Introduction
Wake generally refers to turbulent vortices behind or downstream of a moving object, also known as the trail. For moving non-streaming objects, such as wind turbines and aircraft carriers, the flow separates from the trailing surface and creates vortices that continue to develop downstream and form a wake region. In the wake region, the flow velocity lessens and the turbulence intensity increases, which has a substantial effect on the aerodynamic performance of downstream objects, such as reducing the efficiency of wind turbines in the wake region and making it problematic to predict the aerodynamic characteristics of an aircraft carrier on the carrier.
Numerical simulations are common approaches to examining the aerodynamic characteristics of downstream objects that are affected by the complex low-velocity peak [
1]. Such methods often exploit a coupled solution calculation of the wake field and the downstream object. However, due to the high dimensions, instability, and nonlinearity of the foundation, the computational time of conventional methods is expensive and the reproducibility of the results is generally poor. To address the above issues, according to the characteristic flow structure of the foundation, this paper separates the calculations separated from the foundation and the flow around the downstream object. In particular, an efficient wake reduction methodology is employed to identify the characteristic flow structure of the wake and different scale flow structures are generated through the domain precursor simulation method, based on which the wake effect on the aerodynamic characteristics of the downstream objects is calculated.
Regarding the identification of the characteristic flow structures of wake, proper orthogonal decomposition (POD) is regarded as an efficient and extensively utilized flow reduction scheme. This approach was proposed by Hotelling [
2], and the main idea is to seek the optimal standard orthogonal basis or several bases that best represent the known data in a least-squares sense and employ them to approximate high-dimensional data with low-dimensional models [
3], therefore achieve the goal of simplifying the physical model [
4]. Lumley [
5] proposed the application of this method to identify characteristic structures in complex turbulent flows and analyzed high-dimensional unsteady flows via the POD, which elucidated characteristic flow structures and examined complex turbulent flow phenomena. Nevertheless, with the rapid and continuous development of numerical and experimental techniques, flow data have become progressively massive, becoming problematic for the original POD approach to work with high-dimensional matrices. Subsequently, Sirovich [
6] improved the original POD algorithm using singular value decomposition (SVD) and proposed the snapshot POD algorithm, which is capable of solving problems of large matrix dimensions and making it easier to handle complex high-dimensional flow fields. Currently, this improved POD approach has been broadly employed in complex flow structure analysis [7-9].
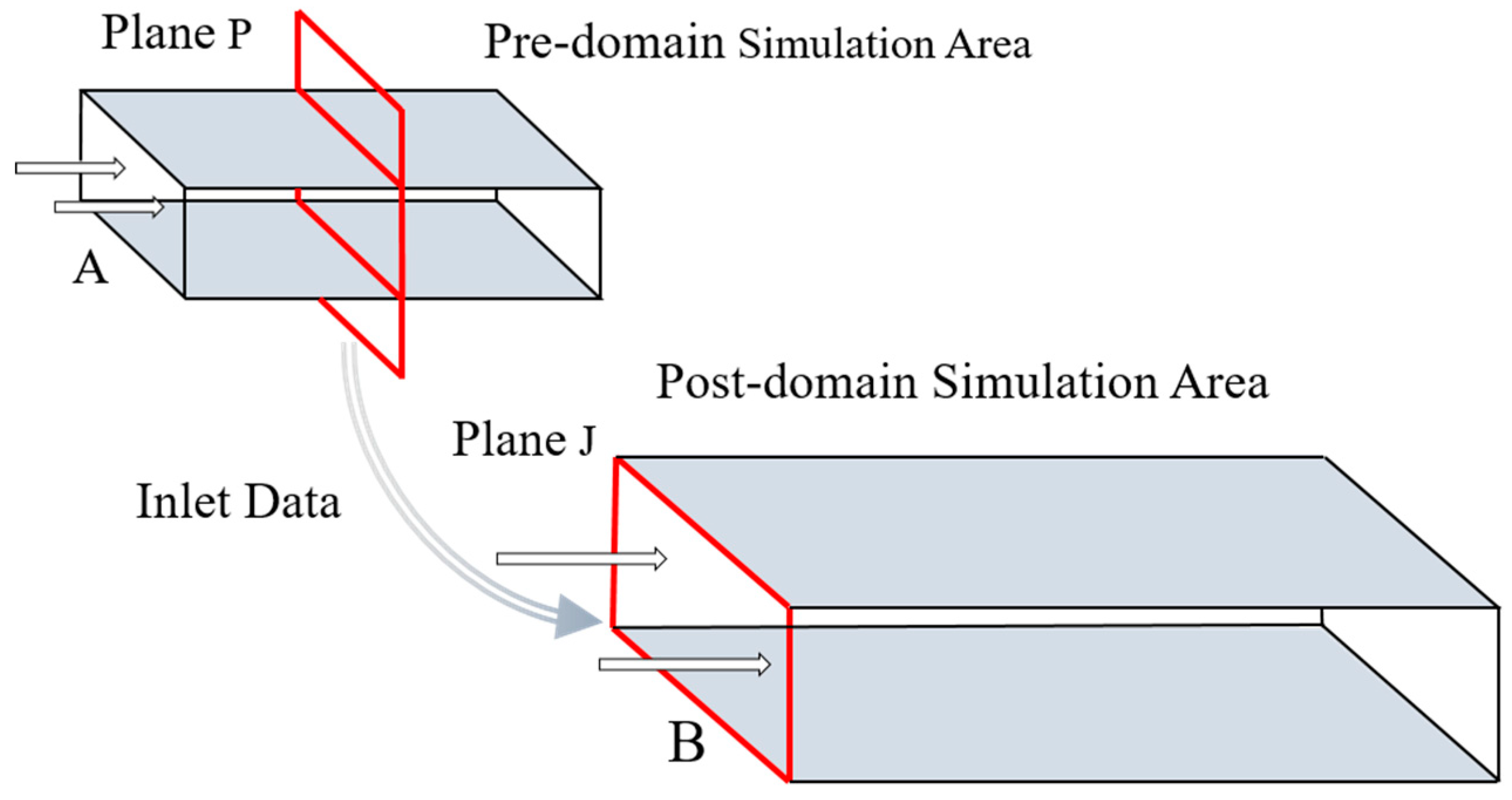
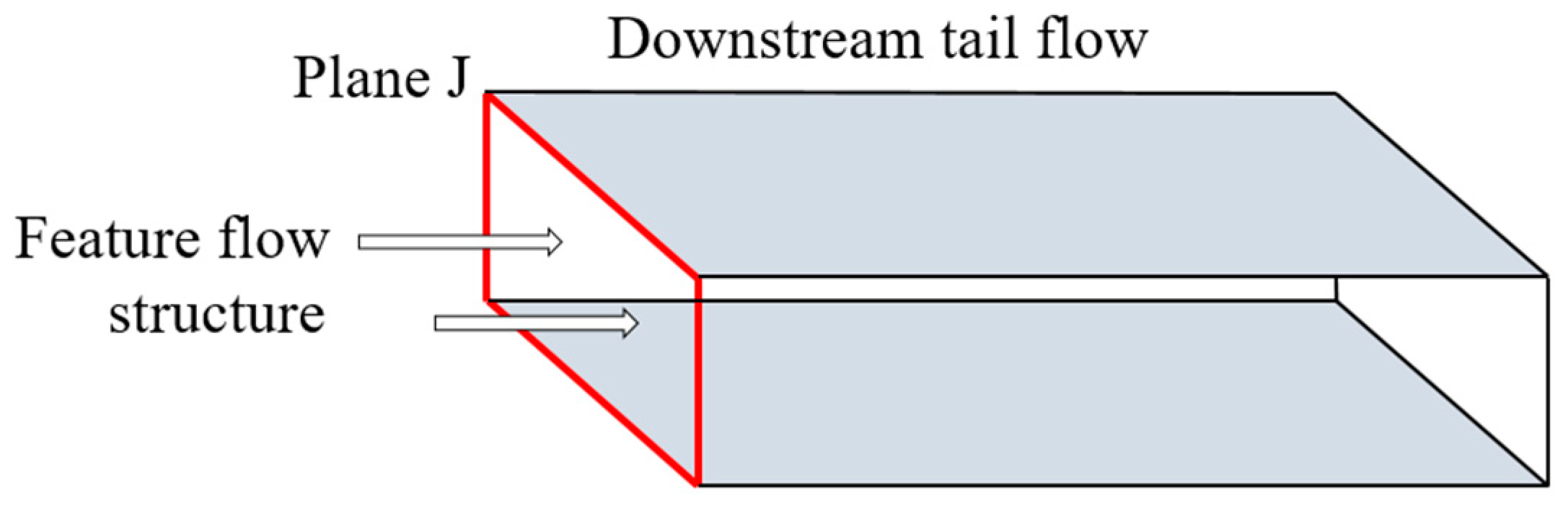
The domain precursor simulation method is often adopted to generate turbulent inflow boundary conditions, as illustrated in
Figure 1. First, an unsteady numerical simulation is performed in domain A, and when the flow field is stabilized, the values of flow variables such as velocity and pressure at each time step are stored on the plane P, perpendicular to the flow direction, for a certain period, which is utilized to generate the input database. Then, by simulating the flow in the main downstream domain, the flow variables at each time step in the inflow database are loaded into inlet surface J of the main domain by interpolating between various grids. This approach has gained remarkable results in atmospheric boundary layer flow simulation and LES analysis of complex turbulent flows. For instance, Fureby et al. [
10] and Lamballais et al. [
11] have applied the domain precursor simulation method to numerically simulate the pipe flow using periodic boundary conditions through reimposing the downstream flow variable at the upstream inlet, creating a more realistic turbulent flow and enabling a faster and more efficient analysis of the coherent structure of the turbulent flow. Wang et al. [
12] implemented the domain precursor simulation approach to store the input flow data of 10,000-time steps in examining the rotating turbulent flows by large-eddy simulation. By reducing the turbulence energy via a scaling method for the momentum of turbulent oscillations, the unphysical flow fields could be transformed into more realistic turbulent fields in a short time.
Based on the snapshots of the POD-based method and the domain precursor simulation method, this paper aims to appropriately mix the efficient flow reduced-order method with the domain decomposition simulation approach to arrive at various scale inflow structures. Then, the changes in the aerodynamic characteristics of the downstream objects are examined.
1. Numerical solution approach for low-speed flow
The Navier-Stokes governing equations of an incompressible flow read as:
where
denotes the velocity vector,
is the density,
represents the pressure field, and
stands for the kinematic viscosity.
The finite volume approach is implemented for the spatial approximation of the governing equations. To this end, the diffusion term is appropriately discretized via a central scheme, whereas the convection term is discretized based on a second-order upwind scheme. The value of a scalar variable
ϕ on the face of a cell can be evaluated as follows:
and the gradient of the aforementioned scalar field (
) is calculated in the following way:
The temporal term in the governing equations can be discretized using the following second-order implicit scheme:
In which represents the current time step, and denotes the residual term.
In this work, the SST (i.e., Shear-Stress Transport) k-ω [
13] model is utilized for turbulence closure. Furthermore, due to the decoupling of velocity and pressure, SIMPLEC (SIMPLE Consistent) algorithm is adopted to evaluate the pressure.
2. POD method and its application
2.1. POD method
Let
V be an arbitrary flow variable, such as velocity, pressure, or vorticity. The sample matrix
of dimension
could be configured by a set of snapshots
obtained within a specified time interval in the following form:
where
denotes the number of grid nodes and
represents the number of snapshots.
The time average of a snapshots set
is stated by:
Let us denote the snapshot fluctuation matrix by
, where:
The key of the POD method is to seek a set or several sets of optimal orthogonal basis functions
to maximize the following expression:
that is to say, to solve the following eigenvalue problem:
where:
Through transforming the spatial dimensions of the matrix
C into the time dimension, the modal representation can be stated as a linear combination of the eigenvalues of the temporal matrix [
14,
15]:
Let , that is, to solve , where denotes the i-th eigenvector associated with the eigenvalue . Since the dimension of the matrix to be solved is only , the computational complexity is substantially reduced compared to the original POD algorithm.
2.2. Validation of the snapshot POD algorithm
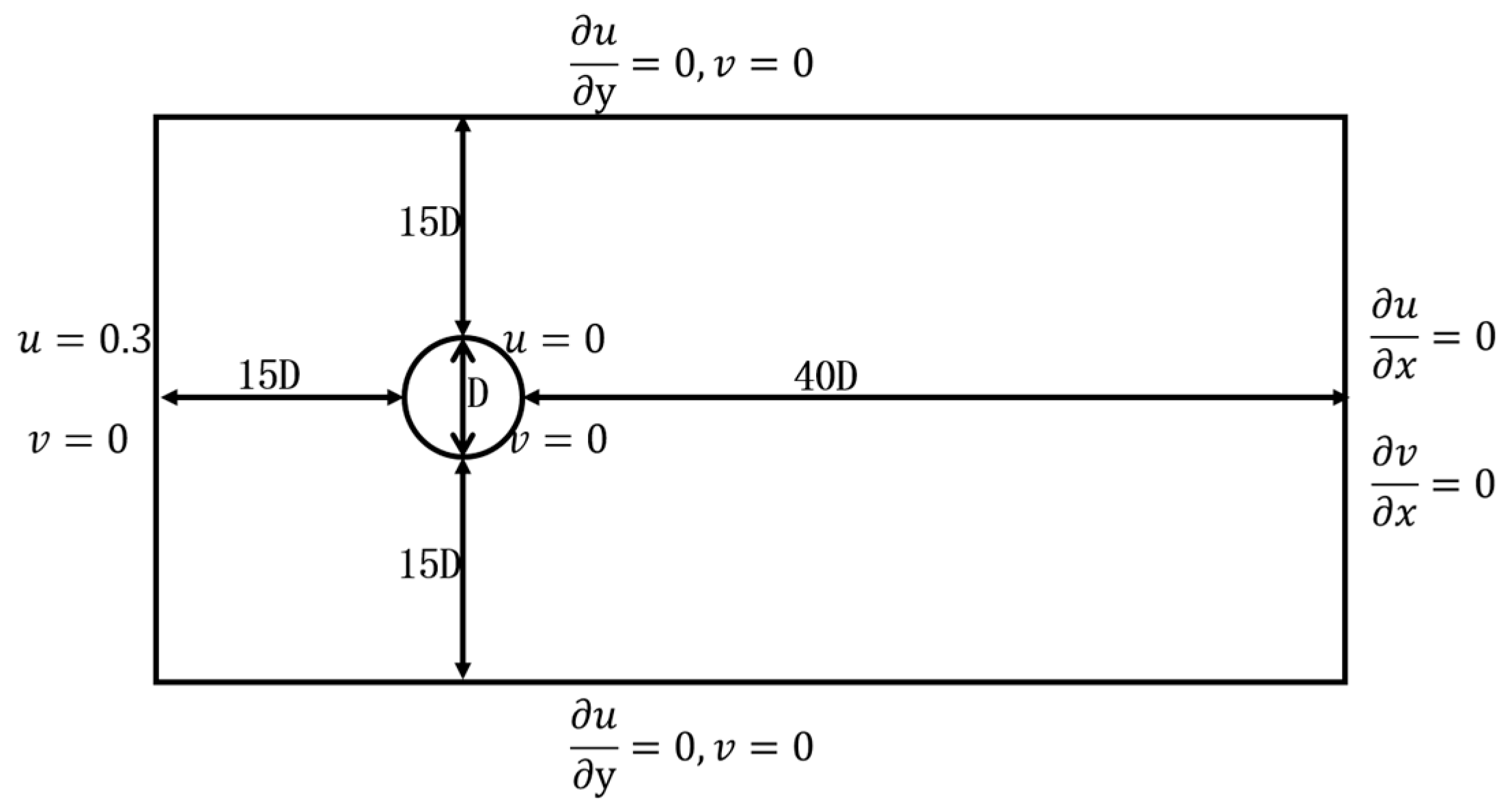
In order to validate the snapshot POD algorithm, the classical wake flow behind a single circular cylinder is chosen, and the Reynolds number is set to 200 based on the diameter. The size of the computational domain is taken according to Refs. [
16,
17], as illustrated in
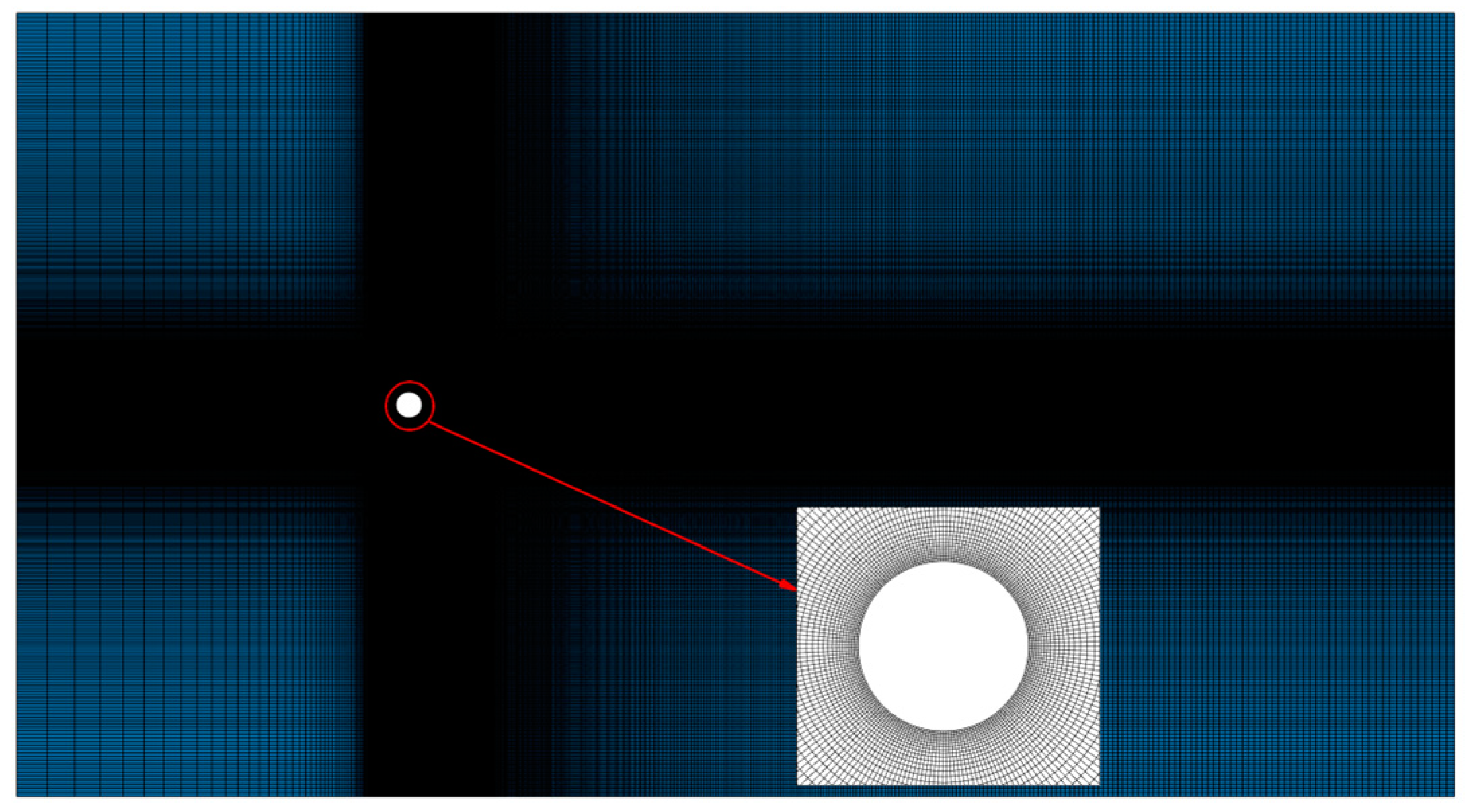
Figure 2. The diameter of the cylinder is set as 0.01 m and the inlet flow velocity is considered to be 0.3 m/s. The computational grid is a structured grid, as demonstrated in
Figure 3. The height of the first grid layer is 10
-5 and the total number of grid cells is 340862. The grid is refined around the cylinder where the flow is sharply altered, and in the region where the wake vortex falls and gradually dissipates from the cylinder. The time step is set equal to 0.001 s and the calculation is performed for 6 s. The time histories of the lift and drag coefficients of the cylinder, denoted by
Cl and
Cd, are illustrated in
Figure 4, where
Ut/D represents the non-dimensional time. It can be seen that after the non-dimensional time of 70, the Kármán vortex street behind the cylinder exhibits stable periodic shedding and the shedding frequency is 6 Hz. Also, the Strouhal number is calculated as S
t=
fD/
U. In
Table 1, the values of
Cl,
Cd, and S
t are compared with those given by Refs. [18-20]. This brief comparison study reveals that the present numerical method is reliable. After that, 2000 sets of flow field vorticity samples during the time period from 4 s to 6 s are selected for POD dimensionality reduction analysis.
Figure 5 illustrates the energy distribution of different POD modes. It can be seen that the modal eigenvalues quickly lessen in the first eight modes, with mode 1 and mode 2 having the highest energy ratios of 67.40% and 25.94%, respectively, contributing to the flow field. The energy of modes 3 and 4 decays to 1.57% and 1.07%, respectively, whereas the energy of modes 5–8 drops below 1.00%, respectively. The higher-order modes contain less energy and their contribution to the flow field can be reasonably neglected. Therefore, in the continuing, the numerical analysis will be performed on the structures based on the first eight modes.
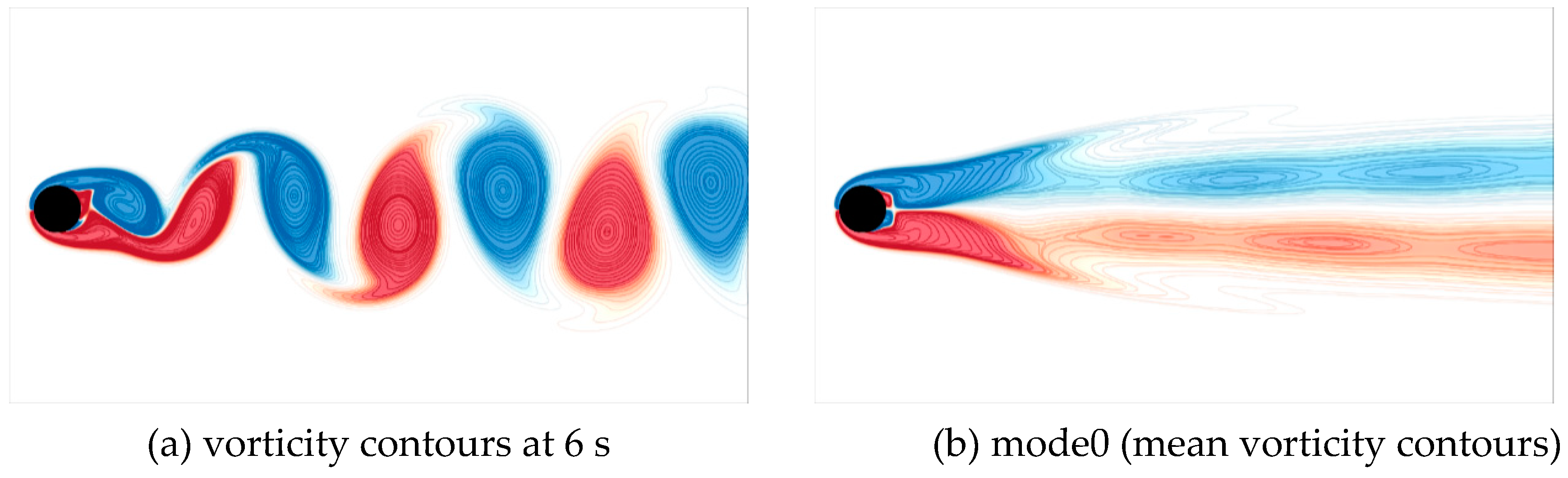
Figure 6(a) and 6(b) illustrate the instantaneous and mean vorticity fields, respectively.
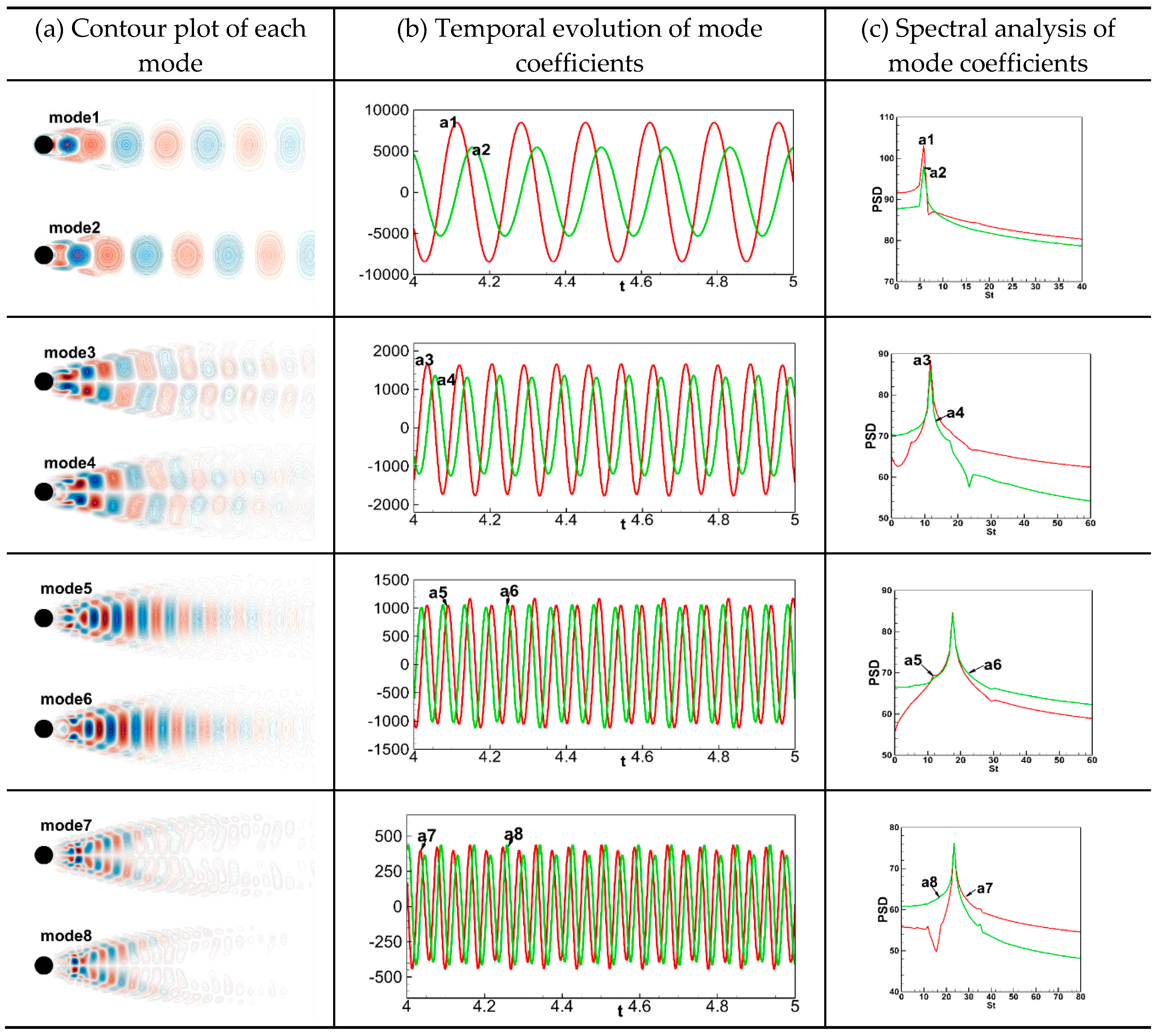
Table 2 presents contour maps, time evolution of mode coefficients, and spectral analysis plots for each POD mode. It can be seen that modes 1&2, modes 3&4, modes 5&6, and modes 7&8 exhibit almost identical structures and the phase differences of their mode coefficients are around π/2. Their main peak values are also close to each other; therefore, modes 1&2, modes 3&4, modes 5&6, and modes 7&8 can be rationally taken into account as paired modes. The spatial structures of modes 1, 3, 5, and 7 are analyzed in detail. Mode 1 (or 2) mainly characterizes the structure of large-scale vortices, which exhibits an up-down symmetrical structure along the flow direction and dominates the periodic shedding of the Kármán vortex street. Mode 3 (or 4) also has a clear vortex structure, but it is more diffuse and smaller compared to mode 1 (or 2) and exhibits an antisymmetric up-down structure along the flow direction. Mode 5 (or 6) and mode 7 (or 8) have similar scattered and chaotic small-scale structures that contribute less to the development of the overall flow. However, mode 7 (or 8) displays a smaller scale structure compared to mode 5 (or 6), and mode 5 (or 6) has an up-down symmetric structure along the flow direction, whereas mode 7 (or 8) exhibits an up-down anti-symmetrical structure. The present POD mode structures are rationally consistent with those in the literature [
21], which demonstrates the reliability of the snapshot POD algorithm implemented in this study.
Figure 6 illustrates the vorticity field and contour map of the mean flow (mode 0) at the simulation time of 6 seconds, where
Figure 6(a) shows the periodic shedding pattern of Kármán vortex street, and
Figure 6(b) demonstrates the static structure of the flow field.
Table 2 presents the contour maps, time coefficients, and spectral analysis graphs of each POD mode. The plotted results indicate that modes 1&2, modes 3&4, modes 5&6, and modes 7&8 have similar structures and the phase differences of their time coefficients are approximately equal to π/2, while their main peak values are also similar. By this virtue, modes 1&2, modes 3&4, modes 5&6, and modes 7&8 can be reasonably considered as paired modes. In the following, the spatial structures of modes 1, 3, 5, and 7 are analyzed in some detail. Mode 1 (or 2) mainly characterizes the large-scale vortex structure of the flow field, which exhibits a symmetric up-down structure distributed along the flow direction and dominates the periodic collapse of the Kármán vortex street; mode 3 (or 4) also exhibits a clear vortex structure, but compared to mode 1 (or 2), it is more dispersed and smaller in structure, and its spatial form shows an up-down anti-symmetric structure, which is distributed along the flow direction; mode 5 (or 6) and mode 7 (or 8) present similar distribution structures, showing scattered and disordered small-scale structures, they contribute less to the overall development of the flow field; however, mode 7 (or 8 ) exhibits a smaller structure scale compared to that of mode 5 (or 6). In addition, mode 5 (or 6) exhibits a symmetrical up-down structure distributed along the flow direction, whereas mode 7 (or 8) presents an anti-symmetric up-down structure distributed along the flow direction. A close scrutiny reveals that the POD mode structures obtained from the simulation of the flow around a single cylinder are consistent with the results in the literature [
18], which demonstrates the reliability of the snapshot POD algorithm implemented in the present investigation.
2.3. Methods for generating various scales inflow for flow simulation
Figure 7 illustrates a schematic representation for generating inflows of different scales. Plane J represents the inlet downstream of the low-velocity wake field. The general idea of this loading method is similar to the domain precursor simulation method presented in
Figure 1. The difference is that the inflow data in the J-plane come from different scale structures obtained via the POD dimension reduction method; however, this also poses a problem. In the domain precursor simulation method, the inlet database is commonly obtained by numerical simulation of real turbulent flows, which possesses characteristics of both temporal and spatial developments of the flow field and is compatible with the N-S equations. When loading such an inlet database with real flow characteristics in the main simulation region, the flow field can quickly transform into a form more consistent with the original flow field. However, for the characteristic structures obtained through POD analysis, during the entrance generating process, the discrepancies between the characteristic structures and the original flow field require more time to develop a real turbulent flow field. Therefore, when we load the flow field with characteristic POD structures as boundary conditions at the inlet, we reconstruct the velocity field with various scale modes and compensate the pressure field to ensure that the reconstructed flow field is closer to the real one, so that rapidly produced an ideal flow field. This approach can be verified in the following sections.
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Numerical simulation of the wake field of low-speed parallel double cylinders in the pre-domain
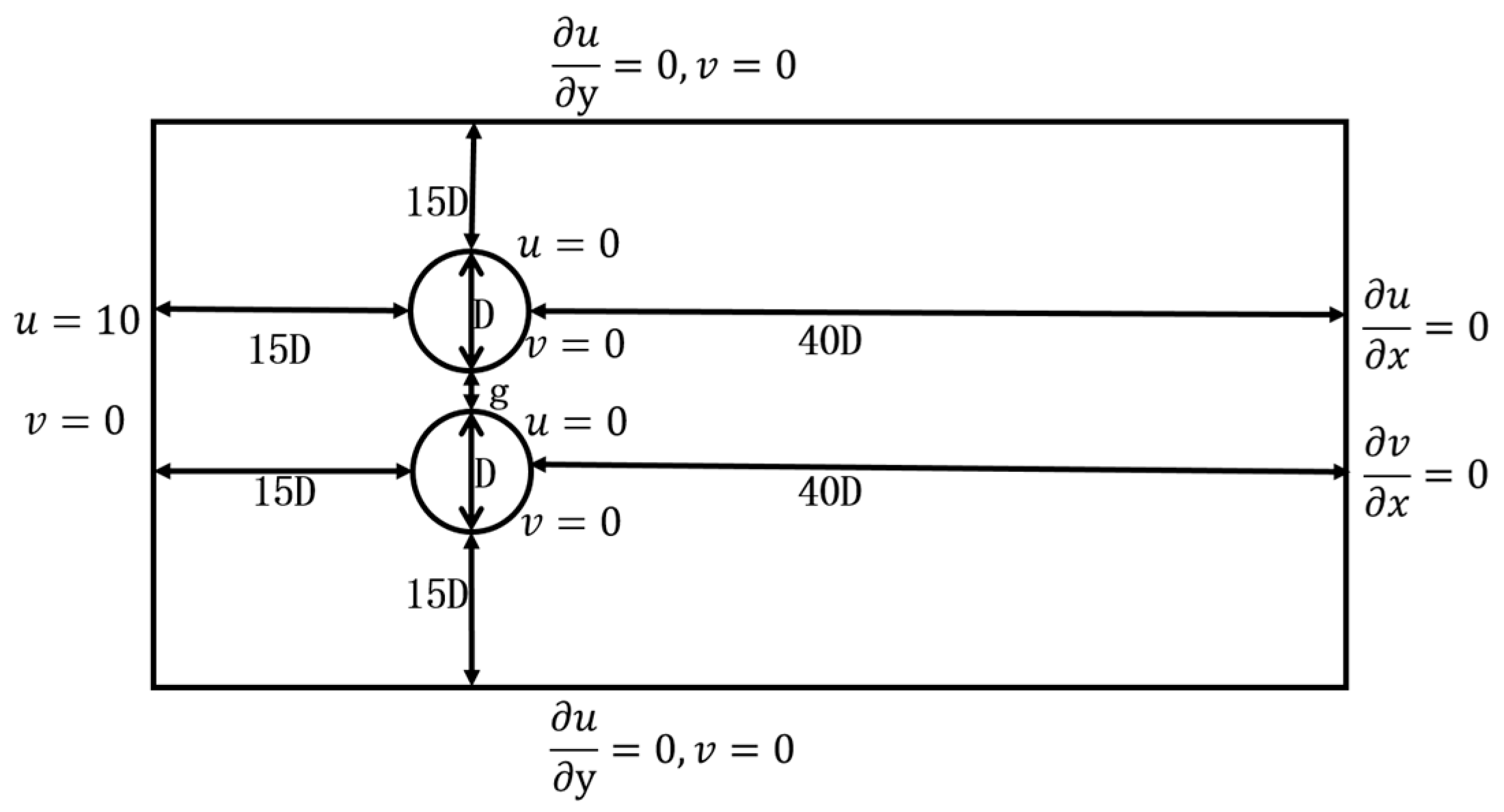
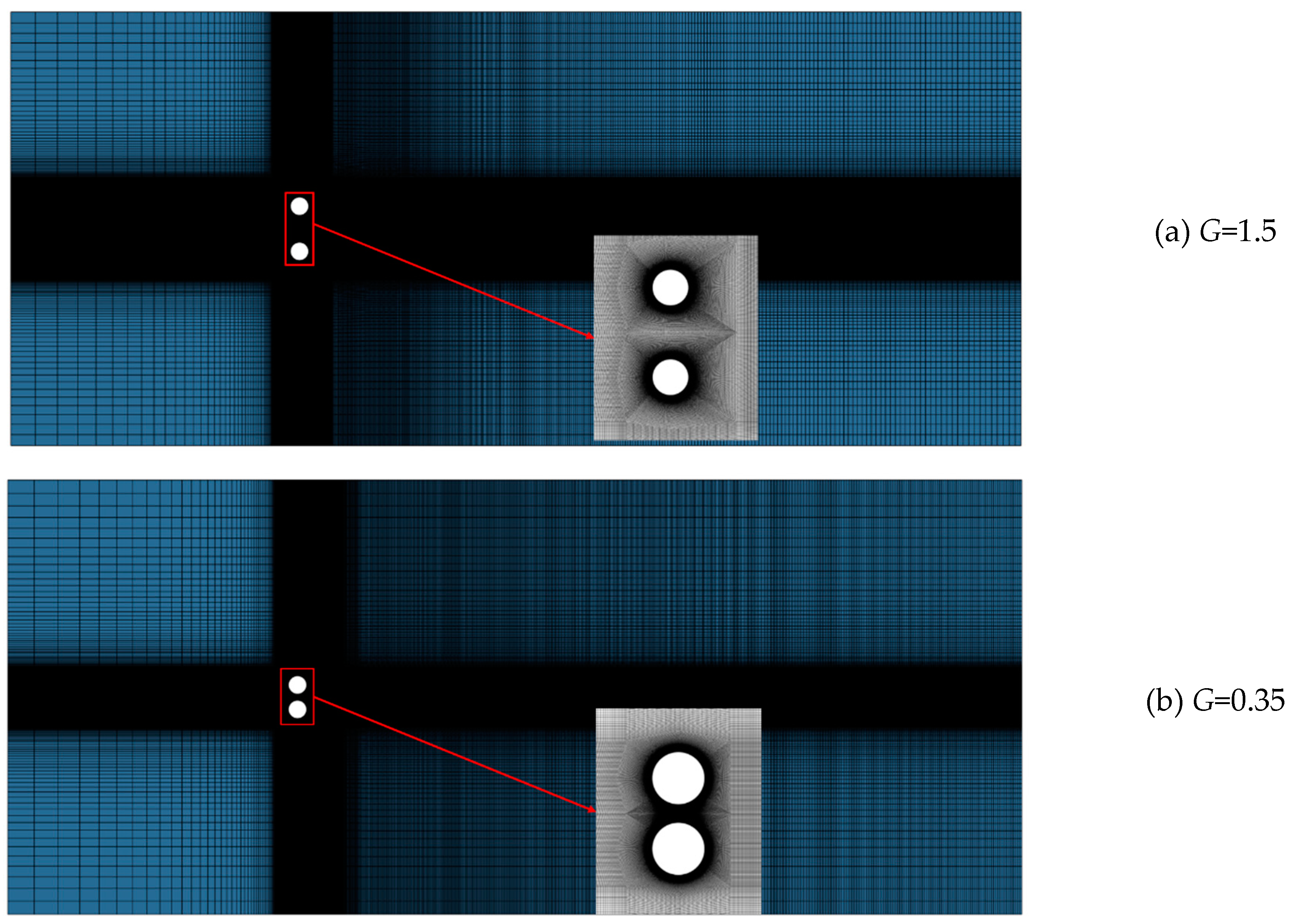
The computational domain and the meshes, used in the numerical simulation of the wake flow field of two parallel circular cylinders with dimensionless inter-distances
G=1.5 and 0.35 (
G=
g/
D), have been illustrated in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9. Both upper and lower cylinders are 1 m in diameter. The height of the first layer of the grid is 10
-4 m. The considered total numbers of grid cells for inter-distances
G=1.5 and 0.35 are 294742 and 373742, respectively. The inlet flow speed is 10 m/s, the Reynolds number is R
e, and the time step is set equal to 0.005 s.
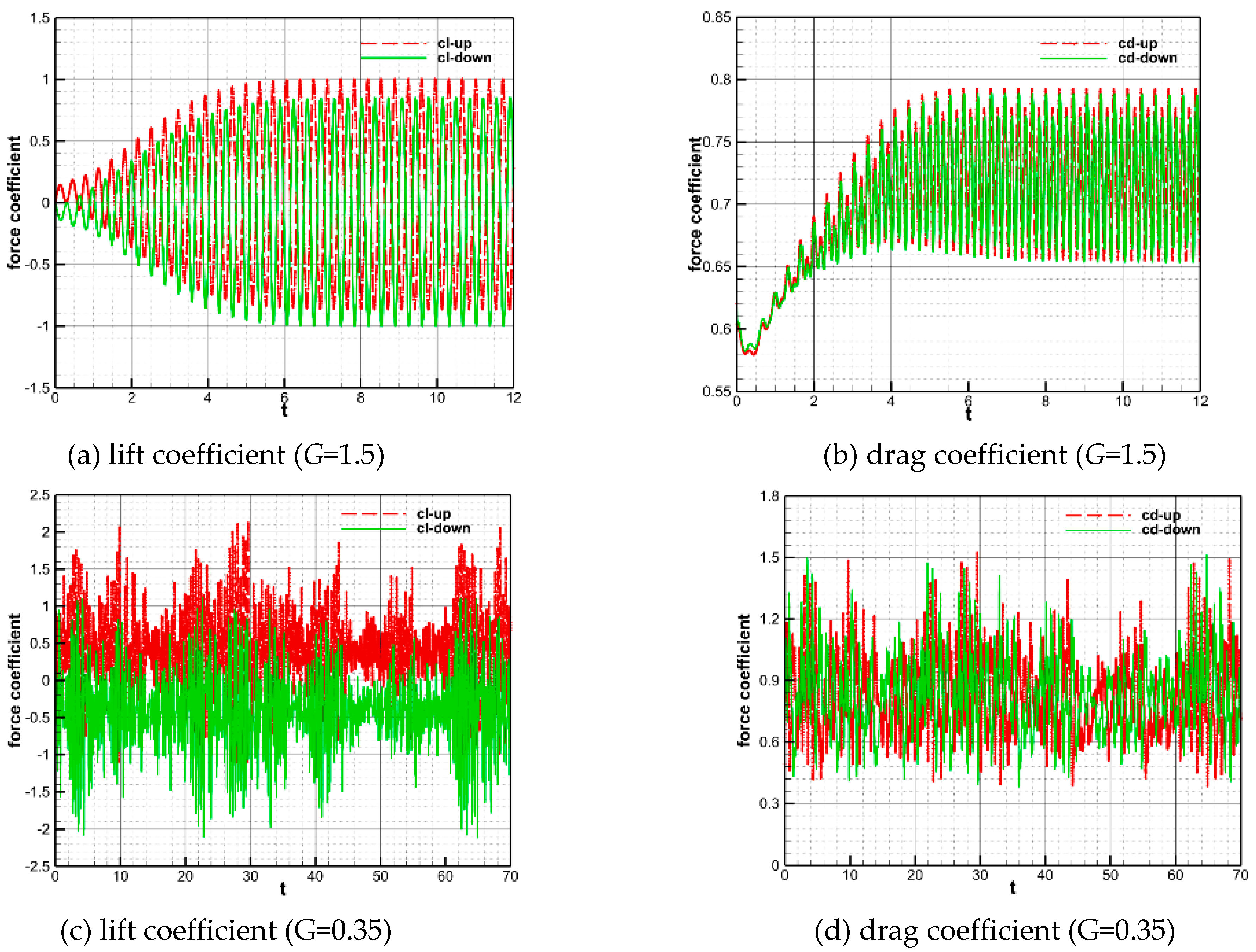
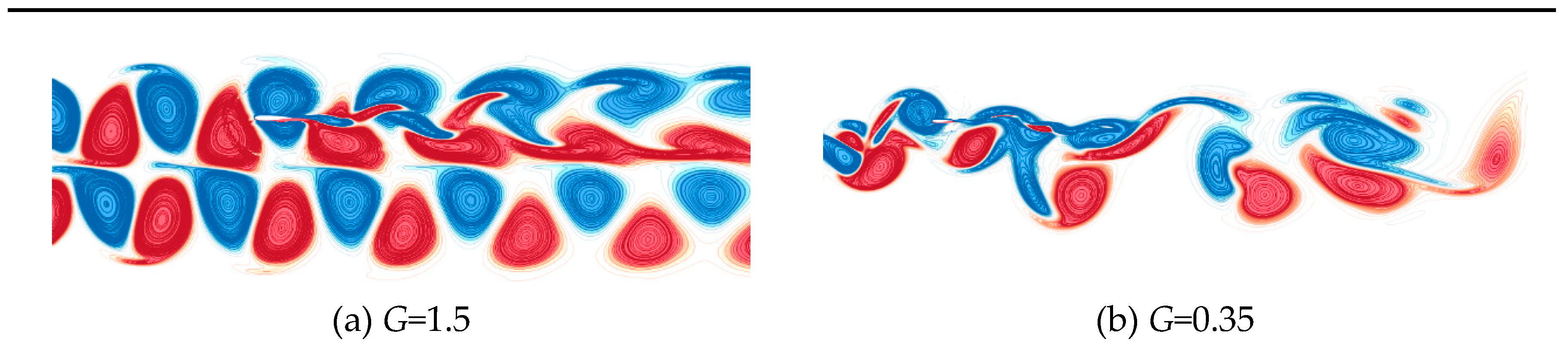
Figure 10 and
Figure 11 illustrate the time histories of aerodynamic force coefficients and vortex lines at four characteristic moments in one period for two parallel circular cylinders with inter-distances
G=1.5 and 0.35. For the double circular cylinders with dimensionless inter-spacing
G=1.5, the plots of lift and drag coefficients of the two cylinders both exhibit stable periodicity after 6 s. Meanwhile, from the characteristics of the vortex structure changes in the vorticity contours, it can be seen that the shedding of the wake vortices is clearly periodic for this cylindrical inter-distance. The vortices are shedding from the surfaces of the two cylinders in a coordinated and opposite direction, and the vortex structure in downstream of the two cylinders remains unchanged. For two cylinders with an inter-distance of
G=0.35, there is no significant variation in the lift and drag coefficients of each cylinder. The vorticity contours reveal that there is a strong interference between the two peaks in this distance of the cylinder. The wake tends to favor one cylinder over a certain period of time and then gradually shift to another over time. In addition, the drag coefficient of the cylinder favored by the wake is substantially higher than the other one. The shedding pattern of the wake is an alternating flipping shedding pattern, which tends to favor one cylinder during a certain time period.
3.2. POD analysis of the wake flow field in the pre-domain
We performed a POD analysis of 3000 velocity samples of the wake flow field for the doubly parallel cylinders with inter-spacings
G=1.5 and 0.35 for the time interval of [10s,25s].
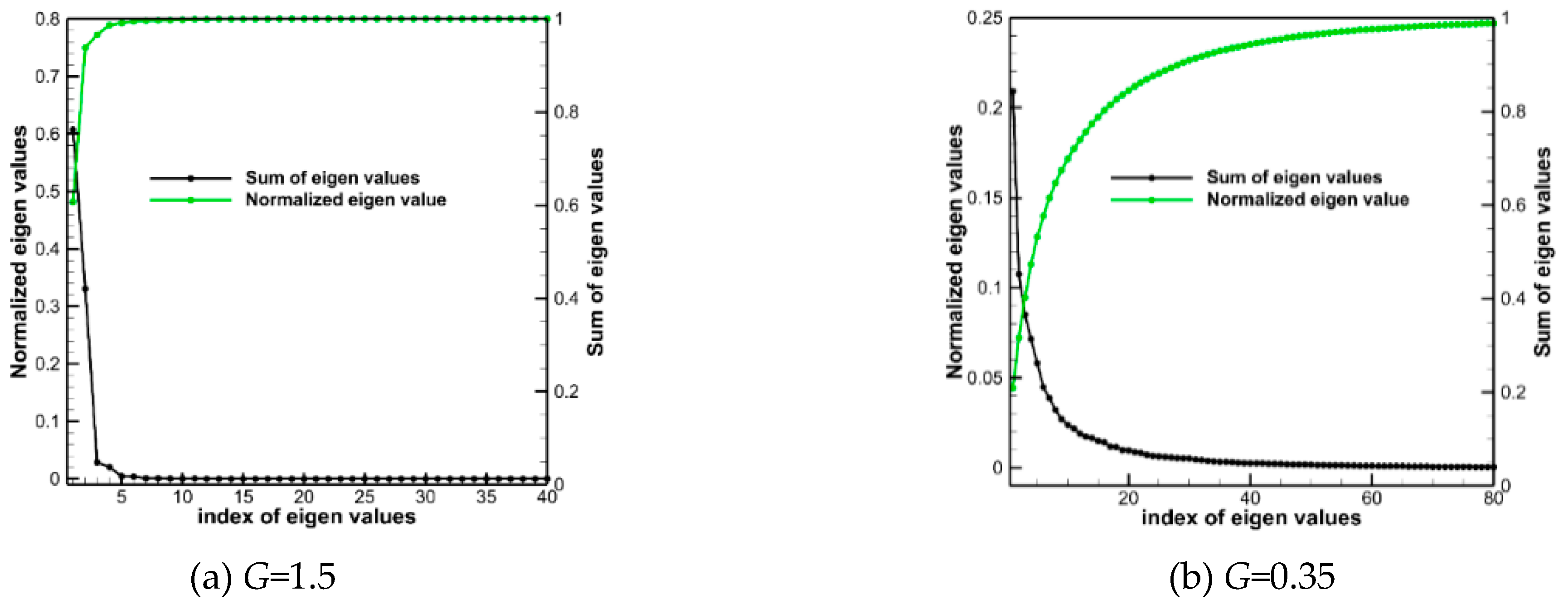
Figure 12 demonstrates the POD modal energy distribution, which sharply reduces with increasing the modal order for both cases. In the case of
G=1.5, the first four modes account for 98.66% of the total energy. The energy content then rapidly reduces to a very small amount with increasing the modal order. In contrast, the energy distribution of the case of
G=0.35 is more scattered such that the first four modes contain only 47.33% of the total energy. It takes up to 30 modes to contain 90.92% of the total energy, indicating that more modes are required to capture most features of the flow field. We analyzed the first eight POD modes of the wake flow field for the cases of
G=1.5 and 0.35.
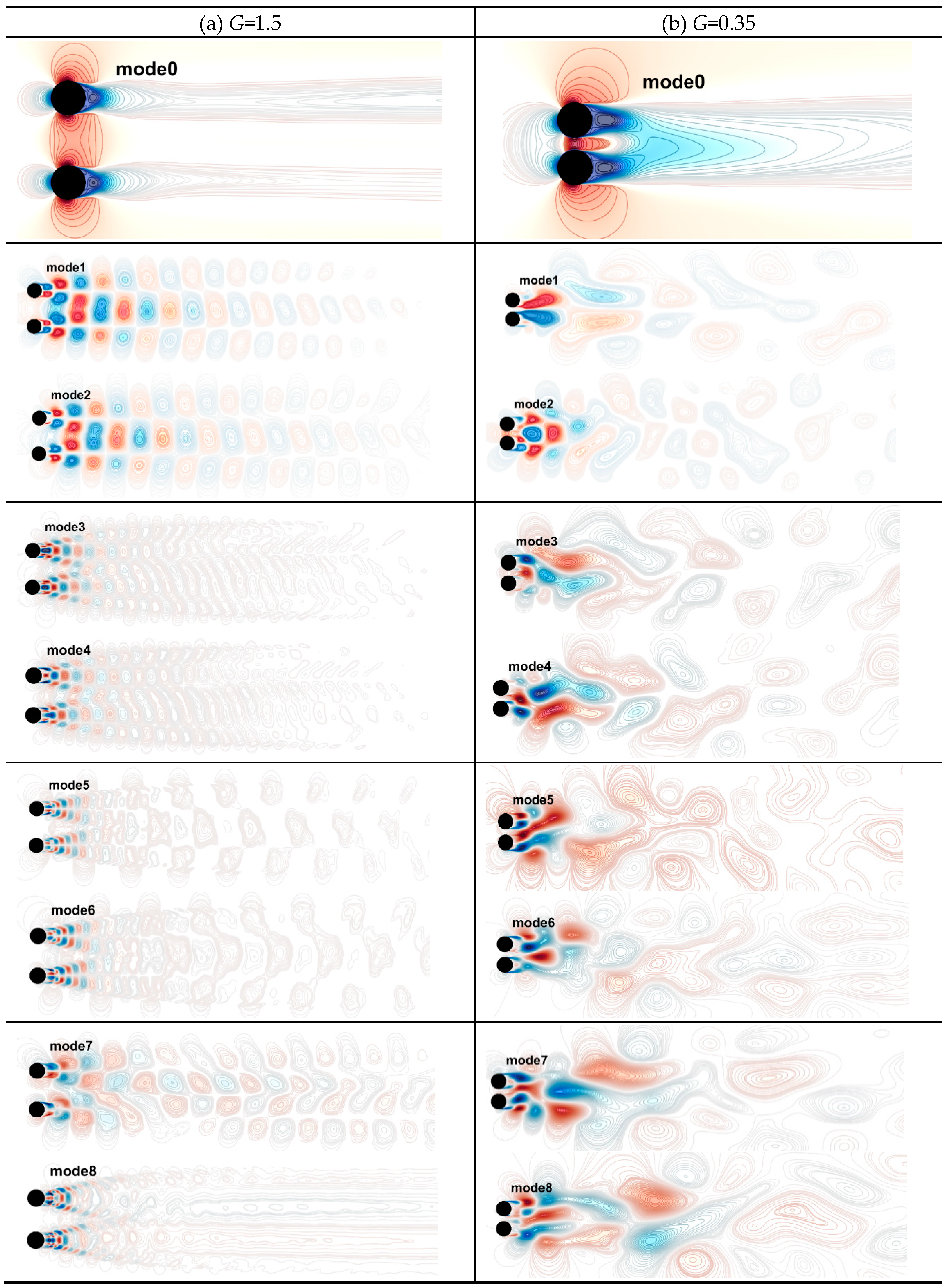
Table 3 presents the first eight POD modes of the flow field with cylinder inter-spacings of
G=1.5 and 0.35. Mode 0 represents the mean flow field, which characterizes the larger-scale static structure. For wake flow POD modes in the case of G=1.5, modes 1&2, modes 3&4, modes 5&6, and modes 7&8 can be reasonably regarded as pairs of modes because the structures and scales are very similar. Therefore, the present analysis mainly focuses on modes 1, 3, 5, and 7. Mode 1 (or 2) represents the main coherent structure of the large-scale flow field, which exhibits an up-down symmetric structure about the flow direction that dominates the synchronous reverse shedding of the wake vortices. Modes 3, 5, and 7 retain the same overall structural form, but the mode structures become denser, and smaller-scale flow structures appear in the flow direction. This is because as the mode order increases further, the energy contained in each mode lessens and the small-scale structures represented by the mode become more abundant. For POD modes with a cylinder inter-spacing of
G=0.35, the percentages of energy available in modes 1-8 in order are 20.91, 10.75, 8.51, 7.16, 5.81, 4.48, 3.86%, and 3.21%. The energy of each mode is almost the same, and the flow structures represented by each mode are also on the same scale. Mode 1 exhibits a slightly asymmetric structure about the centerline, and the symmetry of the structure decreases with the development of the downstream, with the mode structure tending to be biased toward the upper cylinder. The structure of mode 2 tends towards the lower cylinder and is more scattered and smaller than that of mode 1. The structure of mode 3 then shifts back towards the upper cylinder side. This change is repeated for alternating modes. In general, with the increase of order, the evolution of mode structures is consistent with the shedding mode of the wake and the scale of mode structures becomes more scattered and smaller to a certain extent.
3.3. Verification analysis of the full-order wake field generating method in pre-domain
Before generating flow structures at various scales in the post domain, the reliability of the full-scale wake-generating method should be appropriately verified.
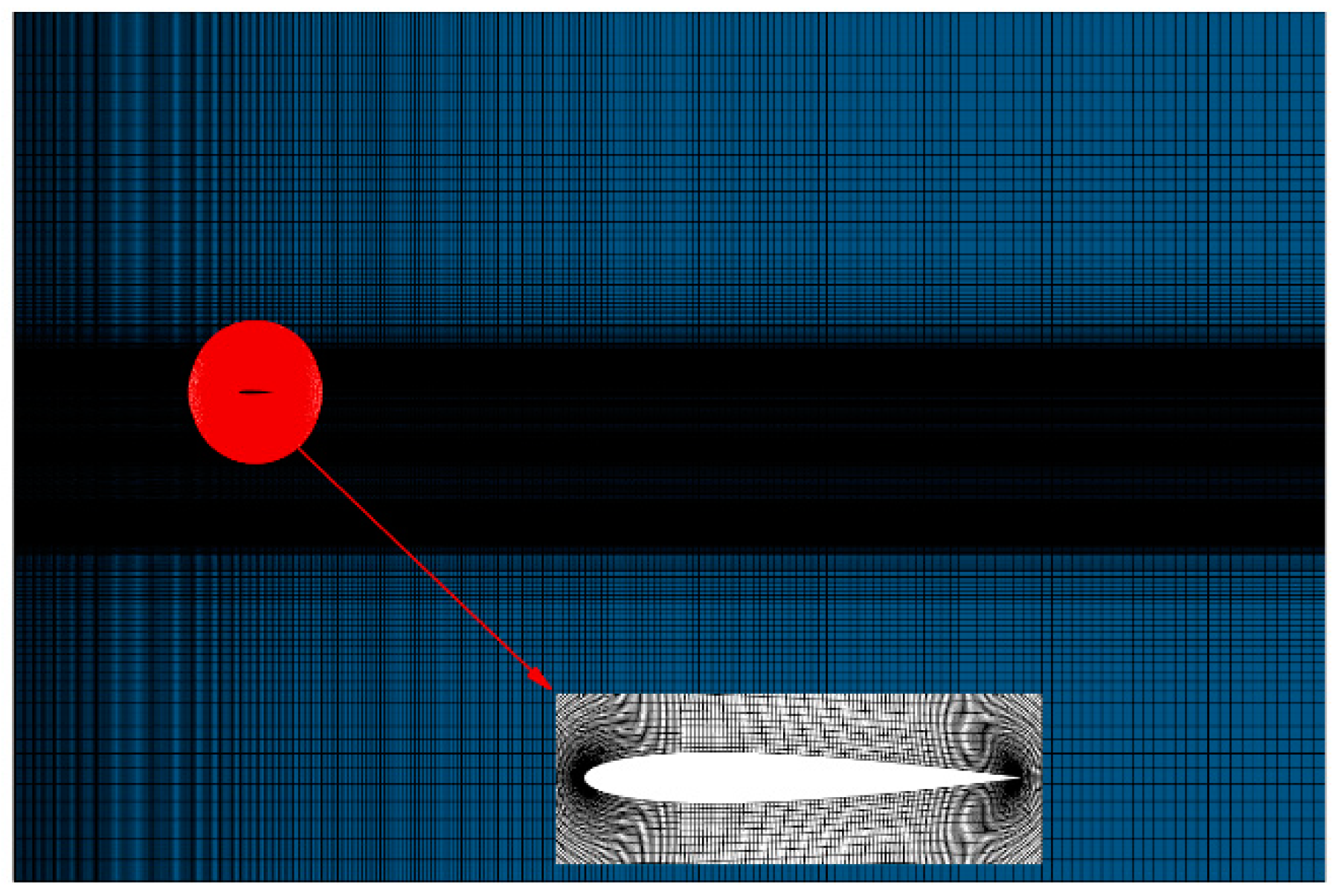
Figure 13 demonstrates the computational model employed in the study, where the red lines in
Figure 13(a) and (b) present the position of pre-domain simulation variables and the inlet position of the post-domain simulation, respectively, and
Figure 13(c) presents the results of a comparison between the aerodynamic coefficient obtained based on the full wake field loading method and those of the coupled calculation of double circular cylinders and an airfoil. To facilitate the comparison study, the computational mesh is kept unchanged in the calculations, and overlapping meshes are used, as demonstrated in
Figure 14. The red mesh represents the foreground mesh around the NACA0012 airfoil, and the entire mesh around the double circular cylinders is utilized as the background mesh of the computational model in
Figure 13(c).
Figure 15 illustrates the instantaneous vorticity contours in the wake field with dimensionless cylinder inter-spacings of
G=1.5 and 0.35. It can be seen that the post-domain flow field in both
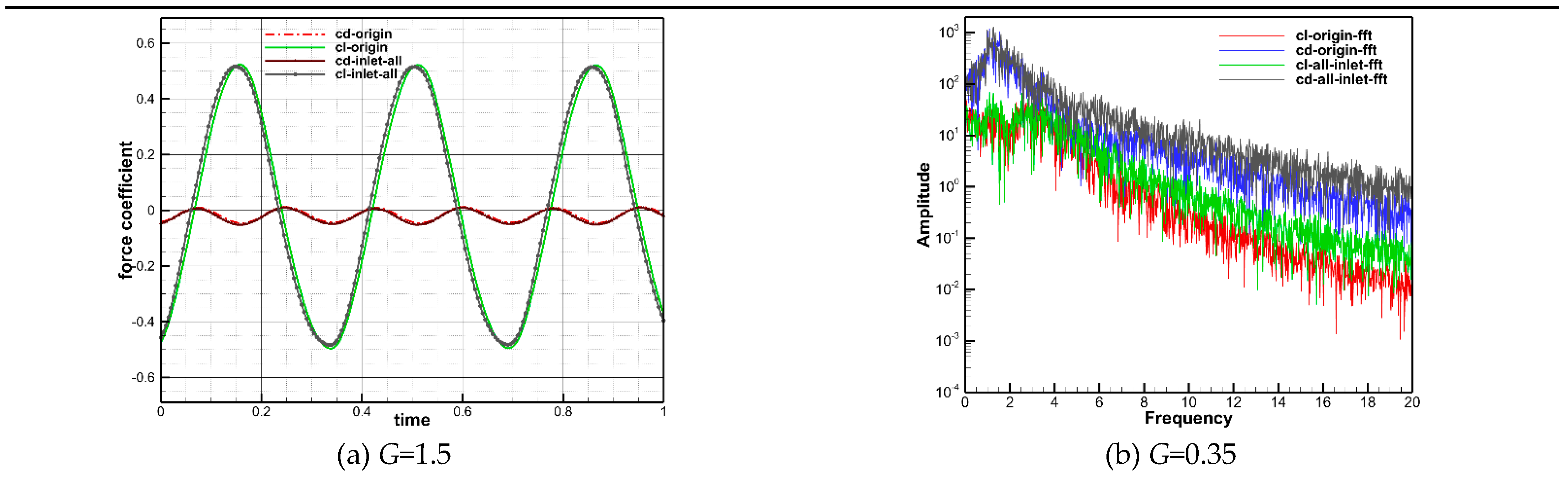
Figure 15(a) and (b) are fully developed and exhibit a high degree of similarity with the actual physical flow. Due to the periodic shedding of the wake vortices behind two side-by-side circular cylinders with a gap of 1.5 m, the lift and drag coefficients of the downstream airfoil demonstrate periodic variations. A comparison of the lift and drag coefficients in one second has been presented in
Figure 16(a), where cd-origin and cl-origin represent the airfoil lift and drag coefficients obtained from the coupled calculation of the two circular cylinders and the airfoil, and cd-inlet-all and cl-inlet represent those obtained via the full-order wake field loading method. The plotted results reveal that the temporal variations of the two results almost have a constant frequency; further, the discrepancy in the amplitudes of the lift coefficient is less than 1% and the difference in the amplitudes of the drag coefficient is less than 3%. Therefore, the reliability of the full-order wake-field loading method for flow around two parallel cylinders with a gap of
G=1.5 is firmly confirmed. The shedding of the vortices in the case of
G=0.35 does not show an obvious periodicity, so it is not possible to directly compare the airfoil lift and drag coefficients. Therefore, the frequency of the amplitude of the lift and drag coefficients are compared and analyzed in
Figure 16(b), in which the expressions “cl-origin-fft” and “cd-origin-fft” stand for the amplitude-frequency obtained by the fast Fourier transform of the lift and drag coefficients obtained by coupling computation. The statements “cl-all-fft” and “cd-all-fft” represent the amplitude frequencies of the lift and drag coefficients obtained by full-order wakefield loading. It can be seen that the amplitude frequencies of airfoil lift and drag coefficients obtained by the two calculation approaches are very close, which also confirms the reliability of the full-order wakefield generation approach when applied to the complex wake field with cylinder inter-distance
G=0.35.
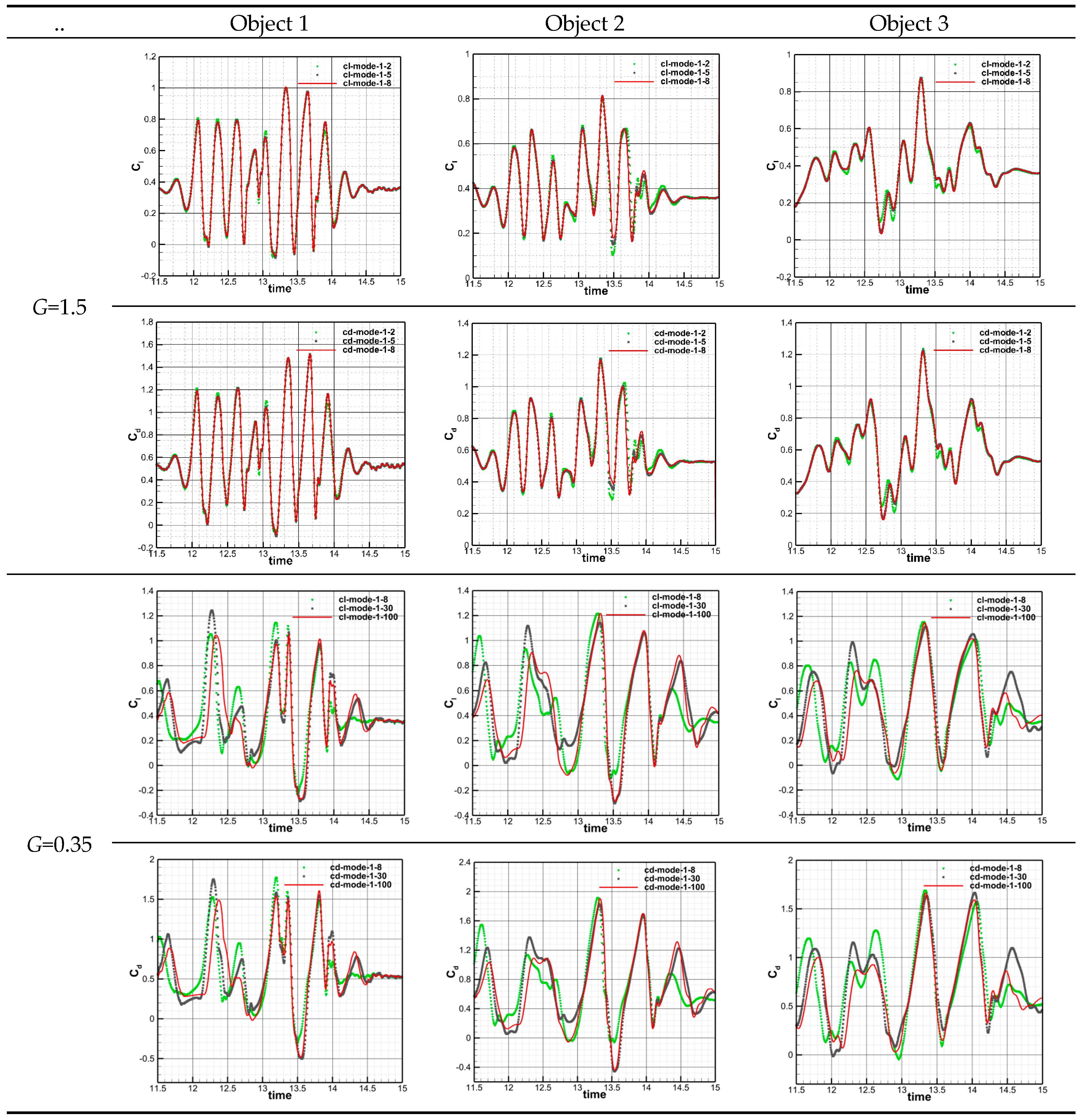
3.4. Effects of various scale flow structures of the wake on the target object for different modes in post-domain.
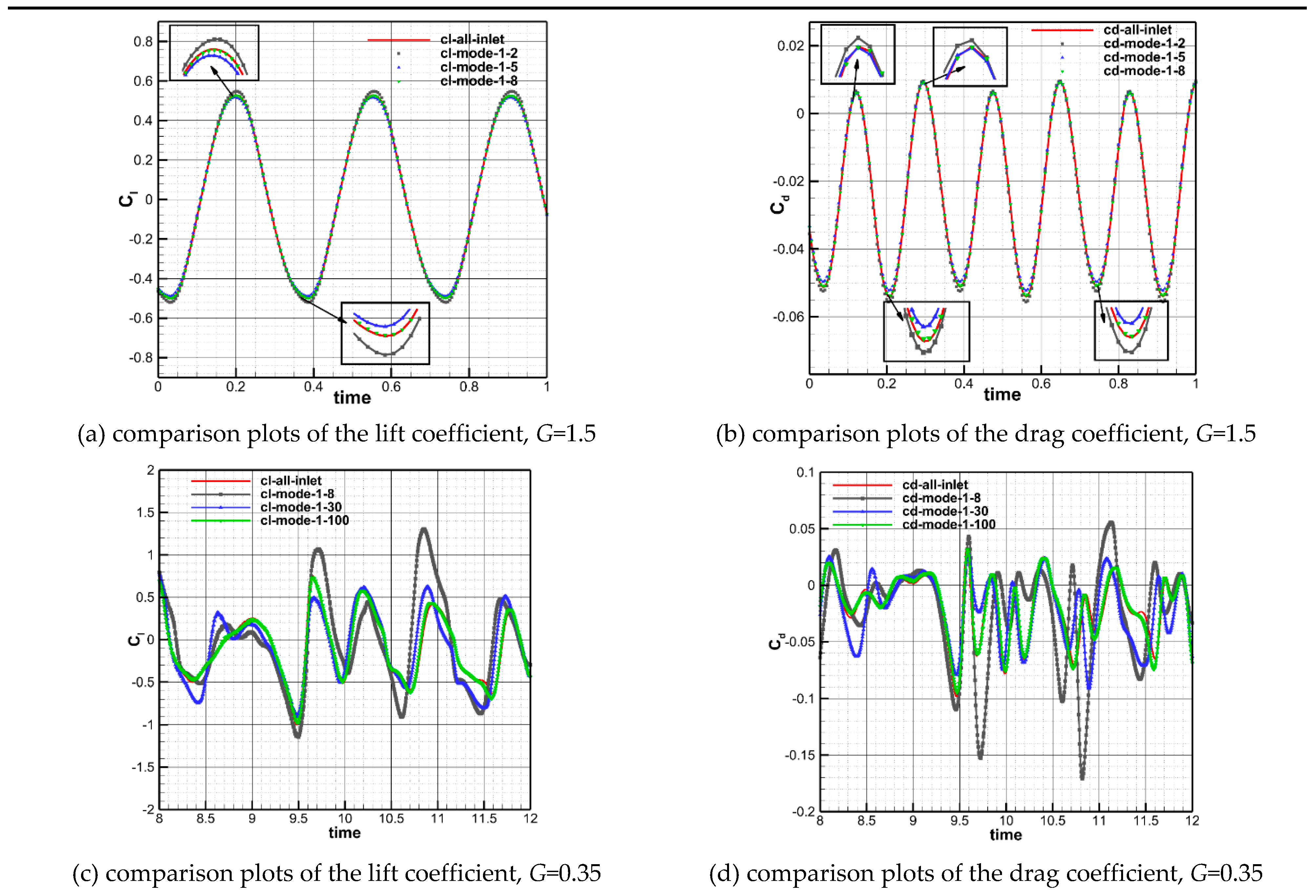
Figure 17 demonstrates a comparison investigation of the effects of different modal production on the aerodynamic characteristics of static airfoils for inter-spacings of
G=1.5 and 0.35. In the figure, the symbols “cl” and “cd” are associated with the lift and drag coefficients of the airfoil, “cl-mode-1-2” represents the lift coefficient obtained from the production of the first two modes, and so on. It can be seen that for the wake with
G=1.5, the first two generated modes can capture the large-scale flow structures in the flow field, and the resulting aerodynamic characteristics of the airfoil are close to those obtained by the full-order flow field, but detail treatment is a bit rough. The difference in the lift coefficient obtained from the first five generated modes is about 2%, which can meet the practical engineering requirements. The first eight modes generated are capable of capturing small-scale features in the flow field. For the wake flow with
G=0.35, the lift and drag coefficients obtained from the first thirty modes are able to produce follow the trends of the full-order wake generating, but with large differences in their magnitudes. This is because the flow structures in lower modes are relatively uneven due to the complexity of the wake flow. The difference in the results obtained from the generation of the first mode is much less, which shows that the existing flow structures in one hundred first modes can meet the practical engineering requirements for this case.
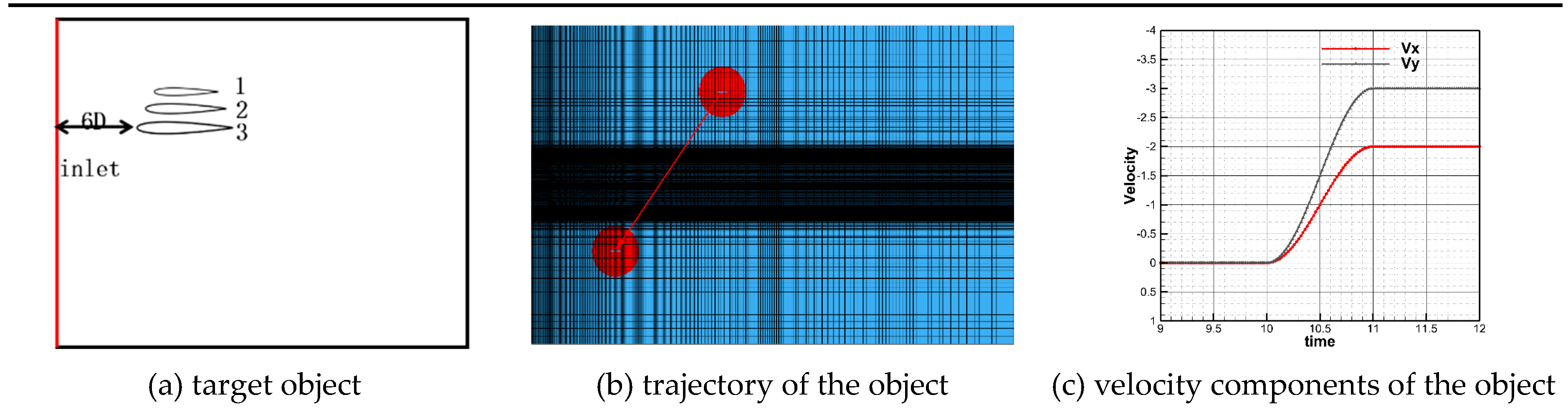
This work investigates the aerodynamic characteristics of target objects in the wake of two parallel cylinders with different scales of flow structures. The effects of cylinder inter-spacing, object size, and object motion mode are also discussed. Eqs. 13 and 14 are the time-dependent functions that prescribe the velocity components of the target objects. In these relations,
l is a parameter related to the airfoil motion mode, which is taken as -0.5, 0, or 0.5 in this study. In
Figure 18(a), model 2 denotes the NACA0012 airfoil, object 1 is a model with half the center of gravity of object 2, and object 3 represents a model with an enlargement of 1.5 times the center of gravity of object 2.
Figure 18(b) presents the trajectory of the target object, and
Figure 18 (c) illustrates the velocity components of the target object expressed by Eqs. (13) and (14) with
l = 0. The target object remains stationary for the first 10 s, then undergoes the motion described by Eqs. (13) and (14) from 10 to 11 s, followed by constant velocity motion until it has completely passed through the wake region. For the case of
l equal to -0.5 and 0.5, the airfoil starts to accelerate at 9.5 s and 10.5 s, respectively and maintains a constant speed until it completely passes through the wake region.
Table 4 presents a comparison of the aerodynamic force coefficients of three different target objects for
l =0 subjected to a load of wake flow structures with cylinder inter-spacing
G=1.5 and 0.35. The obtained results indicate that for the flow structure with
G=1.5, the first five modes could capture the flow characteristics of all three objects suitably, and the aerodynamic characteristics of the obtained objects are compatible with the first eight modes, which is consistent with the results obtained acted upon by the load of the static flow structure of the airfoil. However, a comparison of the aerodynamic force coefficients for three understudy objects indicates that as the model size decreases, the lift and drag coefficients become more periodic with time, and for smaller objects, the aerodynamic force coefficients obtained by loading the first two modes already are in good agreement with those obtained by loading the first eight and five modes, revealing that smaller models respond less to higher flow structures at smaller scales. For the flow structure with cylinder inter-spacing
G=0.35, only the first 30 modes for all three target objects can approximately capture the flow profile, and the aerodynamic characteristics of the downstream targets obtained by the first 100 modes are consistent, which is because to complex and dispersed flow structures below this smaller distance. In addition, by comparing the aerodynamic force coefficients for three target objects with different sizes, it can be concluded that for this distance, with the increase in the size of the object, the lift and drag coefficients become periodic, and for the largest object, the aerodynamic force. The coefficients obtained by loading the first 30 modes are better than the coefficients of the other two smaller bodies, indicating that the larger body responds more to the flow characteristics for this cylinder inter-distances and the characteristic size of the flow structure corresponding to the first 30 modes is slightly larger than object 3.
Table 5 shows the comparison of the aerodynamic coefficients of object 2 for the cases of
G=1.5 and 0.35. The results indicate object 2 accelerates in 9.5 s, 10.0 s, and 10.5 s. It can be seen that for the wake structure with dimensionless inter-distance of
G=1.5, the variations’ trends of the aerodynamic coefficients during a period, when the target object completes acceleration until it completely passes through the wake region, is constant at 9.5 s and 10.5 s. This issue also indicates that 1 s represents only one evolutionary cycle of this wake structure. In addition, by comparing the aerodynamic coefficients of the object obtained from the loading of the first five structures and the first eight modes structures at various moments of acceleration. The plotted results indicate that the loading of the first five modal structures is appropriate for three different acceleration moments, which shows that the responses of different scales of characteristic wake structures to different acceleration moments for this cylinder distance are weak. For the wake structure with distance
G=0.35, the variation’s trends of aerodynamic coefficients are roughly the same for three different moments of acceleration, which indicates that the wake structure reacts slowly at this distance. In addition, by comparing the aerodynamic coefficients of the downstream target object obtained by loading the first thirty structures and one hundred first modal structures at different moments of acceleration, it can be found that the loading of the first thirty modal structures is almost reasonable for three different moments of acceleration instants, indicating that the response of different scales of characteristic wake structures to different acceleration moments for this cylinder inter-distance is weak:
4. Conclusions
Based on the reduced-order modeling methodology and the post-domain simulation approach, this paper aims to investigate the effect of the complex low-speed wake on the aerodynamic characteristics of the downstream target objects. The main results can be summarized as follows:
The flow around the doubly parallel cylinders demonstrates a synchronized and reverse vortex shedding pattern, and the vortex structure along the flow direction remains unchanged in a relatively long region behind the two cylinders until the dimensionless inter-distance is G=1.5. The vortex shedding pattern of the double-cylinder wake exhibits an alternating and flipping vortex shedding pattern that tilts toward one of the cylinders during a certain period of time for the dimensionless inter-distance of G=0.35.
The wake modal structure for G=1.5 is more compact than that in the case of G=0.35, and the wake mode for G=1.5 is generally smoother and more regular. The modal structure evolution with increasing modal order and the shedding are compatible with each other, and the higher-order modal structure is relatively more scattered and smaller in scale.
The wake field for the case of G=1.5 only requires the first five modes to capture the overall flow structure, and the lift and drag coefficients obtained from the fixed downstream object match those obtained with the full wake field. In contrast, the wake field in the case of G=0.35 requires about the first thirty modes to roughly capture the trend of the flow development process.
For the case of moving downstream target object, for the wake with G=1.5, the aerodynamic properties of smaller downstream objects have less influence on the response of higher-order modes with smaller scales. For the wake with dimensionless inter-distance G=0.35, due to the scattered modal structures, the aerodynamic characteristics of the three target objects with different sizes have less influence on the response of the first three large-scale modes, which is directly related to the relative scale of the target object flow structure. Meanwhile, the aerodynamic characteristics of the flow structures of the wake at inter-distances of G=1.5 and 0.35 exhibit consistent responses to the target object at different times, which indicates that the flow structures of the wake exhibit consistent aerodynamic characteristics on the target object at different times.
Acknowledgments
The work was financially supported by National Numerical Wind tunnel Project (Grant No. NNW2019ZT7- B31). This research was also supported in part by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
References
- Qu, F.; Lu, C.; Jiang, Z.F.; Wang, T. CFD numerical simulation of ship air-wake. Chinese Journal of Ship Research. 2009, 4, 23–27. [Google Scholar]
- Hotelling, H. Analysis of a complex of statistical variables in principal components. Journal of Educational Psychology. 1933, 24, 498–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krath, E.H.; Carpenter, F.L.; Cizmas, P.G.A.; Johnston, D.A. An efficient proper orthogonal decomposition based reduced-order model for compressible flows. Journal of Computational Physics. 2021, 426, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, P.; Lumley, J.L.; Berkooz, G. Turbulence, Coherent Structures, Dynamical Systems and Symmetry, Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, England, 1996.
- Lumley, J.L. The structure of inhomogeneous turbulent flows, “in” Atmospheric turbulence and radio wave propagation. 1967, 166-178.
- Sirovich, L. Turbulence and the dynamics of coherent structures. I. Coherent structures. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics. 1987, 45, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premaratne, P.; Tian, W.; Hu, H. A proper-orthogonal-decomposition (POD) study of the wake characteristics behind a wind turbine model. Energies. 2022, 15, 3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Vanka, S.P.; Banerjee, R.; Mangadoddy, N. Dominant modes in a gas cyclone flow field using proper orthogonal decomposition. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research. 2022, 61, 2562–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, A.; Ivln, P. Investigating wake structures in flow past oscillating cylinder using proper orthogonal decomposition. Fluid Dynamics. 2022.
- Fureby, C.; Tabor, G.; Weller, H.G.; Gosman, A.D. A comparative study of subgrid scale models in homogenous isotropic turbulence. Physics of Fluids. 1997, 9, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamballais, E.; Lesieur, M.; Metais, O. Probability distribution functions and coherent structures in a turbulent channel. Physical Review E. 1997, 56, 6761–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Bai, X.S. Large eddy simulations of turbulent swirling flows in a dump combustor: a sensitivity study. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Fluids. 2005, 47, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menter, F.R. Two-equation eddy-viscosity turbulence models for engineering applications. AIAA Journal. 1994, 32, 1598–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Jiang, Y.; Peng, L.L.; Chen, X.W. Fast simulation of nonstationary wind velocity fields by proper orthogonal decomposition interpolation. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics. 2021, 219, 104798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, M.; Dehghan, M.; Khodadadian, A.; Noii, N.; Heitzinger, C.; Wick, T. A reduced-order variational multiscale interpolating element free Galerkin technique based on proper orthogonal decomposition for solving Navier-Stokes equations coupled with a heat transfer equation: Nonstationary incompressible Boussinesq equations. Journal of Computational Physics. 2021, 426, 109875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wu, B.S. The numerical simulation of two dimensional circular flow. Shipbuilding of China. 2007, 48, 533–540. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.Y. Flow field selection and mesh generation of 3D numerical simulation of flow around a circular cylinder. Journal of Waterway and Harbor. 2009, 30, 70–76. [Google Scholar]
- Meneghini, J.R.; Saltara, F.; Siqueira, C.L.R.; Ferrarijr, J.A. Numerical simulation of flow interference between two circular cylinders in tandem and side-by-side arrangements. Journal of Fluids and Structures. 2001, 15, 327–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.X.; Hu, Z.Z. Numerical simulation of viscous flow around unrestrained cylinders. Journal of Fluids and Structures. 2006, 22, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.W. Two-dimensional numerical simulation of flow around a cylinder and vortex-induced vibration. Tianjin University, China, 2010.
- Zhang, Q.S. PIV measurements of unsteady characteristics of separated and reattaching flow on finite blunt plate——vortex dynamics analysis using proper orthogonal decomposition and dynamic mode decomposition. Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China, 2015.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the domain precursor simulation approach.
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the domain precursor simulation approach.
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the computational domain and boundary conditions.
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the computational domain and boundary conditions.
Figure 3.
The considered mesh around a single circular cylinder.
Figure 3.
The considered mesh around a single circular cylinder.
Figure 4.
Time history plots of the lift and drag coefficients of a circular cylinder.
Figure 4.
Time history plots of the lift and drag coefficients of a circular cylinder.
Figure 5.
Energy distribution of different POD modes for the flow over a single cylinder.
Figure 5.
Energy distribution of different POD modes for the flow over a single cylinder.
Figure 6.
Instantaneous and mean vorticity fields.
Figure 6.
Instantaneous and mean vorticity fields.
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of generating different scales of flow structures.
Figure 7.
Schematic representation of generating different scales of flow structures.
Figure 8.
The computational domain of the flow field around the doubly parallel cylinders.
Figure 8.
The computational domain of the flow field around the doubly parallel cylinders.
Figure 9.
The mesh representation around the doubly parallel cylinders.
Figure 9.
The mesh representation around the doubly parallel cylinders.
Figure 10.
The lift and drag coefficients of doubly parallel cylinders with inter-distances of G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 10.
The lift and drag coefficients of doubly parallel cylinders with inter-distances of G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 11.
The vortex contour at different intants for doubly parallel cylinders. with inter-distances of G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 11.
The vortex contour at different intants for doubly parallel cylinders. with inter-distances of G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 12.
POD modal energy distribution of the flow around doubly parallel cylinders with inter-spacing G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 12.
POD modal energy distribution of the flow around doubly parallel cylinders with inter-spacing G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 13.
Computational domain associated with doubly parallel cylinders and downstream NACA0012 airfoil.
Figure 13.
Computational domain associated with doubly parallel cylinders and downstream NACA0012 airfoil.
Figure 14.
The dense mesh diagram of the NACA0012 airfoil in the post-domain.
Figure 14.
The dense mesh diagram of the NACA0012 airfoil in the post-domain.
Figure 15.
Instantaneous vorticity contours in the post-domain obtained by the full-order wake field generating method.
Figure 15.
Instantaneous vorticity contours in the post-domain obtained by the full-order wake field generating method.
Figure 16.
Comparison plots of the lift and drag coefficients of the airfoil.
Figure 16.
Comparison plots of the lift and drag coefficients of the airfoil.
Figure 17.
Influence of different mode generating of the POD on the lift and drag coefficients of the airfoil subjected to static conditions for inter-spacing of G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 17.
Influence of different mode generating of the POD on the lift and drag coefficients of the airfoil subjected to static conditions for inter-spacing of G=1.5 and 0.35.
Figure 18.
Shape, trajectory, and velocity of the downstream target object.
Figure 18.
Shape, trajectory, and velocity of the downstream target object.
Table 1.
The lift and drag coefficients and Strouhal number.
Table 1.
The lift and drag coefficients and Strouhal number.
| |
Parameter |
|
|
|
St |
| Reference |
|
Max |
Min |
|
Max |
Min |
| Present study |
0.54 |
-0.54 |
|
1.34 |
1.261 |
0.2 |
| DW (2010) |
0.594 |
-0.593 |
|
1.56 |
1.49 |
0.2 |
| Wu and Hu (2006) |
0.586 |
-0.582 |
|
1.384 |
1.322 |
0.19 |
| Chen et al. (1999) |
0.63 |
-0.63 |
|
1.53 |
1.43 |
0.18 |
Table 2.
The contour maps, temporal evolution of coefficients, and spectral analysis graphs for each POD mode.
Table 2.
The contour maps, temporal evolution of coefficients, and spectral analysis graphs for each POD mode.
Table 3.
POD modal contour of the flow around doubly parallel cylinders with G=1.5 and 0.35.
Table 3.
POD modal contour of the flow around doubly parallel cylinders with G=1.5 and 0.35.
Table 4.
Comparison of the aerodynamic coefficients of different objects during the process of passing through the wake zone (note: l= 0)
Table 4.
Comparison of the aerodynamic coefficients of different objects during the process of passing through the wake zone (note: l= 0)
Table 5.
Comparison of the aerodynamic coefficients of Object 2 during the process of passing through the wake zone.
Table 5.
Comparison of the aerodynamic coefficients of Object 2 during the process of passing through the wake zone.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).