1. Introduction
Chronic urticaria is a condition with a complex pathogenetic mechanism, which is not fully elucidated. It is characterized by a maculopapular, intensely pruritic rash, accompanied or not by angioedema, which persists for more than 6 weeks. When a specific factor inducing this pathology is not known, it is called chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), the entity we will refer to in this paper [
1,
2]. The cells with a key role in the pathogenesis of chronic urticaria are mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils, whose degranulation (regardless of what mechanisms this is triggered by) leads to the release of preformed vasoactive mediators, the best-known being histamine, proinflammatory mediators, and newly synthesized ones, the most important of which are cytokines. Therefore, among the supported theories related to UCS pathogenesis, inflammation maintained by cytokines plays an essential role. Among the cytokines, the alarmins, with origin in mast cells, seem to have significant roles in triggering inflammation. Additionally, the importance of IL-31 cannot be neglected in the pathogenesis of the disease, especially in relation to itching [
2,
3,
4,
5]. Currently, the approved and universally used therapeutic weapons are second-generation H1 antihistamines. For severe forms that do not yield to four times the dose of antihistamine, a single biological treatment is used - anti-IgE therapy, specifically the monoclonal antibody omalizumab. For some selected cases, ciclosporin or short corticotherapy courses are reserved [
1]. As was mentioned before, these are not enough; many patients remain with uncontrolled forms of the disease, with wheals or itching, which reduces their quality of life. Therefore, the need for new biological therapies is unquestionable [
6].
Chronic spontaneous urticaria, along with other autoimmune and allergic skin diseases such as bullous pemphigoid (BP), psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis, is associated with intense pruritus. Traditionally, histamine and neuropeptides were thought to play a decisive role in itch, but recent evidence suggests that IL-31, also called the pruritogenic cytokine, is a key factor in the mechanism of pruritus [
7,
8,
9]. IL-31 was initially shown to be produced by activated T helper cells, particularly Th2 cells, mast cells, macrophages, and dendritic cells. However, more recent evidence stated that eosinophils are also a major source of this cytokine [
10,
11,
12]. Basophils can express this cytokine, which, through autocrine action, strongly supports the production of other Th2-type cytokines from these cells. These events suggest that the dynamic recruitment of eosinophils and basophils in some autoimmune skin diseases might play a significant role in the severity of IL-31-mediated itch [
13,
14]. Furthermore, these studies state that IL-31, in addition to its pruritic actions, also has potential immunomodulatory roles in supporting Th2-type immunity, which often causes IgE-associated autoimmune diseases including chronic urticaria [
9,
10,
13,
15]. This statement suggests the potential use of therapeutic approaches to block IL-31 receptors (e.g., Nemolizumab) for the treatment of disorders in which IL-31 is involved [
16,
17,
18], possibly also in CSU. In the current study, we set out to see what the implications of IL-31 in CSU are, how its levels vary according to certain clinical and paraclinical parameters of patients with this disease and if we find arguments to support the idea that it could represent a therapeutic target in this pathology.
2. Materials and Methods
A retrospective, analytical study, including 50 patients of the Allergology Department of the Regional Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology in Cluj-Napoca, Romania, diagnosed with chronic spontaneous urticaria according to the international consensus guide was performed. The guide defines CSU as a specific maculopapular rash, accompanied or not by angioedema, which occurs at least twice a week for more than 6 weeks [
1,
2]. The control group consisted of 38 healthy adults who were part of the staff of the Institute, without urticarial symptoms, without skin diseases or diseases accompanied by itching, including malignancy. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the UMF "Iuliu Hatieganu" [AVZ270/10.10.2022] and by the IRGH [12637/11.10.2022]. Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Demographic data and baseline characteristics of all participants were recorded, including age, sex, and serum IL-31 levels. In patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU), additional data were collected, such as the duration of the disease, the severity of the disease, the presence or not of atopy proven by a positive skin prick test to environmental allergens. Complementary paraclinical tests were also performed, including the complete blood count, inflammatory parameters such as ERS and CRP, coproparasitological examination, and total serum IgE. All laboratory analyses were performed at the hospital's central laboratory.
Venous blood samples were taken from all these participants, and the samples were centrifuged. The serum was later frozen and kept at -80 degrees Celsius. IL-31 concentrations in the serum were assessed using a commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), following the manufacturer's instructions (Human IL-31 ELISA Kit, BioLegend, USA).
The UAS7 (Urticaria Activity Score over 7 days) is an internationally authorized tool used to assess the severity of chronic spontaneous urticaria. It combines scores for hives and itch severity over a continuous period of 7 days, with scores ranging from 0 to 42. The hives score ranges from 0 to 3, indicating the level of hives: 0 represents no hives, 1 indicates mild hives (less than 20 hives in 24 hours), 2 corresponds to moderate hives (20–50 hives in 24 hours), and 3 signifies severe hives (more than 50 hives in 24 hours or a large confluent area of hives). Likewise, the itch severity score ranges from 0 to 3, reflecting the intensity of itchiness: 0 signifies no itch, 1 indicates mild itch (present but not bothersome), 2 represents moderate itch (troublesome but not disrupting normal daily activities or sleep), and 3 indicates severe itch (interfering with normal daily activities or sleep). Based on the UAS7 scores, patients' chronic spontaneous urticaria severity is categorized into three disease activity states: scores from 0 to 15 are classified as mild, scores from 16 to 27 are categorized as moderate, and scores from 28 to 42 are considered severe [
19,
20].
Additionally, the weekly itch severity is also grouped into three levels: scores from 0 to 7 are considered mild, scores from 8 to 14 are classified as moderate, and scores from 15 to 21 are categorized as severe.
The DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) is a widely used tool to assess how chronic spontaneous urticaria affects a person's quality of life. It consists of ten questions, each scored from 0 to 3, with higher scores indicating a more significant impact. The total DLQI score can range from 0 to 30, and the scoring breakdown is as follows: 0 to 1 - no impact on quality of life, 2 to 5 - small impact, 6 to 10 - moderate impact, 11 to 20 - very large impact, and 21 to 30 - extremely large impact [
21,
22].
Statistical analysis: The data were reported as the median along with the interquartile range unless specifically mentioned otherwise. To assess the normality of the data distribution, the Shapiro-Wilk test was conducted. For comparisons between the study groups, the Mann-Whitney U test or the Kruskal-Wallis test were utilized, depending on the nature of the data. Categorical data were compared using Pearson’s chi-squared test. The relationships between different parameters were determined using Spearman's correlation, which is appropriate for evaluating non-linear associations. To investigate whether IL-31 could discriminate between healthy controls and urticaria patients, the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve for IL-31 was analyzed, and the area under the curve (AUC) was calculated. GraphPad Prism 9.0 software (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) was used for conducting the statistical analyses and generating graphs. Statistical significance was set at a p-value of < 0.05, indicating that results with p-values lower than this threshold were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical data
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study participants. Note: F, female; M, male. Age is presented as mean+/-SEM.
Table 1.
Characteristics of the study participants. Note: F, female; M, male. Age is presented as mean+/-SEM.
| Characteristic |
CSU patients |
Controls |
| Number, n |
50 |
38 |
| Sex (F/M) |
36/14 |
26/12 |
| Age, yrs. |
50.14+/-2.27 |
44.31+/-1.81 |
| Atopy (Atopic/Non-atopic) |
14/36 |
10/28 |
3.2. Serum IL-31 levels in UCS patients and controls
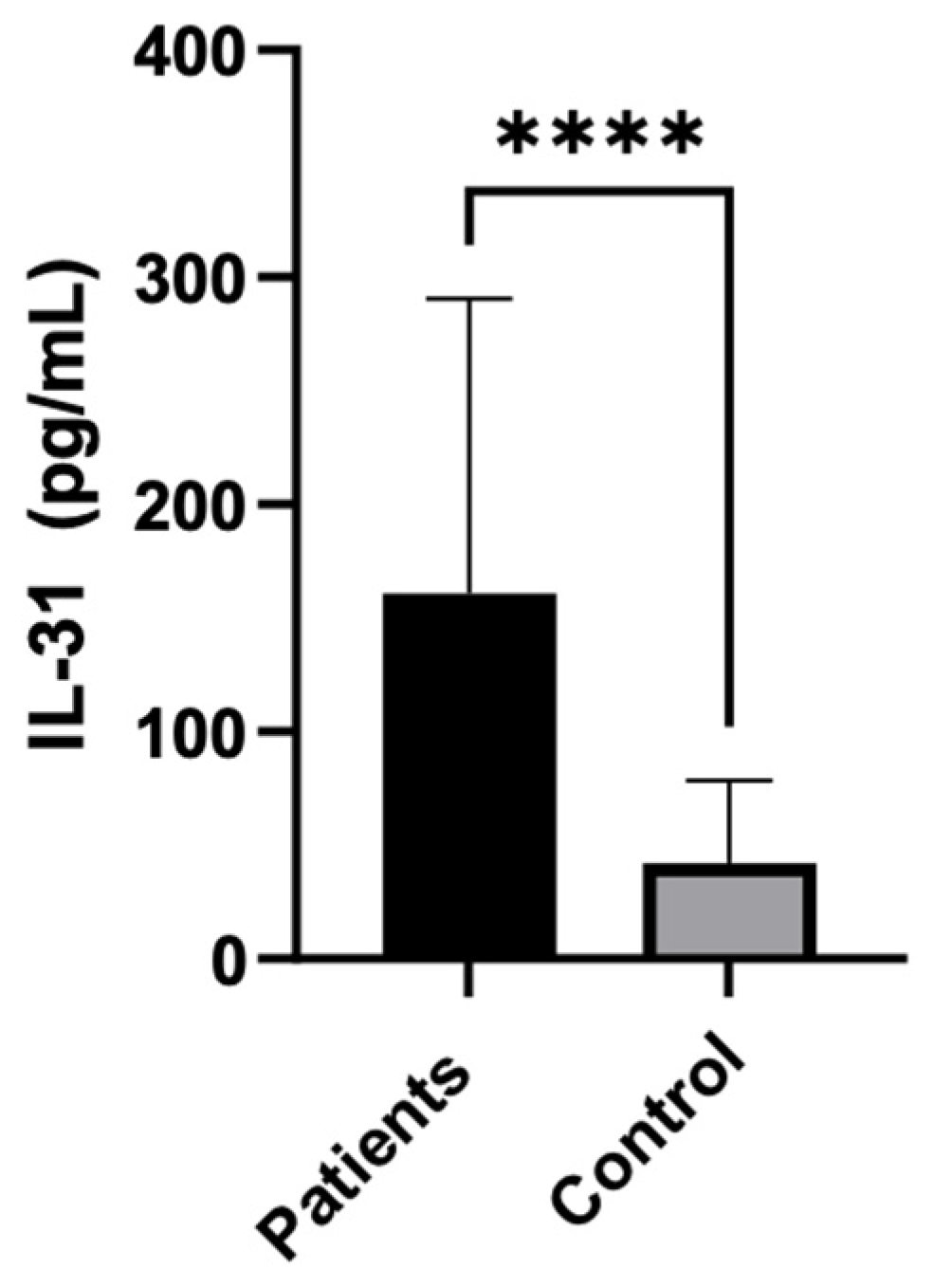
The statistical analysis showed a highly significant difference in serum IL-31 levels between patients and controls, with IL-31 being significantly higher in patients (P < 0.0001). The median IL-31 level in patients was 121.5, while in controls, it was 29.21.
Figure 1.
IL-31 serum levels in CSU patients vs controls.
Figure 1.
IL-31 serum levels in CSU patients vs controls.
Table 2.
The statistical analysis of IL-31 levels between patients and controls.
Table 2.
The statistical analysis of IL-31 levels between patients and controls.
| Test |
Mann Whitney |
| P value |
<0.0001 |
| Exact or approximate P value? |
Exact |
| P value summary |
**** |
| Significantly different (P < 0.05)? |
Yes |
| One- or two-tailed P value? |
Two-tailed |
| Sum of ranks in columns A, B |
2993, 923.5 |
| Mann-Whitney U |
182.5 |
| Difference between medians |
|
| Median of column A |
121.5, n=50 |
| Median of column B |
29.21, n=38 |
| Difference: Actual |
-92.24 |
| Difference: Hodges-Lehmann |
-82.09 |
3.3. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to other paraclinical parameters: eosinophils, inflammation markers and total IgE serum level
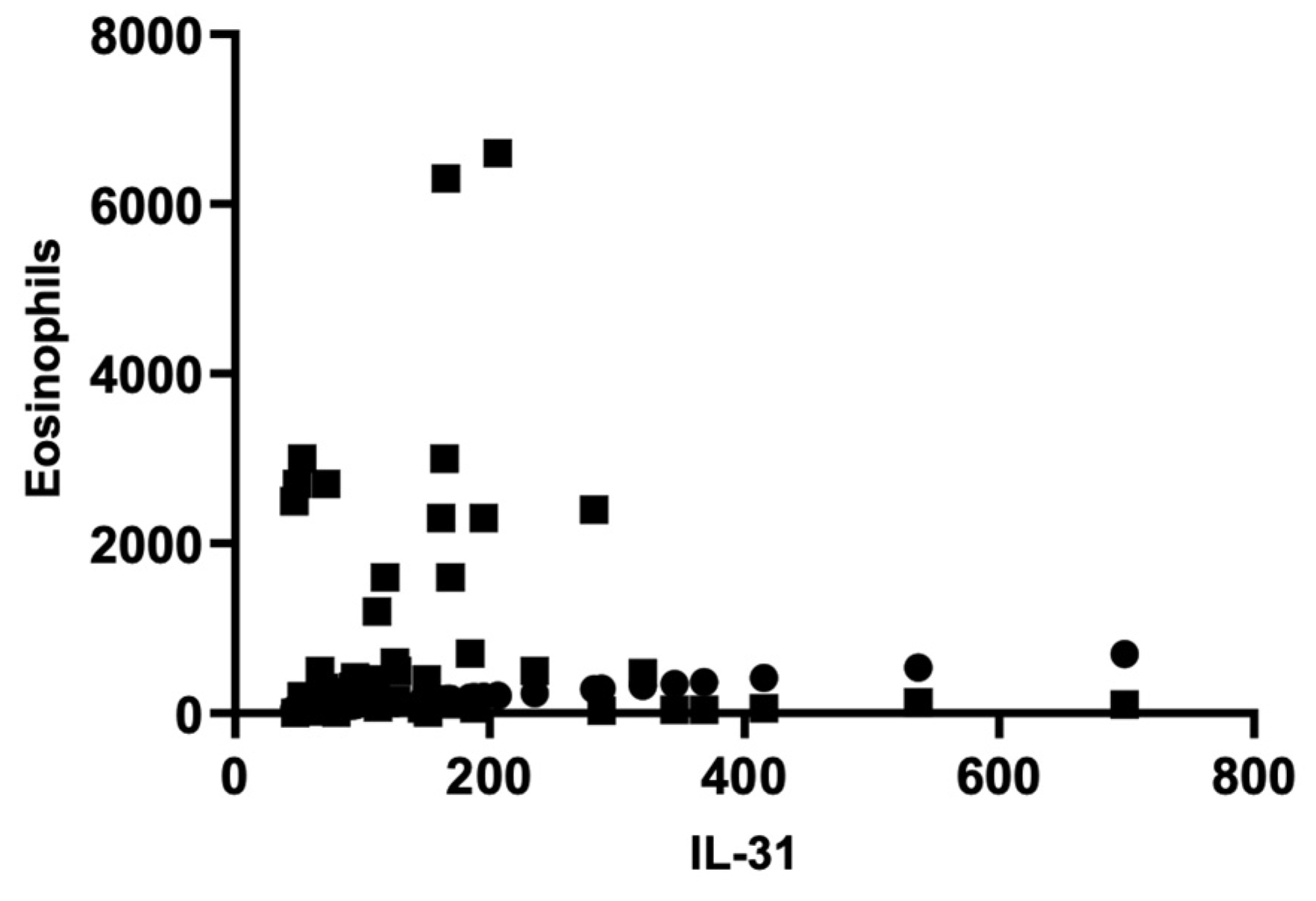
There were no significant correlations between IL-31 levels and other paraclinical parameters, such as serum eosinophils, inflammatory markers like erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) or C-reactive protein (CRP), as well as total IgE levels. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) for the serum level of IL-31 and serum eosinophilsis -0.06714, indicating a weak negative correlation between the two variables. However, this correlation was not statistically significant (P = 0.6432), as the P-value was greater than 0.05. The analysis was based on 50 XY pairs, and it suggested that there was no significant relationship between serum interleukin-31 levels and serum eosinophil levels in patients. Using the same statistical analyses, correlations between IL-31 and ESR, CRP, and total IgE levels were investigated, but no statistically significant associations were found between them.
Figure 2.
Correlation of serum IL-31 and eosinophils.
Figure 2.
Correlation of serum IL-31 and eosinophils.
3.4. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to atopy
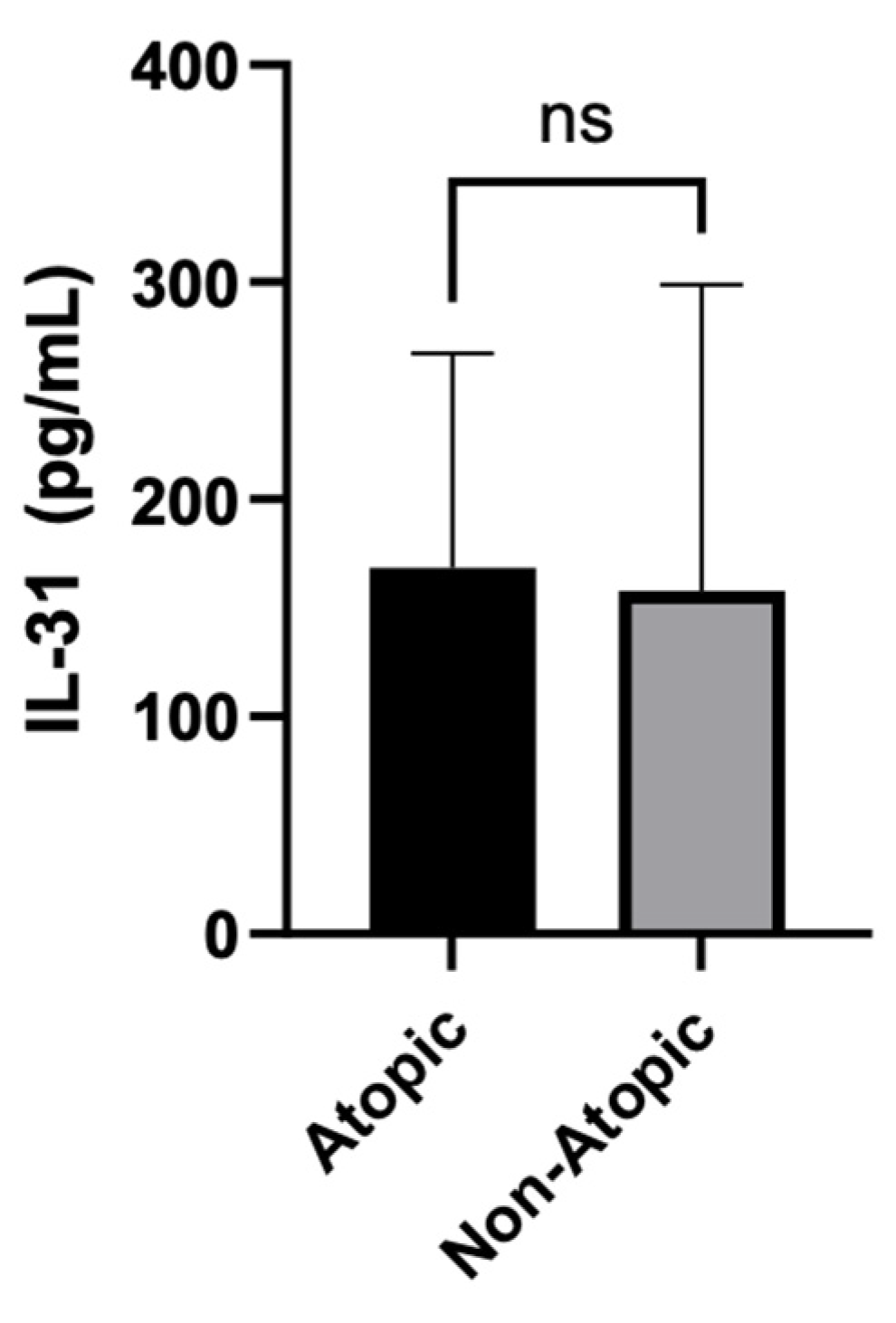
The statistical analysis compared the serum levels of IL-31 between Atopic and Non-Atopic patients. The Mann Whitney test yielded a non-significant P-value of 0.2491, indicating that there was no significant difference in IL-31 levels between these two groups.
Figure 3.
IL-31 serum levels in atopic vs non-atopic patients.
Figure 3.
IL-31 serum levels in atopic vs non-atopic patients.
3.5. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to clinical tools
3.5.1. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to UAS7
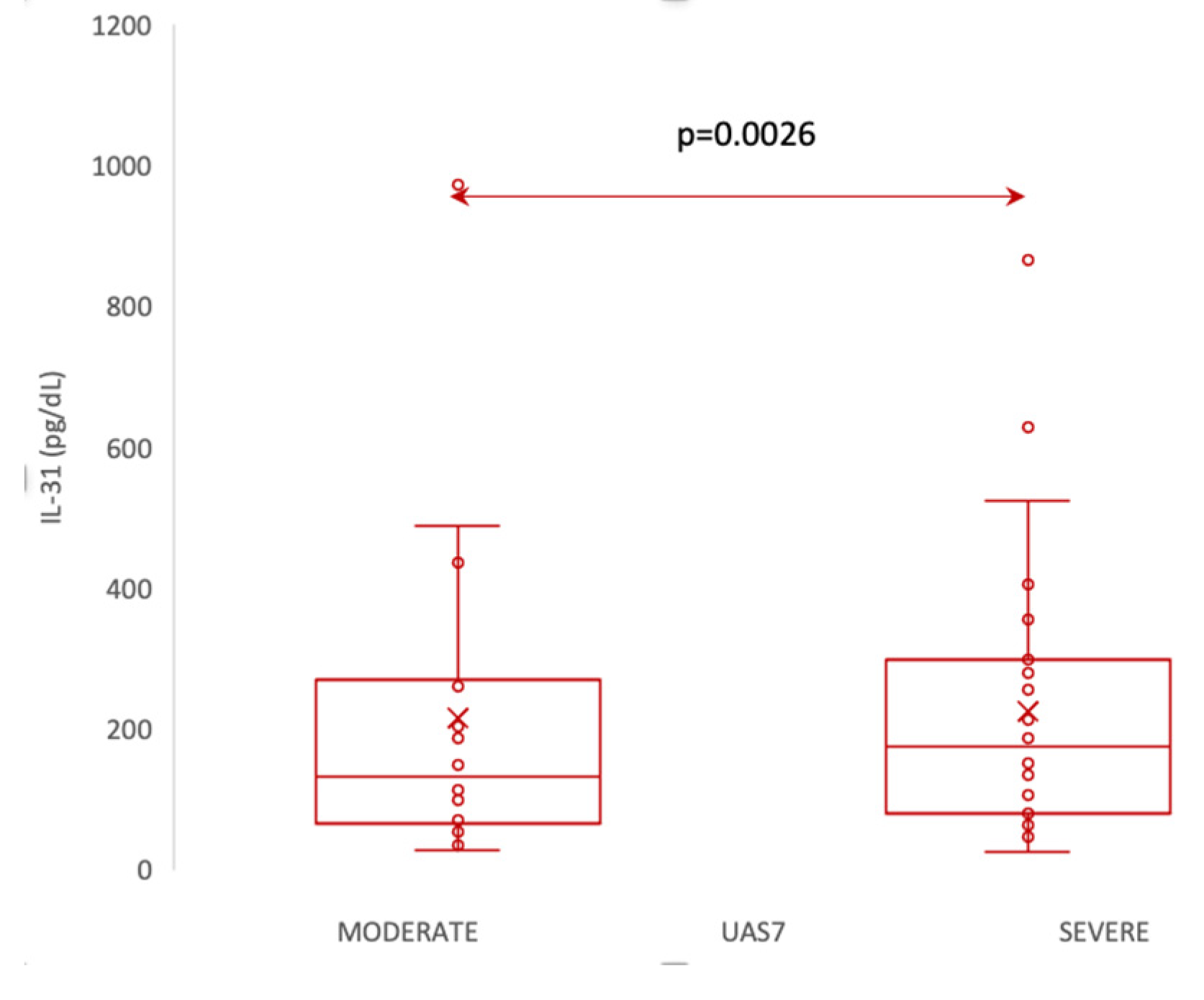
According to UAS7, which, as explained in materials and methods, divides patients into 3 categories of disease severity , our patients fell into the moderate and severe forms, with no patient having the mild form of the disease. Thus, we divided the patients into two categories: moderate and severe, and evaluated whether there are differences in IL-31 levels between them. The statistical analysis employed the Mann-Whitney U Test to compare IL-31 levels between patients with moderate and severe forms of the disease. The mean IL-31 level was 106 (standard deviation 42) for patients with moderate disease and 200 (standard deviation 156) for patients with severe disease. The median IL-31 level for moderate patients was 94, with a range from 80 to 127, while for severe patients, the median was 163, ranging from 77 to 282. The Mann-Whitney U Test showed a significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.0026), suggesting that IL-31 levels were significantly higher in patients with severe disease compared to those with moderate disease. The analysis included 21 patients with a moderate form and 29 patients with a severe form of the disease.
Figure 4.
Serum IL-31 levels in patients with moderate vs severe forms of CSU, according to UAS7.
Figure 4.
Serum IL-31 levels in patients with moderate vs severe forms of CSU, according to UAS7.
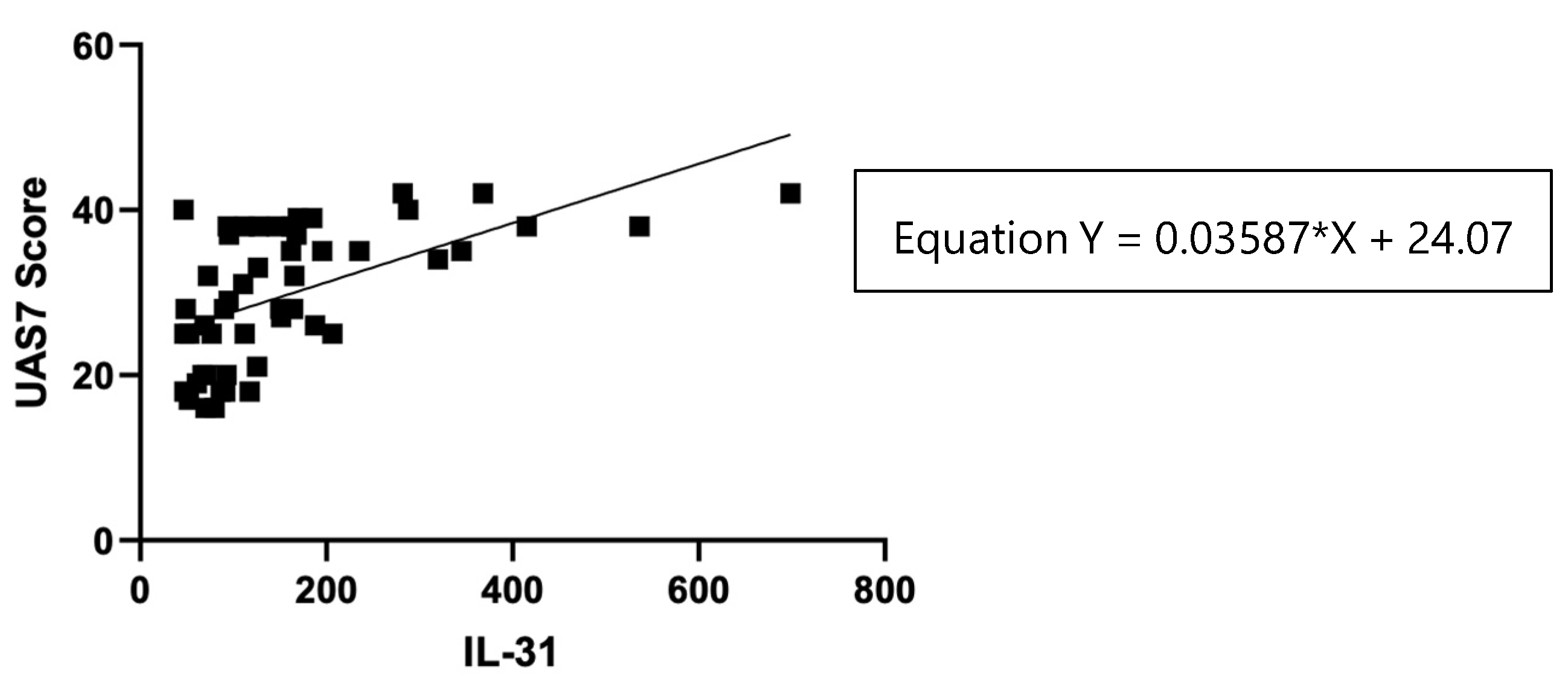
Figure 5.
Correlation of serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients and UAS7 score.
Figure 5.
Correlation of serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients and UAS7 score.
Table 3.
The statistical analysis: IL-31 serum levels and UAS7 score.
Table 3.
The statistical analysis: IL-31 serum levels and UAS7 score.
| Test |
Pearson r |
| r |
0.5673 |
| 95% confidence interval |
0.3431 to 0.7303 |
| R squared |
0.3218 |
| P (two-tailed) |
<0.0001 |
| P value summary |
**** |
| Significant? (alpha = 0.05) |
Yes |
| Number of XY Pairs |
50 |
The statistical analysis showed a significant positive correlation (r = 0.5673, p < 0.0001) between IL-31 serum levels in CSU patients and UAS7 scores, indicating that patients with higher UAS7 scores had higher IL-31 levels.
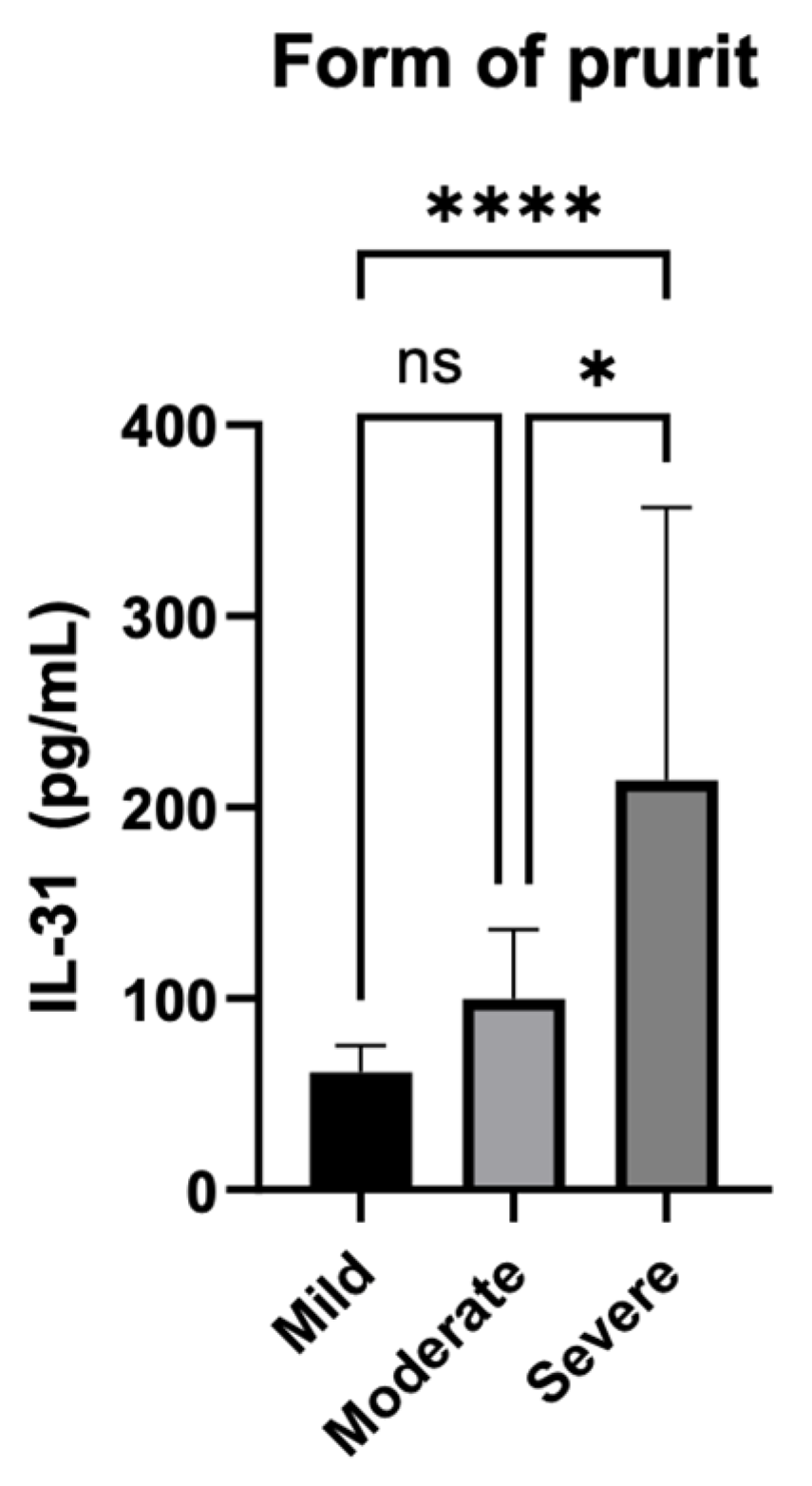
3.5.2. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to the severity of the pruritus
Additionally, as shown in the second subtitle of this paper, the severity of itch was also quantified separately by summing the scores over 7 days, and patients were divided into three categories based on the intensity of the pruritus. Scores from 0 to 7 were considered mild, scores from 8 to 14 were classified as moderate, and scores from 15 to 21 were categorized as severe.
Figure 6.
Serum IL-31 levels and the forms of pruritus quantified by the intensity of itch.
Figure 6.
Serum IL-31 levels and the forms of pruritus quantified by the intensity of itch.
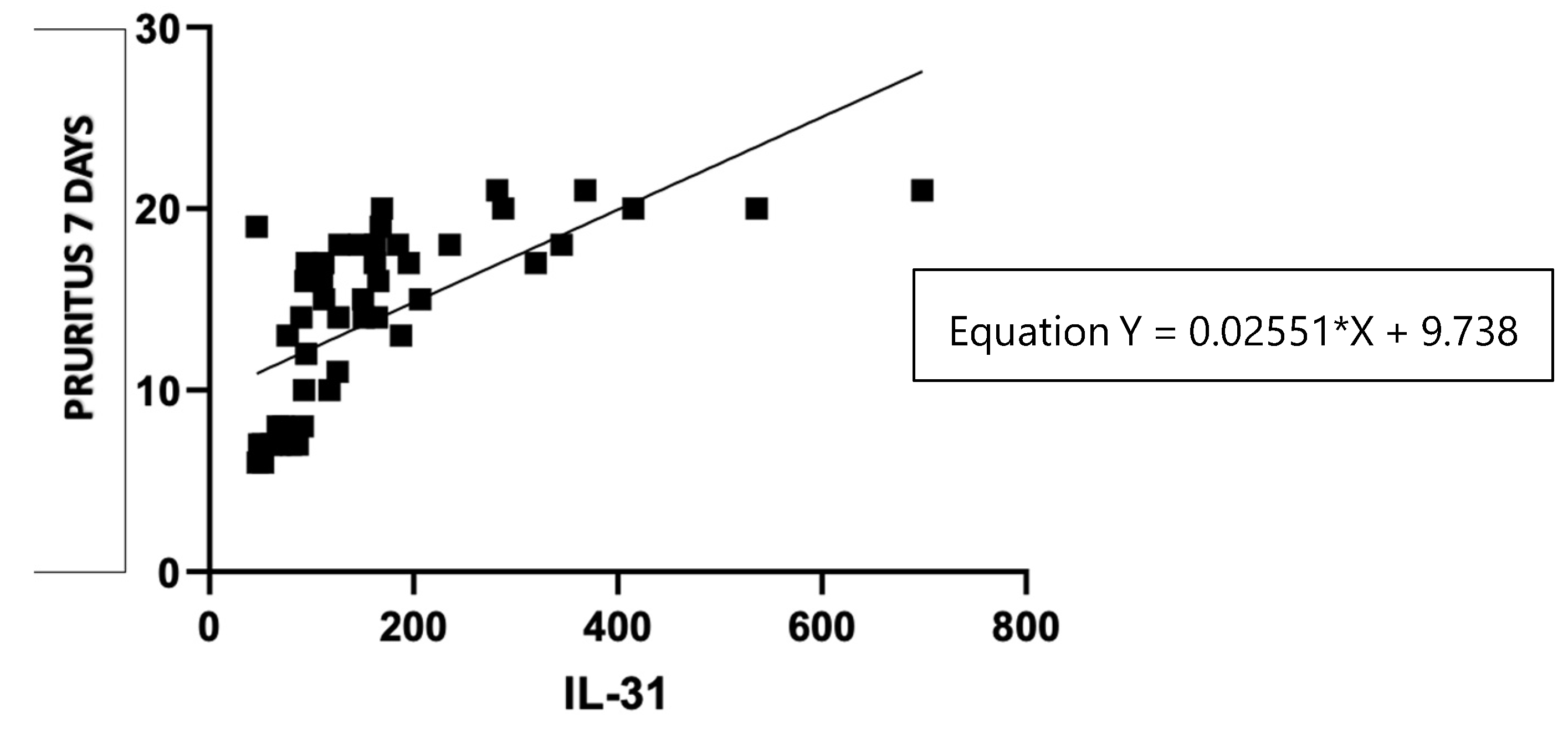
Figure 7.
Correlation of serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients and pruritus score per 7 days.
Figure 7.
Correlation of serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients and pruritus score per 7 days.
The statistical analysis used the Kruskal-Wallis test to examine the association between different forms of pruritus. The test resulted in a highly significant P-value of less than 0.0001, indicating that there were statistically significant differences between the groups with different forms of pruritus. The P-value summary is denoted by ****, confirming the high significance of the result. The test also revealed that the medians of the pruritus scores vary significantly (P < 0.05) among the three groups. The Kruskal-Wallis statistic value is 26.79, which further supports the evidence of significant differences in pruritus scores among the groups.
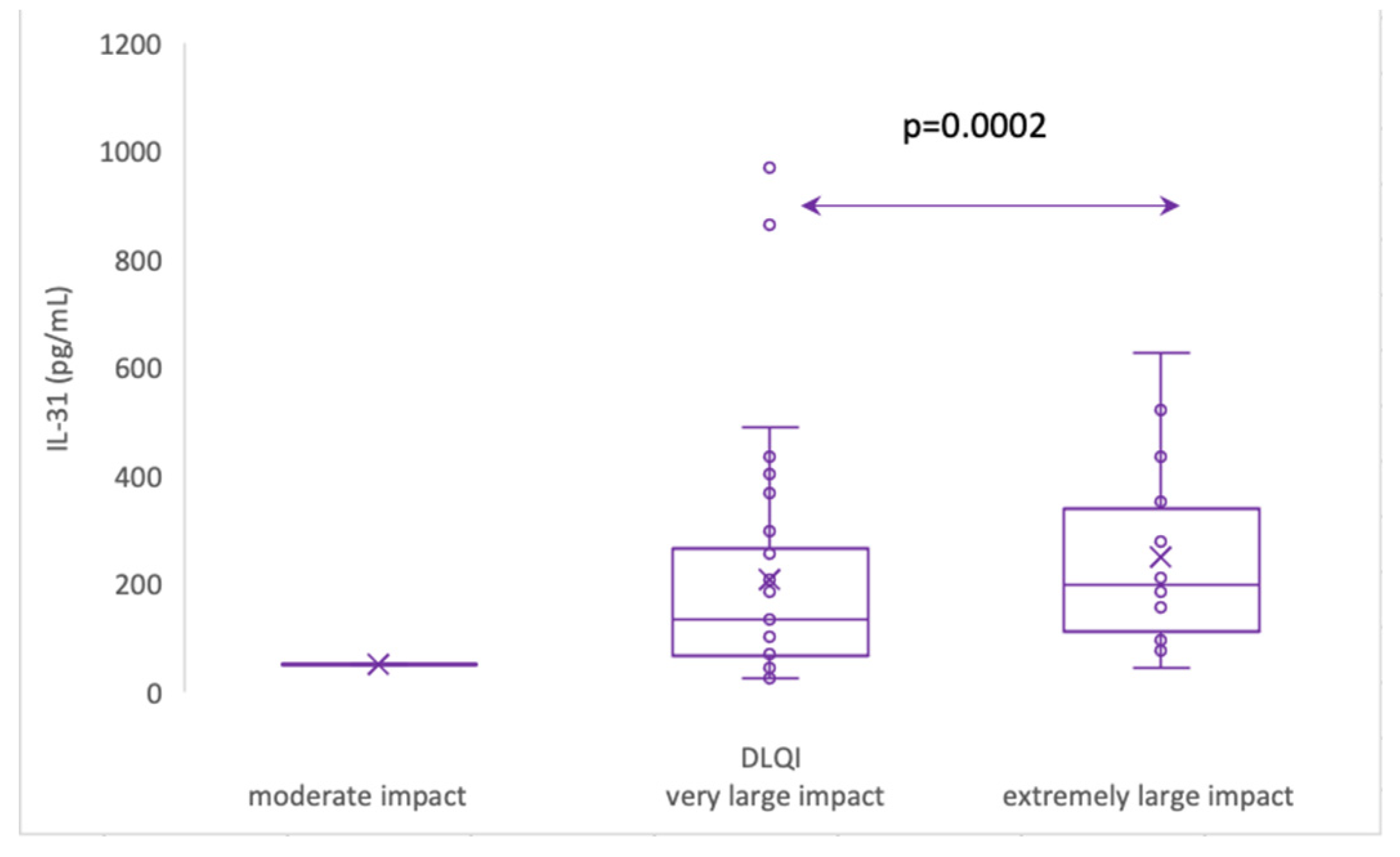
3.5.3. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to DLQI
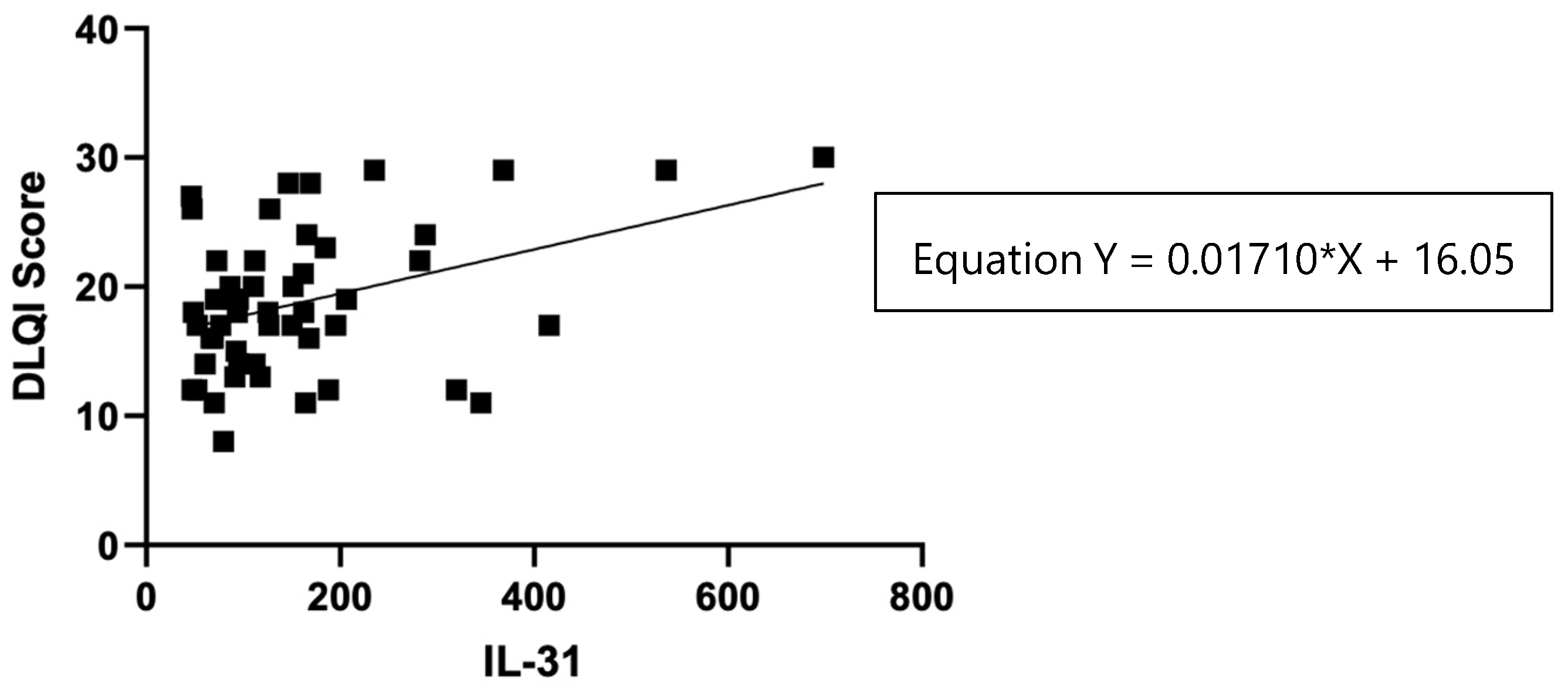
The impact of CSU on patients' quality of life was assessed using the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI), as explained in the Materials and Methods section 2, and the results revealed that patients with a "very important impact" group (n=33) had a mean IL-31 level of 104 (standard deviation 47), with a median of 93, ranging from 70 to 127 pg/ml. On the other hand, the "extremely important impact" group (n=16) exhibited a significantly higher mean IL-31 level of 276 (standard deviation 170), with a median of 244, ranging from 160 to 351 pg/ml. Additionally, it is worth noting that there was one patient with a "moderate" impact on quality of life, as per the DLQI, who had an IL-31 level of 79.635 pg/ml. These findings suggest that higher IL-31 levels may be associated with a more pronounced impact on the quality of life in patients with the disease.
Figure 8.
Serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients with moderate impact, very large impact and extremely large impact on quality of life, according to DLQI.
Figure 8.
Serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients with moderate impact, very large impact and extremely large impact on quality of life, according to DLQI.
Figure 9.
Correlation of serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients and DLQI score.
Figure 9.
Correlation of serum IL-31 levels in CSU patients and DLQI score.
Table 4.
The statistical analysis: IL-31 serum levels and DLQI score.
Table 4.
The statistical analysis: IL-31 serum levels and DLQI score.
| Test |
Pearson r |
| r |
0.3918 |
| 95% confidence interval |
0.1273 to 0.6042 |
| R squared |
0.1535 |
| P value |
|
| P (two-tailed) |
0.0049 |
| P value summary |
** |
| Significant? (alpha = 0.05) |
Yes |
| Number of XY Pairs |
50 |
3.6. Serum IL-31 levels in relation to response to antihistamines AH1
The IL-31 levels in CSU patients and their response to the maximum recommended dose of second-generation h1 antihistamines [
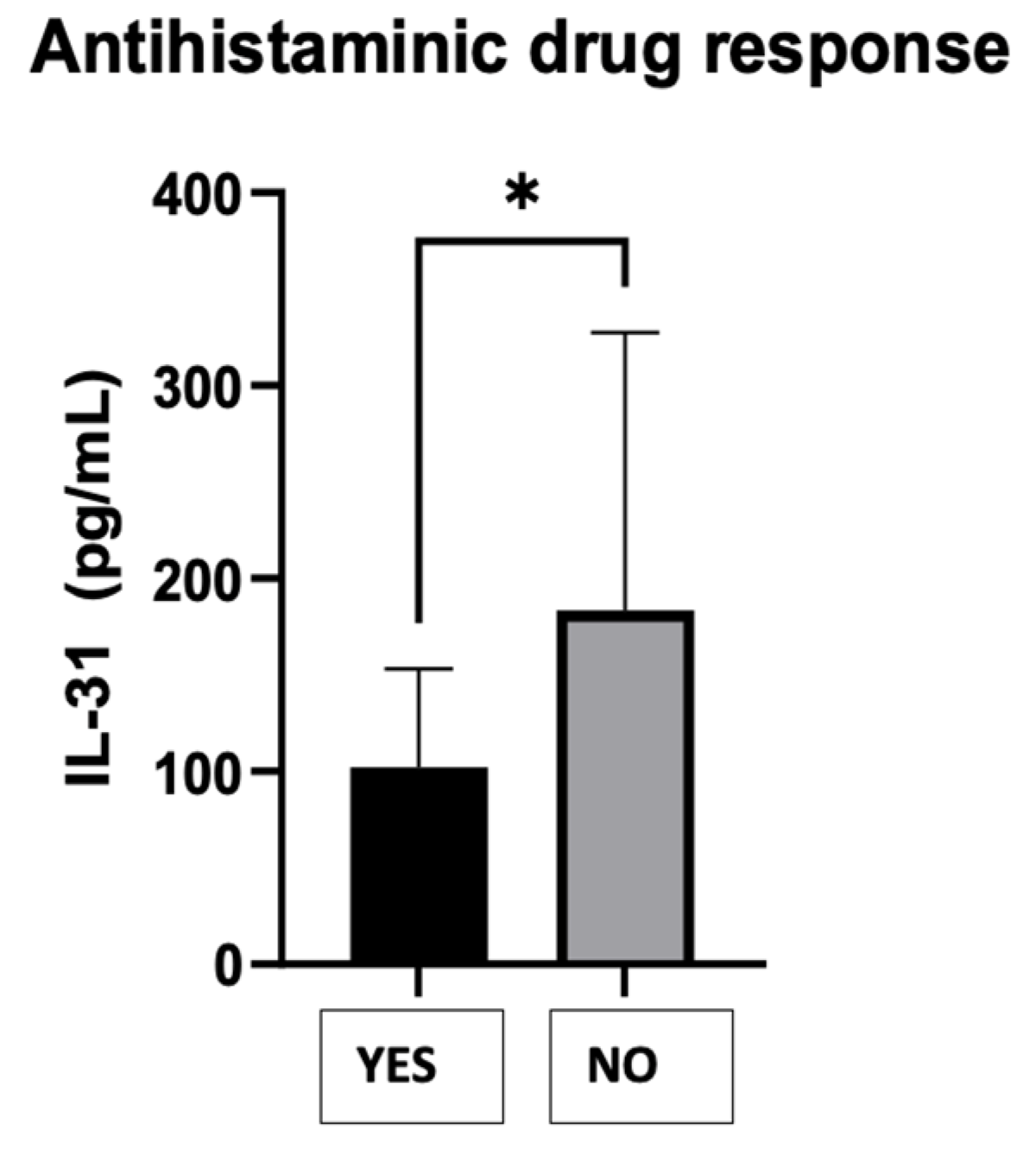
1] were compared, dividing the patients into two groups as follows: those who responded to AH1 - YES and those who did not respond to AH1 requiring the following therapeutic steps - NO. The Mann Whitney test resulted in a P-value of 0.0290, indicating a statistically significant difference in the treatment response between the two groups. The "P value summary" denoted by one asterisk (*) confirms the significance at the alpha level of 0.05. The test used a two-tailed P-value, considering both higher and lower values. The sum of ranks in the "Yes" and "No" groups was 256.5 and 1019, respectively, with a Mann-Whitney U value of 151.5. The difference between the medians of the two groups was 46.06 (actual difference) or 43.56 (Hodges-Lehmann estimate). This suggests that the group with a negative response to the treatment (NO) had a higher median value of serum IL-31 levels (136.9) compared to the group with a positive response (YES) with a median of 90.86.
Figure 9.
CSU patients' serum IL-31 levels and the response to antihistaminics H1.
Figure 9.
CSU patients' serum IL-31 levels and the response to antihistaminics H1.
4. Discussion
Chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) is a debilitating skin disease that has a considerable impact on the daily life of affected patients, both through the characteristic lesions, but especially through itching. It affects approximately 1% of the global population and represents a substantial socio-economic burden with absenteeism from the workplace and high costs for the necessary treatments [
23,
24,
25,
26]. Thus, there is an urgent need to better understand the pathogenesis of CSU to develop improved diagnostic and treatment approaches [
2,
6,
27,
28]. Despite this need, there has been less focus on pruritus in the specialized literature that studies chronic urticaria, the symptom being more pathognomonic for atopic dermatitis, which is why IL-31 was also studied more in this condition [
7,
9,
29]. Based on these considerations, our study aimed to investigate the correlation between the cytokine attributed to pruritus and the severity scores of the urticaria, the intensity of the itch, and the impact on the quality of life of affected patients. Our findings revealed a significant association between IL-31 levels in CSU patients and pruritus intensity, disease severity, and quality of life. Additionally, we observed that patients who responded to the first steps of treatment, up to the maximum dose of H1 antihistamines, have lower serum levels of IL-31 than those who did not respond to these drugs and required other therapeutic steps. Among these therapeutic options, anti-IL-31 therapy could also be considered, as it has been studied in other itchy skin conditions [
7,
9,
29].
IL-31 plays a significant role in cutaneous inflammation and has been extensively studied for its involvement in tissue homeostasis, inflammation, immune defense, neuroimmune circuits, and pruritus [
29,
30,
31,
32,
33,
34]. It belongs to the IL-6-derived cytokine family and is associated with proinflammatory characteristics. While its physiological function is not fully understood, it has been implicated in various inflammatory disorders in humans, such as atopic dermatitis, inflammatory bowel disease, and asthma. IL-31 is produced by TH2 cells and immature dendritic cells, activating neurons and keratinocytes through its receptors IL31RA/OSMRβ. Intradermal application of IL-31 induces itch, further illustrating its ability to activate target neurons [
35,
36]. In our study, we found significantly increased levels of IL-31 in patients with CSU compared to healthy controls, which is consistent with observations from other studies [
4,
5,
30]. This finding supports the inclusion of urticaria in the category of pruritogenic inflammatory skin diseases, like the others mentioned.
During our study, there were no statistically significant differences in the fundamental clinical characteristics of the patients, such as age and sex. Surprisingly, we also noticed the absence of correlations between the serum levels of IL-31 and eosinophils in our patients, despite prior theoretical assumptions suggesting an association between IL-31' and eosinophilic origin [
2]. Furthermore, no significant correlations were identified between non-specific inflammatory markers, such as ESR and CRP, and the serum levels of IL-31. These findings support the notion that IL-31 may not function as a non-specific pro-inflammatory cytokine but rather exhibit distinct characteristics related to the pruritogenic mechanism, as indicated by the observed positive correlations, which will be discussed.
We observed significant correlations between the level of IL-31 and the severity of CSU, as quantified by UAS7. There are other studies that reported associations between IL-31 serum levels and disease severity in patients with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) [
4], atopic dermatitis [
37], and uremic pruritus [
38]. However, recent study found no correlations between IL-31 levels in CSU and psoriasis patients with disease severity, as assessed using UAS7 and PASI scores, respectively. The statistical analysis of the correlations found in our study suggests that there is a linear relationship between these two variables. For each unit increase in the serum levels of IL-31 (X), the severity of urticaria measured by UAS7 (Y) is predicted to increase by 0.03587 units. This equation provides valuable insights into the potential association between IL-31 levels and urticaria severity, allowing for a better understanding of the relationship between these factors in the context of the study. In addition, in support of the link between IL-31 serum levels and the severity of the disease, there are positive correlations between the serum values of this cytokine and the severity of pruritus, measured for 7 days, separately from UAS7.
While other studies have seen correlations between various cytokines and the impact of diseases in the pathogenesis of which they are involved [
9,
29,
34], our study demonstrated a direct proportional relationship between the DLQI score, which evaluates the quality of life of patients with urticaria and the impact of the disease on it, and the serum level of IL -31, showing a positive correlation between these variables. However, further research with a larger sample size is needed to confirm and establish a more robust relationship between IL-31 levels and the impact on the quality of life in this context.
Previous research has shown changes in IL-31 levels following specific treatments. For example, in patients with psoriasis, serum levels of IL-31 were significantly decreased after exposure to narrowband ultraviolet radiation [
39], and successful treatment with omalizumab in patients with CSU resulted in significant reductions in serum levels of IL-31 [
40]. Furthermore, a study in CSU patients who responded positively to omalizumab demonstrated a significant correlation between improved clinical symptoms and decreased IL-31-secreting T cells [
41]. While the current study did not specifically evaluate IL-31 levels after certain treatments, it was observed that patients who did not respond to the antihistamine treatment administered in the first two stages of treatment had higher IL-31 values. Further studies which quantify the IL-31 levels depending on the treatment and the values of other cytokines, it is worth doing to understand more precisely its implications in pathogenesis of this disease, in evolution and response to treatment.
5. Conclusions
IL-31, also known as the pruritus interleukin, has significant implications in CSU, as observed in our study, with significantly higher levels identified in patients compared to controls. The severity of urticaria, measured with UAS7, was also correlated with IL-31 levels, indicating that the intensity of itching and the impact on the quality of life of patients with urticaria, quantified with the DLQI, were all greater with higher IL-31 values. Additionally, patients who did not respond to the antihistamine treatment showed a higher expression of this cytokine in the serum.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța; Data curation, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța and Ioana Adriana Muntean; Formal analysis, Cristian Florea; Investigation, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța; Methodology, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, Ioana Adriana Muntean and Gabriela Filip; Resources, Diana Deleanu; Software, Ioana Adriana Muntean; Supervision, Gabriela Filip; Validation, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța and Gabriela Filip; Writing – original draft, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța; Writing – review & editing, Carmen-Teodora Dobrican-Băruța, Irena Pintea and Gabriela Filip. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work received support from the University of Medicine and Pharmacy "Iuliu Hatieganu" of Cluj-Napoca, Romania through a grant—Proiect Cercetare Doctorala 2019 (PCD 2019), contract number 4276/18.01.2019 and 2462/18/17.01.2020.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the UMF "Iuliu Hatieganu" [AVZ270/10.10.2022] and by the ”Octavian Fodor” Institute of Gastroenterology and Hepatology [12637/11.10.2022].
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to especially thank the chemist Dr. Nicoleta Decea for her support and coordination in performing the IL-31 ELISA determinations.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zuberbier, T, Abdul Latiff, AH, Abuzakouk, M, et al. The international EAACI/GA²LEN/EuroGuiDerm/APAAACI guideline for the definition, classification, diagnosis, and management of urticaria. Allergy. 2022; 77: 734– 766. [CrossRef]
- Dobrican CT, Muntean IA, Pintea I, Petricău C, Deleanu DM, Filip GA. Immunological signature of chronic spontaneous urticaria (Review). Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun;23(6):381. Epub 2022 Apr 8. PMID: 35495604; PMCID: PMC9019689. [CrossRef]
- Kay AB, Clark P, Maurer M and Ying S: Elevations in T-helper-2-initiating cytokines (interleukin-33, interleukin-25 and thymic stromal lymphopoietin) in lesional skin from chronic spontaneous (‘idiopathic’) urticaria. Br J Dermatol 172:1294-1302, 2015.
- Lin, W., Zhou, Q., Liu, C. et al. Increased plasma IL-17, IL-31, and IL-33 levels in chronic spontaneous urticaria. Sci Rep 7, 17797 (2017). [CrossRef]
- Chaowattanapanit S., Choonhakarn C., Salao K., Winaikosol K., Julanon N., Wongjirattikarn R., Foocharoen C., Sompornrattanaphan M. Increased serum IL-31 levels in chronic spontaneous urticaria and psoriasis with pruritic symptoms, Heliyon, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, A, Lebwohl, M, Giménez-Arnau, AM, Hide, M, Armstrong, AW, Maurer, M. Chronic spontaneous urticaria: Focus on pathophysiology to unlock treatment advances. Allergy. 2023; 78: 389- 401. [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly E, Muller A, Lauerma AI, Pivarcsi A, Soto H, Kemeny L, et al. IL-31: a new link between T cells and pruritus in atopic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2006) 117: 411–7. 10.1016/j.jaci.2005.10.033. [CrossRef]
- Gutzmer R, Gschwandtner M, Rossbach K, Mommert S, Werfel T, Kietzmann M, et al. Pathogenetic and therapeutic implications of the histamine H4 receptor in inflammatory skin diseases and pruritus. Front Biosci. (2011) 3:985–94. 10.2741/s203. [CrossRef]
- Gibbs BF, Patsinakidis N, Raap U. Role of the Pruritic Cytokine IL-31 in Autoimmune Skin Diseases. Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 21; 10:1383. PMID: 31281316; PMCID: PMC6598004. [CrossRef]
- Church MK, Kolkhir P, Metz M, Maurer M. The role and relevance of mast cells in urticaria. Immunol Rev. (2018) 282:232–47. 10.1111/imr.12632. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Q, Putheti P, Zhou Q, Liu Q, Gao W. Structures and biological functions of IL-31 and IL-31 receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2008) 19:347–56. 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2008.08.003. [CrossRef]
- Kasraie S, Niebuhr M, Werfel T. Interleukin (IL)-31 induces pro-inflammatory cytokines in human monocytes and macrophages following stimulation with staphylococcal exotoxins. Allergy. (2010) 65:712–21. 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2009. 02255.x. [CrossRef]
- Rauber MM, Pickert J, Holiangu L, Möbs C, Pfützner W. Functional and phenotypic analysis of basophils allows determining distinct subtypes in patients with chronic urticaria. Allergy. (2017) 72:1904–11. 10.1111/all.13215. [CrossRef]
- Raap U, Gehring M, Kleiner S, Rüdrich U, Eiz-Vesper B, Haas H, et al. Human basophils are a source of - and are differentially activated by - IL-31. Clin Exp Allergy. (2017) 47:499–508. [CrossRef]
- Ying S, Kikuchi Y, Meng Q, Kay AB, Kaplan AP. TH1/TH2 cytokines and inflammatory cells in skin biopsy specimens from patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria: comparison with the allergen-induced late-phase cutaneous reaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2002) 109:694–700. [CrossRef]
- Fioranelli M, Roccia MG, Lotti T. Therapy with anti-interleukin-31 receptor A antibody for atopic dermatitis. Dermatol Ther. (2017) 30:e12490. [CrossRef]
- Kabashima K, Furue M, Hanifin JM, Pulka G, Wollenberg A, Galus R, et al. Nemolizumab in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis: Randomized, phase II, long-term extension study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2018) 142:1121–30. [CrossRef]
- Oyama S, Kitamura H, Kuramochi T, Higuchi Y, Matsushita H, Suzuki T, et al. Cynomolgus monkey model of interleukin-31-induced scratching depicts blockade of human interleukin-31 receptor A by a humanized monoclonal antibody. Exp Dermatol. (2018) 27:14–21. [CrossRef]
- Mathias SD, Crosby RD, Zazzali JL, Maurer M and Saini SS: Evaluating the minimally important difference of the urticaria activity score and other measures of disease activity in patients with chronic idiopathic urticaria. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 108: 20-24, 2012.
- Hawro T, Ohanyan T, Schoepke N, Metz M, Peveling-Oberhag A, Staubach P, Maurer M and Weller K: The urticaria activity score-validity, reliability, and responsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract 6: 1185-1190.e1, 2018.
- Baiardini I, Braido F, Bindslev-Jensen C, Bousquet PJ, Brzoza Z, Canonica GW, Compalati E, Fiocchi A, Fokkens W, Gerth van Wijk R, et al: Recommendations for assessing patient-reported outcomes and health-related quality of life in patients with urticaria: A GA(2)LEN taskforce position paper. Allergy 66: 840-844, 2011.
- Weller K, Groffik A, Magerl M, Tohme N, Martus P, Krause K, Metz M, Staubach P and Maurer M: Development and construct validation of the angioedema quality of life questionnaire. Allergy 67: 1289-1298, 2012.
- O'Donnell BF, Lawlor F, Simpson J, Morgan M and Greaves MW: The impact of chronic urticaria on the quality of life. Br J Dermatol 136: 197-201, 1997.
- Parisi CA, Ritchie C, Petriz N and Morelo Torres C: Direct medical costs of chronic urticaria in a private health organization of Buenos Aires, Argentina. Value Health Reg Issues 11: 57-59, 2016.
- Broder MS, Raimundo K, Antonova E and Chang E: Resource use and costs in an insured population of patients with chronic idiopathic/spontaneous urticaria. Am J Clin Dermatol 16:313-321, 2015.
- Graham J, McBride D, Stull D, Halliday A, Alexopoulos ST, Balp MM, Griffiths M, Agirrezabal I, Zuberbier T and Brennan A: Cost utility of omalizumab compared with standard of care for the treatment of chronic spontaneous urticaria. Pharmacoeconomics 34: 815-827, 2016.
- Zhou B, Li J, Liu R, Zhu L, Peng C. The role of crosstalk of immune cells in pathogenesis of chronic spontaneous urticaria. Front Immunol. 2022; 13:879754. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.879754. [CrossRef]
- Yang X, Chen L, Wang S, Wu Y, Zhou X, Meng Z. The correlation between Th17/Treg immune dysregulation and the disease severity in chronic spontaneous urticaria patients. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Jul;11(7): e920. PMID: 37506162; PMCID: PMC10373571. [CrossRef]
- Saleem MD, Oussedik E, D'Amber V, Feldman SR. Interleukin-31 pathway and its role in atopic dermatitis: a systematic review. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017 Nov;28(7):591-599. Epub 2017 Mar 2. PMID: 28145790. [CrossRef]
- Bağci IS, Ruzicka T. IL-31: A new key player in dermatology and beyond. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018;141(3):858– 866. [CrossRef]
- Lai T, Wu D, Li W, et al. Interleukin-31 expression and relation to disease severity in human asthma. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):22835. [CrossRef]
- Lei Z, Liu G, Huang Q, et al. SCF and IL-31 rather than IL- 17 and BAFF are potential indicators in patients with allergic asthma. Allergy 2008;63(3):327–332. [CrossRef]
- West NR, Hegazy AN, Owens BMJ, et al. Oncostatin M drives intestinal inflammation and predicts response to tumor necrosis factorneutralizing therapy in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Med. 2017;23(5):579–589. [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly E, Muller A, Lauerma AI, et al. IL-31: a new link between T cells and pruritus in atopic skin inflammation. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;117(2):411–417. [CrossRef]
- Roosterman D, Goerge T, Schneider SW, Bunnett NW, Steinhoff M. Neuronal control of skin function: the skin as a neuroimmuno-endocrine organ. Physiol Rev. 2006;86(4):1309–1379. [CrossRef]
- Datsi, A., Steinhoff, M., Ahmad, F., Alam, M. and Buddenkotte, J. (2021), Interleukin-31: The “itchy” cytokine in inflammation and therapy. Allergy, 76: 2982-2997. [CrossRef]
- Raap, K. Wichmann, M. Bruder, S. Stander, B. Wedi, A. Kapp, U. et al., Correlation of IL-31 serum levels with severity of atopic dermatitis, J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 122 (2) (2008) 421–423. [CrossRef]
- Ko MJ, Peng YS, Chen HY, Hsu SP, Pai MF, Yang JY, Wen SY, Jee SH, Wu HY, Chiu HC. Interleukin-31 is associated with uremic pruritus in patients receiving hemodialysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Dec;71(6):1151-1159.e1. Epub 2014 Sep 27. PMID: 25270263. [CrossRef]
- Narbutt J, Olejniczak I, Sobolewska-Sztychny D, Sysa-Jedrzejowska A, Słowik-Kwiatkowska I, Hawro T, Lesiak A. Narrow band ultraviolet B irradiations cause alteration in interleukin-31 serum level in psoriatic patients. Arch Dermatol Res. 2013 Apr;305(3):191-5. Epub 2012 Oct 30. PMID: 23108364; PMCID: PMC3606511. [CrossRef]
- Altrichter S, Hawro T, Hänel K, Czaja K, Lüscher B, Maurer M, Church MK, Baron JM. Successful omalizumab treatment in chronic spontaneous urticaria is associated with lowering of serum IL-31 levels. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016 Mar;30(3):454-5. Epub 2014 Nov 4. PMID: 25371135. [CrossRef]
- Rauber MM, Pickert J, Holiangu L, Möbs C, Pfützner W. Omalizumab response correlates with reduced IFN-γ-, IL-10- and IL-31-secreting cells in chronic spontaneous urticaria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2020 Sep;34(9):2078-2085. Epub 2020 May 22. PMID: 31954076. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).