Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
18 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
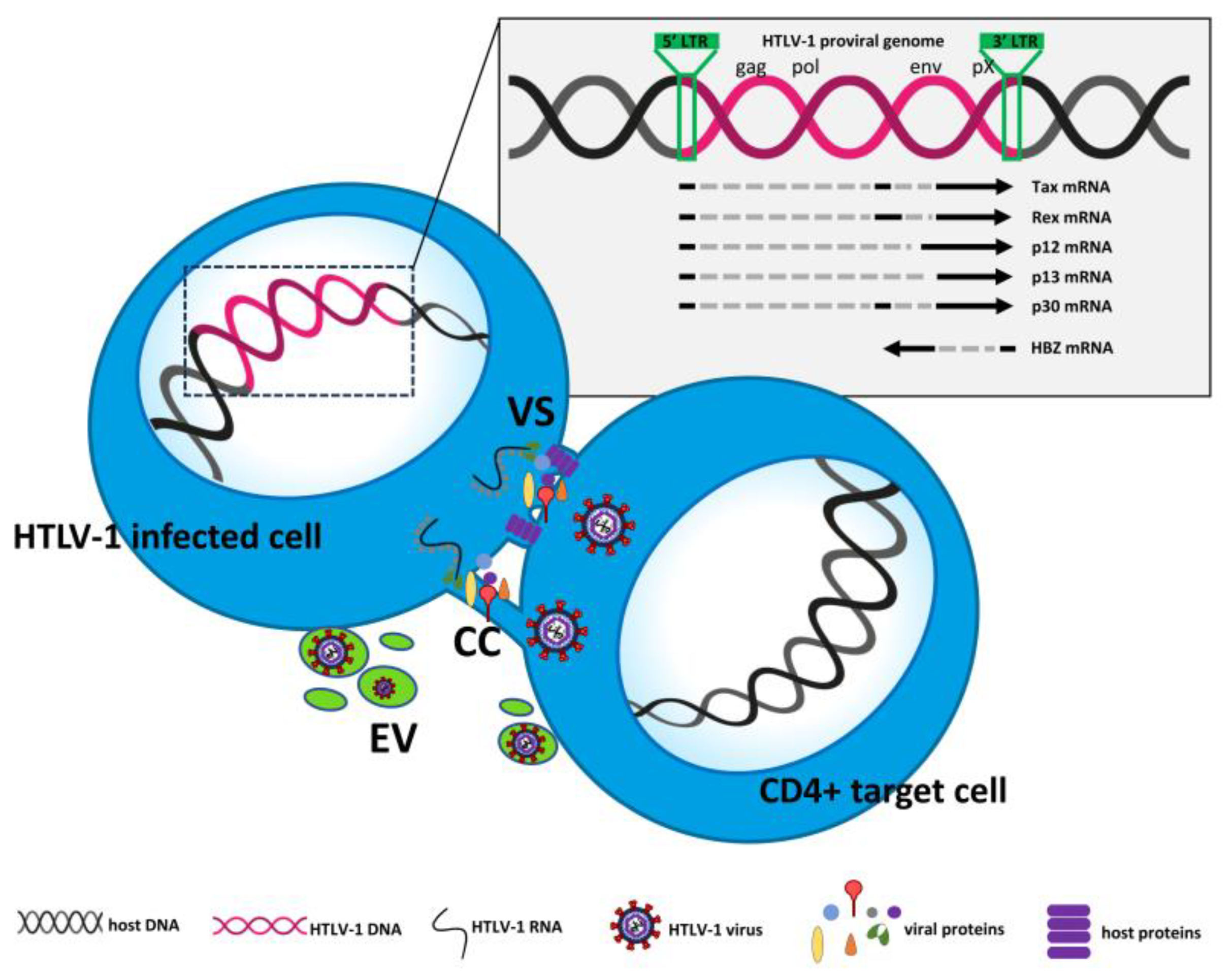
2. HTLV-1 genome and virus transmission and spread
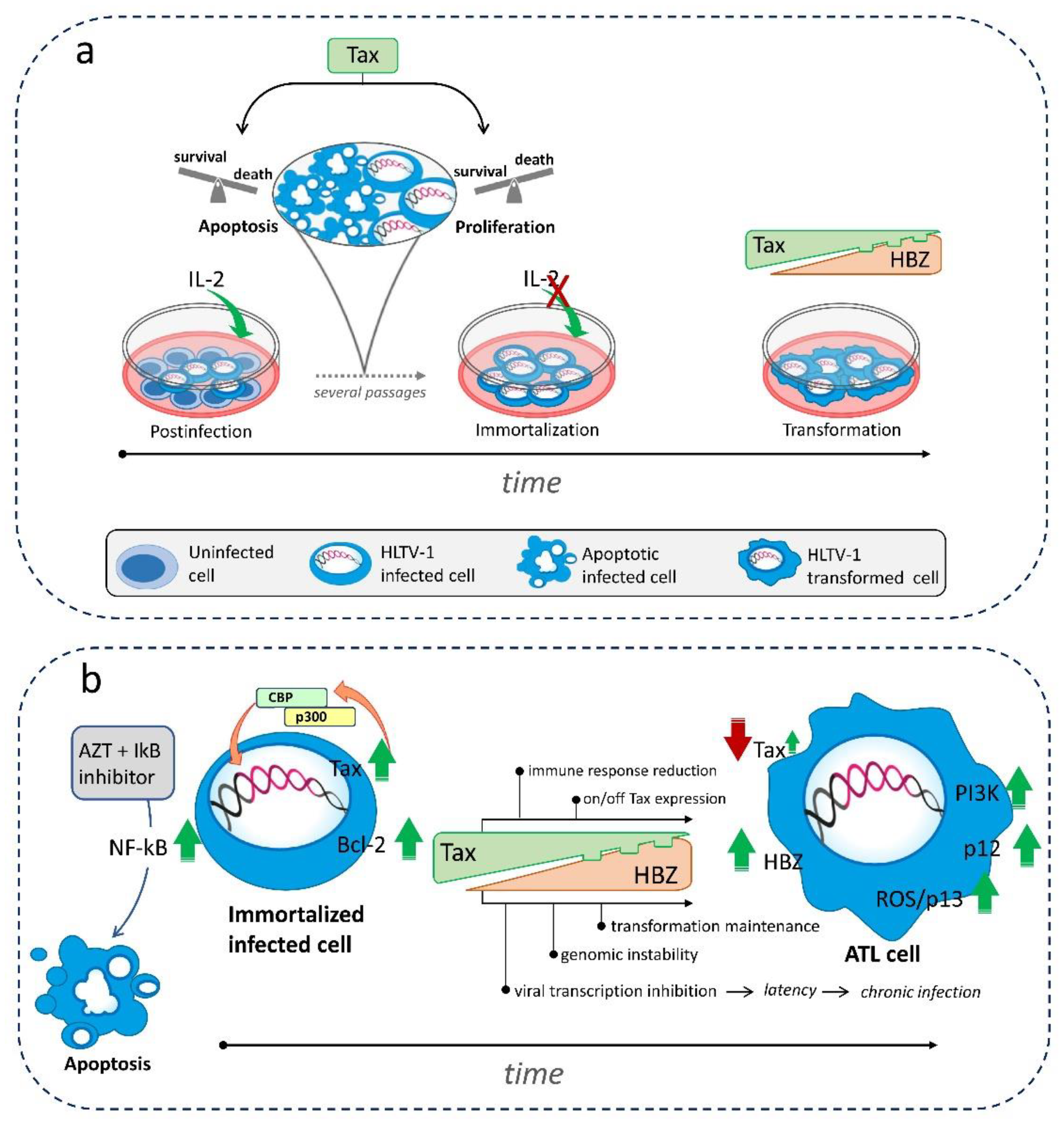
3. ATL and HTLV-1-driven transformation: generalities
4. Tax and cell signalling: role of the transcription factor nuclear NF-κB
5. Latency and leukemogenesis: role of Tax, HBZ and apoptosis
6. Proposals for HTLV-1/ATL-targeted therapy
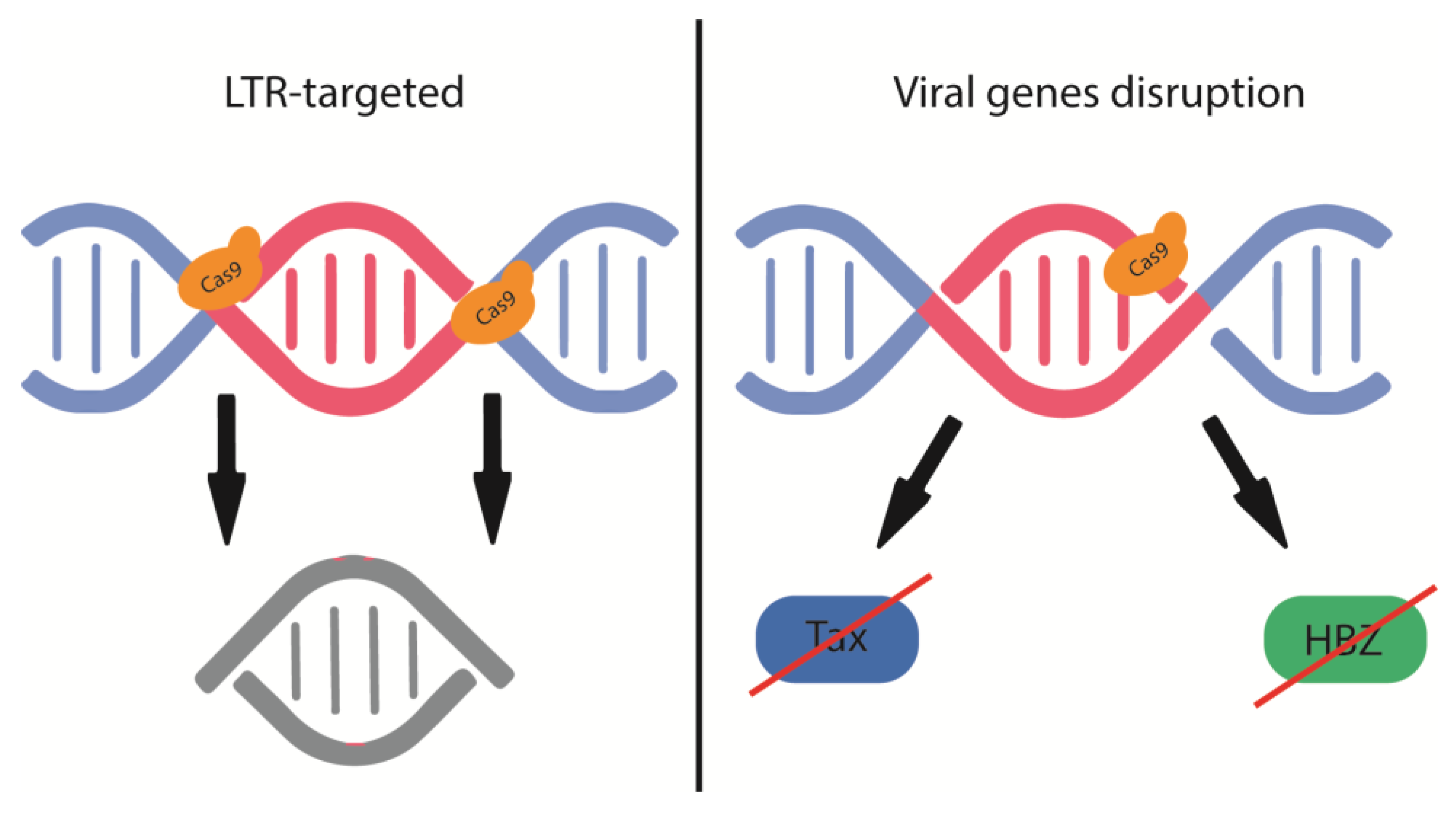
7. Potential of gene editing technology in the eradication of persistent HTLV-1 infection and ATL therapy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gessain, A.; Cassar, O. Epidemiological aspects and world distribution of htlv-1 infection. Front Microbiol 2012, 3, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessain, A.; Ramassamy, J.L.; Afonso, P.V.; Cassar, O. Geographic distribution, clinical epidemiology and genetic diversity of the human oncogenic retrovirus htlv-1 in africa, the world's largest endemic area. Front Immunol 2023, 14, 1043600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percher, F.; Jeannin, P.; Martin-Latil, S.; Gessain, A.; Afonso, P.V.; Vidy-Roche, A.; Ceccaldi, P.E. Mother-to-child transmission of htlv-1 epidemiological aspects, mechanisms and determinants of mother-to-child transmission. Viruses 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lairmore, M.D.; Haines, R.; Anupam, R. Mechanisms of human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 transmission and disease. Curr Opin Virol 2012, 2, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.B.; Melamed, A.; Demontis, M.A.; Laydon, D.J.; Fox, J.M.; Tosswill, J.H.; de Freitas, D.; Price, A.D.; Medcalf, J.F.; Martin, F. , et al. Rapid dissemination of human t-lymphotropic virus type 1 during primary infection in transplant recipients. Retrovirology 2016, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, R.; El Hajj, H.; Kfoury, Y.; de The, H.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A. Controversies in targeted therapy of adult t cell leukemia/lymphoma: On target or off target effects? Viruses 2011, 3, 750–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laverdure, S.; Polakowski, N.; Hoang, K.; Lemasson, I. Permissive sense and antisense transcription from the 5' and 3' long terminal repeats of human t-cell leukemia virus type 1. J Virol 2016, 90, 3600–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, J.; Seiki, M.; Kiyokawa, T.; Yoshida, M. Functional activation of the long terminal repeat of human t-cell leukemia virus type i by a trans-acting factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1985, 82, 2277–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxus, M.; Willems, L. Mechanisms of htlv-1 persistence and transformation. Br J Cancer 2009, 101, 1497–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydoun, H.; Duc-Dodon, M.; Lebrun, S.; Gazzolo, L.; Bex, F. Regulation of the human t-cell leukemia virus gene expression depends on the localization of regulatory proteins tax, rex and p30ii in specific nuclear subdomains. Gene 2007, 386, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, S.; Galli, V.; Moles, R.; Yurick, D.; Khoury, G.; Purcell, D.F.J.; Franchini, G.; Pise-Masison, C.A. Role of htlv-1 orf-i encoded proteins in viral transmission and persistence. Retrovirology 2019, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silic-Benussi, M.; Marin, O.; Biasiotto, R.; D'Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. Effects of human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 (htlv-1) p13 on mitochondrial k+ permeability: A new member of the viroporin family? Febs Lett 2010, 584, 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younis, I.; Khair, L.; Dundr, M.; Lairmore, M.D.; Franchini, G.; Green, P.L. Repression of human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 and type 2 replication by a viral mrna-encoded posttranscriptional regulator. J Virol 2004, 78, 11077–11083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Latil, S.; Gnadig, N.F.; Mallet, A.; Desdouits, M.; Guivel-Benhassine, F.; Jeannin, P.; Prevost, M.C.; Schwartz, O.; Gessain, A.; Ozden, S. , et al. Transcytosis of htlv-1 across a tight human epithelial barrier and infection of subepithelial dendritic cells. Blood 2012, 120, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulherkar, T.H.; Gomez, D.J.; Sandel, G.; Jain, P. Co-infection and cancer: Host-pathogen interaction between dendritic cells and hiv-1, htlv-1, and other oncogenic viruses. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Prooyen, N.; Gold, H.; Andresen, V.; Schwartz, O.; Jones, K.; Ruscetti, F.; Lockett, S.; Gudla, P.; Venzon, D.; Franchini, G. Human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 p8 protein increases cellular conduits and virus transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010, 107, 20738–20743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, D.O.; Al Sharif, S.; Mensah, G.; Cowen, M.; Khatkar, P.; Erickson, J.; Branscome, H.; Lattanze, T.; DeMarino, C.; Alem, F. , et al. Extracellular vesicles from htlv-1 infected cells modulate target cells and viral spread. Retrovirology 2021, 18, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, S.; Harhaj, E.W. Mechanisms of oncogenesis by htlv-1 tax. Pathogens 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overbaugh, J.; Bangham, C.R. Selection forces and constraints on retroviral sequence variation. Science 2001, 292, 1106–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laydon, D.J.; Sunkara, V.; Boelen, L.; Bangham, C.R.M.; Asquith, B. The relative contributions of infectious and mitotic spread to htlv-1 persistence. PLoS Comput Biol 2020, 16, e1007470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaki, M.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Nosaka, K.; Sugata, K.; Utsunomiya, H.; Suehiro, Y.; Shichijo, T.; Yamada, A.; Sugawara, Y.; Hibi, T. , et al. In vivo dynamics and adaptation of htlv-1-infected clones under different clinical conditions. PLoS Pathog 2021, 17, e1009271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, J.M.; Hilburn, S.; Demontis, M.A.; Brighty, D.W.; Rios Grassi, M.F.; Galvao-Castro, B.; Taylor, G.P.; Martin, F. Long terminal repeat circular DNA as markers of active viral replication of human t lymphotropic virus-1 in vivo. Viruses 2016, 8, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, A.; Laydon, D.J.; Al Khatib, H.; Rowan, A.G.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R. Htlv-1 drives vigorous clonal expansion of infected cd8(+) t cells in natural infection. Retrovirology 2015, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunaga, J. Viral, genetic, and immune factors in the oncogenesis of adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma. International Journal of Hematology 2023, 117, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Hajj, H.; Tsukasaki, K.; Cheminant, M.; Bazarbachi, A.; Watanabe, T.; Hermine, O. Novel treatments of adult t cell leukemia lymphoma. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, L.B.; Fuji, S.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A.; Ramos, J.C.; Ratner, L.; Horwitz, S.; Fields, P.; Tanase, A.; Bumbea, H. , et al. Revised adult t-cell leukemia-lymphoma international consensus meeting report. J Clin Oncol 2019, 37, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, T.; Joh, T.; Uike, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Utsunomiya, A.; Yoshida, S.; Saburi, Y.; Miyamoto, T.; Takemoto, S.; Suzushima, H. , et al. Defucosylated anti-ccr4 monoclonal antibody (kw-0761) for relapsed adult t-cell leukemia-lymphoma: A multicenter phase ii study. J Clin Oncol 2012, 30, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Inamoto, Y.; Ito, A.; Watanabe, M.; Takeda, W.; Aoki, J.; Kim, S.W.; Fukuda, T. Lenalidomide treatment for recurrent adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hematol Oncol 2022. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Sakai, H.; Kabasawa, N.; Harada, H. Successful treatment of an aggressive adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma with strong cd30 expression using brentuximab vedotin as combination and maintenance therapy. Intern Med 2023, 62, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izutsu, K.; Makita, S.; Nosaka, K.; Yoshimitsu, M.; Utsunomiya, A.; Kusumoto, S.; Morishima, S.; Tsukasaki, K.; Kawamata, T.; Ono, T. , et al. An open-label, single-arm phase 2 trial of valemetostat for relapsed or refractory adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood 2023, 141, 1159–1168. [Google Scholar]
- Utsunomiya, A.; Izutsu, K.; Jo, T.; Yoshida, S.; Tsukasaki, K.; Ando, K.; Choi, I.; Imaizumi, Y.; Kato, K.; Kurosawa, M. , et al. Oral histone deacetylase inhibitor tucidinostat (hbi-8000) in patients with relapsed or refractory adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma: Phase iib results. Cancer Science 2022, 113, 2778–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuya, H. Current and emerging therapeutic strategies in adult t-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Int J Hematol 2023, 117, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, H.J.; Yang, L.P.; Kuo, Y.L.; Ho, Y.K.; Shih, H.M.; Giam, C.Z. Nf-kappa b hyper-activation by htlv-1 tax induces cellular senescence, but can be alleviated by the viral anti-sense protein hbz. Plos Pathogens 2011, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C.; Ballard, D.W. Persistent activation of nf-kappab by the tax transforming protein of htlv-1: Hijacking cellular ikappab kinases. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6948–6958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimotohno, K.; Takano, M.; Teruuchi, T.; Miwa, M. Requirement of multiple copies of a 21-nucleotide sequence in the u3 regions of human t-cell leukemia virus type i and type ii long terminal repeats for trans-acting activation of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1986, 83, 8112–8116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giam, C.Z.; Xu, Y.L. Htlv-i tax gene product activates transcription via pre-existing cellular factors and camp responsive element. J Biol Chem 1989, 264, 15236–15241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adya, N.; Giam, C.Z. Distinct regions in human t-cell lymphotropic virus type i tax mediate interactions with activator protein creb and basal transcription factors. J Virol 1995, 69, 1834–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Pise-Masison, C.A.; Linton, R.; Park, H.U.; Schiltz, R.L.; Sartorelli, V.; Brady, J.N. Tax relieves transcriptional repression by promoting histone deacetylase 1 release from the human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol 2004, 78, 6735–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; Vargas, J.; Hoffmann, A. Signaling via the nfkappab system. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2016, 8, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, T.; Brown, K.; Franzoso, G.; Siebenlist, U. Kinetic analysis of human t-cell leukemia virus type i tax-mediated activation of nf-kappa b. Mol Cell Biol 1994, 14, 6443–6451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleziunas, R.; Ferrell, S.; Lin, X.; Mu, Y.; Cunningham, E.T., Jr.; Grant, M.; Connelly, M.A.; Hambor, J.E.; Marcu, K.B.; Greene, W.C. Human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 tax induction of nf-kappab involves activation of the ikappab kinase alpha (ikkalpha) and ikkbeta cellular kinases. Mol Cell Biol 1998, 18, 5157–5165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuggetta, M.P.; Bordignon, V.; Cottarelli, A.; Macchi, B.; Frezza, C.; Cordiali-Fei, P.; Ensoli, F.; Ciafre, S.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Mastino, A. , et al. Downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines in htlv-1-infected t cells by resveratrol. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 2016, 35, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hleihel, R.; Skayneh, H.; de The, H.; Hermine, O.; Bazarbachi, A. Primary cells from patients with adult t cell leukemia/lymphoma depend on htlv-1 tax expression for nf-kappab activation and survival. Blood Cancer J 2023, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macaire, H.; Riquet, A.; Moncollin, V.; Biemont-Trescol, M.C.; Duc Dodon, M.; Hermine, O.; Debaud, A.L.; Mahieux, R.; Mesnard, J.M.; Pierre, M. , et al. Tax protein-induced expression of antiapoptotic bfl-1 protein contributes to survival of human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 (htlv-1)-infected t-cells. J Biol Chem 2012, 287, 21357–21370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawakami, H.; Tomita, M.; Matsuda, T.; Ohta, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Fujii, M.; Hatano, M.; Tokuhisa, T.; Mori, N. Transcriptional activation of survivin through the nf-kappab pathway by human t-cell leukemia virus type i tax. Int J Cancer 2005, 115, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogure, Y.; Kataoka, K. Genetic alterations in adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Sci 2017, 108, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Noguchi, K.; Sakai, T.; Kubota-Koketsu, R.; Irie, S.; Matsuo, M.; Taguchi, J.; Abe, K.; Shigematsu, K. Htlv-1 tax-specific memory cytotoxic t lymphocytes in long-term survivors of aggressive-type adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Med 2022, 11, 3238–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasunaga, J.I. Strategies of human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 for persistent infection: Implications for leukemogenesis of adult t-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Front Microbiol 2020, 11, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkouche, A.; Moodad, S.; Hleihel, R.; Skayneh, H.; Chambeyron, S.; El Hajj, H.; Bazarbachi, A. In vivo antagonistic role of the human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 regulatory proteins tax and hbz. PLoS Pathog 2021, 17, e1009219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.; Yamamoto, B.; Li, M.; Phipps, A.J.; Younis, I.; Lairmore, M.D.; Green, P.L. Enhancement of infectivity and persistence in vivo by hbz, a natural antisense coded protein of htlv-1. Blood 2006, 107, 3976–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazon, H.; Lemasson, I.; Polakowski, N.; Cesaire, R.; Matsuoka, M.; Barbeau, B.; Mesnard, J.M.; Peloponese, J.M., Jr. Human t-cell leukemia virus type 1 (htlv-1) bzip factor requires cellular transcription factor jund to upregulate htlv-1 antisense transcription from the 3' long terminal repeat. J Virol 2012, 86, 9070–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernin, C.; Thenoz, M.; Pinatel, C.; Gessain, A.; Gout, O.; Delfau-Larue, M.H.; Nazaret, N.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; Wattel, E.; Mortreux, F. Htlv-1 bzip factor hbz promotes cell proliferation and genetic instability by activating oncomirs. Cancer Res 2014, 74, 6082–6093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlani, G.; Shallak, M.; Tedeschi, A.; Cavallari, I.; Marcais, A.; Hermine, O.; Accolla, R.S. Dual cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of htlv-1-encoded hbz protein is a unique feature of adult t-cell leukemia. Haematologica 2021, 106, 2076–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, C.; Dundr, M.; Johnson, J.M.; Fullen, J.R.; Alonzo, N.; Fukumoto, R.; Princler, G.L.; Derse, D.; Misteli, T.; Franchini, G. Htlv-1-encoded p30ii is a post-transcriptional negative regulator of viral replication. Nat Med 2004, 10, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silic-Benussi, M.; Cavallari, I.; Vajente, N.; Vidali, S.; Chieco-Bianchi, L.; Di Lisa, F.; Saggioro, D.; D'Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. Redox regulation of t-cell turnover by the p13 protein of human t-cell leukemia virus type 1: Distinct effects in primary versus transformed cells. Blood 2010, 116, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, C.; Mulloy, J.C.; Ferrari, M.G.; Johnson, J.M.; Fu, K.; Fukumoto, R.; Trovato, R.; Fullen, J.; Leonard, W.J.; Franchini, G. Htlv-1 p12(i) protein enhances stat5 activation and decreases the interleukin-2 requirement for proliferation of primary human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Blood 2001, 98, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazon, H.; Chauhan, P.S.; Porquet, F.; Hoffmann, G.B.; Accolla, R.; Willems, L. Epigenetic silencing of htlv-1 expression by the hbz rna through interference with the basal transcription machinery. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 5574–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiik, H.; Ramanayake, S.; Miura, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Melamed, A.; Bangham, C.R.M. Time-course of host cell transcription during the htlv-1 transcriptional burst. PLoS Pathog 2022, 18, e1010387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland, K.F.; Haaksma, A.G.; Goudsmit, J.; Krammer, P.H.; Heeney, J.L. Inhibition of apoptosis in t cells expressing human t cell leukemia virus type i tax. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 1994, 10, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Hsu, T.Y.; Lin, R.H.; Su, I.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Yang, C.S. Resistance to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced apoptosis in human t-lymphotropic virus type i-infected t cell lines. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 2002, 18, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauweiler, A.; Garrus, J.E.; Reed, J.C.; Nyborg, J.K. Repression of bax gene expression by the htlv-1 tax protein: Implications for suppression of apoptosis in virally infected cells. Virology 1997, 231, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, N.; Fujii, M.; Cheng, G.; Ikeda, S.; Yamasaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Tomonaga, M.; Yamamoto, N. Human t-cell leukemia virus type i tax protein induces the expression of anti-apoptotic gene bcl-xl in human t-cells through nuclear factor-kappab and c-amp responsive element binding protein pathways. Virus Genes 2001, 22, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlichlia, K.; Moldenhauer, G.; Daniel, P.T.; Busslinger, M.; Gazzolo, L.; Schirrmacher, V.; Khazaie, K. Immediate effects of reversible htlv-1 tax function: T-cell activation and apoptosis. Oncogene 1995, 10, 269–277. [Google Scholar]
- Chlichlia, K.; Busslinger, M.; Peter, M.E.; Walczak, H.; Krammer, P.H.; Schirrmacher, V.; Khazaie, K. Ice-proteases mediate htlv-i tax-induced apoptotic t-cell death. Oncogene 1997, 14, 2265–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zachar, V.; Zdravkovic, M.; Guo, M.; Ebbesen, P.; Liu, X. Role of the fas/fas ligand pathway in apoptotic cell death induced by the human t cell lymphotropic virus type i tax transactivator. J Gen Virol 1997, 78 ( Pt 12), 3277–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, C.; Harrod, R. Distinct p300-responsive mechanisms promote caspase-dependent apoptosis by human t-cell lymphotropic virus type 1 tax protein. Mol Cell Biol 2000, 20, 8580–8589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Walsh, I.; Waterfield, M.; Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. Nf-kappab signaling pathway governs trail gene expression and human t-cell leukemia virus-i tax-induced t-cell death. J Biol Chem 2001, 276, 40385–40388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, C.; Balestrieri, E.; Macchi, B.; Mastino, A. Modulation of apoptosis during htlv-1-mediated immortalization process in vitro. J Med Virol 2004, 74, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahgoub, M.; Yasunaga, J.I.; Iwami, S.; Nakaoka, S.; Koizumi, Y.; Shimura, K.; Matsuoka, M. Sporadic on/off switching of htlv-1 tax expression is crucial to maintain the whole population of virus-induced leukemic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E1269–E1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shudofsky, A.M.D.; Giam, C.Z. Cells of adult t-cell leukemia evade htlv-1 tax/nf-kappab hyperactivation-induced senescence. Blood Adv 2019, 3, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanayake, S.; Moulding, D.A.; Tanaka, Y.; Singh, A.; Bangham, C.R.M. Dynamics and consequences of the htlv-1 proviral plus-strand burst. PLoS Pathog 2022, 18, e1010774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Kandil, A.; Chamias, R.; Huleihel, M.; Godbey, W.T.; Aboud, M. Role of caspase 9 in activation of htlv-1 ltr expression by DNA damaging agents. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3337–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.; Mateus, M.; Thinnes, C.C.; McCullagh, J.S.; Schofield, C.J.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R.M. Glucose metabolism and oxygen availability govern reactivation of the latent human retrovirus htlv-1. Cell Chem Biol 2017, 24, 1377–+. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, A.P.; Kohrt, S.; Aristodemou, A.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R.M.; Thoma-Kress, A.K. Hdac inhibitors panobinostat and romidepsin enhance tax transcription in htlv-1-infected cell lines and freshly isolated patients' t-cells. Front Immunol 2022, 13, 978800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, D.; Lin, E.; Stoffel, V.; Dickson, S.; Khan, Z.K.; Beld, J.; Jain, P. Apigenin improves cytotoxicity of antiretroviral drugs against htlv-1 infected cells through the modulation of ahr signaling. NeuroImmune Pharm Ther 2023, 2, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Maeta, T.; Ito, S. Dimethyl fumarate suppresses the proliferation of htlv-1-infected t cells by inhibiting cbm complex-triggered nf-kappa b signaling. Anticancer Res 2023, 43, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, L.M.; Yuzugullu, H.; Zhao, J.J. Pi3k in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer 2015, 15, 7–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemmati, S.; Sinclair, T.; Tong, M.; Bartholdy, B.; Okabe, R.O.; Ames, K.; Ostrodka, L.; Haque, T.; Kaur, I.; Mills, T.S. , et al. Pi3k alpha and delta promote hematopoietic stem cell activation. Jci Insight 2019, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda, R.; Hayashi, A.; Utsunomiya, A.; Nukada, Y.; Fukui, R.; Itoh, K.; Tezuka, K.; Ohashi, K.; Mizuno, K.; Sakamoto, M. , et al. Alteration of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade in the multilobulated nuclear formation of adult t cell leukemia/lymphoma (atll). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005, 102, 15213–15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuya, H.; Cook, L.B.M.; Rowan, A.G.; Satou, Y.; Taylor, G.P.; Bangham, C.R.M. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-delta (pi3k-delta) is a potential therapeutic target in adult t-cell leukemia-lymphoma. Biomark Res 2018, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, C.; Mori, N. The role of cudc-907, a dual phosphoinositide-3 kinase and histone deacetylase inhibitor, in inhibiting proliferation of adult t-cell leukemia. Eur J Haematol 2020, 105, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, C.; Senba, M.; Mori, N. Butein inhibits nf-kappab, ap-1 and akt activation in adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int J Oncol 2017, 51, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matteucci, C.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Minutolo, A.; Balestrieri, E.; Valletta, E.; Macchi, B.; Mastino, A.; Grelli, S. Inhibition of ikappabalpha phosphorylation potentiates regulated cell death induced by azidothymidine in htlv-1 infected cells. Cell Death Discov 2020, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Mathews Griner, L.A.; Ju, W.; Duveau, D.Y.; Guha, R.; Petrus, M.N.; Wen, B.; Maeda, M.; Shinn, P.; Ferrer, M. , et al. Selective targeting of jak/stat signaling is potentiated by bcl-xl blockade in il-2-dependent adult t-cell leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112, 12480–12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daenthanasanmak, A.; Bamford, R.N.; Yoshioka, M.; Yang, S.M.; Homan, P.; Karim, B.; Bryant, B.R.; Petrus, M.N.; Thomas, C.J.; Green, P.L. , et al. Triple combination of bet plus pi3k and nf-kappab inhibitors exhibit synergistic activity in adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 2346–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchi, B.; Balestrieri, E.; Frezza, C.; Grelli, S.; Valletta, E.; Marcais, A.; Marino-Merlo, F.; Turpin, J.; Bangham, C.R.; Hermine, O. , et al. Quantification of htlv-1 reverse transcriptase activity in atl patients treated with zidovudine and interferon-alpha. Blood Adv 2017, 1, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, J.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, C.H.; Qin, J.; Luo, H. Research progress on the anticancer molecular mechanism of targets regulating cell autophagy. Pharmacology 2023, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, H. The autophagy molecule beclin 1 maintains persistent activity of nf-kappab and stat3 in htlv-1-transformed t lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2015, 465, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauzi, Y.R.; Nakahata, S.; Chilmi, S.; Ichikawa, T.; Nueangphuet, P.; Yamaguchi, R.; Nakamura, T.; Shimoda, K.; Morishita, K. Antitumor effects of chloroquine/hydroxychloroquine mediated by inhibition of the nf-kappab signaling pathway through abrogation of autophagic p47 degradation in adult t-cell leukemia/lymphoma cells. PLoS One 2021, 16, e0256320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozako, T.; Mellini, P.; Ohsugi, T.; Aikawa, A.; Uchida, Y.I.; Honda, S.I.; Suzuki, T. Novel small molecule sirt2 inhibitors induce cell death in leukemic cell lines. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, C.B.; da Cunha, L.S.; Maues, J.H.D.; Pessoa, F.M.C.D.; de Oliveira, M.B.; Ribeiro, R.M.; Lopes, G.S.; de Moraes, M.O.; de Moraes, M.E.A.; Khayat, A.S. , et al. Role of mirnas in human t cell leukemia virus type 1 induced t cell leukemia: A literature review and bioinformatics approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 2022; 23. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Cook, D.E. The contribution of DNA repair pathways to genome editing and evolution in filamentous pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2022, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, C.; Greene, E.C. DNA repair pathway choices in crispr-cas9-mediated genome editing. Trends Genet 2021, 37, 639–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, A.; Takeda, S.; Kariya, R.; Matsuda, K.; Urano, E.; Okada, S.; Komano, J. A novel therapeutic molecule against htlv-1 infection targeting provirus. Leukemia 2013, 27, 1621–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo-Romanos, T.; Karpinski, J.; Millen, S.; Beschorner, N.; Simon, F.; Paszkowski-Rogacz, M.; Lansing, F.; Schneider, P.M.; Sonntag, J.; Hauber, J. , et al. Precise excision of htlv-1 provirus with a designer-recombinase. Mol Ther 2023, 31, 2266–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Shaffer, A.L., 3rd; Ceribelli, M.; Zhang, M.; Wright, G.; Huang, D.W.; Xiao, W.; Powell, J.; Petrus, M.N.; Yang, Y. , et al. Targeting the htlv-i-regulated batf3/irf4 transcriptional network in adult t cell leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 286–297 e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panfil, A.R.; Green, P.L.; Yoder, K.E. Crispr genome editing applied to the pathogenic retrovirus htlv-1. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2020, 10, 580371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaminski, R.; Chen, Y.; Fischer, T.; Tedaldi, E.; Napoli, A.; Zhang, Y.; Karn, J.; Hu, W.; Khalili, K. Corrigendum: Elimination of hiv-1 genomes from human t-lymphoid cells by crispr/cas9 gene editing. Sci Rep 2016, 6, 28213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Guo, D.; Chen, S. Application of crispr/cas9-based gene editing in hiv-1/aids therapy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.; Maori, E.; Quaranta, P.; Matteoli, G.; Maggi, F.; Sgarbanti, M.; Crucitta, S.; Pacini, S.; Turriziani, O.; Antonelli, G. , et al. Crispr/cas9 ablation of integrated hiv-1 accumulates proviral DNA circles with reformed long terminal repeats. J Virol 2021, 95, e0135821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Proposed therapeutic treatment |
Target | Available results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Viral | Cellular | in vitro/ex vivo | in vivo | |
| AZT+IFNα | RT | IFN-receptor other?1 |
Samples from patients a) complete inhibition of RT activity and b) reduction of virus parameters in resp. patients, c) dramatic change in the clonality pattern |
Prolonged survival with respect to untreated patients |
| Idelalisib | ? | PI3K-δ/AKT | inhibition of proliferation in ATL cells | no |
| CUDC-907 | ? | PI3K/HDAC | a) induction of cytotoxicity in HTLV-1-infected cells b) inhibition of HSP90 activity c) increased caspases activity, in ATL cells |
no |
| Butein | ? | AKT/AP1 NF-kB |
a) induction of apoptosis b) inhibition of proliferation in HTLV-1-infected and ATL cells |
no |
| AZT+ Bay 11-7085 |
RT | IκBα phosphorylation | a) increased apoptosis and b) up-reg. pro-apoptotic genes and down-reg. anti-apoptotic genes, in HTLV-1-infected/transformed cells |
no |
| Ruxolitinib+ navitoclax |
? | JAK/STAT Bcl-2/Bcl-xL |
increased cytotoxicity in IL-2–dependent ATL cell lines and ex vivo in lymphocytes from ATL patients | no |
| I-BET762+ Copanlisib+ bardoxolone methyl |
? | BET NF-κB PI3K |
Inhibition of proliferation in ATL cells in vitro and ex vivo samples from patients | Prolonged survival of ATL-bearing xenograft mice |
| Chloroquine/ Hydroxy chloroquine |
? | Autophagic flux |
Ex vivo, from ATL patients: a) inhibition of autophagy b) accumulation of p47 with LC3II, leading to inhibition of NF-κB activation c) proneness to apoptosis |
no |
| NCO-90/141 | ? | Sirtuin 2 | a) increased apoptosis and b) autophagy in ATL cells |
no |
| ? | ? | 12 miRNA | In silico analysis identified 12 miRNA deregulated in HTLV-1 samples predicted to interact with 90 genes | no |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





