Submitted:
10 August 2023
Posted:
11 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant materials
2.2. Fall armyworm bioassays
2.3. Beet armyworm bioassay
2.4. WCR bioassays
2.5. Oxylipin profiling of wounded leaf tissue and WCR-infested root tissues
2.6. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. ZmOPR2 promotes defense against FAW herbivory
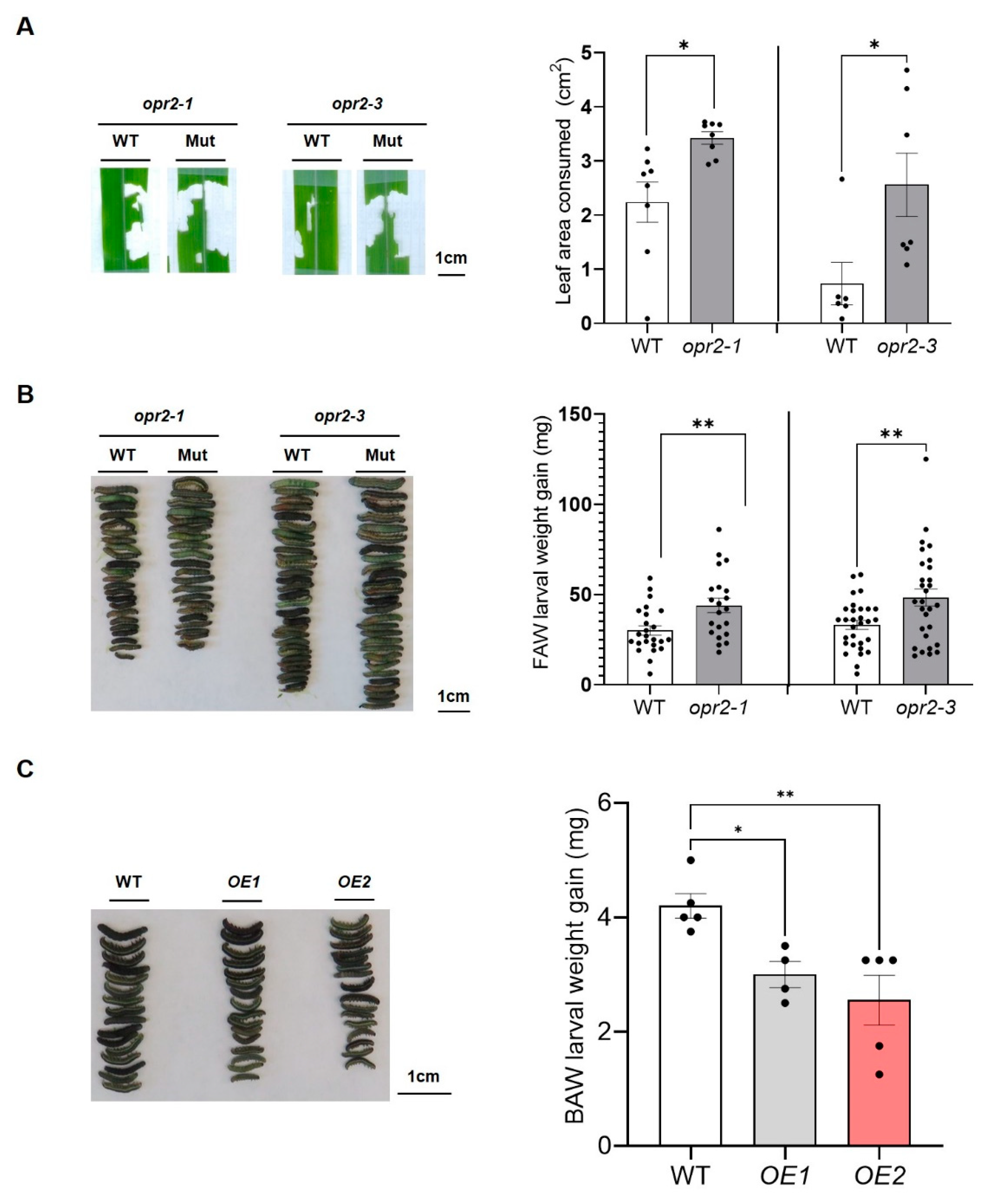
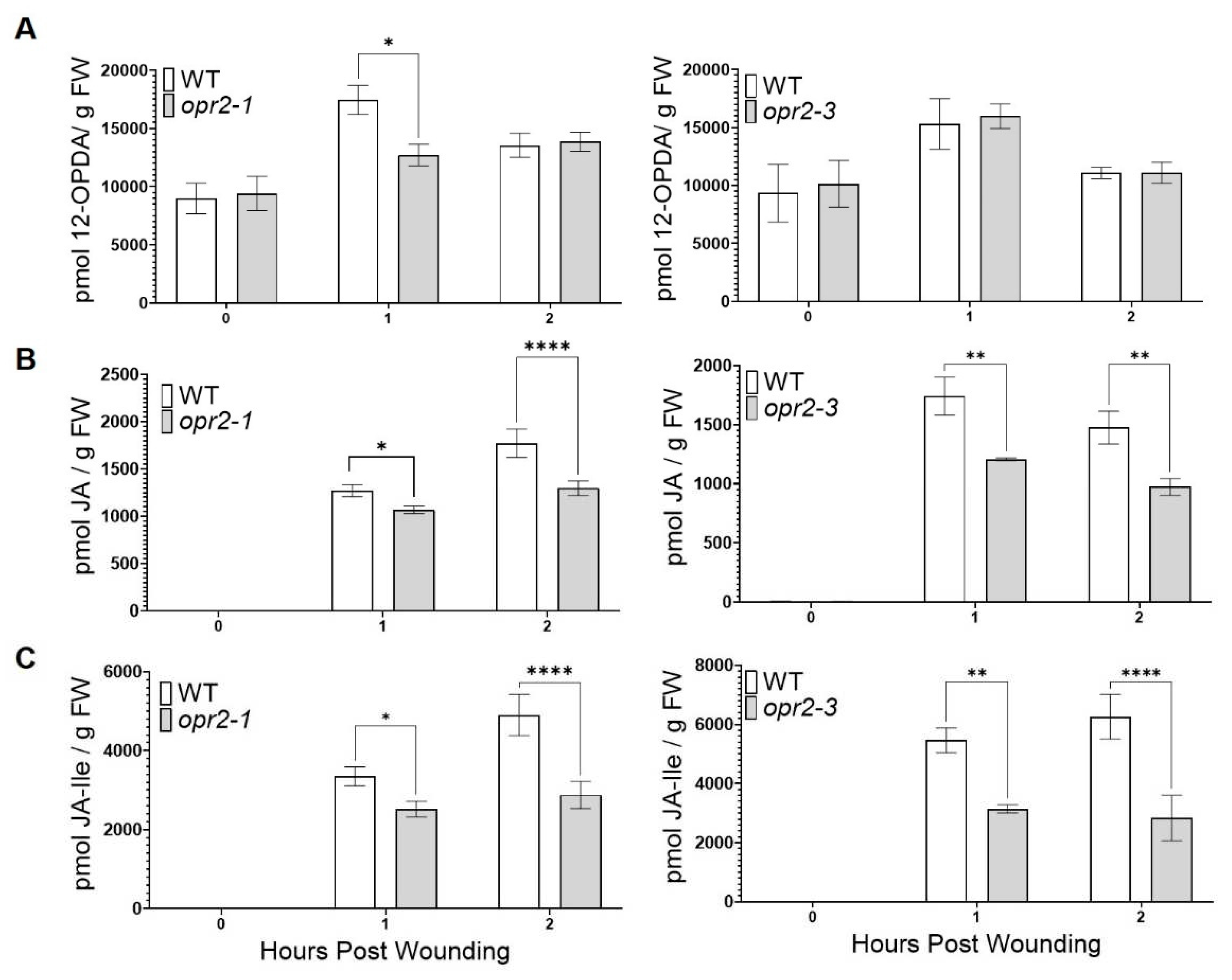
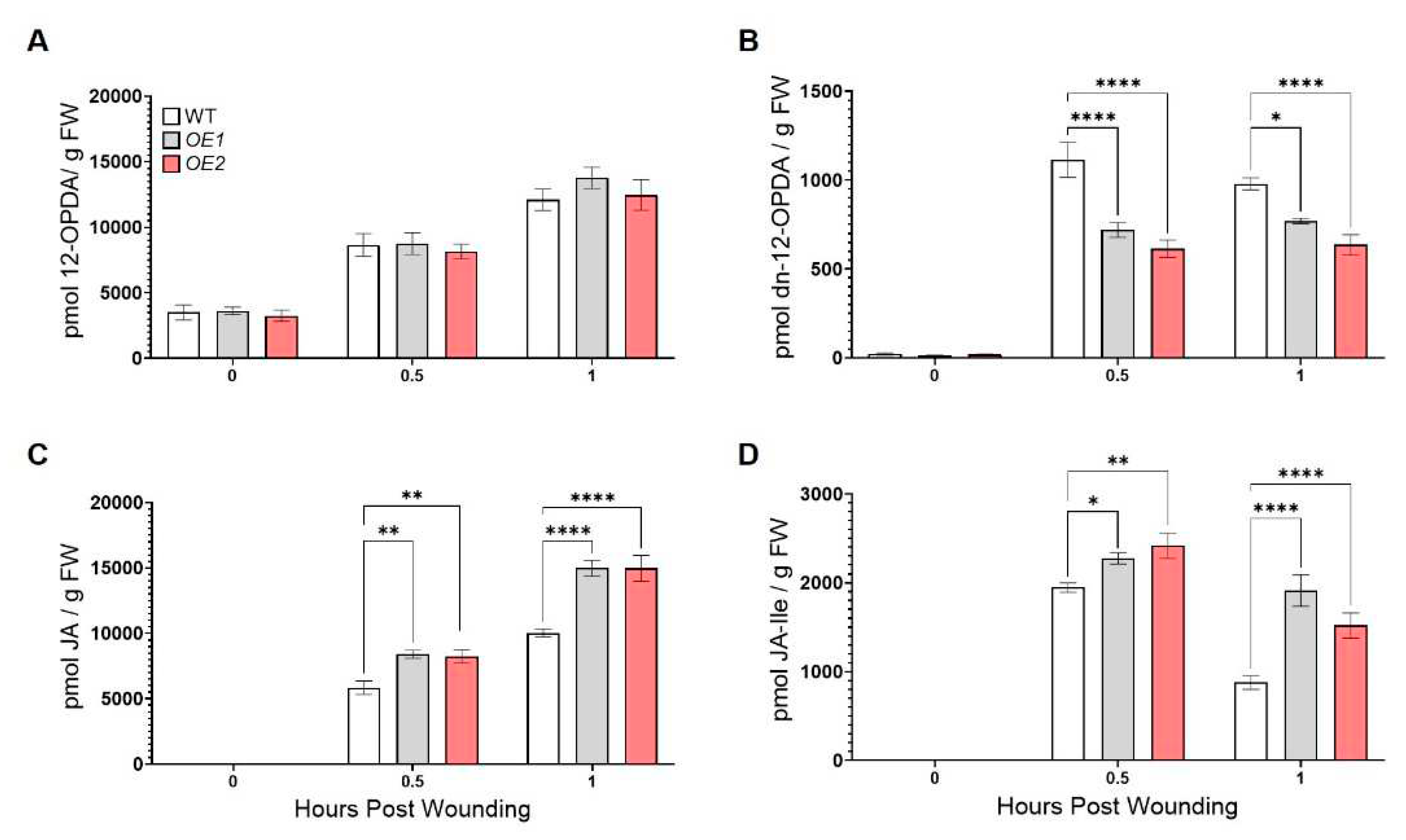
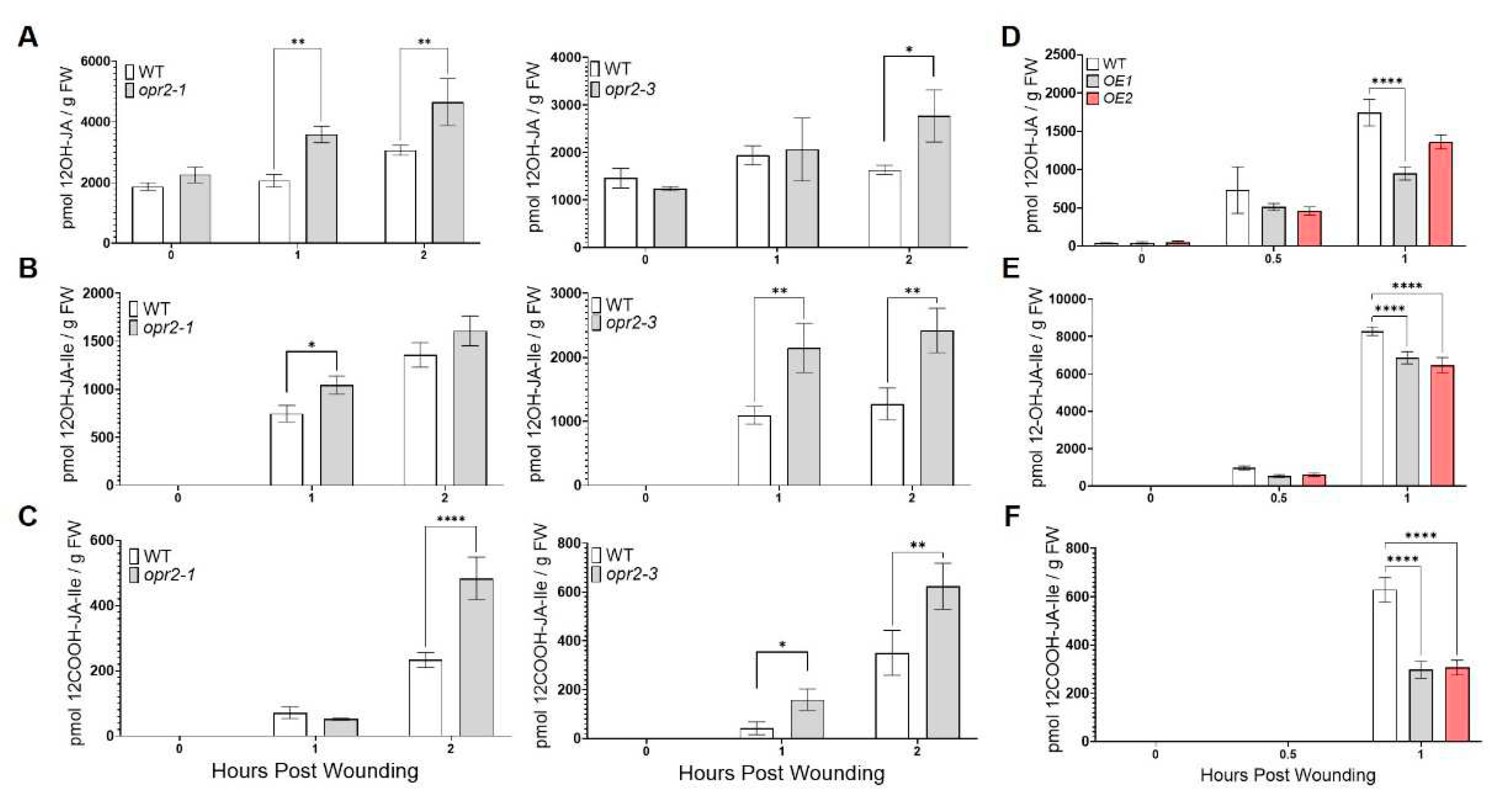
3.2. ZmOPR2 enhances wound-induced JA accumulation
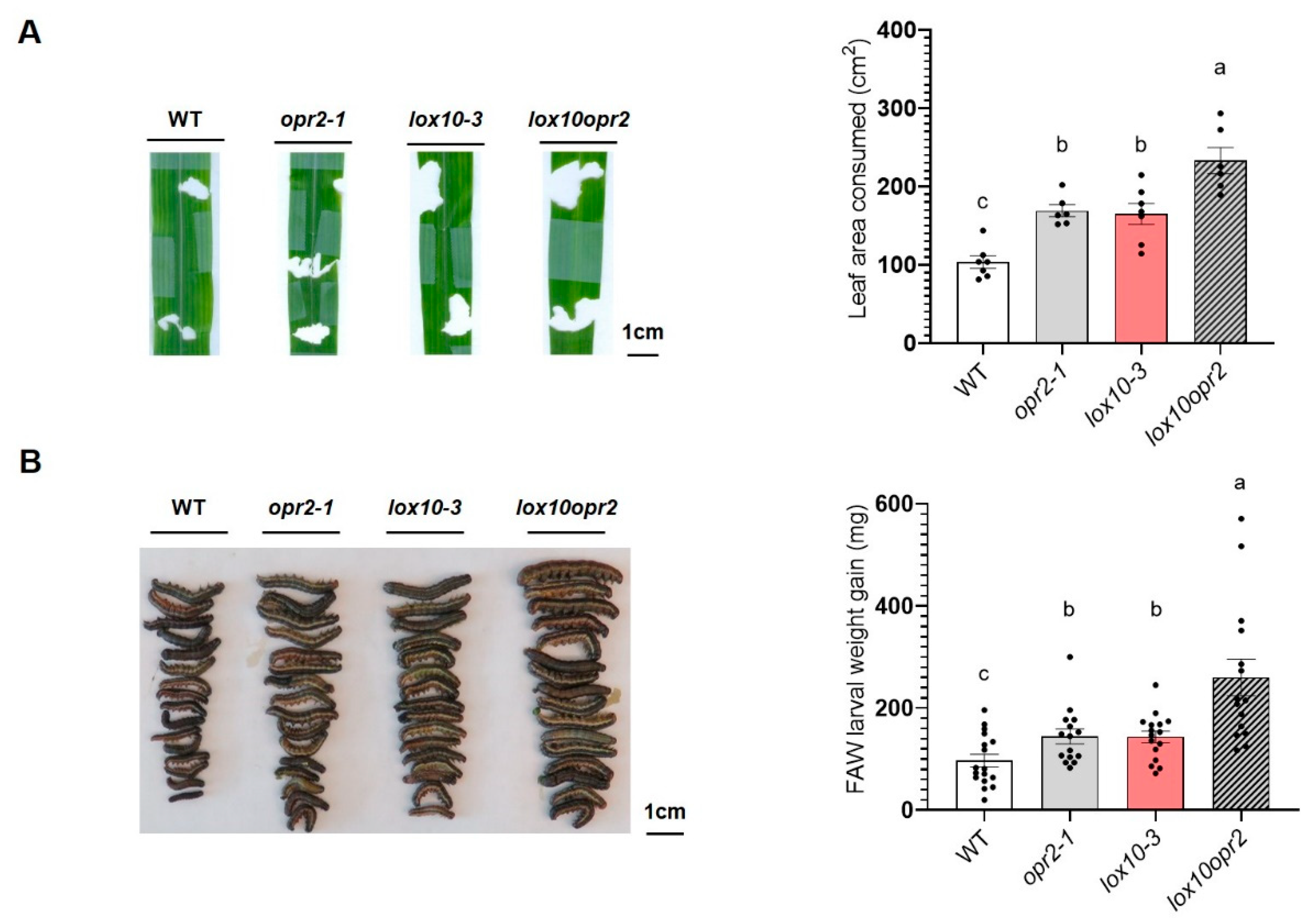
3.3. ZmOPR2 and ZmLOX10 have additive effect on defense against FAW
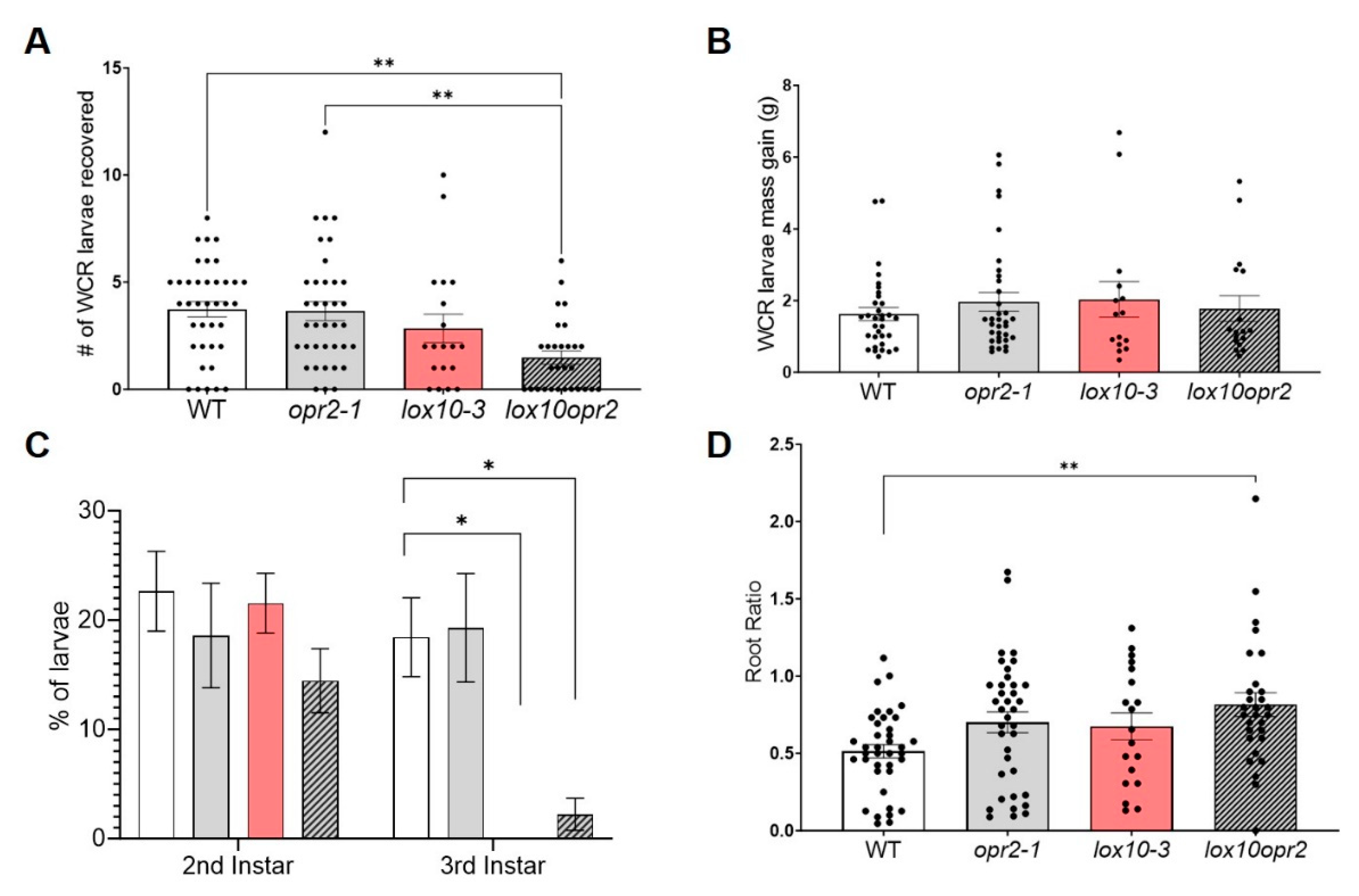
3.4. ZmOPR2 and ZmLOX10 negatively regulate production of insecticidal oxylipins during root herbivory by WCR
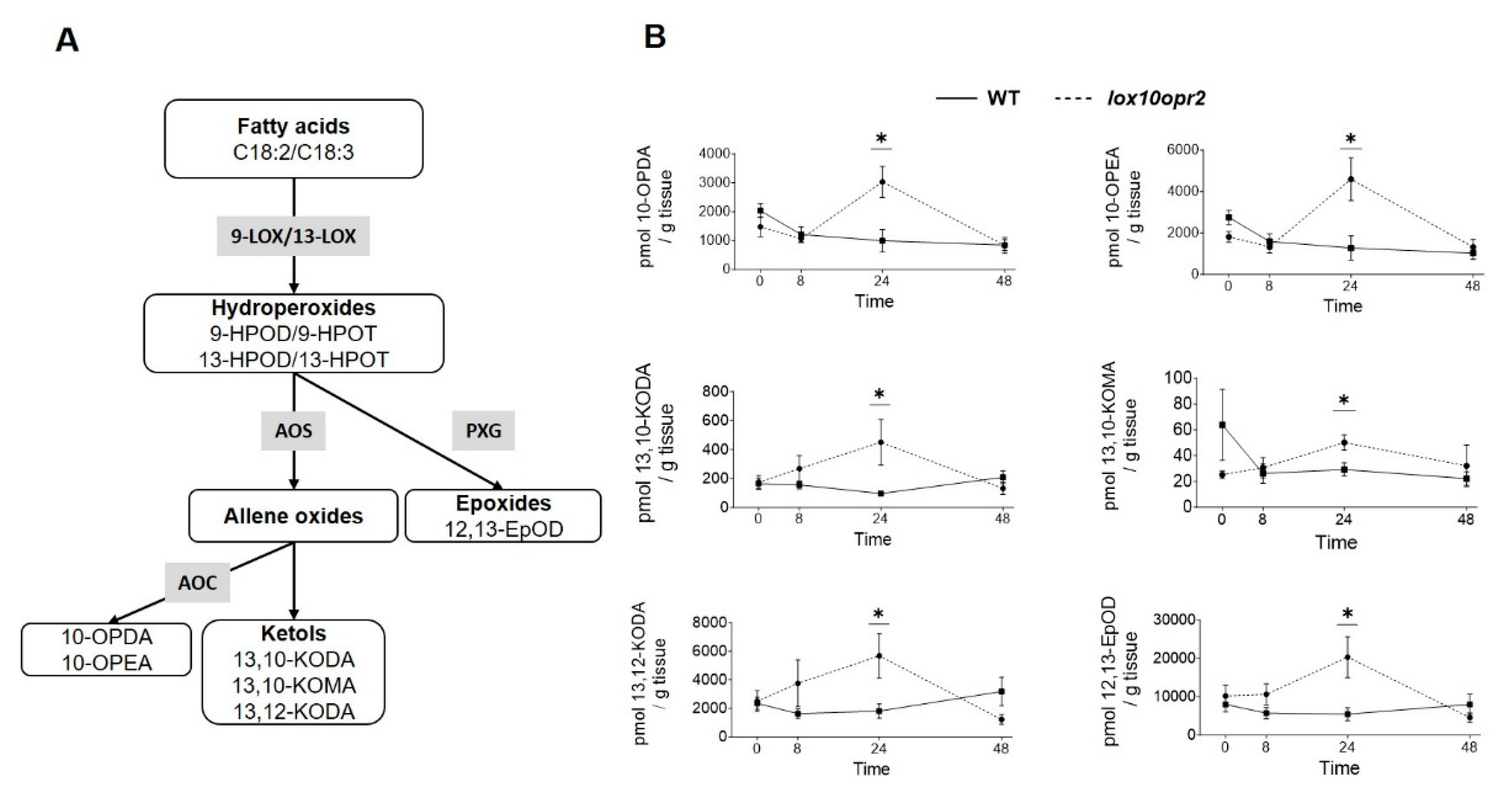
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- USDA, Crop production 2021 Summary. 2022.
- De La Fuente, G. N.; Barrero, I.; Murray, S. C.; Isakeit, T.; Kolomiets, M. V., Improving Maize Production under Drought Stress Traits, Screening Methods, and Environments. In Handbook of Plant and Crop Physiology, CRC Press: 2014.
- de Lange, E. S.; Balmer, D.; Mauch-Mani, B.; Turlings, T. C. J. , Insect and pathogen attack and resistance in maize and its wild ancestors, the teosintes. New Phytologist 2014, 204, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes-Puebla, A. A.; Borrego, E. J.; Kolomiets, M. V.; Bernal, J. S. , Maize biochemistry in response to root herbivory was mediated by domestication, spread, and breeding. Planta 2021, 254, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, A. F.; Bernal, J.; Venâncio, M. G. S.; de Souza, B. H. S.; Carvalho, G. A. , Comparative Tolerance Levels of Maize Landraces and a Hybrid to Natural Infestation of Fall Armyworm. Insects 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal, J. S.; Helms, A. M.; Fontes-Puebla, A. A.; DeWitt, T. J.; Kolomiets, M. V.; Grunseich, J. M. , Root volatile profiles and herbivore preference are mediated by maize domestication, geographic spread, and modern breeding. Planta 2022, 257, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warburton, M. L.; Woolfolk, S. W.; Smith, J. S.; Hawkins, L. K.; Castano-Duque, L.; Lebar, M. D.; Williams, W. P. , Genes and genetic mechanisms contributing to fall armyworm resistance in maize. The plant genome 2023, 16, e20311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenis, M. B., Giovanni; Biondi, Antonio; Calatayud, Paul-André; Day, Roger; Desneux, Nicolas; Harrison, Rhett D; Kriticos, Darren; Rwomushana, Ivan; van den Berg, Johnnie; Verheggen, François; Zhang, Yong-Jun; Agboyi, Lakpo Koku; Ahissou, Régis Besmer; Ba, Malick N; Wu, Kongming, Invasiveness, biology, ecology, and management of the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. Entomologia Generalis 2023, 43, 55.
- Montezano, D. G.; Specht, A.; Sosa-Gómez, D. R.; Roque-Specht, V. F.; Sousa-Silva, J. C.; Paula-Moraes, S. V.; Peterson, J. A.; Hunt, T. E. Host Plants of <i>Spodoptera frugiperda</i> (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in the Americas. African Entomology 2018, 26, 286–300. [Google Scholar]
- Overton, K.; Maino, J. L.; Day, R.; Umina, P. A.; Bett, B.; Carnovale, D.; Ekesi, S.; Meagher, R.; Reynolds, O. L. , Global crop impacts, yield losses and action thresholds for fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda): A review. Crop Protection 2021, 145, 105641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, R.; Abrahams, P.; Bateman, M.; Beale, T.; Clottey, V.; Cock, M.; Colmenarez, Y.; Corniani, N.; Early, R.; Godwin, J. , Fall armyworm: impacts and implications for Africa. Outlooks on Pest Management 2017, 28, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschen, R.; Beale, T.; Bonnin, J. M.; Constantine, K. L.; Duah, S.; Finch, E. A.; Makale, F.; Nunda, W.; Ogunmodede, A.; Pratt, C. F. , Towards estimating the economic cost of invasive alien species to African crop and livestock production. CABI Agriculture and Bioscience 2021, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Christensen, S.; Isakeit, T.; Engelberth, J.; Meeley, R.; Hayward, A.; Emery, R. J.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Disruption of OPR7 and OPR8 reveals the versatile functions of jasmonic acid in maize development and defense. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 1420–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S. A.; Nemchenko, A.; Borrego, E.; Murray, I.; Sobhy, I. S.; Bosak, L.; DeBlasio, S.; Erb, M.; Robert, C. A.; Vaughn, K. A.; Herrfurth, C.; Tumlinson, J.; Feussner, I.; Jackson, D.; Turlings, T. C.; Engelberth, J.; Nansen, C.; Meeley, R.; Kolomiets, M. V. , The maize lipoxygenase, ZmLOX10, mediates green leaf volatile, jasmonate and herbivore-induced plant volatile production for defense against insect attack. The Plant journal: for cell and molecular biology 2013, 74, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Luthe, D. , Key Genes in the JAZ Signaling Pathway Are Up-Regulated Faster and More Abundantly in Caterpillar-Resistant Maize. Journal of chemical ecology 2022, 48, 179–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, M. E.; Sappington, T. W.; Miller, N. J.; Moeser, J.; Bohn, M. O. , Adaptation and invasiveness of western corn rootworm: intensifying research on a worsening pest. Annual review of entomology 2009, 54, 303–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinke, L. J.; Sappington, T. W.; Onstad, D. W.; Guillemaud, T.; Miller, N. J.; Komáromi, J.; Levay, N.; Furlan, L.; Kiss, J.; Toth, F. , Western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte) population dynamics. Agricultural and Forest Entomology 2009, 11, 29–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombaert, E.; Ciosi, M.; Miller, N. J.; Sappington, T. W.; Blin, A.; Guillemaud, T. , Colonization history of the western corn rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera) in North America: insights from random forest ABC using microsatellite data. Biological Invasions 2018, 20, 665–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bažok, R.; Lemić, D.; Chiarini, F.; Furlan, L. , Western Corn Rootworm (Diabrotica virgifera virgifera LeConte) in Europe: Current Status and Sustainable Pest Management. Insects 2021, 12, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechsler, S.; Smith, D. , Has resistance taken root in US corn fields? Demand for insect control. American Journal of Agricultural Economics 2018, 100, 1136–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castano-Duque, L.; Loades, K. W.; Tooker, J. F.; Brown, K. M.; Paul Williams, W.; Luthe, D. S. , A Maize Inbred Exhibits Resistance Against Western Corn Rootwoorm, Diabrotica virgifera virgifera. Journal of chemical ecology 2017, 43, (11–12). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feussner, I.; Wasternack, C. , The lipoxygenase pathway. Annual review of plant biology 2002, 53, 275–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Feussner, I. , The Oxylipin Pathways: Biochemistry and Function. Annual review of plant biology 2018, 69, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego, E. J.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Synthesis and Functions of Jasmonates in Maize. Plants (Basel, Switzerland) 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G. A.; Jander, G. , Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Meldau, S.; Howe, G. A. , Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends in plant science 2012, 17, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, F.; Melotto, M.; Yao, J.; He, S. Y. , Jasmonate signaling and manipulation by pathogens and insects. J Exp Bot 2017, 68, 1371–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasternack, C.; Strnad, M. , Jasmonates: News on Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Action of an Ancient Group of Signaling Compounds. International journal of molecular sciences 2018, 19, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suza, W. P.; Staswick, P. E. , The role of JAR1 in Jasmonoyl-L: -isoleucine production during Arabidopsis wound response. Planta 2008, 227, 1221–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg-Falloure, K. M.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Ketols Emerge as Potent Oxylipin Signals Regulating Diverse Physiological Processes in Plants. Plants (Basel, Switzerland) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Borrego, E.; Park, Y. S.; Gorman, Z.; Huang, P. C.; Tolley, J.; Christensen, S. A.; Blanford, J.; Kilaru, A.; Meeley, R.; Koiwa, H.; Vidal, S.; Huffaker, A.; Schmelz, E.; Kolomiets, M. V. , 9,10-KODA, an α-ketol produced by the tonoplast-localized 9-lipoxygenase ZmLOX5, plays a signaling role in maize defense against insect herbivory. Molecular plant 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Osmani, A. A.; Ahmadi, S. H.; Ogawa, S.; Takagi, K.; Yokoyama, M.; Ban, T. , KODA, an α-ketol derivative of linolenic acid provides wide recovery ability of wheat against various abiotic stresses. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2016, 7, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Saito, T.; Ohkawa, K.; Ohara, H.; Shishido, M.; Ikeura, H.; Takagi, K.; Ogawa, S.; Yokoyama, M.; Kondo, S. , α-Ketol linolenic acid (KODA) application affects endogenous abscisic acid, jasmonic acid and aromatic volatiles in grapes infected by a pathogen (Glomerella cingulata). Journal of plant physiology 2016, 192, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K. D.; Borrego, E. J.; Kenerley, C. M.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Oxylipins Other Than Jasmonic Acid Are Xylem-Resident Signals Regulating Systemic Resistance Induced by Trichoderma virens in Maize. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 166–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K. D.; Gorman, Z.; Huang, P. C.; Kenerley, C. M.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Trichoderma virens colonization of maize roots triggers rapid accumulation of 12-oxophytodienoate and two ᵧ-ketols in leaves as priming agents of induced systemic resistance. Plant signaling & behavior 2020, 15, 1792187. [Google Scholar]
- Schaller, F.; Hennig, P.; Weiler, E. W. , 12-Oxophytodienoate-10,11-reductase: occurrence of two isoenzymes of different specificity against stereoisomers of 12-oxophytodienoic acid. Plant physiology 1998, 118, 1345–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Simmons, C.; Yalpani, N.; Crane, V.; Wilkinson, H.; Kolomiets, M. , Genomic analysis of the 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid reductase gene family of Zea mays. Plant Mol Biol 2005, 59, 323–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaller, F.; Biesgen, C.; Müssig, C.; Altmann, T.; Weiler, E. W. , 12-Oxophytodienoate reductase 3 (OPR3) is the isoenzyme involved in jasmonate biosynthesis. Planta 2000, 210, 979–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strassner, J.; Fürholz, A.; Macheroux, P.; Amrhein, N.; Schaller, A. , A homolog of old yellow enzyme in tomato. Spectral properties and substrate specificity of the recombinant protein. The Journal of biological chemistry 1999, 274, 35067–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehab, E. W.; Kim, S.; Savchenko, T.; Kliebenstein, D.; Dehesh, K.; Braam, J. , Intronic T-DNA Insertion Renders Arabidopsis opr3 a Conditional Jasmonic Acid-Producing Mutant. Plant physiology 2011, 156, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolley, J. P.; Nagashima, Y.; Gorman, Z.; Kolomiets, M. V.; Koiwa, H. , Isoform-specific subcellular localization of Zea mays lipoxygenases and oxo-phytodienoate reductase 2. Plant Gene 2018, 13, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P. C.; Tate, M.; Berg-Falloure, K. M.; Christensen, S. A.; Zhang, J.; Schirawski, J.; Meeley, R.; Kolomiets, M. V. , A non-JA producing oxophytodienoate reductase functions in salicylic acid-mediated antagonism with jasmonic acid during pathogen attack. Molecular plant pathology 2023, 24, 725–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Strnad, M. , Jasmonates: News on Occurrence, Biosynthesis, Metabolism and Action of an Ancient Group of Signaling Compounds. International journal of molecular sciences 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Borrego, E. J.; Gorman, Z.; Huang, P. C.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Relative contribution of LOX10, green leaf volatiles and JA to wound-induced local and systemic oxylipin and hormone signature in Zea mays (maize). Phytochemistry 2020, 174, 112334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McConn, M.; Creelman, R. A.; Bell, E.; Mullet, J. E.; Browse, J. , Jasmonate is essential for insect defense in Arabidopsis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1997, 94, 5473–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, S. A.; Huffaker, A.; Kaplan, F.; Sims, J.; Ziemann, S.; Doehlemann, G.; Ji, L.; Schmitz, R. J.; Kolomiets, M. V.; Alborn, H. T.; Mori, N.; Jander, G.; Ni, X.; Sartor, R. C.; Byers, S.; Abdo, Z.; Schmelz, E. A. , Maize death acids, 9-lipoxygenase–derived cyclopente(a)nones, display activity as cytotoxic phytoalexins and transcriptional mediators. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2015, 112, 11407–11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhage, A.; Vlaardingerbroek, I.; Raaijmakers, C.; Van Dam, N.; Dicke, M.; Van Wees, S.; Pieterse, C. , Rewiring of the Jasmonate Signaling Pathway in Arabidopsis during Insect Herbivory. Frontiers in plant science 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, M. L.; Kang, J. H.; Howe, G. A. , Jasmonate-triggered plant immunity. Journal of chemical ecology 2014, 40, 657–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelberth, J.; Seidl-Adams, I.; Schultz, J. C.; Tumlinson, J. H. , Insect elicitors and exposure to green leafy volatiles differentially upregulate major octadecanoids and transcripts of 12-oxo phytodienoic acid reductases in Zea mays. Molecular plant-microbe interactions: MPMI 2007, 20, 707–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzin, V.; Hojo, Y.; Strickler, S. R.; Bartsch, L. J.; Archer, C. M.; Ahern, K. R.; Zhou, S.; Christensen, S. A.; Galis, I.; Mueller, L. A.; Jander, G. , Rapid defense responses in maize leaves induced by Spodoptera exigua caterpillar feeding. Journal of Experimental Botany 2017, 68, 4709–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, S. A.; Nemchenko, A.; Park, Y. S.; Borrego, E.; Huang, P. C.; Schmelz, E. A.; Kunze, S.; Feussner, I.; Yalpani, N.; Meeley, R.; Kolomiets, M. V. , The novel monocot-specific 9-lipoxygenase ZmLOX12 is required to mount an effective jasmonate-mediated defense against Fusarium verticillioides in maize. Molecular plant-microbe interactions: MPMI 2014, 27, 1263–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzi, A.; Browse, J. , The Arabidopsis male-sterile mutant, opr3, lacks the 12-oxophytodienoic acid reductase required for jasmonate synthesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 2000, 97, 10625–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, P. M.; Lee, P. Y.; Biesgen, C.; Boone, J. D.; Beals, T. P.; Weiler, E. W.; Goldberg, R. B. , The arabidopsis DELAYED DEHISCENCE1 gene encodes an enzyme in the jasmonic acid synthesis pathway. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 1041–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chini, A.; Monte, I.; Zamarreno, A. M.; Hamberg, M.; Lassueur, S.; Reymond, P.; Weiss, S.; Stintzi, A.; Schaller, A.; Porzel, A.; Garcia-Mina, J. M.; Solano, R. , An OPR3-independent pathway uses 4,5-didehydrojasmonate for jasmonate synthesis. Nat Chem Biol 2018, 14, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabay, G.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.; Moriconi, J. I.; Burguener, G. F.; Gualano, L. D.; Howell, T.; Lukaszewski, A.; Staskawicz, B.; Cho, M.-J.; Tanaka, J.; Fahima, T.; Ke, H.; Dehesh, K.; Zhang, G.-L.; Gou, J.-Y.; Hamberg, M.; Santa-María, G. E.; Dubcovsky, J. , Dosage differences in 12-OXOPHYTODIENOATE REDUCTASE genes modulate wheat root growth. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, Z.; Christensen, S. A.; Yan, Y.; He, Y.; Borrego, E.; Kolomiets, M. V. , Green leaf volatiles and jasmonic acid enhance susceptibility to anthracnose diseases caused by Colletotrichum graminicola in maize. Molecular plant pathology 2020, 21, 702–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohli, R. M.; Massey, V. , The oxidative half-reaction of Old Yellow Enzyme. The role of tyrosine 196. The Journal of biological chemistry 1998, 273, 32763–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Bustos-Segura, C.; Degen, T.; Erb, M.; Turlings, T. C. J. , Belowground and aboveground herbivory differentially affect the transcriptome in roots and shoots of maize. Plant Direct 2022, 6, e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erb, M.; Flors, V.; Karlen, D.; De Lange, E.; Planchamp, C.; D’Alessandro, M.; Turlings, T. C. J.; Ton, J. , Signal signature of aboveground-induced resistance upon belowground herbivory in maize. The Plant Journal 2009, 59, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingault, L.; Basu, S.; Vellichirammal, N. N.; Williams, W. P.; Sarath, G.; Louis, J. , Co-Transcriptomic Analysis of the Maize-Western Corn Rootworm Interaction. Plants 2022, 11, 2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




