Submitted:
16 August 2023
Posted:
17 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental section
2.1. Synthesis of AgNPs
2.2. Oxidation reactions
3. Results and discussion
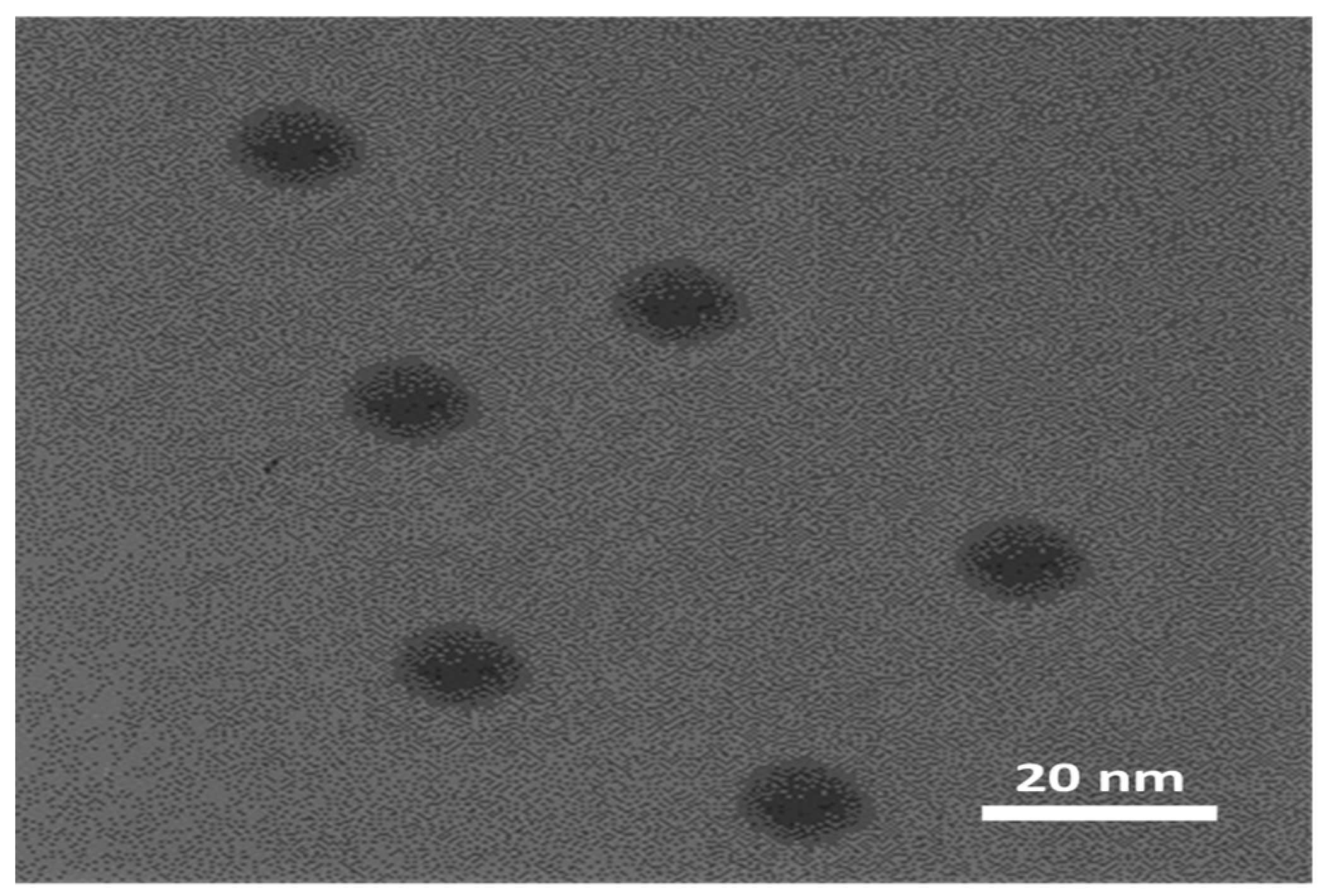
3.1. Characterization of silver nanozymes
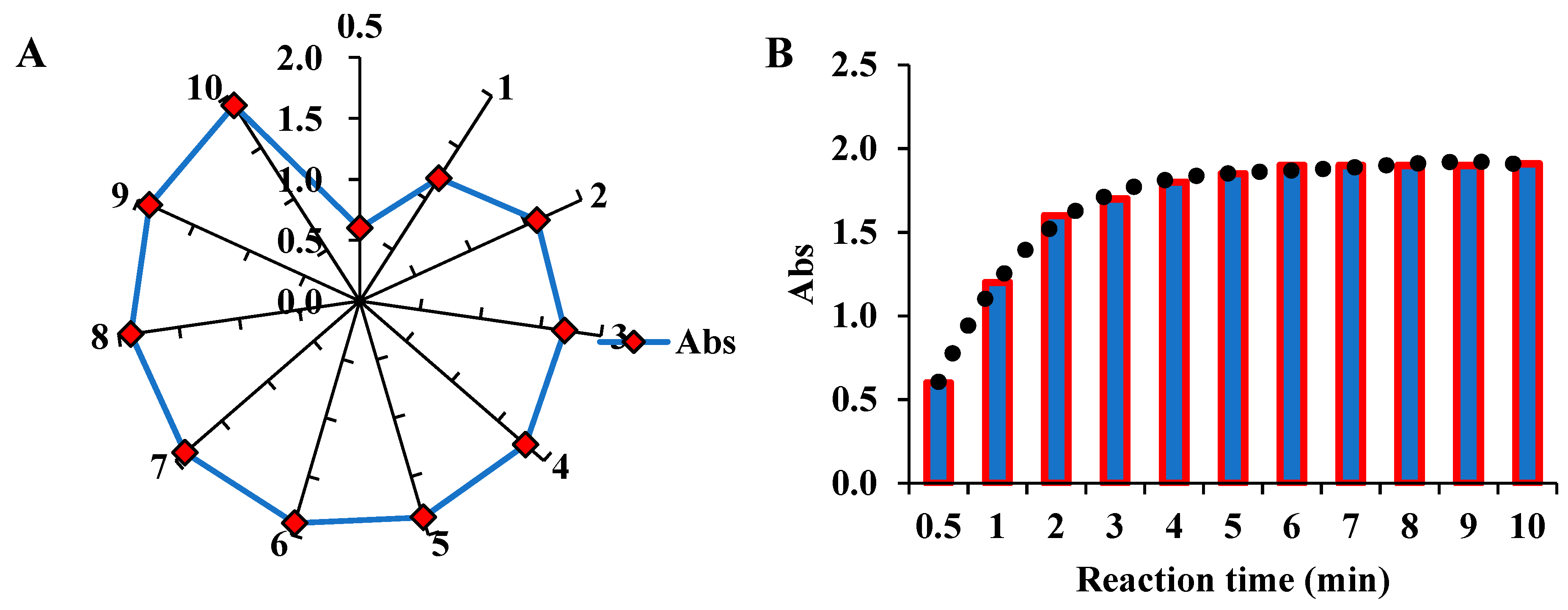
3.2. Time-course studies toward TMB oxidation
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, W.; Chen, B.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Fu, Y. BSA-stabilized Pt nanozyme for peroxidase mimetics and its application on colorimetric detection of mercury(II) ions. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 66, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, A.R.H.; Jangi, M.R.H.; Jangi, S.R.H. Detection mechanism and classification of design principles of peroxidase mimic based colorimetric sensors: A brief overview. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 28, 1492–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Akhond, M.; Absalan, G. A novel selective and sensitive multinanozyme colorimetric method for glutathione detection by using an indamine polymer. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Akhond, M.; Absalan, G. A field-applicable colorimetric assay for notorious explosive triacetone triperoxide through nanozyme-catalyzed irreversible oxidation of 3, 3′-diaminobenzidine. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Nanozymes: Classification, Catalytic Mechanisms, Activity Regulation, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4357–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Akhond, M. Synthesis and characterization of a novel metal-organic framework called nanosized electroactive quasi-coral-340 (NEQC-340) and its application for constructing a reusable nanozyme-based sensor for selective and sensitive glutathione quantification. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhond, M.; Jangi, S.R.H.; Barzegar, S.; Absalan, G. Introducing a nanozyme-based sensor for selective and sensitive detection of mercury(II) using its inhibiting effect on production of an indamine polymer through a stable n-electron irreversible system. Chem. Pap. 2019, 74, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, J.; Heider, D.; Wendel, N.J.; Sperl, N.; Sieber, V. Bacterial Glycosyltransferases: Challenges and Opportunities of a Highly Diverse Enzyme Class Toward Tailoring Natural Products. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homaei, Ahmad Abolpour, Reyhaneh Sariri, Fabio Vianello, and Roberto Stevanato. "Enzyme immobilization: an update." Journal of chemical biology 6 (2013): 185-205. [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Akhond, M.; Dehghani, Z. High throughput covalent immobilization process for improvement of shelf-life, operational cycles, relative activity in organic media and enzymatic kinetics of urease and its application for urea removal from water samples. Process. Biochem. 2019, 90, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Akhond, M. Introducing a covalent thiol-based protected immobilized acetylcholinesterase with enhanced enzymatic performances for biosynthesis of esters. Process. Biochem. 2022, 120, 138–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Galan, C.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R.; Rodrigues, R.C. Potential of Different Enzyme Immobilization Strategies to Improve Enzyme Performance. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2011, 353, 2885–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Akhond, M. High throughput urease immobilization onto a new metal-organic framework called nanosized electroactive quasi-coral-340 (NEQC-340) for water treatment and safe blood cleaning. Process. Biochem. 2021, 105, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H. Introducing a High Throughput Nanozymatic Method for Eco-Friendly Nanozyme-Mediated Degradation of Methylene Blue in Real Water Media. Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H. Low-temperature destructive hydrodechlorination of long-chain chlorinated paraffins to diesel and gasoline range hydrocarbons over a novel low-cost reusable ZSM-5@Al-MCM nanocatalyst: a new approach toward reuse instead of common mineralization. Chem. Pap. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormozi Jangi, S. R. , & Akhond, M. (2021). Ultrasensitive label-free enantioselective quantification of d-/l-leucine enantiomers with a novel detection mechanism using an ultra-small high-quantum yield N-doped CDs prepared by a novel highly fast solvent-free method. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 339, 129901. [CrossRef]
- Hormozi Jangi S., R.; Akhond, M. (2020). High throughput green reduction of tris (p-nitrophenyl) amine at ambient temperature over homogenous AgNPs as H-transfer catalyst. Journal of Chemical Sciences, 132, 1-8. [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Gholamhosseinzadeh, E. Developing an ultra-reproducible and ultrasensitive label-free nanoassay for L-methionine quantification in biological samples toward application in homocystinuria diagnosis. Chem. Pap. 2023, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, Z. , Akhond M., Hormozi Jangi S.R., Absalan G. 2024; 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H. Synthesis and characterization of magnesium-based metal-organic frameworks and investigating the effect of coordination solvent on their biocompatibility. 2023.
- Amany, A. , El-Rab, S. F. G., & Gad, F. (2012). Effect of reducing and protecting agents on size of silver nanoparticles and their anti-bacterial activity. Der Pharma Chemica, 4(1), 53-65.
- Jangi, S.R.H. Determining kinetics parameters of bovine serum albumin-protected gold nanozymes toward different substrates. Qeios 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Davoudli, H.K.; Delshad, Y.; Jangi, M.R.H.; Jangi, A.R.H. A novel and reusable multinanozyme system for sensitive and selective quantification of hydrogen peroxide and highly efficient degradation of organic dye. Surfaces Interfaces 2020, 21, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Leilakouhi, B.; Jangi, S.R.H.; Khorshidi, A. Introducing a novel photo-induced nanozymatic method for high throughput reusable biodegradation of organic dyes. Chem. Pap. 2022, 77, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangi, S.R.H.; Dehghani, Z. Spectrophotometric quantification of hydrogen peroxide utilizing silver nanozyme. 2023.
- Jangi, S.R.H. Effect of daylight and air oxygen on nanozymatic activity of unmodified silver nanoparticles: Shelf-stability. Qeios 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormozi Jangi, S. R. , & Dehghani, Z. (2023). Kinetics and biochemical characterization of silver nanozymes and investigating impact of storage conditions on their activity and shelf-life. Chemical Research and Nanomaterials, 1(4), 25-33.
- Mishra, S.; Abdal-Hay, A.; Rather, S.U.; Tripathi, R.M.; Shekh, F.A. Recent Advances in Silver nanozymes: Concept, Mechanism, and Applications in Detection. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Anderson, S.R.; Singh, S.; Ramanathan, R.; Bansal, V. Nanostructured silver fabric as a free-standing NanoZyme for colorimetric detection of glucose in urine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Z.; Li, H.; Deng, Y.; He, Y. Blue Light-Gated Reversible Silver Nanozyme Reaction Networks that Achieve Life-like Adaptivity. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 5076–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




