1. Introduction
The source of a tectonic earthquake occurs as a result of the complete or partial relaxation of stress accumulated by the Earth’s material during tectonic deformation. At this time, there is a local loss of stability of the medium, its continuity is violated [
1]. As a result, the accumulated elastic strain energy transforms into inelastic one. In the framework of the theory of elasticity and viscoelasticity, the earthquake source is considered as a dislocation, i.e. displacement along a certain fault surface [
2]. In addition to the geometry of this surface, the earthquake source is characterized by orientation and position in space, as well as by the field of the slip vector along the rupture surface. When describing the source, the following assumptions are most often used: the surface geometry is simplified to a flat rectangular area [
3,
4,
5], and the displacement vector is assumed to be constant [
6,
7]. Such simplifications make it possible to obtain analytical solutions to the problem of determining the displacement field of the Earth’s crust at the time of an earthquake [
8].
The Earth’s crust consists of separate layers of rocks. They have various mechanical properties. Direct consideration of these properties when constructing models of mechanical processes occurring in rocks is difficult. It is possible to indirectly take into account the mechanical properties of rocks by introducing stochastic components. Thus, the problem of the probabilistic characteristics of the displacement vector in the earthquake source was previously investigated [
9]. It was shown that the probability distribution of the normalized displacement value has a stability. It is similar to the exponential one, but has a heavy tail. In addition, a compact description of the distribution was proposed using the lognormal law with a negative shift of the density function and winsorization at zero. The described approach, as well as similar ones, were used in modeling displacements of the Earth’s surface to calculate the strength of engineering structures [
10,
11,
12]. Also the effect of adding a slip deficit to the stochastic fault model on the slip distribution in the subduction zone was considered [
13]. An overview of the methods for adding stochastic components into the earthquake source model is presented in Gusev’s paper [
14].
The geometric shape of the fault surface is one of the main characteristics of the earthquake source. Usually, when modeling a source, the fault surface is considered as a plane bounded by a rectangular region or as a composition of such regions [
15,
16,
17]. In this paper, we propose a modified dislocation model of an earthquake source in the form of displacement along a stochastic surface.
The structure of the main part of the paper is as follows.
Section 2 is devoted to the mathematical formulation of the problem of the stress-strain state of the Earth’s crust in the elastic half-space approximation based on the Navier equations. Earthquake source modeling based on systems of equivalent forces is carried out. Solutions are derived for determining the deformations of an elastic half-space under the action of a dislocation along an arbitrary smooth surface. A method for constructing a stochastic displacement surface in an earthquake source is described.
Section 3 contains the results of numerical modeling of the Earth’s crust deformations. The main findings and conclusion are contained in
Section 4.
2. Mathematical formulation
2.1. Stress-strain state of the Earth’s crust
We make a number of standard assumptions when modeling [
18]. We will take into account only the elastic properties of the medium, we will simplify the geometry of the Earth’s crust to a half-space, and we will assume that the medium is homogeneous and isotropic. To describe such a model in a Cartesian coordinate system
let’s use the Navier equations [
19] :
where
are displacement vector components,
are body forces,
are Lame coefficients.
The boundary conditions of the problem (
1) are defined on the surface
and consist in the equality of the following components of the stress tensor to zero:
According to modern concepts, tectonic earthquake source occurs as a result of sliding along the inner surface – the fault plane [
1]. Mathematically, earthquake sources are described by a body force within the excitation area, a displacement jump on the fault surface, or deformation. Note that the displacement along the fault excites the same seismic waves as some system of forces distributed over the fault with zero total moment. In general, the distribution of forces can have a different form, but in the case of an isotropic medium, it can always be chosen as the surface distribution of double pairs of forces. The classical force equivalent of displacement along a fault is the distribution of double pairs of forces.
2.2. Point source. Mindlin solutions
Mindlin [
20,
21] was engaged in solving the problem of determining the displacement field under the action of body forces located inside an elastic half-space and applied to one point. In his works, he solved this problem for differently directed single and double forces, including double forces with moments. Mindlin expressed his solutions in terms of combinations of strain nuclei for elastic space proposed by Kelvin. Mindlin solutions can also be called strain nuclei for an elastic half-space by analogy with the Kelvin solutions. Solutions of the differential equations system (
1) with boundary conditions (
2) can be expressed through these nuclei. Mindlin expressed the solutions in terms of the Galerkin vector. In the present work, equivalent solutions are constructed in the form of displacement vector components.
We take a Cartesian coordinate system. Let
be the
i-th component of the displacement vector at the point
, corresponding to the single force of magnitude
F at the point
in the direction
j. According to Mindlin’s works
can be represented as follows:
where
,
is Kronecker delta,
,
,
,
.
To obtain solutions in the form of strain nuclei, we will take the corresponding partial
derivatives of
:
2.3. Distributed source
Using the Volterra dislocation principle, Steketee showed [
2] that the displacement field caused by movement along the fault plane
in an elastic half-space can be found through a surface integral of the following form:
where
is a dislocation in the
j – th direction across the fault surface
,
are the direction cosines of the normal to the surface element
,
is the
i-th component of the displacement vector at the point
, corresponding to the single force in
j direction with magnitude
F at the point
. If
, then
are strain nuclei corresponding to a double forces without moment (
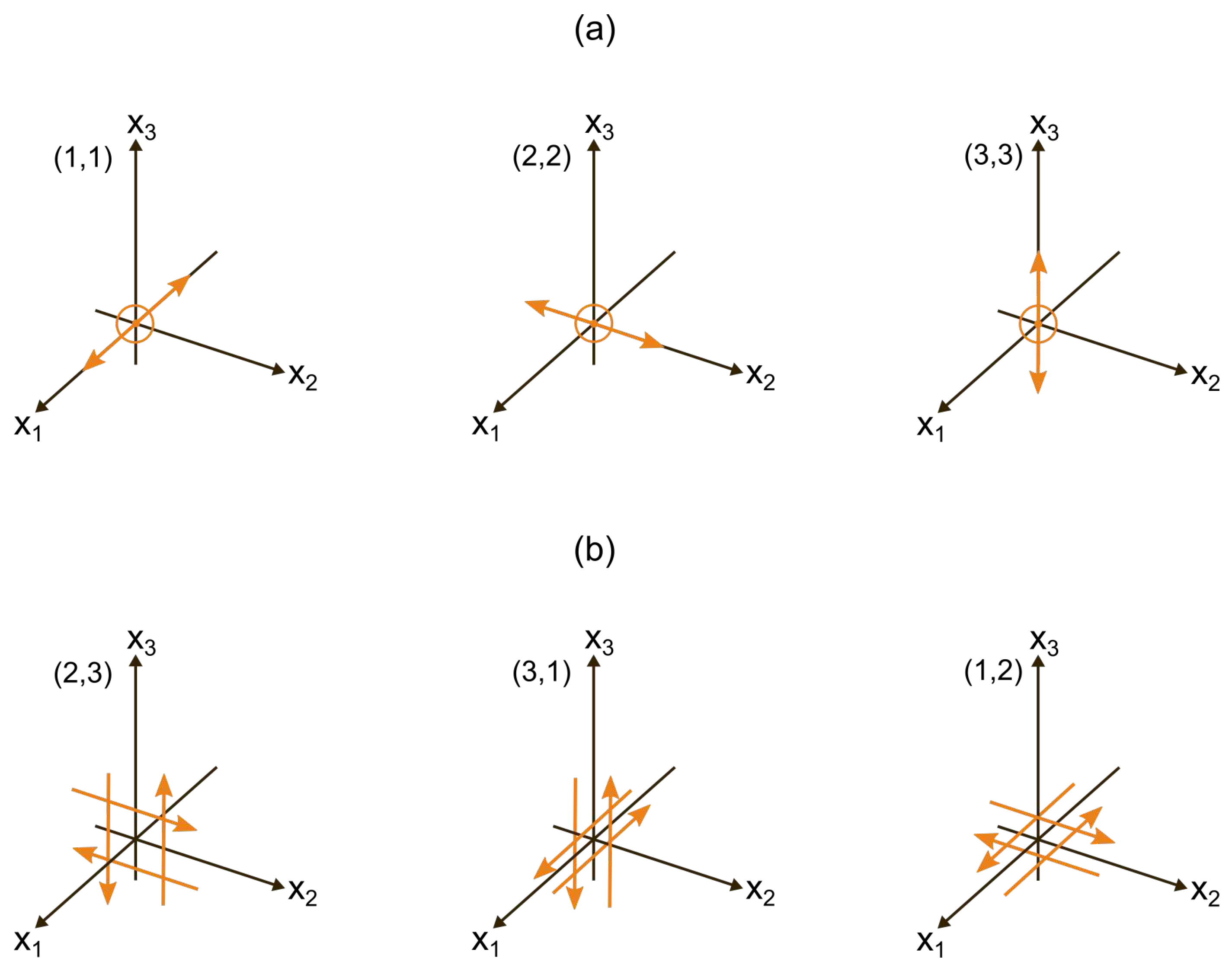
Figure 1a), and
is the strain nuclei combination corresponding to the dilation center. If
, then
are strain nuclei corresponding to two perpendicular pairs of double forces with moments (
Figure 1b).
Figure 1 shows the systems of forces corresponding to strain nuclei combinations
.
In this paper, we will consider earthquake source of strike-slip type . The strain nuclei combination for such an earthquake source is as follows:
Let the fault surface
be explicitly given by the equation
. In this case, the unit normal
at each point
of the surface can be found as follows:
We denote the integrand (
8) by
:
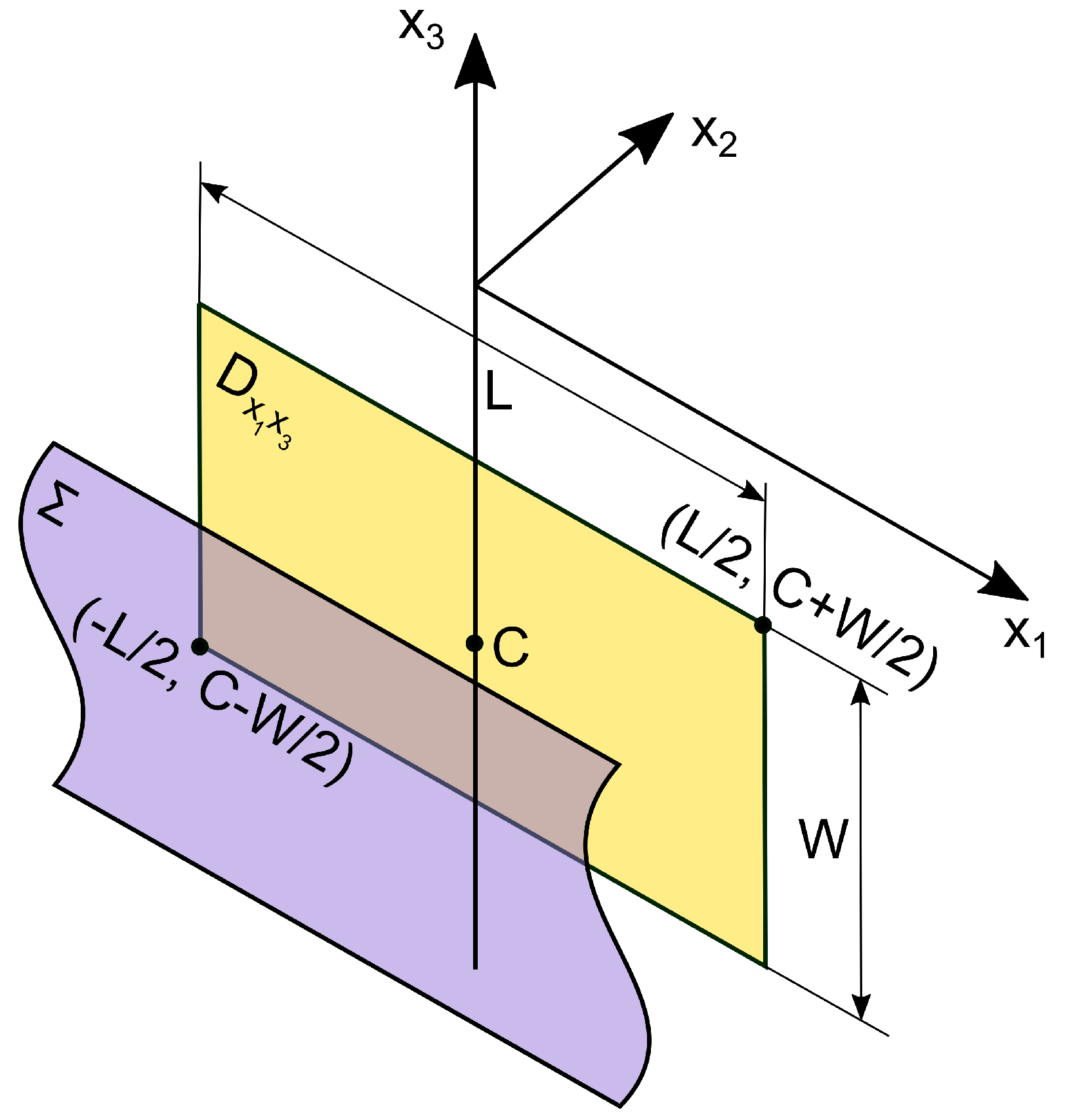
We place the fault surface at the depth . The projection of this surface onto the plane is a rectangular area.
Let us perform parametrization and move from surface integral to double, and then to iterated one:
This expression (
11) allows us to calculate the components of the displacement field vector. The field arises as a result of displacement along the fault surface inside the elastic half-space in the strike direction.
2.4. Dislocation with a constant displacement vector along a finite rectangular surface
We represent the displacement surface as a plane bounded by a rectangular region with dip angle . In this case, the unit normal is . The displacement vector is assumed to be constant. Its components in the case of displacement along strike are equal to , and in the case of displacement along dip: .
In this case, the integral (
8) will take the form:
Given that the surface
is defined by the relation:
, the surface integral will look like this:
2.5. Stochastic geometry of the fault surface
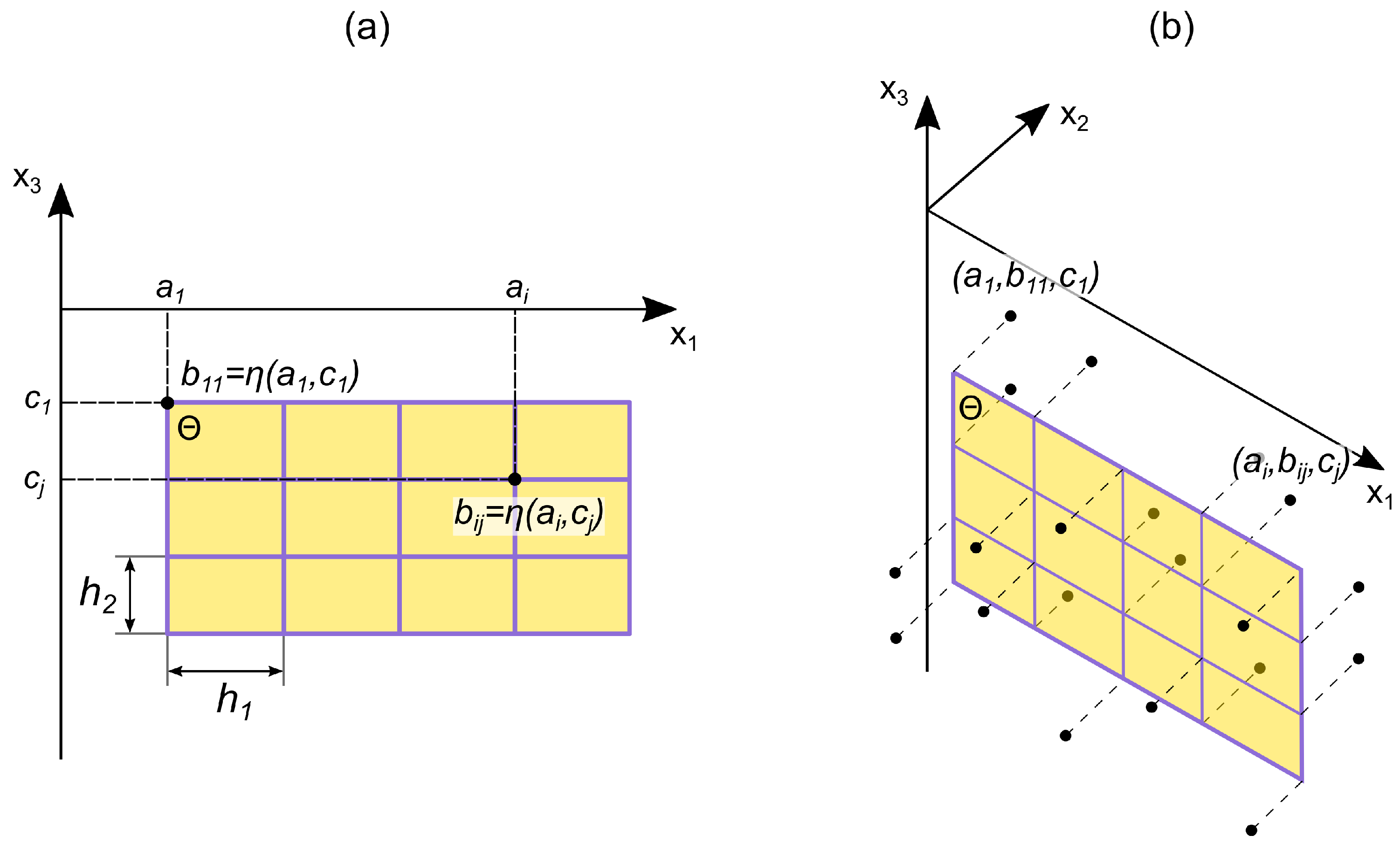
To obtain a stochastic fault surface , we propose to introduce a random deformation of a rectangular flat surface . For this:
We build a two-dimensional grid on the plane
with horizontal and vertical steps
and
respectively (
Figure 3a).
We define a random function
. For simplicity, we assume that
is characterized by a single distribution function for all values of the arguments
. The function
at each grid node (
) determines the value
. These values are the stochastic deformation component of the original plane
(
Figure 3b).
The resulting fault surface
will be determined by the two-dimensional Lagrange interpolation polynomial
constructed from the points
as follows:
where
and
are functions defined in terms of polynomials
and
:
Solutions for displacement on such a surface
in the strike direction can be obtained using the integral (
11), setting the function
. The internal strain and stress fields can be evaluated using the following relations:
Shear stresses [
22,
23,
24] make the greatest contribution to the destruction of rocks. Therefore, to assess the deformations of the Earth’s crust, we use the criterion of maximum shear stresses:
where
are the principle stresses.
We calculate the deformations corresponding to
:
where
is Poisson’s ratio,
E is Young’s modulus.
3. Numerical results
Solving the integral (
11) for an arbitrary smooth surface in an analytical form is difficult. Therefore, in the course of numerical calculations, the Clenshaw-Curtis quadrature method [
25] was used.
3.1. Computational experiment No. 1
The fault surface was located at a depth of
m, its linear dimensions were
m,
m, the displacement value
was assumed to be constant and equal to
m. A grid of size
was set on the fault surface. The random variable in the grid nodes was normally distributed with the parameters
m,
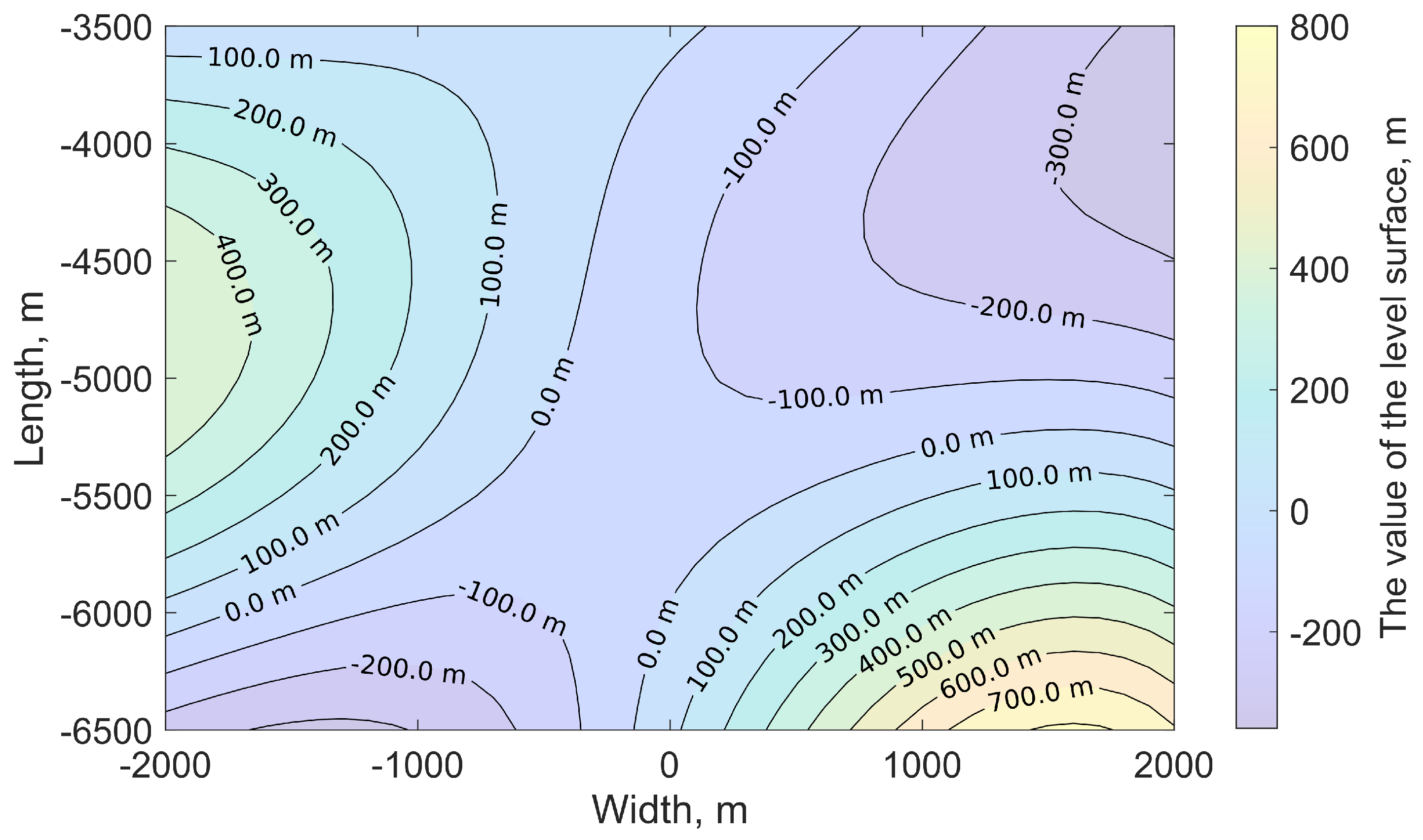
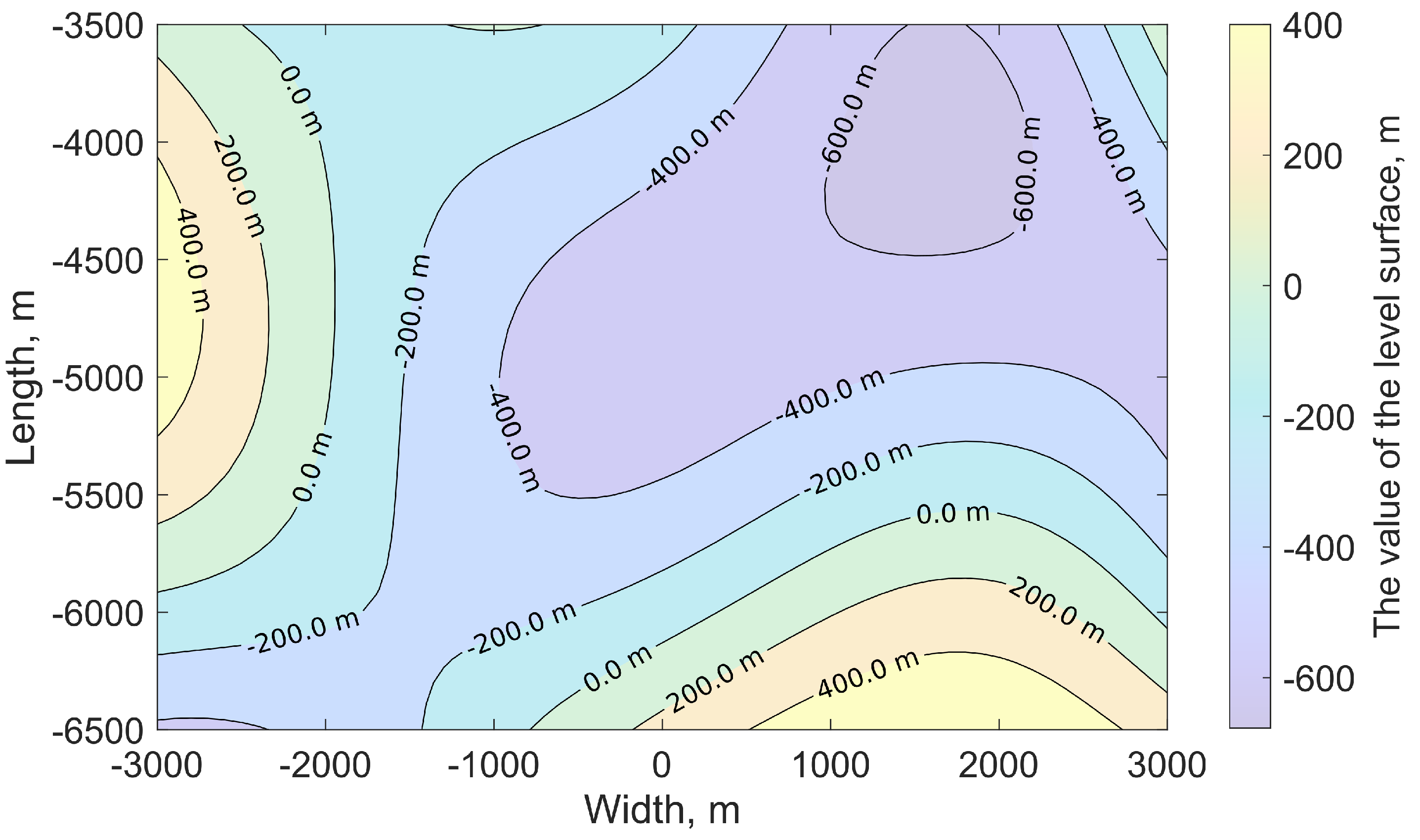
m. The isolines of the stochastic fault surface are shown in
Figure 4.
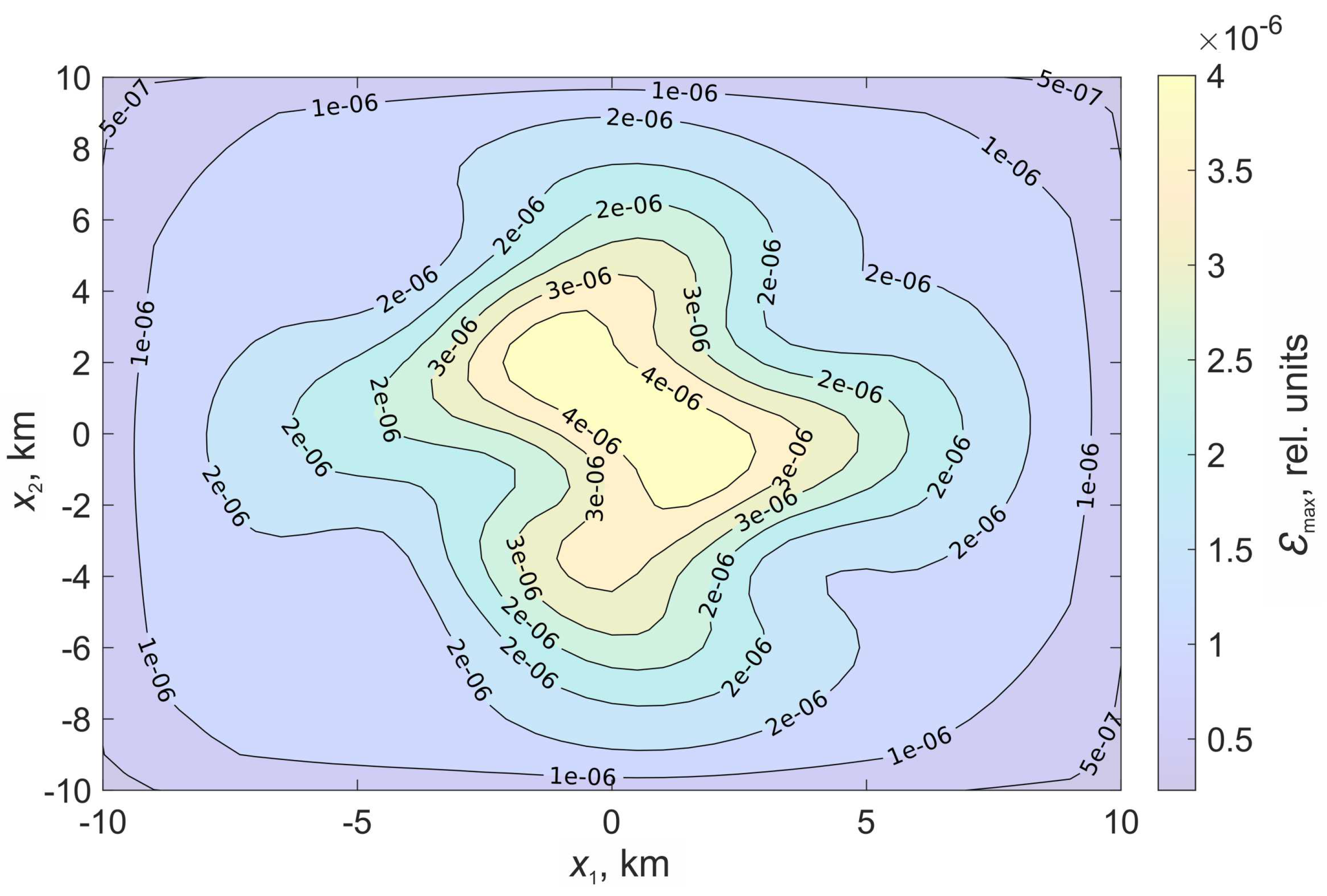
Figure 5 shows the relative deformations
on the surface
, which are formed under the action of displacement along the stochastic surface.
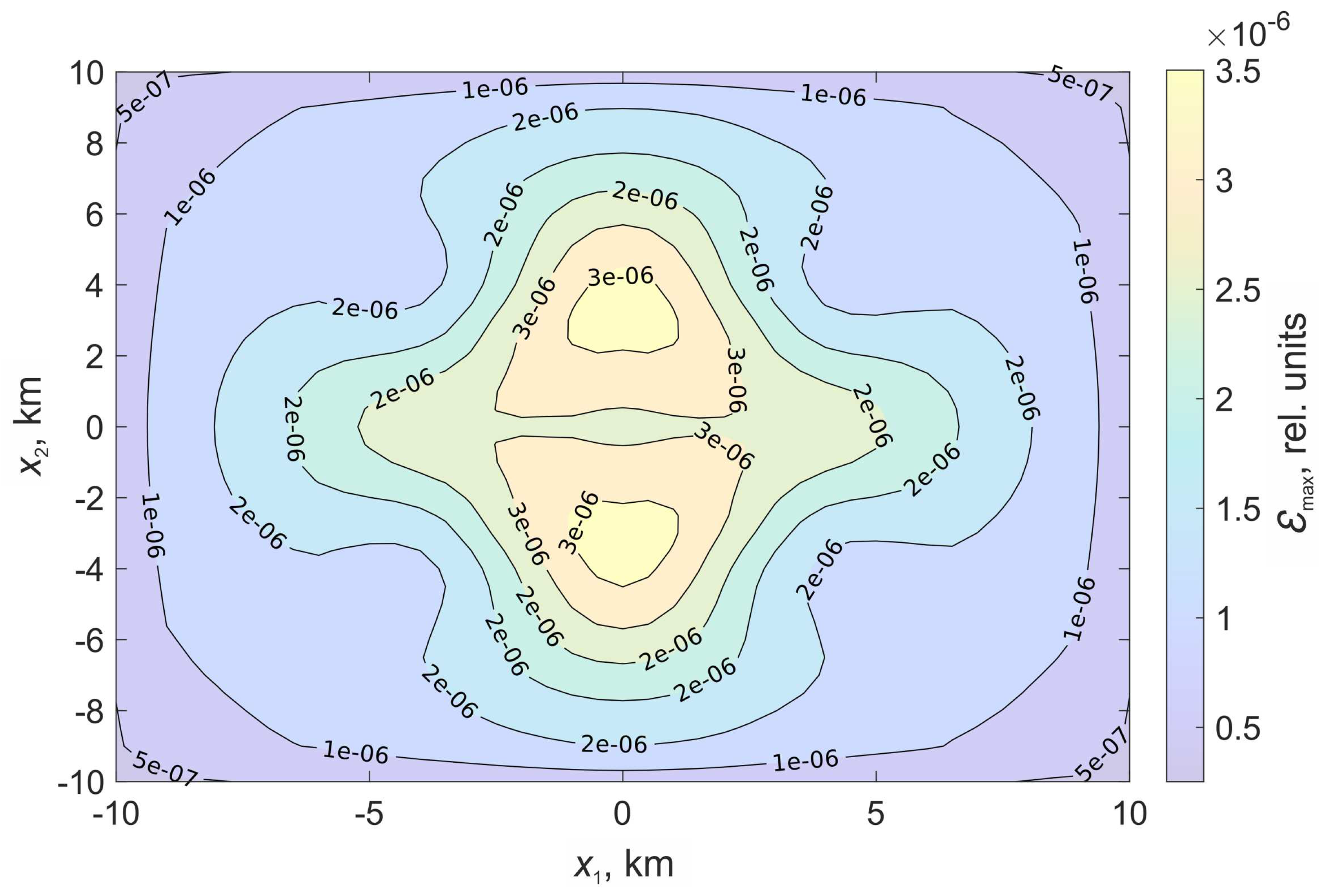
Figure 6 shows the relative deformations, which are formed under the action of displacement along the rectangular part of the plane.
In the case of a stochastic surface, the regions of relative deformations acquire a pronounced asymmetry. There is an increase in the deformation level in the center.
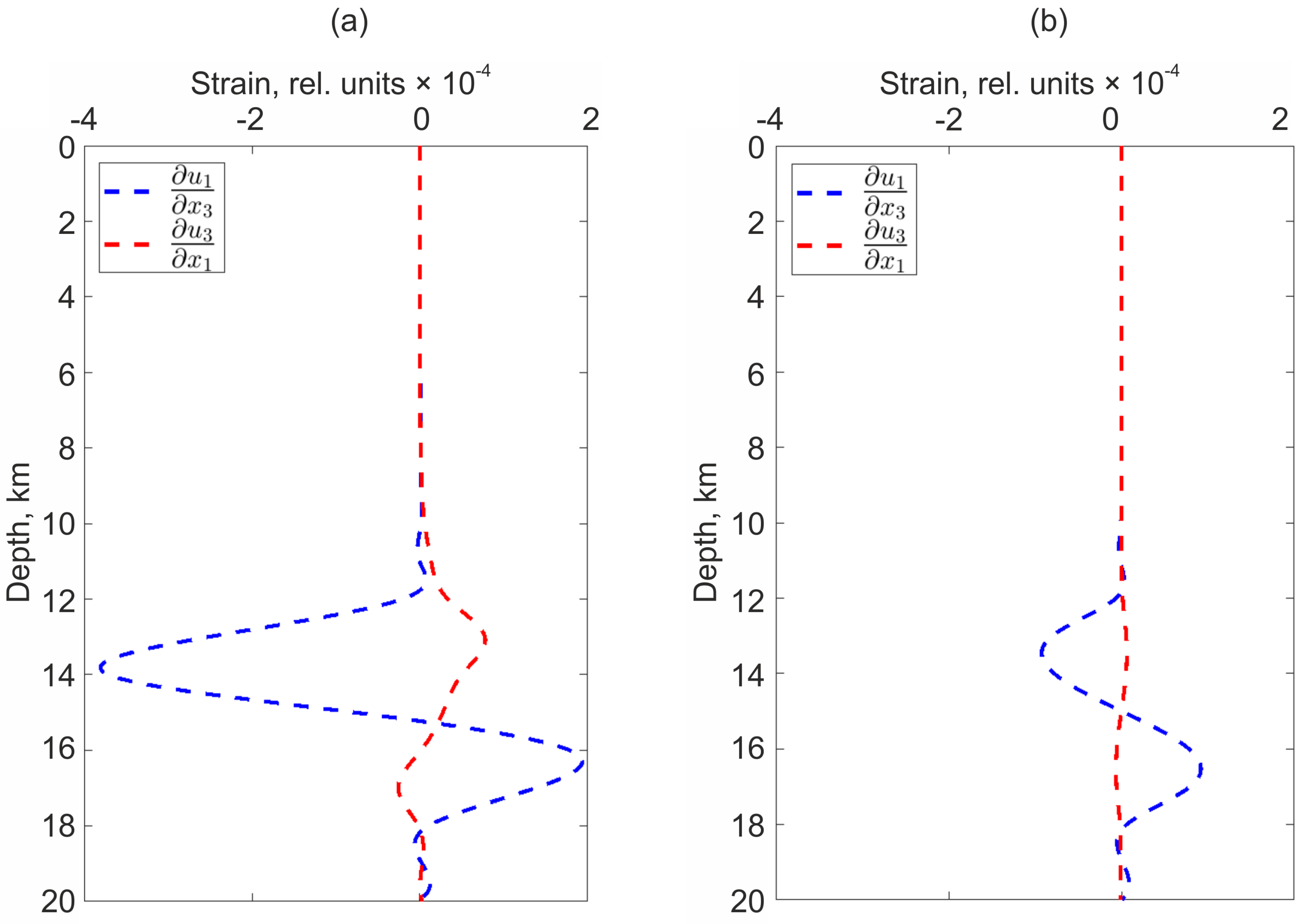
In addition, there are pronounced changes in the derivatives variations of the displacement field with a change in depth. For example,
Figure 7 shows variations at depths up to 20 km (
m,
m,
varies from 0 to - 20000 m).
3.2. Computational experiment No. 2
The fault surface was at a depth of
m, its linear dimensions were
m,
m, the displacement
was assumed to be constant and equal to
. A grid of size
was set on the fault surface. The random variable in the grid nodes is normally distributed with the parameters
m,
m. The isolines of the stochastic discontinuity surface are shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 9 shows the relative deformations
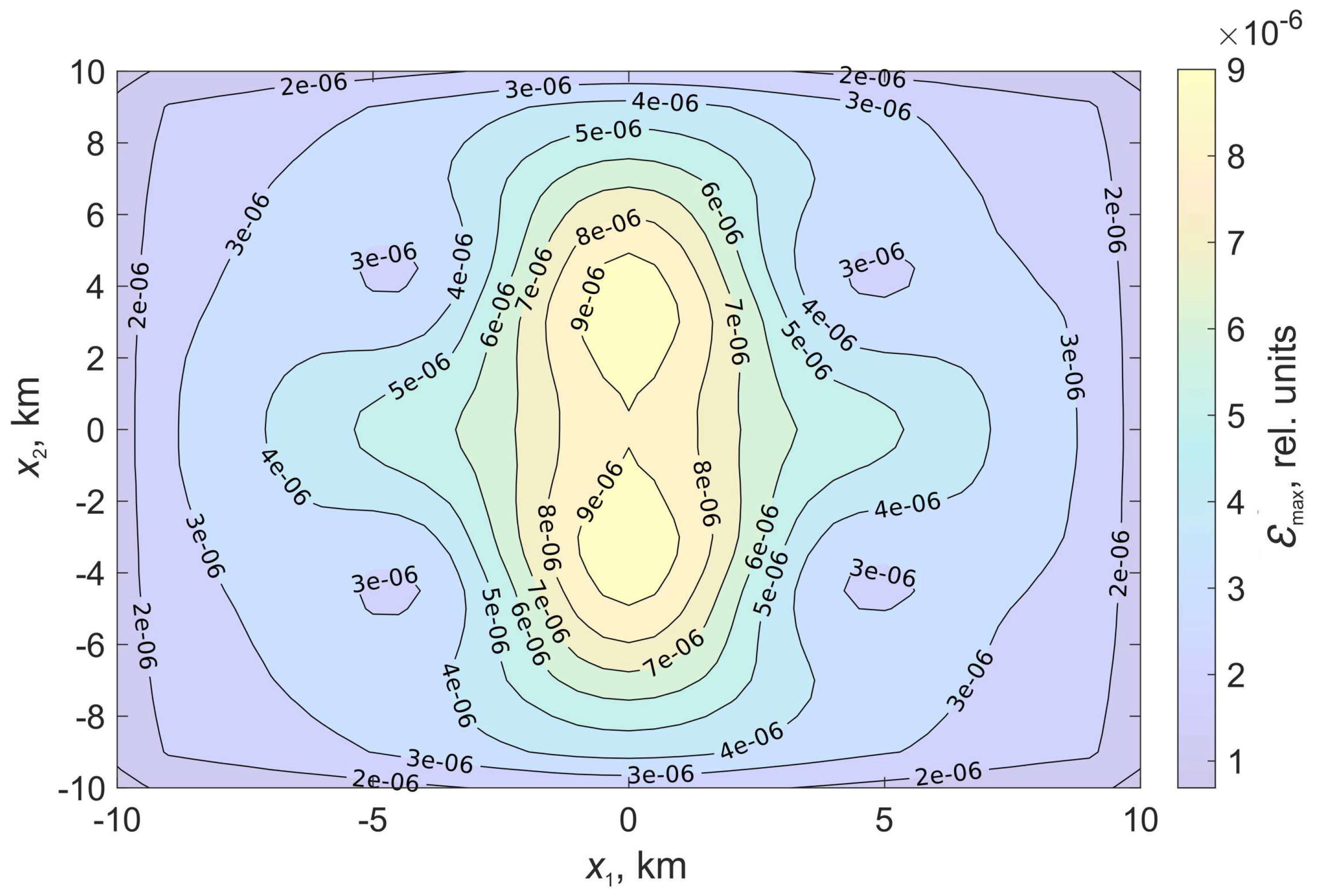
on the surface
, which are formed under the action of displacement along the stochastic surface.
Figure 10 shows the relative deformations, which are formed under the action of displacement along the rectangular part of the plane.
As in the previous experiment, in the case of a stochastic surface, the regions of relative deformations acquire a pronounced asymmetry. There is a significant decrease in the deformation level in the area
. There are also differences in the rate of change of the displacement field vector components in different directions.
Figure 11 shows variations of displacement field derivatives, coordinates are similar to the previous experiment.
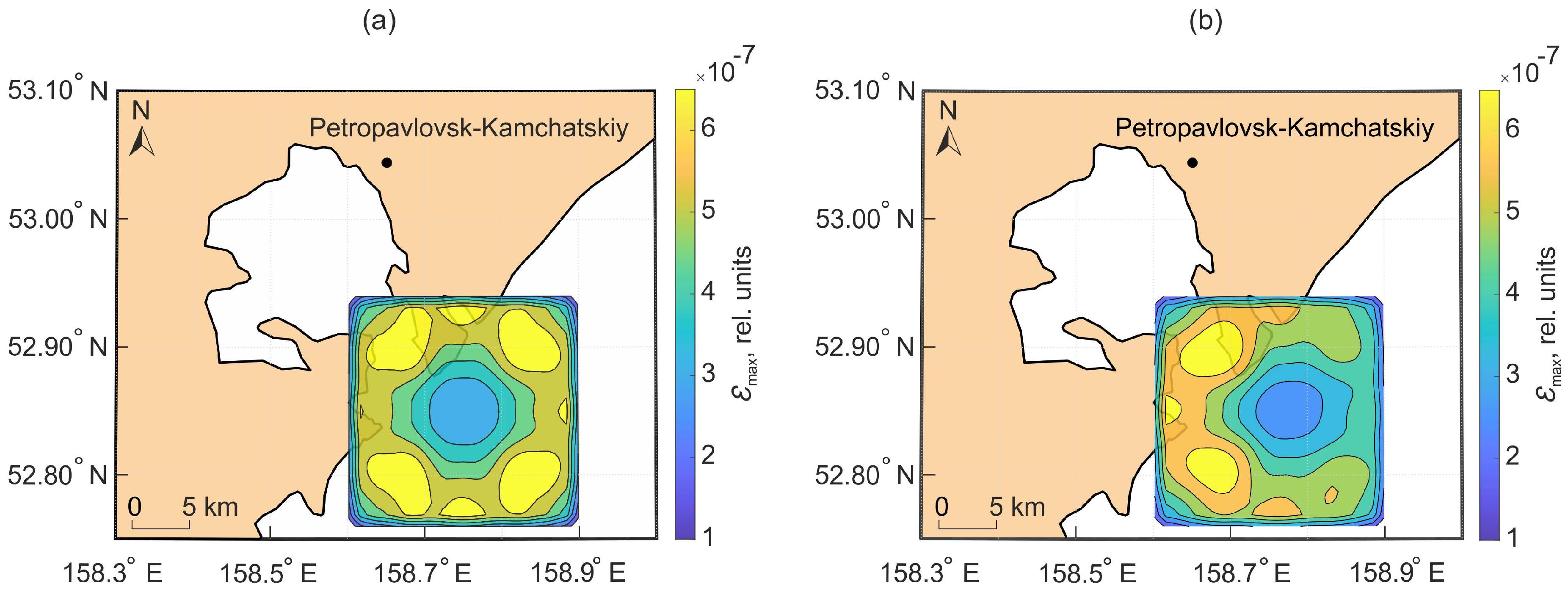
As an example, we consider the distribution of relative deformation areas (
Figure 12) caused by a 2 m displacement along a 6x3 km fault surface located at a depth of 15 km. Such dimensions correspond to an earthquake with a moment magnitude of approximately
on the Kanamori scale. The
Figure 12 shows a fragment of the Kamchatka Peninsula. This is one of the most seismically active regions of the planet. Most Kamchatka earthquakes occur at a distance of 30–150 km from the eastern coast of the peninsula, in the subduction zone adjacent to the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench. Let us assume that the epicenter of this hypothetical earthquake was located near the peninsula in the subduction zone (the epicenter coordinates are 52.85°N, 158.75°E).
It can be seen from the
Figure 12b that in the case of displacement along a stochastic fault surface, deformations increase in the coastal zone. Therefore, their influence there will be higher. Such asymmetry of deformation regions can help explain why signals propagating from the earthquake source do not always reach the zones controlled by geophysical sensors.
4. Conclusion
In this paper, we propose a model of an earthquake source in the form of a strike-slip displacement along a stochastic surface. To do this, a random component is introduced into the classical model, according to which the fault surface is represented as a flat rectangular area. It determines the random deformation of this area. The displacement vector is assumed to be constant. In the case of a stochastic fault surface, the regions of relative deformations acquire a pronounced asymmetry. Thus, adding a stochastic component will help indirectly take into account the heterogeneity of rocks when modeling deformations caused by earthquakes.
In the perspective of further research, we will consider a way to add a stochastic component to the geometry of the discontinuity plane. The presence of common statistical characteristics of the geometry of the surfaces of all earthquake sources seems unlikely. However, the presence of characteristics that directly or indirectly affect the shape of the fault surface is quite possible. In addition, the model can be complicated by adding a random displacement vector.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.; methodology, M.G.; software, A.S. and M.G.; validation, R.P.; formal analysis, R.P.; investigation, M.G.; resources, M.G. and A.S.; data curation, A.S. and M.G.; writing—original draft preparation, M.G. and A.S.; writing—review and editing, R.P.; visualization, A.S. and M.G.; supervision, R.P.; project administration, M.G.; funding acquisition, R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was carried within the framework of the State task on topic (2021–2023) “Physical processes in the system of near space and geospheres under solar and litospheric impact”, registration number AAAA-A21-121011290003-0.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sholz, C. The mechanics of earthquakes and faulting, 3rd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Steketee, J. On Volterra’s dislocations in a semi-infinity elastic medium. Can. J. Phys. 1958, 36, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.; Sarkar, S.; Mondal, D. Creeping effect across a buried, inclined, finite strike-slip fault in an elastic-layer overlying an elastic half-space. GEM - Int. J. Geomath. 2021, 12, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Fu, G.; She, Y.; Zhao, C. Co-seismic internal deformations in a spherical layered earth model. Geophys. J. Int. 2020, 221, 1515–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, D.; Debnath, P. An application of fractional calculus to geophysics: effect of a strike-slip fault on displacement, stresses and strains in a fractional order Maxwell type visco-elastic half space. Int. J. Appl. Math. 2021, 34, 873–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Press, F. Displacements, strains, and tilts at teleseismic distances. J. Geophys. Res. 1965, 70, 2395–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltykov, V.A.; Kugaenko, Y.A. Development of near-surface dilatancy zones as a possible cause for seismic emission anomalies before strong earthquakes. Russ. J. Pac. Geol. 2012, 6, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, Y. Internal deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half-space. Bull. Seismol. Soc. Am. 1992, 82, 1018–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, A. Statistics of the values of the normalized movement at the points of the fault-the focus of the earthquake. Phys. Earth 2011, 3, 24–33. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Lekshmy, P.; Raghukanth, S. Stochastic earthquake source model for ground motion simulation. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2019, 18, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Sang, W.; Zhou, B.; Wang, Z.; Yao, G.; Bi, J. Research on Dynamic Deformation Laws of Super High-Rise Buildings and Visualization Based on GB-RAR and LiDAR Technology. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, Y.; Ding, S. A Stochastic Earthquake Ground Motion Database and Its Application in Seismic Analysis of an RC Frame-Shear Wall Structure. Buildings 2023, 13, 1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, D. T.; Melgar, D. Geodetic coupling models as constraints on stochastic earthquake ruptures: An example application to PTHA in Cascadia. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2021, 126, e2020JB021149. [Google Scholar]
- Gusev, A. Doubly stochastic earthquake source model: “Omega-Square” spectrum and low high-frequency directivity revealed by numerical experiments. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2014, 171, 2581–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Huang, X.; Wang, Z. Focal Mechanism and Regional Fault Activity Analysis of 2022 Luding Strong Earthquake Constraint by InSAR and Its Inversion. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-J.; Chen, Q.; Yang, Y.-H.; Xu, Q. Coseismic Faulting Model and Post-Seismic Surface Motion of the 2023 Turkey–Syria Earthquake Doublet Revealed by InSAR and GPS Measurements. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Su, X. A Crustal Deformation Pattern on the Northeastern Margin of the Tibetan Plateau Derived from GPS Observations. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aki, K.; Richards, P. Quantitative Seismology, 2nd ed.; University Science Books: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Molotnikov, V.; Molotnikova, A. Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mindlin, R. Force at a point in the interior of a Semi-Infinite solid. J. Appl. Phys. 1936, 195, 195–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindlin, R.; Cheng, D. Nuclei of Strain in the Semi-Infinite Solid. J. Appl. Phys. 1950, 21, 926–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, P.-Z.; Miao, S.; Wu, Z.; Feng, X.-T.; Shao, C. Laboratory observation of spalling process induced by tangential stress concentration in hard rock tunnel. Int. J. Geomech. 2020, 20, 04020011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, S. Modified Generalized Maximum Tangential Stress Criterion for Simulation of Crack Propagation and Its Application in Discontinuous Deformation Analysis. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 259, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.; Li, D.; Zhu, Q. Strain Energy Release and Deep Rock Failure Due to Excavation in Pre-Stressed Rock. Minerals 2022, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clenshaw, C.W.; Curtis, A.R. A method for numerical integration on an automatic computer. Numer Math 1960, 2, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).