Submitted:
13 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
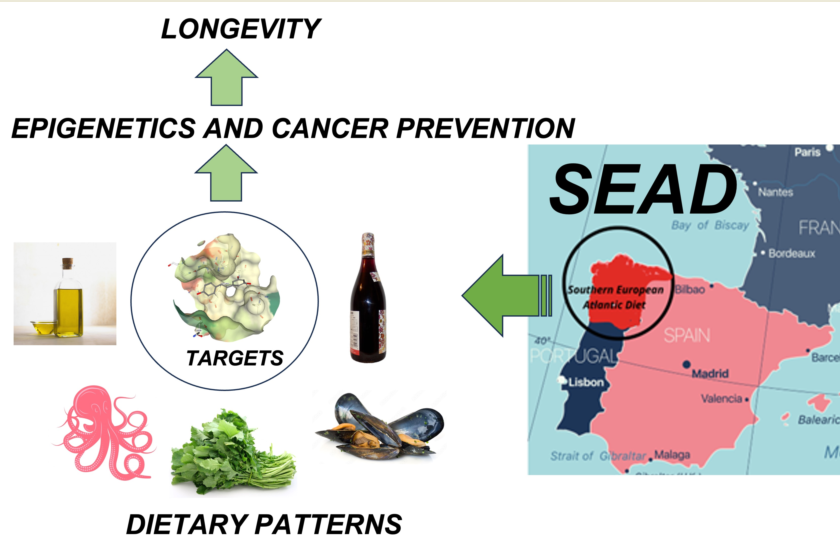
Keywords:
1. Introduction
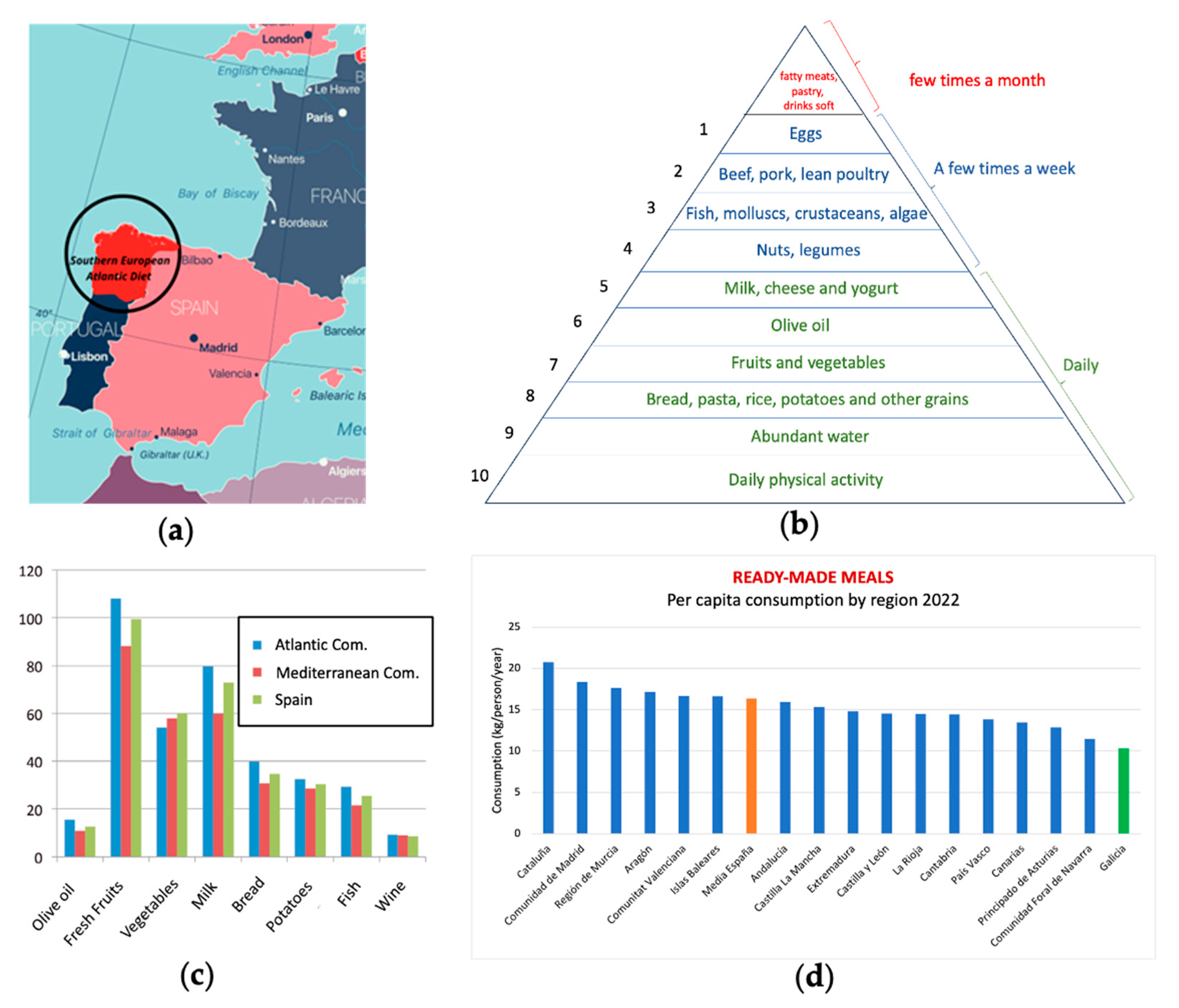

2. Materials and Methods
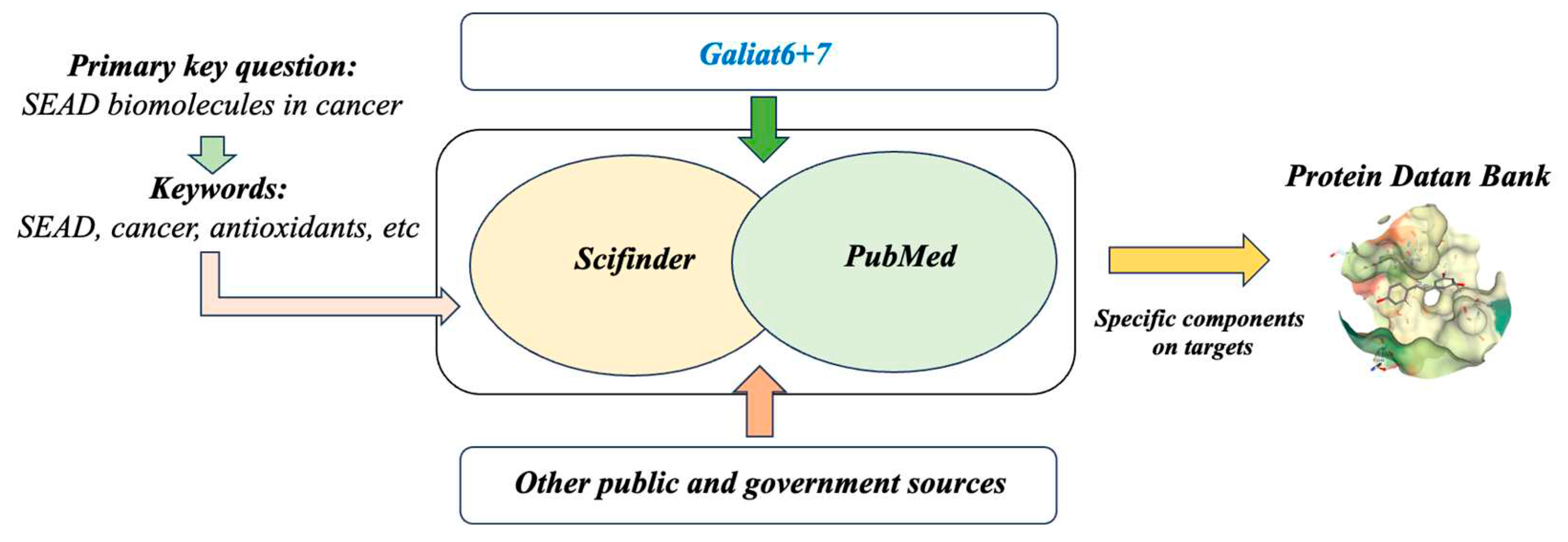
2.1. Research Question and Research Strategy
3. Discussion
3.1. Epigenetics and cancer. Longevity and benefits of the Atlantic diet. Previous studies.
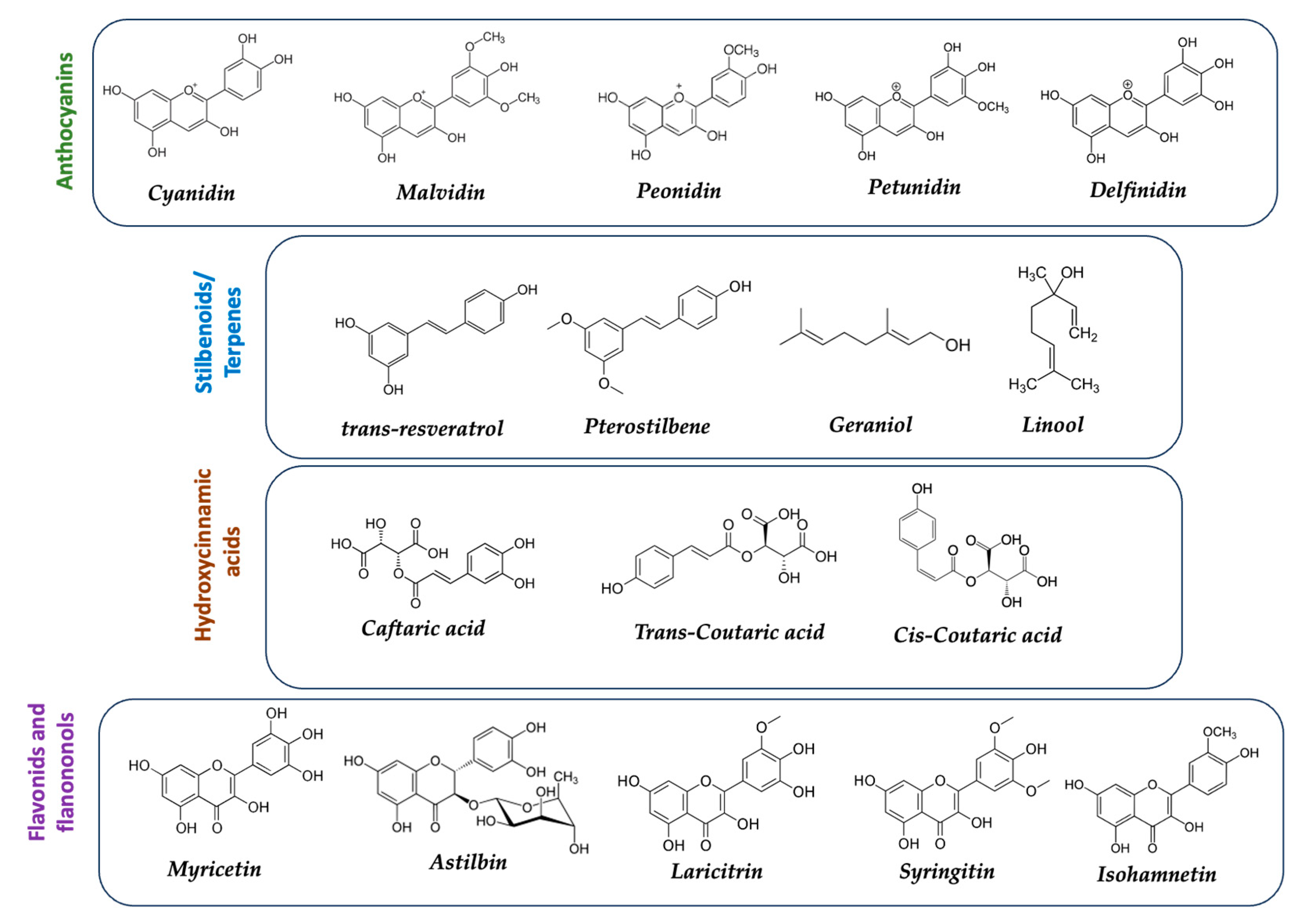
3.2. Nature of the components of the Southern European Atlantic Diet (SEAD)
3.3. Analysis of the foods and key components in the anticancer activity of the SEAD
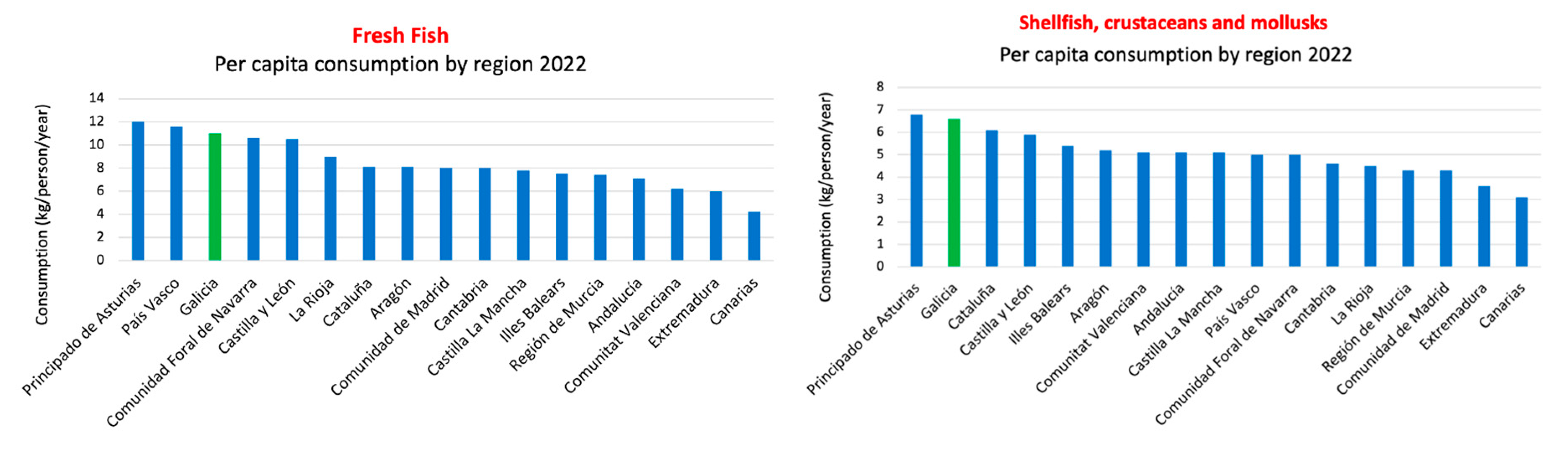
3.3.1. Mostly Consumed Fish and Seafood in the SEAD: Mussels, octopus and cod.
3.3.2. Genuine vegetables of the SEAD: Galician turnip top, garlic, potato, and Padrón pepper
3.3.3. Native olive oil
3.3.4. Native Chestnut of the SEAD
3.3.5. Autochthonous honey in the SEAD
3.3.6. Wines
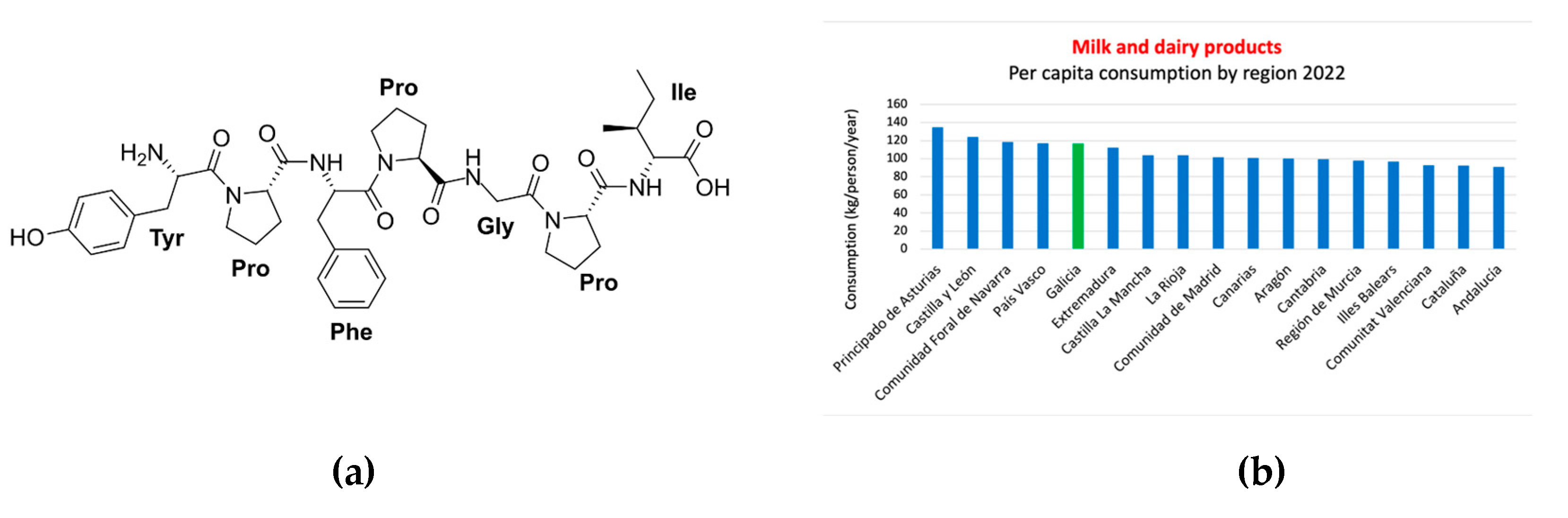
3.3.7. Milk and dairy derivatives
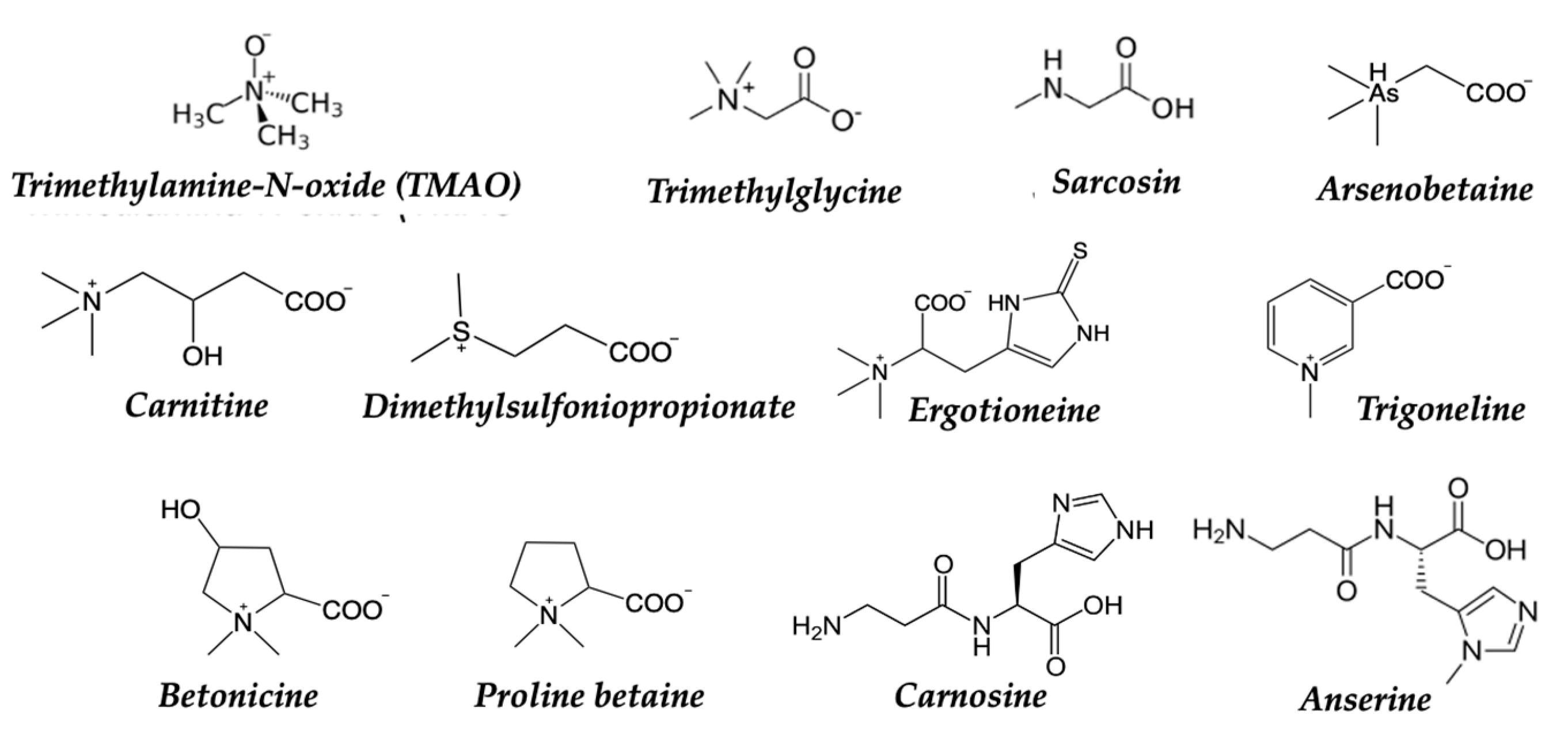
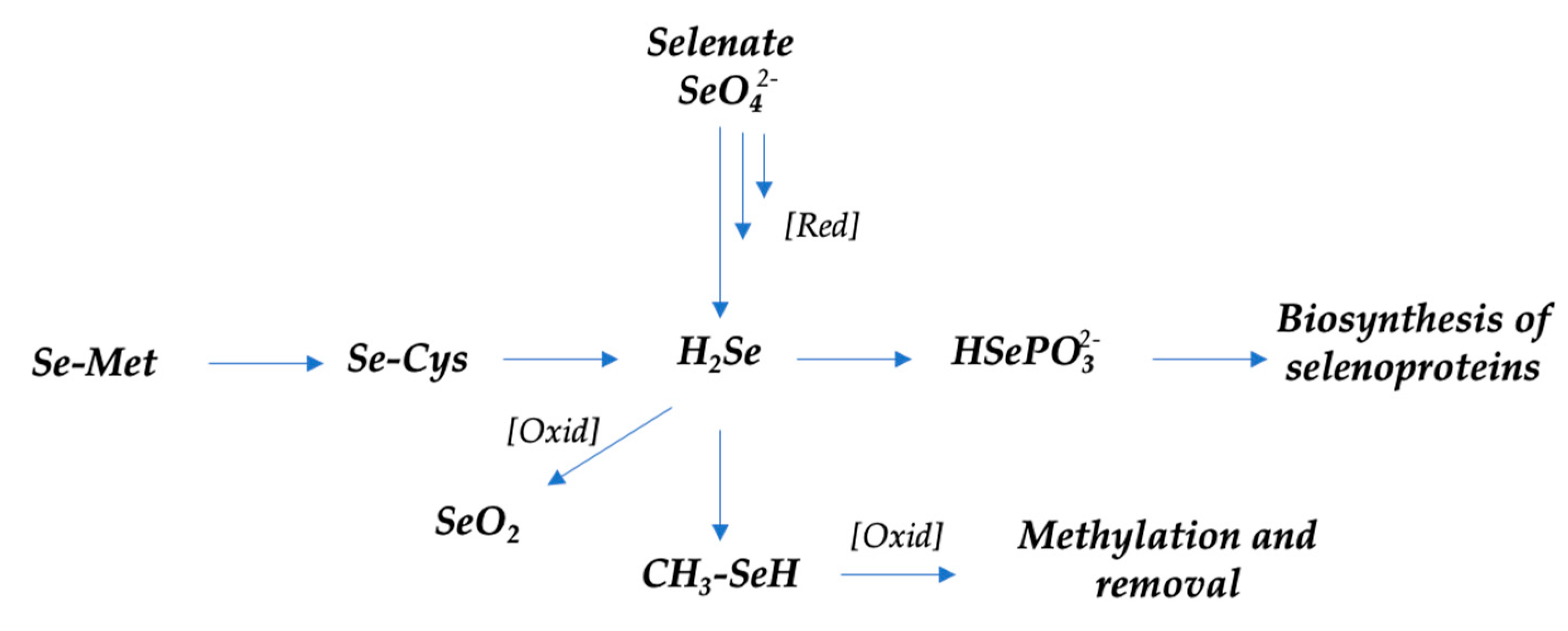
3.3.8. Dietary Supplementation in the SEAD
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Cancer, Https://Www.Who.Int/Health-Topics/Cancer#tab=tab_2, [Accessed 07/12/2023].
- International Agency for Research on Cancer; World Health Organization; Organización Panamericana de la Salud; Organización Mundial de la Salud Código Latinoamericano y Caribeño Contra El Cáncer, Https://Lacdev.Iarc.Who.Int, [Accessed 07/31/2023].
- Kliemann, N.; Al Nahas, A.; Vamos, E.P.; Touvier, M.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; Gunter, M.J.; Millett, C.; Huybrechts, I. Ultra-Processed Foods and Cancer Risk: From Global Food Systems to Individual Exposures and Mechanisms. Br J Cancer 2022, 127, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinberg, A.P.; Levchenko, A. Epigenetics as a Mediator of Plasticity in Cancer. Science 2023, 379, eaaw3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, T.M.; Tollefsbol, T.O. Epigenetic Diet: Impact on the Epigenome and Cancer. Epigenomics 2011, 3, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aune, D. Plant Foods, Antioxidant Biomarkers, and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease, Cancer, and Mortality: A Review of the Evidence. Advances in Nutrition 2019, 10, S404–S421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejera-Pérez, C.; Sánchez-Bao, A.; Bellido-Guerrero, D.; Casanueva, F.F. The Southern European Atlantic Diet. Minerva Endocrinol 2021, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Atlantic Diet – Origin and Features. IJFS 2016, 5. [CrossRef]
- Leis Trabazo, R.; De Lamas Pérez, C.; Castro Pérez, X.; Solla, P. Dieta atlántica. Nutrición y gastronomía en Galicia. Nutr Hosp 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundación Dieta Atlántica Bases Científicas de La Dieta Atlántica; Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico Campus Vida. Universidad de Santiago de Compostela, 2020; ISBN 978-94-17595-97-5.
- Carral, E.V.; Del Río, M.; López, Z. Gastronomy and Tourism: Socioeconomic and Territorial Implications in Santiago de Compostela-Galiza (NW Spain). IJERPH 2020, 17, 6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto González-Garcés Santiso; Federico Vilas Martín, Xosé Antón Álvarez Salgado Ría de Vigo [Material Cartográfico] : Una Aproximación Integral al Ecosistema Marino de La Ría de Vigo; Instituto de Estudios Vigueses.; Vigo, 2008; ISBN 978-84-89599-34-5.
- Lorenzo, P.M.; Izquierdo, A.G.; Rodriguez-Carnero, G.; Fernández-Pombo, A.; Iglesias, A.; Carreira, M.C.; Tejera, C.; Bellido, D.; Martinez-Olmos, M.A.; Leis, R.; et al. Epigenetic Effects of Healthy Foods and Lifestyle Habits from the Southern European Atlantic Diet Pattern: A Narrative Review. Advances in Nutrition 2022, 13, 1725–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación Informe Del Consumo Alimentario de España 2022. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Eu/Alimentacion/Temas/Consumo-Tendencias/Informe-Consumo-2022-Baja-Res_tcm35-655390.Pdf (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Axencia Galega da Calidade Alimentaria .Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación Ternera Gallega. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp/Carnes/IGP_Ternera_Gallega.Aspx (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Axencia Galega da Calidade Alimentaria .Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación Vaca Gallega / Buey Gallego. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp/Carnes/IGP_Vaca_Gallega-Buey_Gallego.Aspx (accessed on 11 July 2023).
- Dirección General de Desarrollo Rural y Agroalimentación. Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Calidad Diferenciada. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp, Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Dirección General de Desarrollo Rural y Agroalimentación. Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Ternera Asturiana. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp/Carnes/IGP_Ternera_Asturiana.Aspx (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Cooperativa Agrícola do Barroso, C. R. L. Direção-Geral de Agricultura e Desenvolvimento Rural Carne de Bovino Cruzado Dos Lameiros Do Barroso. Available online: Https://Tradicional.Dgadr.Gov.Pt/Pt/Cat/Carne/Carne-de-Bovino/552-Carne-de-Bovino-Cruzado-Dos-Lameiros-Do-Barroso-Igp (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Instituto Tecnológico Agrario (ITACYL) IGP Botillo Del Bierzo. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp/Embu_otros/IGP_botillo.Aspx (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Cermeño, P. Marine Planktonic Microbes Survived Climatic Instabilities in the Past. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2012, 279, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumin, J.; Nicolau, E.; Gonçalves De Oliveira Junior, R.; Fuentes-Grünewald, C.; Flynn, K.J.; Picot, L. A Bibliometric Analysis of Microalgae Research in the World, Europe, and the European Atlantic Area. Marine Drugs 2020, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usoltseva, R.V.; Belik, A.A.; Kusaykin, M.I.; Malyarenko, O.S.; Zvyagintsevа, T.N.; Ermakova, S.P. Laminarans and 1,3-β-D-Glucanases. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2020, 163, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, L. Fucoxanthin and Its Metabolite Fucoxanthinol in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Marine Drugs 2015, 13, 4784–4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafael Tojo Sierra, Rosaura Leis Trabazo La Dieta Atlántica. El Pescado y Las Algas. Su Importancia En El Neurodesarrollo y La Función Cerebral; 2009th ed.; Sevizo de Publicacions e Intercambio Científico.Universidad de Santiago de Compostelade USC: Santiago de Compostela, 2009; ISBN 978-84-9887-033-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, A.W.; Na, S.J.; Kim, W.K. Antioxidant Effects of Fucoxanthin Rich Powder in Rats Fed with High Fat Diet. Nutr Res Pract 2013, 7, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Malvar, M.; Benítez-Estévez, A.J.; Leis, R.; Sánchez-Castro, J.; Gude, F. Changes in Dietary Patterns through a Nutritional Intervention with a Traditional Atlantic Diet: The Galiat Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 4233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvo-Malvar, M.; Benítez-Estévez, A.J.; Sánchez-Castro, J.; Leis, R.; Gude, F. Effects of a Community-Based Behavioral Intervention with a Traditional Atlantic Diet on Cardiometabolic Risk Markers: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial (“The GALIAT Study”). Nutrients 2021, 13, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asociación Ourensividad Asociación Ourensividad, Https://Ourensividad.Com, [Accessed 07/31/2023]; Ourense.
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística. Número de Personas Centenarias En Ourense y Lugo.Ministerio de Economía y Hacienda(2022). Https://Www.Ine.Es/Jaxi/Datos.Htm?Path=/T20/E245/P04/Provi/L0/&file=0ccaa003.Px.[Accessed 07/18/2023].
- Bojang, K.P.; Manchana, V. Nutrition and Healthy Aging: A Review. Curr Nutr Rep 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, B.J.; Willcox, D.C.; Suzuki, M. Demographic, Phenotypic, and Genetic Characteristics of Centenarians in Okinawa and Japan: Part 1—Centenarians in Okinawa. Mechanisms of Ageing and Development 2017, 165, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carballo-Casla, A.; Ortolá, R.; García-Esquinas, E.; Oliveira, A.; Sotos-Prieto, M.; Lopes, C.; Lopez-Garcia, E.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. The Southern European Atlantic Diet and All-Cause Mortality in Older Adults. BMC Med 2021, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guallar-Castillón, P.; Oliveira, A.; Lopes, C.; López-García, E.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. The Southern European Atlantic Diet Is Associated with Lower Concentrations of Markers of Coronary Risk. Atherosclerosis 2013, 226, 502–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.; Lopes, C.; Rodríguez-Artalejo, F. Adherence to the Southern European Atlantic Diet and Occurrence of Nonfatal Acute Myocardial Infarction. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2010, 92, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gómez, B.; Rivas-Casais, A.; Lorences-Touzón, R.; Piedrafita-Páez, N.; Muñoz-Ferreiro, N.; Vázquez-Odériz, L.; Romero-Rodríguez, Á. Adherence to and Knowledge about the Atlantic Diet Pattern in the Senior Population of the Galician Region (NW-Spain). Journal of Functional Foods 2022, 91, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GALIAT 6+7; Grupo de Genética, Mejora y Bioquímica de Brásicas - Empresa A Rosaleira Proyecto: Potenciación de Biomoléculas Funcionales En Productos Alimentarios de Origen Gallego a Través de La Investigación Agrobiotecnológica,2017. Available online: Https://Galiat6mas7.Com/Fotos/Biblioteca/2Objetivos.Resultados.Public.AR-Brasicas2017.Pdf (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Sawan, C.; Herceg, Z. Histone Modifications and Cancer. In Advances in Genetics; Elsevier, 2010; Volume 70, pp. 57–85. ISBN 978-0-12-380866-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sapienza, C.; Issa, J.-P. Diet, Nutrition, and Cancer Epigenetics. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 665–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, A.L.; Bailly, N.; Meissner, A. DNA Methylation: A Historical Perspective. Trends in Genetics 2022, 38, 676–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riggs, A.D.; Jones, P.A. 5-Methylcytosine, Gene Regulation, and Cancer. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier, 1983; Volume 40, pp. 1–30. ISBN 978-0-12-006640-7. [Google Scholar]
- Einav Nili, G.-Y.; Saito, Y.; Egger, G.; Jones, P.A. Cancer Epigenetics: Modifications, Screening, and Therapy. Annu. Rev. Med. 2008, 59, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, K.D. DNA Methylation, Methyltransferases, and Cancer. Oncogene 2001, 20, 3139–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casalino, L.; Verde, P. Multifaceted Roles of DNA Methylation in Neoplastic Transformation, from Tumor Suppressors to EMT and Metastasis. Genes 2020, 11, 922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Jia, J.; Du, T.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Fang, D. Overview of Histone Modification. In Histone Mutations and Cancer; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Fang, D., Han, J., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; Volume 1283, pp. 1–16. ISBN 9789811581038. [Google Scholar]
- Bosutti, A.; Zanconati, F.; Grassi, G.; Dapas, B.; Passamonti, S.; Scaggiante, B. Epigenetic and MiRNAs Dysregulation in Prostate Cancer: The Role of Nutraceuticals. ACAMC 2016, 16, 1385–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leva, G.; Garofalo, M.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs in Cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2014, 9, 287–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watier, T.; Mj Sanchez, A. Micro-RNAs, Exercise and Cellular Plasticity in Humans: The Impact of Dietary Factors and Hypoxia. MIRNA 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyalçin, B.; Sanlier, N. The Effect of Diet Components on Cancer with Epigenetic Mechanisms. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2020, 102, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Cruz, N. S.; Bague, A. J. El Cáncer. Orígenes, Prevención y Dieta Durante Su Tratamiento; Ediciones Madrid, 2012; ISBN 978-84-96709-94-2.
- Mladěnka, P. Special Issue Dietary (Poly)Phenols and Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poljsak, B.; Milisav, I. The Role of Antioxidants in Cancer, Friends or Foes? CPD 2019, 24, 5234–5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, H.C.; Patrzyc, H.B.; Budzinski, E.E.; Dawidzik, J.B.; Freund, H.G.; Zeitouni, N.C.; Mahoney, M.C. Profiling Oxidative DNA Damage: Effects of Antioxidants. Cancer Sci 2012, 103, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzińska, A.; Juchaniuk, P.; Oberda, J.; Wiśniewska, J.; Wojdan, W.; Szklener, K.; Mańdziuk, S. Phytochemicals in Cancer Treatment and Cancer Prevention—Review on Epidemiological Data and Clinical Trials. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E. Indoles Derived From Glucobrassicin: Cancer Chemoprevention by Indole-3-Carbinol and 3,3’-Diindolylmethane. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 734334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pudenz, M.; Roth, K.; Gerhauser, C. Impact of Soy Isoflavones on the Epigenome in Cancer Prevention. Nutrients 2014, 6, 4218–4272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.-S.; Chiou, Y.-S.; Ho, C.-T.; Pan, M.-H. Chemoprevention by Resveratrol and Pterostilbene: Targeting on Epigenetic Regulation: Chemoprevention by Resveratrol and Pterostilbene. BioFactors 2018, 44, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandini, D.; Rao, R.; Deepak, B.; Reddy, P. Sulforaphane in Broccoli: The Green Chemoprevention! ! Role in Cancer Prevention and Therapy. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2020, 24, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamoto, K.; Hayashi, H.; Taniai, E.; Morita, R.; Imaoka, M.; Ishii, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Shibutani, M.; Mitsumori, K. Antioxidant N-Acetyl-L-Cysteine (NAC) Supplementation Reduces Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Mediated Hepatocellular Tumor Promotion of Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C) in Rats. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 36, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; He, F.; Wu, C.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Deng, J.; Zhu, G.; Ren, W.; Peng, Y. Betaine in Inflammation: Mechanistic Aspects and Applications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Marca, M.; Beffy, P.; Della Croce, C.; Gervasi, P.G.; Iori, R.; Puccinelli, E.; Longo, V. Structural Influence of Isothiocyanates on Expression of Cytochrome P450, Phase II Enzymes, and Activation of Nrf2 in Primary Rat Hepatocytes. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2012, 50, 2822–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.N.; Kim, Y.-W.; Keum, Y.-S. Mechanisms of Nrf2/Keap1-Dependent Phase II Cytoprotective and Detoxifying Gene Expression and Potential Cellular Targets of Chemopreventive Isothiocyanates. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2013, 2013, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, L.; Wang, Z.-Y. Breast Cancer Cell Growth Inhibition by Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Is Associated with Down-Regulation of Oestrogen Receptor-A36. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 2009, 14, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xunta de Galicia ORDEN de 20 de Marzo de 2019 Por La Que Se Aprueba El Reglamento de La Denominación de Origen Protegida Mexillón de Galicia-Mejillón de Galicia y Su Consejo Regulador. Available online: Https://Www.Xunta.Gal/Dog/Publicados/2019/20190408/AnuncioG0427-290319-0001_es.Html (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Arumugam, M.K.; Paal, M.C.; Donohue, T.M.; Ganesan, M.; Osna, N.A.; Kharbanda, K.K. Beneficial Effects of Betaine: A Comprehensive Review. Biology 2021, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Puyvelde, H.; Dimou, N.; Katsikari, A.; Indave Ruiz, B.I.; Godderis, L.; Huybrechts, I.; De Bacquer, D. The Association between Dietary Intakes of Methionine, Choline and Betaine and Breast Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancer Epidemiology 2023, 83, 102322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G. Important Roles of Dietary Taurine, Creatine, Carnosine, Anserine and 4-Hydroxyproline in Human Nutrition and Health. Amino Acids 2020, 52, 329–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, M.D.; Fraser, S.; Boer, J.C.; Plebanski, M.; De Courten, B.; Apostolopoulos, V. Anti-Cancer Effects of Carnosine—A Dipeptide Molecule. Molecules 2021, 26, 1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, S.P.; Williams, C.S. Selenoproteins in Tumorigenesis and Cancer Progression. In Advances in Cancer Research; Elsevier, 2017; Volume 136, pp. 49–83. ISBN 978-0-12-812016-3. [Google Scholar]
- Kuršvietienė, L.; Mongirdienė, A.; Bernatonienė, J.; Šulinskienė, J.; Stanevičienė, I. Selenium Anticancer Properties and Impact on Cellular Redox Status. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, G.F. Selenium in Global Food Systems. Br J Nutr 2001, 85, 517–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayman, M.P. The Use of High-Selenium Yeast to Raise Selenium Status: How Does It Measure Up? Br J Nutr 2004, 92, 557–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oficina Económica y Comercial de España en Rabat Informe Económico y Comercial En Marruecos. 2022. Available online: Https://Www.Icex.Es/Content/Dam/Es/Icex/Oficinas/097/Documentos/2022/09/Documentos-Anexos/DOC2022914490.Pdf (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Choi, E.-J.; Tang, Y.; Lee, C.B.; Cheong, S.H.; Park, P.-J.; Moon, S.-H.; Kim, E.-K. Investigation of Antioxidant and Anticancer Potential of Taurine by Means of Multiple Chemical and Biological Assays. In Taurine 9; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Marcinkiewicz, J., Schaffer, S.W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2015; Volume 803, pp. 179–189. ISBN 978-3-319-15125-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; He, F.; Kawanokuchi, J.; Wang, G.; Yamashita, T. Taurine and Its Anticancer Functions: In Vivo and In Vitro Study. In Taurine 12; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Schaffer, S.W., El Idrissi, A., Murakami, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; Volume 1370, pp. 121–128. ISBN 978-3-030-93336-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wieboldt, R.; Läubli, H. Glycosaminoglycans in Cancer Therapy. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 2022, 322, C1187–C1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayari, N.; Balti, R.; Ben Mansour, M.; Ben Amor, I.; Graiet, I.; Gargouri, J.; Bougatef, A. Anticoagulant Properties and Cytotoxic Effect against HCT116 Human Colon Cell Line of Sulfated Glycosaminoglycans Isolated from the Norway Lobster ( Nephrops Norvegicus ) Shell. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2016, 80, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, C.M.; Klüppel, M. Chondroitin Sulfate-E Is a Negative Regulator of a Pro-Tumorigenic Wnt/Beta-Catenin-Collagen 1 Axis in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, T.; Ali, S.A.; Ormerod, K.; Brust, A.; Roymanchadi, M.-L.; Ventura, S.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Mercier, A.J.; King, G.F.; et al. Functional Characterization on Invertebrate and Vertebrate Tissues of Tachykinin Peptides from Octopus Venoms. Peptides 2013, 47, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, C.A. The Mammalian Tachykinin Receptors. General Pharmacology: The Vascular System 1995, 26, 911–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawaja, A.M.; Rogers, D.F. Tachykinins: Receptor to Effector. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology 1996, 28, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Sanz, J.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Potriquet, J.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Brust, A.; Wilhelm, P.; Smallwood, T.B.; Clark, R.J.; Fry, B.G.; Alewood, P.F.; et al. ERK and MTORC1 Inhibitors Enhance the Anti-Cancer Capacity of the Octpep-1 Venom-Derived Peptide in Melanoma BRAF(V600E) Mutations. Toxins 2021, 13, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral-Sanz, J.; Fernandez-Rojo, M.A.; Colmenarejo, G.; Kurdyukov, S.; Brust, A.; Ragnarsson, L.; Andersson, Å.; Vila, S.F.; Cabezas-Sainz, P.; Wilhelm, P.; et al. The Structural Conformation of the Tachykinin Domain Drives the Anti-tumoural Activity of an Octopus Peptide in Melanoma BRAF V600E. British J Pharmacology 2022, 179, 4878–4896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Félix, C.; Wilson-Sánchez, G.; Cruz-Ramírez, S.-G.; Velázquez-Contreras, C.; Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Acosta, A.; Machi-Lara, L.; Aldana-Madrid, M.-L.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.-M.; Rocha-Alonzo, F.; et al. Bioactive Lipidic Extracts from Octopus ( Paraoctopus Limaculatus ): Antimutagenicity and Antiproliferative Studies. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013, 2013, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitahia, E.M.; Raheriniaina, C.E.; Bazin, M.A.; Huvelin, J.-M.; Logé, C.; Ranaivoson, E.; Nazih, H. Anti-Proliferative and Pro-Apoptotic Effect of Dichloromethane Extract of Octopus Vulgaris By-Products on Human Breast Cancer Cell Lines. Waste Biomass Valor 2015, 6, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zazueta, M.S.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; García-Romo, J.S.; Noguera-Artiaga, L.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Taboada-Antelo, P.; Campos-Vega, R.; Rosas-Burgos, E.C.; Burboa-Zazueta, M.G.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; et al. Bioactive Compounds from Octopus Vulgaris Ink Extracts Exerted Anti-Proliferative and Anti-Inflammatory Effects in Vitro. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2021, 151, 112119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Zazueta, M.S.; García-Romo, J.S.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Taboada-Antelo, P.; Rosas-Burgos, E.C.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; Martínez-Soto, J.M.; Candia-Plata, M. del C.; Santacruz-Ortega, H. del C.; et al. N-(2-Ozoazepan-3-Yl)-Pyrrolidine-2-Carboxamide, a Novel Octopus Vulgaris Ink-Derived Metabolite, Exhibits a pro-Apoptotic Effect on A549 Cancer Cell Line and Inhibits pro-Inflammatory Markers. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2023, 177, 113829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Zazueta, M.S.; García-Romo, J.S.; Noguera-Artiaga, L.; Luzardo-Ocampo, I.; Carbonell-Barrachina, Á.A.; Taboada-Antelo, P.; Campos-Vega, R.; Rosas-Burgos, E.C.; Burboa-Zazueta, M.G.; Ezquerra-Brauer, J.M.; et al. Octopus Vulgaris Ink Extracts Exhibit Antioxidant, Antimutagenic, Cytoprotective, Antiproliferative, and Proapoptotic Effects in Selected Human Cancer Cell Lines. Journal of Food Science 2021, 86, 587–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeljic, K.; Supic, G.; Magic, Z. New Insights into Vitamin D Anticancer Properties: Focus on MiRNA Modulation. Mol Genet Genomics 2017, 292, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de Agricultura, Pesca y alimentación Listado de Denominaciones de Origen Protegidas e Indicaciones Geográficas Protegidas de Vinos Registradas En La Unión Europea. Available online: Https://Www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/02_vinos_tcm30-426473.Pdf (accessed on 17 July 2023).
- Marta Francisco; Margarita Lema; Pablo Velasco Cultivo de Variedades Tradicionales de Brásicas En La Agricultura Ecológica. Available online: Https://Digital.Csic.Es/Bitstream/10261/87344/6/Cartea_Cultivo_variedades_tradicionales.pdf (accessed on 1 July 2023).
- Cao, Q.; Wang, G.; Peng, Y. A Critical Review on Phytochemical Profile and Biological Effects of Turnip (Brassica Rapa L.). Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 721733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkerk, R.; Schreiner, M.; Krumbein, A.; Ciska, E.; Holst, B.; Rowland, I.; De Schrijver, R.; Hansen, M.; Gerhäuser, C.; Mithen, R.; et al. Glucosinolates in Brassica Vegetables: The Influence of the Food Supply Chain on Intake, Bioavailability and Human Health. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, S219–S219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez-Iglesias, M. j.; Novio, S.; García-Santiago, C.; Cartea, M. e.; Soengas, P.; Velasco, P.; Freire-Garabal, M. Effects of 3-Butenyl Isothiocyanate on Phenotypically Different Prostate Cancer Cells. Int J Oncol 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, A.; He, M.; Krishna Vanaja, D.; Yin, P.; Karnes, R.J.; Young, C.Y.F. Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Inhibits STAT3 Activation in Prostate Cancer Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 878–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciska, E.; Martyniak-Przybyszewska, B.; Kozlowska, H. Content of Glucosinolates in Cruciferous Vegetables Grown at the Same Site for Two Years under Different Climatic Conditions. J Agric Food Chem 2000, 48, 2862–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkashty, O.A.; Tran, S.D. Sulforaphane as a Promising Natural Molecule for Cancer Prevention and Treatment. CURR MED SCI 2021, 41, 250–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, S.M.; Royce, S.G.; Licciardi, P.V.; Karagiannis, T.C. Dietary Sulforaphane in Cancer Chemoprevention: The Role of Epigenetic Regulation and HDAC Inhibition. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 2015, 22, 1382–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.-L.; Zhou, S.-J.; Zhang, X.-M.; Chen, H.-Q.; Liu, W. Sulforaphane Suppresses in Vitro and in Vivo Lung Tumorigenesis through Downregulation of HDAC Activity. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2016, 78, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Jiang, X.; Meng, L.; Dong, X.; Shen, Y.; Xin, Y. Anticancer Activity of Sulforaphane: The Epigenetic Mechanisms and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2018, 2018, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Dashwood, R.H. Epigenetic Regulation of NRF2/KEAP1 by Phytochemicals. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodova, M.; Fu, J.; Watkins, D.N.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Inhibition Provides Opportunities for Targeted Therapy by Sulforaphane in Regulating Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cell Self-Renewal. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Sun, R.; Zhao, T.; Wang, M.; Yan, C.; Liu, P. Sulforaphane Regulates the Proliferation of Leukemia Stem-like Cells via Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway. European Journal of Pharmacology 2022, 919, 174824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Sun, Y.; Huang, X.; Qiao, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, P.; Wang, M. Sulforaphane Inhibits Self-Renewal of Lung Cancer Stem Cells through the Modulation of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway and Polyhomeotic Homolog 3. AMB Expr 2021, 11, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernkopf, D.B.; Daum, G.; Brückner, M.; Behrens, J. Sulforaphane Inhibits Growth and Blocks Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling of Colorectal Cancer Cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 33982–33994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiei, H.; Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z. MicroRNAs as Novel Targets of Sulforaphane in Cancer Therapy: The Beginning of a New Tale? Phytotherapy Research 2020, 34, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Spagnuolo, C.; Russo, G.L.; Skalicka-Woźniak, K.; Daglia, M.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E.; Nabavi, S.F.; Nabavi, S.M. Nrf2 Targeting by Sulforaphane: A Potential Therapy for Cancer Treatment. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2018, 58, 1391–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Palliyaguru, D.L.; Kensler, T.W. Frugal Chemoprevention: Targeting Nrf2 with Foods Rich in Sulforaphane. Seminars in Oncology 2016, 43, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Sung, B.; Kang, Y.J.; Hwang, S.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Im, E.; Kim, N.D. Sulforaphane Inhibits Hypoxia-Induced HIF-1α and VEGF Expression and Migration of Human Colon Cancer Cells. International Journal of Oncology 2015, 47, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crichlow, G.V.; Fan, C.; Keeler, C.; Hodsdon, M.; Lolis, E.J. Structural Interactions Dictate the Kinetics of Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor Inhibition by Different Cancer-Preventive Isothiocyanates. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 7506–7514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Farias, M.; Carrasco-Pozo, C. The Anti-Cancer Effect of Quercetin: Molecular Implications in Cancer Metabolism. IJMS 2019, 20, 3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.-M.; Deng, X.-T.; Zhou, J.; Li, Q.-P.; Ge, X.-X.; Miao, L. Pharmacological Basis and New Insights of Quercetin Action in Respect to Its Anti-Cancer Effects. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 121, 109604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.S.; Bradley, A.R.; Valasatava, Y.; Duarte, J.M.; Prlic, A.; Rose, P.W. NGL Viewer: Web-Based Molecular Graphics for Large Complexes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3755–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Revalde, J.; Paxton, J.W. The Effects of Dietary and Herbal Phytochemicals on Drug Transporters. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2017, 116, 45–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marefati, N.; Ghorani, V.; Shakeri, F.; Boskabady, M.; Kianian, F.; Rezaee, R.; Boskabady, M.H. A Review of Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Immunomodulatory Effects of Allium Cepa and Its Main Constituents. Pharmaceutical Biology 2021, 59, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, H.; Boesch-Saadatmandi, C.; Regos, I.; Treutter, D.; Wolffram, S.; Rimbach, G. Effects of Quercetin and Catechin on Hepatic Glutathione-S Transferase (GST), NAD(P)H Quinone Oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), and Antioxidant Enzyme Activity Levels in Rats. Nutrition and Cancer 2009, 61, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawani, A.; Kumar, A. Structural Insight into the Interaction of Flavonoids with Human Telomeric Sequence. Sci Rep 2015, 5, 17574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megna, B.W.; Carney, P.R.; Nukaya, M.; Geiger, P.; Kennedy, G.D. Indole-3-Carbinol Induces Tumor Cell Death: Function Follows Form. Journal of Surgical Research 2016, 204, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujioka, N.; Fritz, V.; Upadhyaya, P.; Kassie, F.; Hecht, S.S. Research on Cruciferous Vegetables, Indole-3-Carbinol, and Cancer Prevention: A Tribute to Lee W. Wattenberg. Mol Nutr Food Res 2016, 60, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royston, K.J.; Tollefsbol, T.O. The Epigenetic Impact of Cruciferous Vegetables on Cancer Prevention. Curr Pharmacol Rep 2015, 1, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Kong, D.; Wang, Z.; Bao, B.; Hillman, G.G.; Sarkar, F.H. Attenuation of Multi-Targeted Proliferation-Linked Signaling by 3,3′-Diindolylmethane (DIM): From Bench to Clinic. Mutation Research/Reviews in Mutation Research 2011, 728, 47–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błoch-Mechkour, A.; Bally, T.; Sikora, A.; Michalski, R.; Marcinek, A.; Gȩbicki, J. Radicals and Radical Ions Derived from Indole, Indole-3-Carbinol and Diindolylmethane. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 6787–6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, W. Indole-3-Carbinol Stabilizes P53 to Induce MiR-34a, Which Targets LDHA to Block Aerobic Glycolysis in Liver Cancer Cells. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ruan, J.; Zhuang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z. Phytochemicals of Garlic: Promising Candidates for Cancer Therapy. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2020, 123, 109730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asemani, Y.; Zamani, N.; Bayat, M.; Amirghofran, Z. Allium Vegetables for Possible Future of Cancer Treatment. Phytotherapy Research 2019, 33, 3019–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jeong, J.H.; Kwon, S.W.; Lee, S.K.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, J.-H. Z-Ajoene Inhibits Growth of Colon Cancer by Promotion of CK1α Dependent β-Catenin Phosphorylation. Molecules 2020, 25, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaschula, C.H.; Tuveri, R.; Ngarande, E.; Dzobo, K.; Barnett, C.; Kusza, D.A.; Graham, L.M.; Katz, A.A.; Rafudeen, M.S.; Parker, M.I.; et al. The Garlic Compound Ajoene Covalently Binds Vimentin, Disrupts the Vimentin Network and Exerts Anti-Metastatic Activity in Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Luo, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, J.; Wang, M.; Sang, L.; Chang, B.; Wang, B. Allicin in Digestive System Cancer: From Biological Effects to Clinical Treatment. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 903259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, L.; Su, Q. Molecular Mechanisms for the Anti-Cancer Effects of Diallyl Disulfide. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2013, 57, 362–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consellería do Medio Rural Diario Oficial de Galicia (DOGA). 2016. Available online: Https://Www.Xunta.Gal/Dog/Publicados/2016/20160627/AnuncioG0426-140616-0003_es.Pdf (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Devaux, A.; Kromann, P.; Ortiz, O. Potatoes for Sustainable Global Food Security. Potato Res. 2014, 57, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, H.; Goyer, A.; Navarre, D.A. Antioxidants in Potatoes: A Functional View on One of the Major Food Crops Worldwide. Molecules 2021, 26, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolters, A.-M.A.; Uitdewilligen, J.G.A.M.L.; Kloosterman, B.A.; Hutten, R.C.B.; Visser, R.G.F.; Van Eck, H.J. Identification of Alleles of Carotenoid Pathway Genes Important for Zeaxanthin Accumulation in Potato Tubers. Plant Mol Biol 2010, 73, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.R.; Kim, T.S.; Ganga, Z.; Haynes, K.; De Jong, D.; Jahn, M.; Paran, I.; De Jong, W. Segregation of Total Carotenoid in High Level Potato Germplasm and Its Relationship to Beta-Carotene Hydroxylase Polymorphism. Am. J. Pot Res 2006, 83, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedor, J.; Burda, K. Potential Role of Carotenoids as Antioxidants in Human Health and Disease. Nutrients 2014, 6, 466–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministerio de agricultura, Pesca y Alimentación. Pliego de Condiciones IGP Pementos de Galicia. Available online: Https://www.Mapa.Gob.Es/Es/Alimentacion/Temas/Calidad-Diferenciada/Dop-Igp/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Mandal, S.K.; Rath, S.K.; Logesh, R.; Mishra, S.K.; Devkota, H.P.; Das, N. Capsicum annuum L. and Its Bioactive Constituents: A Critical Review of a Traditional Culinary Spice in Terms of Its Modern Pharmacological Potentials with Toxicological Issues. Phytotherapy Research 2023, 37, 965–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapa-Oliver, A.; Mejía-Teniente, L. Capsaicin: From Plants to a Cancer-Suppressing Agent. Molecules 2016, 21, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Vij, A.S.; Sharma, M. Mechanisms and Clinical Uses of Capsaicin. European Journal of Pharmacology 2013, 720, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Xiao, C.; Jiang, W.; Yang, W.; Qin, Q.; Tan, Q.; Lian, B.; Liang, Z.; Wei, C. Capsaicin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Breast Cancer by Down-Regulating FBI-1-Mediated NF-ΚB Pathway. DDDT 2021, Volume 15, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, T.; Ren, B.; Fan, Y.; Liu, T.; Hou, T.; Dan, W.; Liu, B.; Wei, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zeng, J.; et al. Capsaicin Inhibits the Migration, Invasion and EMT of Renal Cancer Cells by Inducing AMPK/MTOR-Mediated Autophagy. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2022, 366, 110043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xue, Y.; Fu, L.; Wang, Y.; He, M.; Zhao, L.; Liao, X. Extraction, Purification, Bioactivity and Pharmacological Effects of Capsaicin: A Review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2022, 62, 5322–5348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Laviada, I. Effect of Capsaicin on Prostate Cancer Cells. Future Oncology 2010, 6, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popescu, G.D.A.; Scheau, C.; Badarau, I.A.; Dumitrache, M.-D.; Caruntu, A.; Scheau, A.-E.; Costache, D.O.; Costache, R.S.; Constantin, C.; Neagu, M.; et al. The Effects of Capsaicin on Gastrointestinal Cancers. Molecules 2020, 26, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Y. Application of Capsaicin as a Potential New Therapeutic Drug in Human Cancers. J Clin Pharm Ther 2020, 45, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.; Lee, S.-H. Anticancer Properties of Capsaicin Against Human Cancer. Anticancer Res 2016, 36, 837–843. [Google Scholar]
- Xunta de Galicia Encuesta Sobre Los Hábitos Alimentarios de La Población Adulta Gallega. 2007. Available online: Https://www.Sergas.Es/Cas/Publicaciones/Docs/SaludPublica/PDF-2153-Es.Pdf (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) Identificadas Veinte Variedades de Olivo Autoctonas de Galicia Únicas En El Mundo. 2022. Available online: Https://Novedades-Ptis.Csic.Es/Digitalizacion-y-Sociedad-Futura/Identificadas-Veinte-Variedades-de-Olivo-Autoctonas-de-Galicia-Unicas-En-El-Mundo/ (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Borzì, A.; Biondi, A.; Basile, F.; Luca, S.; Vicari, E.; Vacante, M. Olive Oil Effects on Colorectal Cancer. Nutrients 2018, 11, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pablos, R.M.; Espinosa-Oliva, A.M.; Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Cano, M.; Arguelles, S. Hydroxytyrosol Protects from Aging Process via AMPK and Autophagy; a Review of Its Effects on Cancer, Metabolic Syndrome, Osteoporosis, Immune-Mediated and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmacological Research 2019, 143, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Las Hazas, M.C.L.; Rubio, L.; Macia, A.; Motilva, M.J. Hydroxytyrosol: Emerging Trends in Potential Therapeutic Applications. CPD 2018, 24, 2157–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilaplana-Pérez, C.; García-Flores, L.A.; Gil-Izquierdo, A. Hydroxytyrosol and Potential Uses in Cardiovascular Diseases, Cancer, and AIDS. Front. Nutr. 2014, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, R.; Fuccelli, R.; Pieravanti, F.; De Bartolomeo, A.; Morozzi, G. Production of Hydrogen Peroxide Is Responsible for the Induction of Apoptosis by Hydroxytyrosol on HL60 Cells. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkinson, L.; Keast, R. Oleocanthal, a Phenolic Derived from Virgin Olive Oil: A Review of the Beneficial Effects on Inflammatory Disease. IJMS 2014, 15, 12323–12334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdeno, A.; Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Rosillo, M.A.; De La Lastra, C.A. Oleuropein, a Secoiridoid Derived from Olive Tree, Inhibits the Proliferation of Human Colorectal Cancer Cell Through Downregulation of HIF-1α. Nutrition and Cancer 2013, 65, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boss, A.; Bishop, K.; Marlow, G.; Barnett, M.; Ferguson, L. Evidence to Support the Anti-Cancer Effect of Olive Leaf Extract and Future Directions. Nutrients 2016, 8, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefanis; Scimè; Accomazzo; Catti; Occhipinti; Bertea; Costelli Anti-Proliferative Effects of an Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Extract Enriched in Ligstroside Aglycone and Oleocanthal on Human Liver Cancer Cell Lines. Cancers 2019, 11, 1640. [CrossRef]
- Emma, M.R.; Augello, G.; Di Stefano, V.; Azzolina, A.; Giannitrapani, L.; Montalto, G.; Cervello, M.; Cusimano, A. Potential Uses of Olive Oil Secoiridoids for the Prevention and Treatment of Cancer: A Narrative Review of Preclinical Studies. IJMS 2021, 22, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newmark, H.L. Squalene, Olive Oil, and Cancer Risk: Review and Hypothesis. Annals NY Acad Sci 1999, 889, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.J. Squalene: Potential Chemopreventive Agent. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 2000, 9, 1841–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorzynik-Debicka, M.; Przychodzen, P.; Cappello, F.; Kuban-Jankowska, A.; Marino Gammazza, A.; Knap, N.; Wozniak, M.; Gorska-Ponikowska, M. Potential Health Benefits of Olive Oil and Plant Polyphenols. IJMS 2018, 19, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, C. Inspired by Nature: Antioxidants and Nanotechnology. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axencia Galega de Calidade Alimentaria. Consellería del Medio Rural Pliego de Condiciones IGP Castaña de Galicia. 2019. Available online: Https://Mediorural.Xunta.Gal/Sites/Default/Files/Produtos/En-Tramitacion/IGP_Castana_de_Galicia_Pliego_de_condiciones_septiembre_2019_CCC.Pdf (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Hu, M.; Yang, X.; Chang, X. Bioactive Phenolic Components and Potential Health Effects of Chestnut Shell: A Review. J. Food Biochem. 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorice, A.; Siano, F.; Capone, F.; Guerriero, E.; Picariello, G.; Budillon, A.; Ciliberto, G.; Paolucci, M.; Costantini, S.; Volpe, M. Potential Anticancer Effects of Polyphenols from Chestnut Shell Extracts: Modulation of Cell Growth, and Cytokinomic and Metabolomic Profiles. Molecules 2016, 21, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazliev, S.; Tursunov, K.; Razzokov, J.; Sharipov, A. Escin’s Multifaceted Therapeutic Profile in Treatment and Post-Treatment of Various Cancers: A Comprehensive Review. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-R.; Sun, L.-Z.; Jia, T.-H.; Jia, D.-F. β-Aescin Shows Potent Antiproliferative Activity in Osteosarcoma Cells by Inducing Autophagy, ROS Generation and Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Loss. J BUON 2017, 22, 1582–1586. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, D.H.J.; Arfuso, F.; Sethi, G.; Wang, L.; Hui, K.M.; Kumar, A.P.; Tran, T. Molecular Targets and Anti-Cancer Potential of Escin. Cancer Letters 2018, 422, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, B.S.; Lee, N.-K.; Na, D.S.; Yu, H.H.; Paik, H.-D. Comparative Analysis of the Antioxidant and Anticancer Activities of Chestnut Inner Shell Extracts Prepared with Various Solvents: Chestnut Inner Shell Extracts for Functional Foods. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 2097–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, W.Y.; Song, G.; Park, J.Y.; Ahn, K.S.; Kwak, H.J.; Park, J.; Lee, J.H.; Um, J.-Y. Ellagic Acid Improves Benign Prostate Hyperplasia by Regulating Androgen Signaling and STAT3. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choubey, S.; Goyal, S.; Varughese, L.R.; Kumar, V.; Sharma, A.K.; Beniwal, V. Probing Gallic Acid for Its Broad Spectrum Applications. MRMC 2018, 18, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enogieru, A.B.; Haylett, W.; Hiss, D.C.; Bardien, S.; Ekpo, O.E. Rutin as a Potent Antioxidant: Implications for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2018, 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axencia galega da calidade alimentaria. Consellería del Medio Rural Pliego de Condiciones y Características IGP Miel de Galicia. 2020. Available online: Https://Mediorural.Xunta.Gal/Sites/Default/Files/Produtos/Entramitacion/Pliego_de_condiciones_Miel_de_Galicia_julio_2020_final.Pdf (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Chan-Zapata, I.; Segura-Campos, M.R. Honey and Its Protein Components: Effects in the Cancer Immunology. J Food Biochem 2021, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhakamy, N.A.; Ahmed, O.A.A.; Fahmy, U.A.; Md, S. Apamin-Conjugated Alendronate Sodium Nanocomplex for Management of Pancreatic Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Rauf, A.; Abu-Izneid, T.; Nadeem, M.; Shariati, M.A.; Khan, I.A.; Imran, A.; Orhan, I.E.; Rizwan, M.; Atif, M.; et al. Luteolin, a Flavonoid, as an Anticancer Agent: A Review. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 112, 108612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Shi, R.; Wang, X.; Shen, H.-M. Luteolin, a Flavonoid with Potential for Cancer Prevention and Therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasoulakis, Z.; Koutras, A.; Syllaios, A.; Schizas, D.; Garmpis, N.; Diakosavvas, M.; Angelou, K.; Tsatsaris, G.; Pagkalos, A.; Ntounis, T.; et al. Breast Cancer Apoptosis and the Therapeutic Role of Luteolin. chr 2021, 116, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasher, P.; Sharma, M.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M.; Chellappan, D.K.; Zacconi, F.; De Rubis, G.; Gupta, G.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Cho, W.C.; et al. Luteolin: A Flavonoid with a Multifaceted Anticancer Potential. Cancer Cell Int 2022, 22, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lolli, G.; Cozza, G.; Mazzorana, M.; Tibaldi, E.; Cesaro, L.; Donella-Deana, A.; Meggio, F.; Venerando, A.; Franchin, C.; Sarno, S.; et al. Inhibition of Protein Kinase CK2 by Flavonoids and Tyrphostins. A Structural Insight. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 6097–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, D.; Sharma, A.; Tuli, H.S.; Sak, K.; Punia, S.; Mukherjee, T.K. Kaempferol – A Dietary Anticancer Molecule with Multiple Mechanisms of Action: Recent Trends and Advancements. Journal of Functional Foods 2017, 30, 203–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Salehi, B.; Sharifi-Rad, J.; Aslam Gondal, T.; Saeed, F.; Imran, A.; Shahbaz, M.; Tsouh Fokou, P.V.; Umair Arshad, M.; Khan, H.; et al. Kaempferol: A Key Emphasis to Its Anticancer Potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; An, Y.; Fang, G. The Mechanism of Anticancer Action and Potential Clinical Use of Kaempferol in the Treatment of Breast Cancer. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2019, 117, 109086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, T.; Kosaka, Y.; Mizuguchi, M. Structural Insight into the Interactions between Death-Associated Protein Kinase 1 and Natural Flavonoids. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7400–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Fu, Y.; Malakhova, M.; Kurinov, I.; Zhu, F.; Yao, K.; Li, H.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Lim, D.Y.; et al. Caffeic Acid Directly Targets ERK1/2 to Attenuate Solar UV-Induced Skin Carcinogenesis. Cancer Prevention Research 2014, 7, 1056–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Museo do Viño Uvas y Vinos de Galicia. Available online: Https://Museovinogalicia.Xunta.Gal/Es/El-Vino/Uvas-y-Vinos-de-Galicia (accessed on 31 July 2023).
- Ren, B.; Kwah, M.X.-Y.; Liu, C.; Ma, Z.; Shanmugam, M.K.; Ding, L.; Xiang, X.; Ho, P.C.-L.; Wang, L.; Ong, P.S.; et al. Resveratrol for Cancer Therapy: Challenges and Future Perspectives. Cancer Letters 2021, 515, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauf, A.; Imran, M.; Butt, M.S.; Nadeem, M.; Peters, D.G.; Mubarak, M.S. Resveratrol as an Anti-Cancer Agent: A Review. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2018, 58, 1428–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshaer, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.J.; Tang, X. Resveratrol: An Overview of Its Anti-Cancer Mechanisms. Life Sciences 2018, 207, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mach, N. Efecto de los polifenoles del vino sobre la prevención del cáncer. NUTRICION HOSPITALARIA 2015, 535–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deus, C.M.; Serafim, T.L.; Magalhães-Novais, S.; Vilaça, A.; Moreira, A.C.; Sardão, V.A.; Cardoso, S.M.; Oliveira, P.J. Sirtuin 1-Dependent Resveratrol Cytotoxicity and pro-Differentiation Activity on Breast Cancer Cells. Arch Toxicol 2017, 91, 1261–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Gerevini, G.T.; Repossi, G.; Dain, A.; Tarres, M.C.; Das, U.N.; Eynard, A.R. Beneficial Action of Resveratrol: How and Why? Nutrition 2016, 32, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasem, R.J. The Estrogenic Activity of Resveratrol: A Comprehensive Review of in Vitro and in Vivo Evidence and the Potential for Endocrine Disruption. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 2020, 50, 439–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo-González, M.; Cancho-Grande, B.; Boso, S.; Santiago, J.L.; Martínez, M.C.; Simal-Gándara, J. Evolution of Flavonoids in Mouratón Berries Taken from Both Bunch Halves. Food Chemistry 2013, 138, 1868–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir-Cerdà, A.; Carretero, I.; Coves, J.R.; Pedrouso, A.; Castro-Barros, C.M.; Alvarino, T.; Cortina, J.L.; Saurina, J.; Granados, M.; Sentellas, S. Recovery of Phenolic Compounds from Wine Lees Using Green Processing: Identifying Target Molecules and Assessing Membrane Ultrafiltration Performance. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 857, 159623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirás-Avalos, J.M.; Bouzas-Cid, Y.; Trigo-Córdoba, E.; Orriols, I.; Falqué, E. Amino Acid Profiles to Differentiate White Wines from Three Autochtonous Galician Varieties. Foods 2020, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sochorova, L.; Prusova, B.; Jurikova, T.; Mlcek, J.; Adamkova, A.; Baron, M.; Sochor, J. The Study of Antioxidant Components in Grape Seeds. Molecules 2020, 25, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravindranathan, P.; Pasham, D.; Balaji, U.; Cardenas, J.; Gu, J.; Toden, S.; Goel, A. Mechanistic Insights into Anticancer Properties of Oligomeric Proanthocyanidins from Grape Seeds in Colorectal Cancer. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garavaglia, J.; Markoski, M.M.; Oliveira, A.; Marcadenti, A. Grape Seed Oil Compounds: Biological and Chemical Actions for Health. Nutr Metab Insights 2016, 9, NMI.S32910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.; Moreira, A.C.; Nazmi, K.; Moniz, T.; Vale, N.; Rangel, M.; Gomes, P.; Bolscher, J.G.M.; Rodrigues, P.N.; Bastos, M.; et al. Lactoferricin Peptides Increase Macrophages’ Capacity To Kill Mycobacterium Avium. mSphere 2017, 2, e00301–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, S.; Fujiwara-Tani, R.; Kishi, S.; Sasaki, T.; Ohmori, H.; Goto, K.; Nakashima, C.; Nishiguchi, Y.; Kawahara, I.; Luo, Y.; et al. Enhancement of Anti-Tumoral Immunity by β-Casomorphin-7 Inhibits Cancer Development and Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer. IJMS 2021, 22, 8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallergi, G. Distinct Signaling Pathways Regulate Differential Opioid Effects on Actin Cytoskeleton in Malignant MCF7 and Nonmalignant MCF12A Human Breast Epithelial Cells. Experimental Cell Research 2003, 288, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanta, S.; Paul, S. Stable Self-Assembly of Bovine α-Lactalbumin Exhibits Target-Specific Antiproliferative Activity in Multiple Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28177–28187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.J.; Santos, H.O.; Howell, S.L.; Pimentel, G.D. Whey Protein in Cancer Therapy: A Narrative Review. Pharmacological Research 2019, 144, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor, R.; Bouzas, C.; Tur, J.A. Beneficial Effects of Dietary Supplementation with Olive Oil, Oleic Acid, or Hydroxytyrosol in Metabolic Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2021, 172, 372–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.-I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covas, M.-I.; Nyyssönen, K.; Poulsen, H.E.; Kaikkonen, J.; Zunft, H.-J.F.; Kiesewetter, H.; Gaddi, A.; De La Torre, R.; Mursu, J.; Bäumler, H.; et al. The Effect of Polyphenols in Olive Oil on Heart Disease Risk Factors: A Randomized Trial. Ann Intern Med 2006, 145, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, S.; Razavi, B.M. hosseinzadeh, hossein A Review of the Effects of Capsicum Annuum L. and Its Constituent, Capsaicin, in Metabolic Syndrome. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 2018, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiha, G.E.-S.; Alqahtani, A.; Ojo, O.A.; Shaheen, H.M.; Wasef, L.; Elzeiny, M.; Ismail, M.; Shalaby, M.; Murata, T.; Zaragoza-Bastida, A.; et al. Biological Properties, Bioactive Constituents, and Pharmacokinetics of Some Capsicum Spp. and Capsaicinoids. IJMS 2020, 21, 5179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela Mosquera, G.; O. Moreiras Tuní; ansón Oliart R., Ávila Torres JM, Cuadrado Vives C., Estalrich Rodríguez Patricia, Del Pozo de la Calle S.; Rodríguez Sangrador M. Consumo de Alimentos En Galicia: La Dieta Atlántica 2004.
- Baladia, E.; Moñino, M.; Martínez-Rodríguez, R.; Miserachs, M.; Russolillo, G.; Picazo, Ó.; Fernández, T.; Morte, V. Uso de Suplementos Nutricionales y Productos a Base de Extractos de Plantas En Población Española: Un Estudio Transversal. Rev Esp Nutr Hum Diet 2022, 26, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, P.; Delmulle, L.; Gulati, O.; Richardson, D.; Ruthsatz, M.; Sievers, H.; Sidani, S. Use of Botanicals in Food Supplements. Ann Nutr Metab 2006, 50, 538–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skeie, G.; Braaten, T.; Hjartåker, A.; Lentjes, M.; Amiano, P.; Jakszyn, P.; Pala, V.; Palanca, A.; Niekerk, E.M.; Verhagen, H.; et al. Use of Dietary Supplements in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition Calibration Study. Eur J Clin Nutr 2009, 63, S226–S238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Feng, Z.; Hao, J.; Shen, W.; Li, X.; Sun, L.; Sharman, E.; Wang, Y.; Wertz, K.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol Protects against Oxidative Damage by Simultaneous Activation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Phase II Detoxifying Enzyme Systems in Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 2010, 21, 1089–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, R.; Huang, H.; Fletcher, A.; Yu, L.; Pham, Q.; Yu, L.; He, Q.; Wang, T. Inhibition of Tumor Growth by Dietary Indole-3-Carbinol in a Prostate Cancer Xenograft Model May Be Associated with Disrupted Gut Microbial Interactions. Nutrients 2019, 11, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, E.; Nisani, S.; Chamovitz, D.A. Indole-3-Carbinol: A Plant Hormone Combatting Cancer. F1000Res 2018, 7, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- A Patil, S.; Addo, J.K.; Deokar, H.; Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Suttle, D.P.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Buolamwini, J.K. Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and Modeling Studies of New Pyrido[3,4-b] Indole Derivatives as Broad-Spectrum Potent Anticancer Agents. Drug Des 2017, 06. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, R.; Pérez-Correa, J.R.; Domínguez, H. Bioactive Properties of Marine Phenolics. Marine Drugs 2020, 18, 501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
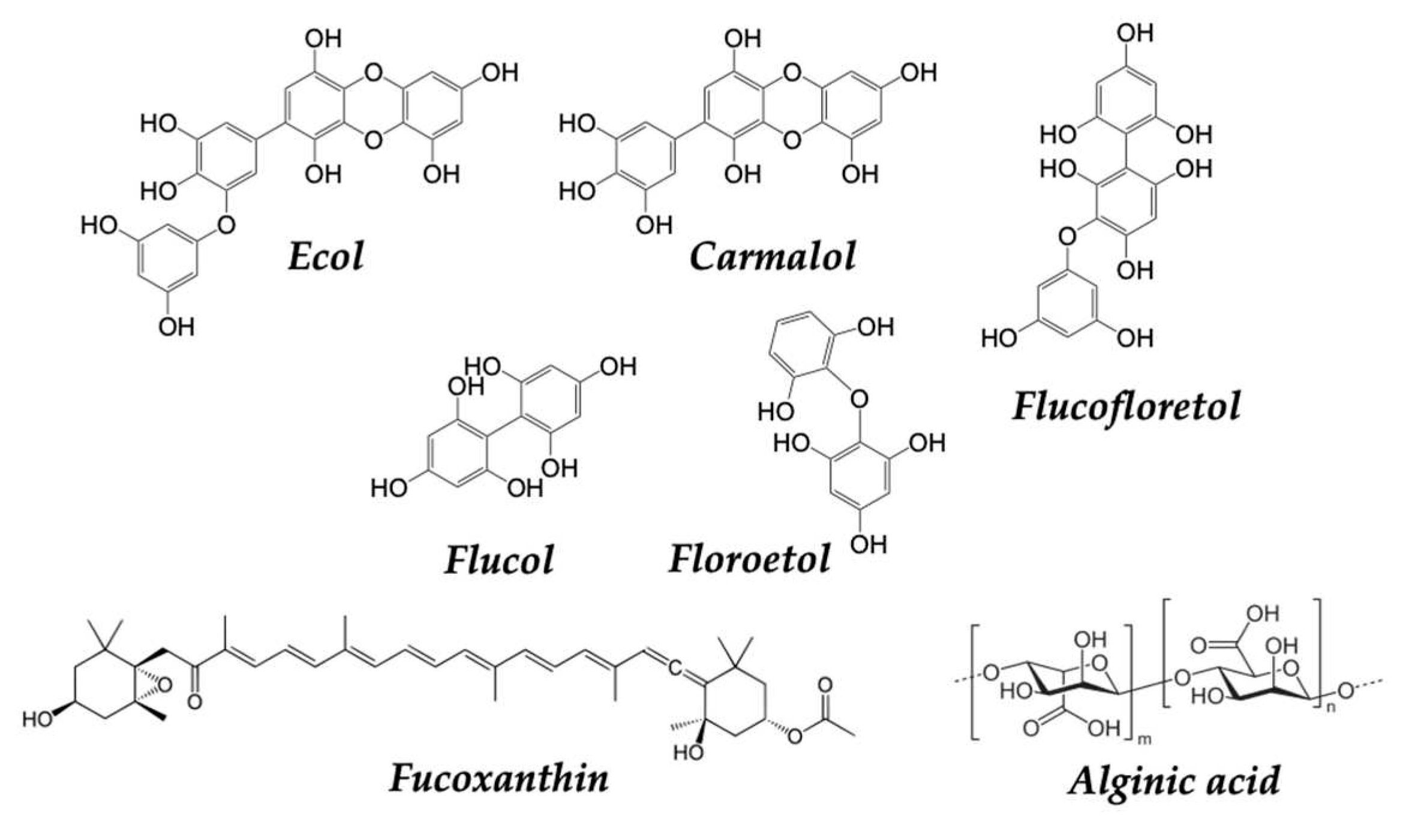
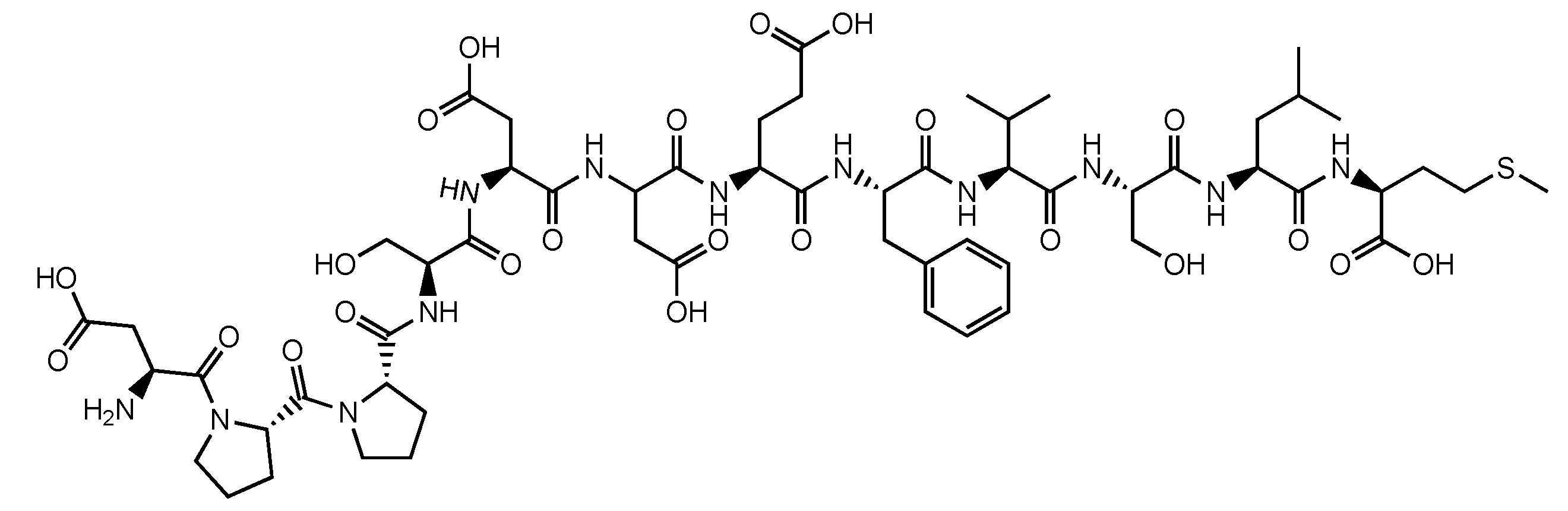
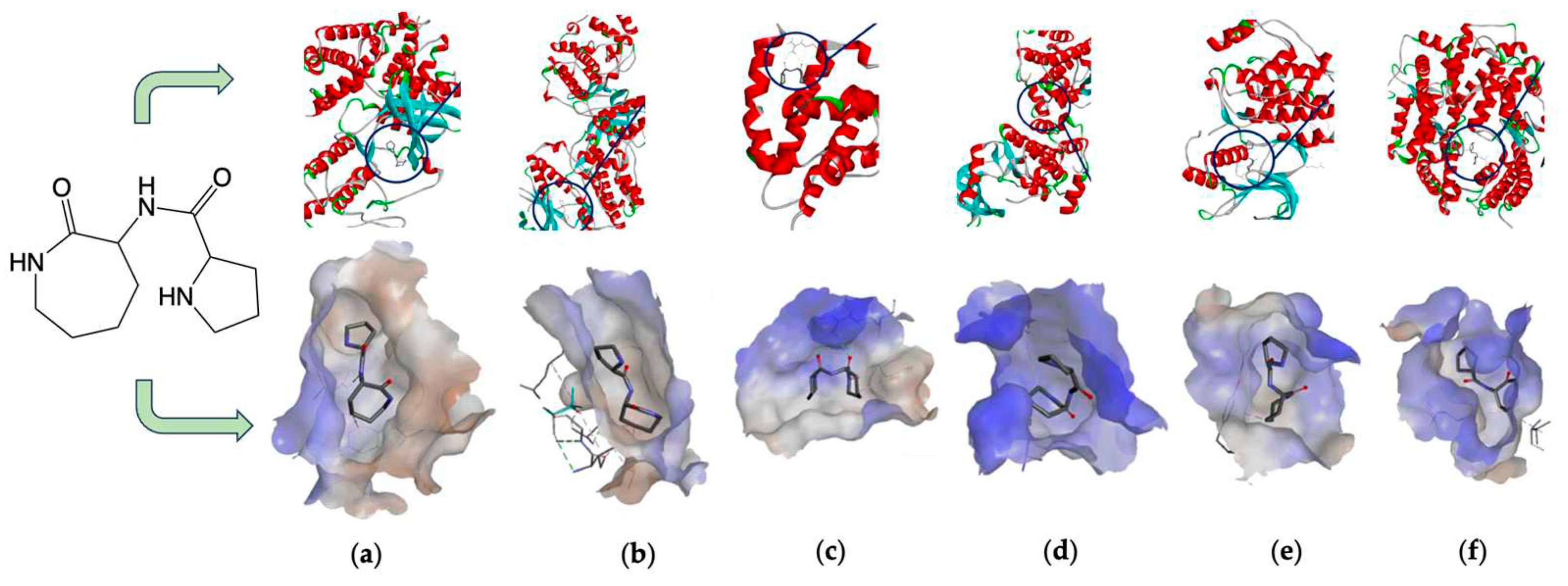
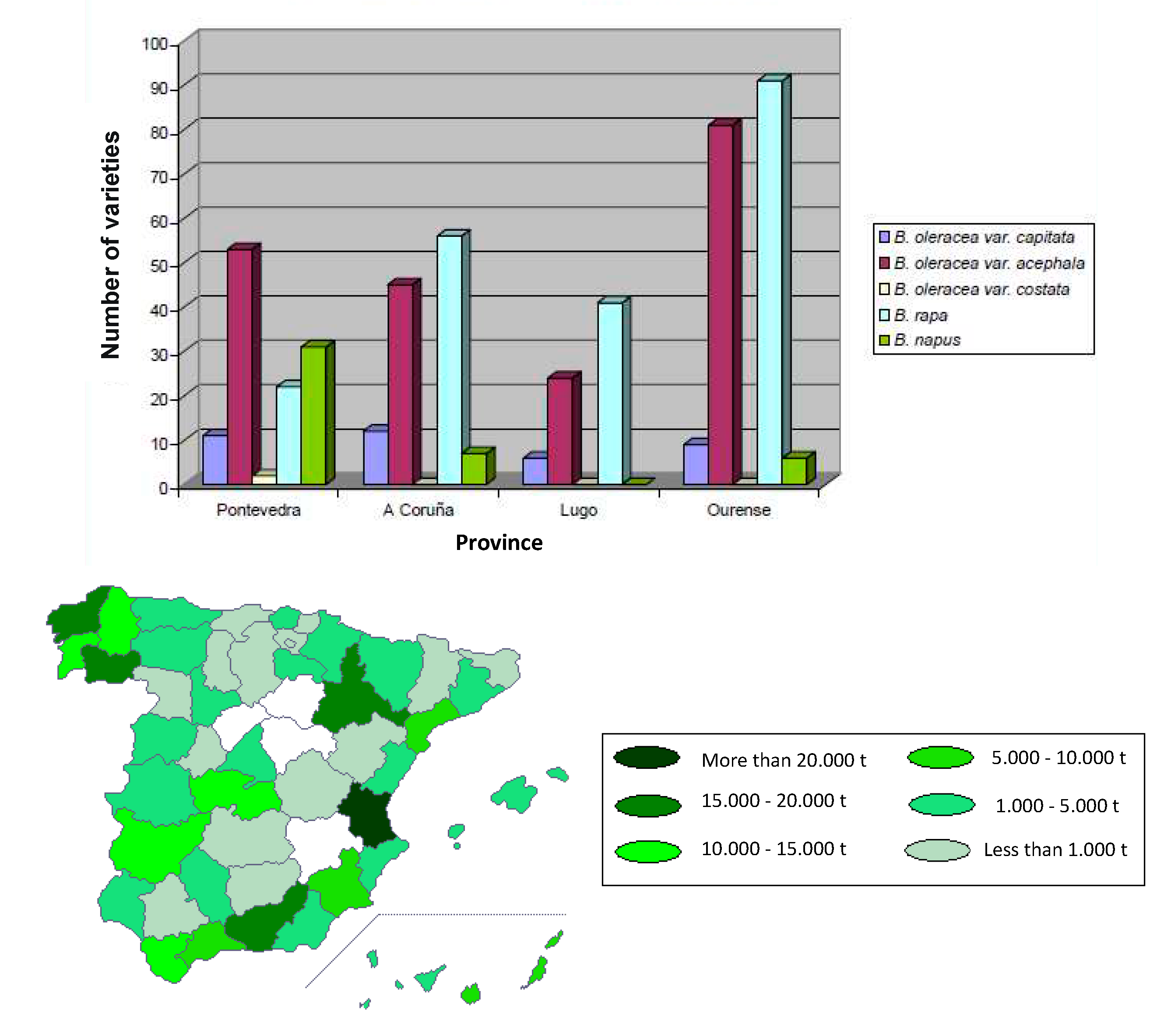
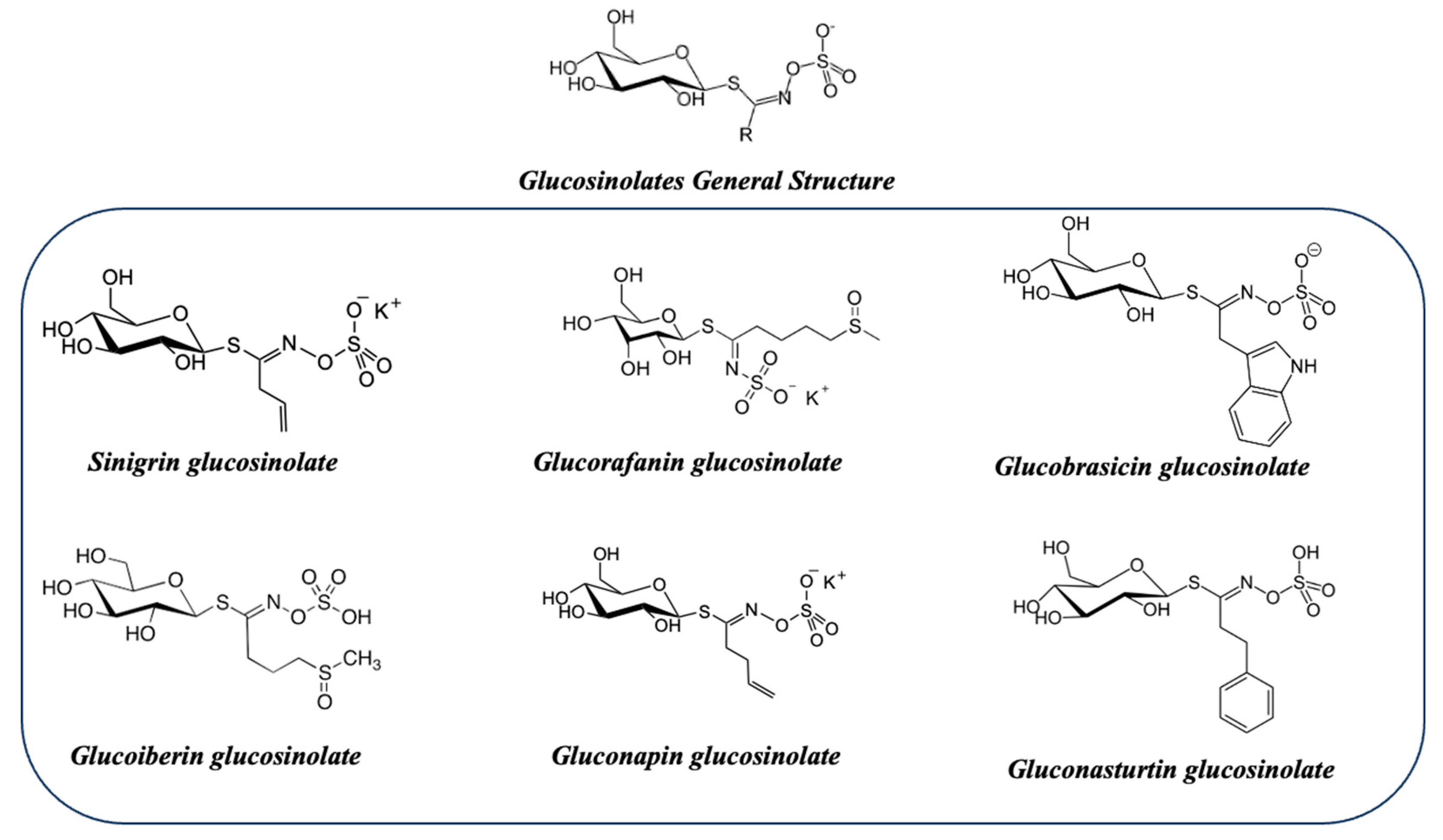
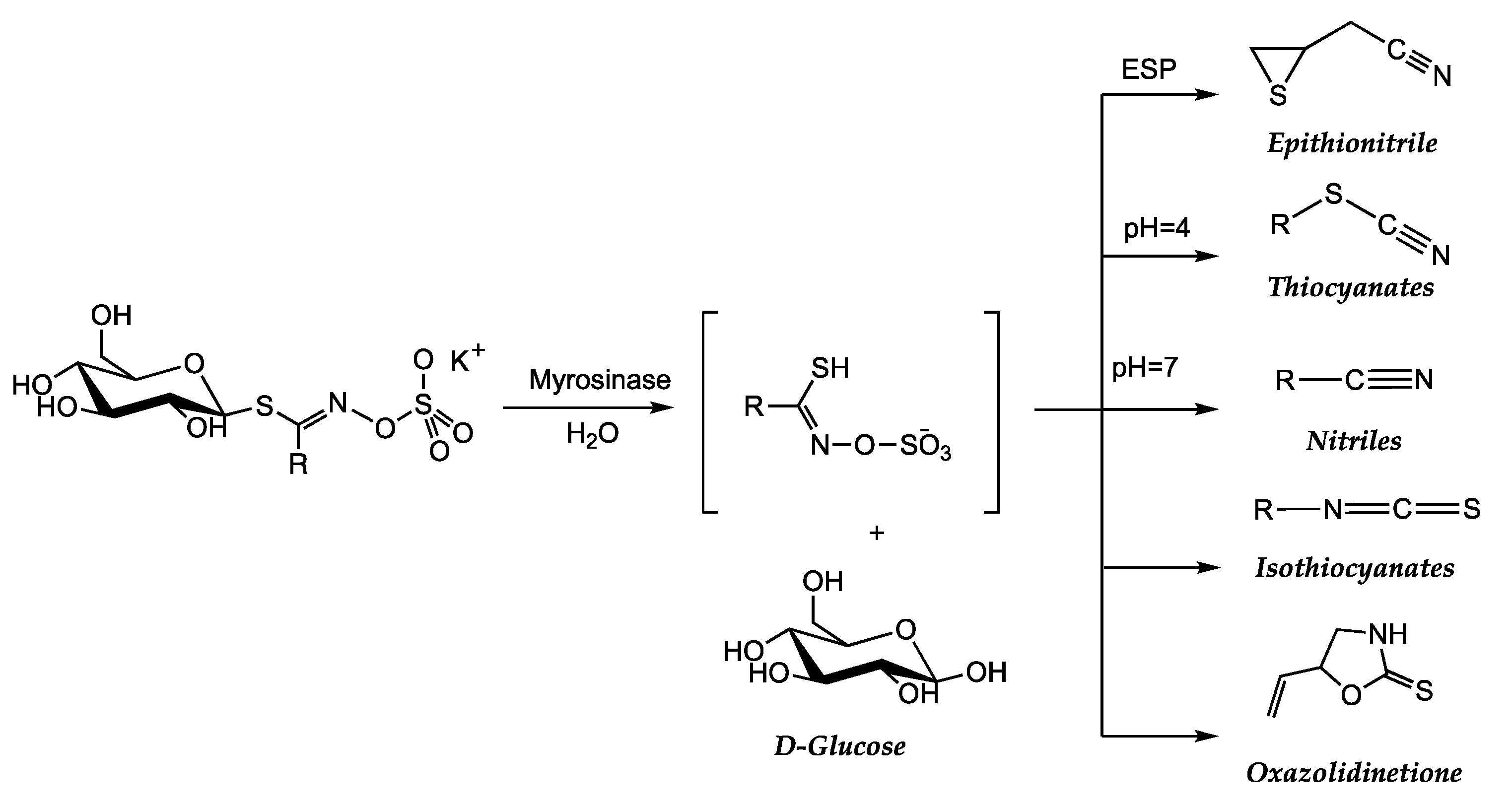
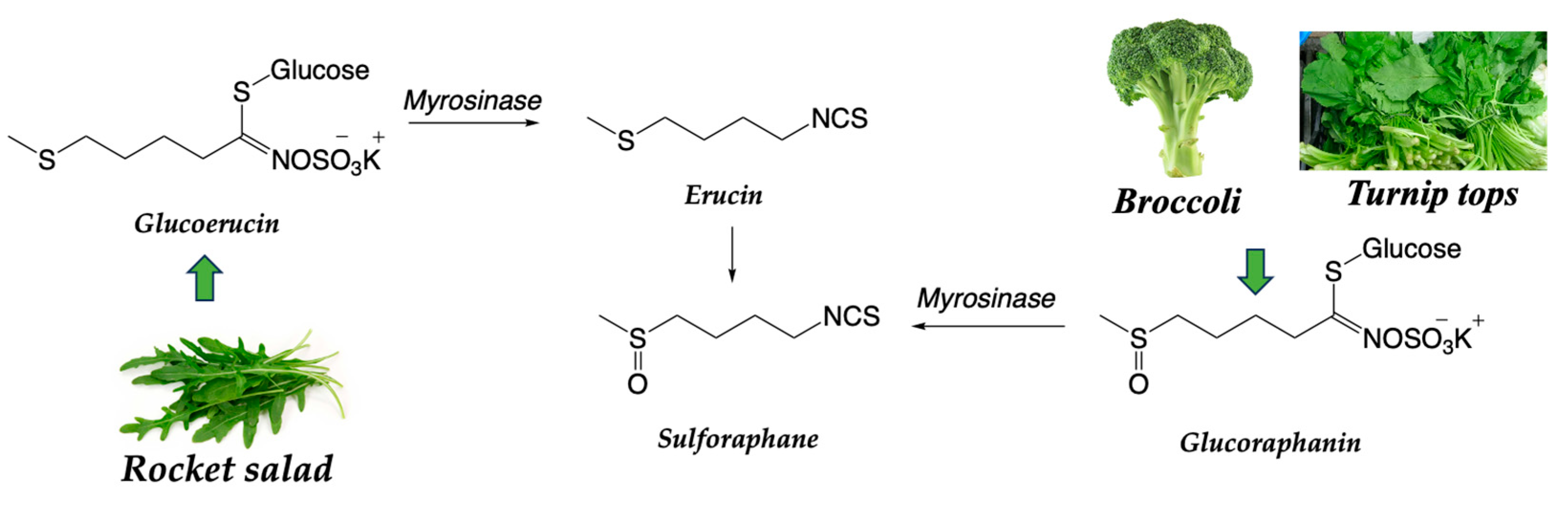

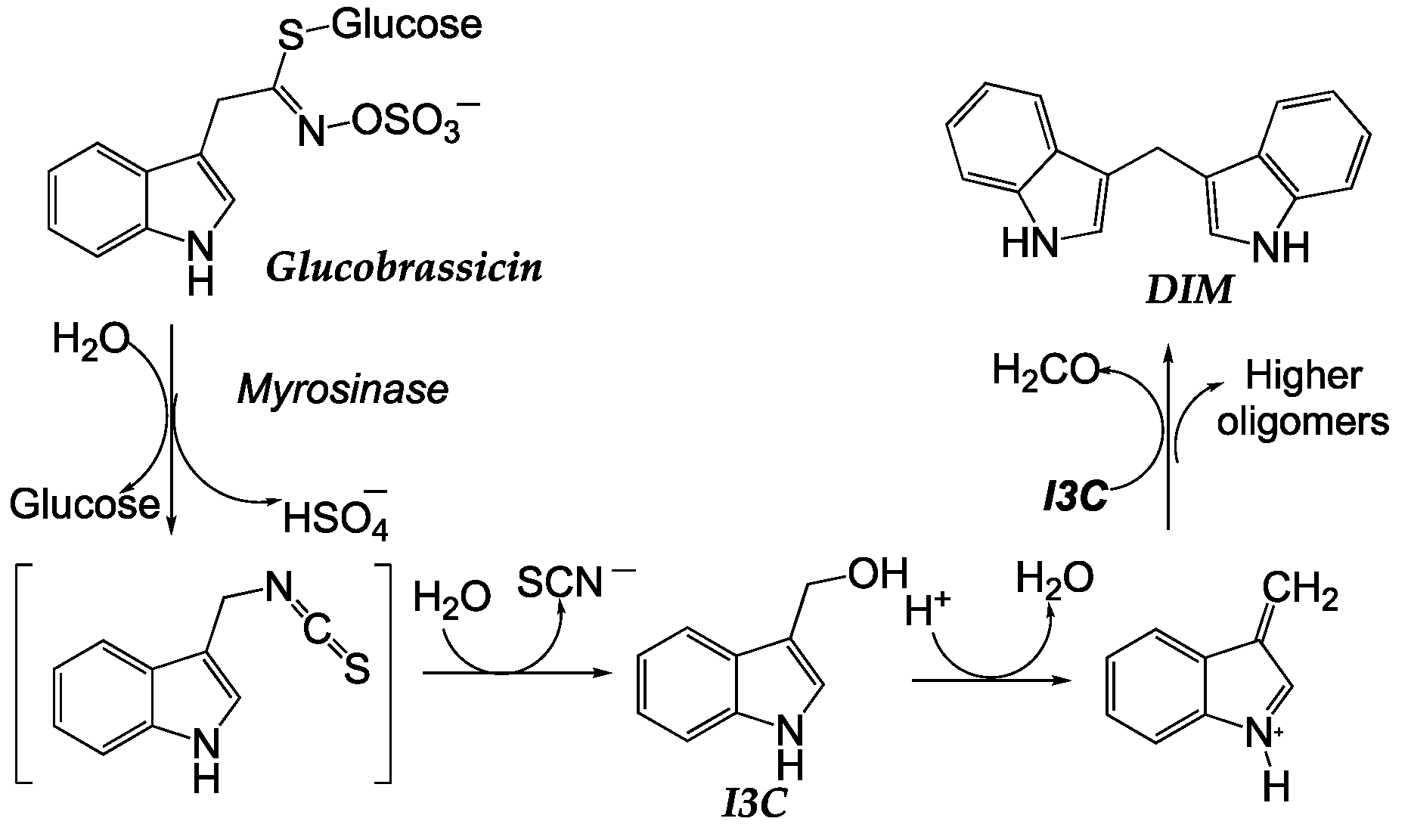
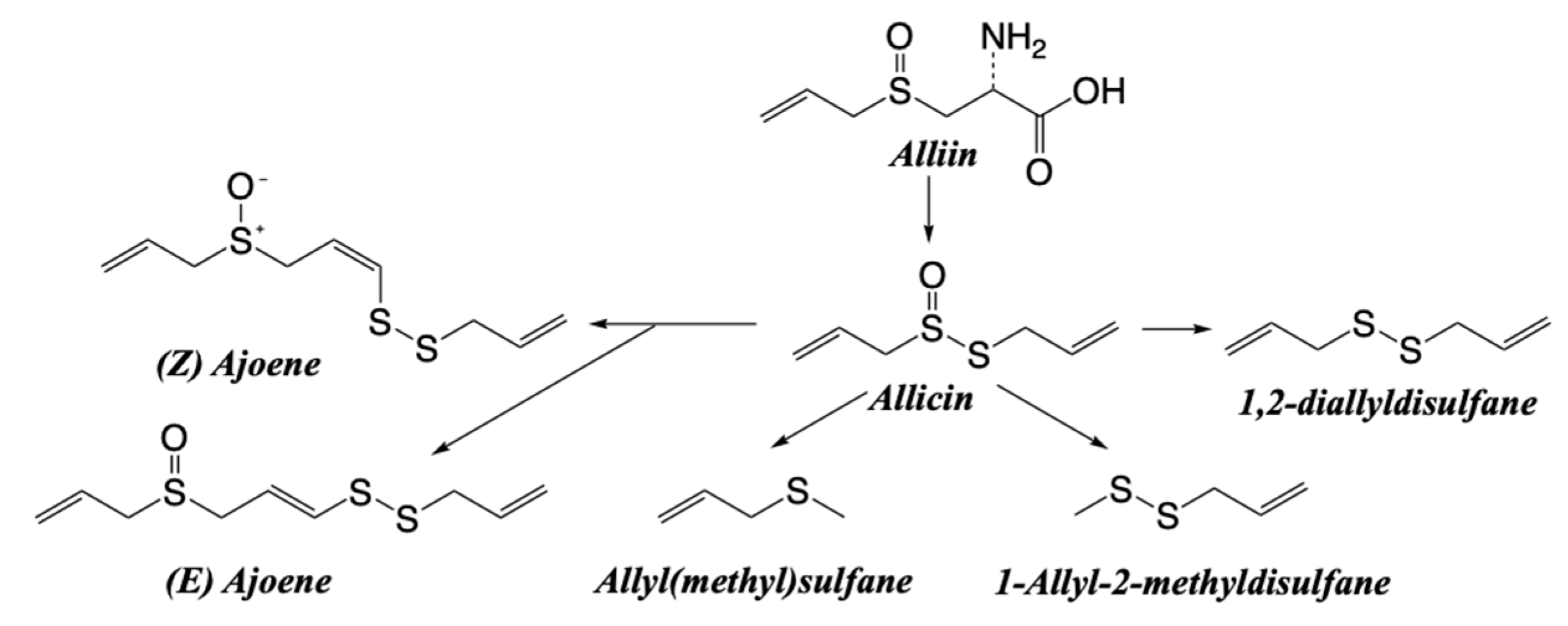
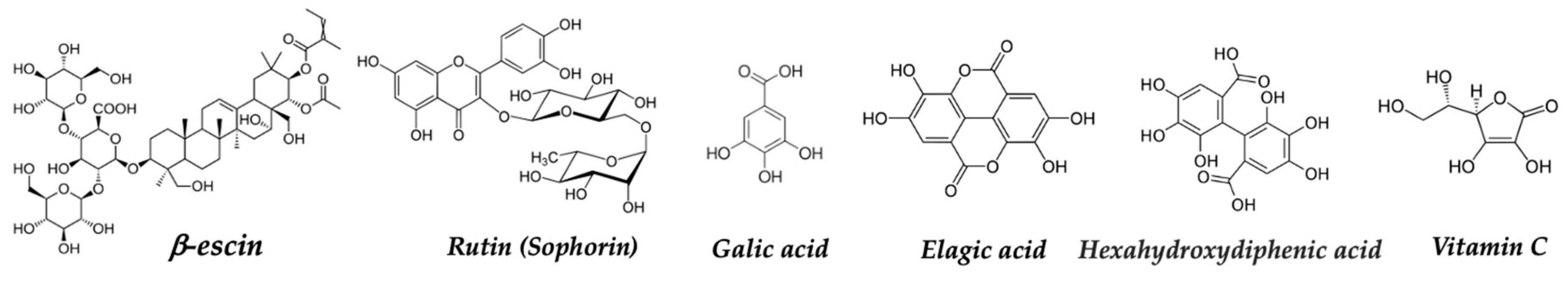
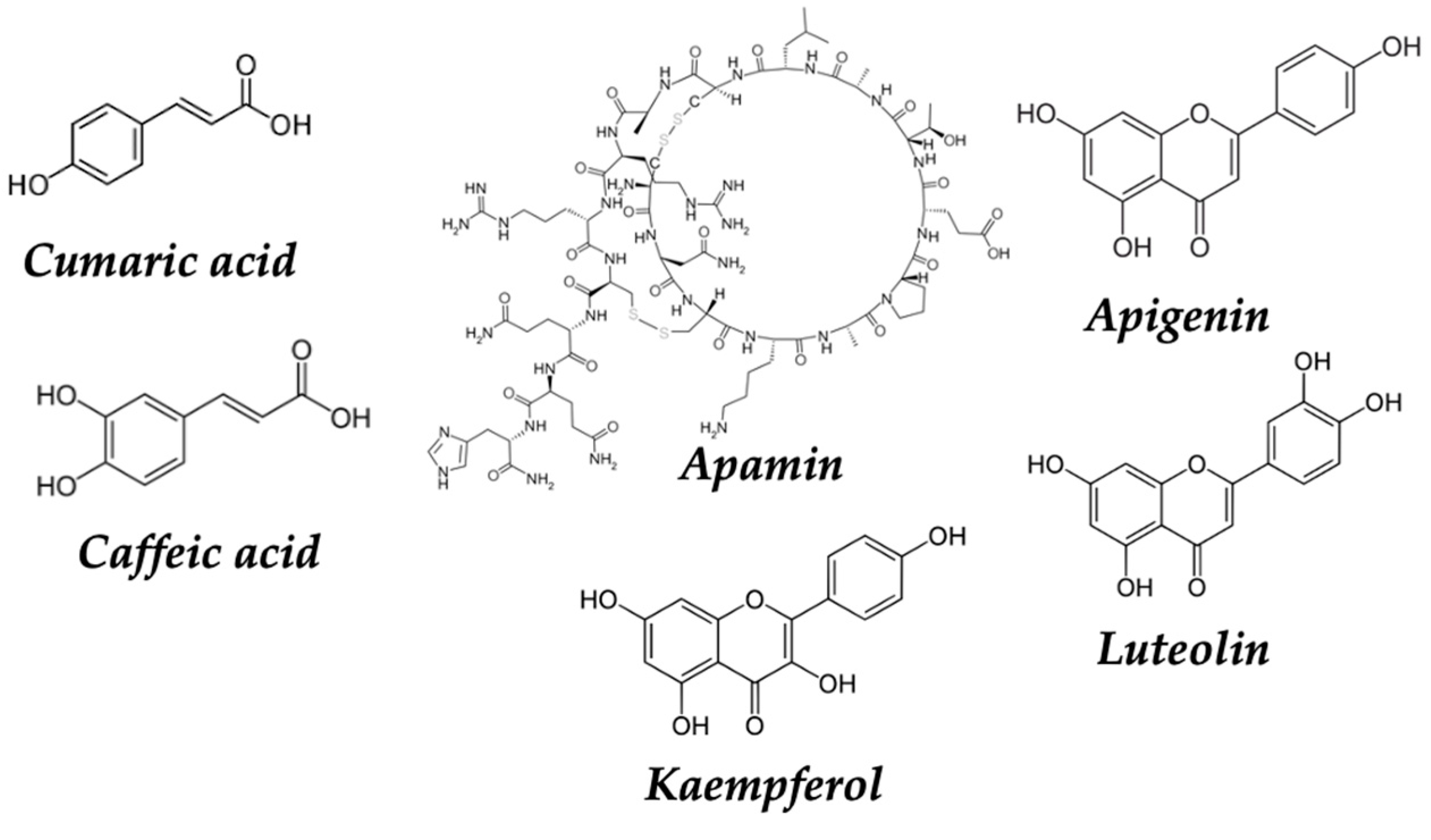

| Dietary source | Main bioactive component | Activity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fish, shellfish, seaweed | Omega-3 fatty acids | Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, Hypocholesterolemic | [25] |
| Betaine (TMG, Anserine, Carnosine) | Anticancer, antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory | [67,68] | |
| Selenium | Antioxidant | [59,60] | |
| Vitamin D | Epigenetic modifications | [89] | |
| Fucoxanthin | Antioxidant | [24] | |
| Octopus | OCTPEP-1 | Anticancer | [83] |
| Selenium | Antioxidant | [59] | |
| Taurin | Antiproliferation | [74] | |
| Ozopromide | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory | [87,88] | |
| Brassicaceae family | Glucosinolate | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer | [37,92] |
| Sulphorafane | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer | [37,96,97,98,99] | |
| Quercetin | Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer | [111,112,115,117] | |
| Indole-3-carbinol | Anticancer | [55,117,123] | |
| 3,3-Diindolylmethane | Anticancer | [120,121] | |
| Onion, garlic, leek | Ajoene | Anticancer | [126] |
| Allicin | Antioxidant, anticancer | [127] | |
| Diallyl sulfide | Antiproliferative, Anticancer | [128,129] | |
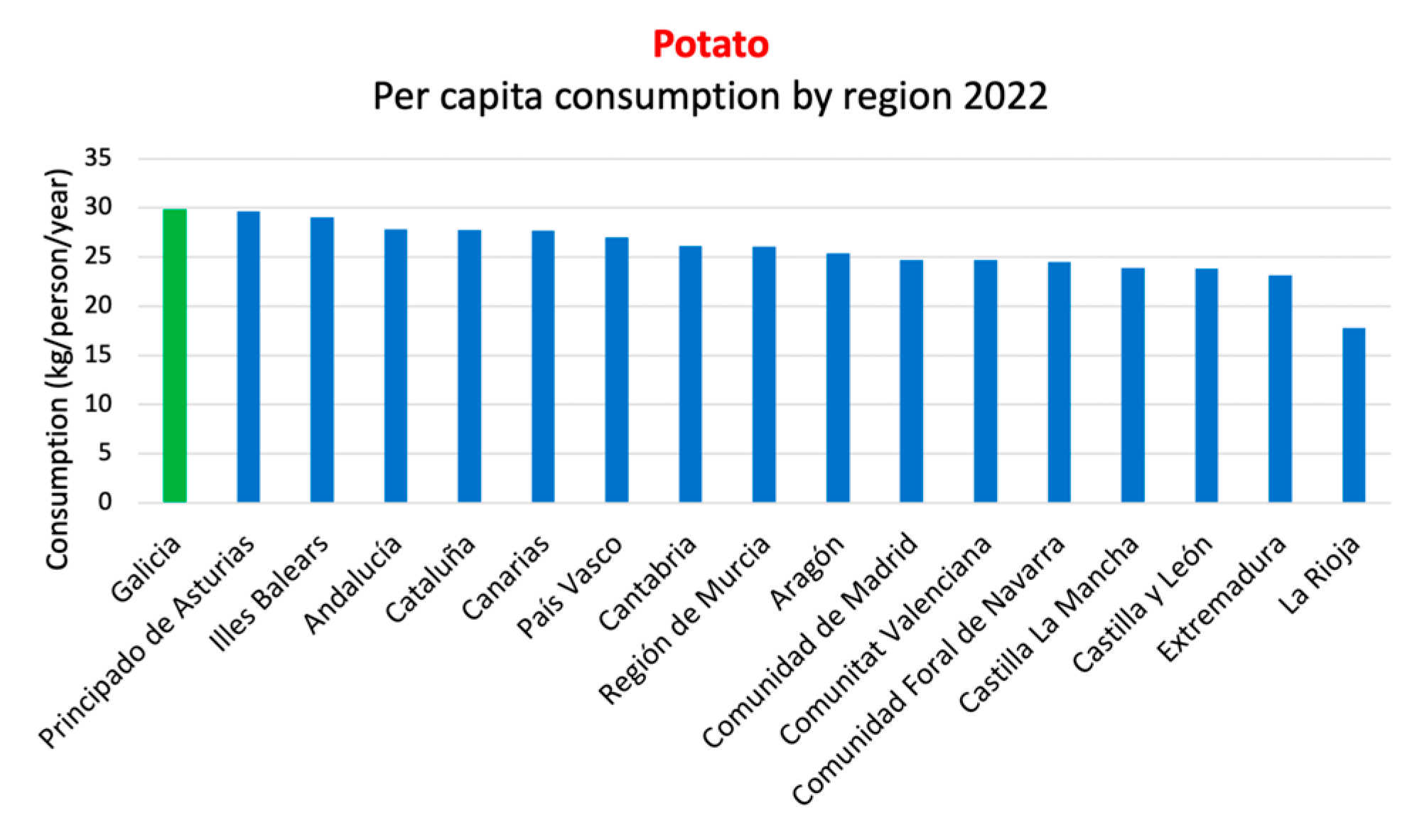
| Potatoes | Carotenoids | Antioxidant | [131,132,133] |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant | [131,132,133] | |
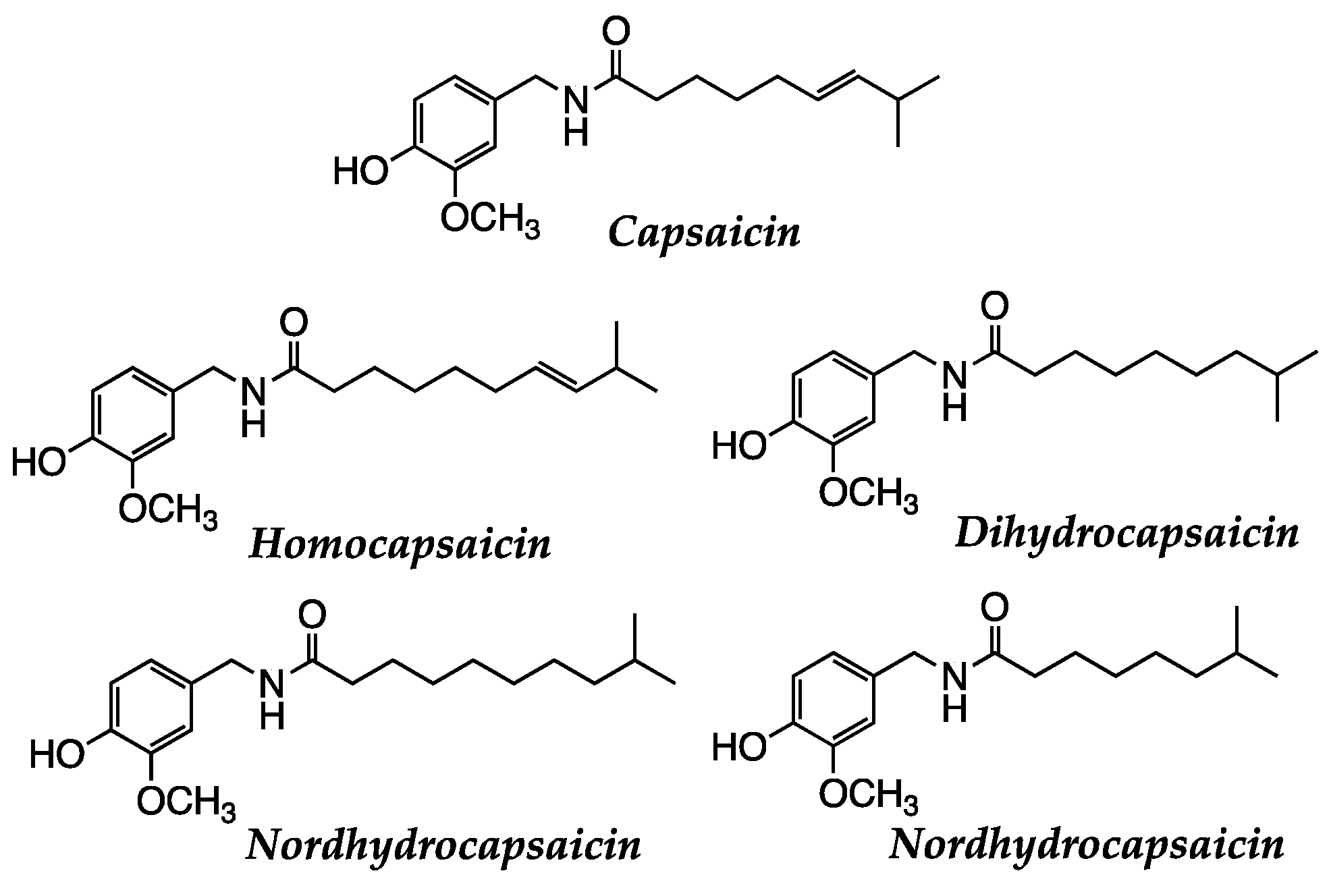
| Peppers of Padrón | Capsaicine | Anticancer, Anti-inflammatory | [138,139,140,141,142,143,144,145] |
| b-Caroten | Antioxidant, Cardioprotective | [134] | |
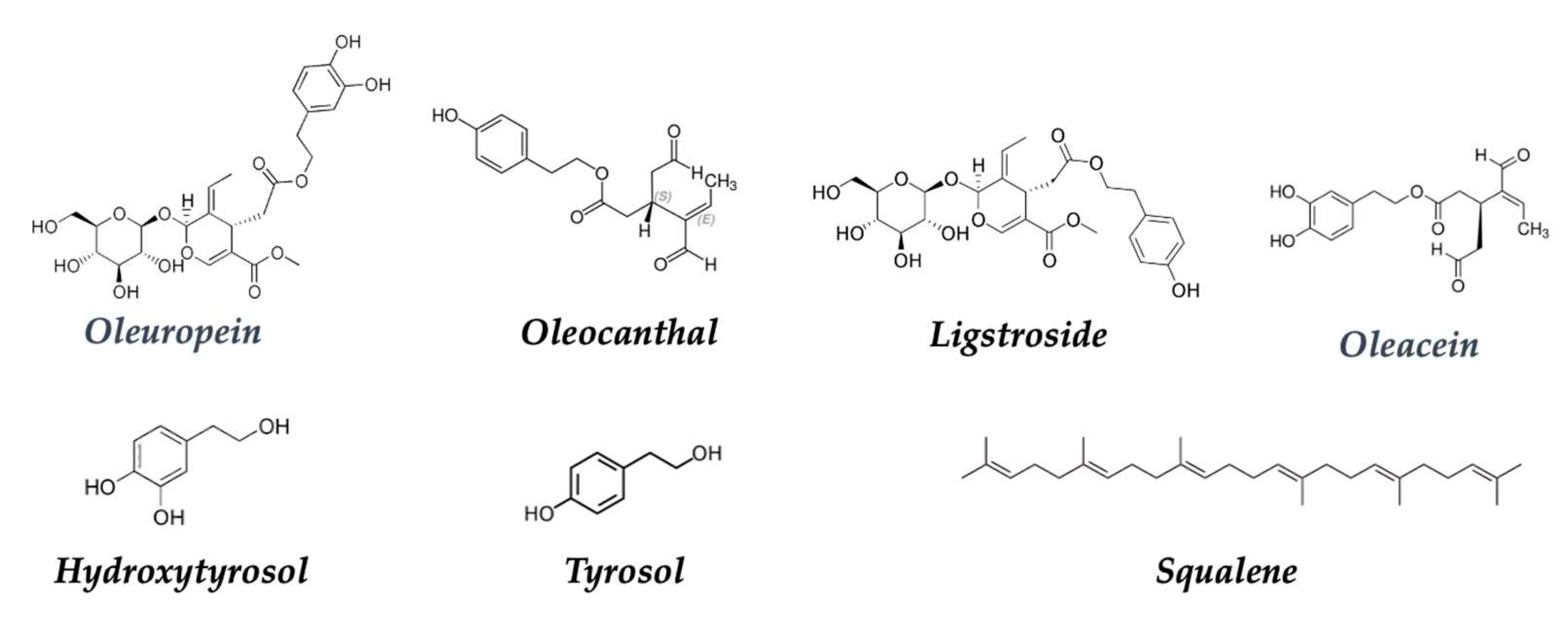
| Olive oil | Hydroxytyrosol | Anticancer | [149,150,151] |
| Oleuropein | Anticancer | [155,156] | |
| Ligstroside | Antioxidant | [157,158] | |
| Oleocanthal | Anti-inflammatory | [154] | |
| Squalene | Antioxidant | [158] | |
| Chestnuts | Tannins | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [164,165] |
| Escin | Anticancer | [165,166,167] | |
| Ellagic acid | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [169] | |
| Rutin | Antioxidant | [171] | |
| Honey | Apamin | Anticancer | [173,174] |
| Apigenin | Anticancer | [179] | |
| Kaempferol | Anticancer | [180,181,182,183,184] | |
| Wine | Resveratrol | Anticancer | [187,188,189,190,191,192] |
| Tannins | Antioxidant, anticancer | ||
| Milk and dairy derivatives | Bioactive peptides | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [200] |
| Lactoferricin | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [200] | |
| Casomorphins | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [201] | |
| Alpha-lactalbumin | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [203] | |
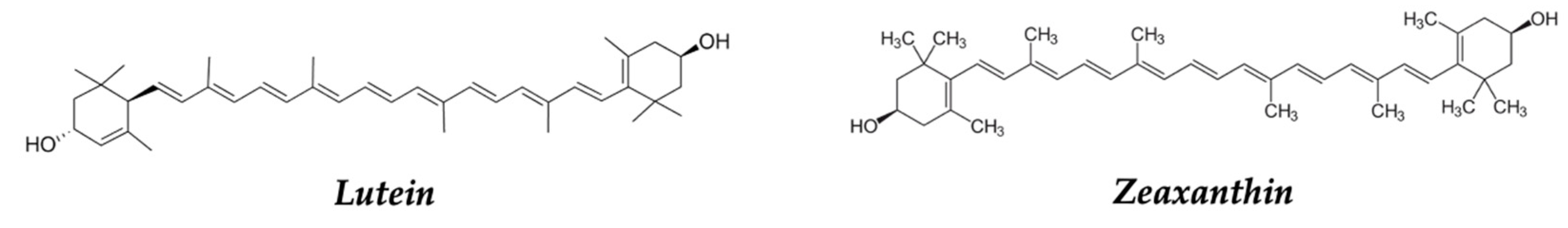
| Paprika, red pepper | Zeaxanthin, lutein | Antioxidant | [132,133,207,208,209] |
| Supplements | Sulphorafane | Anticancer | [37,96,97,98,99] |
| Caspsaicinoids | Antioxidant, Anti-inflammatory, Anticanalgesic | [208] | |
| Hidroxytyrosol | Antioxidant, Anticancer | [213] | |
| Zeaxanthin, lutein | Antioxidant | [132,133] | |
| Indole-3-carbinol | Anticancer | [214,215] | |
| Phlorotannins | Antioxidant, Anticáncer | [217] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





