Submitted:
10 August 2023
Posted:
14 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Data and Method
3.1. Data
3.2. Machine Translations & EVALUATION (- RICK to DESCRIBE MT AND EVAL METRICS)
3.3. Machine Translations - Observations
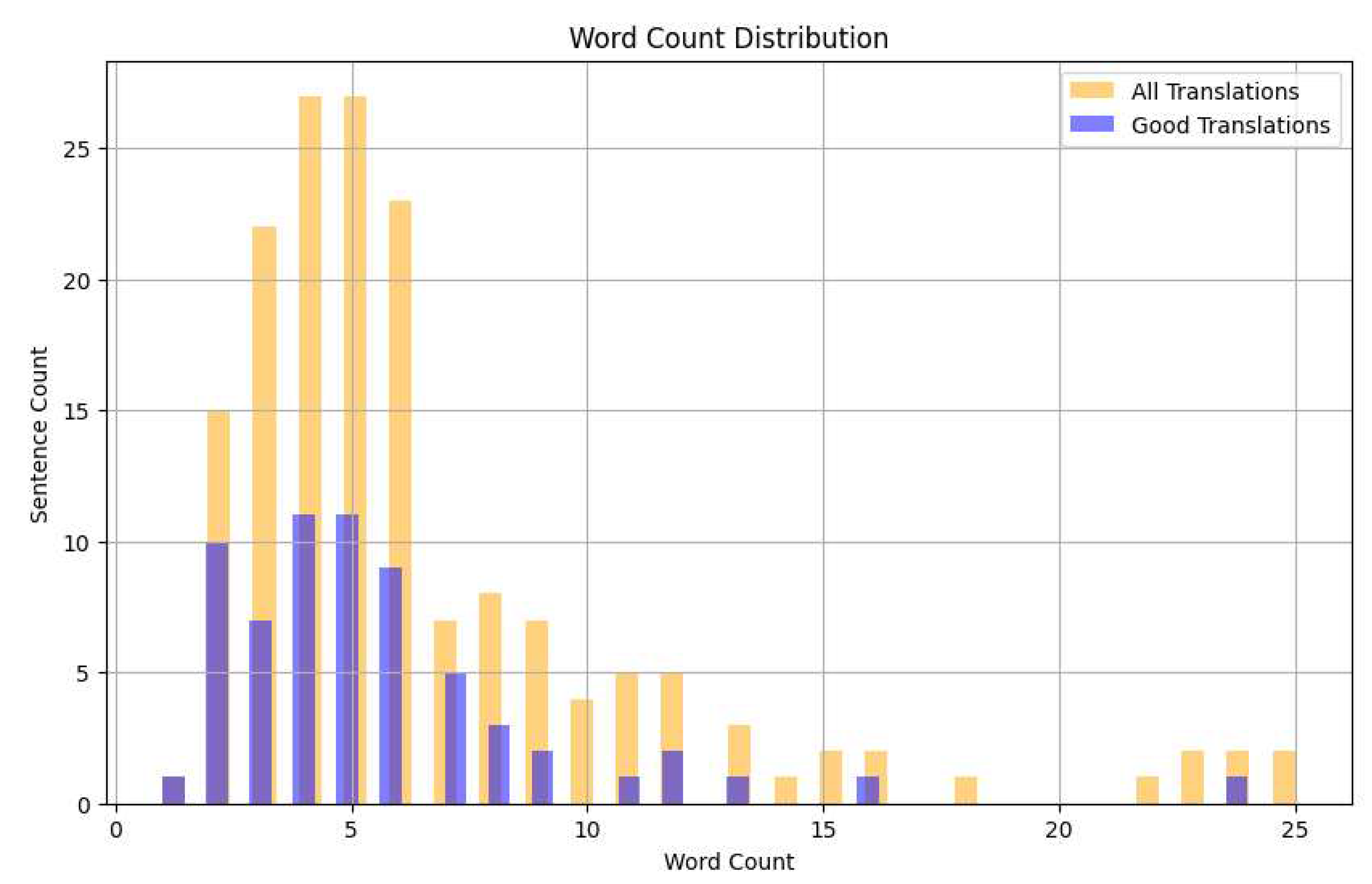
3.4. Data Analysis
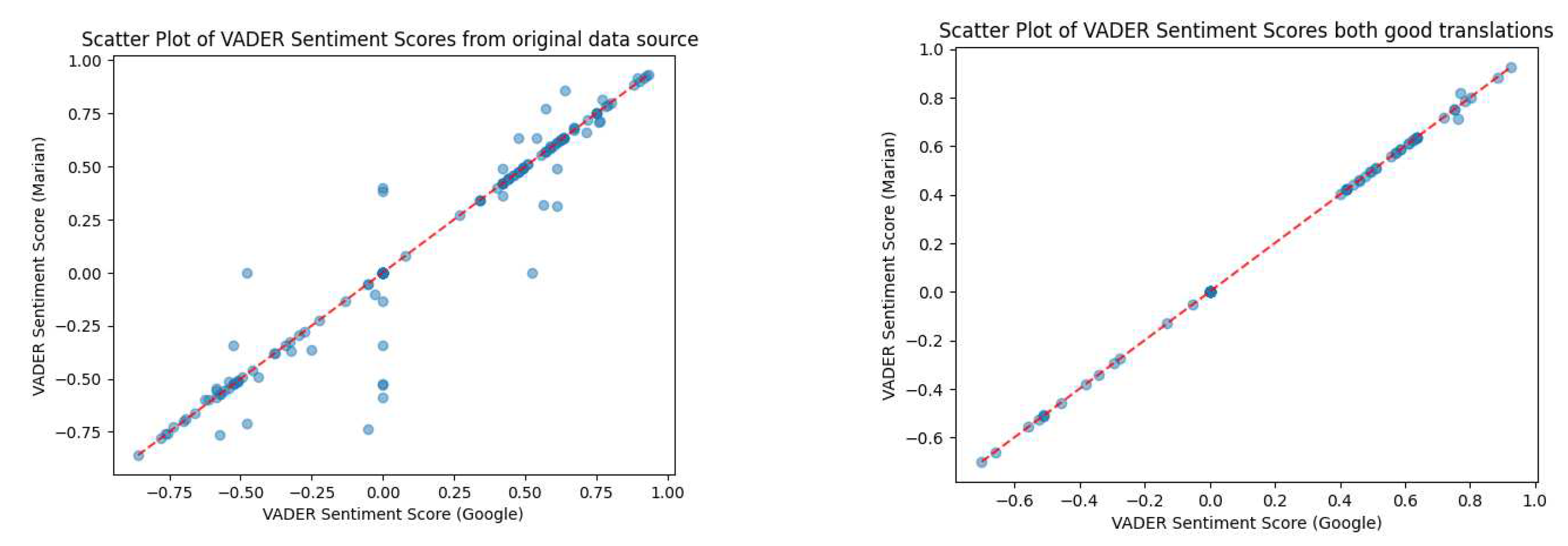
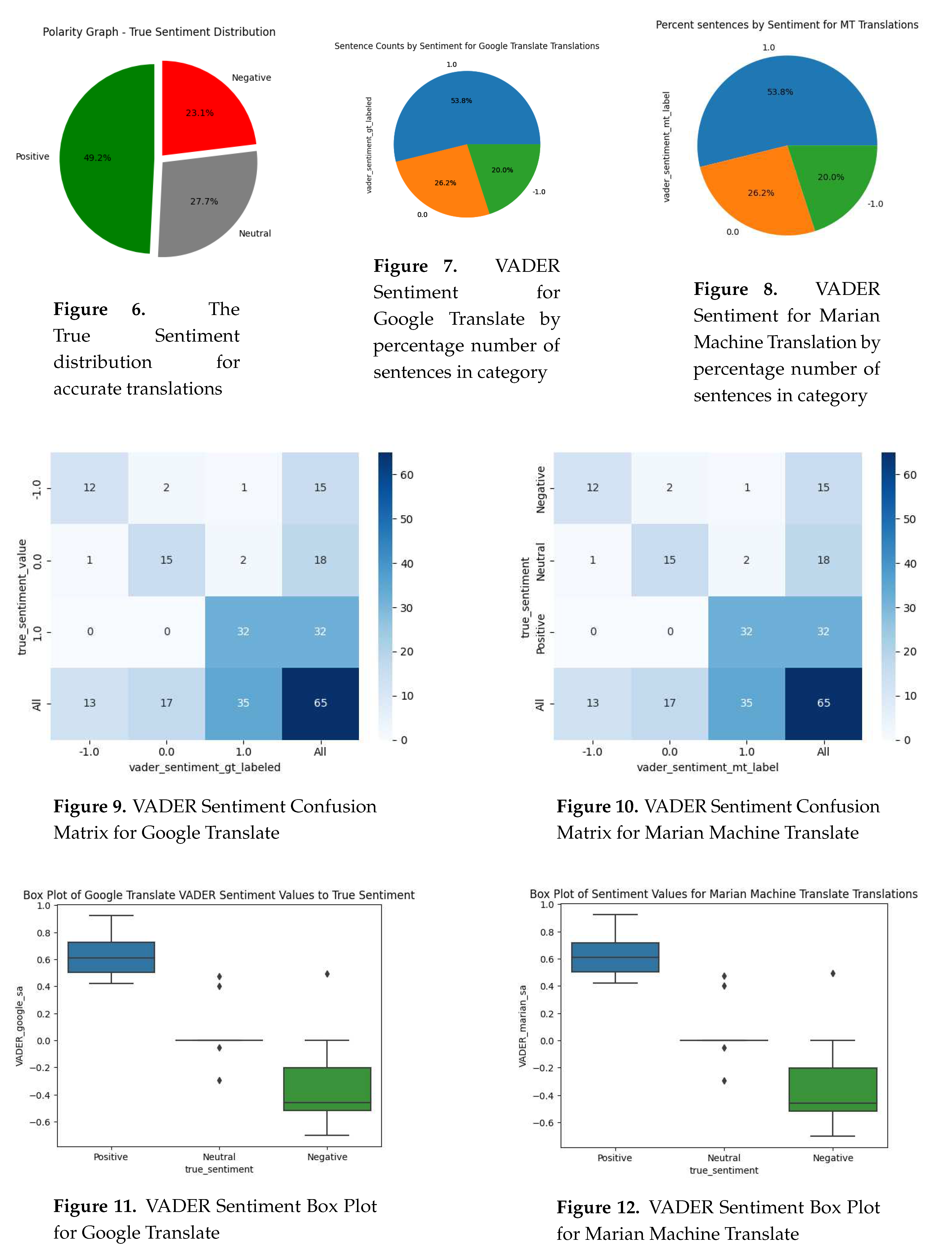
4. Discussion
| Listing 1: Outliers for Neutral |
| Outliers for Neutral: |
| Sentence: La musica americana attrae sempre molti giovani italiani |
| Google Translation: American music always attracts many young Italians |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment: 0.4019 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: I miei amici sono venuti a farmi visita |
| Google Translation: My friends came to visit me |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment: 0.4767 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: Non ho preferenze su cosa fare stasera |
| Google Translation: I have no preferences on what to do tonight |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment: -0.296 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: Domani partiamo per andare in Italia |
| Google Translation: Tomorrow we leave to go to Italy |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment: -0.0516 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Listing 2: Marian MT Outliers for Neutral |
| Outliers for Neutral: |
| Sentence: La musica american attrae sempre molti giovani italiani |
| Marian MT Translation: American music always attracts many young Italians |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment (MT): 0.4019 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: I miei amici sono venuti a farmi visita |
| Marian MT Translation: My friends came to visit me |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment (MT): 0.4767 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: Non ho preferenze su cosa fare stasera |
| Marian MT Translation: I have no preference on what to do tonight |
| True Sentiment: Neutral |
| True Sentiment Value: 0.0 |
| VADER Sentiment (MT): -0.296 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Listing 3: Marian MT Outliers for Negative |
| Outliers for Negative: |
| Sentence: Sei un essere abominevole. |
| Marian MT Translation: You are an abominable being. |
| True Sentiment: Negative |
| True Sentiment Value: -1.0 |
| VADER Sentiment (MT): 0.0 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: Disapprovo la tua scelta! |
| Marian MT Translation: I disapprove of your choice! |
| True Sentiment: Negative |
| True Sentiment Value: -1.0 |
| VADER Sentiment (MT): 0.0 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
| Sentence: Buono a nulla! |
| Marian MT Translation: Good for nothing! |
| True Sentiment: Negative |
| True Sentiment Value: -1.0 |
| VADER Sentiment (MT): 0.4926 |
| −−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−−− |
4.1. Why was polarized Italian made neutral?
5. Limitations
6. Future research
7. Conclusion
References
- Samuel, J., R. Palle, and E. Soares. Textual Data Distributions: Kullback Leibler Textual Distributions Contrasts on GPT-2 Generated Texts with Supervised, Unsupervised Learning on Vaccine & Market Topics & Sentiment. Journal of Big Data: Theory and Practice.
- NLP, M. Natural Language Processing Market. https://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/natural-language-processing-nlp-825.html, 2022. Accessed on 2022-09-05.
- Liu, H., R. Ning, Z. Teng, J. Liu, Q. Zhou, and Y. Zhang. 2023. Evaluating the logical reasoning ability of chatgpt and gpt-4. arXiv arXiv:2304.03439 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, X.P., S.M. Aljunied, S. Joty, and L. Bing. 2023. Democratizing LLMs for Low-Resource Languages by Leveraging their English Dominant Abilities with Linguistically-Diverse Prompts. arXiv arXiv:2306.11372 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S., Y. Sun, Y. Xiang, Z. Wu, S. Ding, W. Gong, S. Feng, J. Shang, Y. Zhao, and C. Pang. 2021. ; others. Ernie 3.0 titan: Exploring larger-scale knowledge enhanced pre-training for language understanding and generation. arXiv arXiv:2112.12731 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ranathunga, S., and N. de Silva. 2022. Some languages are more equal than others: Probing deeper into the linguistic disparity in the nlp world. arXiv arXiv:2210.08523 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cunliffe, D., A. Vlachidis, D. Williams, and D. Tudhope. 2022. Natural language processing for under-resourced languages: Developing a Welsh natural language toolkit. Computer Speech & Language 72: 101311. [Google Scholar]
- Lahoti, P., N. Mittal, and G. Singh. 2022. A survey on nlp resources, tools, and techniques for marathi language processing. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing 22: 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sebastian, M.P. 2023. Malayalam Natural Language Processing: Challenges in Building a Phrase-Based Statistical Machine Translation System. ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing 22: 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J., G. Ali, M. Rahman, E. Esawi, Y. Samuel, and others. 2020. Covid-19 public sentiment insights and machine learning for tweets classification. Information 11: 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J., M.M. Rahman, G.M.N. Ali, Y. Samuel, A. Pelaez, P.H.J. Chong, and M. Yakubov. 2020. Feeling Positive About Reopening? New Normal Scenarios From COVID-19 US Reopen Sentiment Analytics. IEEE Access 8: 142173–142190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M., G.M.N. Ali, X.J. Li, J. Samuel, K.C. Paul, P.H. Chong, and M. Yakubov. 2021. Socioeconomic factors analysis for COVID-19 US reopening sentiment with Twitter and census data. Heliyon 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.M.N., M.M. Rahman, M.A. Hossain, M.S. Rahman, K.C. Paul, J.C. Thill, and J. Samuel. 2021. Public perceptions of COVID-19 vaccines: Policy implications from US spatiotemporal sentiment analytics. , , Vol. 9, p. Healthcare. MDPI 9: 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balahur, A., and M. Turchi. 2014. Comparative experiments using supervised learning and machine translation for multilingual sentiment analysis. Computer Speech & Language 28: 56–75. [Google Scholar]
- Balahur, A., and M. Turchi. Multilingual sentiment analysis using machine translation? Proceedings of the 3rd workshop in computational approaches to subjectivity and sentiment analysis, 2012, pp. 52–60.
- Mohammad, S.M., M. Salameh, and S. Kiritchenko. 2016. How translation alters sentiment. Journal of Artificial Intelligence Research 55: 95–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oueslati, O., E. Cambria, M.B. HajHmida, and H. Ounelli. 2020. A review of sentiment analysis research in Arabic language. Future Generation Computer Systems 112: 408–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proksch, S.O., W. Lowe, J. Wäckerle, and S. Soroka. 2019. Multilingual sentiment analysis: A new approach to measuring conflict in legislative speeches. Legislative Studies Quarterly 44: 97–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poncelas, A., P. Lohar, A. Way, and J. Hadley. 2020. The impact of indirect machine translation on sentiment classification. arXiv arXiv:2008.11257 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Araújo, M., A. Pereira, and F. Benevenuto. 2020. A comparative study of machine translation for multilingual sentence-level sentiment analysis. Information Sciences 512: 1078–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P., K. Pathania, and B. Raman. 2023. Zero-shot learning based cross-lingual sentiment analysis for sanskrit text with insufficient labeled data. Applied Intelligence 53: 10096–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazzed, S., and S. Jayarathna. 2019. A sentiment classification in bengali and machine translated english corpus. 2019 IEEE 20th international conference on information reuse and integration for data science (IRI). 2019 IEEE 20th international conference on information reuse and integration for data science (IRI); IEEE, pp. 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sazzed, S. Cross-lingual sentiment classification in low-resource bengali language. Proceedings of the sixth workshop on noisy user-generated text (W-NUT 2020), 2020, pp. 50–60.
- Berard, A., I. Calapodescu, M. Dymetman, C. Roux, J.L. Meunier, and V. Nikoulina. 2019. Machine translation of restaurant reviews: New corpus for domain adaptation and robustness. arXiv arXiv:1910.14589 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dashtipour, K., S. Poria, A. Hussain, E. Cambria, A.Y. Hawalah, A. Gelbukh, and Q. Zhou. 2016. Multilingual sentiment analysis: state of the art and independent comparison of techniques. Cognitive computation 8: 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, V., and M. Nissim. Sentiment analysis on Italian tweets. Proceedings of the 4th workshop on computational approaches to subjectivity, sentiment and social media analysis, 2013, pp. 100–107.
- Catelli, R., L. Bevilacqua, N. Mariniello, V.S. di Carlo, M. Magaldi, H. Fujita, G. De Pietro, and M. Esposito. 1182. Cross lingual transfer learning for sentiment analysis of Italian TripAdvisor reviews. Expert Systems with Applications. [Google Scholar]
- Porreca, A., F. Scozzari, and M. Di Nicola. 2020. Using text mining and sentiment analysis to analyse YouTube Italian videos concerning vaccination. BMC Public Health 20: 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catelli, R., S. Pelosi, and M. Esposito. 2022. Lexicon-based vs. Bert-based sentiment analysis: A comparative study in Italian. Electronics 11: 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, L., S. Loáiciga, and A. Gulati. 2012. Improving machine translation of null subjects in Italian and Spanish. Proceedings of the Student Research Workshop at the 13th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, vol. 89, p. 81. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann, E. 2019. Machine translation in the field of law: A study of the translation of Italian legal texts into German. Comparative Legilinguistics 37: 117–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawden, R., G.M. Di Nunzio, C. Grozea, I.J. Unanue, A.J. Yepes, N. Mah, D. Martinez, A. Névéol, M. Neves, and M. Oronoz. 2020. ; others. Findings of the WMT 2020 biomedical translation shared task: Basque, Italian and Russian as new additional languages. Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation; pp. 660–687. [Google Scholar]
- Modzelewski, A., W. Sosnowski, M. Wilczynska, and A. Wierzbicki. 2023. DSHacker at SemEval-2023 Task 3: Genres and Persuasion Techniques Detection with Multilingual Data Augmentation through Machine Translation and Text Generation. Proceedings of the The 17th International Workshop on Semantic Evaluation (SemEval-2023); pp. 1582–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S. googletrans: Free and Unlimited Google translate API for Python, 2022. Accessed: 2023-02-27.
- Junczys-Dowmunt, M., R. Grundkiewicz, T. Dwojak, H. Hoang, K. Heafield, T. Neckermann, F. Seide, U. Germann, A. Fikri Aji, N. Bogoychev, A.F.T. Martins, and A. Birch. 2018. Marian: Fast Neural Machine Translation in C++. Proceedings of ACL 2018, System Demonstrations. Melbourne, Australia: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 116–121. [Google Scholar]
- Tiedemann, J., and S. Thottingal. 2020. OPUS-MT – Building open translation services for the World. Proceedings of the 22nd Annual Conference of the European Association for Machine Translation. Lisboa, Portugal: European Association for Machine Translation, pp. 479–480. [Google Scholar]
- Tiedemann, J. 2020. The Tatoeba Translation Challenge – Realistic Data Sets for Low Resource and Multilingual MT. Proceedings of the Fifth Conference on Machine Translation. Online: Association for Computational Linguistics, pp. 1174–1182. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, J., M. Brennan, M. Pfeiffer, C. Andrews, and M. Hale. Garden State Open Data Index for Public Informatics 2023.
- Samuel, J. Response to the March 2023’Pause Giant AI experiments: an open letter’by Yoshua Bengio, signed by Stuart Russell, Elon Musk, Steve Wozniak, Yuval Noah Harari and others…. Elon Musk, Steve Wozniak, Yuval Noah Harari and others…(March 29, 2023), March 20.
- Samuel, J. 2021. A call for proactive policies for informatics and artificial intelligence technologies. Scholars Strategy Network. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.H., V. Kumar, J. Samuel, S. Singh, A. Mannepalli, and R. Anderson. 2023. Artificially Intelligent Readers: An Adaptive Framework for Original Handwritten Numerical Digits Recognition with OCR Methods. Information 14: 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J., R. Kashyap, Y. Samuel, and A. Pelaez. 2022. Adaptive cognitive fit: Artificial intelligence augmented management of information facets and representations. International journal of information management 65: 102505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, J. The Critical Need for Transparency and Regulation amidst the Rise of Powerful Artificial Intelligence Models. https://scholars.org/contribution/critical-need-transparency-and-regulation, 2023. Accessed on 2023-08-02.


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




