Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
18 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
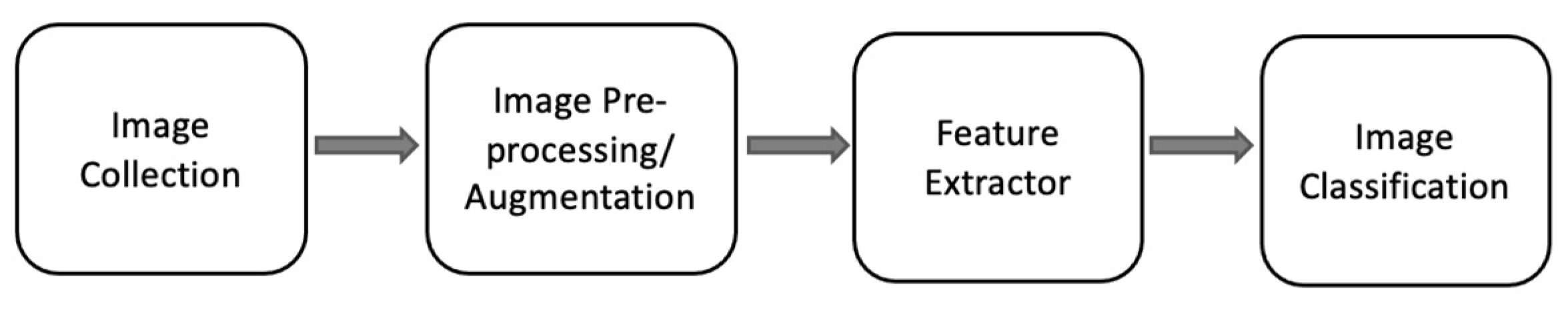
2. Methods
2.1. Data Collection
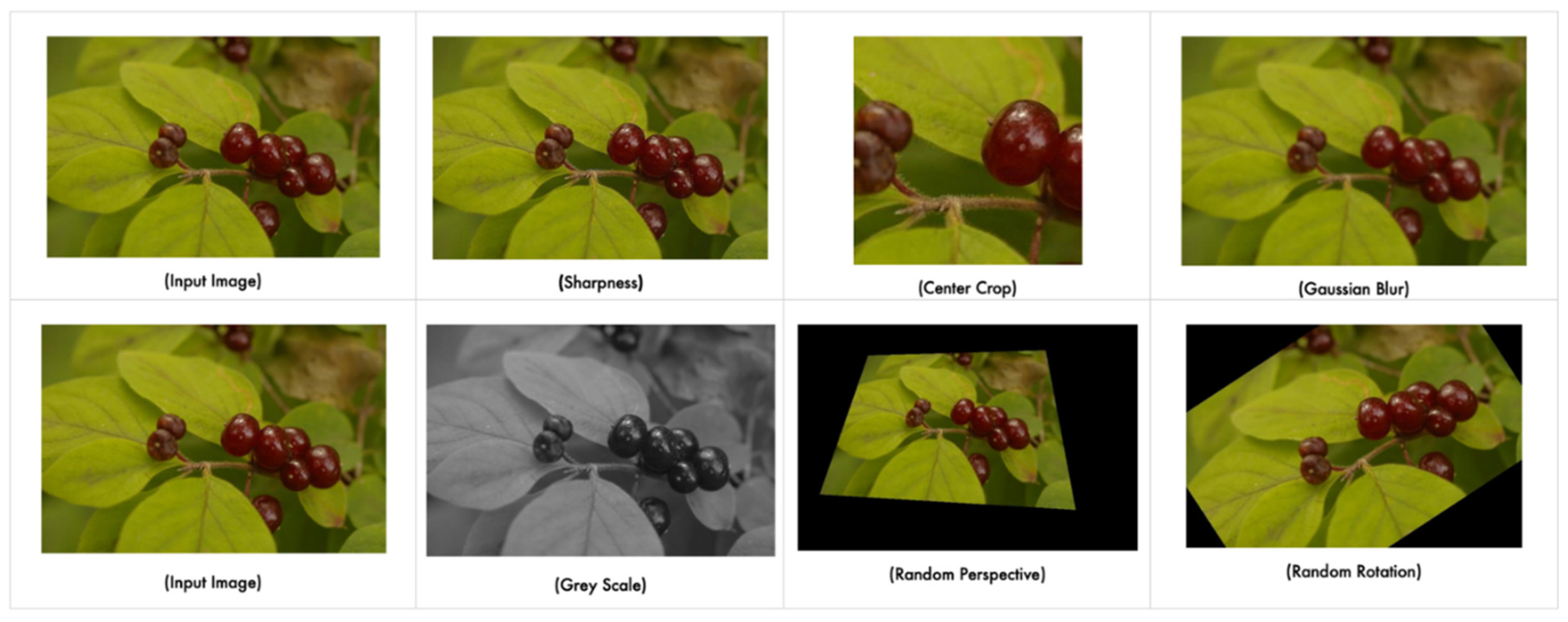
2.2. Image pre-processing
2.3. Convolution Neural Network
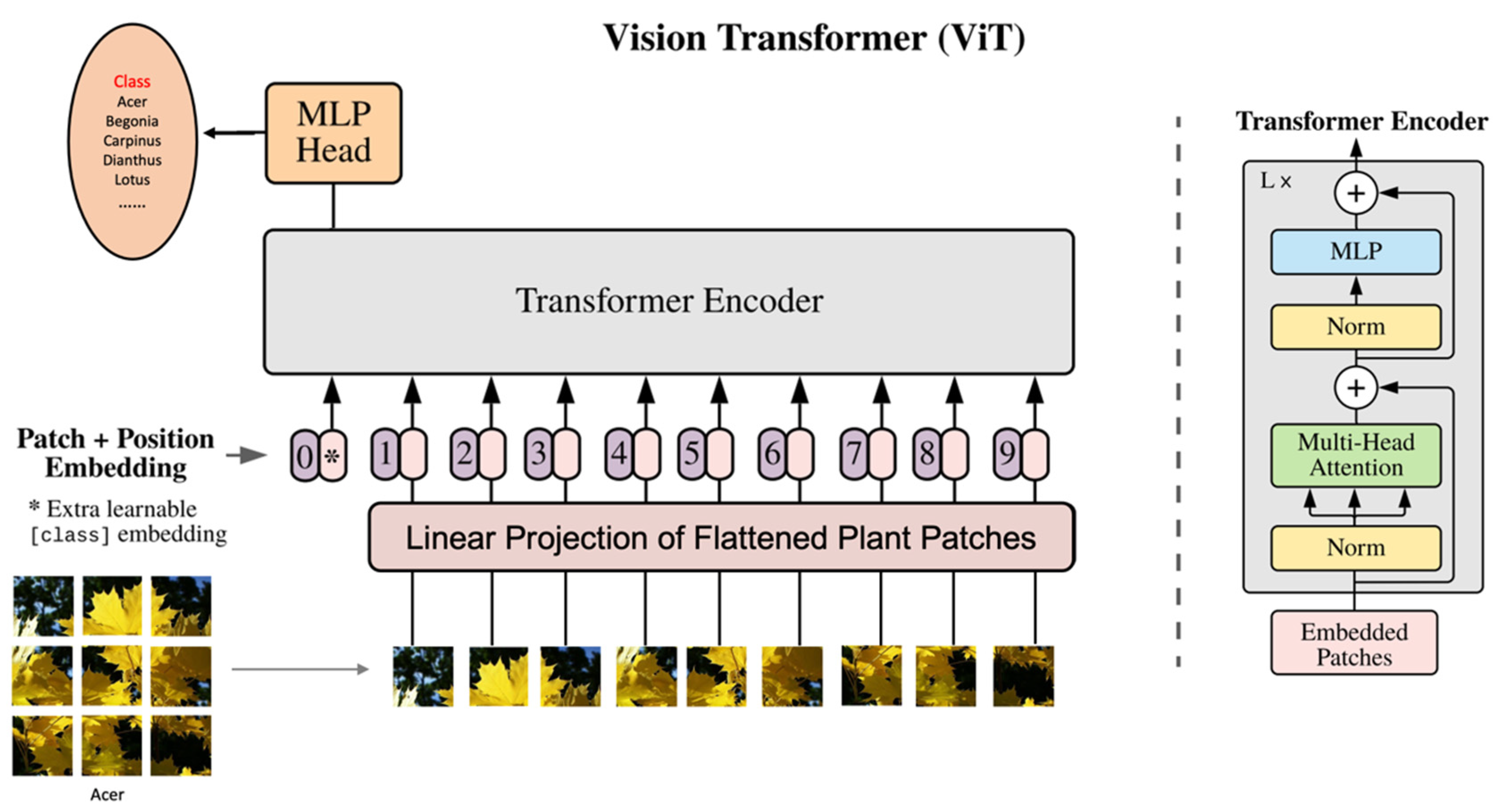
2.4. Vision Transformer
3. Result
3.1. Image pre-processing
3.2. Experiments using CNNs
3.3. Experiments using ViT
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A. Joly et al., “LifeCLEF 2016: Multimedia Life Species Identification Challenges,” Sep. 2016, vol. 9822, pp. 286–310. [CrossRef]
- O. M. Gaston KJ, “Automated species identification: why not?”. [CrossRef]
- J. Deng, W. Dong, R. Socher, L.-J. Li, K. Li, and L. Fei-Fei, “ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database,” in 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009, pp. 248–255. [CrossRef]
- B. Şekeroğlu and Y. İnan, “Leaves Recognition System Using a Neural Network,” Procedia Comput Sci, vol. 102, pp. 578–582, 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. Wäldchen and P. Mäder, “Plant Species Identification Using Computer Vision Techniques: A Systematic Literature Review,” Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, vol. 25, no. 2, pp. 507–543, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Y. LeCun, Y. Bengio, and G. Hinton, “Deep Learning,” Nature, vol. 521, pp. 436–444, May 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Liu, S. Yang, Y. Cheng, and Z. Song, “Plant Leaf Classification Based on Deep Learning,” in 2018 Chinese Automation Congress (CAC), 2018, pp. 3165–3169. [CrossRef]
- I. Heredia, “Large-Scale Plant Classification with Deep Neural Networks,” in Proceedings of the Computing Frontiers Conference, 2017, pp. 259–262. [CrossRef]
- M. v Conde and K. Turgutlu, “Exploring Vision Transformers for Fine-grained Classification,” CoRR, vol. abs/2106.10587, 2021, [Online]. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.10587.
- S. J. Pan and Q. Yang, “A Survey on Transfer Learning,” IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng, vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 1345–1359, 2010. [CrossRef]
- R. Ribani and M. Marengoni, “A Survey of Transfer Learning for Convolutional Neural Networks,” in 2019 32nd SIBGRAPI Conference on Graphics, Patterns and Images Tutorials (SIBGRAPI-T), 2019, pp. 47–57. [CrossRef]
- M. Mehdipour Ghazi, B. Yanikoglu, and E. Aptoula, “Plant identification using deep neural networks via optimization of transfer learning parameters,” Neurocomputing, vol. 235, pp. 228–235, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Dosovitskiy et al., “An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale,” CoRR, vol. abs/2010.11929, 2020, [Online]. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929.
- C. Shorten and T. M. Khoshgoftaar, “A survey on Image Data Augmentation for Deep Learning,” J Big Data, vol. 6, no. 1, p. 60, 2019. [CrossRef]
- D. Guru, Y. H. Kumar, and M. Shantharamu, “Texture Features and KNN in Classification of Flower Images,” International Journal of Computer Applications, Special Issue on RTIPPR, vol. 1, pp. 21–29, Jan. 2010.
- M. Toğaçar, B. Ergen, and Z. Cömert, “BrainMRNet: Brain tumor detection using magnetic resonance images with a novel convolutional neural network model,” Med Hypotheses, vol. 134, Jan. 2020. [CrossRef]
- L. Faes et al., “Automated deep learning design for medical image classification by health-care professionals with no coding experience: a feasibility study,” Lancet Digit Health, vol. 1, no. 5, pp. e232–e242, 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. Geirhos, D. H. J. Janssen, H. H. Schütt, J. Rauber, M. Bethge, and F. Wichmann, Comparing deep neural networks against humans: object recognition when the signal gets weaker. ArXiv 2017, arXiv:1706.06969.
- S. Turaga et al., “Convolutional Networks Can Learn to Generate Affinity Graphs for Image Segmentation,” Neural Comput, vol. 22, pp. 511–538, Sep. 2009. [CrossRef]
- H. Lee, R. Grosse, R. Ranganath, and A. Ng, “Convolutional deep belief networks for scalable unsupervised learning of hierarchical representations,” in Proceedings of the 26th International Conference On Machine Learning, ICML 2009, Sep. 2009, p. 77. [CrossRef]
- A. Krizhevsky, I. Sutskever, and G. E. Hinton, “ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks,” Commun. ACM, vol. 60, no. 6, pp. 84–90, May 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. and Z. X.-P. and Z. X. and S. L. and H. Z.-K. and G. Y. Liu Zhiyu and Zhu, “Hybrid Deep Learning for Plant Leaves Classification,” in Intelligent Computing Theories and Methodologies, 2015, pp. 115–123.
- H. Hiary, H. Saadeh, M. Saadeh, and M. Yaqub, “Flower classification using deep convolutional neural networks,” IET Computer Vision, vol. 12, no. 6, pp. 855–862, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- J. Zou and G. Nagy, “Evaluation of model-based interactive flower recognition,” Proceedings - International Conference on Pattern Recognition, vol. 2, pp. 311–314, 2004. [CrossRef]
- Z. Zhong, L. Zheng, G. Kang, S. Li, and Y. Yang, “Random Erasing Data Augmentation,” 2020. [Online]. Available online: https://github.com/zhunzhong07/Random-Erasing.
- Y. Wu, X. Qin, Y. Pan, and C. Yuan, “Convolution neural network based transfer learning for classification of flowers,” 2018 IEEE 3rd International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, ICSIP 2018, pp. 562–566, Jan. 2019.
- Y. Cui, M. Jia, T.-Y. Lin, Y. Song, and S. Belongie, Class-Balanced Loss Based on Effective Number of Samples. 2019. [CrossRef]
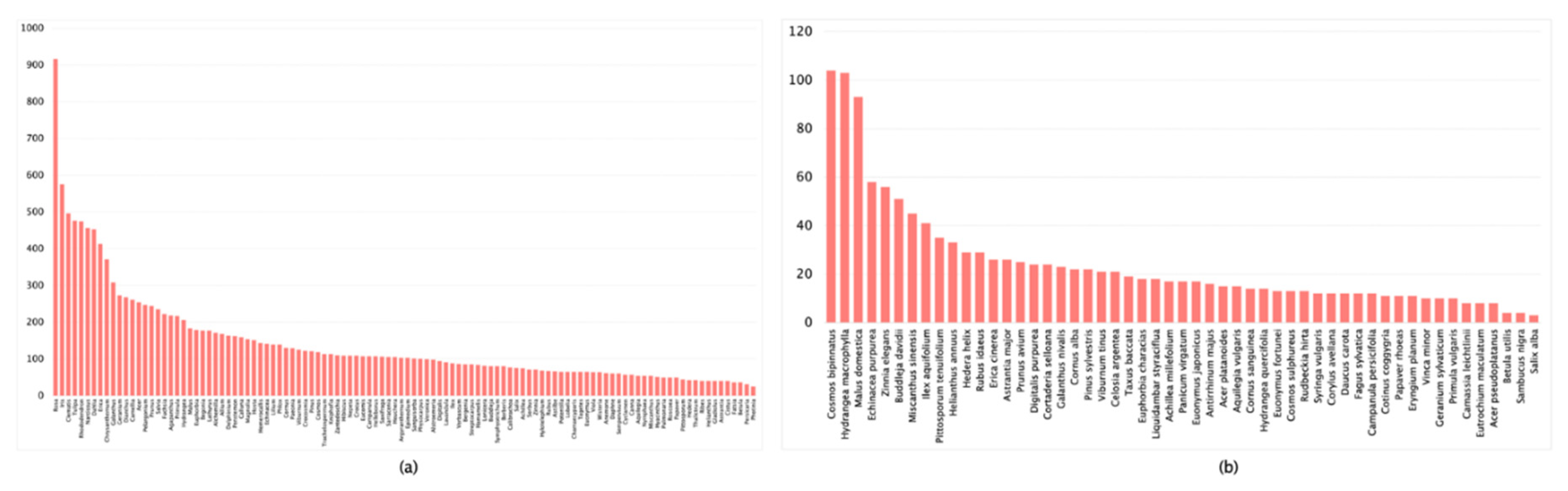
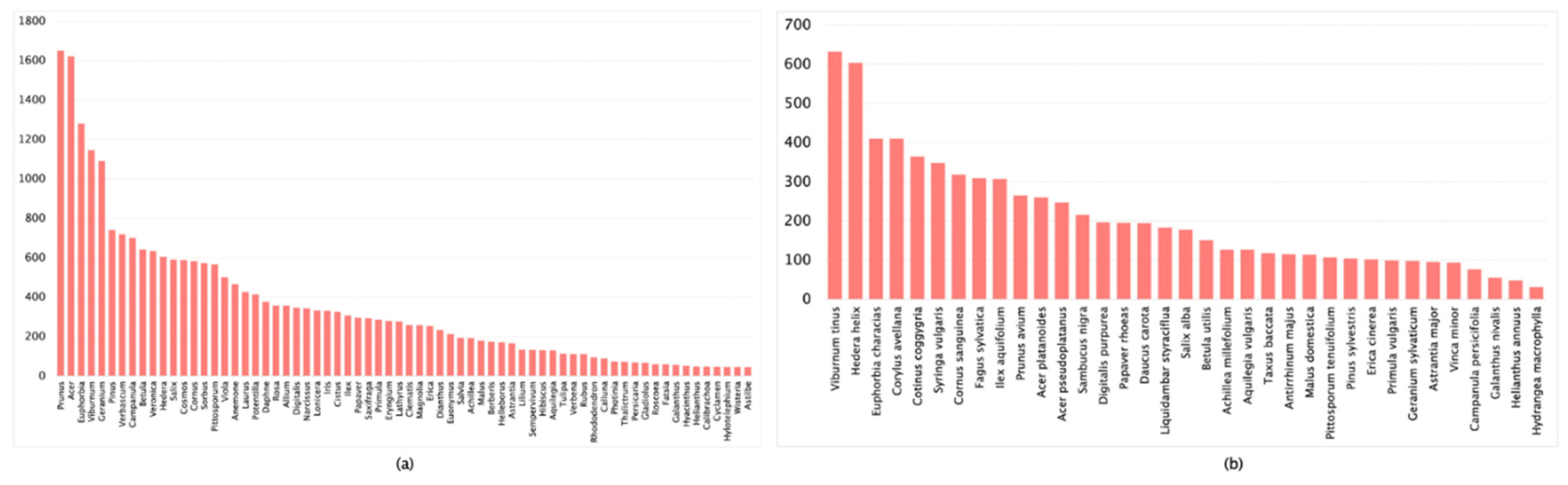
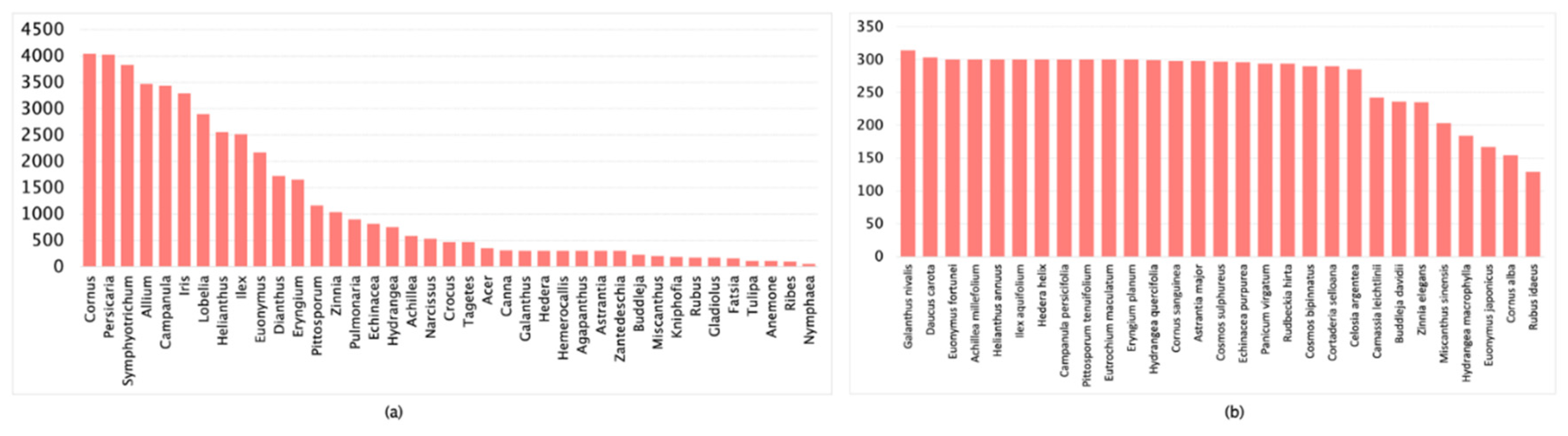
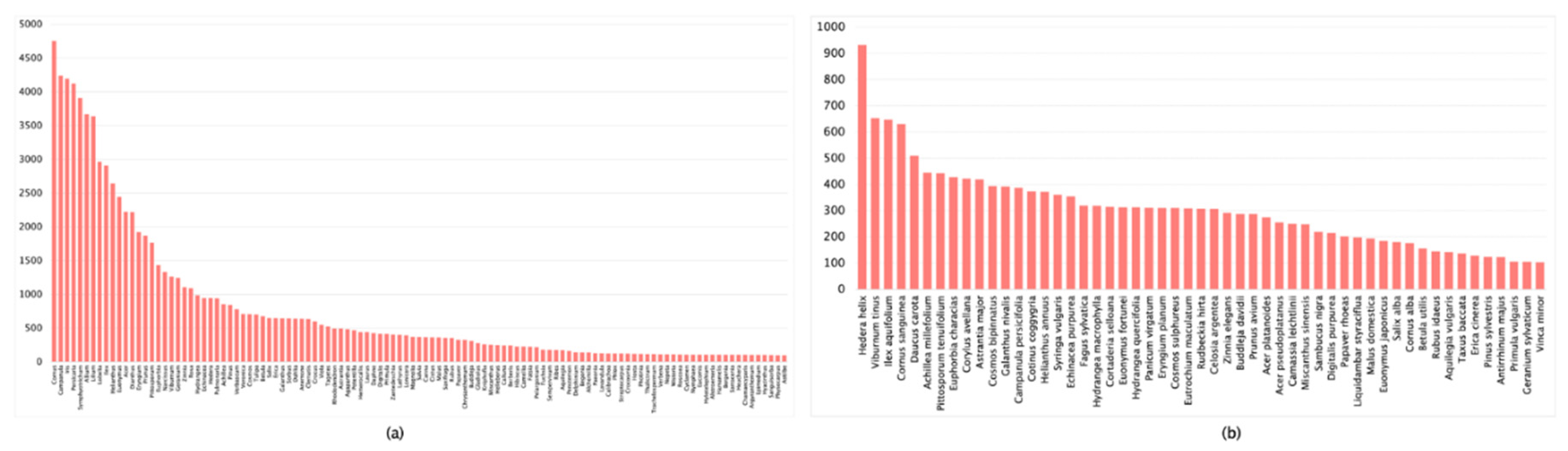

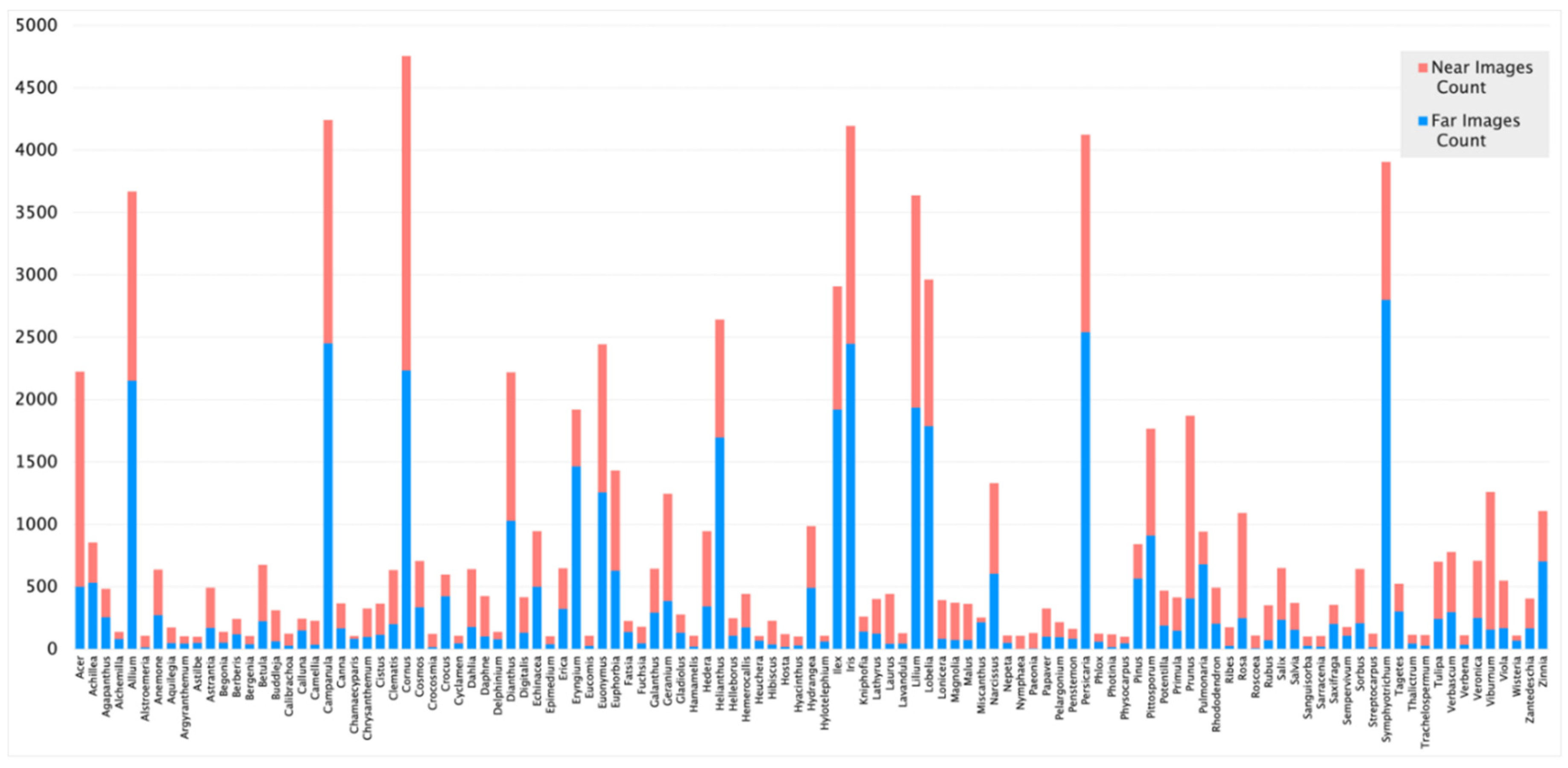
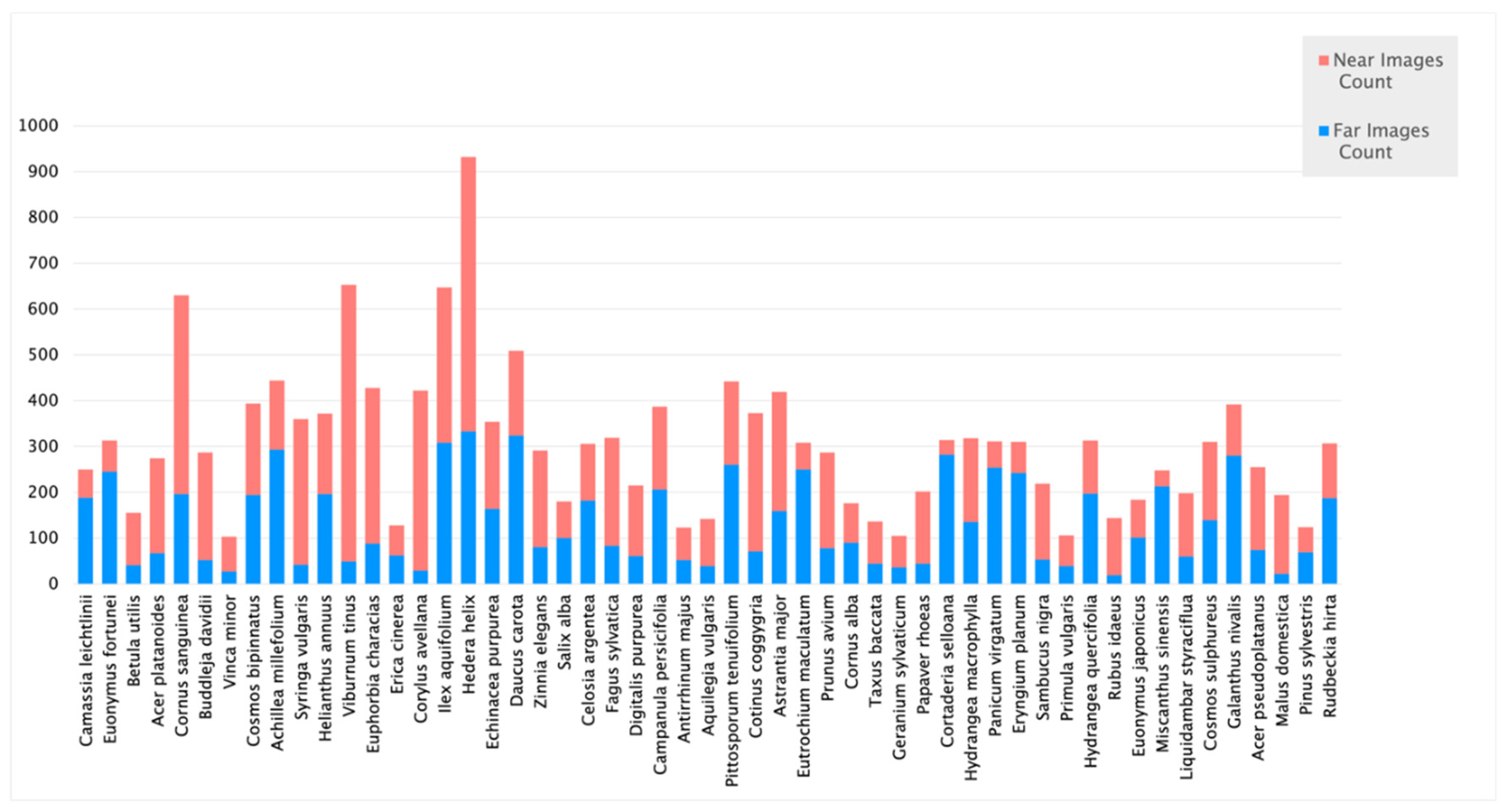
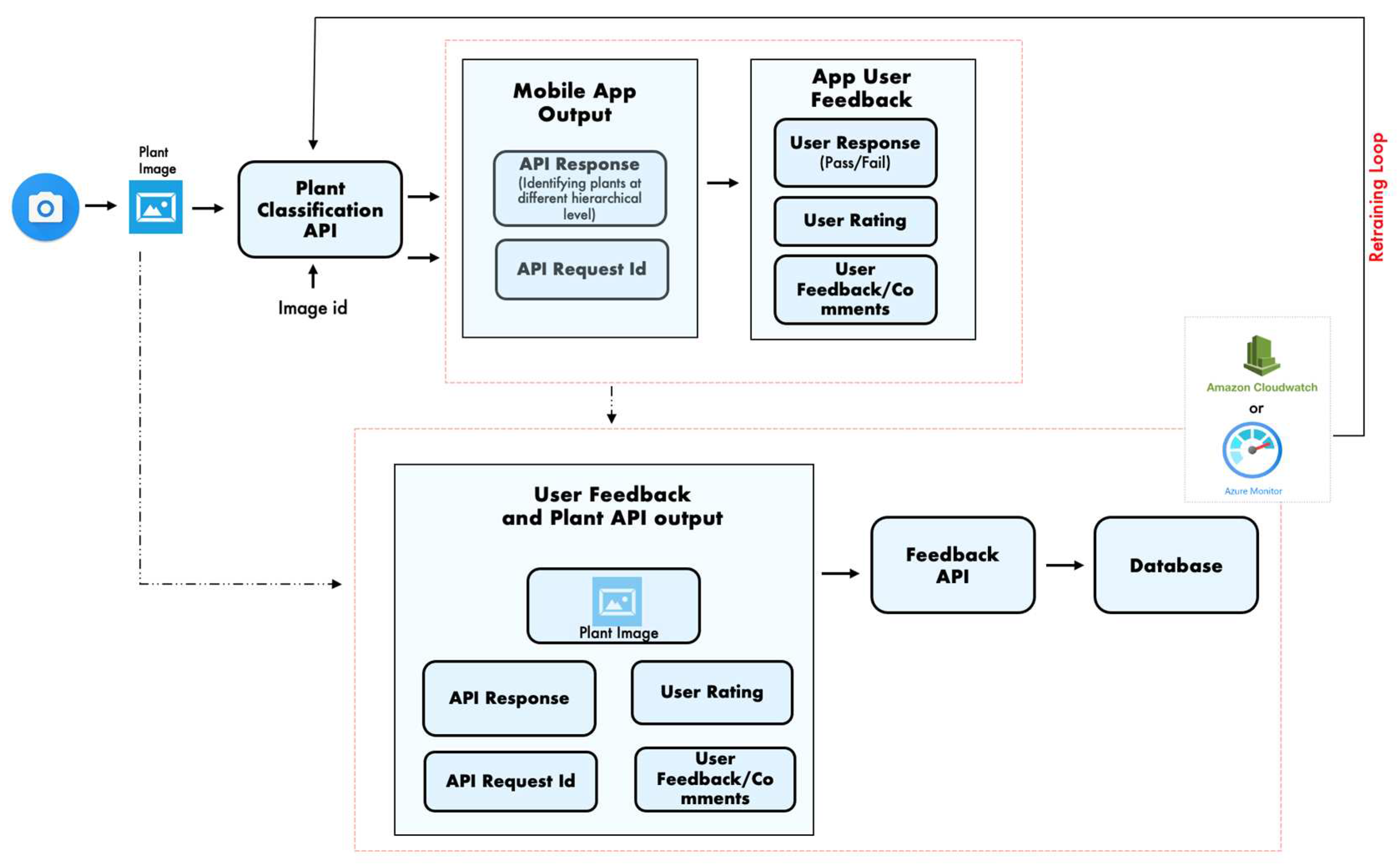
| Dataset | Images Count | Classification Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| Custom dataset (Images taken from PlantCLEF database) | ~ 12k | ~ 83% |
| Experiment | Dataset | Genus/Species | Class Count | Images Count | Augmentation | Images Count (Augmented) | CNN Model | Epochs | Training Time | Validation Accuracy | Test accuracy | Test Accuracy (Top 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | RHS | Genus | 39 | 10k | No | - | InceptionV3 | 35 | 2h 30 min | 76% | 35% | - |
| 2. | RHS | Genus | 39 | 10k | Yes | 30k | ResNet50 | 20 | 4h 50 min | 58% | 25% | - |
| 3. | RHS + PlantCLEF | Genus | 334 | 46k | Yes | 220K | ResNet50 | 60 | 14h | 68% | 23% | - |
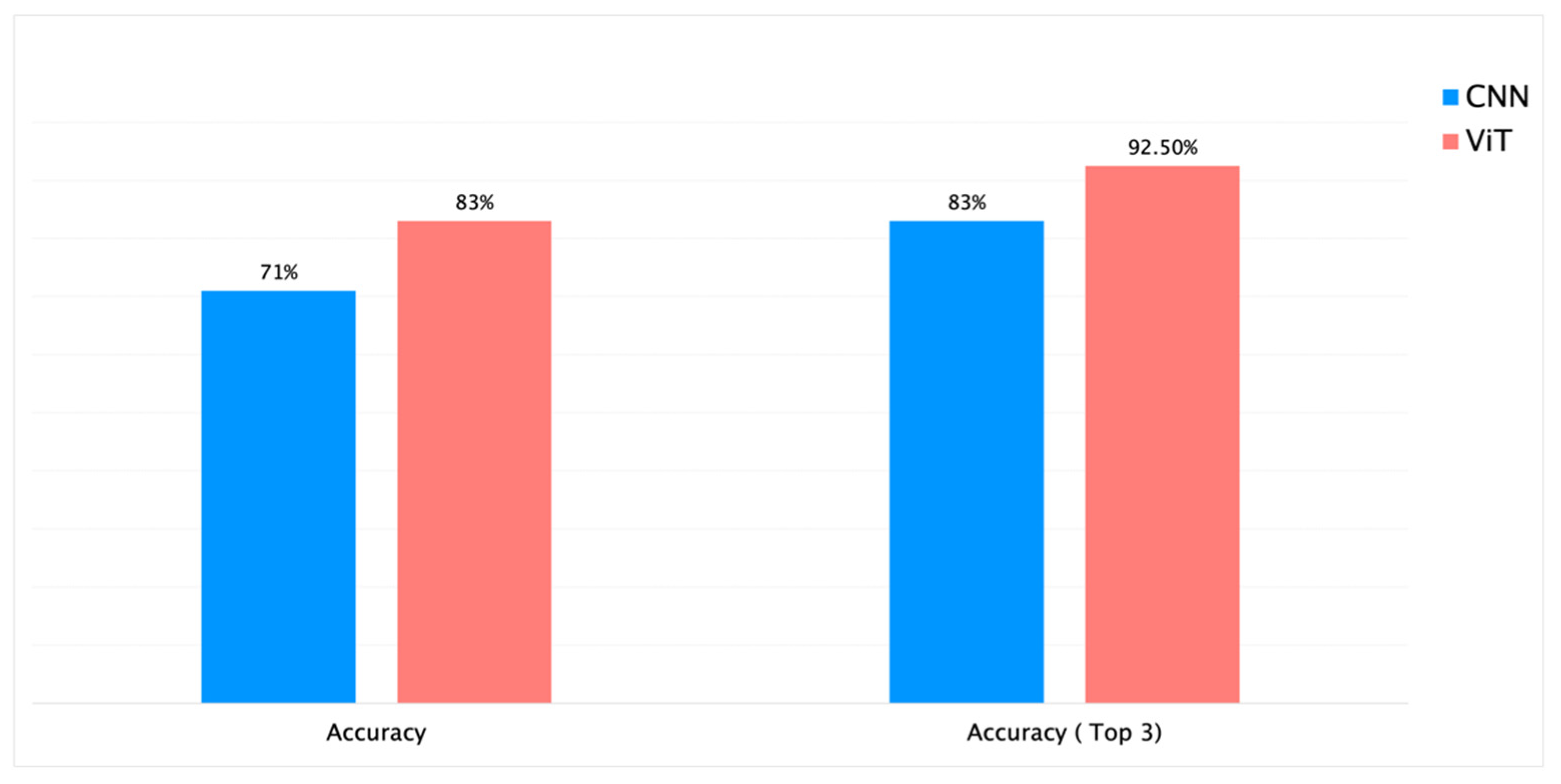
| 4. | RHS + PlantCLEF + iNaturalist | Genus | 113 | 88k | Yes | 300K | ResNet-RS-420 | 82 | 26h 15min | 83% | 71% | 83% |
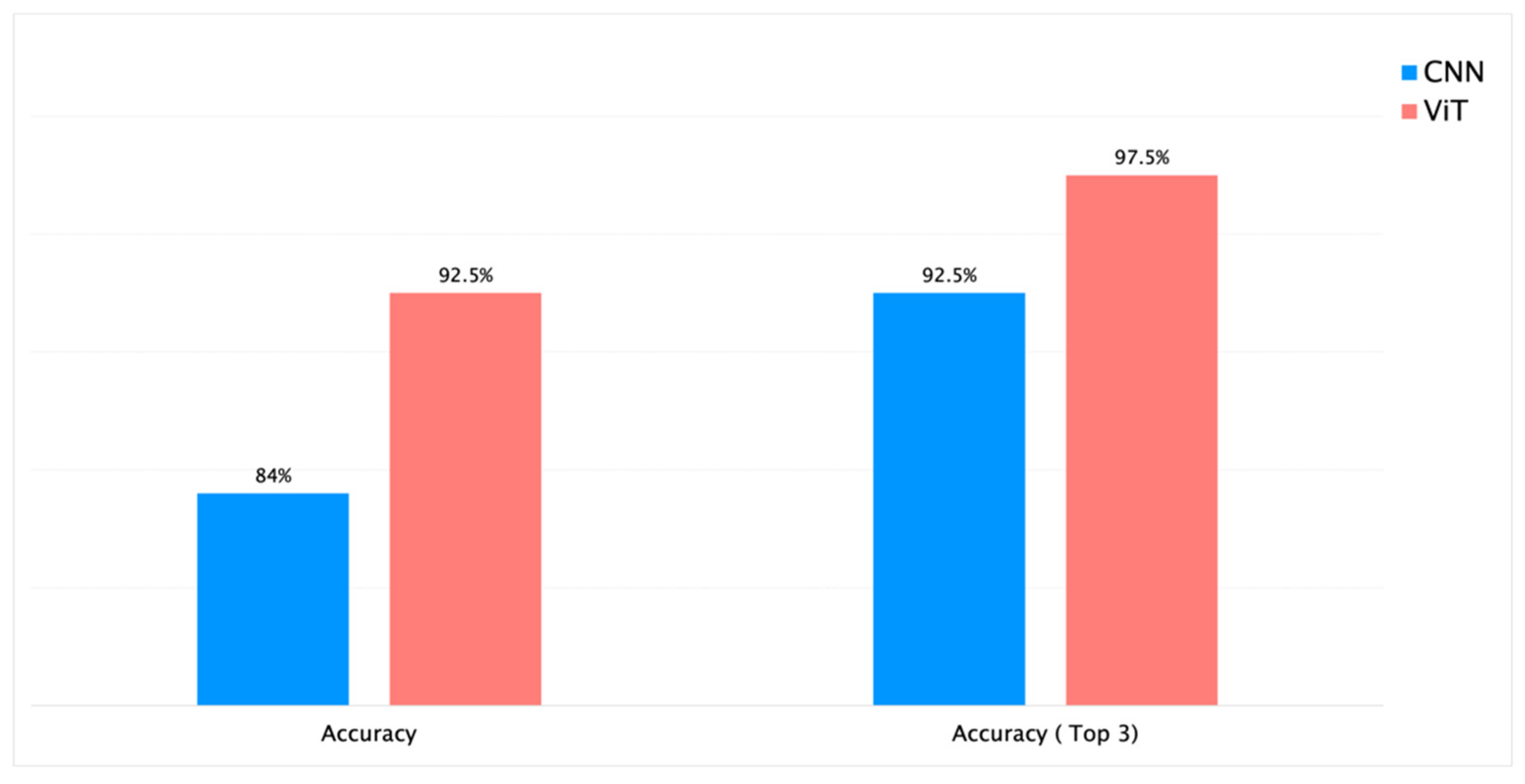
| 5. | RHS + PlantCLEF + iNaturalist | Species | 53 | 16k | Yes | 150K | ResNet-50 | 65 | 16h 25min | 94% | 84% | 92.5% |
| Experiment | Dataset | Genus/Species | Class Count | Images Count | Augmentation | Images Count (Augmentation) | CNN Model | Epochs | Training time | Validation Accuracy | Test accuracy | Test Accuracy (Top 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6. | RHS + PlantCLEF + iNaturalist | Genus | 113 | 88k | Yes | 300K | ViT | 70 | 30h | 86% | 83% | 92.5% |
| 7. | RHS + PlantCLEF + iNaturalist | Species | 53 | 16k | Yes | 150K | ViT | 50 | 17h | 96% | 92.5% | 97.5% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





