Submitted:
15 August 2023
Posted:
16 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
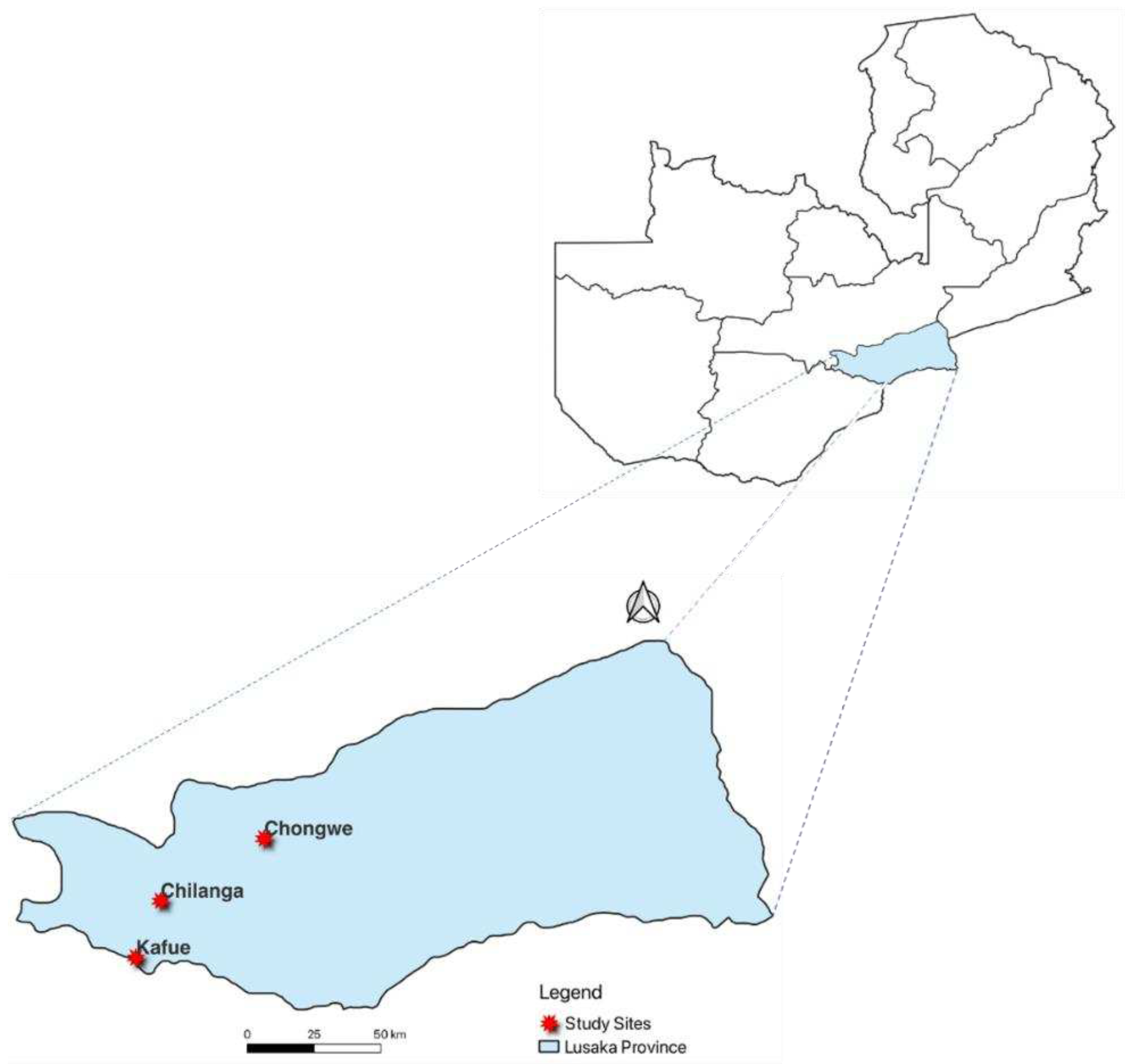
2.1. Study Design and Study Site
2.2. Sample Collection, Preparation, and RNA Extraction
2.3. Genomic Screening for Group A Rotavirus
2.4. Whole Genome Sequencing
2.5. Sequence Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Detection of Group A Rotaviruses
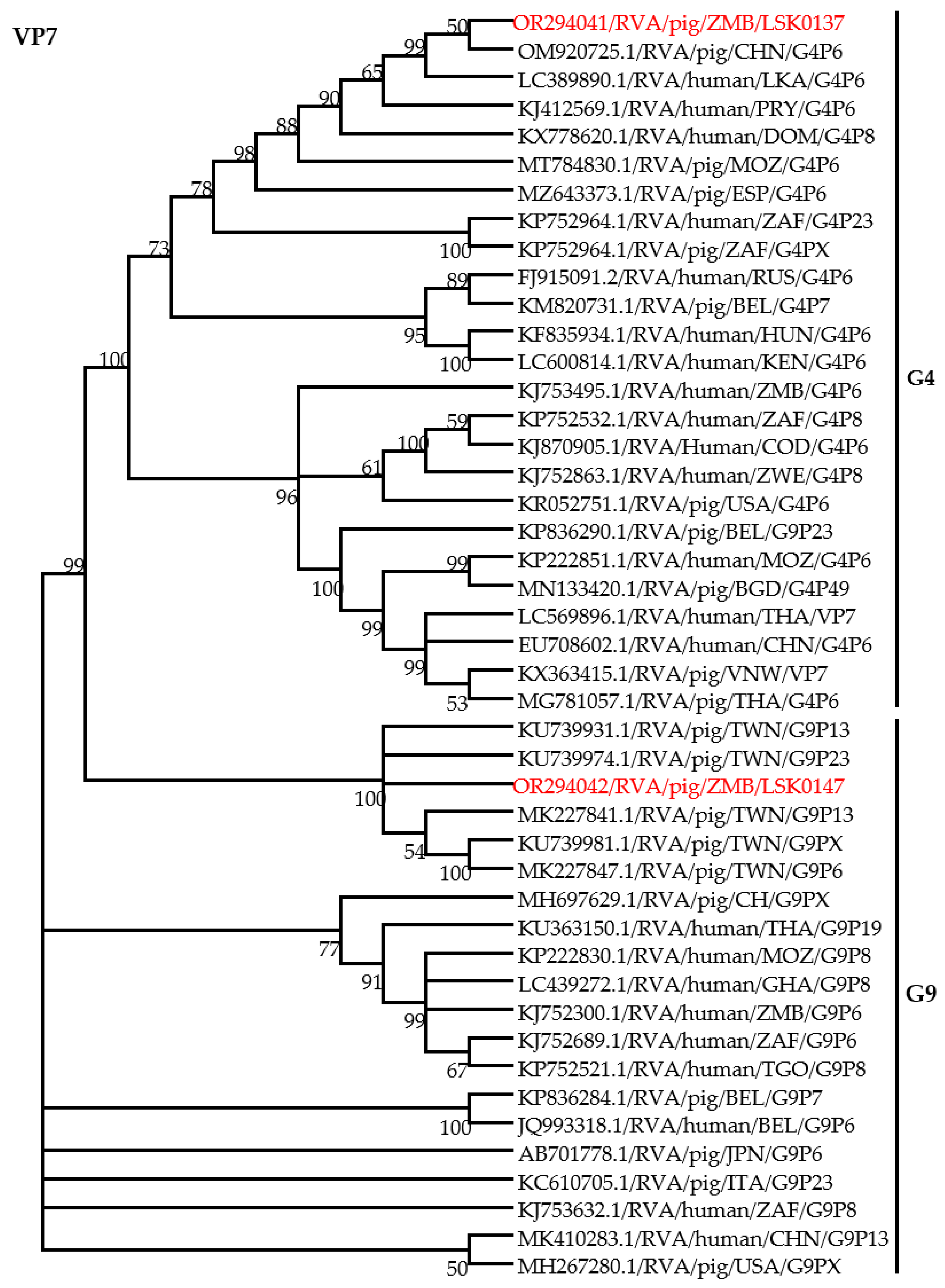
3.2. Genotyping of Group A Rotavirus Using VP7 Gene
3.3. Whole Genome Sequence Analysis and Genetic Constellation Determination
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis of RVA Structural Proteins Genes
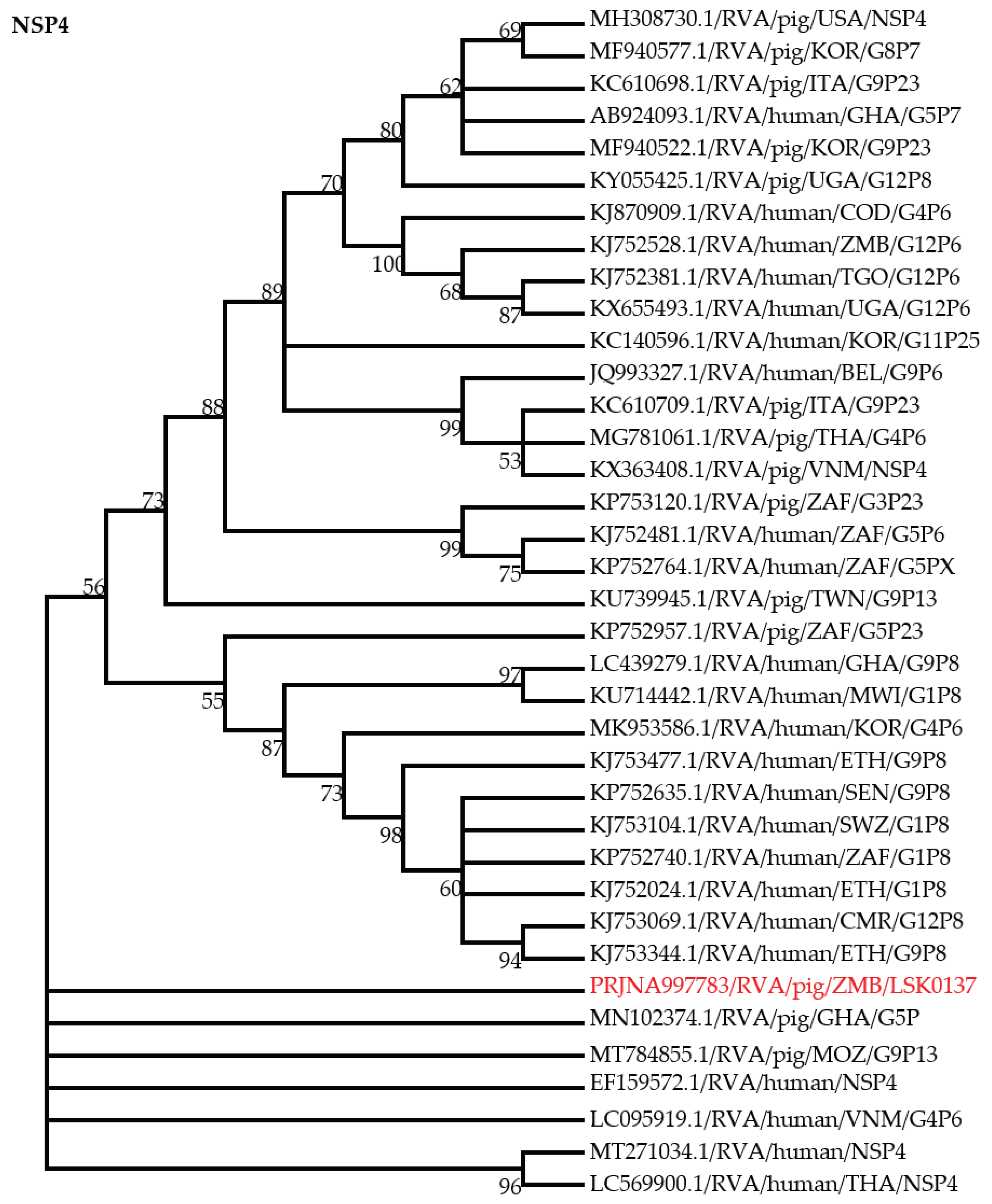
3.4. Phylogenic Analysis of RVA Nonstructural Proteins Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palombo, E.A. Genetic Analysis of Group A Rotaviruses: Evidence for Interspecies Transmission of Rotavirus Genes. Virus Genes 2002, 24, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeller, M.; Patton, J.T.; Heylen, E.; De Coster, S.; Ciarlet, M.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J. Genetic Analyses Reveal Differences in the VP7 and VP4 Antigenic Epitopes between Human Rotaviruses Circulating in Belgium and Rotaviruses in Rotarix and RotaTeq. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 966–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, A.D.; Victor, J.C.; Carey, M.E.; Tate, J.E.; Atherly, D.E.; Pecenka, C.; Diaz, Z.; Parashar, U.D.; Kirkwood, C.D. Experiences with Rotavirus Vaccines: Can We Improve Rotavirus Vaccine Impact in Developing Countries? Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1215–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heylen, E.; Likele, B.B.; Zeller, M.; Stevens, S.; De Coster, S.; Conceição-Neto, N.; Van Geet, C.; Jacobs, J.; Ngbonda, D.; Van Ranst, M.; et al. Rotavirus Surveillance in Kisangani, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Reveals a High Number of Unusual Genotypes and Gene Segments of Animal Origin in Non-Vaccinated Symptomatic Children. PLoS One 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shachakanza, J.; Zulu, J.M.; Maimbolwa, M. Incidence of Rotavirus Infection among Under-Five Children Attending Health Centres in Selected Communities of Ndola, Copperbelt Province, Zambia. Health (Irvine. Calif). 2019, 11, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boene, S.S.; João, E.D.; Strydom, A.; Munlela, B.; Chissaque, A.; Bauhofer, A.F.L.; Nabetse, E.; Latifo, D.; Cala, A.; Mapaco, L.; et al. Prevalence and Genome Characterization of Porcine Rotavirus A in Southern Mozambique. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 87, 104637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amimo, J.O.; Junga, J.O.; Ogara, W.O.; Vlasova, A.N.; Njahira, M.N.; Maina, S.; Okoth, E.A.; Bishop, R.P.; Saif, L.J.; Djikeng, A. Detection and Genetic Characterization of Porcine Group A Rotaviruses in Asymptomatic Pigs in Smallholder Farms in East Africa : Predominance of P [ 8 ] Genotype Resembling Human Strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 175, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakalinga, J.J.; Misinzo, G.; Msalya, G.M.; Shayo, M.J.; Malakalinga, J.R. Prevalence and Genetic Diversity of Rotavirus Group a in Piglets in Southern Highlands and Eastern Tanzania. SSRN Electron. J. 2022, 8, e11750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stubbs, S.C.B.; Quaye, O.; Acquah, M.E.; Adadey, S.M.; Kean, I.R.L.; Gupta, S.; Blacklaws, B.A. Full Genomic Characterization of a Porcine Rotavirus Strain Detected in an Asymptomatic Piglet in Accra, Ghana. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyer, A.; Poljšak-Prijatelj, M.; Barlič-Maganja, D.; Marin, J. Human, Porcine and Bovine Rotaviruses in Slovenia: Evidence of Interspecies Transmission and Genome Reassortment. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1690–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amimo, J.O.; Vlasova, A.N.; Saifa, L.J. Detection and Genetic Diversity of Porcine Group a Rotaviruses in Historic (2004) and Recent (2011 and 2012) Swine Fecal Samples in Ohio: Predominance of the G9P[13] Genotype in Nursing Piglets. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2013, 51, 1142–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weldegebriel, G.; Mwenda, J.M.; Chakauya, J.; Daniel, F.; Masresha, B.; Parashar, U.D.; Tate, J.E. Impact of Rotavirus Vaccine on Rotavirus Diarrhoea in Countries of East and Southern Africa. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7124–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakalinga, J.J.; Misinzo, G.; Msalya, G.M.; Kazwala, R.R. Rotavirus Burden, Genetic Diversity and Impact of Vaccine in Children under Five in Tanzania. Pathogens 2019, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokoena, F.; Esona, M.D.; Seheri, L.M.; Nyaga, M.M.; Magagula, N.B.; Mukaratirwa, A.; Mulindwa, A.; Abebe, A.; Boula, A.; Tsolenyanu, E.; et al. Whole Genome Analysis of African G12P[6] and G12P[8] Rotaviruses Provides Evidence of Porcine-Human Reassortment at NSP2, NSP3, and NSP4. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, J.L.; Kirkwood, C.D.; Gerna, G.; Clemens, J.D.; Rao, M.R.; Naficy, A.B. Characterization of Unusual G8 Rotavirus Strains Isolated from Egyptian Children. 1999, 144, 1381–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esona, M.D.; Armah, G.E.; Geyer, A.; Steele, A.D. Detection of an Unusual Human Rotavirus Strain with G5P [ 8 ] Specificity in a Cameroonian Child with Diarrhea. 2004, 42, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wandera, E.A.; Hatazawa, R.; Tsutsui, N.; Kurokawa, N.; Kathiiko, C.; Mumo, M.; Waithira, E.; Wachira, M.; Mwaura, B.; Nyangao, J.; et al. Genomic Characterization of an African G4P[6] Human Rotavirus Strain Identified in a Diarrheic Child in Kenya: Evidence for Porcine-to-Human Interspecies Transmission and Reassortment. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 96, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tacharoenmuang, R.; Guntapong, R.; Upachai, S.; Singchai, P.; Fukuda, S.; Ide, T.; Hatazawa, R.; Sutthiwarakom, K.; Kongjorn, S.; Onvimala, N.; et al. Full Genome-Based Characterization of G4P[6] Rotavirus Strains from Diarrheic Patients in Thailand: Evidence for Independent Porcine-to-Human Interspecies Transmission Events. Virus Genes 2021, 57, 338–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, Y.H.; Ghosh, S.; Tang, W.F.; Pang, B.B.; Liu, M.Q.; Peng, J.S.; Zhou, D.J.; Kobayashi, N. Genomic Characterization of G3P[6], G4P[6] and G4P[8] Human Rotaviruses from Wuhan, China: Evidence for Interspecies Transmission and Reassortment Events. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2015, 33, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degiuseppe, J.I.; Beltramino, J.C.; Millán, A.; Stupka, J.A.; Parra, G.I. Complete Genome Analyses of G4P[6] Rotavirus Detected in Argentinean Children with Diarrhoea Provides Evidence of Interspecies Transmission from Swine. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts-Mills, J.A.; Steele, A.D. Rotavirus Vaccine Impact in Africa: Greater than the Sum of Its Parts? Lancet Glob. Heal. 2018, 6, e948–e949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saif, L.J.; Vlasova, A.N.; Morrow, W.E.M. Rotaviral Diarrhea in Pigs. 1980, 1–6.
- Meta-analysis, C.A.; Mwila-kazimbaya, K.; Bosomprah, S.; Simuyandi, M.; Chisenga, C.C.; Munsaka, S. IMedPub Journals Efficacy and Effectiveness of Rotavirus Vaccine on Incidence of Diarrhoea Among. 2018, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, S.; Page, N.A.; Steele, A.D.; Peenze, I.; Cunliffe, N.A. Rotavirus Strain Types Circulating in Africa: Review of Studies Published during 1997-2006. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagomi, O.; Nakagomi, T. Genetic Diversity and Similarity among Mammalian Rotaviruses in Relation to Interspecies Transmission of Rotavirus. Arch. Virol. 1991, 120, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Rahman, M.; Lemey, P.; Van Ranst, M. Phylodynamic Analyses of Rotavirus Genotypes G9 and G12 Underscore Their Potential for Swift Global Spread. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2010, 27, 2431–2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuns, S.; Desmarets, L.M.B.; Heylen, E.; Zeller, M.; Dedeurwaerder, A.; Roukaerts, I.D.M.; Van Ranst, M.; Matthijnssens, J.; Nauwynck, H.J. Porcine Group a Rotaviruses with Heterogeneous VP7 and VP4 Genotype Combinations Can Be Found Together with Enteric Bacteria on Belgian Swine Farms. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Ciarlet, M.; McDonald, S.M.; Attoui, H.; Bányai, K.; Brister, J.R.; Buesa, J.; Esona, M.D.; Estes, M.K.; Gentsch, J.R.; et al. Uniformity of Rotavirus Strain Nomenclature Proposed by the Rotavirus Classification Working Group (RCWG). Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 1397–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, P.; Matthijnssens, J.; Rahman, M.; Van Ranst, M. RotaC: A Web-Based Tool for the Complete Genome Classification of Group A Rotaviruses. BMC Microbiol. 2009, 9, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthijnssens, J.; Van Ranst, M. Genotype Constellation and Evolution of Group A Rotaviruses Infecting Humans. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2012, 2, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.; Ghosh, S.; Bagchi, P.; Dutta, D.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Kobayashi, N.; Chawla-Sarkar, M. Full Genomic Analyses of Human Rotavirus G4P[4], G4P[6], G9P[19] and G10P[6] Strains from North-Eastern India: Evidence for Interspecies Transmission and Complex Reassortment Events. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 1343–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaraket, H.; Charide, R.; Kreidieh, K.; Dbaibo, G.; Melhem, N.M. Update on the Epidemiology of Rotavirus in the Middle East and North Africa. Vaccine 2017, 35, 6047–6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasova, A.N.; Amimo, J.O.; Saif, L.J. Porcine Rotaviruses: Epidemiology, Immune Responses and Control Strategies. Viruses 2017, 9, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alaoui Amine, S.; Melloul, M.; El Alaoui, M.A.; Boulahyaoui, H.; Loutfi, C.; Touil, N.; El Fahime, E. Evidence for Zoonotic Transmission of Species A Rotavirus from Goat and Cattle in Nomadic Herds in Morocco, 2012–2014. Virus Genes 2020, 56, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, H.; Qian, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R. Infection, Genetics and Evolution Identification of Circulating Porcine – Human Reassortant G4P [ 6 ] Rotavirus from Children with Acute Diarrhea in China by Whole Genome Analyses. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 20, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandera, E.A.; Hatazawa, R.; Tsutsui, N.; Kurokawa, N.; Kathiiko, C.; Mumo, M.; Waithira, E.; Wachira, M.; Mwaura, B.; Nyangao, J.; et al. Genomic Characterization of an African G4P[6] Human Rotavirus Strain Identified in a Diarrheic Child in Kenya: Evidence for Porcine-to-Human Interspecies Transmission and Reassortment. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021, 96, 105133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.K.; Choi, S.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, E.J.; Hyun, J.; Kim, H.S. Whole-Genome Analysis of Rotavirus G4P[6] Strains Isolated from Korean Neonates: Association of Korean Neonates and Rotavirus P[6] Genotypes. Gut Pathog. 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simwaka, J.C.; Mpabalwani, E.M.; Seheri, M.; Peenze, I.; Monze, M.; Matapo, B.; Parashar, U.D.; Mufunda, J.; Mphahlele, J.M.; Tate, J.E.; et al. Diversity of Rotavirus Strains Circulating in Children under Five Years of Age Who Presented with Acute Gastroenteritis before and after Rotavirus Vaccine Introduction, University Teaching Hospital, Lusaka, Zambia, 2008 – 2015. Vaccine 2018, 3–7, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, M.; Kajihara, M.; Changula, K.; Mori-Kajihara, A.; Ogawa, H.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Mweene, A.S.; Simuunza, M.; Yoshida, R.; Carr, M.; et al. Identification of Group A Rotaviruses from Zambian Fruit Bats Provides Evidence for Long-Distance Dispersal Events in Africa. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 63, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishimoto, M.; Kajihara, M.; Tabata, K.; Itakura, Y.; Toba, S.; Ozono, S.; Sato, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Ito, N.; Changula, K.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Distinct Rotavirus A in Bat and Rodent Hosts. J. Virol. 2023, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elschner, M.; Prudlo, J.; Hotzel, H.; Otto, P.; Sachse, K. Nested Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction for the Detection of Group A Rotaviruses. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2002, 49, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeset, R.V.; Udnæs, H.C.; Guneriussen, T.; Koren, H.; Malnes, E.; Solberg, R.; Alfnes, E. Improving Runoff Simulations Using Satellite-Observed Time-Series of Snow Covered Area. Nord. Hydrol. 2003, 34, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngomane, T.; Seheri, M. Genetic Diversity of Group a Rotavirus Strains Circulating in Porcine from Five Provinces in South Africa during 2007, 2008 and 2015. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.A.; Mouw, C.; Jutla, A.; Akanda, A.S. Quantification of Rotavirus Diarrheal Risk Due to Hydroclimatic Extremes Over South Asia: Prospects of Satellite-Based Observations in Detecting Outbreaks. GeoHealth 2018, 2, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amimo, J.O.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Githae, D.; Wamalwa, M.; Djikeng, A.; Nasrallah, G.K. Metagenomic Analysis Demonstrates the Diversity of the Fecal Virome in Asymptomatic Pigs in East Africa. Arch. Virol. 2016, 161, 887–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpabalwani, E.M.; Simwaka, J.C.; Mwenda, J.M.; Matapo, B.; Parashar, U.D.; Tate, J.E. Sustained Impact of Rotavirus Vaccine on Rotavirus Hospitalisations in Lusaka, Zambia, 2009–2016. Vaccine 2018, 36, 7165–7169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atii, D.J.I.; Ojeh, C.K. Subgroup Determination of Group A Rotaviruses Recovered from Piglets in Nigeria. 1995, 8, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahiro, T.; Takaki, M.; Chandrasena, T.G.A.N.; Rajindrajith, S.; Iha, H.; Ahmed, K. Human-Porcine Reassortant Rotavirus Generated by Multiple Reassortment Events in a Sri Lankan Child with Diarrhea. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2018, 65, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
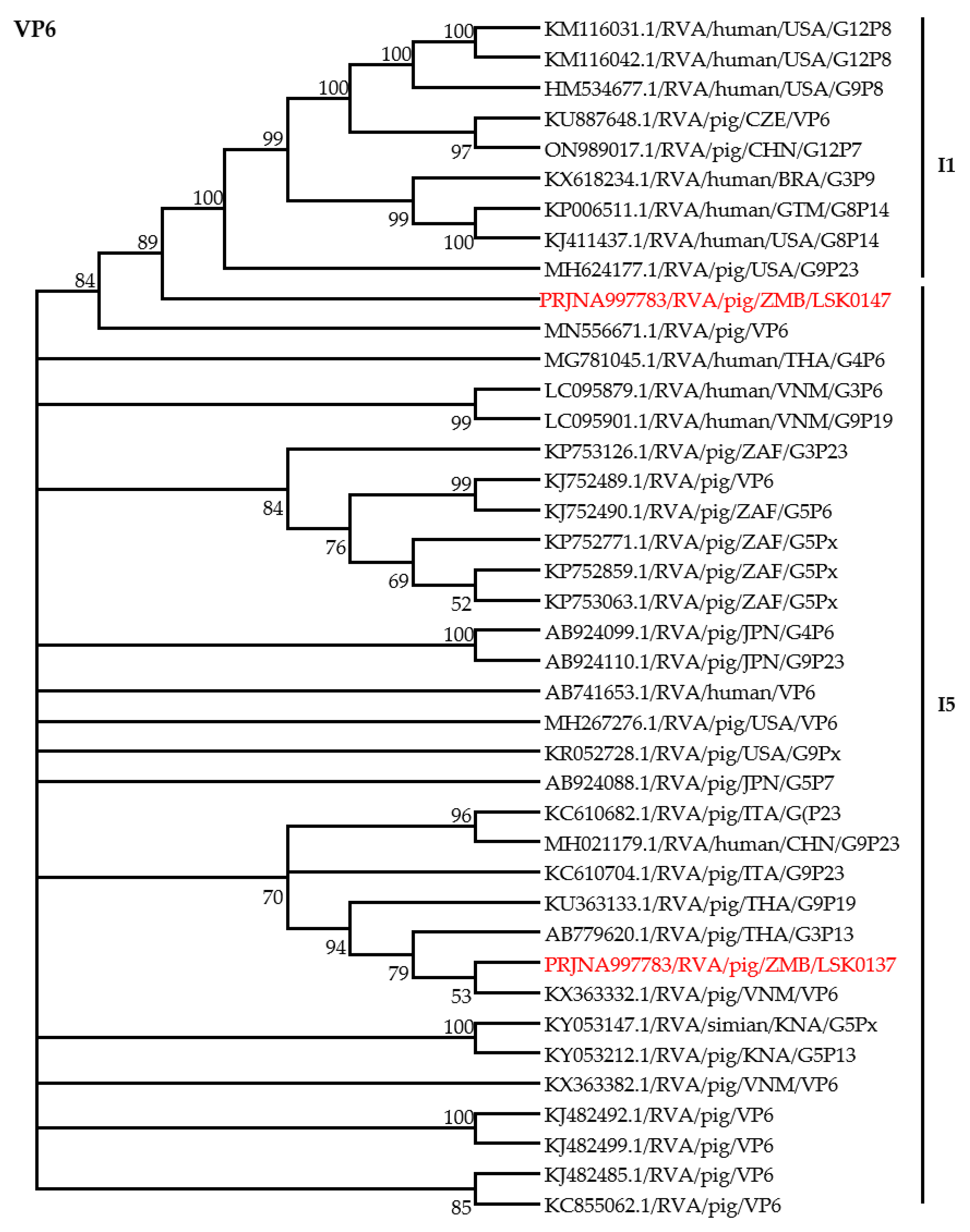
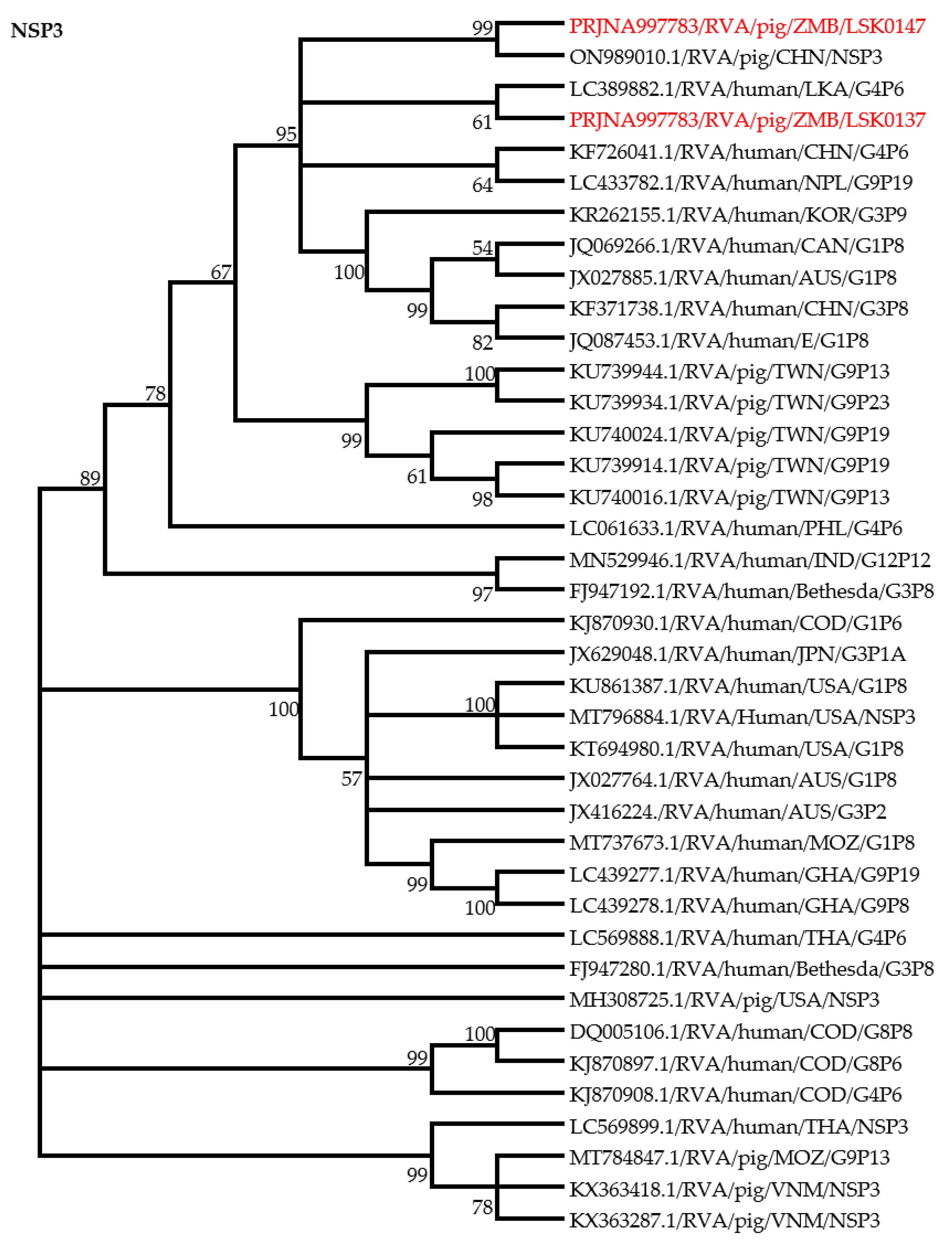



| Variable | Levels | PCR “+ve” |
PCR “-ve” |
Odds ratio | 95% CI | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | Dry | 11 | 72 | 1 | ||
| Rainy | 23 | 42 | 3.58 | 1.62 – 8.34 | 0.00209 | |
| Diarrhea | No | 6 | 41 | 1 | ||
| Yes | 28 | 73 | 2.62 | 1.06 – 7.47 | 0.0494 | |
| Age | Grower | 1 | 9 | 1 | ||
| Piglet | 18 | 31 | 5.23 | 0.87 – 100.40 | 0.1310 | |
| Weaner | 15 | 74 | 1.82 | 0.31 – 34.91 | 0.5817 |
| Variable | Levels | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Season | Dry | 1 | ||
| Rainy | 3.13 | 1.37 – 7.47 | 0.00781 | |
| Diarrhea | No | 1 | ||
| Yes | 1.61 | 0.59 – 4.88 | 0.36649 | |
| Age | Grower | 1 | ||
| Piglet | 4.18 | 0.62 – 83.71 | 0.20829 | |
| Weaner | 1.68 | 0.25 – 33.39 | 0.64534 |
| Sample ID | GenBank Accession no. |
Stool | Closest Sequence | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Country | Host | Genotype VP7 Gene |
% Identity | |||
| 14 | OR294031 | Diarrhea | China | Pig | G9 | 96.17 |
| 18 | OR294032 | Diarrhea | China | Human | G5 | 94.68 |
| 31 | OR294033 | Diarrhea | China | Pig | G9 | 96.38 |
| 32 | OR294034 | Diarrhea | China | Pig | G9 | 96.05 |
| 34 | OR294035 | Diarrhea | Ghana | Pig | G5 | 87.52 |
| 41 | OR294036 | Diarrhea | China | Pig | G9 | 96.42 |
| 42 | OR294037 | Diarrhea | China | Pig | G9 | 95.84 |
| 71 | OR294038 | Diarrhea | China | Human | G5 | 94.48 |
| 72 | OR294039 | Diarrhea | China | Human | G5 | 94.28 |
| 77 | OR294040 | Normal | China | Human | G5 | 94.01 |
| 137 | OR294041 | Diarrhea | China | Human | G4 | 97.1 |
| 147 | OR294042 | Diarrhea | Taiwan | Human | G9 | 92.2 |
| Sample ID | Bioproject Accession No. |
Gene | Genotype | Cut Off % Value |
BLASTn %Identity |
Similar Strain from GenBank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | VP7 | G4 | 80 | 97.24 | RVA/Human-wt/CHN/2018/G4P[6] |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | VP4 | P[6] | 80 | 95.58 | RVA/Human-wt/CHN/B24-R2/2019/P6 VP4 |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | VP6 | I5 | 85 | 96.02 | RVA/Pig-wt/VNM/14150_53/VP6 |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | VP1 | R1 | 83 | 95.20 | RVA/Human-tc/VNM/NT0042/2007/G4P[6] |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | VP2 | C1 | 84 | 96.39 | RVA/Human-wt/CHN/R1954/2013/G4P[6] |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | VP3 | M1 | 81 | 95.74 | RVA/Human-wt/RUS/2015 VP3 |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | NSP1 | A8 | 79 | 97.35 | RVA/Human-tc/VNM/NT0042/2007/G4P[6] |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | NSP2 | N1 | 85 | 96.76 | RVA/Human-tc/VNM/NT0042/2007/G4P[6] |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | NSP3 | T1 | 85 | 95.91 | Human rotavirus A strain GX54 |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | NSP4 | E1 | 85 | 97.97 | RVA/Pig/China/FJSH01/2021/G26P[23 |
| LSK0137 | PRJNA997783 | NSP5 | H1 | 91 | 98.83 | RVA/Human-wt/BRA/HST327/1999/G4P[6] |
| LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 LSK0147 |
PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 PRJNA997783 |
VP7 VP4 VP6 VP1 VP2 VP3 NSP1 NSP2 NSP3 NSP4 NSP5 |
G9 P[x] I5 R1 C1 M1 Ax N1 T1 E1 H1 |
80 80 85 83 84 81 79 85 85 85 91 |
94.22 93.15 94.54 96.97 92.25 98.68 96.31 96.85 97.60 98.21 99.58 |
RVA/Human-wt/TWN/G9P19 RVA/Pig-wt/VNM/14150_54/VP4 Porcine rotavirus strain JN-1 VP6 RVA/Human-wt/THA/PK2015-1-0001 VP1 RVA/Human-wt/LKA/R1207/2009/G4P[6] RVA/Pig-wt/VNM/14225_44/VP3 RVA/Human-wt/CHN/E931/2008/G4P[6] Porcine rotavirus A isolate GDJM1NSP2 Pig-wt/CHN/CN127/2021/G12P[7] NSP3 RVA/Human-tc/VNM/NT0001/2007/G3P[6] RVA/Human-wt/LKA/R1207/2009/G4P[6] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





