were evaluated for thermostability at 50 °C. For this, the samples were incubated at 50°C in a thermoblock that ensures constant temperature. Every 15 minutes, a suitable volume was taken from them, so that the final concentration of laccase in the tank was 2.55 nM, and the laccase activity was measured.
To determine the laccase activity, 100 mM acetate buffer, pH 5 was used, and ABTS was used as a substrate at a concentration of 1.4 mM (the final concentration in the tank). The ABTS was oxidized to the radical species which is colored green thus allowing monitoring in the visible. Monitoring was done at 420 nm where ABTS•+ has an extinction coefficient of 36000 M-1 cm-1. Enzyme activity was measured in enzyme units (U). An enzyme unit (1 U) represents the amount of enzyme that produces one µmol of ABTS•+ (or consumes one µmol of ABTS) for 1 minute under the given conditions.
3. Results
The laccase from
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum has 12 lysines/molecule that are likely to be involved in the nucleophilic attack on the activated PEG.
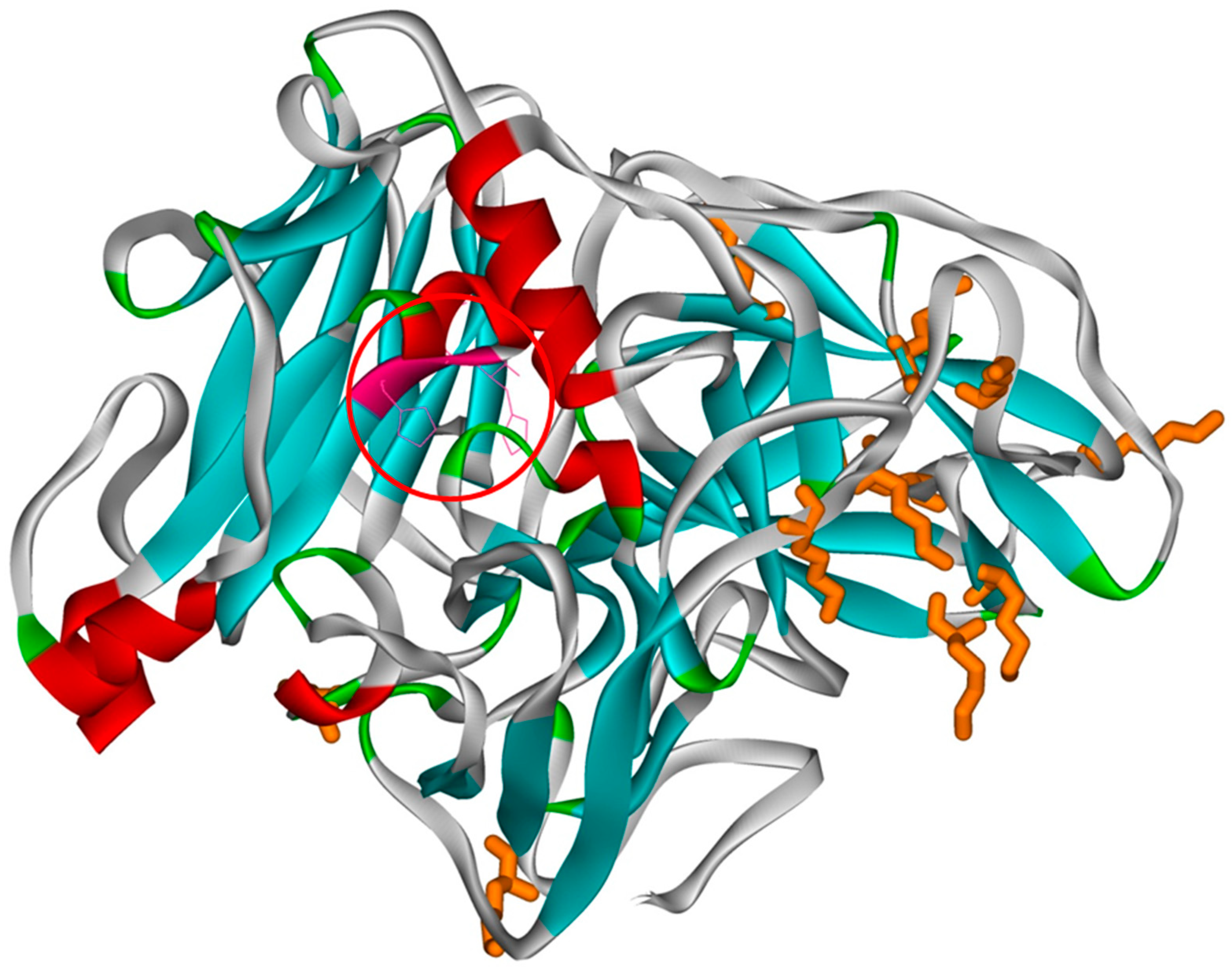
Figure 1 shows the tertiary structure of the laccase from the organism
Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in which the lysines are highlighted. During the PEGylation process, PEG is covalently linked to the amino group in lysines. As can be seen, the distribution of lysines on the surface of the laccase is uneven, and the active site is not located near a lysine, therefore there is no risk of blocking the access of the substrate to the active site. Even if the lysines are unevenly distributed on the laccase surface due to the increased size of the modified PEG (approximately 78 Å) and the increased hydration capacity, even at a small degree of PEGylation the protein surface is strongly modified (the size of a laccase molecule is 60x60x76 Å, with a total surface of ~ 13000 Å
2).
After the PEGylation reaction, it is necessary to remove the excess PEG, which is done by steric exclusion chromatography. In
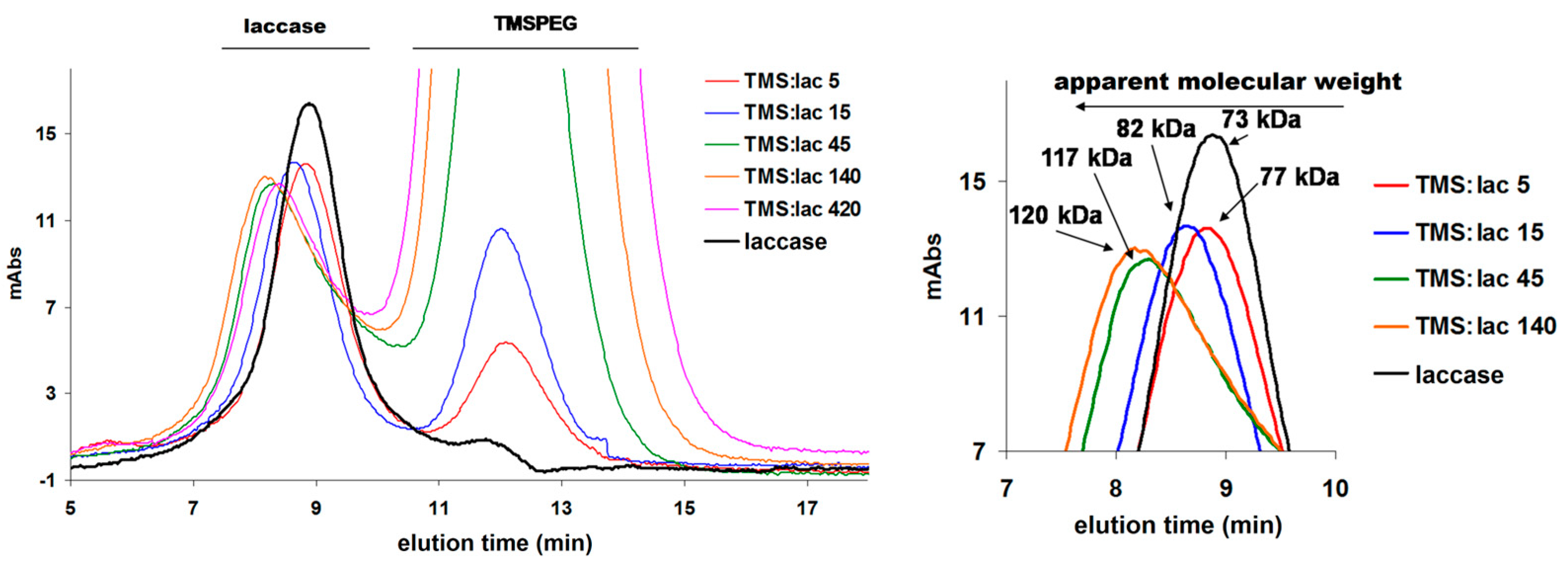
Figure 2 it can be seen that as the excess of TMS-PEG increases, the protein comes out in a shorter time, which means that it has a higher molecular mass. At an excess of 5, very little of the protein is PEGylated, PEGylation being visible at an excess greater than 15. It is also observed how a saturation occurs in PEGylation, that is, at an excess of 420 no increase in mass compared to the excess of 140.
Figure 3 shows how the apparent molecular mass increases from 73 (native laccase mass) to 77, 82, 117, 120 kDa at TMS-PEG/laccase molar excesses of 5, 15, 45, and 140 respectively. Although one could calculate how many PEG units are attached to a laccase molecule, the calculations are still inaccurate due to the fact that in steric exclusion what matters is not the molar mass but the volume of the protein; and because PEG is very well hydrated and flexible, it occupies a much larger volume than that which corresponds to the mass of a PEG unit, leading to large errors (~20 PEG units/laccase, but laccase has only 12 available lysines, of which are many very close and would not allow a high degree of PEGylation due to steric factors).
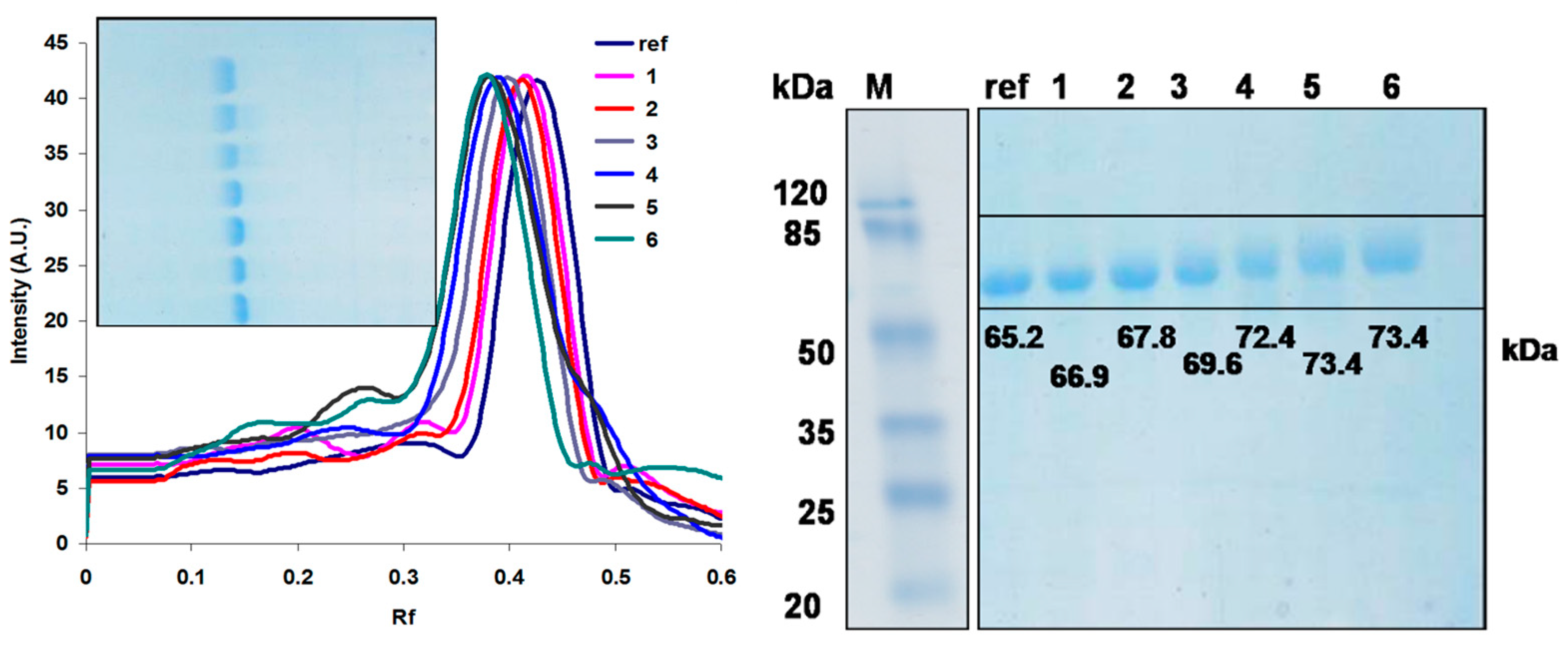
A more suitable method for analyzing the degree of PEGylation, at an analytical level, is electrophoresis. In
Figure 3 we have the SDS electrophoretic gel of the 6 samples and pure laccase. By making a calibration curve based on protein markers, we calculated the average apparent mass of each sample. It can be seen how pure laccase is 65.2 kDa, and then at a molar excess of 5 it increases to 66.9 kDa, which means a difference of 1.7 kDa/laccase and knowing the mass of one PEG unit (2.4 kDa) means that on average there are 0.7 PEG units /laccase (probably the largest part of the protein population is monoPEGylated, an extremely small one is diPEGylated and the rest is unmodified laccase. At an excess of 15 the average number of PEG units/laccase is 1.1, this increases slightly up to 3.4 at an excess of 140, this value remaining constant even at an excess of 420 (saturation). Detailed calculations are in
Table 2. This is most likely due to steric effects, the lysines being very close to each other and not allowing all of them to be available for attack at TMS-PEG This increase can be seen and calculated exactly using a program (TLC Analyzer) with the help of which we obtain the electrophoretic profile of the bands on the gel (
Figure 3) and with the help of which the Rf can be calculated exactly.
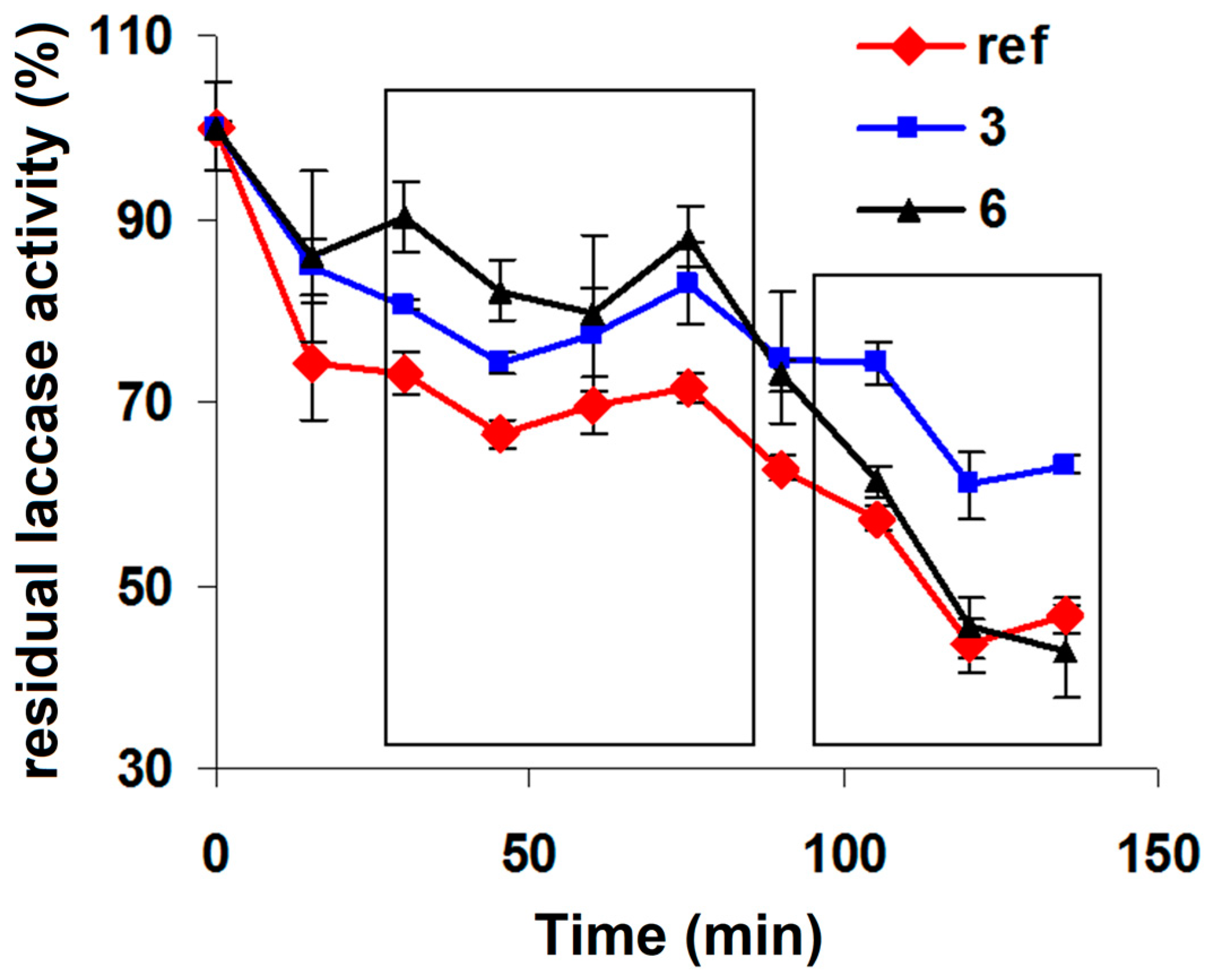
Following the purification and analysis of the samples, 2 samples were chosen (sample 3 and sample 6), one at a molar excess of 15 and one at 420, one with 0.7 units of PEG/laccase and one with 3.4 units of PEG/laccase and were studied their thermostability at 50°C.
Figure 4 shows the kinetic profile of the laccase activity in the 2 samples and the reference (pure laccase). It is clear how at low reaction times the two PEGylated laccase samples are more stable than the reference, sample 6 being more stable than sample 3. At longer incubation times at high temperature, sample 3 remains the most stable, while sample 6 (the one with a high degree of PEGylation) decreases in stability compared to the reference. This can be explained by the fact that too high a degree of PEGylation leads to the destabilization of the tertiary structure of the laccase and therefore to the decrease of the thermostability in the long term. Therefore, an average degree of PEGylation is preferable in order to obtain an optimum.