Submitted:
09 August 2023
Posted:
11 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
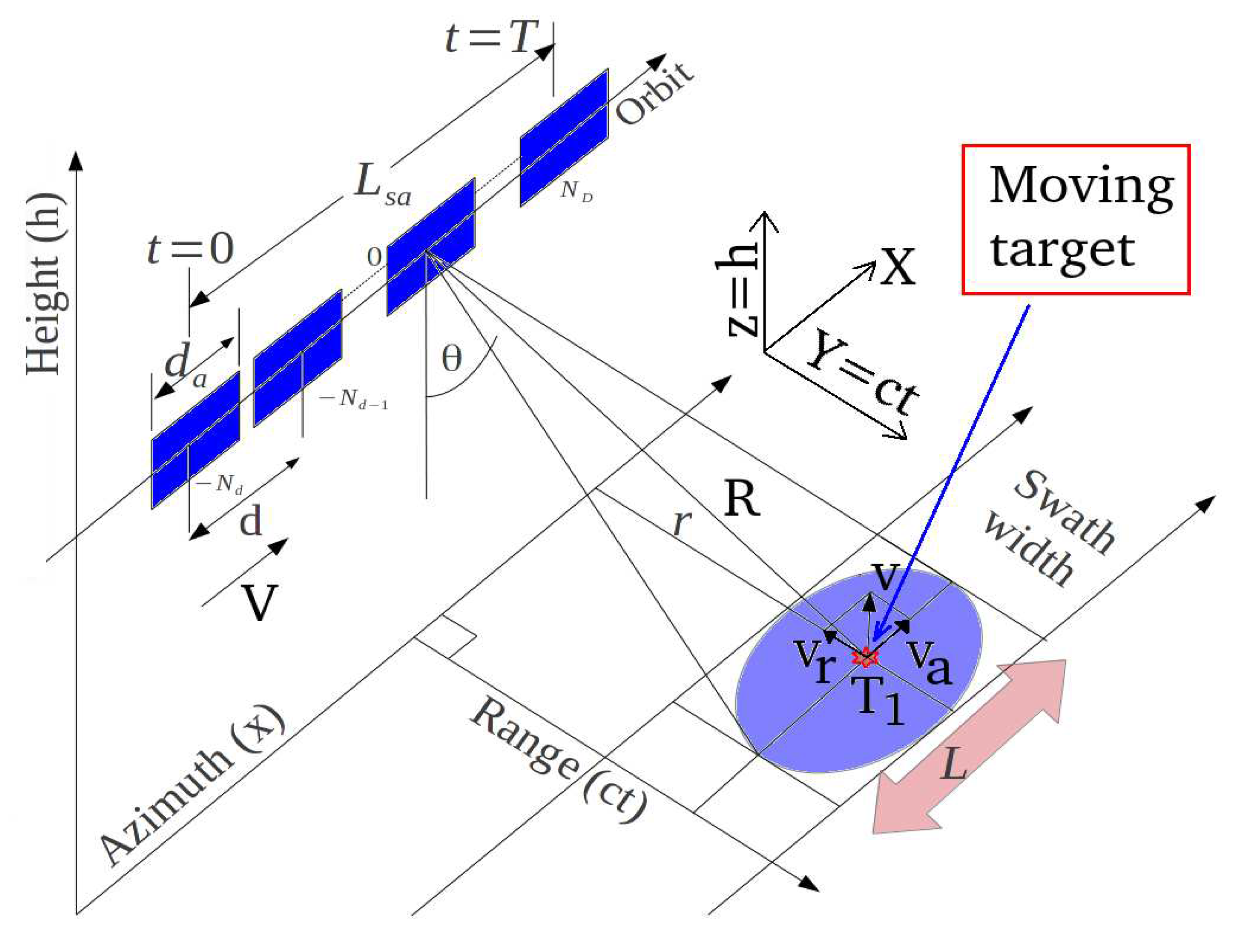
2. Methodology
- r is the zero-Doppler distance (constant);
- R is the slant-range;
- is the reference range at ;
- is the physical antenna aperture length;
- V is the platform velocity;
- d is the distance between two range acquisitions;
- is the total synthetic aperture length;
- t is the acquisition time variable;
- T is the observation duration;
- and are the start and stop time acquisition respectively;
- is the azimuth electromagnetic footprint width;
- is the incidence angle of the electromagnetic radiation pattern;
- V is the platform velocity.
2.1. Doppler Sub-Apertures Model
2.2. Doppler Sub-Aperture Strategy
- anomalous azimuth displacement in the presents of target constant range velocity;
- azimuth smearing in the presence of target azimuth velocity or target range accelerations;
- range-walking phenomenon, visible as range defocusing, in the presence of target range speed, backscattered energy is detected over one or more range resolution cells.
- (due to range velocity);
- (due to range acceleration);
- (due to azimuth velocity).
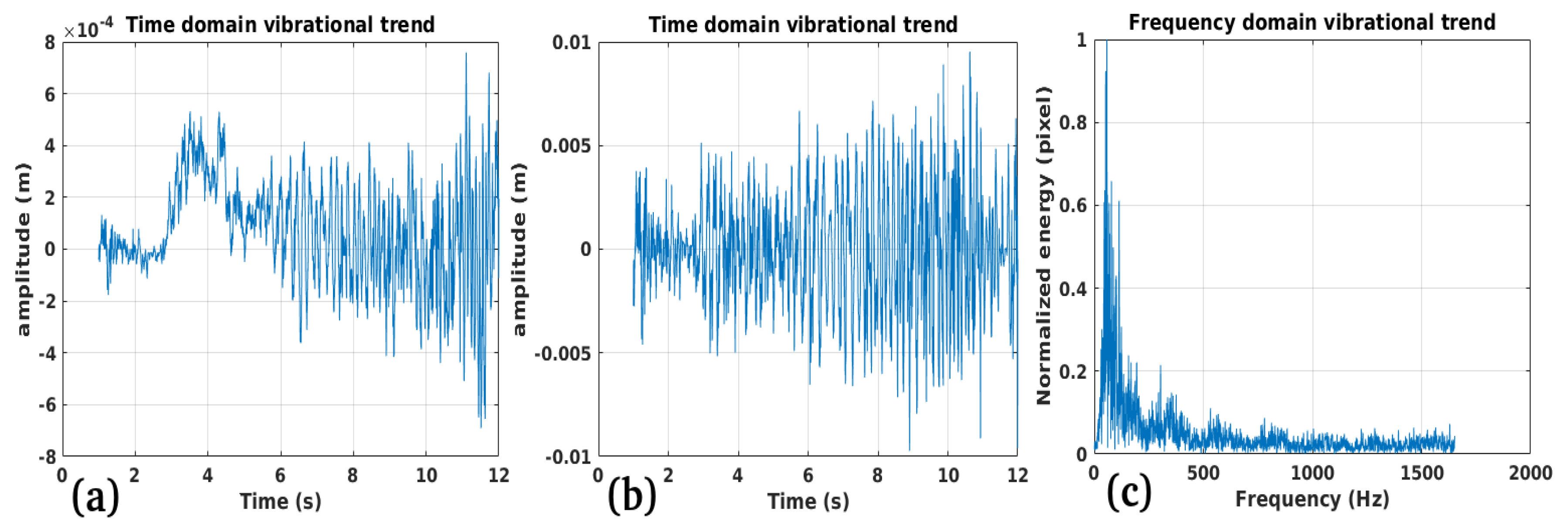
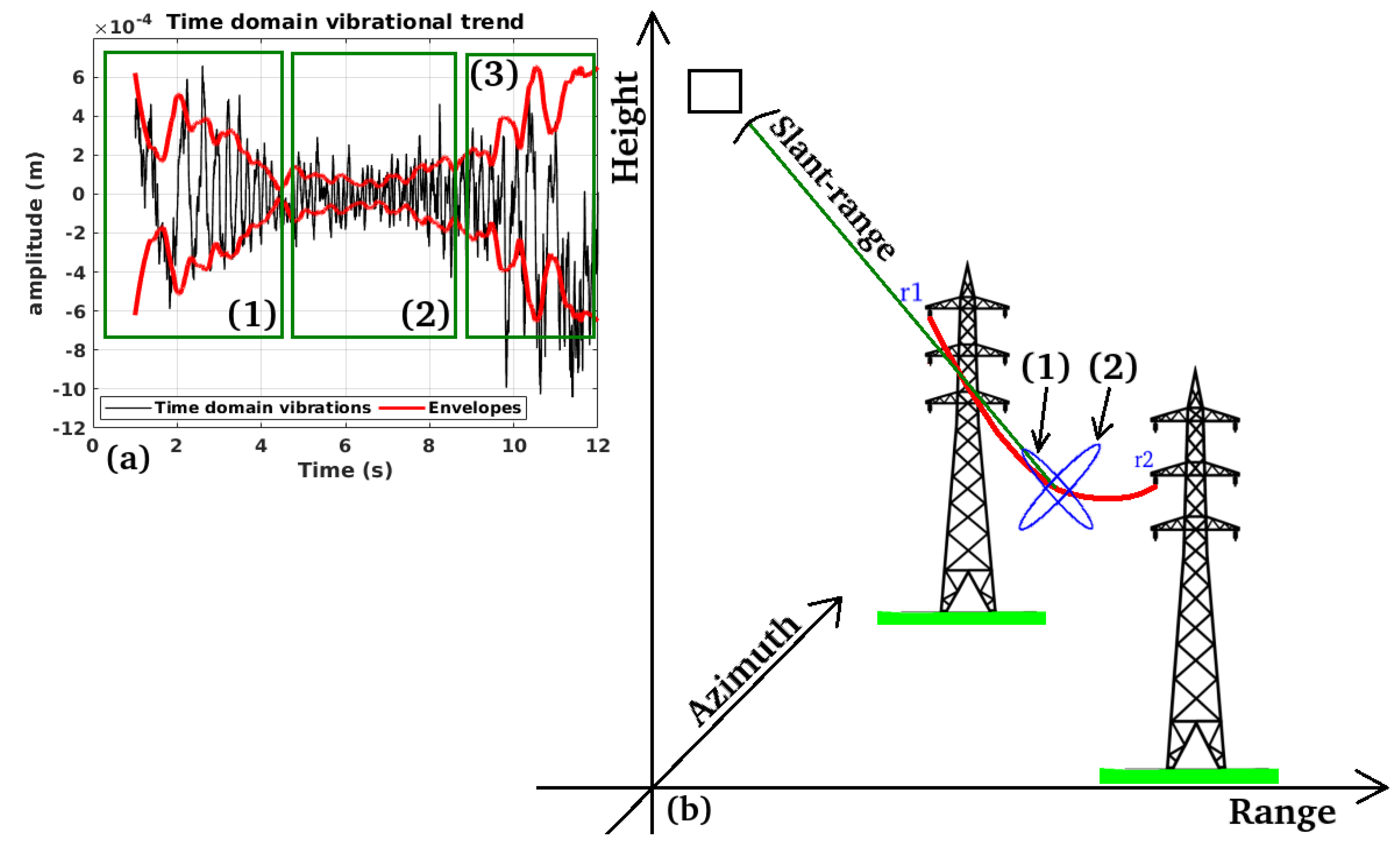
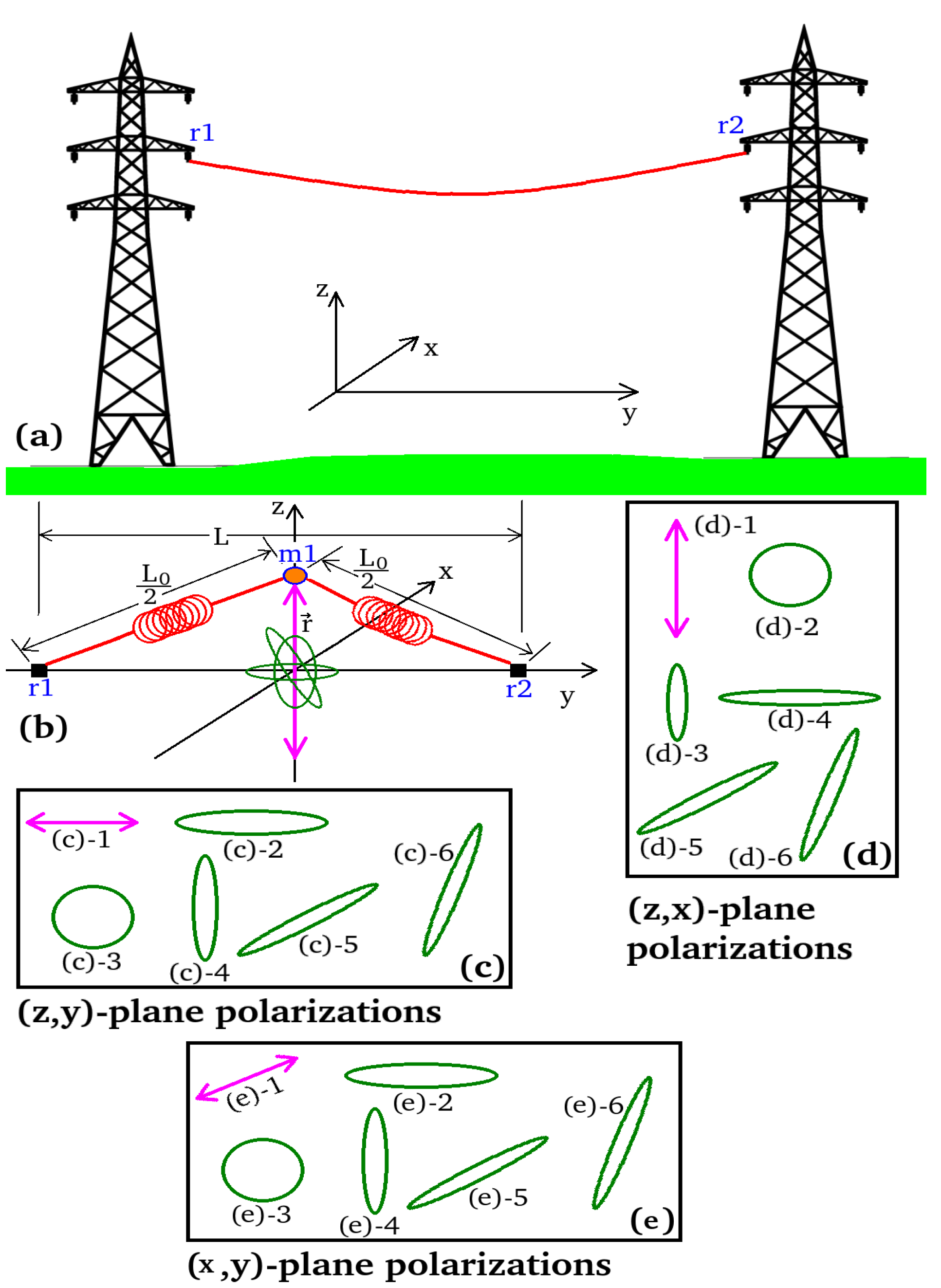
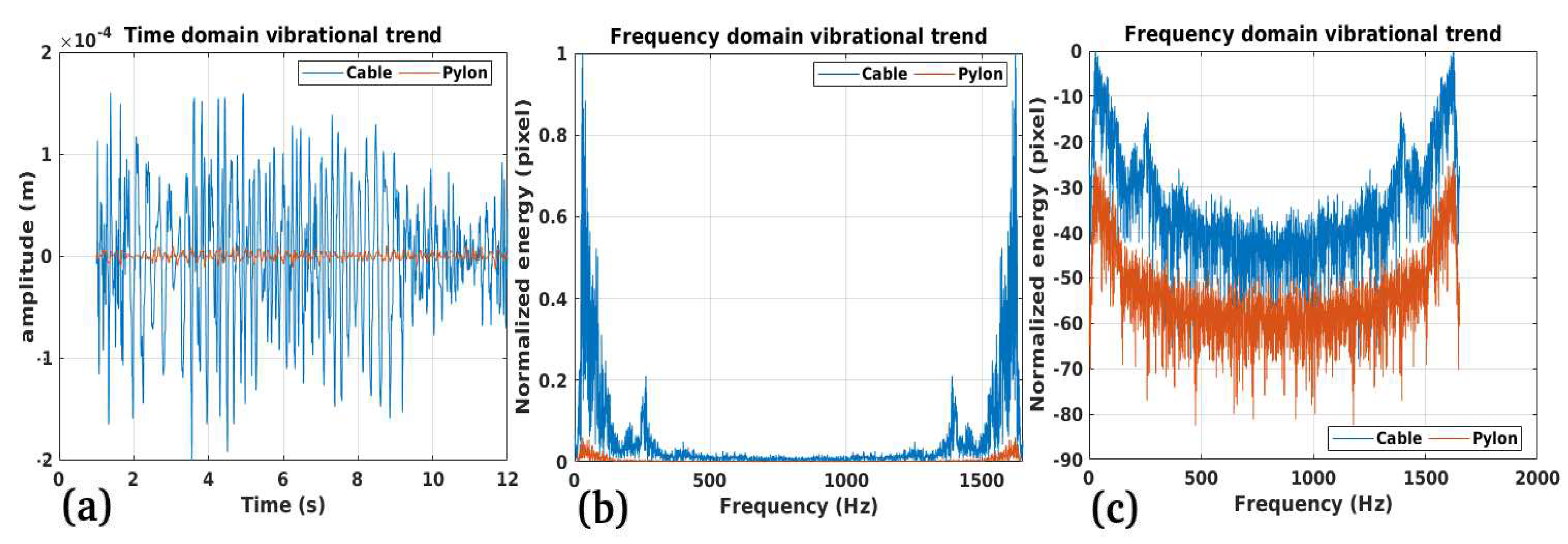
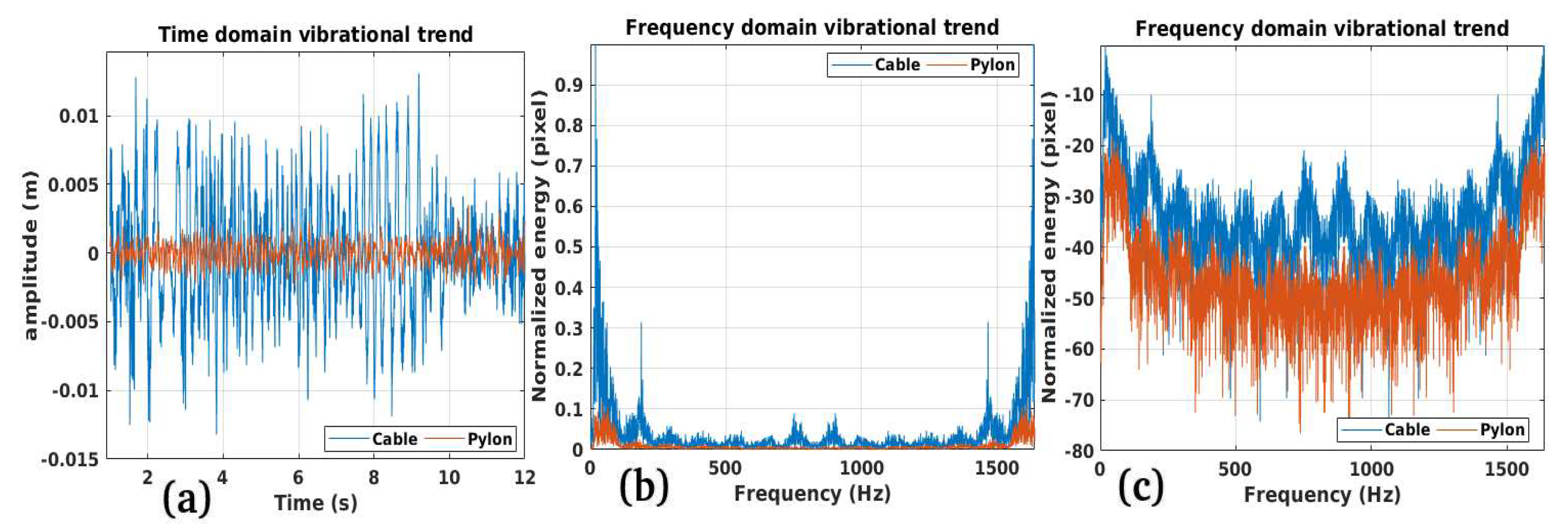
2.3. Vibrational Model of Cables and EPTC-HM
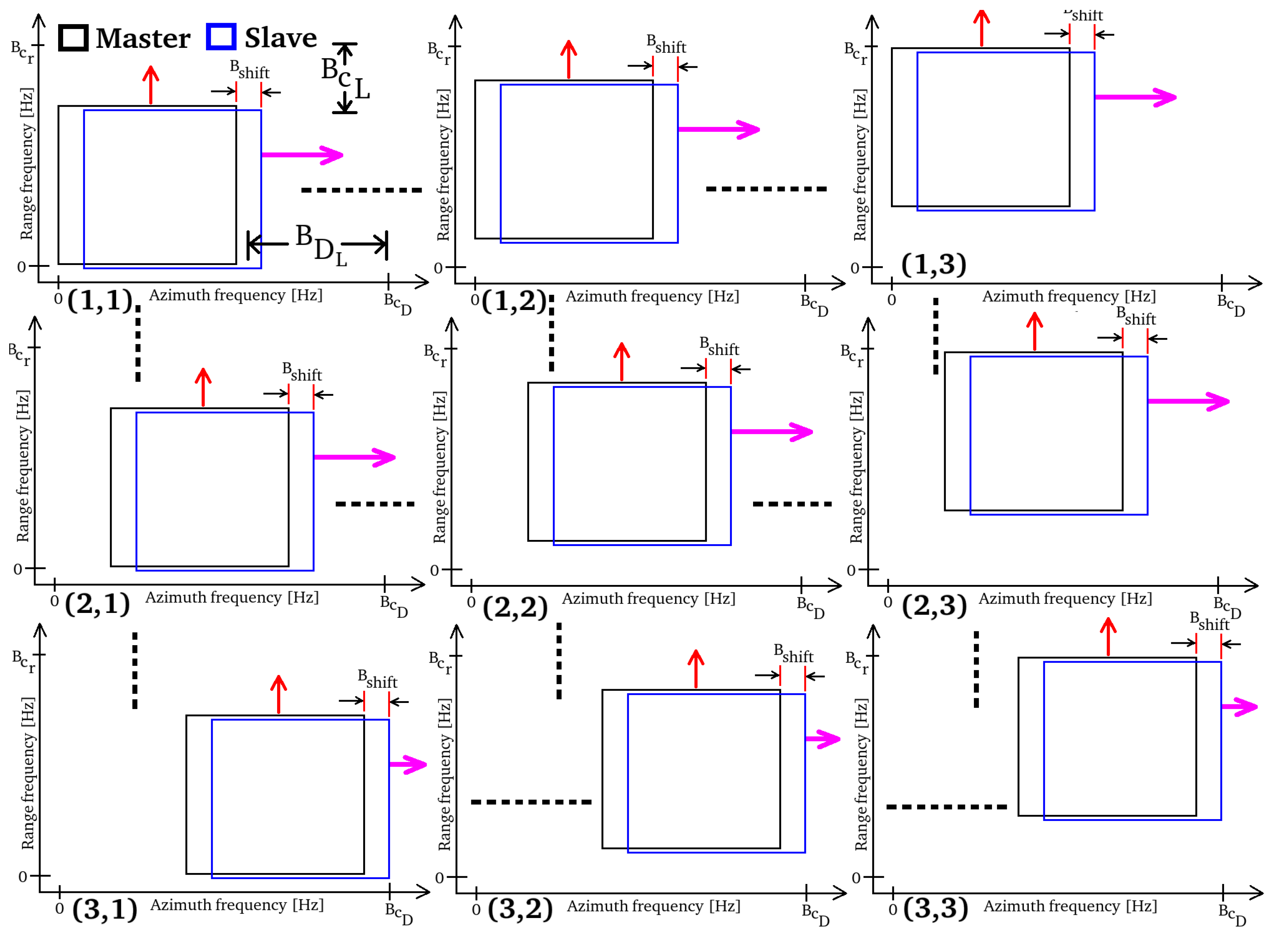
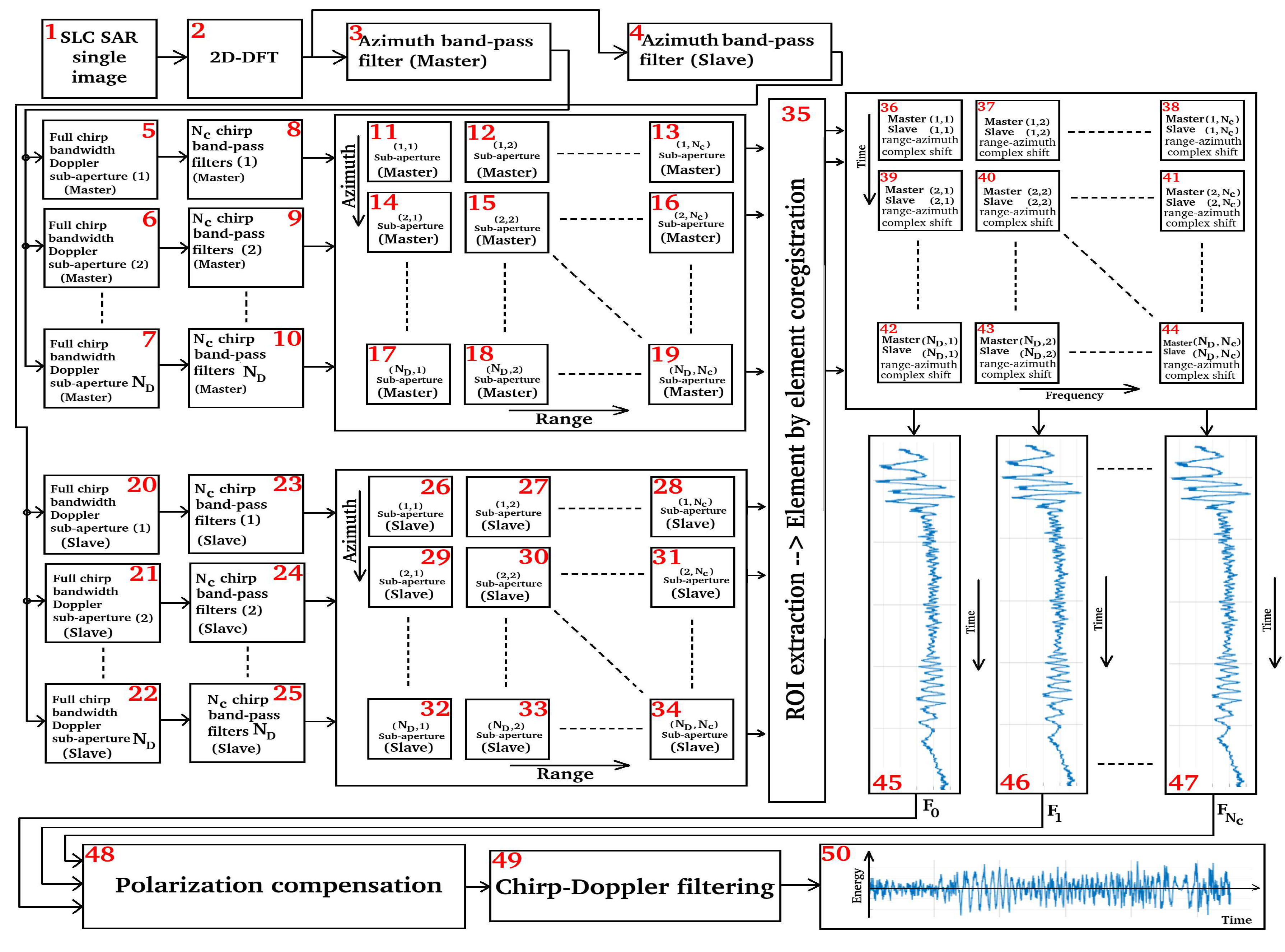
2.4. Processing Framework
- block 36 coregisters sub-matrix 11 with sub-matrix 26;
- block 37 coregisters sub-matrix 12 with sub-matrix 27;
- block 38 coregisters sub-matrix 13 with sub-matrix 28;
- block 39 coregisters sub-matrix 14 with sub-matrix 29;
- block 40 coregisters sub-matrix 15 with sub-matrix 30;
- block 41 coregisters sub-matrix 16 with sub-matrix 31;
- block 42 coregisters sub-matrix 17 with sub-matrix 32;
- block 43 coregisters sub-matrix 18 with sub-matrix 33;
- block 44 coregisters sub-matrix 19 with sub-matrix 34.
3. Experimental results


| SAR parametrer | Value |
|---|---|
| Chirp bandwidth | 300 MHz |
| Doppler bandwidth | 24 kHz |
| PRF | 3.3 kHz |
| PRT | 0.303 ms |
| Antenna length | 6 m |
| Type of acquisition | Spotlight |
| Polarization | HH |
| Acquisition duration | 12.5 s |
| Platform velocity | 7 km/s |
| Observation height | 650000 m |
| Coregistrator parametrer | Value |
|---|---|
| Oversampling factor | 1800 |
| Number of points | 1 |
| Reference window | |
| Search pixel window | |
| Correlation window 16 | 6 m |
| Correlation strategy | 2D cross correlation |
| Use DEM | No |
| Record | Case Study | Reference frame | Point label | Reference Figure | Coordinates (Lat) | Coordinates (Lon) | Experiment type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
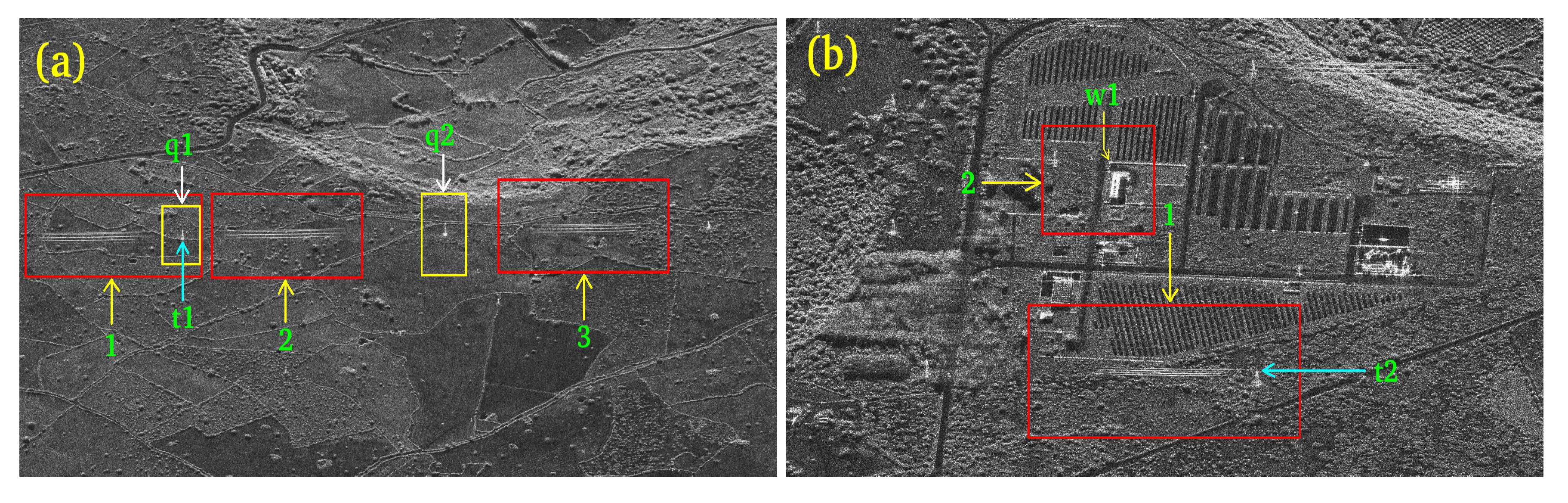
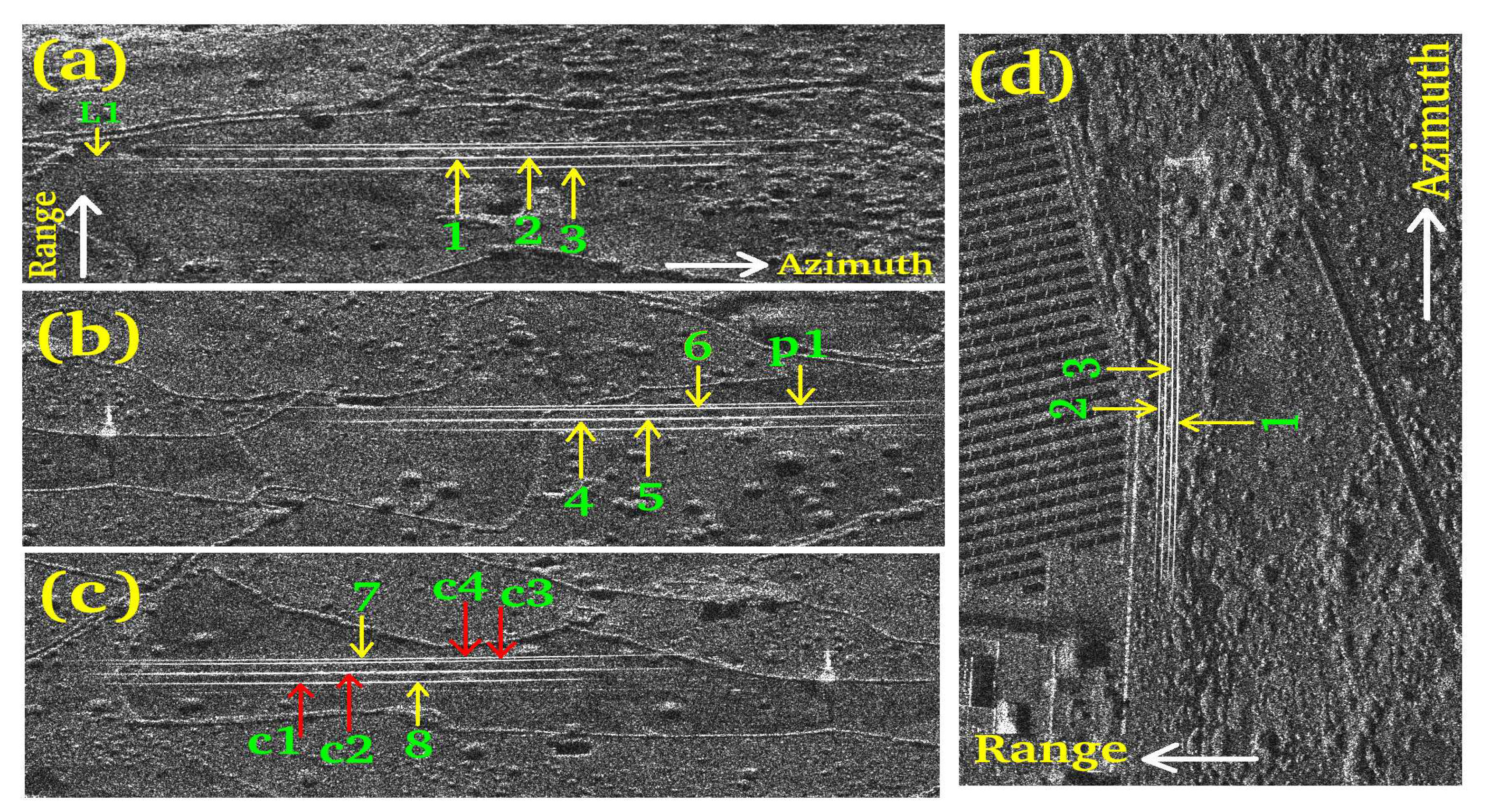
| 1 | 1 | 1 (Figure 7) (a) | 1 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 2 | 1 | 1 (Figure 7) (a) | 2 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 3 | 1 | 1 (Figure 7) (a) | 3 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 4 | 1 | 2 (Figure 7) (a) | 4 | Figure 8 (b) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 5 | 1 | 2 (Figure 7) (a) | 5 | Figure 8 (b) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 6 | 1 | 2 (Figure 7) (a) | 6 | Figure 8 (b) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 7 | 1 | 2 (Figure 7) (a) | 7 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 8 | 1 | 3 (Figure 7) (a) | 8 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 9 | 2 | 3 (Figure 7) (b) | 9 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 10 | 2 | 3 (Figure 7) (b) | 10 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 11 | 2 | 3 (Figure 7) (b) | 11 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 12 | 4 | 3 (Figure 7) (a) | c1 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 13 | 4 | 3 (Figure 7) (a) | c2 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 14 | 4 | 3 (Figure 7) (a) | c3 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 15 | 4 | 3 (Figure 7) (a) | c4 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 16 | 4 | 1 (Figure 7) (a) | q1 | Figure 7 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 17 | 4 | 1 (Figure 7) (b) | q2 | Figure 7 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 18 | 4 | 1 (Figure 7) (b) | c1 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 19 | 4 | 1 (Figure 7) (b) | c2 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 20 | 4 | 1 (Figure 7) (b) | c3,c4 | Figure 8 (c) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Measurement |
| 21 | 2 | 1 (Figure 8 (a) | w1 | Figure 8 (b) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 22 | 2 | 1 (Figure 8 (b) | t2 | Figure 8 (b) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 23 | 2 | 1 (Figure 8 (b) | t1 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 34 | 3 | 1 (Figure 7) (a) | L1 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 25 | 3 | 1 (Figure 7) (b) | t2 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 26 | 3 | 2 (Figure 7) (b) | w1 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 20 | 3 | 1 (Figure 7) (b) | p1 | Figure 8 (a) | 41,076998 | 8.857188 | Performance |
| 21 | 3 | none | none | Figure 31 | 42.008071 | 12.544222 | Validation |
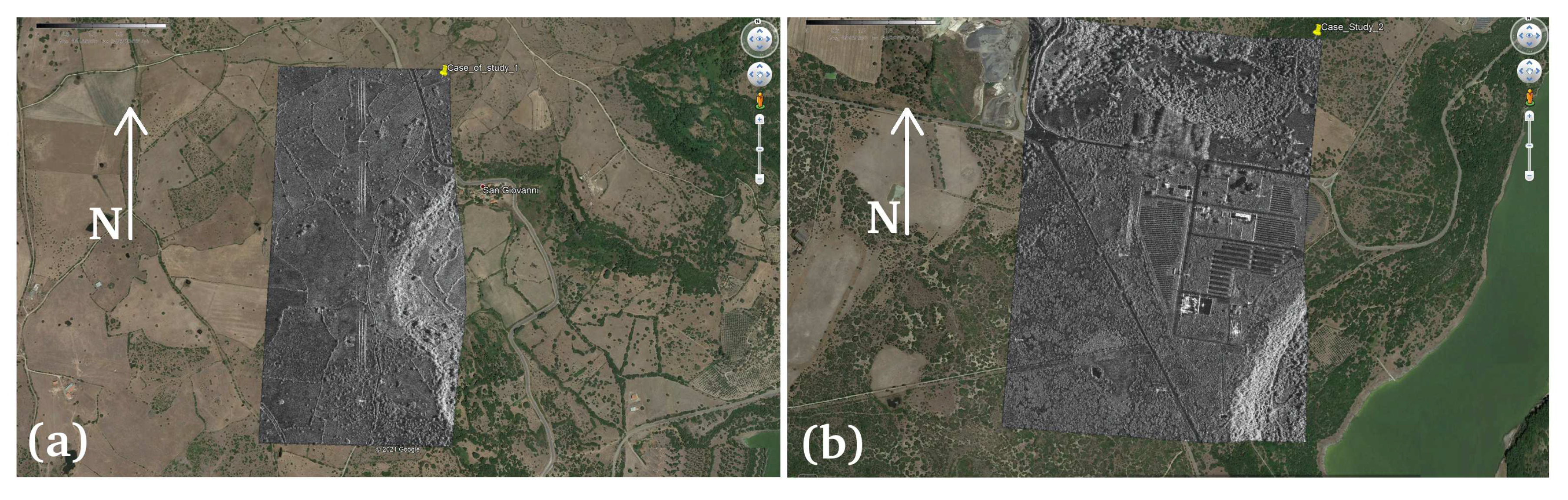
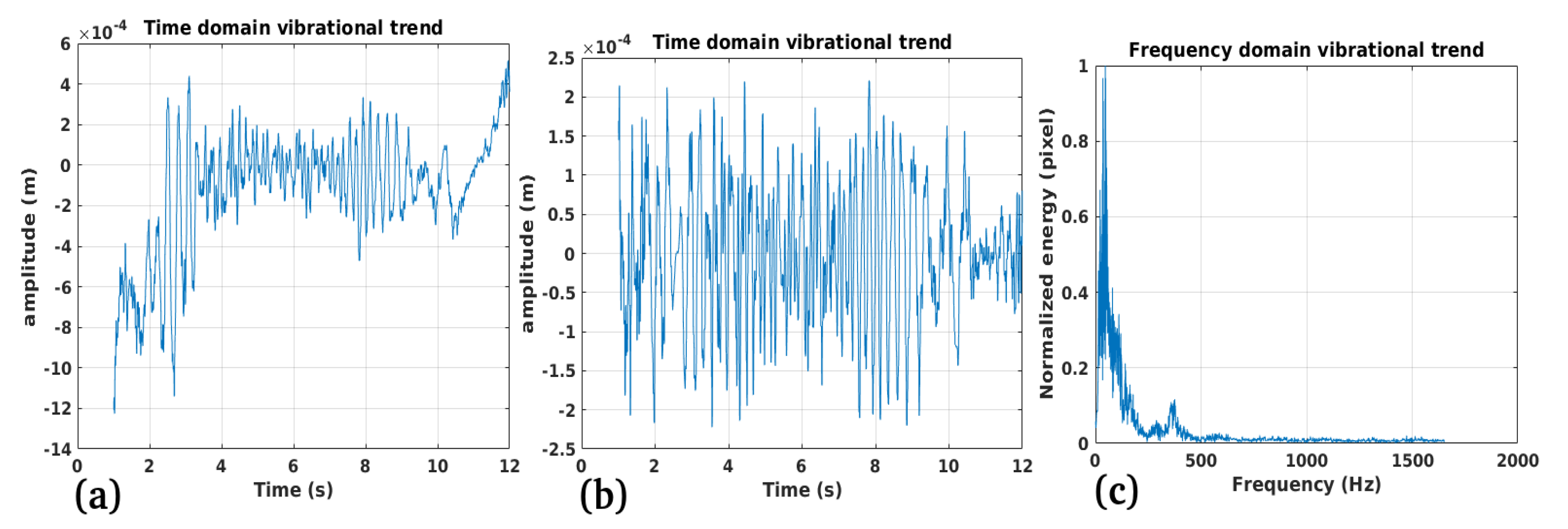
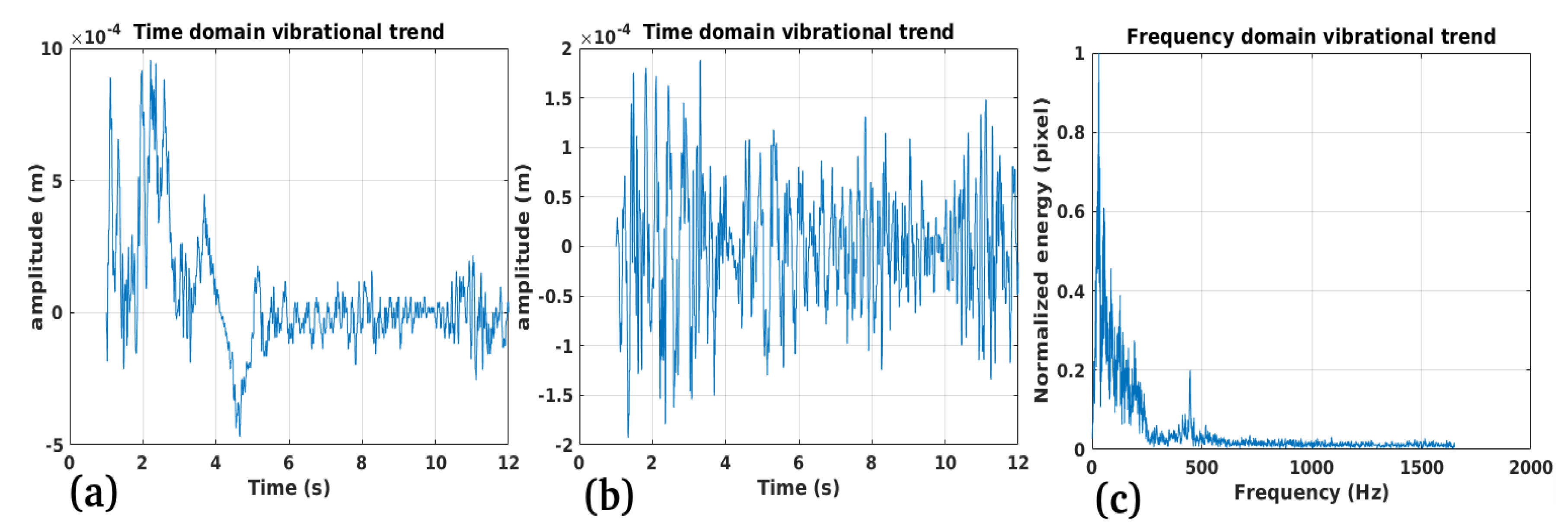
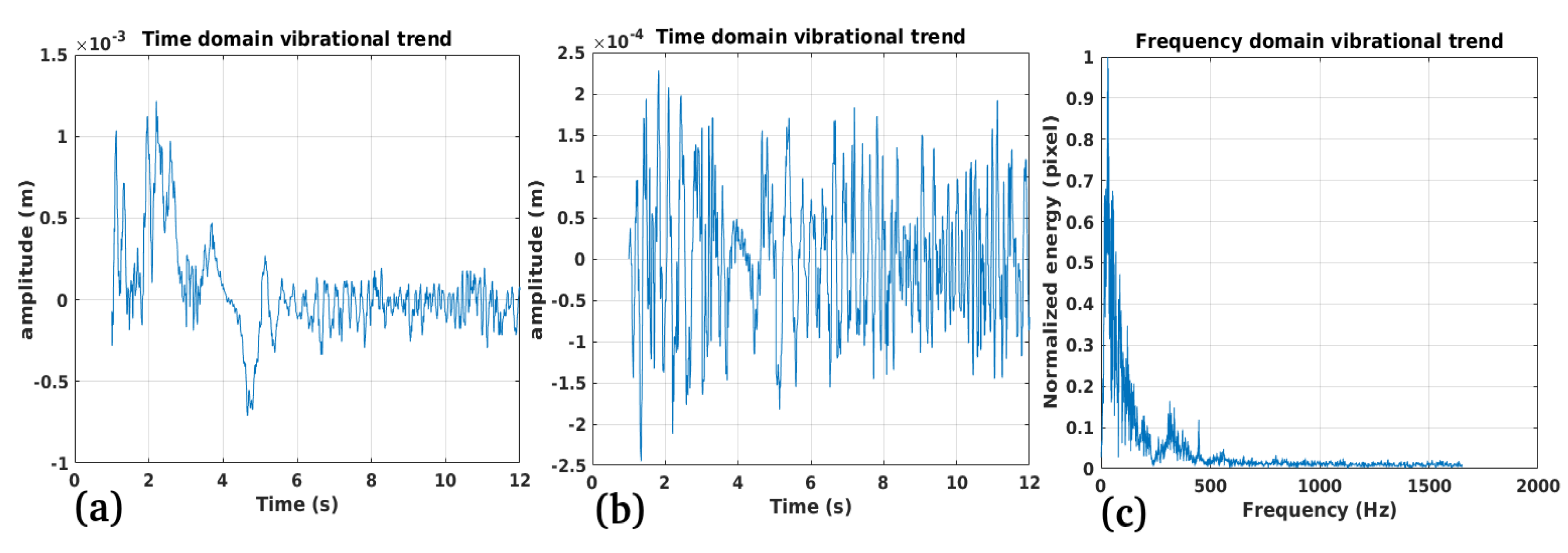
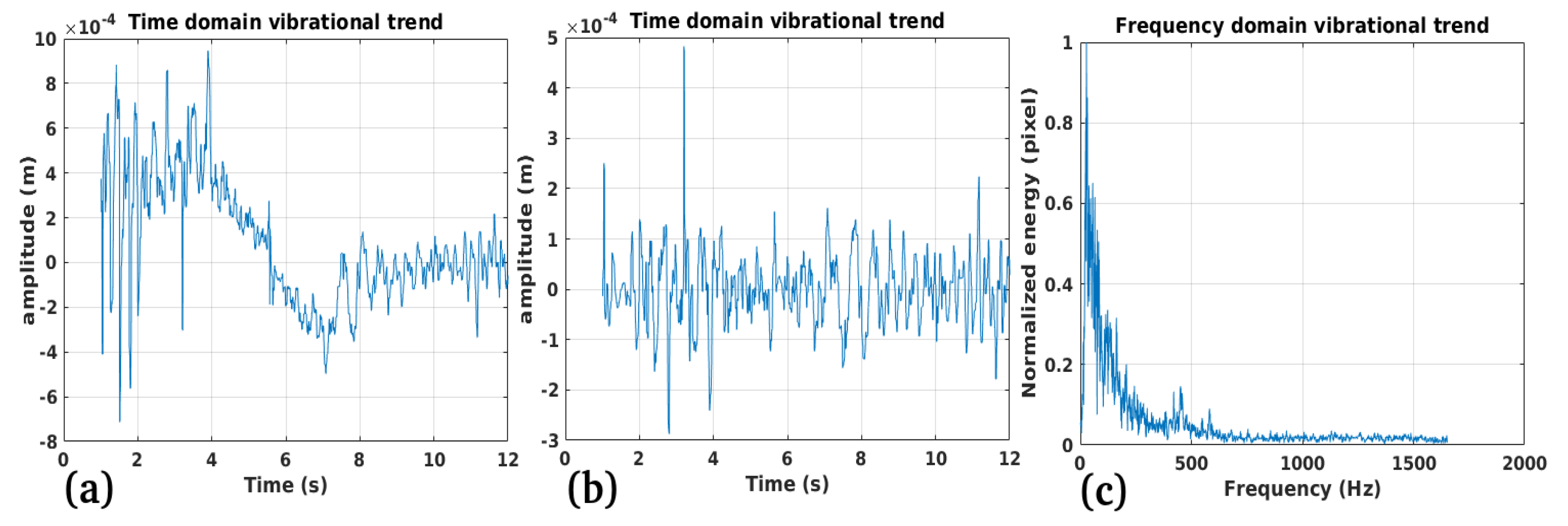
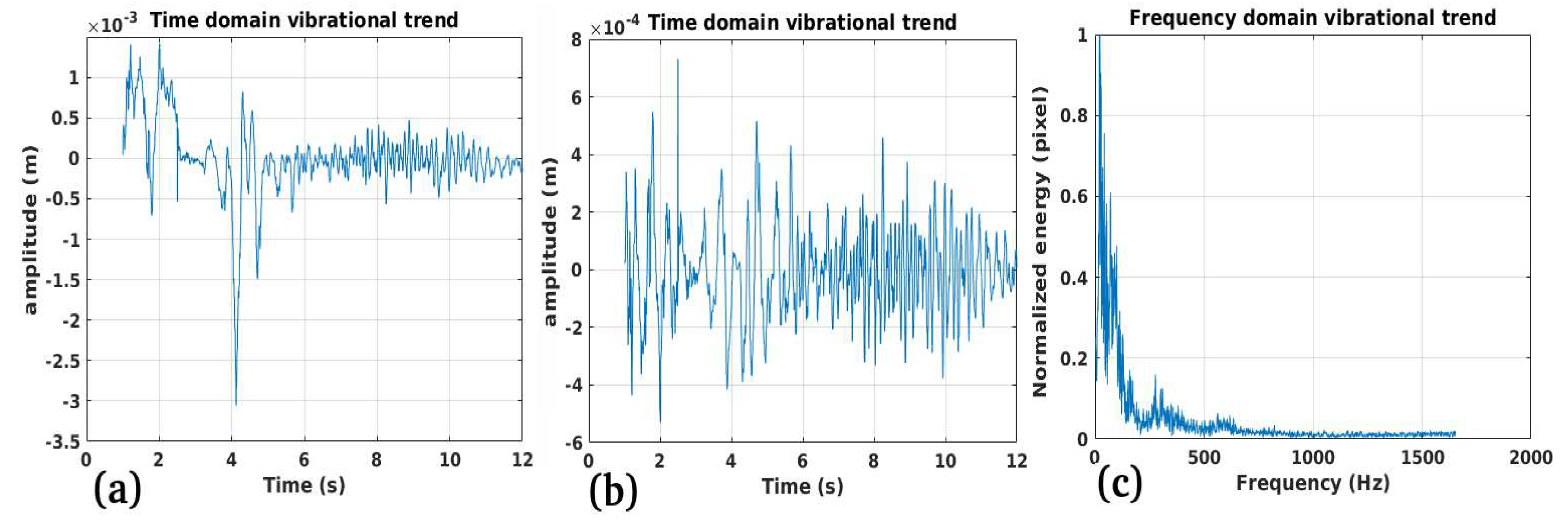
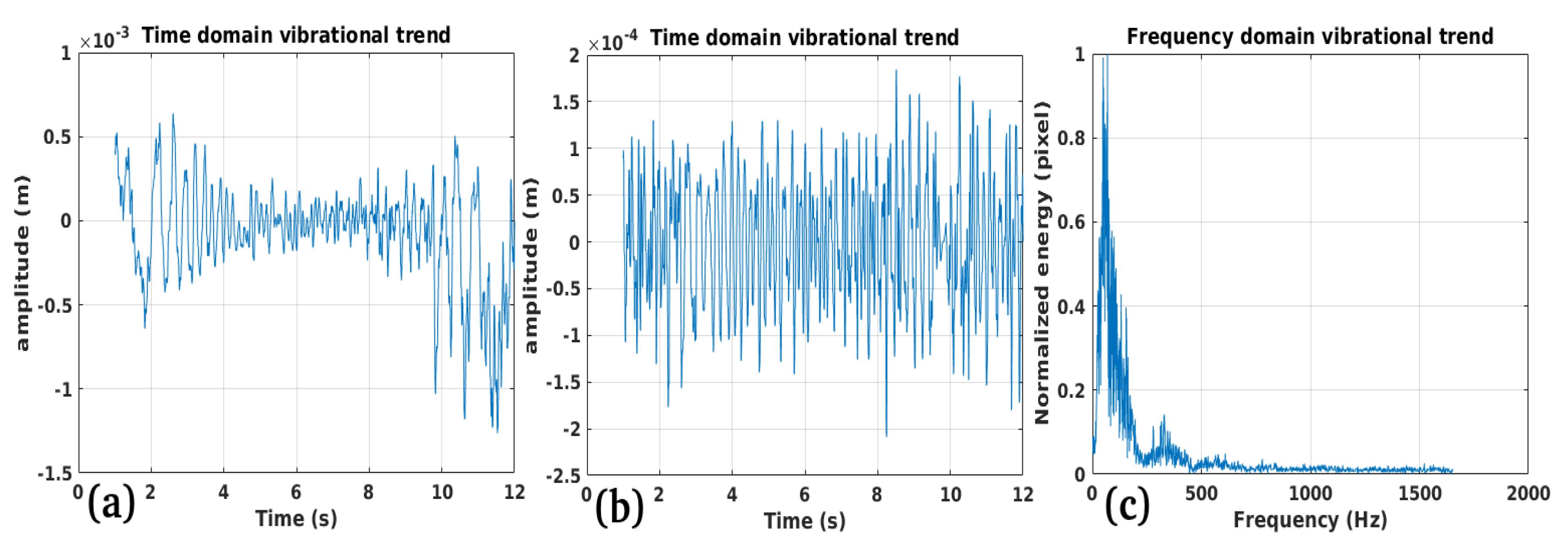
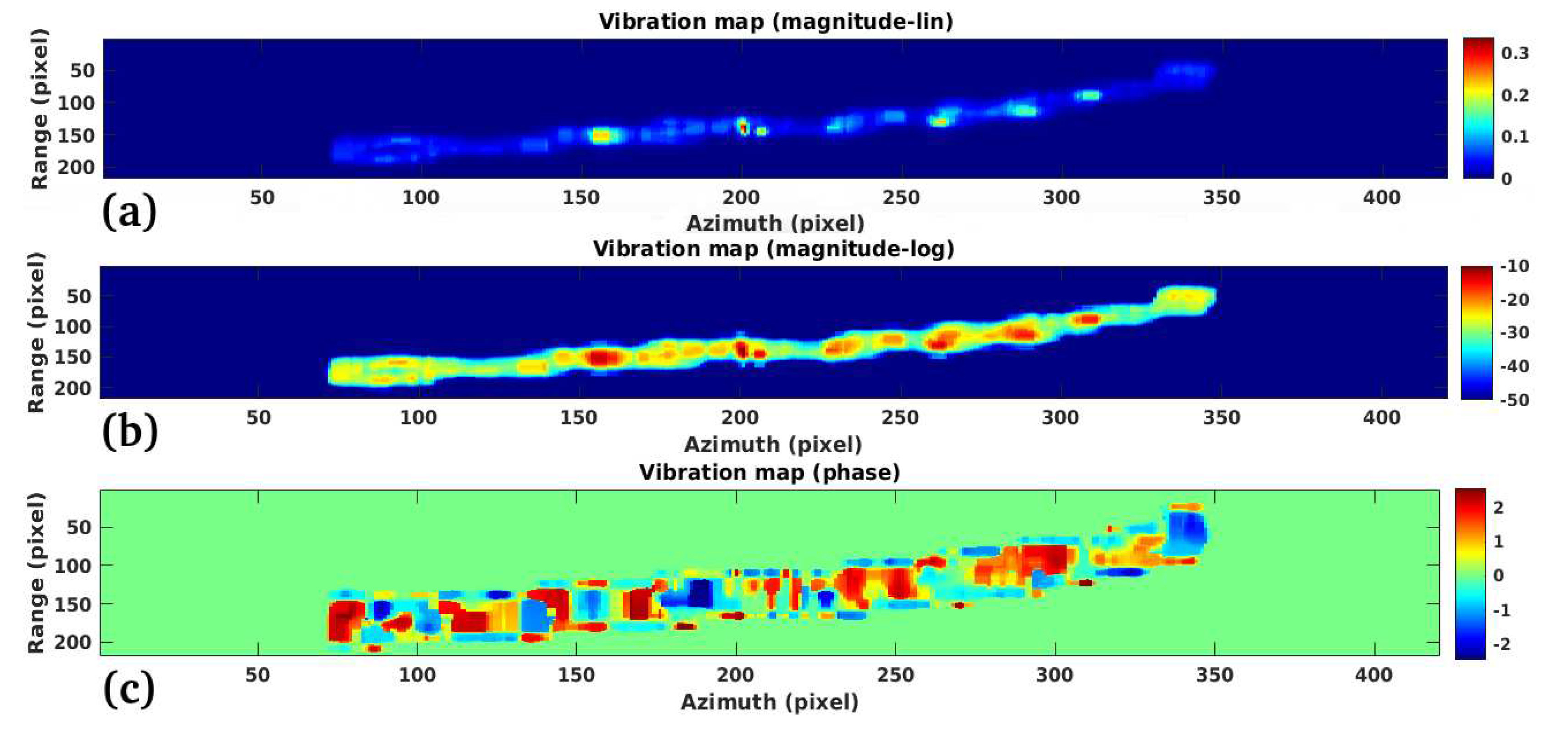
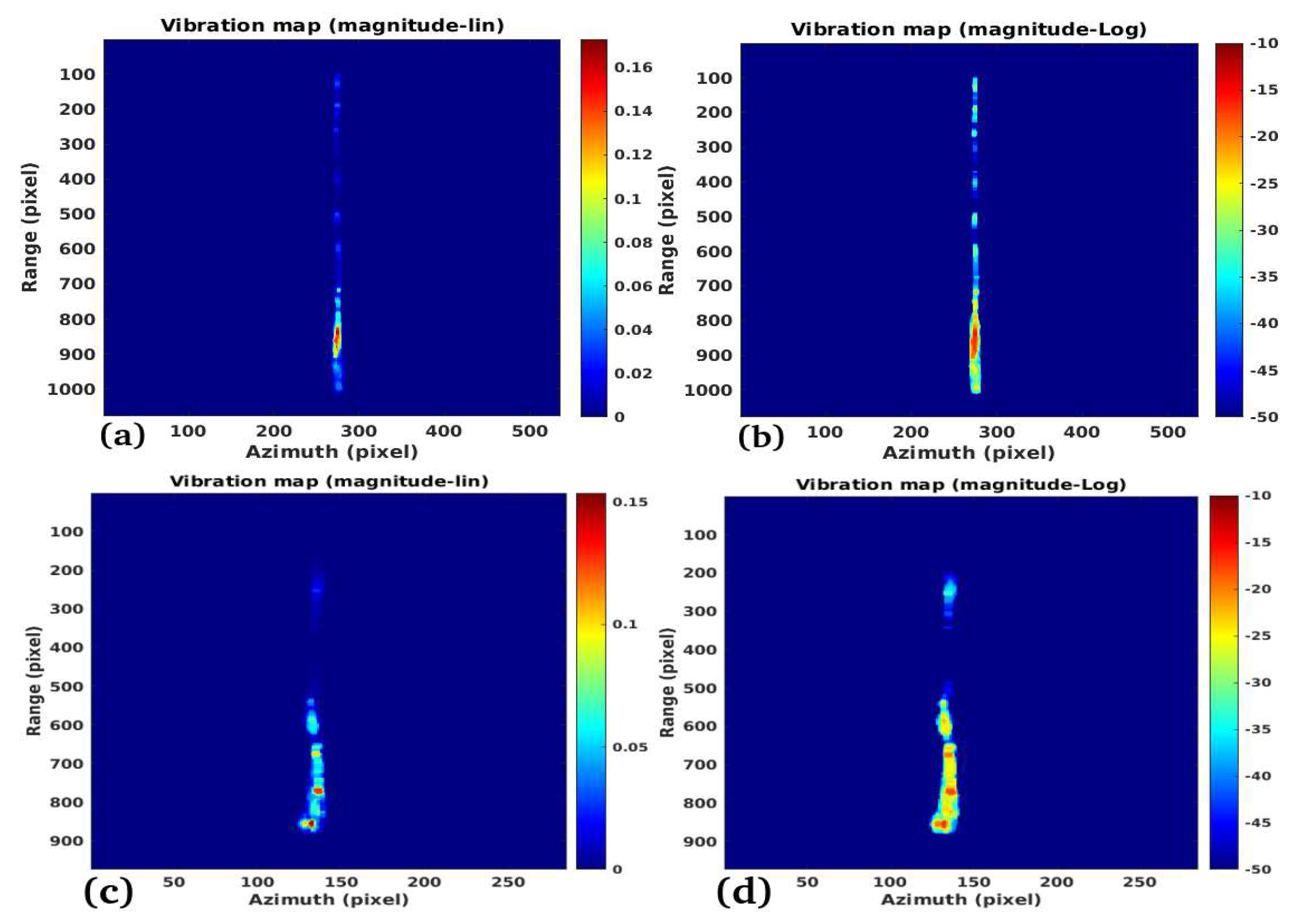
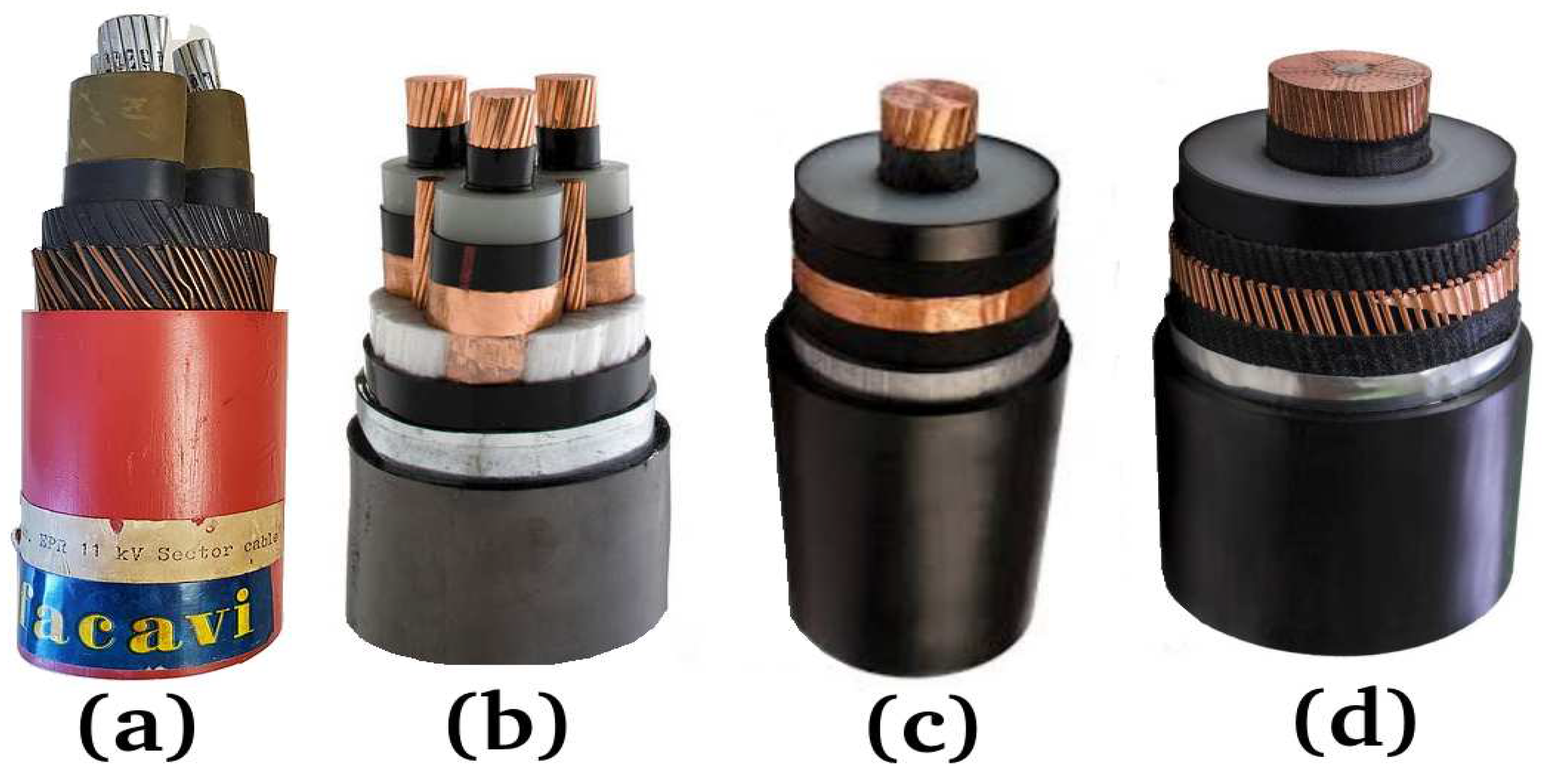
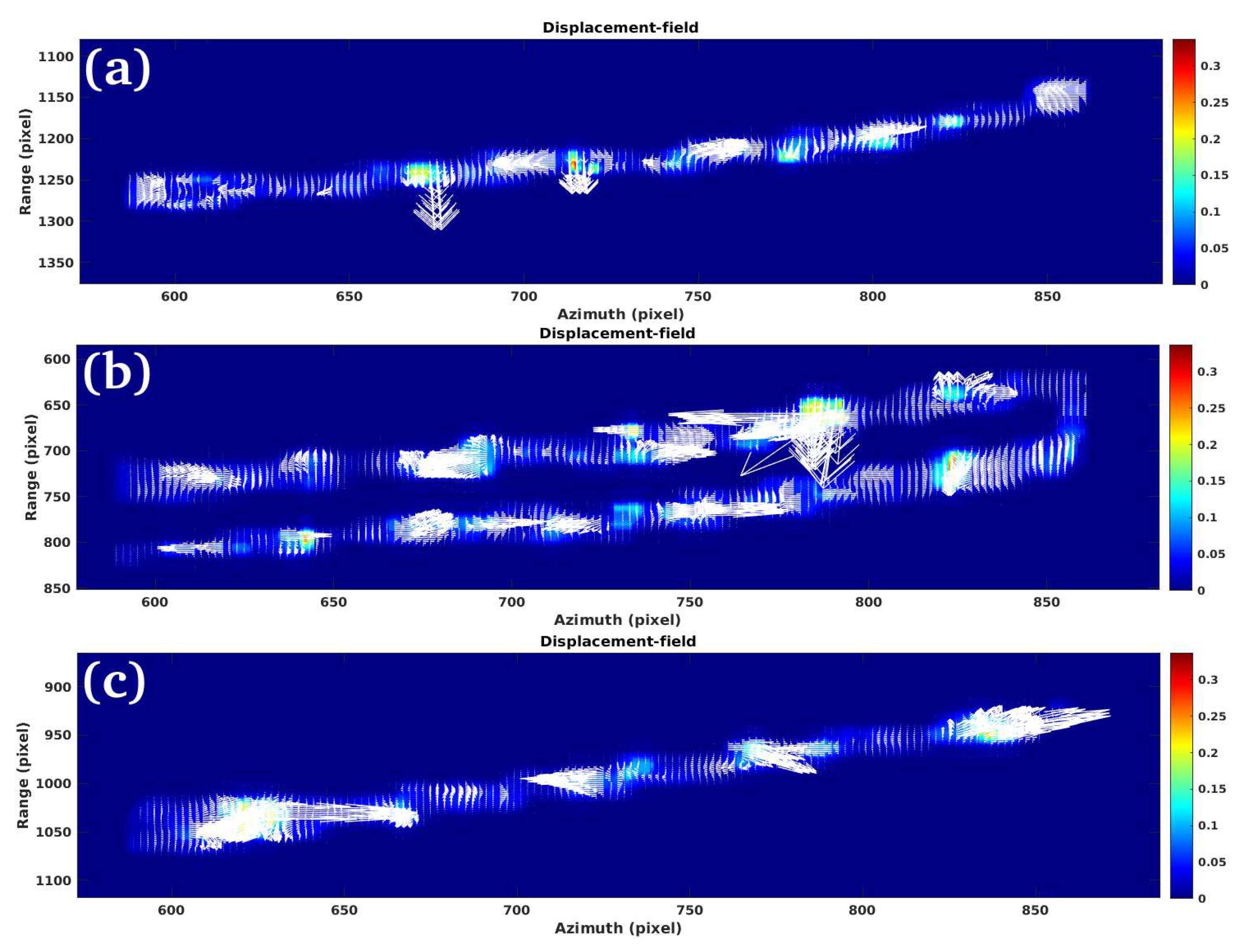
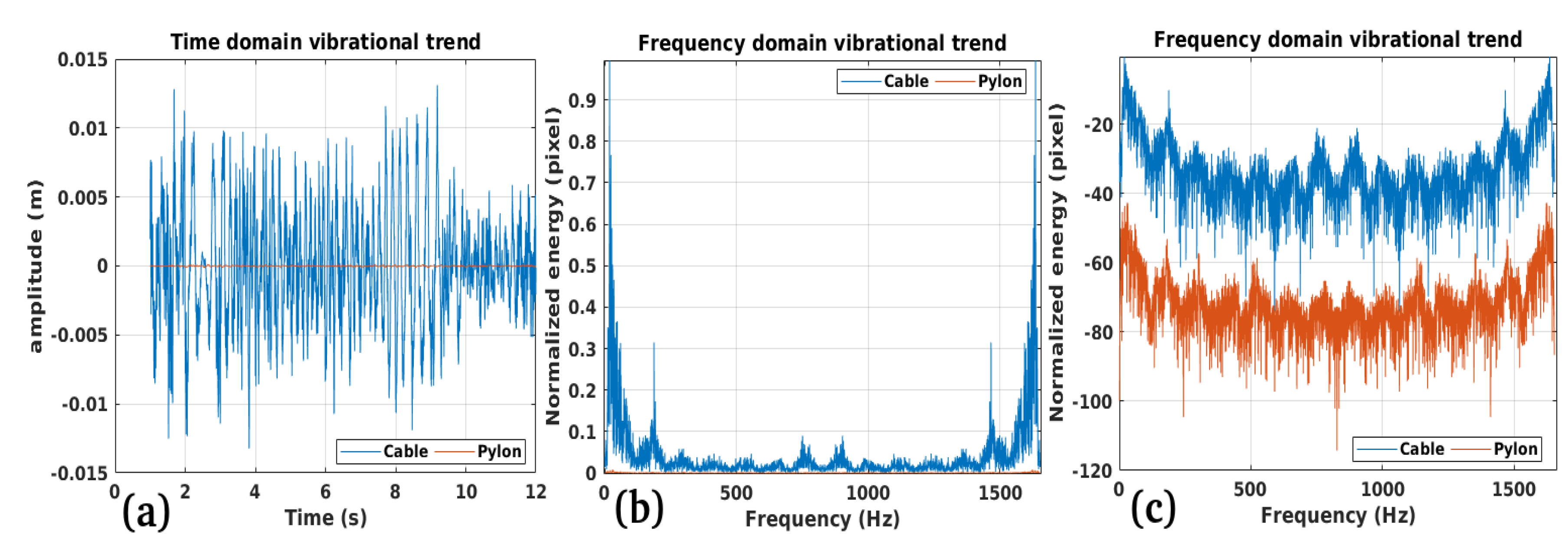
3.1. Study Case 1
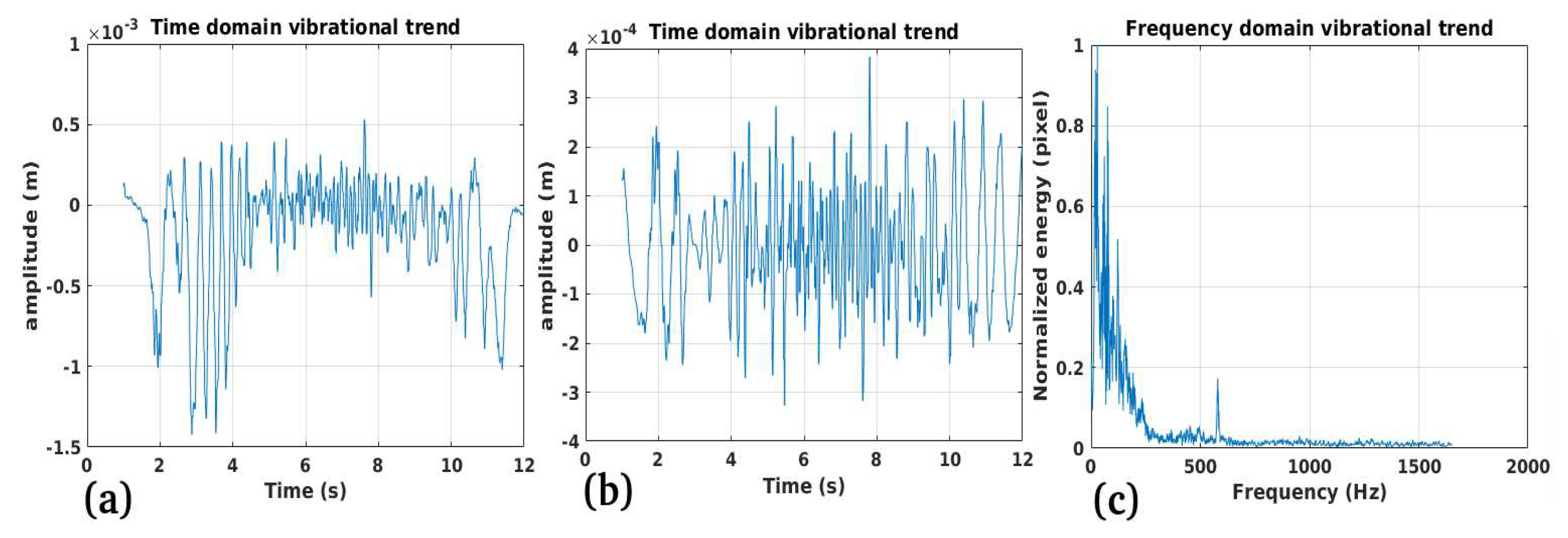
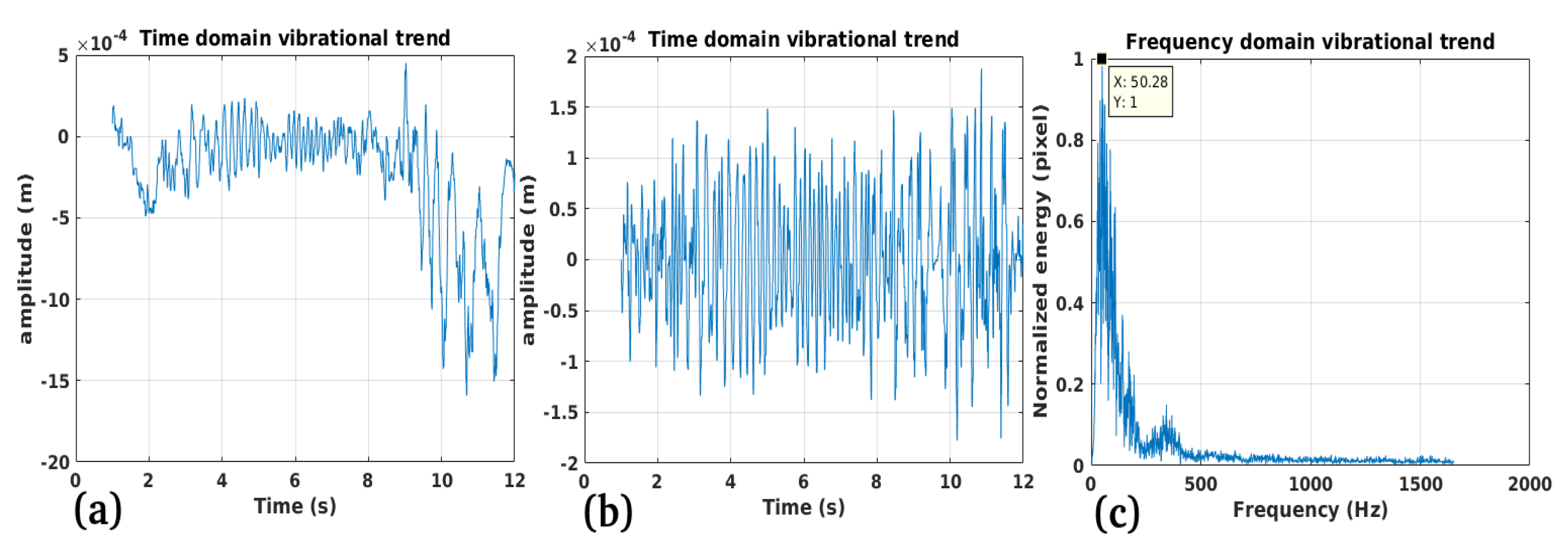
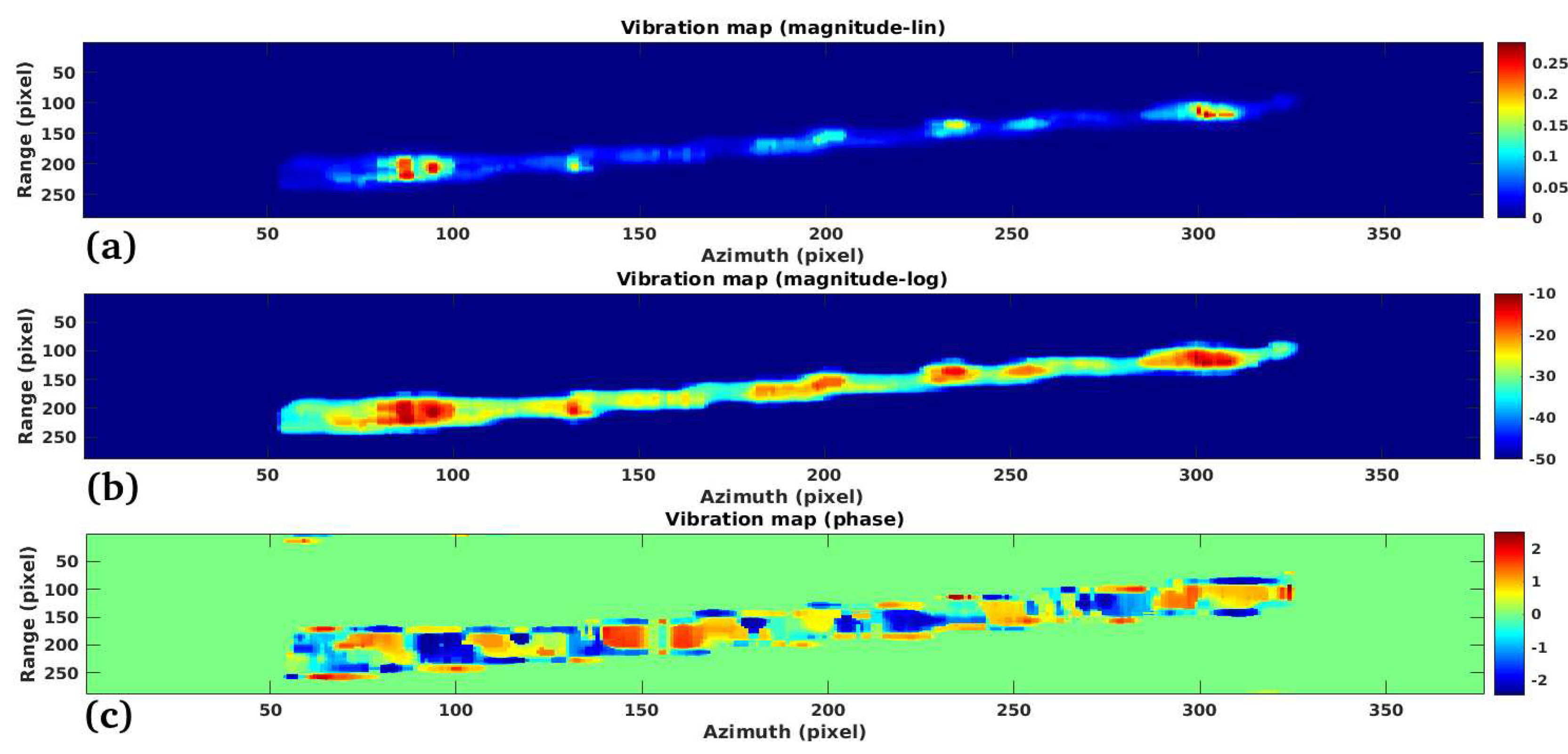
3.2. Study Case 2
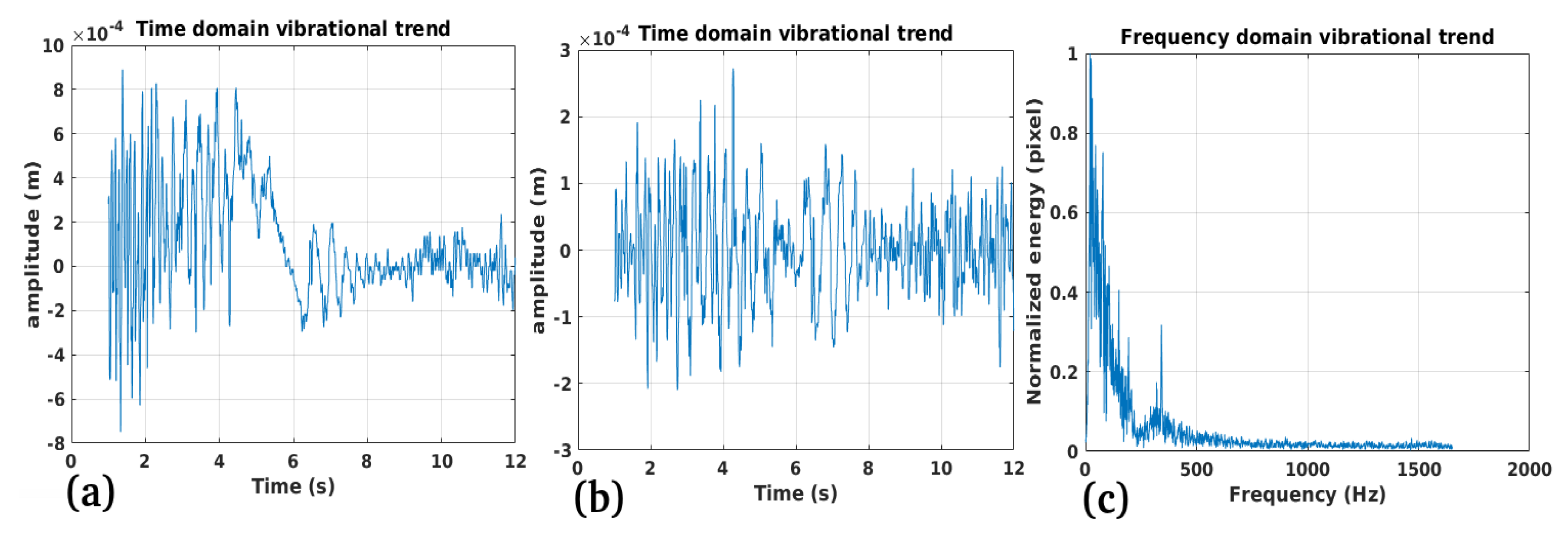
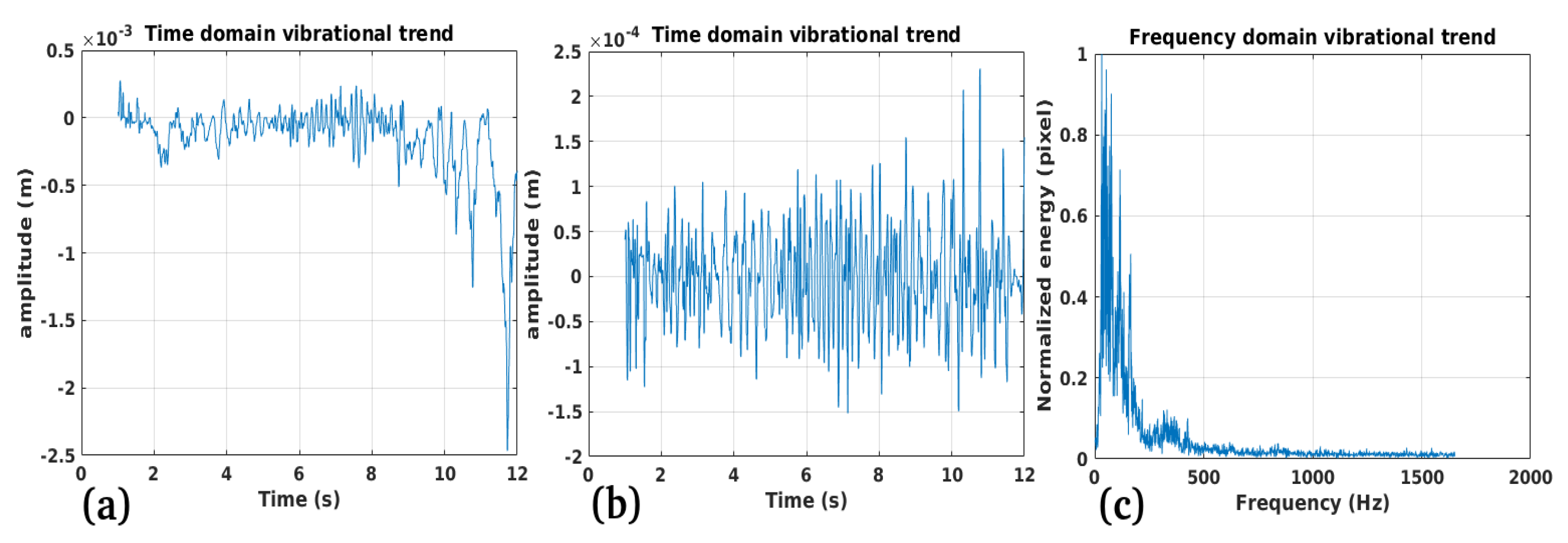
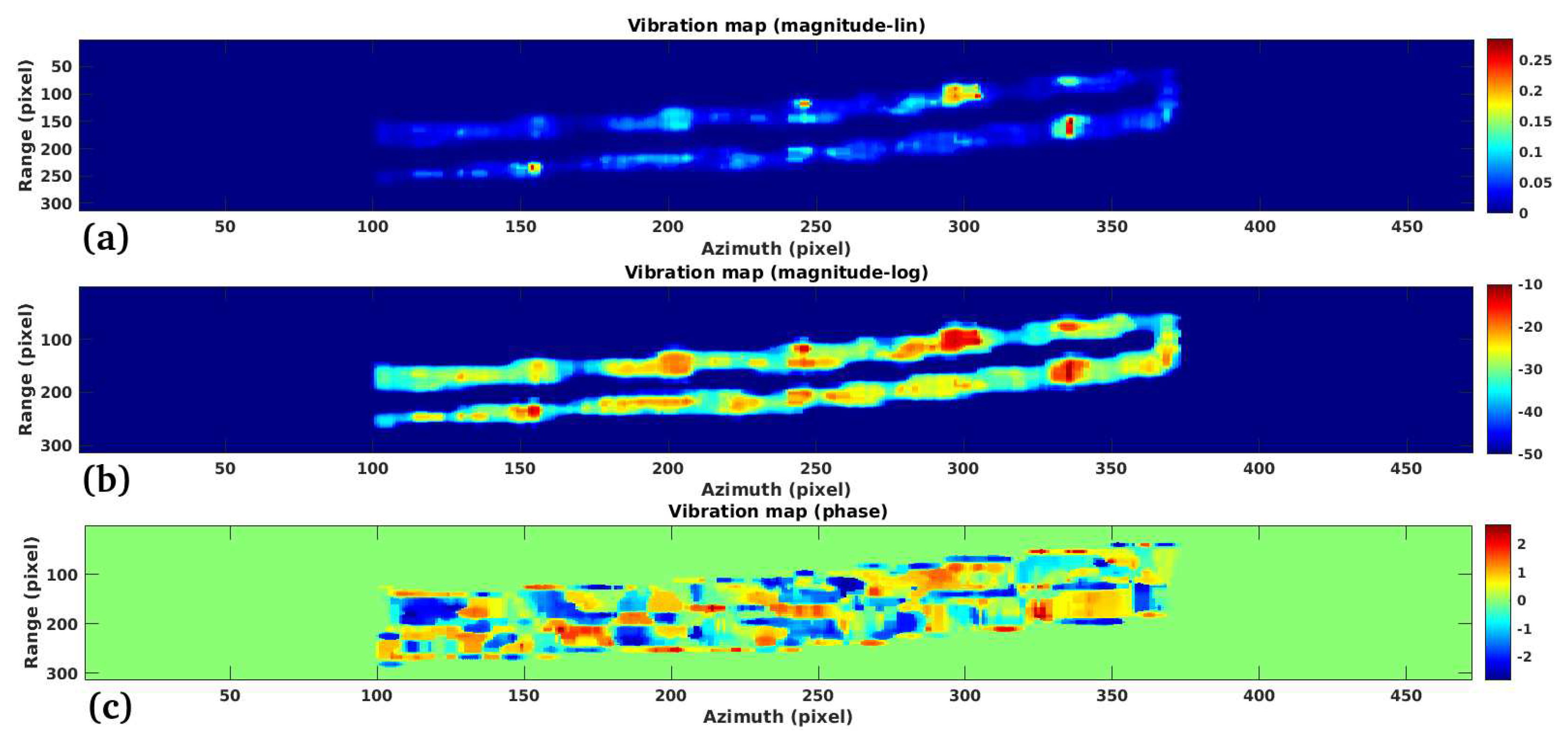
3.3. Study Case 3
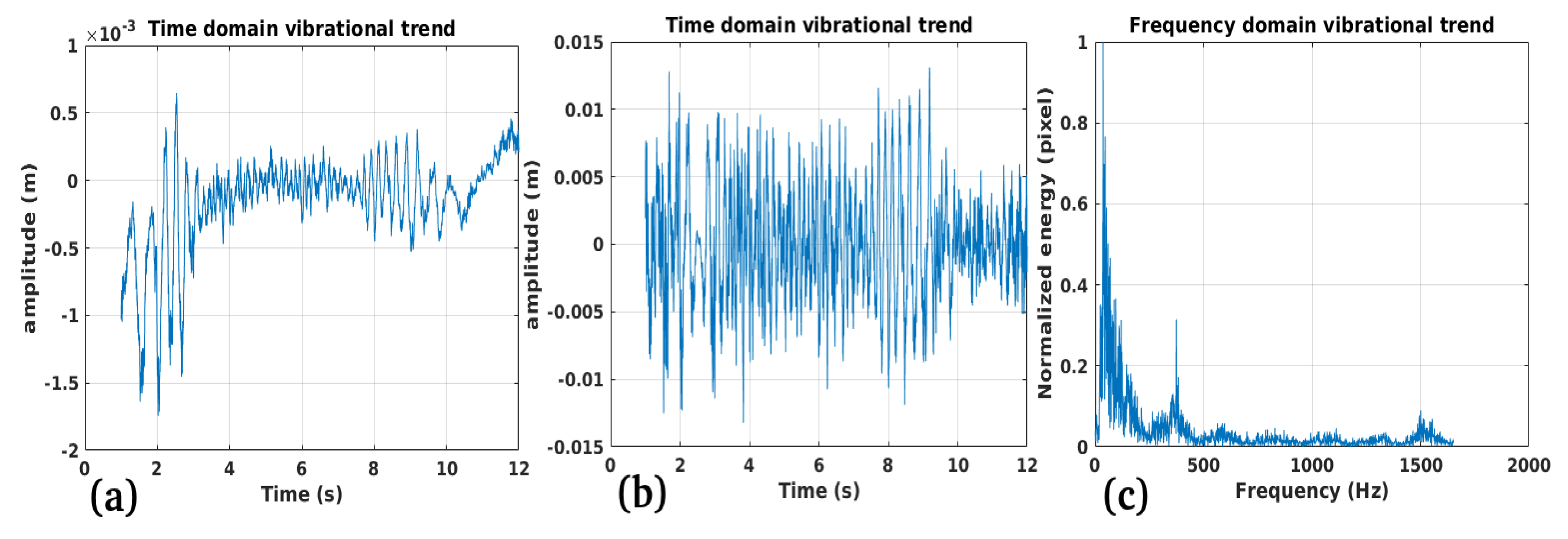
3.4. Study Case 4
Performance:
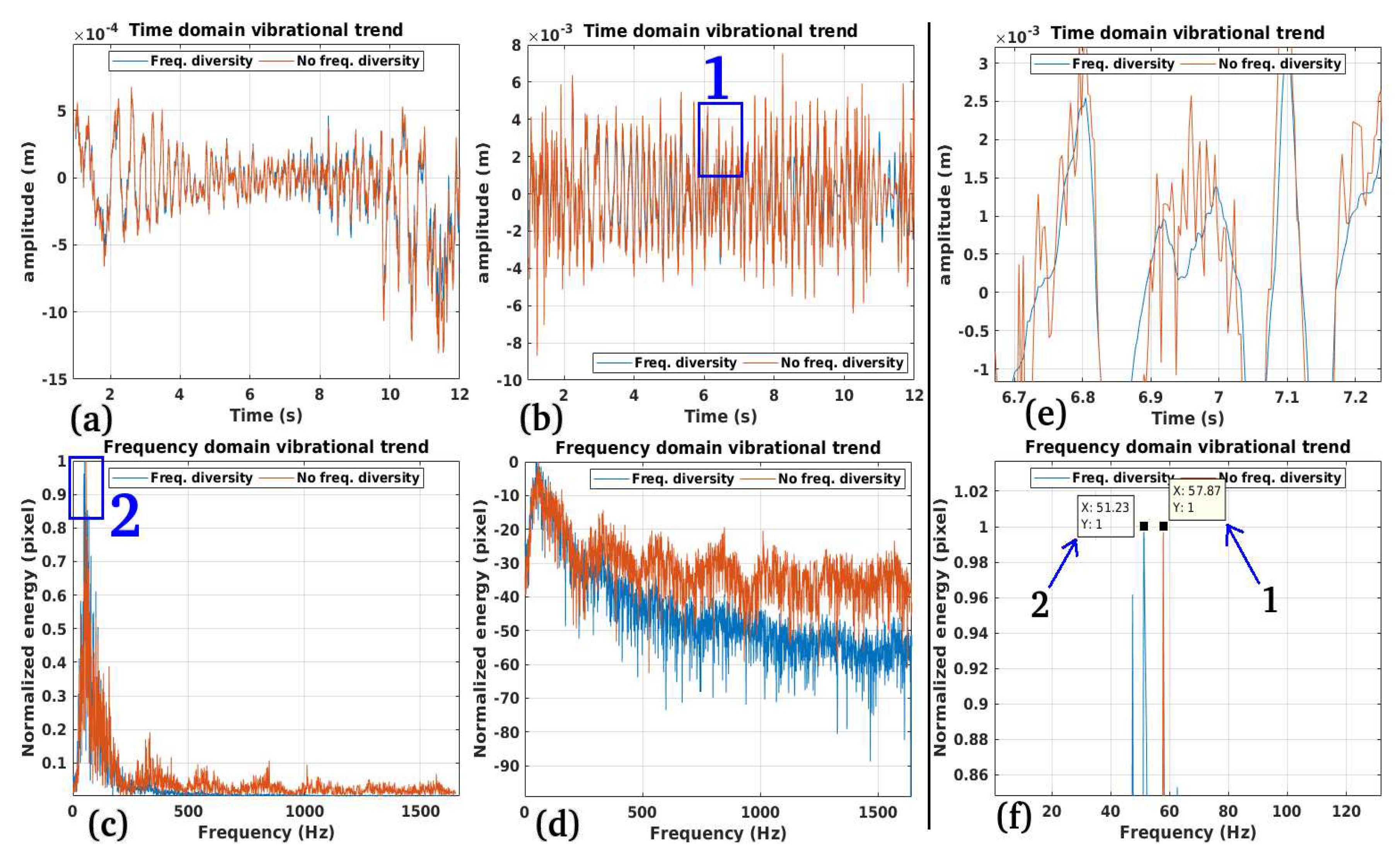

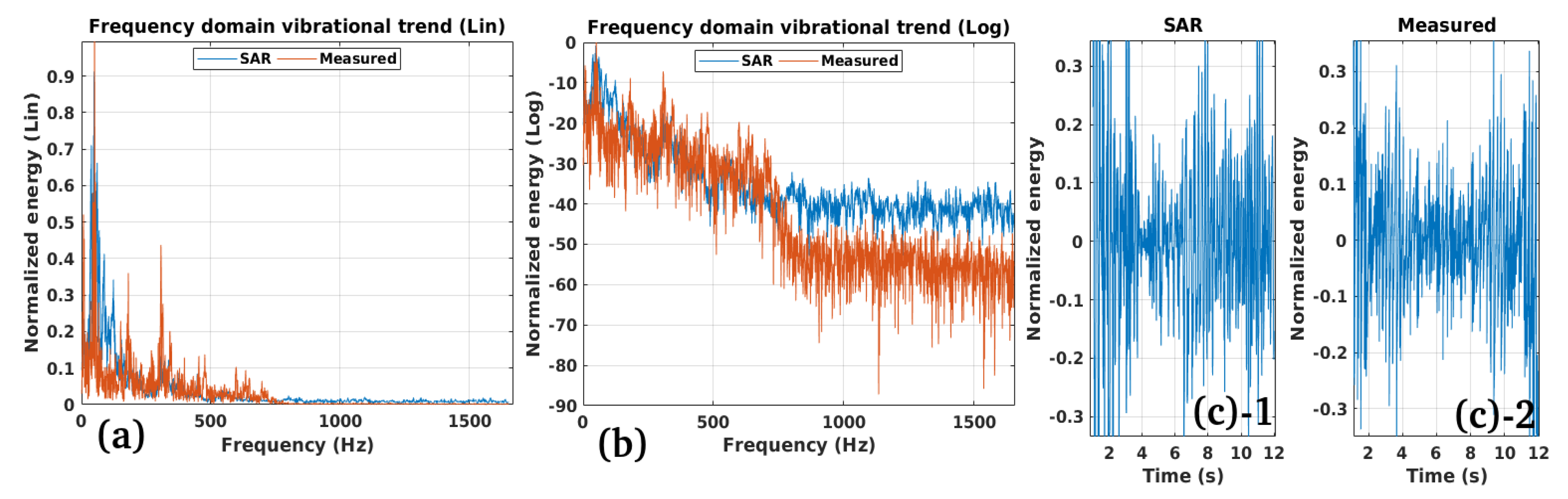
Validation:
Limitations:
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Chen, H.P. Structural health monitoring of large civil engineering structures; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, C.P.; Lohman, R.B.; Jordan, T.E. InSAR constraints on soil moisture evolution after the March 2015 extreme precipitation event in Chile. Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaert, D.P.S.; Hamlington, B.D.; Buzzanga, B.; Jones, C.E. Spaceborne Synthetic Aperture Radar Survey of Subsidence in Hampton Roads, Virginia (USA). Scientific Reports 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnol, A.; Aochi, H.; Raucoules, D.; Veloso, F.M.L.; Koudogbo, F.N.; Fumagalli, A.; Chiquet, P.; Maisons, C. Wavelet-based analysis of ground deformation coupling satellite acquisitions (Sentinel-1, SMOS) and data from shallow and deep wells in Southwestern France. Scientific Reports 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raspini, F.; Carlà, T.; Intrieri, E.; Bardi, F.; Farina, P.; Ferretti, A.; Colombo, D.; Novali, F.; Casagli, N. Perspectives on the prediction of catastrophic slope failures from satellite InSAR. Scientific Reports 2019, 9, 13158. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, J.S.; Koontz, J.A. Cable vibration—Methods of measurement. Electrical Engineering 1936, 55, 490–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, H.L.; García-Souto, J.A.; Sanz, J. Measurements of mechanical vibrations at magnetic cores of power transformers with fiber-optic interferometric intrinsic sensor. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics 2000, 6, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, R.G.; Edwards, K.S. A new method for real-time monitoring of high-voltage transmission-line conductor sag. IEEE transactions on power delivery 2002, 17, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, G.; Bocciolone, M.; Cheli, F.; Cigada, A.; Manenti, A. Large wind-induced vibrations on conductor bundles: laboratory scale measurements to reproduce the dynamic behavior of the spans and the suspension sets. IEEE Transactions on power delivery 2005, 20, 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangl, H.; Bretterklieber, T.; Brasseur, G. A feasibility study on autonomous online condition monitoring of high-voltage overhead power lines. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2009, 58, 1789–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahami, M.; Gourbi, A.; Tilmatine, A.; Dascalescu, L. Numerical analysis of the induced corona vibrations on high-voltage transmission lines affected by rainfall. IEEE Transactions on power delivery 2011, 26, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, B.; Guerard, S.; Lilien, J.L. Original real-time observations of aeolian vibrations on power-line conductors. IEEE transactions on power delivery 2011, 26, 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Pan, J.; Huang, H.; Zhou, J. Transmission of vibration of a power transformer from the internal structures to the tank. In Proceedings of the Acoustics 2012 Fremantle: Acoustics, Development and the Environment, Fremantle, Australia, 21–23 Novermber 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, F. COSMO-SkyMed staring spotlight SAR data for micro-motion and inclination angle estimation of ships by pixel tracking and convex optimization. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 766. [Google Scholar]
- Biondi, F.; Addabbo, P.; Orlando, D.; Clemente, C. Micro-motion estimation of maritime targets using pixel tracking in COSMO-SkyMed synthetic aperture radar data—An operative assessment. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, F.; Addabbo, P.; Ullo, S.L.; Clemente, C.; Orlando, D. Perspectives on the structural health monitoring of bridges by synthetic aperture radar. Remote Sensing 2020, 12, 3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, F.; Addabbo, P.; Clemente, C.; Ullo, S.L.; Orlando, D. Monitoring of Critical Infrastructures by Micromotion Estimation: The Mosul Dam Destabilization. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing 2020, 13, 6337–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curlander, J.C.; McDonough, R.N. Synthetic aperture radar: systems and signal processing. Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Raney, R.K. Synthetic Aperture Imaging Radar and Moving Targets. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems 1971, AES-7, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufillaro, N.B. Nonlinear and chaotic string vibrations. American Journal of Physics 1989, 57, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.R.; Seelamantula, C.S. On the selection of optimum Savitzky-Golay filters. IEEE transactions on signal processing 2012, 61, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




