Submitted:
17 August 2023
Posted:
21 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Soil Properties
1.2. Soil Information Data Source
1.3. Machine Learning
1.3.1. Machine Learning Modelling Techniques and Algorithms
1.3.2. Performance Evaluation
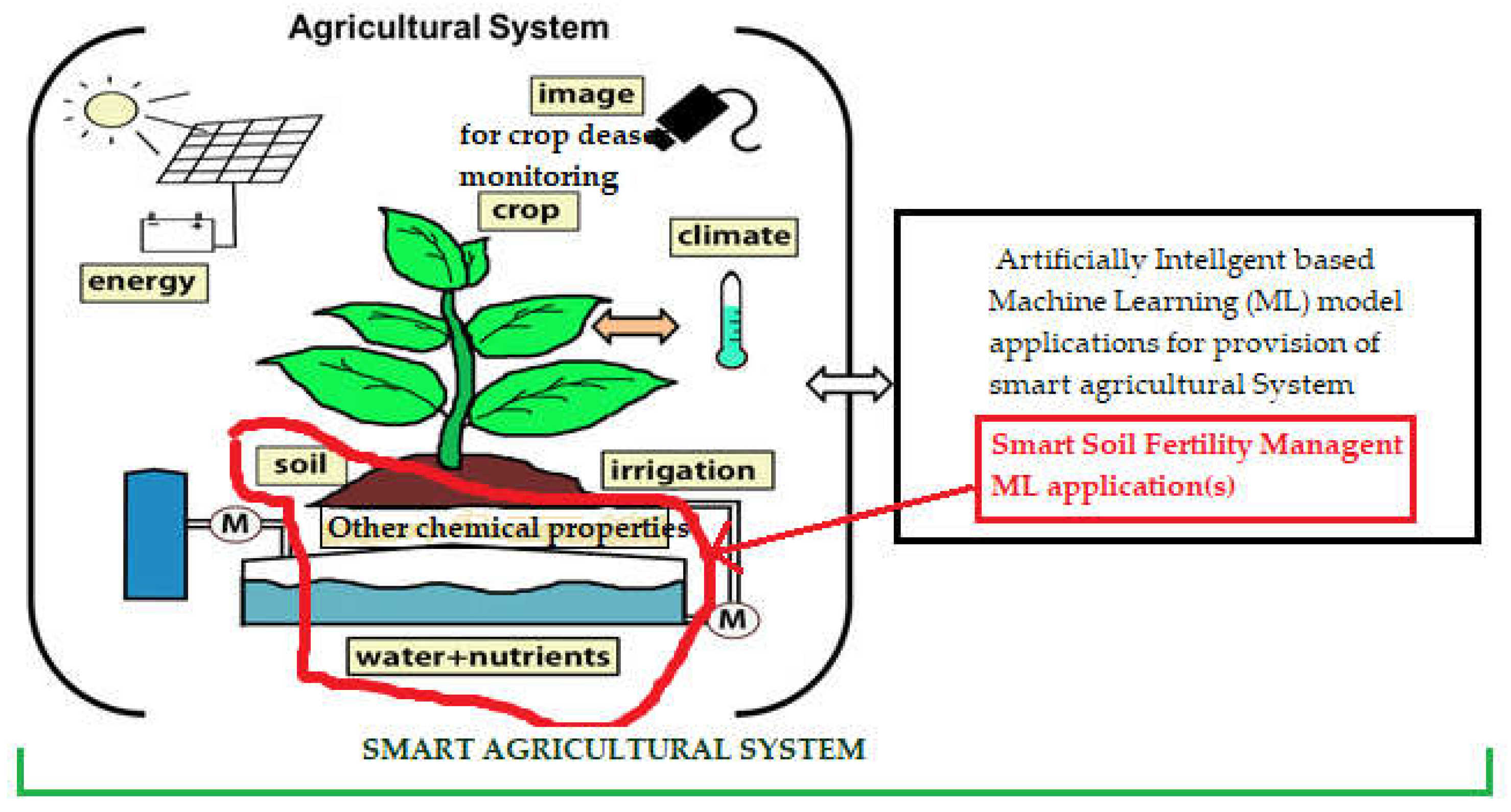
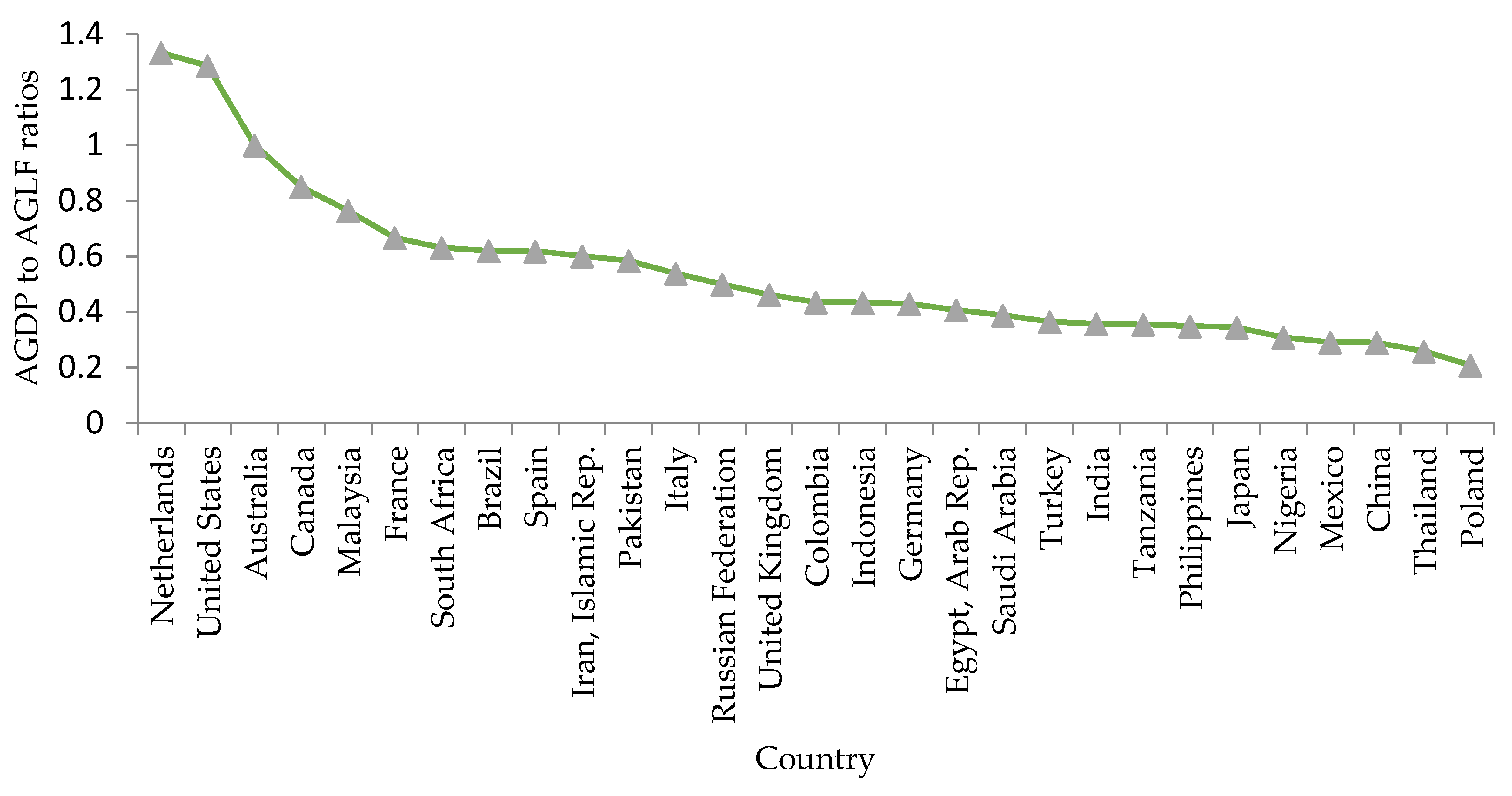
2. Data-Driven ICT and Impact of Machine learning in Agriculture
3. Materials and Methods
4. Machine Learning for Soil Nutrients Analysis and Fertility Status Prediction
5. Findings and Discussion
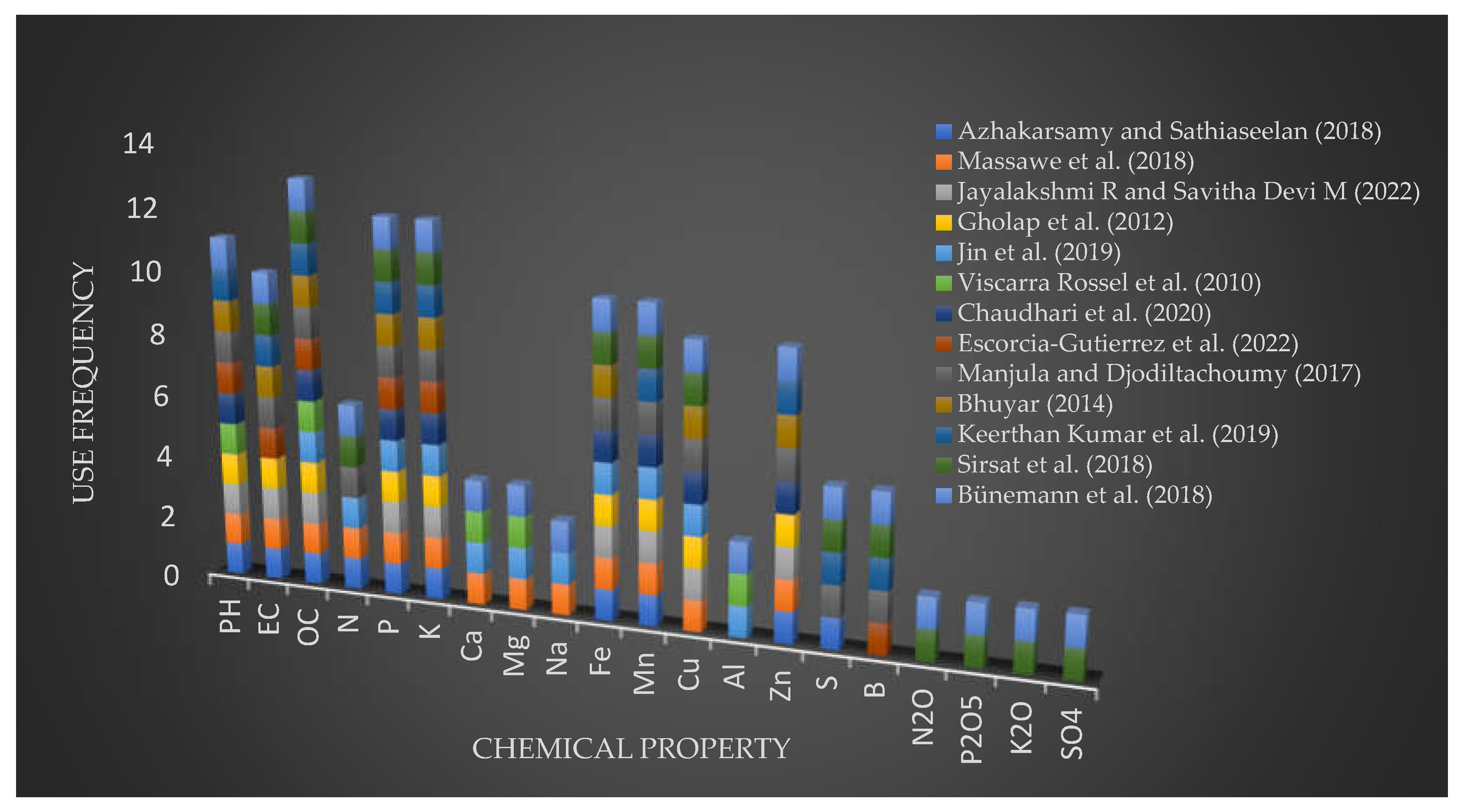
5.1. Identification of Soil Properties for modelling soil fertility status Prediction
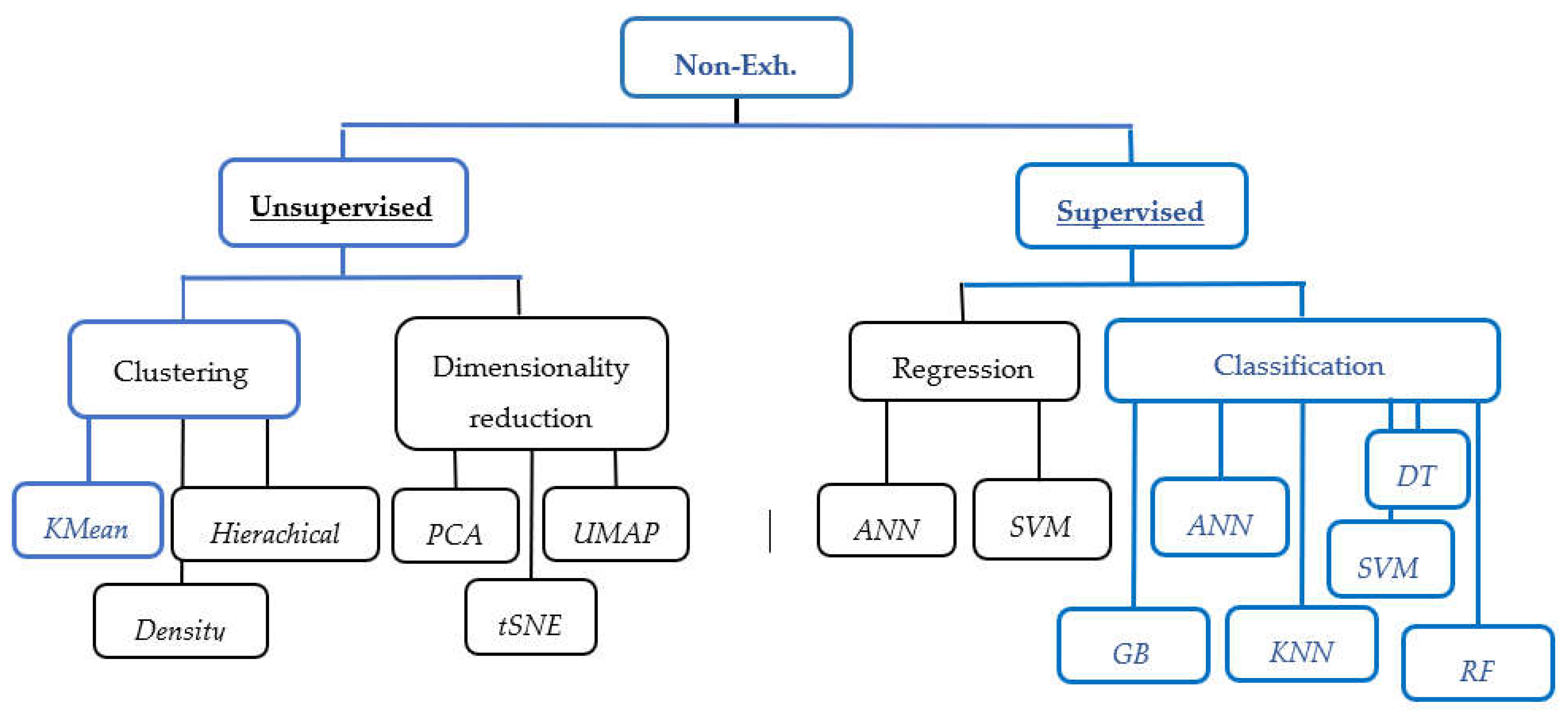
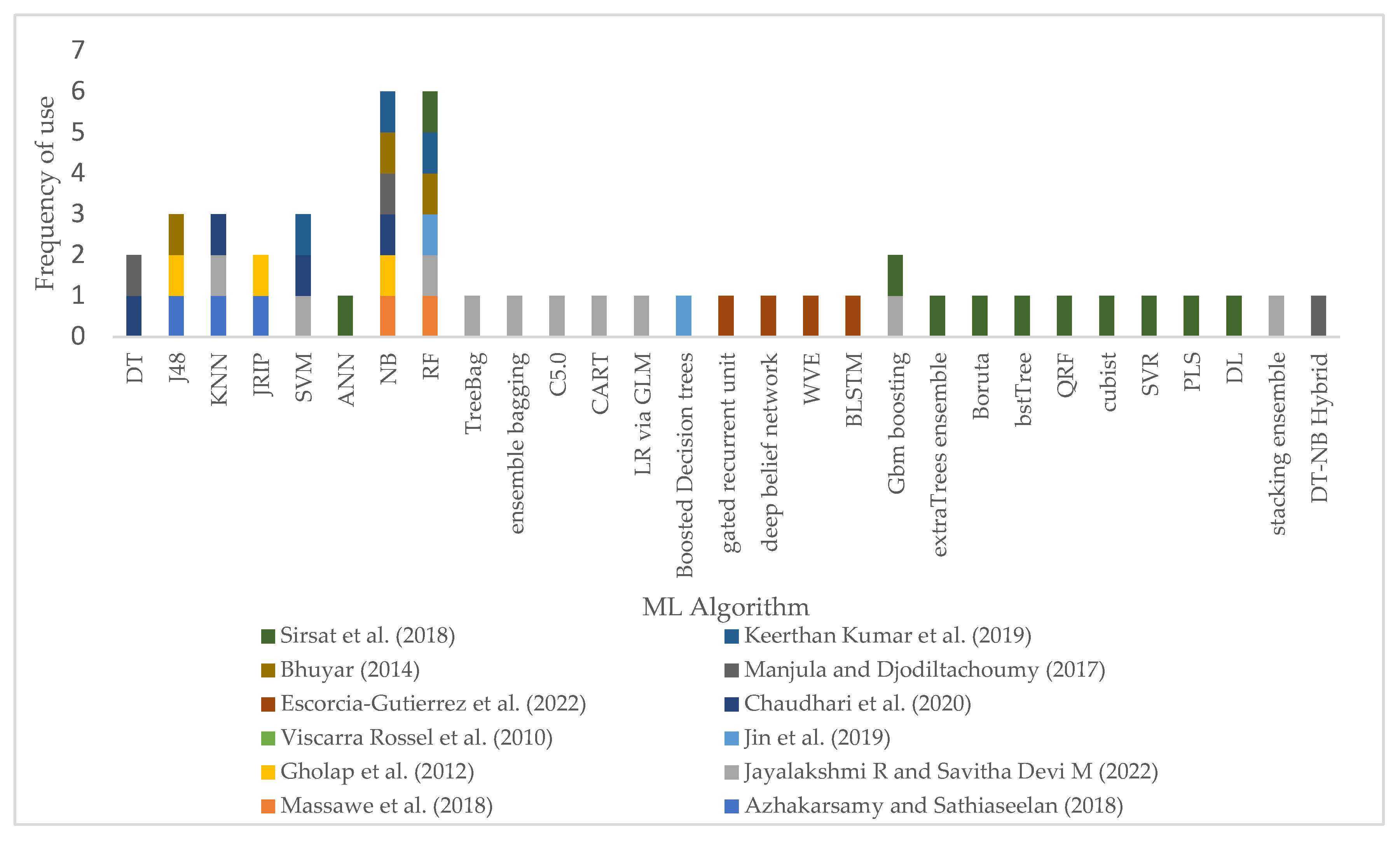
5.2. Identification of Applied Machine Learning Algorithms in Modelling soil fertility status Prediction
5.3. Exploited Features, Target Classes, and Reported Model Performances
5.3.1. Exploited Features and Target Classes
5.3.2. Reported Model Performances
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manjula, E.; Djodiltachoumy, S. Data Mining Technique to Analyze Soil Nutrients Based on Hybrid Classification. IJARCS 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massawe, B. H.; Subburayalu, S. K.; Kaaya, A. K.; Winowiecki, L.; Slater, B. K. Mapping Numerically Classified Soil Taxa in Kilombero Valley, Tanzania Using Machine Learning. Geoderma 2018, 311, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrández-Pastor, F. J.; García-Chamizo, J. M.; Nieto-Hidalgo, M.; Mora-Martínez, J. Precision Agriculture Design Method Using a Distributed Computing Architecture on Internet of Things Context. Sensors 2018, 18, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bünemann, E. K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R. E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T. W.; Mäder, P. Soil Quality–A Critical Review. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherlinka, V. Soil Fertility: Influencing Factors Аnd Improvement Strategies. Available online: https://eos.com/blog/soil-fertility/ (accessed on 9 August 2023).
- FAO. The Future of Food and Agriculture – Trends and Challenges; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. Agricultural Outlook 2016-2025., 2016.
- Ishengoma, F.; Athuman, M. Internet of Things to Improve Agriculture in Sub Sahara Africa-a Case Study. 2018.
- Jayaraman, P.; Yavari, A.; Georgakopoulos, D.; Morshed, A.; Arkayd, Z. Internet of Things Platform for Smart Farming: Experiences and Lessons Learnt. 2016.
- Sirsat, M. S.; Cernadas, E. G.; Delgado, M. F.; Khan, R. Classification of Agricultural Soil Parameters in India. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2017, 135, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirsat, M. S.; Cernadas, E. G.; Delgado, M. F. Application of Machine Learning to Agricultural Soil Data. PhD Thesis, Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayabaskar, P. S.; Sreemathi, R.; Keertanaa, E. Crop Prediction Using Predictive Analytics. In 2017 International Conference on Computation of Power, Energy Information and Commuincation (ICCPEIC); IEEE, 2017; pp. 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Kavvadias, V.; Papadopoulou, M.; Vavoulidou, E.; Theocharopoulos, S.; Malliaraki, S.; Agelaki, K.; Koubouris, G.; Psarras, G. Effects of Carbon Inputs on Chemical and Microbial Properties of Soil in Irrigated and Rainfed Olive Groves. In Soil Management and Climate Change; Elsevier, 2018; Volume 137, p. 150. [Google Scholar]
- Gholap, J.; Ingole, A.; Gohil, J.; Gargade, S.; Attar, V. Soil Data Analysis Using Classification Techniques and Soil Attribute Prediction. arXiv arXiv:1206.1557, 2012.
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Liber, K. A Comprehensive Support Vector Machine-Based Classification Model for Soil Quality Assessment. Soil and Tillage Research 2016, 155, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerson, S.; Cranston, R. E.; Liss, P. S. Redox Species in a Reducing Fjord: Equilibrium and Kinetic Considerations. Deep Sea Research Part A. Oceanographic Research Papers 1979, 26, 859–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kommineni, M.; Perla, S.; Yedla, D. B. A Survey of Using Data Mining Techniques for Soil Fertility. 2018.
- Rajeswari, V.; Arunesh, K. Analysing Soil Data Using Data Mining Classification Techniques. Indian journal of science and Technology 2016, 9, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, K. M.; Isaak, S.; Rashid, N. C. A.; Ngajikin, N. H.; Bahru, U. J. NPK Detection Spectroscopy on Non-Agriculture Soil. Jurnal Teknologi 2016, 78, 227–231. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilaris, A.; Kartakoullis, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F. X. A Review on the Practice of Big Data Analysis in Agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2017, 143, 23–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Weindorf, D. C.; Wang, D.; Chakraborty, S. Characterizing Soils via Portable X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer: 4. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC). Geoderma 2015, 239, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, M.; Meliyo, J.; Wu, W.; Chen, J.; Shepherd, K.; Ekise, C.; Simbila, W.; Sila, A. M.; Zhan, Y.; Mulvey, J. Tanzania Soil Information Service (TanSIS). 2018. [CrossRef]
- Alpaydin, E. Introduction to Machine Learning; MIT press, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Baştanlar, Y.; Özuysal, M. Introduction to Machine Learning. miRNomics: MicroRNA biology and computational analysis.
- Bonaccorso, G. Machine Learning Algorithms; Packt Publishing Ltd, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz, J.; Kirsch, D. Machine Learning for Dummies, IBM limited edition.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- McQueen, R. J.; Garner, S. R.; Nevill-Manning, C. G.; Witten, I. H. Applying Machine Learning to Agricultural Data. Computers and electronics in agriculture 1995, 12, 275–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Mishra, D.; Santra, G. H. Applications of Machine Learning Techniques in Agricultural Crop Production: A Review Paper. Indian Journal of Science and Technology 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T. Machine Learning; McGraw Hill: Ithaca, NY, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Ayodele, T. O. Types of Machine Learning Algorithms. In New advances in machine learning; IntechOpen, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Anifowose, F. Hybrid Machine Learning Explained in Nontechnical Terms. JPT. Available online: https://jpt.spe.org/hybrid-machine-learning-explained-nontechnical-terms (accessed on 9 October 2022).
- Nilsson, N. J. Introduction to Machine Learning (Draft Version), Department of Computer Science, 1999. Available online: https://ai.stanford.edu/~nilsson/MLbook.pdf.
- Golge, E. Brief History of Machine Learning. A Blog From a Human-engineer-being. Available online: http://www.erogol.com/brief-history-machine-learning/.
- Chaurasia, V.; Pal, S. Performance Analysis of Data Mining Algorithms for Diagnosis and Prediction of Heart and Breast Cancer Disease. 2017.
- Burbidge, R.; Trotter, M.; Buxton, B.; Holden, S. Drug Design by Machine Learning: Support Vector Machines for Pharmaceutical Data Analysis. Computers & chemistry 2001, 26, 5–14. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Tan, J.; Han, D.; Zhu, H. From Machine Learning to Deep Learning: Progress in Machine Intelligence for Rational Drug Discovery. Drug discovery today 2017, 22, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhatrao, K.; Gaykar, A.; Dhawan, A.; Jha, R.; Honrao, V. Predicting Students’ Performance Using ID3 and C4. 5 Classification Algorithms. arXiv arXiv:1310.2071, 2013.
- Durairaj, M.; Vijitha, C. Educational Data Mining for Prediction of Student Performance Using Clustering Algorithms. International Journal of Computer Science and Information Technologies 2014, 5, 5987–5991. [Google Scholar]
- Ameri, S.; Fard, M. J.; Chinnam, R. B.; Reddy, C. K. Survival Analysis Based Framework for Early Prediction of Student Dropouts. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management; ACM, 2016; pp. 903–912. [Google Scholar]
- Mduma, N.; Kalegele, K.; Machuve, D. A Survey of Machine Learning Approaches and Techniques for Student Dropout Prediction. Data Science Journal 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlee, J. Data Mining with Weka; 2016.
- Castle, N. An Introduction to Machine Learning Algorithms. Oracle + Datascience.
- Kamilaris, A.; Prenafeta-Boldú, F. X. Deep Learning in Agriculture: A Survey. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2018, 147, 70–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep Learning. nature 2015, 521, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masri, D.; Woon, W. L.; Aung, Z. Soil Property Prediction: An Extreme Learning Machine Approach. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing; Springer, 2015; pp. 18–27. [Google Scholar]
- Sathya, R.; Abraham, A. Comparison of Supervised and Unsupervised Learning Algorithms for Pattern Classification. International Journal of Advanced Research in Artificial Intelligence 2013, 2, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Solomatine, D. P. Machine Learning in Soil Classification. Neural networks 2006, 19, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, P. A Few Useful Things to Know about Machine Learning. Communications of the ACM 2012, 55, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S. D.; Channe, H. P. Comparative Study of K-NN, Naive Bayes and Decision Tree Classification Techniques. International Journal of Science and Research 2016, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Quinlan, J. R. Induction of Decision Trees. Machine learning 1986, 1, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholap, J. Performance Tuning of J48 Algorithm for Prediction of Soil Fertility. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1208.3943 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Melville, P.; Mooney, R. J. Constructing Diverse Classifier Ensembles Using Artificial Training Examples. IJCAI 2003, 3, 505–510. [Google Scholar]
- Melville, P.; Shah, N.; Mihalkova, L.; Mooney, R. J. Experiments on Ensembles with Missing and Noisy Data. In International Workshop on Multiple Classifier Systems; Springer, 2004; pp. 293–302. [Google Scholar]
- Pastur-Romay, L. A.; Cedrón, F.; Pazos, A.; Porto-Pazos, A. B. Deep Artificial Neural Networks and Neuromorphic Chips for Big Data Analysis: Pharmaceutical and Bioinformatics Applications. International journal of molecular sciences 2016, 17, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegelmann, H.; Sontag, E. Computational Power of Neural Networks. Journal of Computer and System Sciences 1995, 50, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yedjour, D.; Benyettou, A. Symbolic Interpretation of Artificial Neural Networks Based on Multiobjective Genetic Algorithms and Association Rules Mining. Applied Soft Computing 2018, 72, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumelhart, D. E.; Hinton, G. E.; Williams, R. J. Learning Representations by Back-Propagating Errors. Cognitive modeling 1988, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochreiter, S. Investigations on Dynamic Neural Networks. Diploma, Technische Universität München 1991, 91. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S. Studies on Dynamic Neural Networks [in German]. Diploma Thesis, TU Münich, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-Vector Networks. Machine Learning 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.; S, G.; A, S. Support Vector Method for Function Approximation, Regression Estimation, and Signal Processing,; Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; Mozer, M., Jordan, M., Petsche, T., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Poorinmohammad, N.; Mohabatkar, H.; Behbahani, M.; Biria, D. Computational Prediction of Anti HIV-1 Peptides and in Vitro Evaluation of Anti HIV-1 Activity of HIV-1 P24-Derived Peptides. Journal of Peptide Science 2015, 21, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Machine learning 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T. K. Random Decision Forests. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition; 1995; 1, pp. 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marr, B. A Short History of Machine Learning – Every Manager Should Read. Forbes 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Badillo, S.; Banfai, B.; Birzele, F.; Davydov, I. I.; Hutchinson, L.; Kam-Thong, T.; Siebourg-Polster, J.; Steiert, B.; Zhang, J. D. An Introduction to Machine Learning. Clinical pharmacology & therapeutics 2020, 107, 871–885. [Google Scholar]
- Bengio, Y. Learning Deep Architectures for AI. Foundations and trends® in Machine Learning 2009, 2, 1–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y. Convolutional Networks for Images, Speech, and Time Series. The handbook of brain theory and neural networks 1995, 3361, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Pearce, J.; Ferrier, S. Evaluating the Predictive Performance of Habitat Models Developed Using Logistic Regression. Ecological modelling 2000, 133, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, J. A. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Methodology: The State of the Art. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 1989, 29, 307–335. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Obuchowski, N. A.; Bullen, J. A. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curves: Review of Methods with Applications in Diagnostic Medicine. Physics in Medicine & Biology 2018, 63, 07TR01. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, J. How to Calculate Precision, Recall, and F-Measure for Imbalanced Classification. Machine Learning Mastery. Available online: https://machinelearningmastery.com/precision-recall-and-f-measure-for-imbalanced-classification/ (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Soleymani, R.; Granger, E.; Fumera, G. F-Measure Curves: A Tool to Visualize Classifier Performance under Imbalance. Pattern Recognition 2020, 100, 107146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.; McCool, C.; Dayoub, F.; Sunderhauf, N.; Upcroft, B. Evaluation of Features for Leaf Classification in Challenging Conditions. In 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision; IEEE, 2015; pp. 797–804. [Google Scholar]
- Osisanwo, F. Y.; Akinsola, J. E. T.; Awodele, O.; Hinmikaiye, J. O.; Olakanmi, O.; Akinjobi, J. Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms: Classification and Comparison. International Journal of Computer Trends and Technology (IJCTT) 2017, 48, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Witten, I. H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M. A.; Pal, C. J. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques; Morgan Kaufmann, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Solutions, E. Accuracy, Precision, Recall & F1 Score: Interpretation of Performance Measures. Exsilio Blog. https://blog.exsilio.com/all/accuracy-precision-recall-f1-score-interpretation-of-performance-measures/. (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Minh, D. H. T.; Ienco, D.; Gaetano, R.; Lalande, N.; Ndikumana, E.; Osman, F.; Maurel, P. Deep Recurrent Neural Networks for Mapping Winter Vegetation Quality Coverage via Multi-Temporal SAR Sentinel-1. arXiv arXiv:1708.03694, 2017.
- Kumar, A. Cohen Kappa Score Python Example: Machine Learning. Data Analytics. https://vitalflux.com/cohen-kappa-score-python-example-machine-learning/. (accessed on 2 September 2022).
- Cohen’s Kappa: Learn It, Use It, Judge It. KNIME. Available online: https://www.knime.com/blog/cohens-kappa-an-overview (accessed on 24 September 2022).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. Journal of machine learning research 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Michalski, R. S. Learning by Being Told and Learning from Examples: An Experimental Comparison of the Two Methods of Knowledge Acquisition in the Context of Development an Expert System for Soybean Disease Diagnosis. International Journal of Policy Analysis and Information Systems 1980, 4, 125–161. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri Bodaghabadi, M.; Moghimi, A.; Navidi, M. N.; Ebrahimi Meymand, F. Modeling of Yield and Rating of Land Characteristics for Corn Based on Artificial Neural Network and Regression Models in Southern Iran. Desert 2018, 23, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Devi, M. P. K.; Anthiyur, U.; Shenbagavadivu, M. S. Enhanced Crop Yield Prediction and Soil Data Analysis Using Data Mining. International Journal of Modern Computer Science 2016, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Negied, N. K. Expert System for Wheat Yields Protection in Egypt (ESWYP). International Journal of Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering (IJITEE) 2014, 2278–3075. [Google Scholar]
- Saini, H. S.; Kamal, R.; Sharma, A. N. Web Based Fuzzy Expert System for Integrated Pest Management in Soybean. International Journal of Information Technology 2002, 8, 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Azhakarsamy, R.; Sathiaseelan, J. G. R. Comparison of Classifiers to Predict Classification Accuracy for Soil Fertility; SSRN Scholarly Paper ID 3315395; Social Science Research Network: Rochester, NY, 2018; Available online: https://papers.ssrn.com/abstract=3315395 (accessed on 12 April 2022).
- Ramane, D. V.; Patil, S. S.; Shaligram, A. D. Detection of NPK Nutrients of Soil Using Fiber Optic Sensor. In International Journal of Research in Advent Technology Special Issue National Conference ACGT 2015; 2015; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Adamchuk, V. I.; Hummel, J. W.; Morgan, M. T.; Upadhyaya, S. K. On-the-Go Soil Sensors for Precision Agriculture. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 2004, 44, 71–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupicka, J.; Sarec, P.; Novak, P. Measurement of Electrical Conductivity of Fertilizer NPK 20-8-8. In Proceedings of the international scientific conference; Latvia University of Agriculture; 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kannathasan, N. A Survey on Data Mining and Pattern Recognition Techniques for Soil Data Mining. IJCSI International Journal of Computer Science Issues 2011, 8. [Google Scholar]
- CIA Factbook. Labor force - by occupation. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/factbook/fields/labor-force-by-occupation (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- CIA Factbook. GDP - composition by sector. Available online: https://www.indexmundi.com/factbook/fields/gdp-composition-by-sector (accessed on 29 April 2019).
- Haq, K.; Officer, G. E. Managing and Reviewing the Literature. Strategies 2014, 9, 10–15. [Google Scholar]
- Keshav, A.; Cheriton, D. R. How to Read a Paper. 2013, 2.
- Sultan, M.; Miranskyy, A. Ordering Stakeholder Viewpoint Concerns for Holistic and Incremental Enterprise Architecture: The W6H Framework. arXiv arXiv:1509.07360, 2015.
- Sultan, M.; Miranskyy, A. Ordering Interrogative Questions for Effective Requirements Engineering: The W6H Pattern. In 2015 IEEE Fifth International Workshop on Requirements Patterns (RePa); IEEE, 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sultan, M.; Miranskyy, A. Ordering Stakeholder Viewpoint Concerns for Holistic Enterprise Architecture: The W6H Framework. In Proceedings of the 33rd Annual ACM Symposium on Applied Computing; ACM; 2018; pp. 78–85. [Google Scholar]
- Hebb, D. O. The Organization of Behaviour New York; Wiley & Sons, 1949. [Google Scholar]
- Markoff, J. BUSINESS TECHNOLOGY; What’s the Best Answer? It’s Survival of the Fittest. New York Times 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Jayalakshmi, R.; Savitha Devi, M. Mining Agricultural Data to Predict Soil Fertility Using Ensemble Boosting Algorithm. International Journal of Information Communication Technologies and Human Development (IJICTHD) 2022, 14, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R. A.; Rizzo, R.; Demattê, J. A. M.; Behrens, T. Spatial Modeling of a Soil Fertility Index Using Visible–Near-Infrared Spectra and Terrain Attributes. Soil science society of America journal 2010, 74, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Azzari, G.; You, C.; Di Tommaso, S.; Aston, S.; Burke, M.; Lobell, D. B. Smallholder Maize Area and Yield Mapping at National Scales with Google Earth Engine. Remote sensing of environment 2019, 228, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjula, E.; Djodiltachoumy, S. Data Mining Technique to Analyze Soil Nutrients Based on Hybrid Classification. International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keerthan Kumar, T. G.; Shubha, C.; Sushma, S. A. Random Forest Algorithm for Soil Fertility Prediction and Grading Using Machine Learning. Int J Innov Technol Explor Eng 2019, 9, 1301–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhari, R.; Chaudhari, S.; Shaikh, A.; Chiloba, R.; Khadtare, T. D. Soil Fertility Prediction Using Data Mining Techniques. Bulletin Monumental 2020, 21, 8. [Google Scholar]
- Sirsat, M. S.; Cernadas, E.; Fernández-Delgado, M.; Barro, S. Automatic Prediction of Village-Wise Soil Fertility for Several Nutrients in India Using a Wide Range of Regression Methods. Computers and electronics in agriculture 2018, 154, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorcia-Gutierrez, J.; Gamarra, M.; Soto-Diaz, R.; Pérez, M.; Madera, N.; Mansour, R.F. Intelligent Agricultural Modelling of Soil Nutrients and PH Classification Using Ensemble Deep Learning Techniques. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyar, V. Comparative Analysis of Classification Techniques on Soil Data to Predict Fertility Rate for Aurangabad District. Int. J. Emerg. Trends Technol. Comput. Sci 2014, 3, 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- Gholap, J.; Ingole, A.; Gohil, J.; Gargade, S.; Attar, V. Soil Data Analysis Using Classification Techniques and Soil Attribute Prediction. arXiv arXiv:1206.1557, 2012.
- Malamsha, A. J.; Dida, M. A.; Moebs, S. 2-Stage Hybrid Based Heterogeneous Ensemble Committee Machine for Improving Soil Fertility Status Prediction Performance. In International Conference for Technological Advancement in Embedded and Mobile Systems; ICTA-EMOS, 2023. [Google Scholar]
| Classes | Test result positive (+ve) | Test result negative(–ve) |
|---|---|---|
| Actual +ve | True +ve(TP) | False -ve (FN) |
| Actual –ve | False +ve (FP) | True -ve (TN) |
| Author | Chemical Properties (features) | Dataset Size | Technique (ML algorithms) | Number of fertilities target classes | Max Accuracy/ROC Performance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
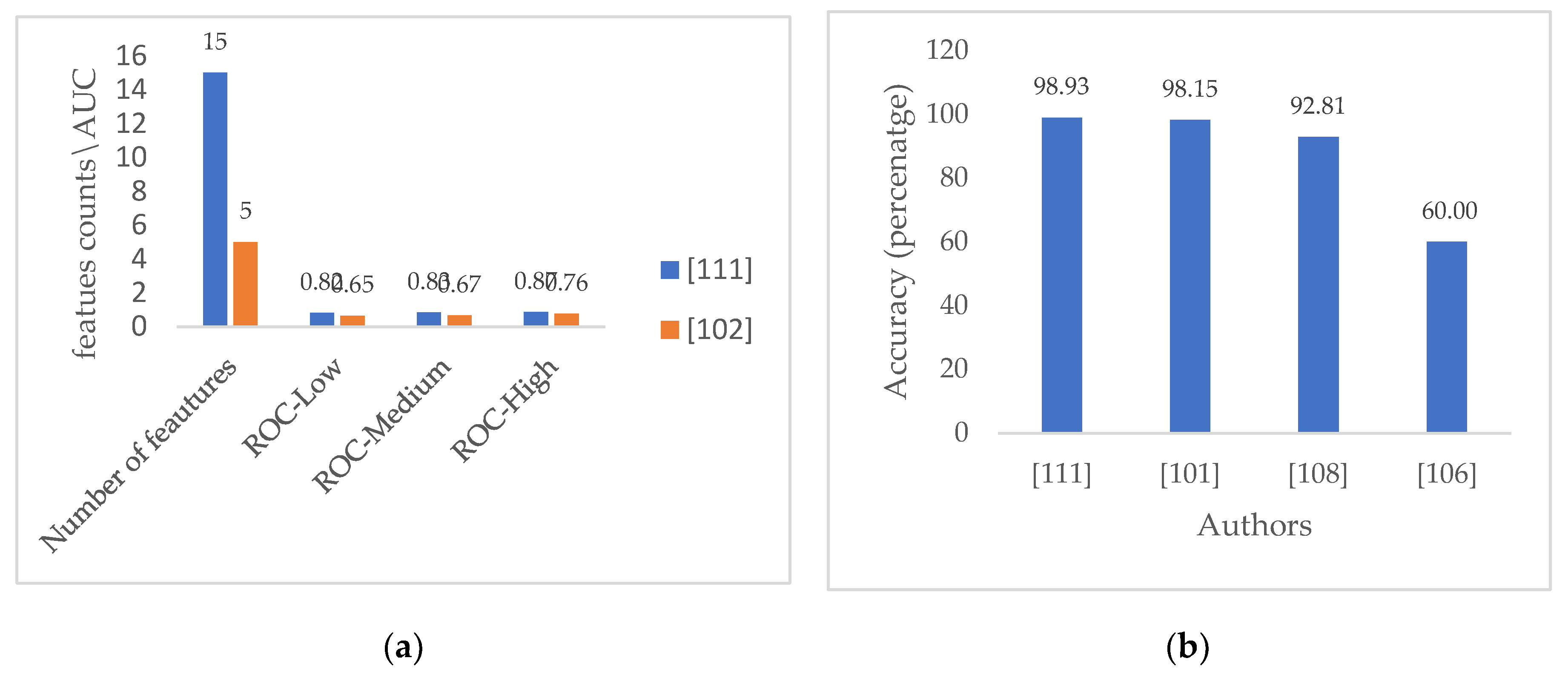
| [111] | OC, pH, EC, TN, P, Ca, K, Mg, Na, S, Mn, Al, Zn, Fe, B | 6260 | GB, RF, SVM, KNN, DT | 3 (low, medium, and high) | 98.93%, AUC 0.87, 0.83. 0.82 for respective high, medium, and low fertility classes |
| [101] | PH, EC, Fe, Zn, Mn,Cu, OC, P, K | 1430 | TreeBag and RF ensemble bagging, boosting C5.0 and boosting Gbm, KNN, CART, SVM, LR via GLM stacking ensemble | 2 (ideal and not ideal) | 98.15 |
| [102] | PH, OC, Ca, Mg, Al | - | Boosted decision trees | 3 (highly fertile, fertile, and least fertile) | 0.76, 0.67, 0.65 for respective high, medium, and low fertility classes |
| [87] | PH, EC, N, P, K, OC, S, Fe, Mn, Zn | 127 | J48, KNN, JRip, NB, SVM, ANN with 10Fold CV and % split | 2 (fertile and not fertile) | 97 |
| [108] | PH, OC,EC, P, K, B | 144 | gated recurrent unit (GRU), deep belief network (DBN), andbidirectional long short term memory (BiLSTM), and WVE | low, medium, and high for target classes, pH level divided into four classes strongly acidic, highly acidic, moderately acidic, and slightly acidic. | 0.9281% for fertility status, and 0.9497% for PH |
| [105] | EC, K, pH, Mn, Zn, S, P, B, OC | Unspecified | Random Forest Classifier, Support Vector Machine, and Gaussian NB | 3 (Low, medium, and high) | 72.74%, 63.33%, 50.78% |
| [107] | EC, OC, N2 O, P2 O5, Fe, Mn, Zn, and B | 930 | NN, DL, SVR, RF, PLS, bagging and boosting, QR and extraTrees ensemble, Boruta, bstTree and gbm; QRF, cubist and svr. | 3 (Low, medium, and high) per element or compounds | - OC (Acc= 86.45% Kappa= 69.60%) - Fe (Acc= 79.03% Kappa= 56.19%) - P2O5 (Acc= 79.46% Kappa= 52.51%) - Mn (Acc= 86.13% Kappa= 71.08%) - Zn (Acc= 97.63% Kappa= 81.03%) |
| [109] | PH, EC, Fe, Cu, Zn,Mn, OC, P, K | 1639 | J48, Naïve Bayes, Random Forest | 6 (Very low, Low, Medium, Medium high, high, very high) | 98.17, 77.18,97.92 |
| [106] | PH, EC,OC, P, K, Fe,Zn, Mn, Cu | Unidentified | SVM, KNN, Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes | 3 (High, medium , low) | 60% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





