Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
18 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Color analysis
3.1.1. Lemon
3.1.2. Energy drink
3.1.3. Coffee
3.1.4. Tea
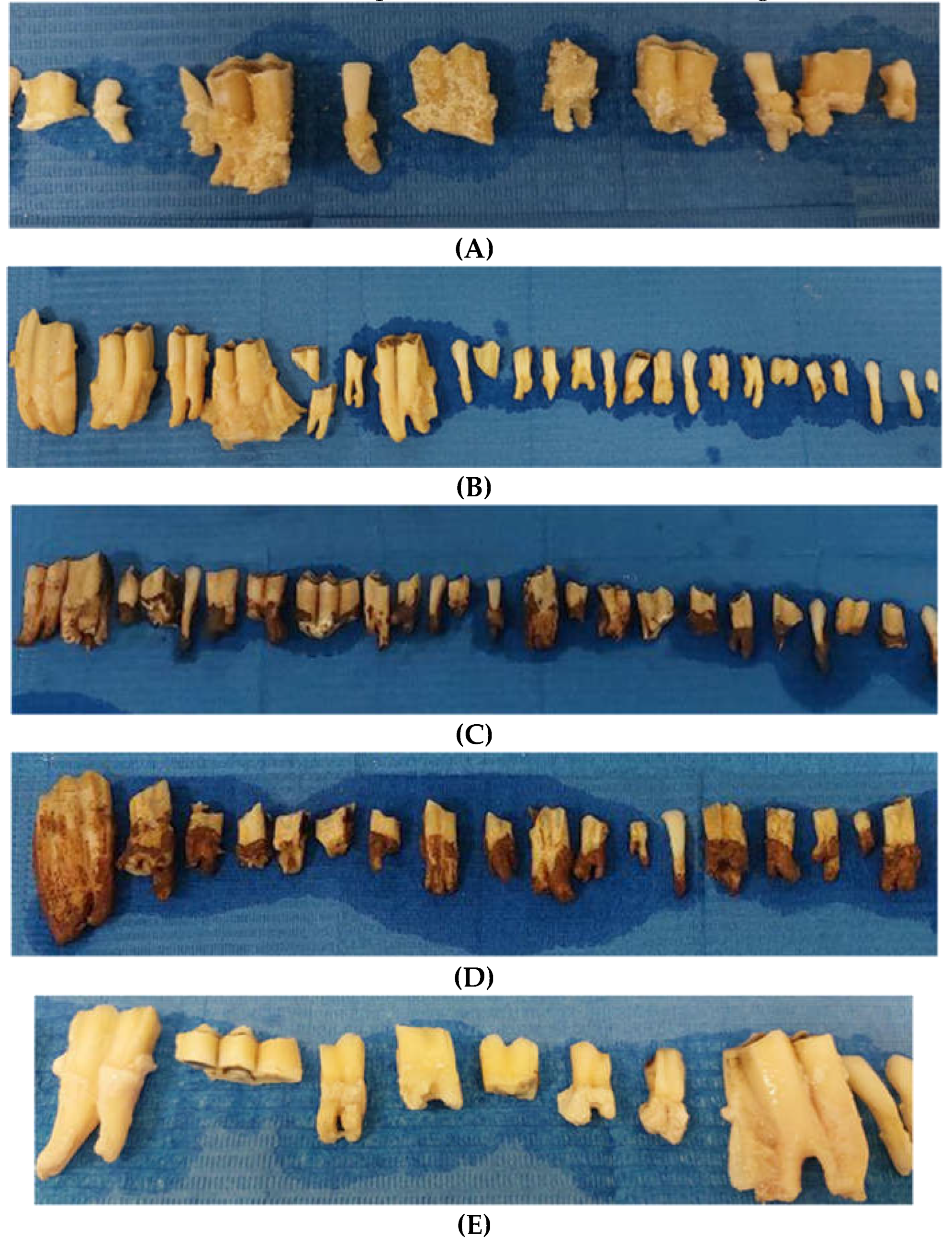
3.2. Qualitative surface aspect
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Imfeld T. Dental erosion. Definition, classification and links. Eur J Oral Sci. 1996 Apr;104(2 ( Pt 2)):151-5. [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino S, Bissoli A, Caporaso L, Iarussi F, Pulcini R, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux disease and dental erosion: A modern review. Japanese J Gastroenterol Res 2021, 1, 1003.
- Couselo M, Ibáñez V, Ortolá P, Carazo E, Valdés E, Vila JJ. Adequate timing of diagnostic tests for gastroesophageal reflux in children with esophageal atresia. Cir Pediatr. 2023 Jan 1;36(1):5-11. English, Spanish. [CrossRef]
- Monda M, Costacurta M, Maffei L, Docimo R. Oral manifestations of eating disorders in adolescent patients. A review. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 2021 Jun;22(2):155-158. [CrossRef]
- Jaeggi T, Lussi A. Prevalence, incidence and distribution of erosion. Monogr Oral Sci. 2014;25:55-73. [CrossRef]
- Lussi A, Carvalho TS. Erosive tooth wear: a multifactorial condition of growing concern and increasing knowledge. Monogr Oral Sci. 2014;25:1-15. [CrossRef]
- Devadiga D, Shetty P, Hegde MN. Characterization of dynamic process of carious and erosive demineralization - an overview. J Conserv Dent. 2022 Sep-Oct;25(5):454-462. [CrossRef]
- Lussi A, Schlueter N, Rakhmatullina E, Ganss C. Dental erosion--an overview with emphasis on chemical and histopathological aspects. Caries Res. 2011;45 Suppl 1:2-12. [CrossRef]
- Bartlett DW, Evans DF, Smith BGN: The relationship between gastrooesophageal reflux disease and dental erosion. J Oral Rehabil 1996, 23, 289–297. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laserre JF: Recherches sur l’usure dentaire et evaluation «in vitro» de biomateriaux restaurateurs avec le simulateur d’usure UVSB2, thése pour le doctorat en Sciences Odontologiques Université de Bordeaux 2, 2003.
- Larsen MJ: Dissolution of enamel. Scand J Dental Res 1973, 81, 518–522.
- Lussi A, Jaeggi T, Scharer S: The influence of different factors on in vitro enamel erosion. Caries Res 1993, 27, 387–393. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambon DL, Brand HS, Veerman EC. Dental erosion in the 21st century: what is happening to nutritional habits and lifestyle in our society? Br Dent J. 2012, 213, 55–57. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsunni, AA. Energy Drink Consumption: Beneficial and Adverse Health Effects. Int J Health Sci. 2015, 9, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghozayel M, Ghaddar A, Farhat G, Nasreddine L, Kara J, Jomaa L. Energy drinks consumption and perceptions among University Students in Beirut, Lebanon: A mixed methods approach. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0232199. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saads Carvalho T, Lussi A. Chapter 9: Acidic Beverages and Foods Associated with Dental Erosion and Erosive Tooth Wear. Monogr Oral Sci 2020, 28, 91–98.
- Kitchens M, Owens BM. Effect of carbonated beverages, coffee, sports and high energy drinks, and bottled water on the in vitro erosion characteristics of dental enamel. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2007 Spring;31(3):153-9. [CrossRef]
- Parker, A. S., Patel, A. N., Al Botros, R., Snowden, M. E., McKelvey, K., Unwin, P. R., et al. (2014). Measurement of the efficacy of calcium silicate for the protection and repair of dental enamel. Journal of Dentistry, 42, S21–9. [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y., Li, X., Deng, Y., Sun, J. N., Tao, D., Chen, H., et al. (2014). Mode of action studies on the formation of enamel minerals from a novel toothpaste containing calcium silicate and sodium phosphate salts. Journal of Dentistry, 42, S30–S38. [CrossRef]
- Ionta, F. Q., dos Santos, N. M., Mesquita, I. M., Dionísio, E. J., Cruvinel, T., Honório, H. M., et al. (2019). Is the dentifrice containing calcium silicate, sodium phosphate, and fluoride able to protect enamel against chemical mechanical wear? An in situ/ex vivo study. Clinical Oral Investigations, 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Stookey GK. The effect of saliva on dental caries. J Am Dent Assoc. 2008 May;139 Suppl:11S-17S. [CrossRef]
- Cochrane NJ, Reynolds EC: Calcium phosphopeptides – mechanisms of action and evidence for clinical efficacy. Adv Dent Res 2012, 24, 41–47. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cochrane NJ, Cai F, Huq NL, Burrow MF, Reynolds EC: New approaches to enhanced remineralization of tooth enamel. J Dent Res 2010, 89, 1187–1197. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattousch TJ, van der Veen MH, Zentner A. Caries lesions after orthodontic treatment followed by quantitative light-induced fluorescence: a 2-year follow-up. Eur J Orthod. 2007 Jun;29(3):294-8. [CrossRef]
- van der Veen MH, Mattousch T, Boersma JG. Longitudinal development of caries lesions after orthodontic treatment evaluated by quantitative light-induced fluorescence. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2007 Feb;131(2):223-8. [CrossRef]
- Dowd, F.J. Saliva and dental caries. Dent Clin North Am 1999, 43, 579–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstone LM: Remineralization of human enamel in vitro. Proc R Soc Med 1972, 65, 906–908.
- Philip N. State of the Art Enamel Remineralization Systems: The Next Frontier in Caries Management. Caries Res. 2019;53(3):284-295. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li H, Liu W, Zhou HJ, Sun Y, Zhang M, Wang J, Limer A, Owens G, Joiner A. In vitro dentine tubule occlusion by a novel toothpaste containing calcium silicate and sodium phosphate. J Dent. 2020;103S:100024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong J, Newcombe RG, Matheson JR, Weddell L, Edwards M, West NX. A randomised controlled trial investigating efficacy of a novel toothpaste containing calcium silicate and sodium phosphate in dentine hypersensitivity pain reduction compared to a fluoride control toothpaste. J Dent. 2020 Jul;98:103320. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood NJ, Jones SB, Chapman N, Joiner A, Philpotts CJ, West NX. An interproximal model to determine the erosion-protective effect of calcium silicate, sodium phosphate, fluoride formulations. Dent Mater. 2018 Feb;34(2):355-362. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornby K, Ricketts SR, Philpotts CJ, Joiner A, Schemehorn B, Willson R. Enhanced enamel benefits from a novel toothpaste and dual phase gel containing calcium silicate and sodium phosphate salts. J Dent. 2014 Jun;42 Suppl 1:S39-45. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joiner A, Schäfer F, Naeeni MM, Gupta AK, Zero DT. Remineralisation effect of a dual-phase calcium silicate/phosphate gel combined with calcium silicate/phosphate toothpaste on acid-challenged enamel in situ. J Dent. 2014, 42 (Suppl. 1), S53–S59. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones SB, Davies M, Chapman N, Willson R, Hornby K, Joiner A, West NX. Introduction of an interproximal mineralisation model to measure remineralisation caused by novel formulations containing calcium silicate, sodium phosphate salts and fluoride. J Dent. 2014, 42 (Suppl. 1), S46–S52. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanatta RF, Ávila DMDS, Maia MM, Viana ÍEL, Scaramucci T, Torres CRG, Borges AB. Protection of calcium silicate/sodium phosphate/fluoride toothpaste with serum on enamel and dentin erosive wear. J Appl Oral Sci. 2021 Oct 1;29:e20210081. [CrossRef]
- Moras CG, Acharya SR, Adarsh UK, Unnikrishnan VK. Regenerative biomineralization potential of commercially available remineralizing agents as a preventive treatment approach for tooth erosion - An in vitro laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy analysis. J Conserv Dent. 2023 Mar-Apr;26(2):165-169. [PubMed]
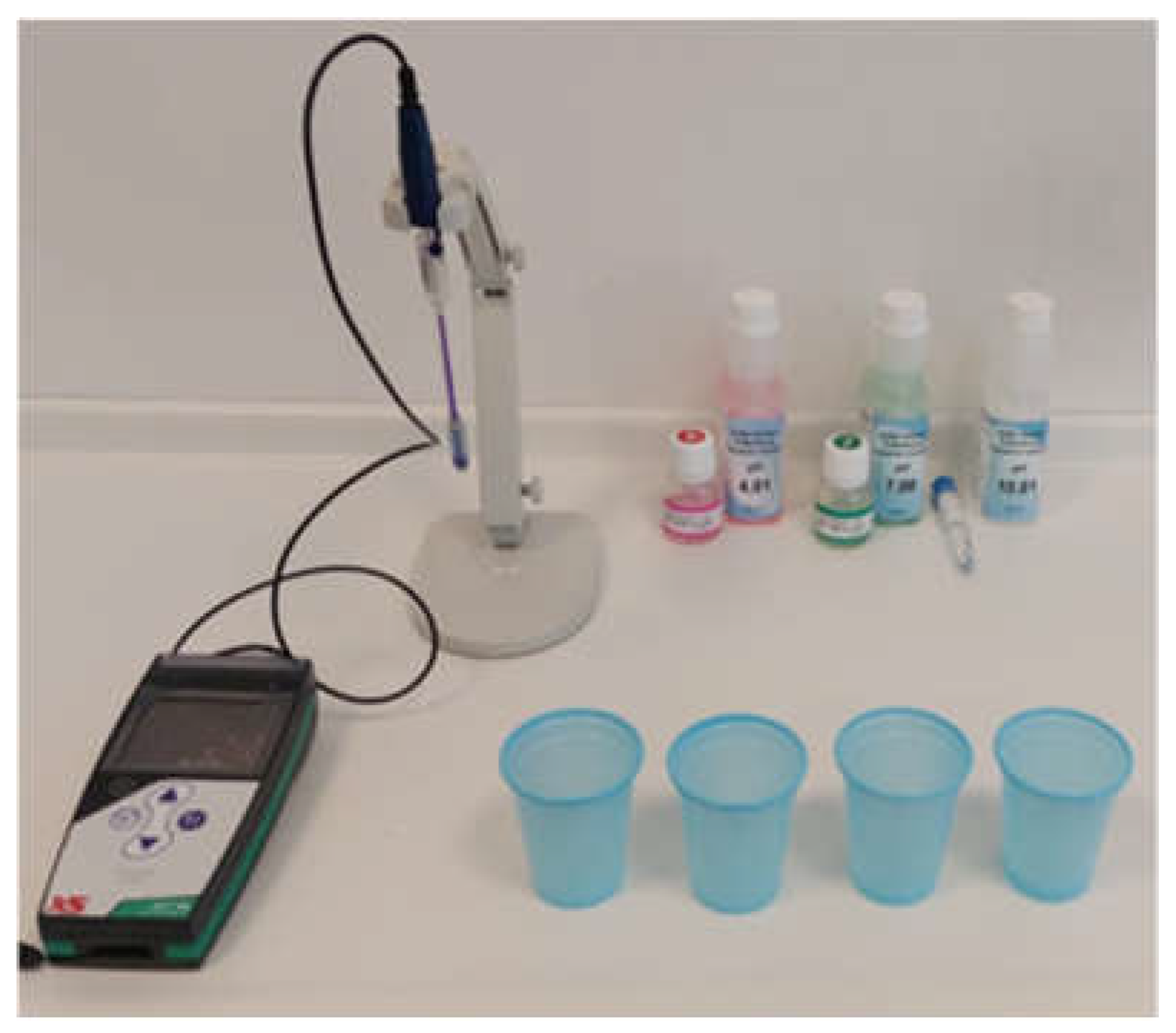


| Solution | pH |
|---|---|
| Lemon juice | 3.1 |
| Energy drink | 3.3 |
| Coffee | 5 |
| Tea | 4.9 |
| Physiologic solution | 5.8 |
| Tube | Composition |
|---|---|
| Tube A | Water, Glycerin, Calcium Silicate, PEG 8, Hydrated Silica, Trisodium, Phosphate, Sodium Phosphate, PEG-60, Sodium Laury Sulfate, Sodium Monofluorophosphate (1450 ppm), flavour, Sythetic Fluorphlogopite, Sodium Saccharin, Polyacrylic Acid, Tin Oxide, Limonene |
| Tube B | Water, Glycerin, Cellulose Gum, Sodium Fluoride, Benzyl Alcohol, Ethylhexylglycerin, Phenoxyethanol, Sodium Fluoride (1450 ppm) |
| Solution | Mean(SD)/Median* | t/Z* | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lemon juice | Pre | 8.85(4.45) | 7.8 | 0.000 a |
| Post | 4.93(6.66) | |||
| Energy drink | Pre | 9* | 4.204* | 0.000 a |
| Post | 8* | |||
| Coffee | Pre | 13* | 4.159* | 0.000 a |
| Post | 13* | |||
| Tea | Pre | 10* | 3.886* | 0.000 a |
| Post | 8* |
| OP | CHA | RO | SM | ZWE | OZ | CZ | RZ | SZ | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pre | 89 | 20 | 50 | 0 | 5 | 15 | 11 | 23 | 1 | 214 |
| Post | 52 | 6 | 12 | 28 | 0 | 28 | 3 | 8 | 24 | 161 |
| Total | 141 | 26 | 62 | 28 | 5 | 43 | 14 | 31 | 25 | 375 |
| Chi Square | 105.066 | |||||||||
| df | 8 | |||||||||
| p-value | 3.92*10-19 a | |||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





