1. Introduction
Restoration of bone defects in the maxillofacial region after surgical interventions is a well-known topical problem. The successive stages of bone regeneration: inflammation, formation of a soft callus and then hard tissue, and finally remodeling of the newly formed bone are often a long-term chronic process.
In the field of applied dentistry, researchers offer a variety of plastic materials that, when in contact with bone, can cause an osteogenesis reaction, replacing bone tissue defects. The inclusion of low molecular weight bioregulatory peptides in the composition of chitosan structures stimulates the early appearance of signs of reparative osteogenesis, which indicates a rather high osteoaffinity of the compositions with the formation of a dense fragment of bone and bone marrow, as well as osteons, starting from the 30th day, by more than 40% [
1].
However, it is known that with a large area of bone damage, real physiological repair is not able to eliminate the defect on its own, and the use of many polymeric structures does not provide the expected effect of regeneration [
2,
3,
4]. In the absence of automaterial, the creation of functional bone using highly biocompatible substrates capable of self-organizing molecular architecture with high biocompatibility and the presence of exogenous growth factors can close a large bone defect [
5,
6]. From this point of view, the same chitosan construct of a high degree of purification and deacetylation with a glomerular conformation of the molecule up to nanosizes in reaction with chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronate, heparin, and alginate can be a promising starting material [
7].
The idea of using the proposed polysaccharide construct is to significantly increase its functionality, on the one hand, as a system for transferring target ingredients through the compartment in the osteogenic process, and on the other hand, the formation of a newly formed bone and obtaining signs of early bone formation [
8].
Histological and immunohistochemical studies show that chitosan matrices create conditions for neovascularization in vivo at the early stages of implantation and are suitable for tissue engineering [
9]. In cases of early regeneration of bone tissue during the elimination of defects of a critical size, the management of angiogenesis is an obligatory process and is accompanied by the binding and release of angiogenic growth factors [
10,
11], the early formation of the periodontium itself with high vascularization [
12]. This indicates the conjugation of the processes of osteogenesis and angiogenesis [
13].
Additional protonation of the amino group (NH
2) in the chitosan molecule, for example, with the help of weak ascorbic acid, makes it possible to increase the effectiveness of the control of angiogenic reactions in the periodontium [
14]. Physical cross-linking of biopolymers to obtain soft hydrogels with a three-dimensional structure makes it possible to use them in tissue engineering [
15] as delivery systems for hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate, starch and cellulose, or their chemical derivatives to the area of damaged maternal bone tissue [
16,
17].
With long-term bone regeneration in the maxillofacial region, it is important to control the preservation of the structural integrity and function of the hydrogel matrix until the formation of new bone tissue with the transfer of the entire matrix to the area of the bone defect. It is very important that early active osteogenesis proceeds under conditions of an anti-inflammatory reaction, since the structure of chitosan forms electrostatic and concentration gradients for cells, metabolites, and water, which sets them in motion towards the polymer. This reduces the degree of inflammation both at the site of polymer dislocation and in the peripheral zone [
18].
Large bone defects, especially in the maxillofacial region, are eliminated for a very long time and require replacement with an auto-material.
An artificial structure based on natural polysaccharides and apatites can successfully solve this problem with careful selection of a combination of polymers. The initial positive therapeutic effect of the proposed design in the experiment will make it possible to set the following tasks of elucidating the mechanisms of action on bone tissue.
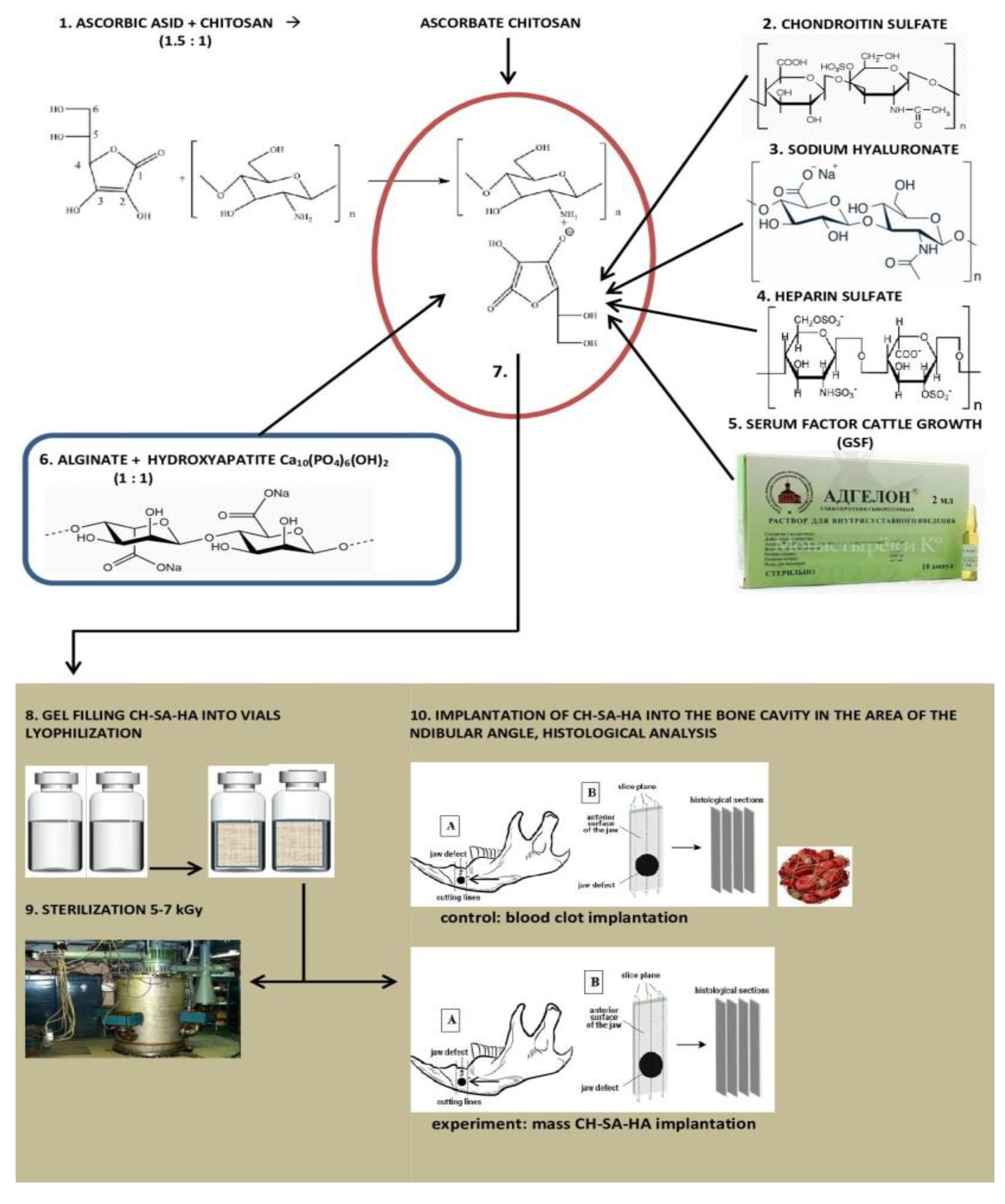
The authors of the article in the study used the CH-SA-HA construct, which includes a complex of polycationic and polyanionic polysaccharides: chitosan ascorbate, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronate, heparin, serum growth factor (SGF), alginate and hydroxyaptite. Each ingredient has a reason to be used to activate osteogenesis in the maxillofacial region. Physical or chemical synthesis of chitosan with other polymers significantly increases the mechanical strength and gives elasticity to the hydrogel [
19]. The mutual penetration of individual polymers forms a hydrogel network that reinforces the structure. Such combined meshes were obtained using alginate and chitosan [
20] or hyaluronic acid [21, 22] for the purpose of bone tissue bioengineering. Combination of chitosan with alginate-hydroxyapatite framework [
23,
24] stabilizes the gel matrix by forming polyelectrolyte complexes, ties the scaffold together and forms a compact structure. The authors did not use low molecular weight crosslinkers in their work, such as glutaraldehyde, carbodiimide, epoxy compounds, despite the ability to react with such chemical functional groups as carboxyl, hydroxyl, and sulfhydryl. Serious disadvantages of these spacers are either high cytotoxicity [
25] or a fast degradation profile and low mechanical strength [
26,
27].
Earlier studies [
28] demonstrated the role of SGF when added to a collagen-chitosan complex that contained most of the ingredients from the CH-SA-HA formulation (chitosan ascorbate, chondroitin sulfate, sodium hyaluronate, heparin sulfate). The presence of SGF in mouse embryonic fibroblast culture significantly increased DNA synthesis in cells. This finding allowed the authors of this work to include this growth factor in the CH-SA-HA construct. It is noteworthy that the delivery of growth factor to the area of bone regeneration requires preliminary protection from enzymatic protein hydrolysis. It is known that such protection can be created using hydrogels and polysaccharide-protein scaffolds [
29]. Prolonged kinetics is formed upon conjugation of growth factors and copolymers of chitosan-sodium alginate. To significantly increase the sorption of the growth factor and the release time, it is necessary to include a sulfated polysaccharide molecule, for example, heparin, in the copolymer. Different concentrations of heparin can regulate the rate of release of the active substance. The mechanism of prolongation is to prevent the interaction between the anionic groups of alginate and growth factors. Great prospects for the start of early angiogenesis for the purpose of bone reconstruction open up when 3-4 growth factors are included in the proposed combination of biopolymers. Their sequential release into the medium can accurately mimic angiogenesis [[
30,
31].
The inclusion of other polymers or inorganic compounds in the alginate is associated with a significant improvement in the mechanical and functional qualities of the new design. Favorable conditions for bone defect regeneration are observed during implantation of an octacalcium phosphate and alginate construct [
32]. At the same time, alginate selectively binds divalent cations, for example, calcium and magnesium, which is the basis for the formation of a stable hydrogel [
33]. It has been established that the inclusion of hydroxyapatite in scaffolds based on sodium alginate increases the stability of the scaffolds and opens up access to the cell surface [
34], improves biocompatibility, changes the microrelief of the matrix surface, increases adhesion and migration of osteoblasts [
35]. Frameworks based on alginate and hydroxyapatite enhance the local elimination of the bone defect, since they do not cause inflammatory effects [
36]. Such constructions provide good attachment and proliferation of preosteoblastic cells, differentiation of osteoblasts [
37].The inclusion of the apatite component in the chitosan structure is supposedly designed to stimulate the vascular endothelium during the exchange of calcium and phosphate already at an early stage of angiogenesis [
38]. Due to the high chemical solubility of apatite structures with the release of ionized calcium and phosphates into the medium, it leads to a direct induction of angiogenesis [
39] and the formation of vascular branches [
40]. Thus, researchers associate direct induction of angiogenesis with the participation of the calcium phosphate environment with direct activation of fibroblasts capable of secreting angiogenic growth factors (VEGF, βFGF and TGFβ). This result creates favorable conditions for adhesion, translation and proliferation of endothelial cells of the great vessels with the preservation of their vascular phenotype [
41]. The temporary stability of the polysaccharide matrix in the tissue fluid is important for the full start of the osteogenesis process. Thus, the aim of the study was to obtain morphometric evidence of early bone tissue regeneration in comparison with the classical control in a bone critical size defect.
The innovation of the experiment lies in obtaining a new design that can be introduced into a wide dental (and not only) practice in order to eliminate bone defects of a critical size of various origins in patients.
The hypothesis of effective early osteogenesis consists in obtaining the effect of early vascular endothelization of not only the walls of the bone defect in the presence of a polysaccharide matrix, but also endothelization of the matrix itself. The selection of polysaccharides with a certain molecular weight and dose, the method of synthesis to control the rate of degradation, as well as obtaining the effect of the rapid formation of the spongy and compact part of the bone, poses the immediate tasks of the regeneration mechanisms analyzing of under these conditions.
2. Materials and methods
All manipulations with the animals were performed following the regulations specified in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Research Council, 2011). The work was approved: complex scientific theme No. 01201362513 (2013/01/01 – 2021/01/01) "Fundamental and applied scientific and technical developments of nano-level biopolymer structures and technologies for their production for use in cell and tissue engineering in socially significant human diseases"; Section "Dentistry". Research topic: "Restoration of the structure of the bone tissue of the maxillofacial region using polysaccharide polymers with extensive traumatic defects in conditions of subcompensated diabetes mellitus." Bioethical Commission for Working with Animals by the Ethics Committee of the Voino-Yasenetsky Krasnoyarsk State Medical University of the Ministry of Health Russian Federation (Protocol No2 of 10/28/2019).
2.1. Composition of CH-SA-HA construction
The Developer is SBEU HPT Krasnoyarsk State Medical University, Russia. Gel mass chitosan-alginate-hydroxyapatite (CH-SA-HA) containing a 2% solution of chitosan ascorbate (CH) (dissolution of the polymer in ascorbic solution acid in a ratio of 1: 1.5) with a molecular weight of 695 kDa and a degree of deacetylation of 95% (a triply purified chitosan obtained in Vostok-Bor-1, Dal'negorsk, Russia; Specifications (No 9289-067-004721224-97), including, per 1 g of dry chitosan ascorbate, 5-100 mg of sodium chondroitin sulfate (Sigma), 10-100 mg of sodium hyaluronate (Sigma), 2,5-5 mg of heparin sulfate (Russia, Pharm.Art. (No 42-1327-99), 110 mcg/d serum growth factors in cattle "adgelon" (SLL "Endo-Pharm-A", Moscow region, Schcholkovo, Russia, Specifications (No 113910- 001-01897475-97), 4% sodium alginate (Pharm.Art. No 42-3383-97 or Specifications (No 15-544-83; Arkhangelsk algal plant. Co), including 50 wt% amorphous hydroxyapatite (5-20 nm, Russia, Pharm.Art. No 42-3790- 99 or GOST 12.1.007-76) (SA-HA), in the ratio of chitosan ascorbate and sodium alginate 1:1 (CH-SA-HA) [
42]. The gel mass was placed into vials in a volume of 2 ml, lyophilized and sterilized electronically.
7.2 grams of chitosan are added to the prepared solution of ascorbic acid (Pharm.Art. No 42-2668-95) with stirring at a temperature of + 20-22° C, the mass is stirred for 4-5 hours until the chitosan is completely dissolved. Aqueous solutions of sodium salts of chondroitin sulfuric acid, hyaluronic acid, and heparin are successively added to the resulting 4% chitosan solution with constant slow stirring using a magnetic stirrer in a total volume equal to the volume of chitosan ascorbate. The introduction of each subsequent ingredient is carried out after the homogeneous mixing of the previous one with the chitosan gel. As a result, a 2% chitosan polyionic complex is obtained. Next, a 4% aqueous solution (gel) of sodium alginate is prepared, 50% (by dry weight) of hydroxyapatite is added. The finished chitosan solution is thoroughly mixed with the sodium alginate solution using a high-speed mixer.
2.2. Experimental animals
The conditions of biological test systems in the CDI CI correspond to Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th edition, 2011, NRC, USA (Manual on the content and use of laboratory animals, 8th edition, 2011, national research Committee, USA). The maintenance of animals in individually ventilated cells from polysulfone Sealsafe, 461×274×228 mm (production TECHNIPLAST. P. A.). The rooms, which contain biological test systems, controlled temperature (18-24° C), humidity (30-70%), illumination (12/12 h), the multiplicity of air (XII without recirculation). Control of climatic parameters is carried out in accordance with the SOP "control of climatic parameters in the premises of the vivarium." The distribution of feed and water is carried out at a fixed time, the change of litter is made once a week in accordance with the SOP "preparation of cells for biological test systems. Marking. Change of bedding, feed, water".
2.3. Modeling defects of the critical size of the mandibular angle in rats
The study was conducted on 84 female Wistar rats weighing 200-250 g. Laboratory animals were divided into 1 control and 1 study group. Each group was subjected to a morphometric study at 3 and 5 days, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8 and 10 weeks. The study group included 40 animals, in which an extensive defect in the lower jaw was modeled, followed by the filling of the bone cavity with a polymeric construct: chitosan ascorbate-sodium alginate-hydroxyapatite (CH-SA-HA). The control group included 44 animals with an identical bone cavity filled with a natural intraoperative blood clot at the same time of observation. Anesthesia was performed using a mixture of tiletamine/zolazepam at a dose of 2 mg/rat (Zoletil 100, Vibrac, France) and xylazil (Rometar, Bioveta, Czech Republic) at a dose of 0.02 ml/rat in a ratio of 1:1. The mixture was injected in a volume of 0.5 ml intramuscularly, then the skin in the lower jaw area was treated using an aqueous solution of chlorhexidine, an incision was made on the lower jaw in the area of the masticatory ridge 1.5-2 cm long masseter and periosteum, a rounded three-wall defect 4 x 5 x 5 mm3 in size was applied on the masticatory ridge with a dental spherical burr. While burring, the bone was cooled with an aqueous 0.2% chlorhexidine solution (series CHG-013/17 J. Amphrey Laboratories, India). The cavity of the bone defect was dried with tampons and filled with CH-SA-HA lyophilic mass or auto-blood clot formed when bleeding from a wound, the defect was closed with periosteum, and the skin was sutured with separate 5.0 monofilament sutures. The wound was treated with 1% aqueous solution of chlorhexidine. In order to prevent the development of the inflammatory process, all animals were injected intramuscularly with the antibacterial drug Ceftriaxone at a dose of 8 mg/rat, the antihistamine drug Suprastin at a dose of 0.1 mg/rat. Within three days after surgery, the animals received Tramadol 2.5 mg 2 times a day. During the first day, access to water was provided. Feeding was carried out 24 hours after the operation with an exclusively liquid mixture "Polyproten-Nefro" using soy protein Supra 760 (USA) (LLC "Protenfarma", Russia) for 3 days. Medical support was provided by a broad-spectrum antibiotic (ceftriaxone at a dose of 8 mg/rat), antispasmodics, and vasodilators. The sutures were removed on the 7th day after surgery.
2.4. Morphological analysis of bone tissue
The mandibles of the animals were placed in a 10% solution of buffered formalin, then fragments of the bodies of the mandibles were separated in the area of the postoperative defect with the capture of unchanged bone along the perimeter for 5 mm and placed in the decalcifying solution "Trilon B" for a period of 24-48 hours. The decalcified fragments were dehydrated in increasing concentrations of isopropyl alcohol and embedded in paraffin wax. On a MicroTec CUT4050 microtome, serial sections (20-25 sections) of 4-5 µm in thickness were made in the transverse plane (relative to the animal's body) through the entire area of the bone defect in the area of its outer and inner walls. Sections were stained with hematoxylin-eosin and picrofuchsin according to van Gieson. The morphological study was carried out on an Olympus BX45 microscope with an Olympus DP 25 attachment for photo-video documentation and the Cell^D software package, as well as with scanning histological preparations in a FLASH 250 3D HISTECH histoscanner (Hungary). Histo-morphometric evaluation was performed on digital micrographs, which were obtained using the software "Cell^D" and "NIS-Elements Document", while morphometric measurements were performed in the program "JMicroVision 1.2.7". Digital histological sections obtained as a result of scanning micro-preparations in a histoscanner were evaluated using the CaseViewer Ver.2.3 Build 2.3.9.99276 3D HISTECH software (Hungary).
Bone tissue recovery was assessed according to the following histomorphometric criteria: volumetric density of bone and connective tissue (BV (%), the percentage ratio of the volume occupied by bone structures to the total volume of the histological section); thickness of bone trabeculae (BTT (mm), the criterion stipulates that the bone trabecula is a thin plate, measurements were taken between the edges of the bone trabecula (5-8 measurements in relation to each trabecula with the calculation of the median); intertrabecular spaces (ITS (mm), the distance between the edges of the cancellous bone trabeculae, the calculation is made in accordance with the so-called parallel plate model: BV minus BTT (mm); volumetric density of osteoid and vessels (OS (%), the percentage ratio of the surface of bone trabeculae occupied by osteoid to the total bone surface); numerical density of inflammatory cell infiltrate (%) (fibroblasts, segmented leukocytes, histiocytes, giant multinucleated cells); bulk density of the implant (%); free bone surface area (FS (%), the percentage of the non-eroded surface of bone trabeculae and the surface not occupied by osteoblasts, osteoclasts to the total bone surface); area filled with osteoblastic cells of bone trabeculae (OBS, the percentage ratio of the surface of bone trabeculae occupied by osteoblasts to the total bone surface); eroded (osteoclastic) surface of bone trabeculae area (ES (%), the percentage ratio of the surface of bone trabeculae with the formation of gaps to the total bone surface, includes the surface occupied by osteoclasts. The numerical density of cell structures was measured as the number of cells in relation to the area of the field of view. The relative density of the measured structures was determined by the formula: RDS (%) = (Sa/St)*100, where Sa is the total area of all selected areas, St is the area of the digital image.
2.5. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis of data and the creation of graphic illustrations were carried out using the free software computing environment "R, version 4.2.1" and the programming language "R". The assessment of the obtained variables in relation to compliance with the normal (Gaussian) distribution was carried out on the basis of the Shapiro-Wilk test, as well as on the basis of the graphical method (Quantile-Quantile plot). Most of the variables obtained obeyed the normal distribution law, and the cases of deviation of the variables from the normal distribution were not pronounced. For variables deviating from the normal distribution, the following methods of data transformation were used to achieve compliance with the normal distribution: with right-sided (positive) skewness, square roots were taken from the obtained values, and in the case of left-sided (negative) skewness, the formula was used -
, where “X” is the value obtained. Descriptive statistics of the obtained data were presented as median, 25% and 75% quartiles (Me[Q
1;Q
3]). During the choosing statistical tests for assessing the type I error (α) and the sensitivity of the criterion (1-β), parametric methods of statistical analysis were used: one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), for paired comparisons of independent variables, Welch's t-test was used, for multiple comparisons, we used Bonferroni amendment. The presented variants of assessments were carried out taking into account the equality of variances, the variables under study, as well as taking into account the level of sensitivity of the criteria not lower than p=0.75. To assess the error of the first kind, taking into account the small volume of the studied samples, the threshold value p=0.01 was used. The design of the pilot study is shown in
Figure 1.
3. Results
3.1. Morphological analysis of bone tissue restoration in the early stages in the defect zone.
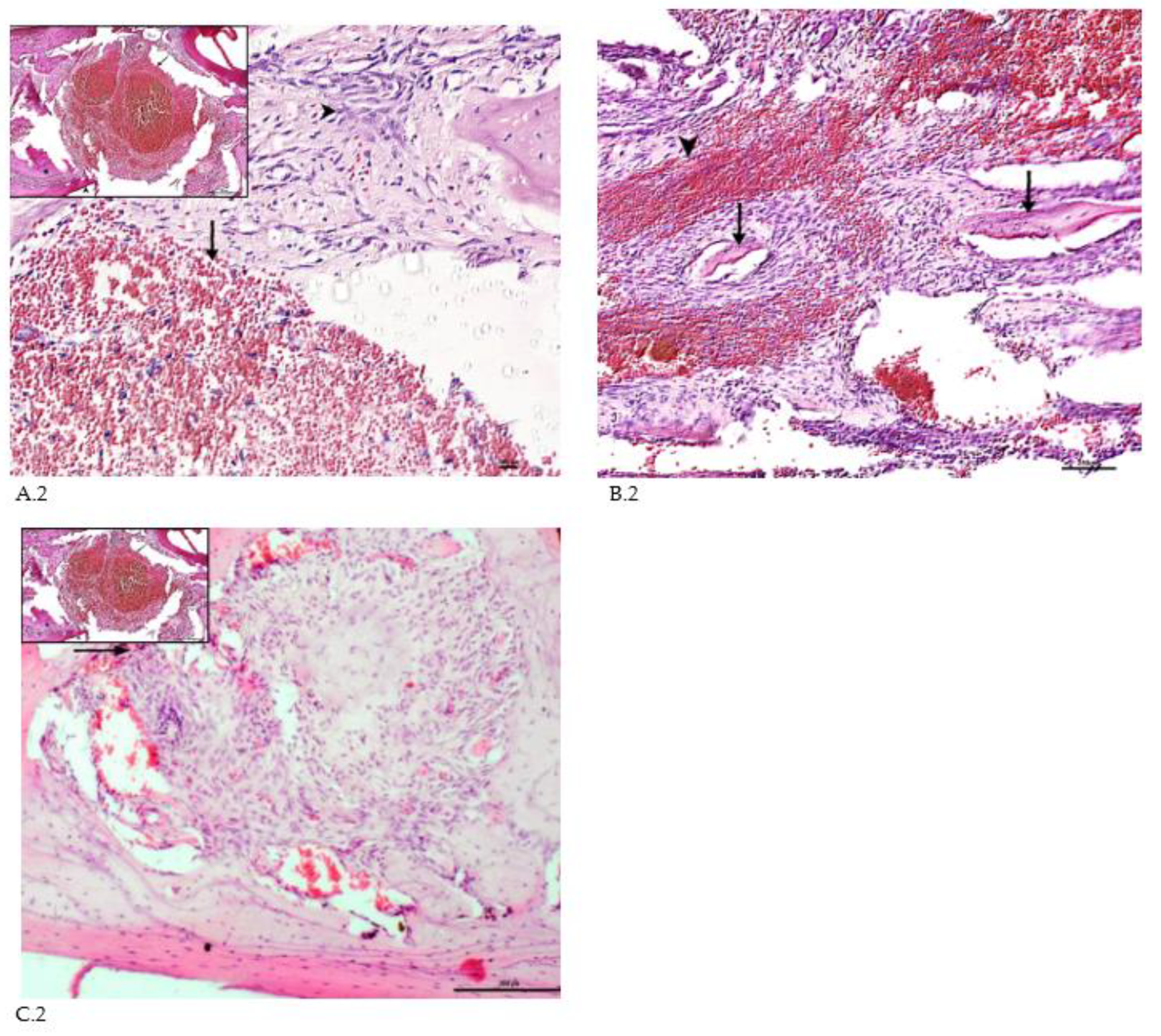
Plain microscopy of histological preparations in the area of the postoperative defect of the lower jaws of healthy rats removed after 3 days of the experiment revealed extensive foci of hemorrhagic impregnation (Fig.A.2, upper left corner) in combination with severe inflammatory infiltration and a clear predominance of segmented leukocytes. Among other cells of the inflammatory infiltrate, the presence of lymphocytes, histiocytes, fibroblasts and plasma cells was noted. There were also visualized signs of the formation of granulation tissue with a pronounced edematous extracellular matrix and numerous thin-walled capillaries. In histological preparations from the group with implanted "CH-SA-HA" biopolymer, along with the changes described above, abundant, diffusely distributed amphophilic granules of a foreign substance were determined. In histological preparations on the 5th and 7th days of the experiment, a similar microscopic picture was noted with an important feature, which was characterized by the appearance of eosinophilic "islands" of bone tissue formation with the presence of cubic and polygonal cells on the surfaces of cells with weakly basophilic cytoplasm and spherical nuclei - osteoblasts (Fig.B.2). Single large cells with multiple spherical nuclei and homogeneous "foamy" cytoplasm - osteoclasts - were also detected. In some preparations, these cells were absent. In separate preparations on the 7th day of the experiment of both study groups, along with bone tissue, the formation of small areas of cartilage tissue was noted. In the walls of the bone defect, the migration of mesenchymal stromal cells towards the blood clot is typical in the earliest stages (Fig.A.2). For the control group, after 1 week, only the filling of the bone cavity with immature connective tissue is typical (Fig.C.2). Thus, the processes of bone formation, even in the early stages, are the most active in the experimental group of animals.
Figure 2.
Regeneration of a bone defect in the lower jaw at the early stages of the experiment. A.2 – experimental group, day 3 of the experiment, there is no bone tissue at the site of the defect, mesenchymal stromal cells (^) migrate to the area of the blood clot (↑) for further differentiation into osteoblasts; in the upper left corner of the control group, day 3 of the experiment, a formed defect with a blood clot (↑) is visible, the periodontal ligament (*) and the cortical plate of the lower jaw (^) are visible; B.2 - CH-SA-HA group, day 7 of the experiment, islets of regenerating bone tissue (↑) in the area of hemorrhagic impregnation (^); C.2 – control group, day 7 of the experiment, the bone defect is filled with immature connective tissue (↑).
Figure 2.
Regeneration of a bone defect in the lower jaw at the early stages of the experiment. A.2 – experimental group, day 3 of the experiment, there is no bone tissue at the site of the defect, mesenchymal stromal cells (^) migrate to the area of the blood clot (↑) for further differentiation into osteoblasts; in the upper left corner of the control group, day 3 of the experiment, a formed defect with a blood clot (↑) is visible, the periodontal ligament (*) and the cortical plate of the lower jaw (^) are visible; B.2 - CH-SA-HA group, day 7 of the experiment, islets of regenerating bone tissue (↑) in the area of hemorrhagic impregnation (^); C.2 – control group, day 7 of the experiment, the bone defect is filled with immature connective tissue (↑).
The assessment of the numerical density of the inflammatory infiltrate was made per unit area - 0.043 mm2, which corresponded to the area of the field of view displayed on the monitor screen at x400 magnification. The presented histomorphometric criterion was not studied after the experiment period of 3 weeks due to the complete elimination of pathomorphological signs of inflammation. As shown in
Table 1, in multiple comparisons using one-way analysis of variance, there was a significant influence of factors such as the timing of the experiment and group affiliation at each time interval of the experiment. Indicators of the numerical density of the inflammatory infiltrate in the early stages after surgery significantly increased daily in both studied groups (p<0.01), while in the group of animals with implanted biopolymer "CH-SA-HA" the objective indicator of cell infiltration from the 3rd to the 7th day of the experiment increased by 57% (p<0.01), while in the control group the same range of changes was only 36% (p<0.01)(
Table 1).
Thus, the processes occurring at week 1 correspond to the first stage of bone tissue regeneration (the formation of an osteoid island) and are characterized by the appearance of inflammatory infiltrate cells, the number of which increases every day, and osteoblastic differon cells that trigger the process of osteogenesis. When comparing the ongoing process of regeneration in the animals of the control and experimental groups, it follows that in the animals of the experimental group, the inflammation process is less pronounced, osteoblasts appear in greater numbers earlier, and osteoid islands are formed already in the first week.
3.2. Regeneration of bone tissue in the defect area within 2-4 weeks
After 2 weeks of observation in both study groups, there was a more than twofold decrease in the volume of the numerical density of the inflammatory infiltrate (p<0.01). In pairwise comparisons, the numerical density of the inflammatory infiltrate in the experimental group was significantly lower (P<0.01) at all estimated time intervals of the experiment, except for the period of 3 weeks In pairwise comparisons, the digital values of the numerical density of the inflammatory infiltrate in the peripheral zone of the bone defect (experiment) were significantly lower by more than 2 times (p<0.01) compared with the values in the zone of the bone defect proper (
Table 2).
The application of a large bone injury in the lower jaw triggers the mechanism of early bone resorption in both groups with an active osteoclastic reaction, especially at the periphery of the defect (
Table 1, 2, 3), followed by active replacement with new bone. The activity of bone resorption in the peripheral zone exceeds 12-15 times when compared with the area of the bone defect. The control group of animals is characterized by a long reaction of bone destruction with a slower formation of spongy and especially compact bone (p<0.01).
On the 2nd and 3rd weeks of the experiment, formed bone beams were visualized in the area of the inflicted defect, on the surfaces of which numerous osteoblasts were detected, mostly of a cubic shape (Fig. A.3, B.3). The volume density of bone tissue and the osteoblastic surface during these periods prevail in the preparations of the experimental group animals (
Table 2). The volume of surfaces of bone beams occupied by osteoblasts in preparations of 3 weeks was noticeably lower when compared with preparations of previous time intervals. In both study groups, few osteoclasts were detected with the formation of characteristic lacunae (Fig. A.3. The structure of most bone beams was characterized by ordered fibers. The density of cellular infiltrate in comparison with the previous time intervals was noticeably lower among the dense connective tissue structures and was characterized by mild infiltration, mainly by histiocytes and fibroblasts. In the group of animals after CH-SA-HA implantation, diffusely distributed, finely dispersed amphophilic granules containing a polysaccharide construct were detected.
Figure 3.
Changes in the area of the bone defect characterizing the active phase of bone tissue regeneration in healthy and experimental groups of rats: A.3 - CH-SA-HA group, 2nd week of the experiment. On the surface of the bone beams (
*), multiple osteoblasts are visible (
↑), and a formed gap with an osteoclast is also visible (

). Hematoxylin-eosin staining; B.3 - control group. 2nd week of the experiment, the osteoblastic surface of the bone beams is significantly less in comparison with the experimental group (
↑). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Figure 3.
Changes in the area of the bone defect characterizing the active phase of bone tissue regeneration in healthy and experimental groups of rats: A.3 - CH-SA-HA group, 2nd week of the experiment. On the surface of the bone beams (
*), multiple osteoblasts are visible (
↑), and a formed gap with an osteoclast is also visible (

). Hematoxylin-eosin staining; B.3 - control group. 2nd week of the experiment, the osteoblastic surface of the bone beams is significantly less in comparison with the experimental group (
↑). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
By the end of 1 week after surgery, the volumetric density of bone tissue increases many times, both in the experiment and in the control. However, starting from the 2nd week, the value of BS in the experiment significantly exceeds the control results. In fact, in the first month of the experiment, the bulk of the newly formed bone tissue with high growth rates of the spongy and compact components is laid in the experiment (
Table 2). A high inflammatory reaction in the intrinsic zone of the bone defect is combined with a low level of inflammation in the peripheral zone and a stable picture of bone tissue volume at a distance of 5 mm from the zone of inflammation in the first 6 weeks of the experiment (p<0.01). Filling the surface of the bony trabeculae with cell mass leads to thickening of the trabeculae and contraction of the intertrabecular spaces and the inactive free bone surface. In the first 2 weeks, the increase in the thickness of bone trabeculae in the experiment is 100%, in the control 83%. The walls of the bone cavity in the control after 3 weeks - in the form of thin bone beams with pronounced intertrabecular spaces and poor cell mass (Figure A.4).
The 4th week in the experimental group shows a newly formed bone in the defect zone, a large proportion of the surfaces of the bone beams are already free from cells, which indicates a partial process of completion of osteogenesis. (Figure B.4). However, in almost all periods of registration, the spongy part of the bone wall of the defect in the experimental group was filled significantly higher with osteoblastic cell mass (
Table 1,
Table 2,
Table 3). The analysis shows that after 4 weeks, a late final stage of bone resorption is formed, as indicated by a significantly higher number of osteoclastic type cells with the formation of lacunar surfaces. In the bones of the experimental group of animals, signs of small focal accumulations of the implanted polymer are preserved.
Figure 4.
A.4 – The control group, 3rd week of the experiment, formed thin bone trabeculae in the area of the defect (
↑) with pronounced intertrabecular spaces (
), bone trabeculae are covered with cell mass (
^); B.4 - CH-SA-HA group, 4 weeks. Visible bone beams with predominantly free surfaces (↑) and intertrabecular spaces (
^), the adjacent peripheral area with the growth of maturing connective tissue (
*). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Figure 4.
A.4 – The control group, 3rd week of the experiment, formed thin bone trabeculae in the area of the defect (
↑) with pronounced intertrabecular spaces (
), bone trabeculae are covered with cell mass (
^); B.4 - CH-SA-HA group, 4 weeks. Visible bone beams with predominantly free surfaces (↑) and intertrabecular spaces (
^), the adjacent peripheral area with the growth of maturing connective tissue (
*). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Thus, the follow-up period of 2–4 weeks corresponds to the following stages of osteogenesis (osteoid and osteoid calcification stages), during which spongy bone is formed, represented by bone trabeculae and wide intertrabecular spaces filled with developing bone marrow. Reticulofibrous bone tissue is involved in the construction of this bone. The processes occurring during these periods are characterized by a decrease in the number of inflammatory infiltrate, high osteoblastic activity. Animals of the experimental group in the indicated time periods are characterized by a high volumetric density of the newly formed bone tissue.
3.3. Regeneration of bone tissue in the defect area within 6-10 weeks
After 6 weeks (
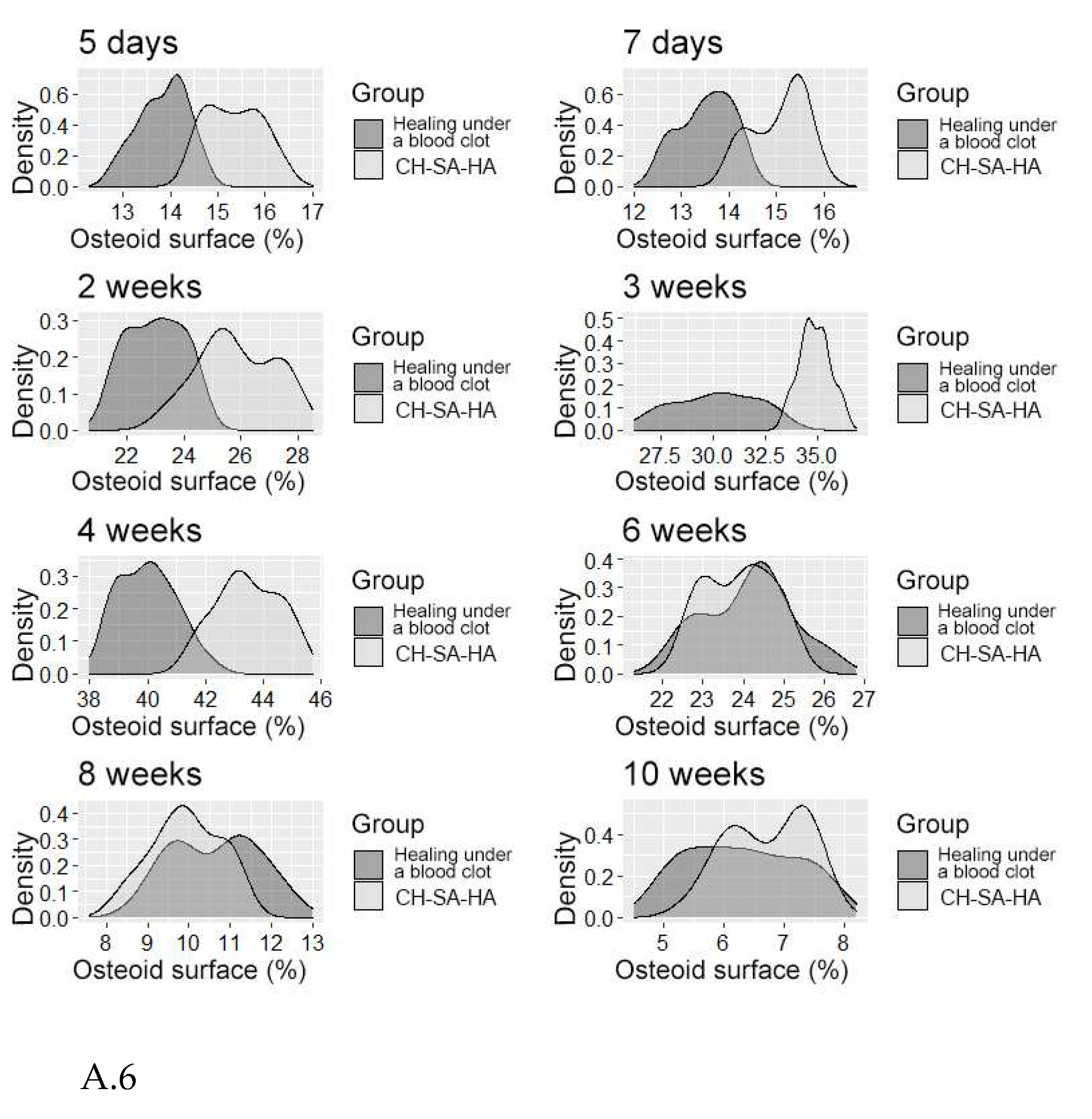
Table 3), the activity of osteomalacia processes sharply and steadily decreases to its original value. Active early and prolonged (within 6 weeks) osteoblastic reaction in the experimental group provides early formation of the osteoid matrix, ready for the mineralization of new bone. The processes of osteoblastic reaction and osteoid formation proceed dynamically and synchronously (Figure A.5, A.6).
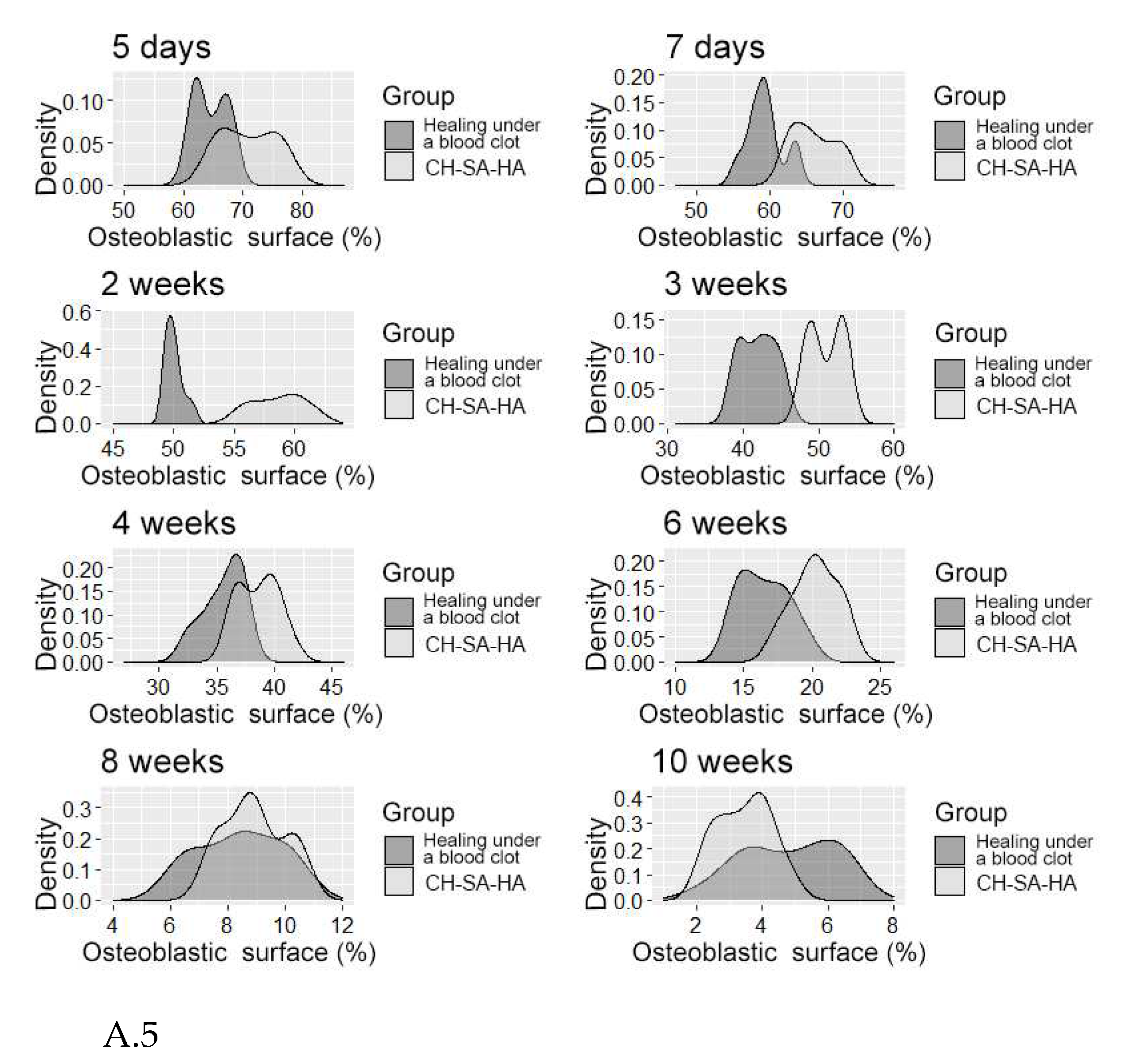
Figure 5.
A- The density distribution of the variable is "osteoblast surface".
Figure 5.
A- The density distribution of the variable is "osteoblast surface".
Figure 6.
A - The distribution density of the variable is "osteoid surface".
Figure 6.
A - The distribution density of the variable is "osteoid surface".
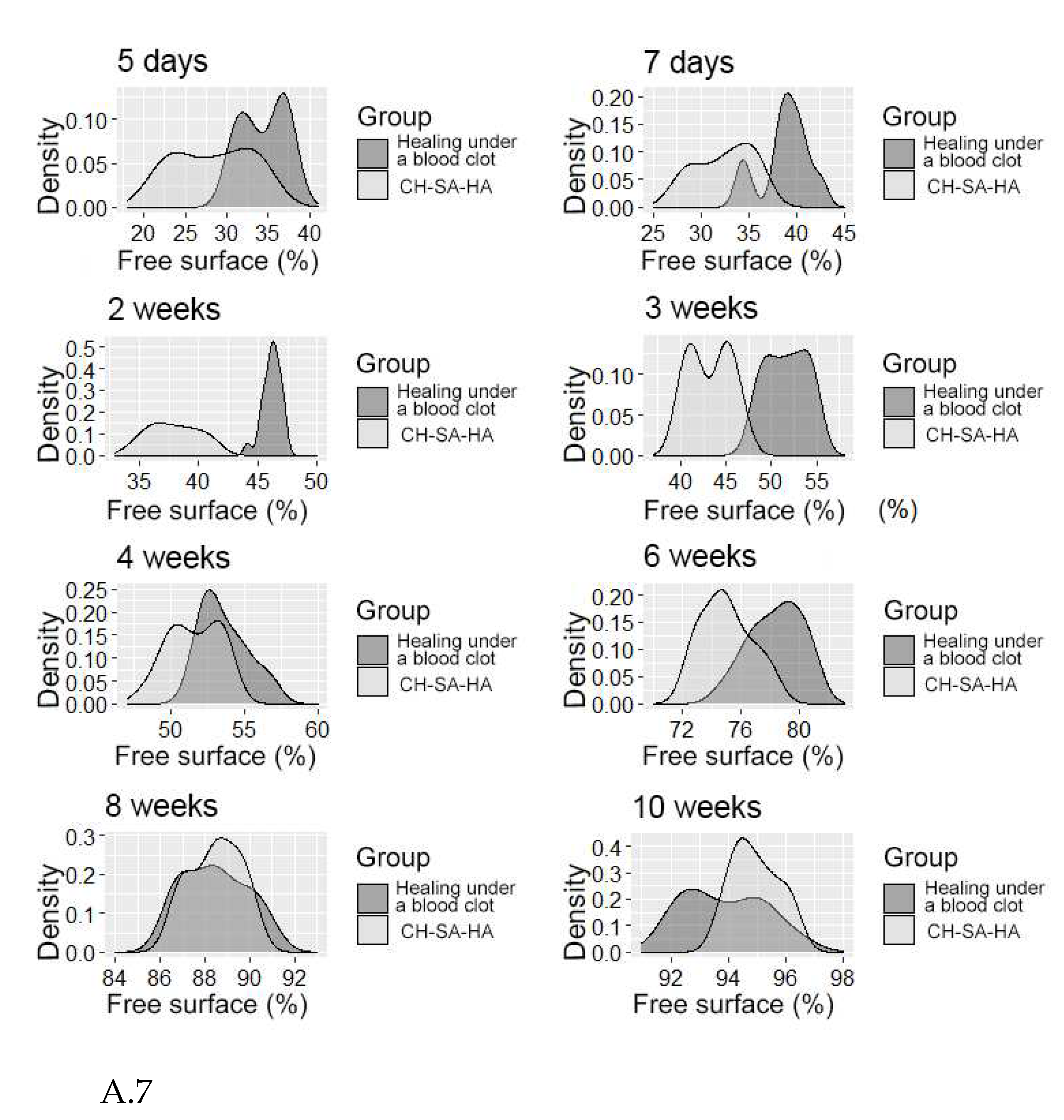
It should be pointed out that the activity in the dynamics of osteogenesis in the control group is significantly lower than the results of the experiment. The inactive zone of the bone cavity walls (FS%) occupies a significant area during the first 6 weeks of the regeneration process (Figure A.7).
Figure 7.
A- The distribution density of the variable is the "free surface" in the studied groups at different times of the experiment.
Figure 7.
A- The distribution density of the variable is the "free surface" in the studied groups at different times of the experiment.
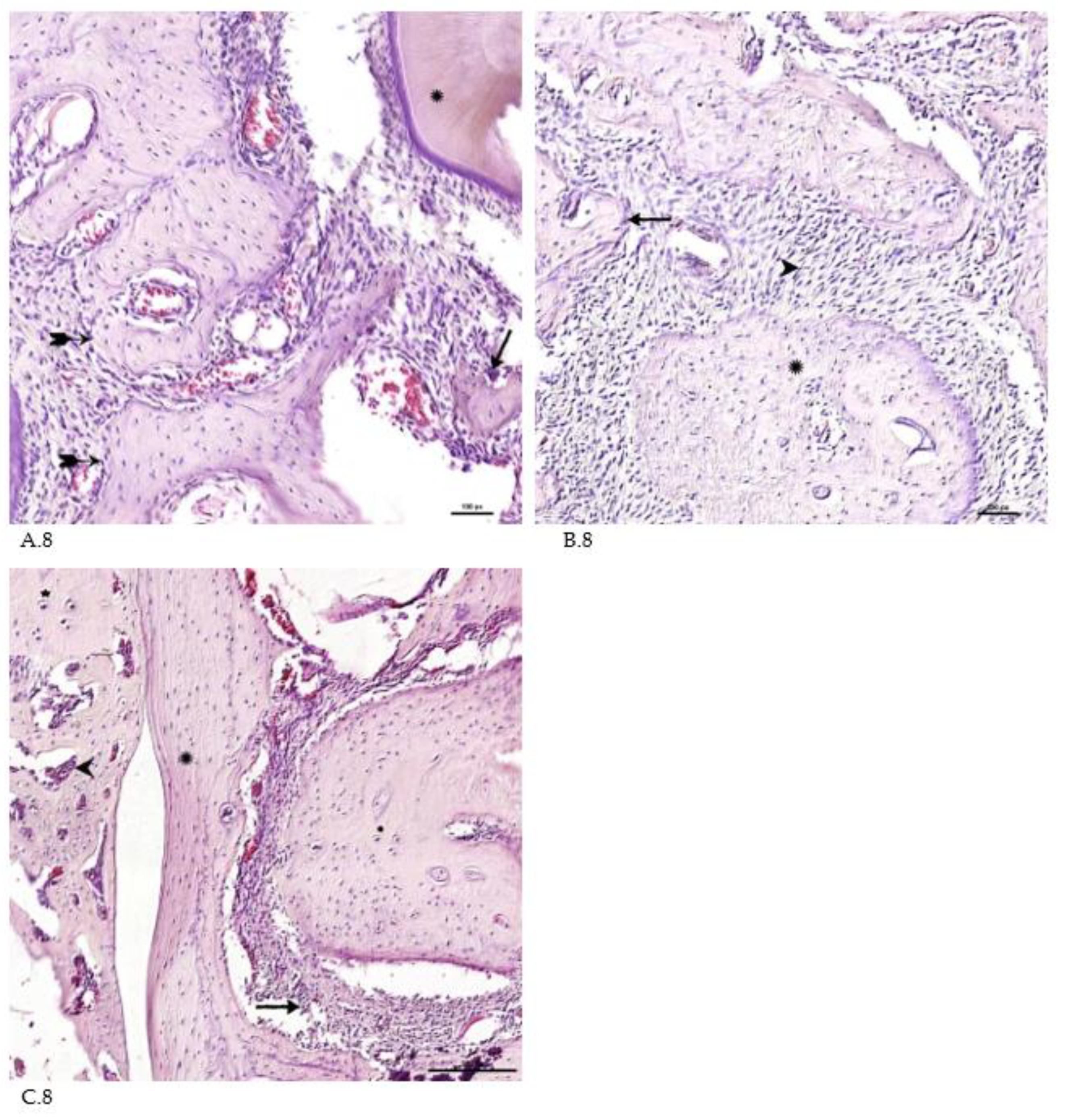
During the 6th and 8th weeks, spongy bone tissue predominates at the defect site with oriented bone trabeculae, flattened osteoblasts and single osteoclasts (Fig.A.8). 6 weeks after implantation of the CH-SA-HA biopolymer, rare small-focal accumulations of amphophilic granules with graft remnants were determined. After 8.10 weeks, foreign bodies were not detected. An important result is the active closure of a bone cavity of a critical size with full-fledged cancellous and compact bone, with formed osteons and Haversian canals with a vascular component (Figures B.8, C.8).
Figure 8.
Late terms of reorganization of the bone cavity in the experimental group. A.8 - 6 weeks, oriented bone beams with a mass of flattened osteoblasts (
), adjacent peripheral area with proliferation of maturing connective tissue, active vascular endothelialization of bone regeneration, single osteoclasts (
↑), organization of compact bone and periodontal ligament (
*); B.8 - 8 weeks, large amount of spongy (
^) and compact (
*) bone tissue with cellular reaction on the bone beams (
↑) and the formation of many micro-vessels; C.8 – experimental group, 10 weeks, the mandibular defect is closed by a compact bone, in the border zone there is mature connective tissue (
↑), in the adjacent bone tissue (
*) - reactive bone marrow structures (
^), formed osteons (*), many Haversian canals with a vascular component; Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Figure 8.
Late terms of reorganization of the bone cavity in the experimental group. A.8 - 6 weeks, oriented bone beams with a mass of flattened osteoblasts (
), adjacent peripheral area with proliferation of maturing connective tissue, active vascular endothelialization of bone regeneration, single osteoclasts (
↑), organization of compact bone and periodontal ligament (
*); B.8 - 8 weeks, large amount of spongy (
^) and compact (
*) bone tissue with cellular reaction on the bone beams (
↑) and the formation of many micro-vessels; C.8 – experimental group, 10 weeks, the mandibular defect is closed by a compact bone, in the border zone there is mature connective tissue (
↑), in the adjacent bone tissue (
*) - reactive bone marrow structures (
^), formed osteons (*), many Haversian canals with a vascular component; Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Thus, 6-10 weeks of the experiment correspond to the last stage of osteogenesis (formation of a compact bone or differentiation of reticufibrous bone tissue into lamellar bone tissue). At 6-8 weeks, high osteoblastic activity is still observed, the volume of the resulting bone increases and osteoclast cells are active, participating in the processes of tissue reorganization. All of these processes are most active in the experimental group of animals. By the 10th week of the experiment, lamellar bone tissue is formed, which is characterized by the presence of osteons in the bone trabeculae and the formation of Haversian canals. Animals of the experimental group are characterized by a high volumetric density of the emerging bone in earlier periods of regeneration.
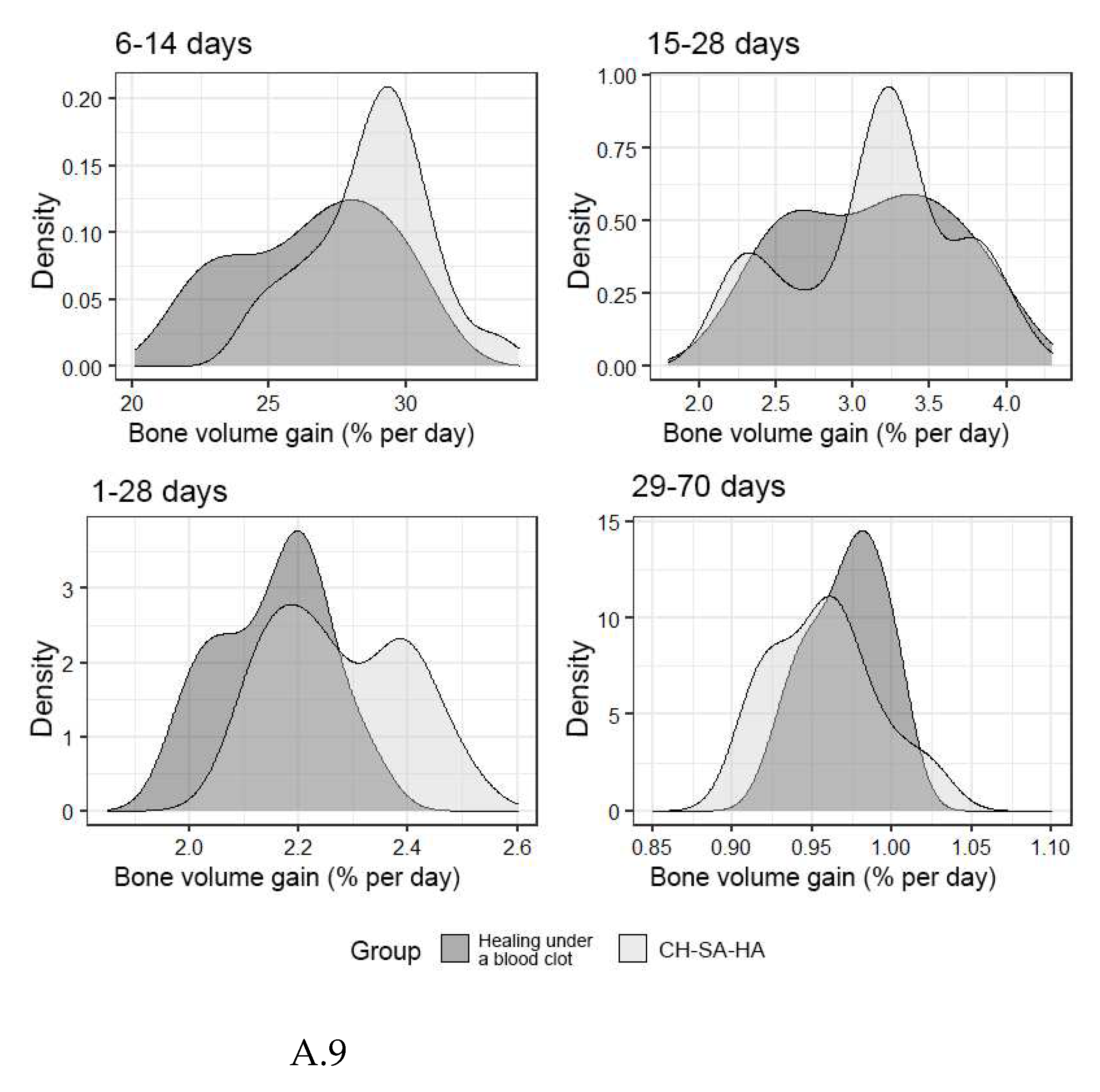
An important final result of bone defect regeneration is the rate of bone tissue growth as a percentage for 1 day. The results show that with an arbitrary choice of time intervals 1-28 days, 6-14 days, 15-28 days, 29-70 days, 1-70 days, the activity of osteogenesis processes changes significantly. One-way statistical analysis (ANOVA) established the significance (p<0.01) of the influence of the experimental period factor on the variable under consideration. Even though the growth rate for the entire period of the experiment (70 days) was 0.94% per day in the group with implanted CH-SA-HA biopolymer and 0.96% per day in the control group, a high rate of bone tissue growth in the focus regeneration was observed in the time interval of 6-14 days. In the group with implanted biopolymer, the growth rate was 28.9% per day, and in the control group this figure was 27.2% per day. Statistical analysis based on Welch's T-test showed that this difference was significant (p<0.01). Analysis over a randomly selected period of 1-28 days also revealed significant differences (p<0.01) in favour of the group of animals implanted with CH-SA-HA biopolymer (Fig.A.9).
Figure 9.
A - The density of the distribution of the variable - "increase in bone volume" in the study groups at randomly selected intervals of the experiment.
Figure 9.
A - The density of the distribution of the variable - "increase in bone volume" in the study groups at randomly selected intervals of the experiment.
4. Summary
Early specialization of the cell mass on the walls of bone defects, proliferation and transition of osteoblasts into the structure during its biodegradation with rapid rearrangement of the bar structure and the formation of spongy bone is a characteristic reaction to the implantation of a complex polysaccharide matrix. Such a preliminary result is very important when it comes to eliminating an extensive bone cavity in a significant reduction in inflammatory infiltration in the area of damage, given the specificity of the microbial flora in the oral cavity. It should be noted that during the period of 70 days of the experiment, the most active periods of osteogenesis were revealed, which occupy the earliest period of bone formation compared to the control. The encouraging results of the study form a promising direction not only in maxillofacial surgery, but also in the field of dental transplantology, where tight contact between implants and bone is required.
Analysis of the results of regeneration of the spongy and compact parts of the bone in the works of other authors shows that the use of the product of the apatite base of the bone octacalcium phosphate (Ca
8H
2(PO
4)
6 ·5H2O), found in human dentin, is due to a higher activity of inclusion in the early process of bone regeneration [
43]. However, the implantation of such a construction into a human lower jaw defect 40 mm long, formed after the removal of a residual cyst with apical periodontitis, leads to the filling of the bone defect in the alveolar region only within 12 months against the background of the formation of the vascular network [
44].
The inclusion of chitosan in the complex, in addition to its other useful properties, is also due to the launch of the vascular network formation [
45].
The non-inclusion of collagen in the CH-SA-HA construct in this work is due to the initially poor mechanical properties of the polymer, which limit its use in biomedicine [
46,
47]. Despite the excellent biodegradable and high adhesive properties of collagen, maintaining active cell growth [
48], the mechanical properties of collagen matrices are difficult to tune in a wide range of values, collagen itself is not very well amenable to direct chemical modification without affecting its structure or biological activity. The triple helical structure of collagen is easily destroyed by environmental conditions (eg, pH, temperature), the number of engineering manipulations that can be achieved using collagen is limited [
49].
However, when protein ingredients are included in the constructs, there is always a risk of intensifying the inflammatory reaction in the defect zone and, as a result, subsequent destruction of both the maternal and newly formed tissues. For example, the inclusion of fibrin as a matrix is designed to support the initial stages of tissue regeneration. Despite the presence of this substrate, which is naturally associated with vasculature growth factors, increased fibrosis and scar tissue formation cannot be ruled out. This reaction prevents physiological tissue regeneration [
50].
And, nevertheless, the authors in their works do not refuse the use of type I collagen in combination with polysaccharides. Intermolecular crosslinking using physical or chemical methods [
51,
52] improves the framework properties of collagen. Co-polymerization of collagen and chitosan successfully solves this problem [
53], including the protective functions of macrophages and fibroblasts [
54], a significant increase in the biostability and antimicrobial activity of collagen.
Numerous publications on bone regeneration after the formation of a critical size bone cavity show that self-implantation of a multilayer microfiber of chitosan with a molecular weight of 200–300 kDa and a degree of deacetylation of 90% into a 5 mm femoral defect using mesenchymal stem cells differentiated in osteoblasts within 12 weeks does not lead to the final filling of the defect. Compared with the use of a bone allograft, the results of the regeneration volume were 1.5 times lower (p<0.01) [
55]. A blinded assessment revealed a mean score of 4.4 ± 1.3 for the implants made of chitosan and 5.9 ± 0.8 for bone allograft. The results showed strong statistical significance (p < 0.0001), as determined by one-way ANOVA. At the same time, a comparative analysis of the formation of vessels in the regenerate did not reveal the advantage of either chitosan or bone allograft (as determined by one-way ANOVA, p = 0.1419). A comparison of data from the experimental groups yielded no statistically significant differences, in terms of osteoclast numbers (one-way ANOVA; p = 0.7474).
Counting the number of osteoblasts in the defect zone revealed a clear advantage of the bone allograft (one-way ANOVA; p = 0.0077). The difficulty of closing large bone defects is confirmed in detailed studies by Casillas-Santana, M.A. et al. (2023). Using colloidal chitosan in combination with nano-hydroxyapatite or silver nanoparticles in the study, the authors did not achieve complete regeneration of a bone defect of a critical size after 6-8 weeks of observation, and received only 75% healing [
56]. This result was rated by the authors as very good. The low result of regeneration in many studies is probably due to the absence of anionic polysaccharides in the chitosan structure, for example, sodium alginate, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronate, and heparin in certain weight ratios that modify chitosan into a nanocomponent of the complex. Prospects for the use of complex chitosan constructs lie in the ability of the polymer itself to induce active osteogenic differentiation of stem cells and retain this property not only in vitro, but also in vivo. Such complex polymer structures with the inclusion of growth factors (for example, alginate + VGF
165, BMP
2) and a program of simultaneous elution into the bone cavity will allow closing bone defects of a critical size of any localization [
57]. Current reviews on the problems of periodontal restoration indicate that further extensive research is required with a need to focus on improving the biological interfacing between the graft material and the host tissues. Further approaches in the field of periodontal regeneration will rely on a combination of therapies with using improved biomaterial options [
58].
Discussion
Obtaining a morphological picture of early bone formation due to the active formation of the osteoid surface, starting from 5-7 days after surgery, and confirmation of this process during the first month after injury indicates the role of the polymer structure in the advanced regeneration of the cancellous part of the bone. The authors believe that the creation of specialized technologies and technical means for obtaining osteogenic matrices for direct transplantation into bone tissue defects in animals and humans is very important for subsequent widespread use in medical practice. Successfully constructed osteogenic matrices, when in contact with the wall of the bone cavity, are able to reduce or even exclude certain stages of osteogenesis, for example, the cartilaginous stage of development, and trigger the mechanisms of early bone formation. The absence of a well-perfused substrate in the affected area in the early stages after extensive trauma to the bone tissue, the lack of the ability of synthetic materials that do not contain growth factors and osteogenic cells to cover large bone defects of a critical size [
59] is one of the main problems in the long-term restoration of the integrity of cancellous and compact bones. Preservation of the viability of the mass of cellular material over a large extent of the bone defect should consist of obtaining a highly vascularized module in an artificial matrix and creating conditions for its integration into a hard tissue. The formation of microvessels is the basis for the physiologically active process of bone formation [
60]. Despite the successful solution of the issue of the beginning of early bone formation, the first stage of the process of reconstruction of the vascular network remains insufficiently understood from the point of view of the mechanism of contact interaction between the vascular endothelium and artificial or natural polymers. If polymer matrices in the form of nanoparticles are used (this design was used in the work of the authors), then this enhances the efficiency of the delivery of vector molecules to cells and leads to overexpression of angiogenesis molecules, enhances endothelial recruitment and new formation of blood microvessels [
61]. Stimulation of proliferation and translation of the vascular endothelium occurs outside the vascular wall into the tissue compartment [
62,
63,
64]. Using this postulate, it should be clarified that the formation of microvessels in the body of the matrix is an earlier stage of reconstruction, followed by osteogenesis [
62,
65,
66]. At the same time, one of the important conditions for the rapid integration of building material is, in addition to degradation, high biocompatibility, the manifestation of its own angiogenic qualities, the ability to block polysaccharide and protein structures on the microbial cell surface, which provide transmembrane transport, and the ability to block pain conduction on somatic cells. These properties are known to be possessed by natural polysaccharide materials of cationic, anionic or amphoteric structure. Modern approaches to solving the problem of vascularization also include the introduction of low molecular weight serum growth factors into the injury zone (for example, the serum growth factors in cattle "adgelon" used in the work) based on a biodegradable polymer framework, which plays the role not only of a depot of dislocation of growth factors, but also of a program their prolonged elution as a result of a certain rate of polymer biodegradation. Dosed elution of growth factors from a modern polysaccharide matrix forms new capillaries [
67]. Uncovering the mechanisms of the initial stages of angiogenesis will solve the problem of critical early osteogenesis. Thus, early vascular endothelialization of the artificial matrix is a primary promising task and will mean the oriented sprouting of precursors or specialized cells, as well as signalling molecules of intercellular interaction, and, as a result, an active process of early osteogenesis [
68]. Tight contact of the initially cell-free polysaccharide copolymer matrix with spongy and compact plates of the bone cavity with a certain filling of polymers with angiogenesis products triggers the process of matrix endothelization. Upon contact with the maternal vascular network, induced proliferation of the vascular endothelium and its translation into the subintimal zone occur, which culminates in an intensive neoplasm of microvessels. Under favourable conditions, this process captures the zone of the artificial matrix. The initial start of endothelialization ends with the rapid filling of the cell-free matrix with the vascular network. The osteoblastic and osteoclastic microenvironment of the vascular implant stimulates the rapid formation of cancellous and compact bone from the periphery to the centre of the implant. It is very important that the artificially created vascular network does not regress after the complete degradation of the implant. The use of sodium alginate in the work was based on the results of modern research on the use of this polymer for tissue engineering [
69,
70,
71]. However, weak mechanical strength and low activity of cell binding, especially in the hydrated state [
72], low thermal and electrical conductivity, and antibacterial activity during the creation of the polymer scaffold required the inclusion of other polymers in this design. The inclusion of other polymers or inorganic compounds in the alginate significantly improves the mechanical and functional properties of the new design. This is especially important when solving the problem of eliminating a bone tissue defect of a critical size. It has been shown that the inclusion of hydroxyapatite in scaffolds based on sodium alginate increases the stability of the scaffolds and opens access to the cell surface [
68], improves biocompatibility, changes the microrelief of the matrix surface, and increases adhesion and migration of osteoblasts [
35]. It has been shown [
36] that scaffolds based on alginate and hydroxyapatite enhance the local elimination of a bone defect since they do not cause inflammatory effects. The inclusion of various amounts of hydroxyapatite or alginate in the overall design reduces the rate of degradation in tissues.
It is known that the use of a chitosan membrane as a single polymer leads to the formation of new bone and cementum in single-wall intraosseous defects in large experimental animals [
73]. Physical or chemical synthesis with other polymers significantly increases the mechanical strength and elasticity of the hydrogel [
19]. The mutual penetration of individual polymers with the formation of hydrogel networks reinforces the structure, which is considered one of the best technologies for obtaining a composite with high mechanical properties [
74]. Such combined meshes were developed using alginate and chitosan [
20] or hyaluronic acid [
21,
22] for the purpose of bone tissue bioengineering. If a combination of chitosan with an alginate–hydroxyapatite framework is obtained [
24,
75,
76], then the gel matrix is stabilized due to the formation of polyelectrolyte complexes. The complexes are formed as a result of a weak interaction of oppositely charged chemical groups of COO
- alginate and NH
3+ of chitosan. In addition, NH
3+ groups can interact with PO
43- hydroxyapatite groups, linking the framework together and forming a more compact structure. In this case, porosity and degradation rate decrease, and mechanical stability increases [
76]. If we are talking about the destruction of periodontal tissues in the experiment, then filling a bone defect with a complex of chitosan with a polyanionic structure, for example, collagen [
77], leads to inhibition of the apical migration of the epithelium and active formation of new bone and cementum. Such dynamics are due to the induction of the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into cementoblasts. The introduction of additional natural polysaccharide polymers into the structure leads to obtaining not only excellent mechanical strength, but, which is very important, to the active implementation of cellular functions such as adhesion, proliferation and differentiation. For example, a composite scaffold consisting of a combination of chitosan, alginate, hydroxyapatite, and cellulose nanocrystals possesses such properties, which is especially valuable for bone tissue engineering. Attention should be paid to the use of sulfated polysaccharides such as heparin in the preparation of functional copolymers. Three sulfo groups in the heparin molecule allow large rigid linear polymers to be converted into nanosized globules, which predetermines their high mobility in living animal tissues [
7]. The high specific affinity of heparin for growth factors, for example, bFGF, is due to the presence of a mechanism of active electrostatic interaction between the negatively charged sulfate groups of heparin and the positively charged amino acid residues of the growth factor [
35]. The high affinity of heparin for growth factors ensures high protein loading into the construct. The higher the growth factor loading, the higher the effect of angiogenesis. It has been established that bioactive growth factors must be slowly released from scaffolds to achieve long-term therapeutic effects [
78]. Long-term dosed release into the medium, for example, of the main fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) significantly increases the angiogenic effect and capillary density in a short time [
79,
80]. However, this growth factor has a short half-life [
81] and rapid diffusion from the injury site. Therefore, its practical application should be carried out in combination with a polysaccharide matrix. A copolymer alginate-chitosan structure containing additional anionic polysaccharides as a delivery system for growth factors can be a promising solution in the formation of a vascular bed not only in the bone cavity, but also in the polymer matrix proper.
Statement of Authorship
Patlataya, N. - participated in the design, participated in the acquisition of investments, drafted the manuscript, ensuring integrity and accuracy; Bolshakov I. - participated in the concept and design, participated in the acquisition of material and analysis, compiled the manuscript, critically edited the manuscript; Levenets A. - contributed to the idea, contributed to the interpretation of the results, critically revised the manuscript; Medvedeva N. - participated in the design, analysis and interpretation of the results of morphometric measurements, critically edited the manuscript; Khorzhevskii V. - participated in the design, analysis and interpretation of the results of morphometric measurements, critically edited the manuscript; Cherkashina M. - professional English translation of medical information, preparation of a literature review for a specific project. All authors gave their final approval and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Protocol of the Bioethical Commission for Working with Animals at the Local Ethics Committee of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Prof. V.F. Voino-Yasenetsky Krasnoyarsk State Medical University" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation (No1 November 30, 2017). The Application for Scientific Experimental Research has been provided in the following wording: To the chairman of the local ethics committee Prof. Demko I.V. from Prof. Department of Operative Surgery and topographic anatomy Bolshakov I.N.
Petition. In connection with the implementation of a complex scientific topic (headed by Prof. I. N. Bolshakov) No. 01201362513 (2013.01.01-2021.01.01) "Fundamental and applied scientific and technical development of nano- level biopolymer structures and technologies for their production for use in cellular and tissue engineering for socially significant human diseases "I ask permission to conduct experimental scientific work in the section of medicine" dentistry "on animals (white laboratory rats) according to the research protocol, research objectives, design, analysis plan). The study protocol was registered with the local ethical committee of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Education Prof. V.F. Voino-Yasenetsky Krasnoyarsk State Medical University" of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. The protocol was prepared and registered before the research.
The maintenance and disposal of experimental animals corresponds to the sanitary and epidemiological standard established for an educational and scientific institution in the Russian Federation.
 ). Hematoxylin-eosin staining; B.3 - control group. 2nd week of the experiment, the osteoblastic surface of the bone beams is significantly less in comparison with the experimental group (↑). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
). Hematoxylin-eosin staining; B.3 - control group. 2nd week of the experiment, the osteoblastic surface of the bone beams is significantly less in comparison with the experimental group (↑). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
 ). Hematoxylin-eosin staining; B.3 - control group. 2nd week of the experiment, the osteoblastic surface of the bone beams is significantly less in comparison with the experimental group (↑). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
). Hematoxylin-eosin staining; B.3 - control group. 2nd week of the experiment, the osteoblastic surface of the bone beams is significantly less in comparison with the experimental group (↑). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.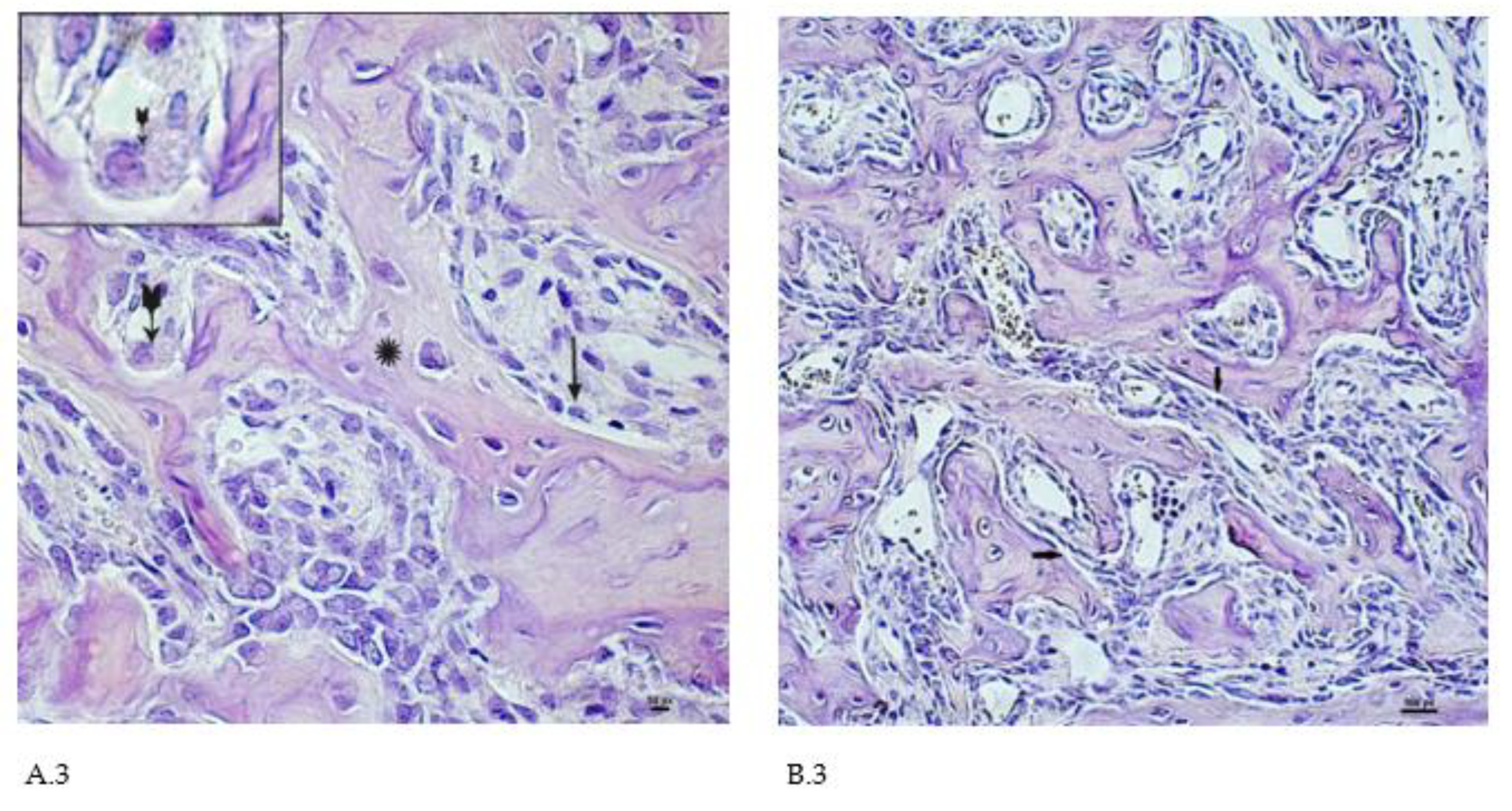
 ), bone trabeculae are covered with cell mass (^); B.4 - CH-SA-HA group, 4 weeks. Visible bone beams with predominantly free surfaces (↑) and intertrabecular spaces (^), the adjacent peripheral area with the growth of maturing connective tissue (*). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
), bone trabeculae are covered with cell mass (^); B.4 - CH-SA-HA group, 4 weeks. Visible bone beams with predominantly free surfaces (↑) and intertrabecular spaces (^), the adjacent peripheral area with the growth of maturing connective tissue (*). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
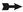 ), bone trabeculae are covered with cell mass (^); B.4 - CH-SA-HA group, 4 weeks. Visible bone beams with predominantly free surfaces (↑) and intertrabecular spaces (^), the adjacent peripheral area with the growth of maturing connective tissue (*). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
), bone trabeculae are covered with cell mass (^); B.4 - CH-SA-HA group, 4 weeks. Visible bone beams with predominantly free surfaces (↑) and intertrabecular spaces (^), the adjacent peripheral area with the growth of maturing connective tissue (*). Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
 ), adjacent peripheral area with proliferation of maturing connective tissue, active vascular endothelialization of bone regeneration, single osteoclasts (↑), organization of compact bone and periodontal ligament (*); B.8 - 8 weeks, large amount of spongy (^) and compact (*) bone tissue with cellular reaction on the bone beams (↑) and the formation of many micro-vessels; C.8 – experimental group, 10 weeks, the mandibular defect is closed by a compact bone, in the border zone there is mature connective tissue (↑), in the adjacent bone tissue (*) - reactive bone marrow structures (^), formed osteons (*), many Haversian canals with a vascular component; Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
), adjacent peripheral area with proliferation of maturing connective tissue, active vascular endothelialization of bone regeneration, single osteoclasts (↑), organization of compact bone and periodontal ligament (*); B.8 - 8 weeks, large amount of spongy (^) and compact (*) bone tissue with cellular reaction on the bone beams (↑) and the formation of many micro-vessels; C.8 – experimental group, 10 weeks, the mandibular defect is closed by a compact bone, in the border zone there is mature connective tissue (↑), in the adjacent bone tissue (*) - reactive bone marrow structures (^), formed osteons (*), many Haversian canals with a vascular component; Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
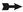 ), adjacent peripheral area with proliferation of maturing connective tissue, active vascular endothelialization of bone regeneration, single osteoclasts (↑), organization of compact bone and periodontal ligament (*); B.8 - 8 weeks, large amount of spongy (^) and compact (*) bone tissue with cellular reaction on the bone beams (↑) and the formation of many micro-vessels; C.8 – experimental group, 10 weeks, the mandibular defect is closed by a compact bone, in the border zone there is mature connective tissue (↑), in the adjacent bone tissue (*) - reactive bone marrow structures (^), formed osteons (*), many Haversian canals with a vascular component; Hematoxylin-eosin staining.
), adjacent peripheral area with proliferation of maturing connective tissue, active vascular endothelialization of bone regeneration, single osteoclasts (↑), organization of compact bone and periodontal ligament (*); B.8 - 8 weeks, large amount of spongy (^) and compact (*) bone tissue with cellular reaction on the bone beams (↑) and the formation of many micro-vessels; C.8 – experimental group, 10 weeks, the mandibular defect is closed by a compact bone, in the border zone there is mature connective tissue (↑), in the adjacent bone tissue (*) - reactive bone marrow structures (^), formed osteons (*), many Haversian canals with a vascular component; Hematoxylin-eosin staining.