Submitted:
11 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
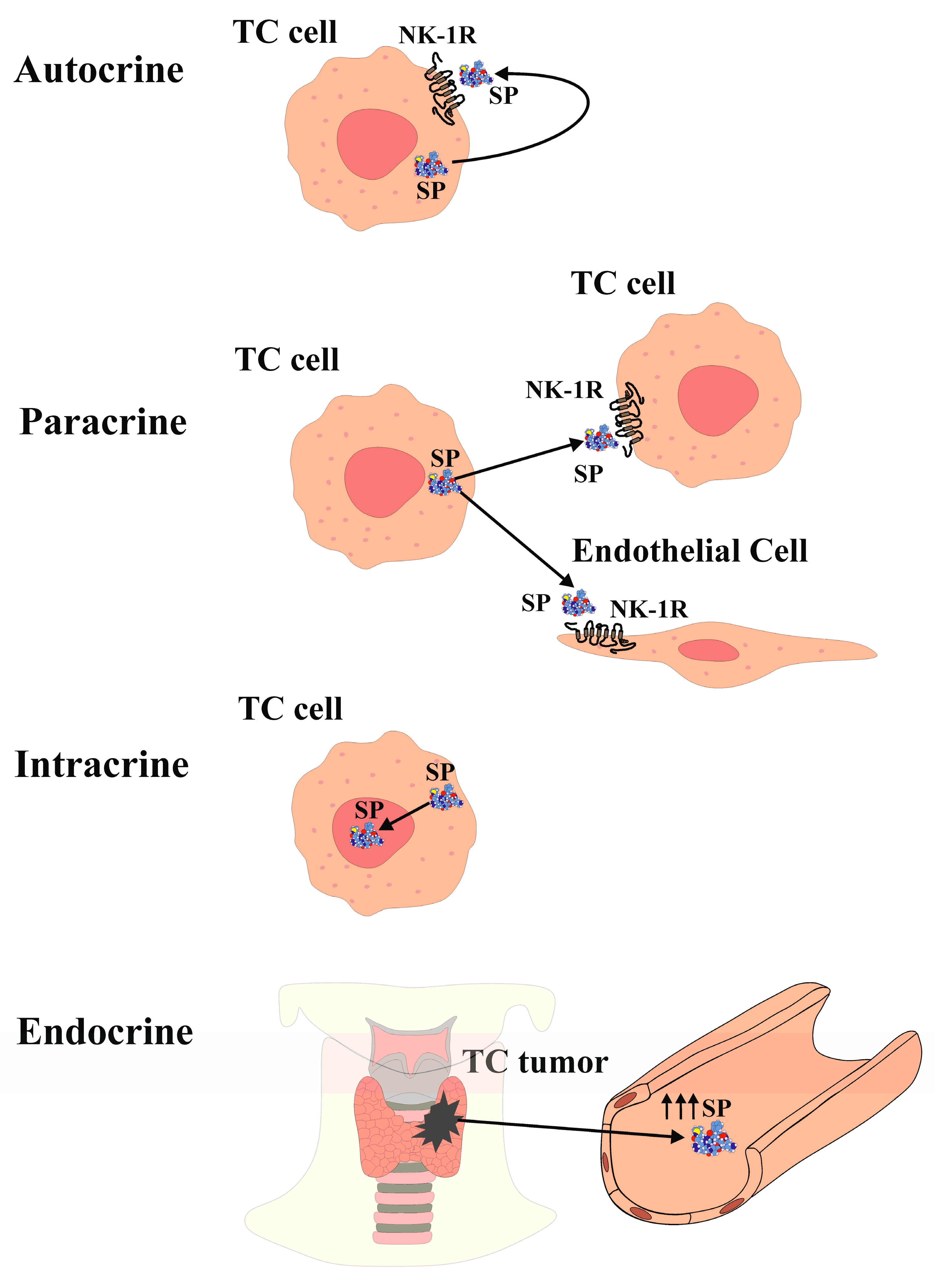
2. Substance P and Neurokinin-1 Receptor in Thyroid Cancer
3. NK-1R Antagonists as Novel Therapeutic Agents in Thyroid Cancer Treatment
3.1. Therapeutic Effect of NK-1R Antagonists as Anti-proliferative and Pro-apoptotic Agents in TC
3.2. Therapeutic Effect of NK-1R Antagonists as Anti-angiogenic Drugs in TC
3.3. Therapeutic Effect of NK-1R Antagonists in Counteracting the Warburg Effect in Cancer
3.4. Therapeutic Effect of NK-1R Antagonists as Anti-Metastatic Agents in Cancer
3.5. Safety and Efficacy of NK-1R Antagonists in Thyroid Cancer Therapy
3.6. Chemotherapy versus NK-1R Antagonists (Aprepitant) in TC Patients
4. Conclusion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, RL.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87-108. [CrossRef]
- Sherman SI. Thyroid carcinoma. Lancet 2003, 361, 501-11.
- Kim, KW.; Park, Y.J., Kim, E.H. Elevated risk of papillary thyroid cancer in Korean patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Head Neck 2011, 33, 691-5.
- Pusztaszeri, M.P.; Sadow, P.M.; Faquin. W.C. CD117: a novel ancillary marker for papillary thyroid carcinoma in fine-needle aspiration biopsies. Cancer Cytopathol. 2014, 122, 596-603. [CrossRef]
- Ragazzi, MA.; Ciarrocchi, V.; Sancisi, G.; Gandolfi, A.; Bisagni, A.; Piana S. Update on anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: morphological, molecular, and genetic features of the most aggressive thyroid cancer. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 790834.
- Haugen, B.; Sherman, S.I. Evolving approaches to patients with advanced differentiated thyroid cancer. Endocrine Reviews 2013, 34, 439-455. [CrossRef]
- Aschebrook-Kilfoy, B.; Schechter, R.B.; Shih, Y.C.; Kaplan, E.L; Chiu, B.C.; Angelos, P.; et al. The clinical and economic burden of a sustained increase in thyroid cancer incidence. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2013, 22, 1252-9. [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, M.; Ohashi, Y.; Schichijo, S.; Christian, C.; Sudduth-Klinger, J.; Harrowe, G.; et al. Multiple intracellular signalling pathways of the neuropeptide SP receptor. J. Neurosci. Res. 1992, 32, 437-43.
- Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Díez, J.J.; Durán, M.; Grande, E. Advances in thyroid cancer treatment: latest evidence and clinical potential. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2015, 72, 22-38. [CrossRef]
- Pennefather, J.N.; Lecci, A.; Candenas, M.L.; Patak, E.; Pinto, F.M.; Maggi, C.A. “Tachykinins and tachykinin receptors: a growing family.” Life sciences 2004, 74, 1445-63. [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Blount, P.; Sachais, B.S.; Hershey, A.D.; Raddatz, R.; Krause, J. Ligand binding kinetics of substance P and neurokinin A receptors stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells and evidence for differential stimulation of inositol 1, 4, 5-triphosphate and cyclic AMP second messenger responses. J. Neurochem. 1992, 59,740-5. [CrossRef]
- Fong, T.M.; Anderson, S.A.; Yu, H.; Huang, R.R.; Strader, C.D. Differential activation of intracellular effector by two isoforms of human neurokinin-1 receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 41,24-30.
- Berger, M.; Neth, O.; Ilmer, M.; Garnier, A.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; de Agustín Asencio, J.C.; et al. Hepatoblastoma cells express truncated neurokinin-1 receptor and can be growth inhibited by aprepitant in vitro and in vivo. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60: 985-94. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao. L.; Xiong, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, M.; Yang, J.; Yao, Z. Roles of full-length and truncated neurokinin-1 receptors on tumor progression and distant metastasis in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 140,49-61. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.F.; Argüelles, S.; Rosso, M.; Medina, R.; Coveñas, R.; Ayala, A.; Muñoz, M. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is Essential for the Viability of Human Glioma Cells: A Possible Target for Treating Glioblastoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6291504. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz. M.; Coveñas.; Esteban, F.; Redondo, M. The substance P/NK-1 receptor system: NK-1 receptor antagonists as anti-cancer drugs. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 441-63.
- Munoz, M.; Covenas, R. The Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant: An Intelligent Bullet against Cancer? Cancers (Basel) 2020, 12. 2682.
- Muñoz, M.; Pérez, A.; Rosso, M.; Zamarriego, C.; Rosso, R. Antitumoral action of the neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist L-733,060 on human melanoma cell lines. Melanoma Res. 2004, 14, 183-8. [CrossRef]
- Molinos-Quintana, A.; Trujillo-Hacha, P.; Piruat, J.I.; Bejarano-Garcia, J.A.; Garcia-Guerrero. E.; Perez-Simon, J.A.; Munoz, M. Human acute myeloid leukemia cells express Neurokinin-1 receptor, which is involved in the antileukemic effect of Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Invest. New Drugs 2019, 37,17-26. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M. The NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant as a broad-spectrum antitumor drug. Invest. New. Drugs 2010, 28, 187-93. [CrossRef]
- Isorna, I.; Esteban, F.; Solanellas, J.; Coveñas, R.; Muñoz, M. The substance P and neurokinin-1 receptor system in human thyroid cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Eur. J. Histochem. 2020, 64,3117. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Coveñas, R. A new frontier in the treatment of cancer: NK-1 receptor antagonists. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 504-16. [CrossRef]
- Skrabanek, P.; Cannon, D.; Dempsey, J.; Kirrane, J.; Neligan, M.; Powell D. Substance P in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid. Experientia 1979, 35, 1259-60. [CrossRef]
- Holm, R.; Sobrinho-Simões, M.; Nesland, J.M.; Gould, V.E.; Johannessen, J.V. Medullary carcinoma of the thyroid gland: an immunocytochemical study. Ultrastruct. Pathol. 1985, 8, 25-41. [CrossRef]
- Hennig, I.M.; Laissue, J.A.; Horisberger, U.; Reubi, J.C. Substance-P receptors in human primary neoplasms: tumoral and vascular localization. Int. J. Cancer 1995, 61, 786-92. [CrossRef]
- Asadi, M.; Mirdoosti, S.M.; Majidi, S.; Boroumand, N.; Jafarian, A.H. Hashemy, S.I. Evaluation of serum substance P level and tissue distribution of NK-1 receptor in papillary thyroid cancer. Middle East J. Cancer. 2021, 12,491-8. [CrossRef]
- González-Moles, M.A..; Mosqueda-Taylor, A.; Esteban, F.; Gil-Montoya, J.A.; Díaz-Franco, M.A.; Delgado, M et al. Cell proliferation associated with actions of the substance P/NK-1 receptor complex in keratocystic odontogenic tumours. Oral Oncol. 2008, 44, 1127-33. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Carranza, A.; Coveñas, R. Increased nuclear localization of substance P in human gastric tumor cells. Acta. Histochem. 2017, 119, 337-42. [CrossRef]
- Feng, F.; Yang, J.; Tong, L.; Yuan, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hong, L et al. Substance P immunoreactive nerve fibres are related to gastric cancer differentiation status and could promote proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells. Cell. Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 623-9. [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.; Robles-Frías, M.J.; Coveñas, R.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Muñoz, M. The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human primary gastric and colon adenocarcinomas and is involved in the antitumor action of L-733,060 and the mitogenic action of substance P on human gastrointestinal cancer cell lines. Tumor Biol. 2008, 29, 245-54. [CrossRef]
- Esteban, F.; González-Moles, M.A.; Castro, D.; Martín-Jaén, M. del M.; Redondo, M.; Ruiz-Avila, I.; et al. Expression of substance P and neurokinin-1-receptor in laryngeal cancer: linking chronic inflammation to cancer promotion and progression. Histopathology 2009, 54, 258-60. [CrossRef]
- Brener, S.; González-Moles, M.A.; Tostes, D.; Esteban, F.; Gil-Montoya, J.A.; Ruiz-Avila, I.; et al. A role for the substance P/NK-1 receptor complex in cell proliferation in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2323-9.
- Muñoz, M.; González-Ortega, A,; Rosso M, Robles-Frías MJ, Carranza, A.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; et al. The substance P/neurokinin-1 receptor system in lung cancer: focus on the antitumor action of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Peptides 2012, 38, 318-25. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Robles-Frías, M.J.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Rosso, R.; González-Ortega, A.; et al. The NK-1 receptor is expressed in human melanoma and is involved in the antitumor action of the NK-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant on melanoma cell lines. Lab. Invest. 2010, 90, 1259-69. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; González-Ortega, A.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Carranza, A.; García-Recio, S.; Almendro, V.; et al. The neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant is a promising candidate for the treatment of breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1658-72. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Pavón, A.; Rosso, M.; Salinas-Martín, M.V.; Pérez, A.; Carranza, A.; et al. Immunolocalization of NK-1 receptor and substance P in human normal placenta. Placenta 2010, 31, 649-51. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Muñoz, M.F.; Ayala, A. Immunolocalization of Substance P and NK-1 Receptor in ADIPOSE Stem Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017,118,4686-4696.
- Kramer, M.S.; Cutler, N.; Feighner, J.; Shrivastava, R.; Carman, J.; Sramek, J.J.; Reines, S.A.; Liu, G.; Snavely, D.; Wyatt-Knowles, E.; et al: Distinct mechanism for antidepressant activity by blockade of central substance P receptors. Science 1998, 281,1640-1645.
- Ortiz-Prieto, A.; Bernabeu-Witte, J.; Zulueta-Dorado, T.; Lorente-Lavirgen, A.I.; Muñoz, M. Immunolocalization of substance P and NK-1 receptor in vascular anomalies. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 97-102. [CrossRef]
- Koh, Y.H.; Tamizhselvi, R.; Bhatia, M. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase, through nuclear factor-kappaB and activator protein-1, contribute to caerulein-induced expression of substance P and neurokinin-1 receptors in pancreatic acinar cells. J Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2010; 332. 940-8. [CrossRef]
- Walczak-Drzewiecka, A.; Ratajewski, M.; Wagner, W.; Dastych, J. HIF-1alpha is up-regulated in activated mast cells by a process that involves calcineurin and NFAT. J. Inmunol. 2008, 181, 1665-72. [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Sharif, T.R.; Sharif, M. Substance P-induced mitogenesis in human astrocytoma cells correlates with activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 1996, 56. 4983-91.
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Involvement of substance P and the NK-1 receptor in cancer. Peptides 2013, 48, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Recio, S.; Fuster, G.; Fernandez-Nogueira, P. Substance P autocrine signaling contributes to persistent HER2 activation that drives malignant progression and drug resistance in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013,73, 6424-6434. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Rosso, M.; Pérez, A.; Coveñas, R.; Rosso, M.; Zamarriego, C.; et al. The NK1 receptor is involved in the antitumoural action of L-733,060 and in the mitogenic action of substance P on neuroblastoma and glioma cell lines. Neuropeptides 2005,39, 427-32. [CrossRef]
- Guha, S.; Eibl, G.; Kisfalvi, K.; Fan, R.S.; Burdick, M.; Reber, H.; et al. Broad-spectrum G protein-coupled receptor antagonist, [D-Arg1, DTrp5,7,9, Leu11] SP: a dual inhibitor of growth and angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 2738-45.
- 47. Castagliuolo I, Valenick L, Liu J, Pothoulakis C. Epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates substance P-induced mitogenic responses in U-373 MG cells. J Biol Chem. 2000 Aug 25;275(34):26545-50. [CrossRef]
- Akazawa, T.; Kwatra, S.G.; Goldsmith, L.E.; Richardson, M.D.; Cox, E.A.; Sampson, J.H.; et al. A constitutively active form of neurokinin 1 receptor and neurokinin 1 receptor-mediated apoptosis in glioblastomas. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1079-86. [CrossRef]
- Ziche, M.; Morbidelli, L.; Pacini, M.; Geppetti, P.; Alessandri, G.; Maggi, C.A. Substance P stimulates neovascularization in vivo and proliferation of cultured endothelial cells. Microvasc. Res. 1990, 40,264-278. [CrossRef]
- Rubinow, K.B. An intracrine view of sex steroids, immunity, and metabolic regulation. Mol. Metab. 2018, 15,92-103. [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, D. Contribution of phenylalanine side chain intercalation to the TATA-box binding protein-DNA interaction: molecular dynamics and dispersion-corrected density functional theory studies. J. Mol. Model. 2014, 20,2499. [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.M.; Leeman, S.E.; Niall, H.D. Amino-acid sequence of substance P. Nat. New. Biol. 1971,232,86-7. [CrossRef]
- Skrabanek, P.; Cannon, D.; Dempsey, J.; Kirrane, J.; Neligan, M.; Powell, D.. “Substance P in medullary carcinoma of the thyroid.” Experientia 1979, 35, 1259-60. [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.; Tucker, K.L.; Sage, T.; Kaiser, W.J.; Barrett, N.E.; Lowry, P.J.; et al. Peripheral tachykinins and the neurokinin receptor NK1 are required for platelet thrombus formation. Blood 2008, 111, 605-12. [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Siepmann, D.; Herrgott, I.; Sunderkötter, C.; Luger, T.A. Targeting the neurokinin receptor 1 with aprepitant: a novel antipruritic strategy. PLoS One 2010,5, e10968.
- Coveñas, R.; Muñoz, M. “Involvement of the Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor System in Cancer” Cancers 2022, 14,3539.
- Alsaeed, M.A.; Ebrahimi, S.; Alalikhan, A.; Hashemi. S.F.; Hashemy, S.I. The Potential In Vitro Inhibitory Effects of Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonist, Aprepitant, in Osteosarcoma Cell Migration and Metastasis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022,8082608. [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O. On the origin of cancer cells. Science 1956, 123,309-314. [CrossRef]
- Medrano, S.; Gruenstein, E.; Dimlich, R.V. Substance P receptors on human astrocytoma cells are linked to glycogen breakdown. Neurosci. Lett. 1994, 167, 14-8. [CrossRef]
- Vasko, VV.; Saji, M. Molecular mechanisms involved in differentiated thyroid cancer invasion and metastasis. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2007, 19,11-7.
- Sporn, M.B. The war on cancer. Lancet 1996, 347,1377-81.
- Meshki, J.; Douglas, S.D.; Hu, M.; Leeman, S.E.; Tuluc, F. Substance P induces rapid and transient membrane blebbing in U373MG cells in a p21-activated kinase-dependent manner. PLoS One 2011, 6, e25332. [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yuan, S.; Cheng, J.; Kang, S.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J. Substance P promotes the progression of endometrial adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2016, 26, 845-50. [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Javid, H.; Afshari, A.R.; Mashkani, B.; Hashemy, S.I. Substance P accelerates the progression of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via MMP-2, MMP-9, VEGF-A, and VEGFR1 overexpression. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47,4263-4272. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Safety of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists. Expert. Opin. Drug. Saf. 2013, 12, 673–685. [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.K.; Kohli, A. Aprepitant. [Updated 2022 Sep 22]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022.
- Turner, R.D.; Birring, S.S. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Inhibition and Cough. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021,203,672-674. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Berger. M.; Rosso, M.; Gonzalez-Ortega, A.; Carranza, A.; Coveñas, R. Antitumor activity of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists in MG-63 human osteosarcoma xenografts. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 44,137-46. [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Crespo, J.C.; Crespo, J.P.; Coveñas, R. Neurokinin-1 receptor antagonist aprepitant and radiotherapy, a successful combination therapy in a patient with lung cancer: A case report. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 11,50-54.
- Tebas, P; Spitsin, S.; Barrett, J.S.; Tuluc, F.; Elci, O.; Korelitz, J.J.; Wagner, W.; Winters, A.; Kim, D.; Catalano, R.; Evans, D.L.; Douglas, S.D. Reduction of soluble CD163, substance P, programmed death 1 and inflammatory markers: phase 1B trial of aprepitant in HIV-1-infected adults. AIDS 2015, 29, 931-9.
- Robinson, P.; Coveñas, R.; Muñoz, M. Combination Therapy of Chemotherapy or Radiotherapy and the Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonist Aprepitant: A New Antitumor Strategy? Curr. Med. Chem. 2023,30,1798-1812.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




